
Terminology Enabled Spatio-temporal Analysis and Visualization for
Preterm Birth Data in the US
Kui Wang and Lixia Yao
Department of Health Sciences Research, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, U.S.A.
Keywords: Preterm Birth, Metropolitan Statistical Areas, Claims Database, Controlled Terminology.
Abstract: Preterm birth can lead to many health problems in infants, including brain damage, neurologic disorders,
asthma, intestinal problems and vision problems, but the exact cause of preterm birth is unclear. In this
study, we investigated if geographic location or the environment can contribute to preterm birth by building
a customized data model based on multiple controlled terminologies. We then performed a large-scale
quantitative analysis to understand the relationships between the prevalence of preterm birth, the biological
mothers’ demographic information and the Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSAs) of their primary
residency from 2010 to 2014. More specifically we considered education, income, race and marital status
information of 388 MSAs from the US Census Bureau. The results demonstrated that the overall preterm
birth rate for the United States decreased during 2010 to 2014, with Chicago-Naperville-Elgin (Illinois)
Metro Area, Houston-Sugar Land (Texas) Metro Area and Billings (Montana) Metro Area observing the
most visible improvement. There are statistically significant correlations between race distribution,
education level and preterm birth. But median income, marital status and insurance coverage ratio are found
irrelevant to preterm birth. This study demonstrated the power of controlled terminologies in integrating
medical claims data and geographic data to study preterm birth for first time. The customized common data
model and the interactive tool for online visualizing a large preterm dataset from both the temporal and
spatial perspectives can be used for future public health studies of many other diseases and conditions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Preterm birth refers to the birth of a baby before 37
weeks of gestational age (Spong, 2013). According
to World Health Organization there are 15 million
preterm newborns each year across the world, and
75% of deaths of children under age 5 are related to
preterm birth. In 184 countries, the national preterm
birth rate ranges from 5% to 18% for the total
population of newborns. In 2016, the preterm birth
rate across all 50 states in the US was about 9.6%,
which is marked as grade C according to a scoring
mechanism developed by the March of Dimes, a
nonprofit organization promoting the health of
mothers and children. Preterm birth can lead to
many serious long-term health problems for infants,
including brain damage, behavior problems,
neurological disorders, intestinal problems, vision
problems, hearing loss and dental problems.
Therefore, fully understanding the causes of preterm
birth becomes important for early prevention and
management. In one study, Goldenberg et al.
(Goldenberg et al., 2008) indicated that preterm birth
may relate to previous preterm birth, race (African
American women have higher rate of preterm birth),
periodontal disease, and low maternal body-mass
index. In another study, Kramer et al. (MR and CR,
2008) investigated the distribution of very preterm
birth rates by race across Metropolitan Statistical
Areas (MSAs) during 2002 to 2004 using the
National Center for Health Statistics natality files
and found that residential segregation is an
important social determinant of racial disparities. In
our study, we investigate how important a role
geographic location or the environment plays in
effecting preterm birth using a more recent and
larger dataset. More specifically, we conducted a
comprehensive analysis on the correlation between
preterm birth prevalence, the biological mothers’
demographic information and MSAs of the mothers’
primary residency from 2010 to 2014. We also
considered the education, income, race and marital
status information of 388 MSAs from the US Census
Bureau.
510
Yao, L. and Wang, K.
Terminology Enabled Spatio-temporal Analysis and Visualization for Preterm Birth Data in the US.
DOI: 10.5220/0006647505100518
In Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2018) - Volume 5: HEALTHINF, pages 510-518
ISBN: 978-989-758-281-3
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 BACKGROUND AND
MATERIALS
2.1 Preterm Birth Data
The average length of pregnancy for a normal birth
is 38 to 40 weeks. The preterm birth (also called
premature labor) means delivery of the infant before
37 weeks of pregnancy. In 2015, preterm birth
affected about 1 in every 10 infants born in the
United States, whereas it was 1 in every 12 births in
2006 (Martin et al., 2009). Infants delivered before
full term tend to have more breathing problems,
brain damage, cerebral palsy, behavioral and
psychological problems, or even death. The exact
reason of preterm birth is not fully understood.
