
Classification of Helitron’s Types in the C.elegans Genome based on
Features Extracted from Wavelet Transform and SVM Methods
Rabeb Touati, Imen Messaoudi, Afef ElloumiOueslati and Zied Lachiri
Dept. Electrical Engineering, SITI Laboratory, University of Tunis el Manar, National Engineering School, Tunis, Tunisia
Keywords: Transposable Elements (TES), Helitrons, C.elegans, SVM, Kernel-tricks, FCGS, CWT, Energy-wavelet.
Abstract: Helitrons, a sub-class of the Transposable elements class 2, are considered as an important DNA type. In
fact, they contribute in mechanism’s evolution. Till now, these elements are not well studied using the
automatic tools. In fact, the researches done in helitron's recognition are based only on biological
experiments. In this paper, we propose an automatic method for characterizing helitrons by global signature
and classifying the helitron’s types in C.elegans genome. For this goal, we used the Complex Morlet
Wavelet Transform to generate helitron’s signatures (helitron’s scalograms presentation) and to extract the
features of each category. Then, we used the SVM-classifier to classify these 10 helitron’s families. After
testing different kernels and using the cross validation function, we present the best classification results
given by the RBF-kernel with c=60, σ=0. 0000000015625 and OAO approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
The SVM classifier is proved to be effective
supervised algorithm in solving recognition problems
of the 2 classes and multi-class. It is applied to solve
statistical learning problems (Shawe-Taylor, 1998;
Poulter, 2005). The technique is based on structural
risk minimization (SRM) problems (Shawe-Taylor,
1998; Vapnik, 1998). It has been widely used in
different domains in data mining (NORINDER,
2003), bio-informatics studies (Mateos, 2002), DNA
(ÖZ, 2013) and molecular genetics (Furey, 2000) due
to its inherent discriminating learning and its
generalization capabilities.
SVMs have a major advantage that is the ability
to deal with samples of a very higher dimensionality.
For these reason, we used the SVM classifier as
classifier technique for the classification of particular
transposable elements which are highly
heterogeneous in size and which transpose by rolling
circle replication; helitrons. Helitrons use a “cut-and
paste” mechanism to transpose. These TEs are
discovered in all eukaryotic genomes and the main
challenges in cell biology is the location and
identification of these elements. The first discovered
of the helitrons in the plants (Arabidopsis Thaliana
and Oryza sativa) and in the nematode (C.elegans ).
Now, they have been identified in a diverse range of
species, protists to mammals (Kapitonov, 2001;
Poulter, 2005; Hood, 2005, Du 2008). Helitrons
sequences are widespread and highly heterogeneous.
On a large scale, these sequences suggest that they
are capable of duplicating and shuffling exon
domains (Morgante, 2005; Lai, 2005; Du,2009;
Schnable, 2009). Helitron’s classification algorithms
are based on the alignment theory which uses a
comparison between the searched area and an
helitron reference (Tempel, 2007; Sweredoski, 2008;
Du, 2008; Edgar, 2004). The major problem
encountered here is the lack of references (Xiong,
2014; Yang, 2009). On the other hand, Wicker et al.
(Wicker, 2007) produced a system of classification
for the eukaryotic transposable elements. Their
objective was to have hierarchical classification
system able to divide the transposable elements into
two main classes: class 1 (retrotransposons) and class
2 (DNA transposon). Till now, the dynamic and
structure of this helitron’s sequence is not well
studied. Besides, with the high variability of
helitronic sequences, the systematic classification
becomes an obstacle. In this work, we focus on
helitron sequences to characterize and categorize
these transposable elements. We show that when
using statistical concept of coding technique, we are
able to identify some helitrons. Meanwhile, we
thought of a standard method which classifies
helitrons, and that can help non-specialists to
Touati, R., Messaoudi, I., ElloumiOueslati, A. and Lachiri, Z.
Classification of Helitron’s Types in the C.elegans Genome based on Features Extracted from Wavelet Transform and SVM Methods.
DOI: 10.5220/0006631001270134
In Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2018) - Volume 3: BIOINFORMATICS, pages 127-134
ISBN: 978-989-758-280-6
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
127

annotate these elements. A key components of this
system is the combination of three steps. First,
coding the DNA with the Frequency Chaos Game
Signal (FCGS); second, applying the Complex
Morlet Wavelet Transform (CWT) to have the
helitron features; third, using the Support Vector
Machines (SVMs) as a classification technique.
Following that, we divide this paper into four
sections. The second section represents the materials
and methods. The third section provides the
experimental results and discusses the proposed
methods. The last section is the conclusion.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
In this work, the Support vector machine have been
used for the helitron sequences classification based
on the CWT applied to FCGS2. In the figure 1 we
illustrate the work steps: the first steps we extracted
the genomique sequences database of helitron’s types
from NCBI for the Caenorhabditis elegans genome (a
worm) (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank).
The second step consists in coding the genomic
sequence into a 1D signal by using the FCGS2
coding technique. Then, a signals database of eacg
helitron is established. In the third step, the analysis
window (CWT) is applied on the obtained signal.
