
Modelling Weightlifting “Training-Diet-Competition” Cycle
Ontology with Domain and Task Ontologies
Piyaporn Tumnark
1,3
, Miguel Abreu
2
, Miguel Macedo
2
, Paulo Cardoso
2
,
Jorge Cabral
2
and Filipe Conceição
1
1
Faculty of Sport, University of Porto, Porto, Portugal
2
Industrial Electronics Department, University of Minho, Braga, Portugal
3
Faculty of Sports Science, Kasetsart University, Kamphaeng Saen Campus, Nakorn Pathom, Thailand
Keywords: Ontology, Nutrition, Weightlifting, Biomechanics, Semantics, Reasoning.
Abstract: Studies in weightlifting have been characterized by unclear results, and paucity of information. This is due to
the fact that enhancing the understanding of the mechanics of successful lift requires collaborative
contributions of several stakeholders such as coach, nutritionist, biomechanist, and physiologist as well as the
aid of technical advances in motion analysis, data acquisition, and methods of analysis. Currently, there are
still a lack of knowledge sharing between these stakeholders. The knowledge owned by these experts are not
captures, classified or integrated into an information system for decision-making. In this study, we propose
an ontology-driven weightlifting knowledge model as a solution for promoting a better understanding of the
weightlifting domain as a whole. The study aims to build a knowledge framework for Olympic weightlifting,
bringing together related knowledge subdomains such as training methodology, biomechanics, and dietary
while modelling the synergy among them. In so doing, terminology, semantics, and used concepts will be
unified among researchers, coaches, nutritionists, and athletes to partially obviate the recognized limitations
and inconsistencies. The whole weightlifting "training-diet-competition" (TDC) cycle is semantically
modelled by conceiving, designing, and integrating domain and task ontologies with the latter devising
reasoning capability toward an automated and tailored weightlifting TDC cycle.
1 INTRODUCTION
In weightlifting, enhancing the understanding of the
mechanics of successful lift requires collaborative
contributions of several stakeholders such as coach,
nutritionist, biomechanist, and physiologist as well as
the aid of technical advances in motion analysis, data
acquisition, and methods of analysis. Currently, there
are still a lack of knowledge sharing between these
stakeholders. The knowledge owned by these experts
are not captures, classified or integrated into an
information system for decision-making. This
challenge leads to the problem of paucity of
information and inconsistencies of results regarding
an integrated biomechanical analysis, training
methodology, and nutrition analysis. In this study, we
propose an ontology-driven weightlifting knowledge
model as a solution for promoting a better under-
standing of the weightlifting domain as a whole.
Among many techniques, ontology is selected
because it has been wide accepted as a useful method
to simulate human proficiency in narrowly defined
domain during the problem solving stage, by
integrating descriptive, procedural, and reasoning
knowledges. It can unify concepts and terminologies
among weightlifting stakeholders, while partially
helping obviate the paucity and heterogeneity of
existing results. However, the weightlifting
knowledge model should be scalable to easily
integrate further related domain of weight-lifting, and
also used to support the implementation of
weightlifting recommender systems.
Literature about sport ontologies is rare. There are
only few ontologies targeting sport domain. For
example, Muthulakshmi (2015) developed an
ontology for sport training through e-learning which
is based on a query template for a storage and retrieval
of sports information. It has a basic concept of sports
ontology complemented with physiological variable
measured before and after events, as well as with
physical activity. Nwe Ni Aung and Naing (2011)
presented information retrieval from Sports Domain
Tumnark, P., Abreu, M., Macedo, M., Cardoso, P., Cabral, J. and Conceição, F.
Modelling Weightlifting “Training-Diet-Competition” Cycle Ontology with Domain and Task Ontologies.
DOI: 10.5220/0006929402070214
In Proceedings of the 10th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2018) - Volume 2: KEOD, pages 207-214
ISBN: 978-989-758-330-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
207

Ontology using First-Order Logic rules and they
retrieved relevant semantic relationships between
concepts from it. Contrary to most of existing
ontology-based information retrieval systems which
use concepts mapping, they use semantic
relationships between ontology of concepts to
retrieve more relevant and correct results. Zhai and
Zhou (2010) proposed a sport ontology addressing
fine-grained granularity and wide coverage of
information for semantic retrieval for sports
information in www. They used SPARQL query
language to realize the intelligent retrieval at semantic
level according to the relations of “synonymy of”,
“kind of” and “part of” between sports concepts.