We used the MarketScan® Commercial Claims
and Encounters Database (Truven Health Analytics)
with data for nearly 230 million unique patients
since 1995. This database contains specific health
services records from active employees, early
retirees, and their families in a large number of
employer-based health plans and public and
government organizations. The database captures all
aspects of care for insurance reimbursable services
including outpatient physician office visits, hospital
stays, emergency department visits, home care
services and outpatient prescription drug claims. It
has the advantage of representing a large cross-
section of individuals under the age of 65 and with
private health insurance, including our targeted
population of women with preterm labor. All patient
data in the MarketScan Commercial Claims and
Encounters Database are de-identified and this study
is considered exempt from approval by the Mayo
Clinic Institutional Review Board.
We used inpatient admissions table from the
MarketScan Commercial Claims and Encounters
Database, during 2010 to 2014 and selected cases
where the principal diagnosis code indicated a
preterm birth (coded by ICD-9-CM, International
Classification of Disease, Ninth Revision, Clinical
Modifications), starting with 644 or 765. Code 644
refers to early or threatened labor, and code 765
refers to disorders relating to short gestation and low
birth-weight. The MarketScan Commercial Claims
and Encounters Database also reports where each
patient lives in relation to the MSAs.
2.2 Metropolitan Statistical Areas
An MSA is a contiguous geographical area in the
United States with a relatively high population
density at its core and close economic ties. It is
typically composed of one or more adjacent counties
or county equivalents that have at least one urban
core area with a population of at least 50,000. The
outlying counties can be included if they have strong
social and economic ties to the central counties. For
example, New York-Newark-Jersey City is the
largest MSA with a population of 20 million in
2016. By definition, the MSA is an evolving concept
over time. According to the US Census Bureau,
there were 374 MSAs before 2013 and the number
has increased to 388. More details are given in the
next section (Methodology). MSA is arguably a
better geographic context for the public health
studies as it includes social and economic
considerations such as employment and commute.
2.3 US Census Bureau Data
The US Census Bureau serves as the leading source
of quality data on the nation's people and economy.
They provide a tool called American FactFinder,
which offers a user-friendly interface to find, view,
modify and download a variety of census data from
different MSAs. We downloaded race distribution
(percentage of white, African American, Asian),
economic factors (median income, percentage of
poverty and percentage with health insurance), and
social factors (education in terms of percentage of
high school and above, percentage of bachelor’s
degree and above, and marital status) for each
MSAs. We also used the total population, female
population and female population who had
pregnancy in the past 12 months as the denominator
when calculating the prevalence.
Figure 1: The Workflow for Temporal and Spatial
Analysis and Visualization of Preterm Birth Data in the
United States.
Claim data
Census
data
Cleaning &
Preprocessin
g
Mapping &
Linking
Visualization
Correlation &
Regression
Analysis
Terminology Enabled Spatio-temporal Analysis and Visualization for Preterm Birth Data in the US
511

3 METHODOLOGY
Our approach for analysing and visualizing the
preterm birth data consists of six modules, as
illustrated in Figure 1. Below we explain the steps of
claims data cleaning, mapping and linking claims
data and census data, visualization, correlation and
regression analysis in more depth.
3.1 Claim Data Cleaning and
Preprocessing
After filtering the inpatient admissions table from
the MarketScan Commercial Claims and Encounters
Database using principal diagnosis codes 644 and
765, we still needed to clean the data manually
because there were missing values and errors. Table
1 summarizes how we handled various erroneous or
dirty cases in the claims data.
Table 1: The erroneous cases that have gone through
manual cleaning and preprocessing.