Therefore, we obtain a set of wavelet coefficients
which we use to generate a helitron features
database. In the fourth step, we extract the features
relative of wavelet energy. This suitable wavelet-
based features database are prepared for the
classification of helitrons. Then, the feature
extraction step has a direct impact on the
performance of our classification systems. This
database is divided into two sub-databases: training
(70%) and testing (30%). In the final step, we have
employed the energy features as an input of SVM
classifier. Then, we apply the Support vector
machine (SVM) that we use the cross-validation
function to varied the kernels parameters and find the
best accuracy rates.
Figure 1: SVM-Helitrons recognizer Flowchart.
2.1 FCGS
2
Technique
The Frequency Chaos Game Signal order 2 is a new
coding technique based on the apparition’s
frequencies (apparition’s probabilities) of all 2
successive nucleotides groups in an entry genomic
sequence (Fiser, 1994; Messaoudi, 2013; Messaoudi,
2014; Messaoudi, 2014, Messaoudi, 2014). The
probability of a given dinucleotide (
) is
calculated by the following equation:
(1)
With
represents the apparition number of two
nucleotides in the entire sequence
The
represents the length of entry genomic
sequence (in base pairs: bp).
As known,a sequence of DNA is the combination
of 4 letters: A, T, C and G.
Then, the chromosomal sequences contains 42
possible dinucleotides: {AA, AC, AT, GG, GC …
TT}. So, the dinucleotide’s counting concern the
occurrence number of each of all of these elements.
After that, to encode the genomic sequence
regarding a dinucleotide (i), each element found in
the position (k) on the chromosome is replaced by its
occurrence’s probability:
(2)
The FCGSignal order 2 is the sum of all of the
dinucleotide indicators (
):
(3)
The chromosome is represented by a signal that
reflecting the dinucleotide’s temporal evolution in
the sequence.
2.2 Features Extraction
The DNA signal has a complex nature which requires
a pertinent tool to analyze its content. In this work,
the Continuous Wavelet Transform is applied on the
obtained FCGS2 signal using a Complex Morlet
wavelet as analysis window. The CWT decomposes a
given signal into a sum of windows called wavelets.
The latters are obtained by translating and expanding
a mother wavelet ψ(t) (Grossmann, 1984; Merry,
2005; Tse, 2007; NAJMI, 1997; Oueslati, 2015). The
set of wavelet windows is obtained by:
(4)
BIOINFORMATICS 2018 - 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
128

Here * is the complex conjugate. The mother wavelet
is the Complex Morlet function which is expressed
by:
(5)
Here
is the oscillation’s number. The continuous
wavelet transform is performed by applying this
formula:
(6)
The final result is a matrix of coefficients which we
use to generate the scalogram representation by
considering the absolute value of these coefficients
(Figure 2). Thus, we encode all chromosomes of
C.elegans genome by FCGS
2
. After that, we apply
the CWT along 64 scales with the parameter (ɷ
0
=
5.4285). We established the wavelet coefficients
database that represents helitron structures by
particular behaviours (Messaoudi, 2014, Touati,
2016; Oueslati, 2015). These time-frequency
representation can be used to our classification
system. Besides the helitrons composition variability
in the genome, these elements are also variable in
size. Given this, the wavelet coefficients matrix leads
to a set of features which is not balanced in size.
However, the SVM method is limited when it is
applied for imbalanced datasets. For this reason, the
choice of the optimal dimensionality reduction
method for the wavelet analysis is important since it
keeps the computation cost very low and the
classification accuracy very high. Here, we propose
to calculate the energy-wavelet as a features for our
classification system (Amin, 2015).
Therefore, we calculate the energy wavelet value
for each matrix by frequency axis. This method can
balance these features.
(7)
Where, L is the length of signal.
The final results of reduced features (energy-
wavelet) are vector have size 64 (equal to scales).
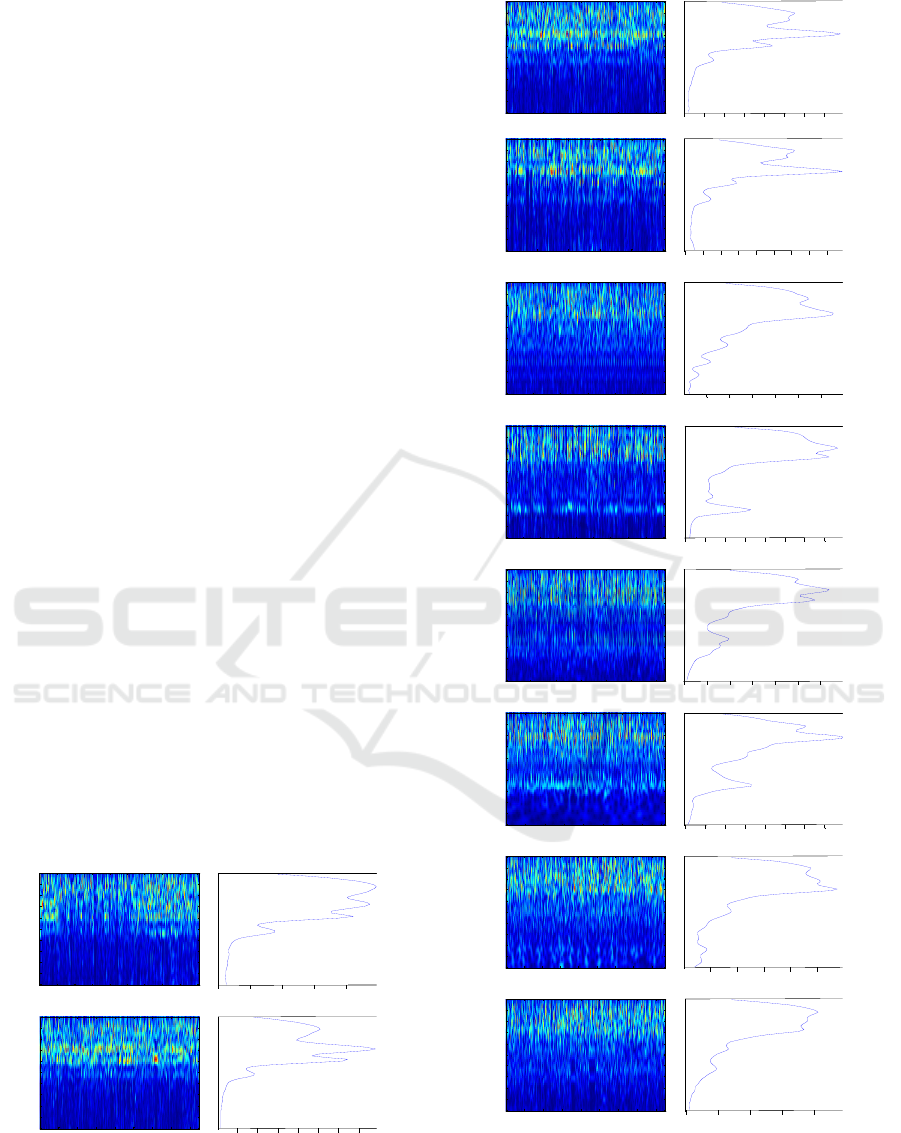
Each vector present one helitron. The figure 2
represents examples of the helitron’s scalograms
presentation and their corresponding energy vector.
2.3 Multi-class Support Vector
Machines
Support Vector Machines (SVMs) were first
proposed by Vladimir Vapnik in 1995 (Vapnik,
1995; Cortes, 1995). They are part of supervised
learning methods based on the theory of Structural
Risk Minimization (SRM). The Support Vector
Machines (SVMs) are very effective supervised
algorithm to solve recognition problems (Vapnik,
1995). SVMs have been the core of numerous
domains such as bioinformatics studies, molecular
genetics, DNA, data mining and psychiatry. In order
to estimate the helitrons in DNA sequence, we use
the SVM classification method which aims to find
the optimal hyper-plane that separates two different
classes. The SVM approach consists of constructing
one or several hyper-planes in order to separate the
different classes while maximizing margin. An
optimal hyperplan was defined by Vapnik and Cortes
(Vapnik, 1998) as the linear decision function with
maximal margin between the vectors of the two
classes. The hyper-plan can be described as:
Where w is a dimensional vector and b is a scalar.
The SVM determines a hyperplane that corresponds
to f(x) =0 for linearly separable data. The support
vectors, the samples closed to the hyper-plan
boundaries, are used to decide which hyper-plan
should be selected since this set of vectors is
separated by the optimal hyper-plan. The input
samples are mapped into a high dimensional feature
space by a space φ function for non-linearly
separable case:
(9)
The decision function is described by:
Practically, the real issue is often multi-classes.
Multi-class SVM classifier aims to give labels to
instances using SVMs, where the labels are drawn
from a finite set of several elements. Multi-class
problem can be taken as multiple binary
classification problems. Three approaches exist to
extend SVM linear classifiers to a multi-class
classifiers are; One-Against-One (OAO) (Knerr,
1990; Hsu, 2002), One-Against-All (OAA)
(Cristianini, 2000) and Directed Acyclic Graph
(DAG) (Platt, 2000). In this work, a simple execution
of a multi class SVM is supported by using the freely
available LibSVM library and implementing it in
MATLAB platform (Chang, 2011). One of the major
tricks of SVM is the Kernel functions. In the case
where non-linear separation is possible, these
functions are used. In addition, the kernel function
can be explained as a measure of similarity between
the input samples xi and xj (Schölkopf, 2001), which
allows SVM classifiers to meet the separation rule
Classification of Helitron’s Types in the C.elegans Genome based on Features Extracted from Wavelet Transform and SVM Methods
129
even with highly divergent and complex boundaries.
Although several choices for the kernel function are
available, including linear, polynomial, sigmoid,
RBF we have focused in finding the best kernel. In
this work RBF kernel give the best results. Below,
we give the equation of the RBF (radial basis
function) kernel:
The accuracy of the classifier is highly sensitive on
the choice of parameter gamma; it must be tuned to
control the amount of smoothing. The behaviors of
SVM change when σ becomes too small and when it
becomes too large. We calculate, using cross-
validation function, the kernel parameters: c and σ.