Categories
Action
No unique patient identifier
(ENROLID), age (DOBYR) or
location (MSA)
Remove
Multiple claim records for one
unique patient identifier (those are
most likely to be duplications, as
clinically it is unlikely for one
woman to have multiple preterm
labor in any calendar year)
Consolidate and
use the latest
record
Reported ages for the same patient
identifier were inconsistent
Adopt the oldest
age
Reported age for patient with
preterm children is too young or too
old (e.g., 8 years old or 72 years
old): (The average age of a young
woman’s first period (menarche) is
12 to 13 in the United
States(Anderson et al., 2003) and
women older than 65 years old are
more likely to go on Medicare and
unlikely to have pregnancy and
preterm birth
Remove records
with reported
age younger
than 12 or older
than 65
3.2 Mapping and Linking Claims and
Census Data using MSA
MSAs are the most important keys that connect the
claims data with census data in this study. However
the total number of MSAs in claims data is 398 from
2010 to 2013, and 408 in 2014, while the total
number of MSAs defined in census data is 374
during 2010 and 2012, and 388 from 2013 and later.
To address this challenge, we manually built three
MSA mapping tables between claims and census
data for the time periods of 2010 – 2012, 2013 and
2014. Table 2 gives an incomplete snapshot of how
we built the mapping table for 2013. Actual
complete mapping table contains 75 records.
Table 2: A snapshot of the MSA Mapping table for 2013.
MSA From
Claims data
MSA From
Census Data
Actions
10540
New data added
11300
Combine into
26900
11340
Combine into
24860
11640
New data added
from 41980
13220
New data added
14060
14010
Change to 14010
14484
14460
Change to 14460
14600
Combine into
35840
15680
New data added
15764
Combine into
14460
15804
Combine into
37980
Eventually we created a data file consisting both
the count of preterm birth for each MSA and the
social and economic factors for each MSA,
including total population, female population,
female population having pregnancy in the past 12
months, median income, marital status, percentage
of population with education level higher than high
school or bachelor’s degree, percentage of popula-
tion living in poverty, percentage of population with
insurance coverage and race distribution.
3.3 Controlled Vocabulary Enabled
Data Model Development
Many data mining and text mining work in
biomedicine have demonstrated the issue and
challenge of heterogeneous data integration and
multi-dimensional information standardization. This
project is no exception. We thus adopted the design
principal of the Fast Healthcare Interoperability
Resources (FHIR) (Hong et al., 2017), the state-of-
HEALTHINF 2018 - 11th International Conference on Health Informatics
512

Figure 2: Data Model and Terminology Standards. Box
indicates medical objects and the underline highlights
object property.
art clinical datastandard developed by HL7 for
exchanging biomedical data. We designed a specific
data model (illustrated in Figure 2) for fast and easy
querying, analyzing and visualizing both spatial and
temporal data for preterm birth. This data model is
enhanced by adopting ICD-9-CM and our newly
created MSAs mapping. Thus it can be easily
generalized to studying other diseases and
conditions.
3.4 Online Interactive Visualization
using D3
Communicating high-dimensional data (i.e., both
temporal and spatial data) to end users or decision
makers who might be not familiar with quantitative
research is always challenging. One solution is to
use interactive visualizations, so that those people
can obtain actionable information instead of a vast
amount of convoluted statistical numbers. In this
particular project, in order to disseminate the data
and findings in our analysis and facilitate clinicians
and public health researchers to better address the
issue of preterm birth, we developed an online
interactive visualization tool using D3, a JavaScript
library for visualizing data with HTML, SVG, and
CSS. The URL of our open-access visualization tool
is https://wangku.github.io/Visualizations/preterm-
birth.html. Users can select the year or MSA to view
the related data instantaneously.
3.5 Correlation Analysis and
Regression Analysis
In order to investigate the relationship between
prevalence of preterm birth and social and economic
factors for various MSAs, we first performed a
correlation analysis based on Pearson Correlation
Coefficient (PCC). PCC measures the linear
correlation between two variables X and Y. In
theory, the value of PCCs fall into [-1, 1] whereas 1
is complete positive linear correlation (two variables
are identical), 0 is no linear correlation, and −1 is
total negative linear correlation. In practice, a PCC
of 0.1 is considered small correlation, while 0.3
considered medium and 0.5 considered large for the
social sciences (Cohen, 1988, Cohen, 1992).
Next we built multiple regression models to learn
if we can predict the prevalence of preterm birth (Y,
or the dependent variable of interest) based on all or
some of the social and economic factors (Xi, or
independent predictor variables). Mathematically a
multiple linear regression can be expressed as:
Y = α + β
1
X
1
+ β
2
X
2
+ β
3
X
3
+ ⋯ + β
M
X
M
+ ε
(1)
Where Y is the dependent variable and X
i
is the
independent variables. By looking at the PCCs
between prevalence of preterm birth with all 10
independent variable (See Figure 3 for example), we
realized that they do not have linear relationships.
Thus, we further adopted nonlinear multiple
regression to add some nonlinear transformation to
the dependent variable Y and/or independent
variables X
i
before fitting them into the linear model
of Equation (1). More specifically, after multiple
tries of different transformations, we set Y = θ / y,
where θ is the constant, and X
i
= log(x
i
), as shown
in Equation (2).
θ 𝑦
⁄
= α + β
1
log
(
x
1
)
+ β
2
log
(
x
2
)
+ ⋯ +β
M
log (x
M
)
(2)
Both correlation and regression analyses were
done in R, as the huge and powerful libraries in R
make such analysis easy and flexible.
Terminology Enabled Spatio-temporal Analysis and Visualization for Preterm Birth Data in the US
513

Figure 4: The histogram of preterm birth at different female ages for top 5 largest MSAs and all MSAs, 2010-2014.
Figure 3: A scotterplot of preterm birth prevalence vs.
median income, 2014.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
We first visualize the distribution of preterm birth
cases across different ages and MSAs during 2010 to
2014, as a validity check of the claims datasets. The
Figure 4 shows the histogram of preterm birth for
the 5 largest MSAs (in terms of population) and all
388 MSAs over the period of five years. The x-axis
is the women’s age and y-axis is the percentage of
preterm births. We observed that nationwide, most
preterm birth cases occur to the age group of 28 to
33 years old, with the percentage peaking at the age
of 30. Each of these age groups accounts for 6.25%
to 7.1% of all preterm birth cases in the country
during 2010 to 2014. This is not surprising as these
ages are the most fertile years for American women.
All the New York, Chicago, Los Angeles, Houston
and Dallas metropolitan areas follow a bell shape
curve in terms of preterm birth occurrence. It seems
that preterm birth in Chicago metropolitan area is
more clustered in the age range of 28 and 35, while
preterm birth in both Houston and Dallas is much
more spread out to all ages.
With verified confidence about the quality of the
claims data, we visualize the prevalence of preterm
birth across the United States from 2010 and 2014
(Figure 5). In this visualization, we used the total
female population for each MSA as the denominator
when calculating the prevalence value. The color
from green to red is mapped to show small to large
prevalence rates. The complete visualization for all
five years and each MSA can be viewed through our
interactive visualization tool online (https://wangku.
github.io/Visualizations/preterm-birth.html). It is
shown in Figure 5 that the overall preterm birth rate
declined during the five-year period. The color tone
of the map became more orange in 2014, compared
HEALTHINF 2018 - 11th International Conference on Health Informatics
514

Table 3: The top 3 MSAs with highest prevalence each
year during 2010 to 2014.
2010
Erie, Pennsylvania
Columbia, South Carolina
Charleston-North Charleston, South Carolina
2011
Evansville, Indiana-Kentucky
Anderson, Indiana
Indianapolis-Carmel, Indiana
2012
Midland, Texas
Odessa, Texas
Billings, Montana
2013
Charleston-North Charleston, South Carolina
Idaho Falls, Idaho
Evansville, Indiana-Kentucky
2014
Idaho Falls, Idaho
Lake Charles, Louisiana
Williamsport, Pennsylvania
to red and dark red in 2010. The high prevalence of
preterm birth (>2.0e-4) in 2014 only happened to
sporadic MSAs including Idaho Falls Idaho, Lake
Charles Louisiana, Williamsport Pennsylvania,
Monroe Michigan and Spartanburg South Carolina.