This function consists in setting up a grid-search for
σ and c (Hsu, 2009; Kuncheva, 2004).
In this work, we use the following couples (c, σ):
c= σ= [2
-6
, 2
-5
,…., 2
9
, 2
10
]
3 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
Helitrons are a families that have variable structures
and their identification is a major topic.
Here, we can visually characterize the repetitive
patterns in helitrons using the scalogram
representation resulted from the CWT analysis of the
FCGS2 coding. These specific periodic patterns can
characterize helitrons independently of their nature.
Note that the C.elegans organism contains 10
helitron families which are: {Helitron1 (H1),
Helitron2 (H2), HelitronY1 (Y1), HelitronY1A
(Y1A), HelitronY2 (Y2), HelitronY3 (Y3),
HelitronY4 (Y4), NDNAX1, NDNAX2 and
NDNAX3}.
H1
Y1A
Y1
Y4
N3
H2
Y2
Y3
N1
N2
Figure 2: Helitron particular scalograms and energy-
wavelet vector for each helitron’s types.
0 0.5 1 1.5 2
x 10
6
Amplitude
ondmorFCGS2 helitron 1 of the C.elegans:1-107933
Normalized Frequency
Nucleotide Position
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
x 10
4
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
2 4 6 8 10 12 14
x 10
6
Amplitude
ondmorFCGS2 helitron Y1A of the C.elegans:1-425487
Normalized Frequency
Nucleotide Position
0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4
x 10
5
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
x 10
6
Amplitude
ondmorFCGS2 helitron Y1 of the C.elegans:1-212264
Nucleotide Position
Normalized Frequency
0.5 1 1.5 2
x 10
5
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
x 10
6
Amplitude
ondmorFCGS2 helitron Y4 of the C.elegans:1-253070
Nucleotide Position
Normalized Frequency
0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5
x 10
5
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
x 10
6
Amplitude
ondmorFCGS2 NDNAX3 of the C.elegans:1-116760
Nucleotide Position
Normalized Frequency
2 4 6 8 10
x 10
4
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5
x 10
6
Amplitude
ondmorFCGS2 helitron 2 of the C.elegans:1-182314
Nucleotide Position
Normalized Frequency
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
x 10
4
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
0 2 4 6 8 10 12
x 10
5
Amplitude
ondmorFCGS2 helitron Y2 of the C.elegans:1-63742
Nucleotide Position
Normalized Frequency
1 2 3 4 5 6
x 10
4
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5
x 10
5
Amplitude
ondmorFCGS2 helitron Y3 of the C.elegans:1-16404
Nucleotide Position
Normalized frequency
2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
2 4 6 8 10
x 10
5
Amplitude
ondmorFCGS2 NDNAX1 of the C.elegans:1-43718
Normalized Frequency
0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4
x 10
4
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
0 0.5 1 1.5 2
x 10
6
Amplitude
ondmorFCGS2 NDNAX2 of the C.elegans:1-85107
Nuceotide Position
Normalized Frequency
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
x 10
4
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
BIOINFORMATICS 2018 - 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
130
3.1 Time Frequencies Signature of
Each Helitron’s Types
For each helitron’s types we represent (figure 2) the
helitrons scalograms and the corresponding energy-
vector which are marked by sharp signatures and
distinguished periodic structures. Here, for each
helitron’s types our idea is to concatenate all signals
and applied the CWT to these signals to visualize the
globally signature. We can clearly see that for each
helitron’s types have a specific signature around the
specific frequency band. So, we can distinguish the
periodic motifs for each helitron by a high level of
energy around frequencies. The energy-wavelet
vector reflect the power of the energy that correspond
to the frequency bound.
More of this, we can see that we have similarities
between some helitron’s types which are;
• Helitron1_CE and HelitronY1A_CE
• HelitronY1_CE and HelitronY1A_CE
• Helitron1_CE and Helitron4_CE
• Helitron2_CE and HelitronY2
Figure 2 represents the helitron’s scalograms that
have a remarkable and repetitive motifs that have
high energy around a frequency. Also, we have the
specific, energy vector values for each helitron’s
types.
3.2 SVM-Helitron’s Classification
A genomic sequence of DNA can be analyzed using
digital signal processing techniques (Tsonis, 1996;
Adorjan, 2002 ). In this work, we combined analysis
technique (CWT) and classification technique
(SVMs) to classify helitrons.
In the first step, we extracted the genomic
helitron’s database and we applied the FCGS2
coding method. In the second step, we prepared our
feature database which contains the frequencies
features (energy-wavelet) of these sequences. These
features have been extracted based on the CWT
applied to the FCGS2 signal. After that, we calculate
the energy correspond to each scales to balance the
features extracted from the CWT. Then, we splitted
the data into two sub-databases: 70% for training and
30% for testing (Table 1). Finally step, we made the
classification accuracy of two approaches of multi-
class SVM: OAO and OAA. A comparison between
the four kernels-SVM based methods can be
conducted; linear, Polynomial, RBF and sigmoid.