Table 3 lists the top 3 MSAs with highest prevalence
of preterm birth for each year 2010 through 2014.
Table 4 and Table 5 summarize the PCCs and P-
values between the prevalence of preterm birth and
each dependent variable. The major difference is the
calculation of the prevalence rate. Table 4 used the
female population having pregnancy in the past 12
months as the denominator when calculating
prevalence; on the other hand, Table 5 used the total
female population of each MSA. To our surprise, the
results in Table 4 were no better than those in Table
5. For example, there are only seven statistically
significant (P < 0.05) PCCs, which suggest some
weak positive correlation between the ratio of
African American and prevalence of preterm births.
By verifying the definition and collection of US
Census Bureau Data on female population having
pregnancy in past 12 months, we realized that this
might be due to a caveat in the dataset – the data was
calculated by averaging 5-year estimate instead of
the exact past 12 months because some MSAs had
missing data for certain years.
Table 4: Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient (PCC) and P value only for pregnant population.
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
PCC
P
-
value
PCC
P
-
value
PCC
P
-
value
PCC
P
-
value
PCC
P
-
value
Highschool rate
0.076
0.142
0.013
0.807
-0.060
0.253
0.005
0.928
0.002
0.965
Bachelor rate
0.023
0.662
-0.065
0.217
-0.075
0.156
-0.012
0.831
-0.080
0.125
Median income
0.055
0.289
-0.069
0.193
-0.083
0.116
-0.041
0.442
-0.067
0.195
Poverty rate
-0.170
0.001
-0.037
0.478
0.026
0.626
0.053
0.323
-0.015
0.777
Unmarried rate
0.011
0.835
0.065
0.216
0.049
0.352
0.083
0.121
0.020
0.696
White rate
0.050
0.340
0.064
0.226
0.066
0.212
-0.106
0.049
0.023
0.656
African
American rate
0.107
0.039
0.049
0.350
0.054
0.302
0.145
0.007
0.119
0.022
American
Indian rate
-0.085
0.102
0.049
0.350
-0.069
0.192
-0.013
0.803
-0.105
0.045
Asian rate
-0.068
0.190
-0.096
0.068
-0.114
0.030
-0.025
0.645
-0.097
0.062
Insurance
Coverage Rate
-
-
-
-
-0.025
0.629
-0.034
0.534
-0.027
0.604
Terminology Enabled Spatio-temporal Analysis and Visualization for Preterm Birth Data in the US
515
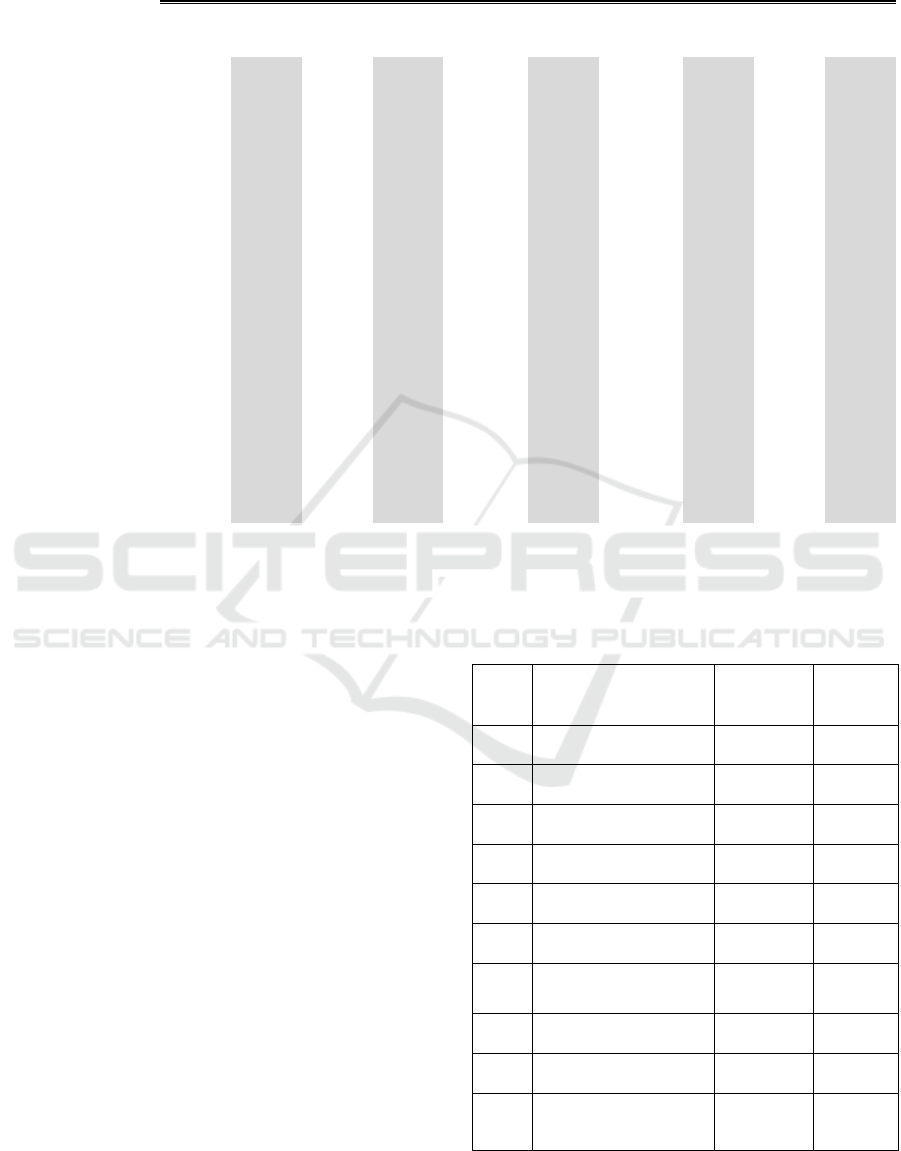
Table 5: Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient (PCC) and P value only for all female population.