Moreover, based on our experiments, the OAO
approach given the best results when we used the
RBF kernel. The experimental results of the multi-
class SVM based method are shown in Table 2,
Table 3 and Table 4 which represent the
classification rates obtained with RBF-kernel with
optimal parameters (c and gamma) and with the
OAO approach.
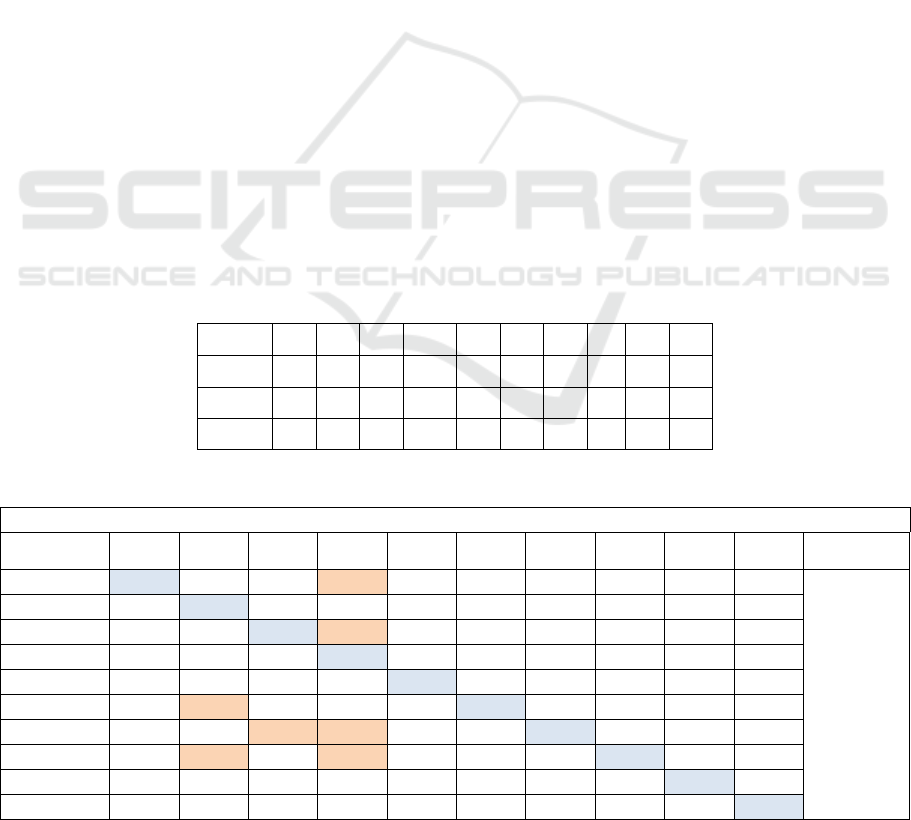
Table 1: SVM-helitrons database.
H1
H2
Y1
Y1A
Y2
Y3
Y4
N1
N2
N3
number
197
469
483
1093
337
117
523
77
188
134
training
137
328
338
765
236
83
368
54
131
94
testing
60
141
145
328
101
34
155
23
57
40
Table 2: Confusion matrix expose the classification results of all helitron’s types used RBF-SVM and OAO approach.
OAO and RBF-kernel with c= 60 and g= 0.0000000015625
Helitron’s
class
H1
H2
Y1
Y1A
Y2
Y3
Y4
N1
N2
N3
H1
25,64
12,82
12,82
46,15
0
0
2,56
0
0
0
58.48 %
(424/725)
H2
1,07
75,26
1,07
13,97
6,45
0
1,07
0
1,07
0
Y1
2,06
9,27
36,08
39,17
1,03
0
10,30
1,03
1,03
0
Y1A
5,50
5,50
8,71
74,31
1,37
0,45
3,21
0,45
0,45
0
Y2
0
23,52
0
4,41
70,58
1,47
0
0
0
0
Y3
0
21,73
0
17,39
0
60,86
0
0
0
0
Y4
0
7,54
19,81
38,67
0,94
0
32,07
0
0,94
0
NDNAX1
0
18,75
0
25
0
0
0
43,75
6,25
6,25
NDNAX2
0
8,10
0
21,62
5,40
0
0
0
64,86
0
NDNAX3
0
14,28
0
14,28
0
0
0
0
0
71,42
Classification of Helitron’s Types in the C.elegans Genome based on Features Extracted from Wavelet Transform and SVM Methods
131
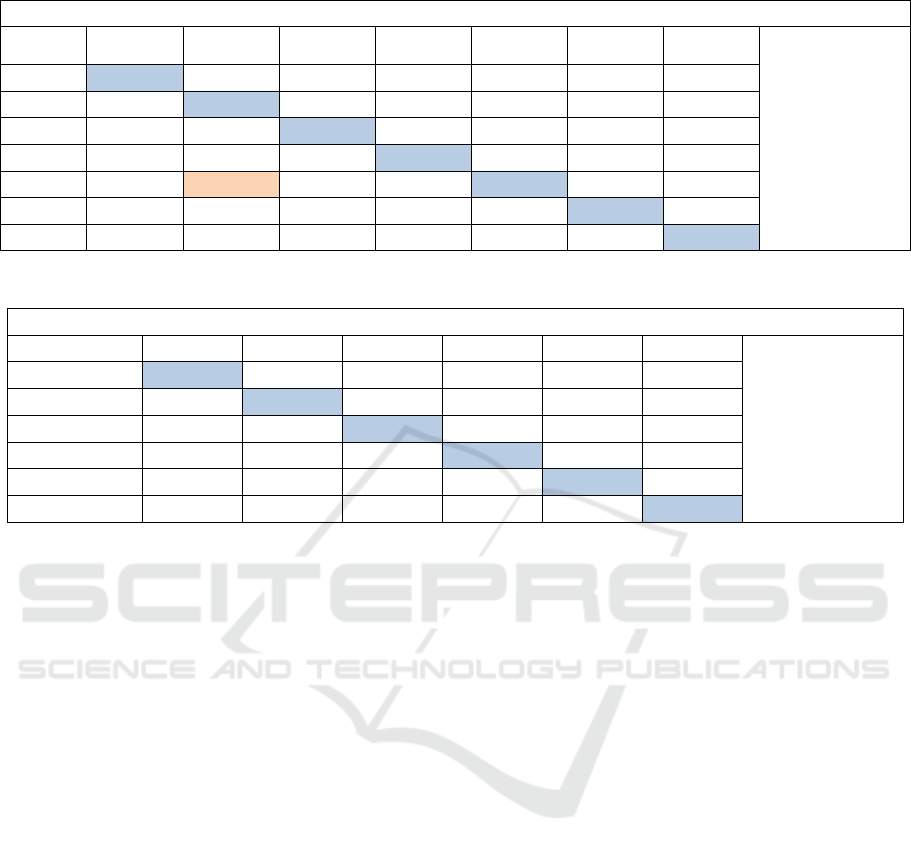
Table 3: Confusion matrix expose the classification results of 7 helitron’s types used RBF-SVM and OAO approach.
OAO approach and RBF-kernel with c= 60 and g= 0.0000000015625
Helitron’s
class
H2
Y1A
Y2
Y3
Y4
N2
N3
71.20 %
(408/573)
H2
76,34
13,97
6,45
0
2,15
1,075
0
Y1A
6,88
85,32
1,37
0,45
5,96
0
0
Y2
23,52
4,41
70,58
1,47
0
0
0
Y3
16,73
12,39
0
70,86
0
0
0
Y4
7,54
47,16
0,94
0
42,45
1,88
0
N2
8,10
21,62
5,40
0
0
64,86
0
N3
14,28
14,28
0
0
0
0
71,42
Table 4: Confusion matrix expose the classification results of 6 helitron’s types used RBF-SVM and OAO approach.
OAO and RBF-kernel with c= 60 and g= 0.0000000015625
Helitron’s class
H2
Y1A
Y2
Y3
N2
N3
80.2998% (375//467)
H2
86,36
6,12
6,45
0
1,07
0
Y1A
6,88
90,82
1,37
0,45
0,45
0
Y2
4,52
4,41
89,60
1,47
0
0
Y3
10,73
17,39
0
71,88
0
0
N2
8,1
19,62
5,4
0
67,86
0
N3
10,28
9,28
0
0
0
80,44
Here, using the Cross-Validation function we
found the optimal value of 2 parameters: (σ) the
kernel width and (c) the regularization parameter.
Overall, the kernel width σ =0.0000000015625, the
penalty c=60 and the SVM-RBF have given best
accuracy rates of the classification system of all
helitron’s types (acc= 58.5%), the classification