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
PCC
P
-
value
PCC
P
-
value
PCC
P
-
value
PCC
P
-
value
PCC
P
-
value
Highschool rate
0.017
0.746
-0.090
0.086
-0.175
0.001
-0.072
0.180
-0.064
0.219
Bachelor rate
0.012
0.822
-0.101
0.050
-0.110
0.035
-0.051
0.348
-0.095
0.047
Median income
0.081
0.117
-0.054
0.310
-0.063
0.235
-0.029
0.586
-0.040
0.439
Poverty rate
-0.137
0.008
0.038
0.474
0.118
0.025
0.102
0.057
0.037
0.474
Unmarried rate
-0.012
0.818
0.043
0.418
0.029
0.581
0.050
0.350
-0.001
0.991
White rate
-0.047
0.365
-0.050
0.347
-0.037
0.481
-0.172
0.001
-0.049
0.351
African
American rate
0.145
0.005
0.103
0.051
0.100
0.056
0.163
0.002
0.149
0.004
American
Indian rate
-0.036
0.482
-0.073
0.046
-0.020
0.699
0.016
0.771
-0.081
0.118
Asian rate
-0.043
0.410
-0.071
0.177
-0.090
0.086
0.004
0.941
-0.069
0.188
Insurance
Coverage Rate
-
-
-
-
-0.030
0.567
0.004
0.934
-0.032
0.536
In Table 5, we are able to confirm the known risk
factor of African American women with full
confidence. Our analysis demonstrated that the ratio
of African American women is positively correlated
to preterm birth for all five years. The PCCs and P
values were 0.145 (P=0.005), 0.103 (P=0.051),
0.100 (P=0.056), 0.163 (P=0.002) and 0.149
(P=0.004) from 2010 to 2014, respectively. More
interestingly, we also found that education,
particularly the percentage of residents with college
degrees in each MSA, is weakly and negatively
correlated to the prevalence of preterm birth in 2011,
2012 and 2014. This means the higher the
percentage of women with college degrees, the
lower the prevalence of preterm birth. Such a result
suggests highly educated women can be less likely
to have preterm birth due to the advantages of a
good education. Women with more high education
are probably more financially more secure, have a
healthier life style and less amount of stress. Other
variables, such as median income, unmarried rate,
and insurance coverage rate seem clearly unrelated
to preterm birth. Poverty rate in 2010 showed weak
negative correlation with preterm birth rate with
statistical significance, but in 2012 it showed a weak
positive correlation with preterm birth rate with
statistical significance. Further investigation with
more data may be needed.