system of seven helitron’s types (acc= 71.20 %) and
the classification system of six helitron’s types (acc=
80.29 %). The confusion matrix in the table 2
confirm the existence of the similarities between the
helitrons cited in the first part of experimental
results. The helitrons have a highest rates;
Helitron2_CE (75%), HelitronY1A_CE (74%) and
NDNAX3_CE (71%) and HelitronY2 (70%) were
obtained using OAO approach of SVM-RBF(c =60
and σ =0. 0000000015625).
The confusion matrix in the table 3 represent the
results of classification of 7 helitron’s types (without
HelitronY1, HelitronY1 and NDNAX1). The
confusion matrix in the table 4 represent the results
of classification of 6 helitron’s types (without
HelitronY1, HelitronY1, HelitronY4 and NDNAX1).
By eliminating the helitrons which have a great
similarity the classification rate increased.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we characterized each helitron’s types
by a specific signatures. In fact, with the resulting the
scalograms representation from the CWT analysis
applied to FCGS2 coding technique. Then, we came
to visually distinguish each helitron’ families based
on its specific time frequencies signature. Based on
this, we have used the CWT analysis to extract the
features (energy-wavelet) sets for the overall
helitrons SVM-classification. Moreover, we
investigated the optimal parameters of Kernel-SVM
and features representations. Based on our
experiments, the recognition system of all helitron’s
types was improved when we have chosen the best
parameters of the RBF-kernel (c=60 and
σ=0.0000000015625) which gave the best accuracy
rates .For the classification of the not similar
helitron’s types, the best classification rate was
obtained for the HelitronsY1A_CE class which value
is 90% with c = 60, σ = 0.0000000015625 and using
the OAO approach. Two other notable helitron’s
classes have shown high accuracy rate:
HelitronsY2_CE and Helitron2_CE with the value of
89% and 86% respectively. The obtained results
demonstrated the successfulness of the features
(energy-wavelet) extracted from the CWT analysis
applied to the FCGS2 signals to classify helitron’s
BIOINFORMATICS 2018 - 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
132

sequences in C.elegans. The novelty of this work
resides in the fact of the all helitron’s classification
using the energy of matrix contains the coefficient of
wavelet (time-frequencies presentation). These
energy-vector can characterize each helitrons by
specific frequencies that have energy around the
specific frequency.