Table 6: Results for nonlinear multiple regression.
Independent
Variable
Beta
Estimate
P-value
X
1
Highschool rate
-2.6354
0.281
X
2
Bachlor rate
1.2506
0.019
X
3
Median income
- 6.0663
1.16e-06
X
4
Poverty rate
- 2.6725
0.001
X
5
Unmarried rate
0.1401
0.927
X
6
White rate
-4.6095
4.31e-08
X
7
African American
rate
- 0.4400
0.0001
X
8
American Indian rate
0.1007
0.366
X
9
Asian rate
- 0.1535
0.388
X
10
Insurance coverage
rate
0.9101
0.946
HEALTHINF 2018 - 11th International Conference on Health Informatics
516
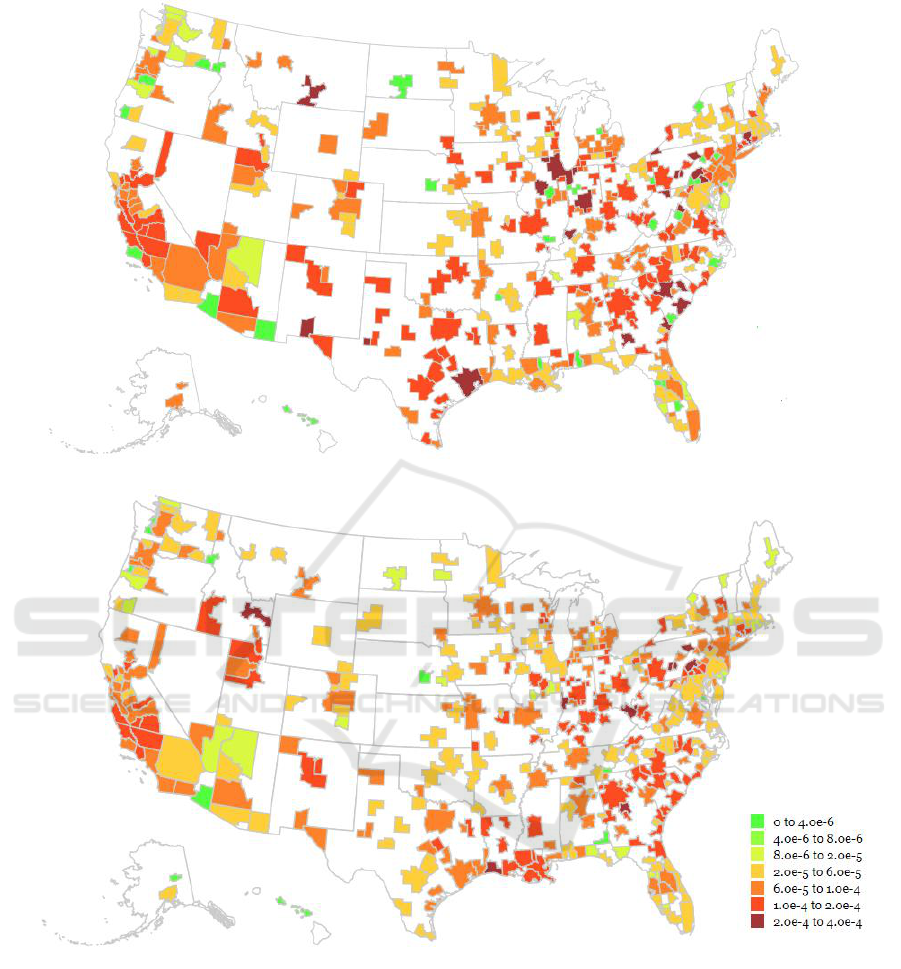
Figure 5: Prevalence of preterm birth in the United States, 2010 vs. 2014.