REFERENCES
Amin, H. U., Malik, A. S., Ahmad, R. F., Badruddin, N.,
Kamel, N., Hussain, M., & Chooi, W. T. 2015. Feature
extraction and classification for EEG signals using
wavelet transform and machine learning
techniques. Australasian physical & engineering
sciences in medicine, 38(1), 139-149.
Chang, C. C., & Lin, C. J. 2011. LIBSVM: a library for
support vector machines. ACM transactions on
intelligent systems and technology (TIST), 2(3), 27.
Du, C., Fefelova, N., Caronna, J., He, L., & Dooner, H. K.
2009. The polychromatic Helitron landscape of the
maize genome. Proceedings of the National Academy
of Sciences, 106(47), 19916-19921.
Du, C., Caronna, J., He, L., & Dooner, H. K. 2008.
Computational prediction and molecular confirmation
of Helitron transposons in the maize genome. Bmc
Genomics, 9(1), 51.
Edgar, R. C. 2004. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment
with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic acids
research, 32(5), 1792-1797.
Norinder, U. 2003. Support vector machine models in drug
design: applications to drug transport processes and
QSAR using simplex optimisations and variable
selection. Neurocomputing, 55(1), 337-346.
Mateos, A., Dopazo, J., Jansen, R., Tu, Y., Gerstein, M., &
Stolovitzky, G. 2002. Systematic learning of gene
functional classes from DNA array expression data by
using multilayer perceptrons. In Genome
Research, 12(11), 1703-1715.
Öz, E., & Kaya, H. 2013. Support vector machines for
quality control of DNA sequencing. Journal of
Inequalities and Applications, 2013(1), 85.
Furey, T. S., Cristianini, N., Duffy, N., Bednarski, D. W.,
Schummer, M., & Haussler, D. 2000. Support vector
machine classification and validation of cancer tissue
samples using microarray expression data.
Bioinformatics, 16(10), 906-914.
Hsu, C. W., & Lin, C. J. 2002. A comparison of methods
for multiclass support vector machines. IEEE
transactions on Neural Networks, 13(2), 415-425.
Hsu,C.W., Chang, C.C. and Lin, C. J. 2009. A practical
guide to support vector classification,” Department of
Computer Science and Information Engineering
National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan,
Available: www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/ cjlin/
Shawe-Taylor, J., Bartlett, P. L., Williamson, R. C., &
Anthony, M. 1998. Structural risk minimization over
data-dependent hierarchies. IEEE transactions on
Information Theory, 44(5), 1926-1940.
Vapnik, V.N., Vapnik,V. 1998. “Statistical learning
theory,” New York : Wiley,.
Vapnik, V., 1995. The nature of statistical learning theory,”
Springer Verlag New York, Inc. New York,
Gutschoven, B., & Verlinde, P. 2000. Multi-modal identity
verification using support vector machines (SVM).
In Information Fusion, 2000. FUSION 2000.
Proceedings of the Third International Conference
on (Vol. 2, pp. THB3-3). IEEE.
Poulter, R. T. M., & Goodwin, T. J. D. 2005. DIRS-1 and
the other tyrosine recombinase retrotransposons.
Cytogenetic and genome research, 110(1-4), 575-588.
Hood, M. E. 2005. Repetitive DNA in the automictic
fungus Microbotryum violaceum. Genetica, 124(1), 1-
10.
Kapitonov, V. V., & Jurka, J. 2001. Rolling-circle
transposons in eukaryotes. Proceedings of the National
Academy of Sciences, 98(15), 8714-8719.
Lai, J., Li, Y., Messing, J., & Dooner, H. K. 2005. Gene
movement by Helitron transposons contributes to the
haplotype variability of maize. Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of
America, 102(25), 9068-9073.
Schnable, P. S., Ware, D., Fulton, R. S., Stein, J. C., Wei,
F., Pasternak, S., ... & Minx, P. 2009. The B73 maize
genome: complexity, diversity, and dynamics. Science,
326(5956), 1112-1115.
Tempel, S. 2007. Dynamique des hélitrons dans le genome
d'Arabidopsis thaliana: développement de nouvelles
stratégies d'analyse des éléments transposables
(Doctoral dissertation, Université Rennes 1).
Sweredoski, M., DeRose-Wilson, L., & Gaut, B. S. 2008.
A comparative computational analysis of
nonautonomous helitron elements between maize and
rice. BMC genomics, 9(1), 467.