In the end we built multiple regression models to
analyze and validate the impact of each independent
variable. Table 6 shows the results for year 2012.
Our model included all 10 is independent variables,
after the nonlinear transformations shown in
Equation 2 in the Methodology section. The
independent variables education (percentage of
bachlor’s degree or higher), median income, poverty
rate, unmarried rate and race distribution (i.e.,
African American rate and white rate) are shown to
have P values less than 0.05. The R
2
is 0.1471 and
adjusted R
2
is 0.1228 for the multiple regression
model. This means these independent variables can
explain about 14.71% variation in the dependent
variable without adjustment of the number of
independent variable, or 12.25% variation in the
dependent variable after adjustment of the number of
independent variables. We also uses the Step
function in R to perform backward elimination of
nonsignificant independent variables, and received a
Terminology Enabled Spatio-temporal Analysis and Visualization for Preterm Birth Data in the US
517

model with the exactly the same five independent
variables, including education (percertage of
bachlor’s degree or higher), median income, poverty
rate, unmarried rate and race distribution (i.e., rate of
white and African American). This result is
consistent with the correlation analysis result and
confirms that race, education level, median income
and poverty rate may play a secondary role, in
addition to the patient-specific risk factors, including
smoking, alcohol use, illegal drug usage, stress, poor
nutrition and poor health of the mother, and family
violence.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this study, we investigated the utility of controlled
terminologies and common data model in
heterogeneous data integration and data analytics
using the clinical case of preterm birth. We examined
a large US medical claims database and census data
and explored novel spatio-temporal analysis and
visualization for public health research. We found
that the overall preterm birth rate for the U.S.
decreased during 2010 to 2014. There are
statistically significant, yet weak correlations
between race distribution, education level and
preterm birth. But median income, marital status and
insurance coverage ratio are found irrelevant. Our
study has two major limitations: 1) we do not have
the linked data for each patient and thus cannot
study the more meaningful correlations between
preterm birth cases and various social and economic
variables; and 2) MSA still represents a very coarse
representation of patients’ geographic information
and limits our capability to investigate how the
environmental factors such as air and water
pollutants impact preterm birth in the United States.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We are grateful to Dr. Feichen Shen and Jingzhi
Liang for their kind feedback during the
development of the manuscript. We also thank
Scientific Publications at Mayo Clinic for language
editing and proofreading.
REFERENCES
Anderson, S. E., Dallal, G. E. & Must, A. 2003. Relative
weight and race influence average age at menarche:
results from two nationally representative surveys of US
girls studied 25 years apart. Pediatrics, 111, 844-50.
Cohen, J. 1988. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral
sciences, Hillsdale, N. J., L. Erlbaum Associates.
Cohen, J. 1992. A power primer. Psychol Bull, 112, 155-9.
Goldenberg, R. L., Culhane, J. F., Iams, J. D. & Romero, R.
2008. Epidemiology and causes of preterm birth.
Lancet, 371, 75-84.
Hong, N., Wang, K., Yao, L. & Jiang, G. Visual FHIR: An
Interactive Browser to Navigate HL7 FHIR
Specification. Healthcare Informatics (ICHI), 2017
IEEE International Conference on, 2017. IEEE, 26-30.
Martin, J. A., Kirmeyer, S., Osterman, M. & Shepherd, R.
A. 2009. Born a bit too early: recent trends in late
preterm births. NCHS Data Brief, 1-8.
M. R., K. & C. R., H. 2008. Place matters: variation in the
black/white very preterm birth rate across U.S.
metropolitan areas, 2002-2004. Public Health Rep, 123,
576-85.
Spong, C. Y. 2013. Defining "term" pregnancy: recom-
mendations from the Defining "Term" Pregnancy
Workgroup. JAMA, 309, 2445-6.
HEALTHINF 2018 - 11th International Conference on Health Informatics
518