Xiong, W., He, L., Lai, J., Dooner, H. K., & Du, C. 2014.
HelitronScanner uncovers a large overlooked cache of
Helitron transposons in many plant
genomes. Proceedings of the National Academy of
Sciences, 111(28), 10263-10268.
Yang, L., & Bennetzen, J. L. 2009. Structure-based
discovery and description of plant and animal
Helitrons. Proceedings of the National Academy of
Sciences, 106(31), 12832-12837.
Wicker, T., Sabot, F., Hua-Van, A., Bennetzen, J. L., Capy,
P., Chalhoub, B., ... & Paux, E. 2007. A unified
classification system for eukaryotic transposable
elements. Nature Reviews Genetics, 8(12), 973-982.
Fiser, A., Tusnady, G. E., & Simon, I. 1994. Chaos game
representation of protein structures. Journal of
molecular graphics, 12(4), 302-304.
Merry, R. J. E., & Steinbuch, M. 2005. Wavelet theory and
applications. literature study, Eindhoven university of
technology, Department of mechanical engineering,
Control systems technology group.
Morgante, M., Brunner, S., Pea, G., Fengler, K., Zuccolo,
A., & Rafalski, A. 2005. Gene duplication and exon
shuffling by helitron-like transposons generate
Classification of Helitron’s Types in the C.elegans Genome based on Features Extracted from Wavelet Transform and SVM Methods
133

intraspecies diversity in maize. Nature genetics, 37(9),
997.
Messaoudi, I., Oueslati, A. E., & Lachiri, Z. 2013.
Complex Morlet wavelet analysis of the DNA
frequency chaos game signal and revealing specific
motifs of introns in C.elegans. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1306.5109.
Messaoudi, I., Oueslati, A. E., & Lachiri, Z. 2014.
Revealing Helitron signatures in Caenorhabditis
elegans by the Complex Morlet Analysis based on the
Frequency Chaos Game Signals. In IWBBIO (pp. 1434-
1444).
Messaoudi, I., Oueslati, A. E., & Lachiri, Z. 2014. Wavelet
analysis of frequency chaos game signal: a time-
frequency signature of the C. elegans DNA. EURASIP
Journal on Bioinformatics and Systems
Biology, 2014(1), 16.
Messaoudi, I., Elloumi-Oueslati, A., & Lachiri, Z. (2014).
Building specific signals from frequency chaos game
and revealing periodicities using a smoothed Fourier
analysis. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational
Biology and Bioinformatics, 11(5), 863-877.
Touati, R., Massaoudi, I., Oueslati, A. E., Lachiri, Z., &
Ellouze, N. 2016. Nucleosome location method based
on morlet wavelet analysis scalograms investigation.
In Advanced Technologies for Signal and Image
Processing (ATSIP), 2016 2nd International
Conference on (pp. 307-312). IEEE.
Grossmann, A., & Morlet, J. 1984. Decomposition of
Hardy functions into square integrable wavelets of
constant shape. SIAM journal on mathematical
analysis, 15(4), 723-736.
Tse, N. C., & Lai, L. L. 2007. Wavelet-based algorithm for
signal analysis. EURASIP Journal on Applied Signal
Processing, 2007(1), 169-169.
Najmi, A. H., & Sadowsky, J. 1997. The continuous
wavelet transform and variable resolution time-
frequency analysis. Johns Hopkins APL Technical
Digest, 18(1), 134-140.
Oueslati, A. E., Messaoudi, I., Lachiri, Z., & Ellouze, N.
2015. A new way to visualize DNA’s base succession:
the Caenorhabditis elegans chromosome
landscapes. Medical & biological engineering &
computing, 53(11), 1165-1176.
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V.N. 1995. Support-Vector Networks,
Machine Learning, springer, NewYork, vol. 20, no. 3,
pp. 273-297,.
Schölkopf, B. 2001. The kernel trick for distances.
In Advances in neural information processing
systems (pp. 301-307).
Kuncheva, L. I. 2004. Combining pattern classifiers:
methods and algorithms,” John Wiley & Sons.
Knerr, S., Personnaz, L., & Dreyfus, G. 1990. Single-layer
learning revisited: a stepwise procedure for building
and training a neural network. Neurocomputing:
algorithms, architectures and applications, 68(41-50),
71.
Cristianini, N. and Shawe-Taylor, J. 2000. An Introduction
to Support Vector Machines and other Kernel-based
Learning Methods,” Cambridge, UK: Cambridge
University Press.
Platt, J. C., Cristianini, N., & Shawe-Taylor, J. 2000. Large
margin DAGs for multiclass classification. In Advances
in neural information processing systems (pp. 547-
553).
Tsonis, A. A., Kumar, P., Elsner, J. B. 1996. Wavelet
analysis of DNA sequences,” Physical Review E, vol.
53, no 2, p. 1828.
Adorján, P., Distler, J., Lipscher, E., Model, F., Müller, J.,
Pelet, C.,.. & Howe, A. 2002 Tumour class prediction
and discovery by microarray-based DNA methylation
analysis. Nucleic acids research, 30(5), e21-e21.
BIOINFORMATICS 2018 - 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
134