Although ontology-based works regarding to food
and nutrition is not new and some of them already
provided useful artefacts, there are not many studies
using integrated ontology approach to combine
knowledge from various domains to generate diet and
exercise suggestions. Dragoni et al. (2017) presented
PerKApp which aims to provide a full-fledged
platform supporting the monitoring of people
behaviours while persuading them to follow healthy
lifestyles. They used semantic technologies for
modelling all relevant information and for fostering
reasoning activities by combining user-generated
data and domain knowledge. The integrated ontology
supports the creation of the dynamic interfaces used
by domain experts for designing monitoring rules.
Mihnea et al. (2011) proposed recommender system
of workout and nutrition for runners by integrating
web crawling and ontology. The system is a mixture
between experts’ knowledge and a social dimension
in generating the nutrition and workout plan. The
system provides information to users regarding the
workout and treatment recommendations, in case of
injury, alongside diet plan that best suits them, based
on their profile information, food preferences, and
goals.
With respect to works discussed in the literature,
this study aims to conceive and design an ontology-
enriched knowledge model to guide and support the
implementation of “Recommender system of workout
and nutrition for weightlifters”. In doing so, it will
propose: (i) understanding the weightlifting training
system, from both qualitative and quantitative
perspectives, following a modular ontology
modelling, (ii) understanding the weightlifting diet
following a modular ontology modelling, (iii)
semantically integrating weightlifting and nutrition
ontologies to mainly promote nutrition and
weightlifting snatch exercises interoperability, (iv)
extending modular ontology scope by mining rules
while analysing open data from the literature, and (v)
devising reasoning capability toward an automated
weightlifting “training-diet-competition” cycle
supported by previously mined rules. To the best of
our knowledge, this kind of design is innovative with
respect to the other systems due to the collaborative
contributions of several stakeholders such as coach,
nutritionist, and biomechanist for supporting the
monitoring of training and nutriton status of
weightlifter.
This paper is divided into four sections. Section 1
presents an introduction; Section 2 describes the
followed methodology for the ontology development;
Section 3 describes the constructed ontology and
rules derived from the development process. Finally,
some conclusion remarks are mentioned in the
Section 4.
2 METHODS
Based on the guidelines proposed by Chi et al. (2015),
the following approach is proposed to ontologically
model and design of the weightlifting TDC cycle.
2.1 Establishing the Domain Scope and
Analysing Problem Scenarios
Managing training and competition performance of
weightlifters is a very challenging problem due to the
interplay among multiple sources of unobserved
heterogeneity at athletes’ profile, competition,
training model, dietary protocol, research, resource,
or year level. It involves several knowledge sources,
spreading into several information dimensions such
as nutrition, training, and biomechanics (Figure 1).
Nutritional knowledge includes the definition of
dietary protocol, energy expenditure estimation,
energy balance, as well as food composition in terms
of macro- and micro-nutrients. Dietary protocol as a
concept, includes recommended food intake
according to athletes’ preferences and restrictions at
specific training and competition instants. Coaching
and training knowledge supports a qualitative
analysis technique which includes a controlled
vocabulary. It consists of common terms to alleviate
semantic differences between training methods,
lifting exercises and their phases concepts, as well as
barbell and body kinematics and kinetics. The
training dimension is mostly represented by
descriptive terms or abstract values. They are
regarding lifting exercises’ performance which can be
mapped to ground values measured in real-time by
biomechanics analysis systems or energy expenditure
measurement devices. Biomechanics knowledge
KEOD 2018 - 10th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
208

supports a quantitative analysis approach based on
ground values and it includes a controlled vocabulary
consisting of sub-concepts (e.g., calibration method,
acquisition method, and analysis method,) and
concepts like lifting analysis, resource, and muscle
activity.
To implement the problem scenarios analysis, we
firstly tackle individually each information
dimension of the training-diet-competition (TDC)
cycle and only then formalize the problem solving
according to the following two sets of non-logical
axioms, required to estimate and/or measure
performance, as well as to examine and monitor the
designed and prescribed training to each individual
athlete.
Figure 1: The problem solving for improving weightlifting
ability.
2.1.1 Assessment and Monitoring of
Nutrition Dietary Features
Several prediction equations and method of analyses
will be required to estimate and measure the energy
expenditure which depends on muscular activation
and muscle contraction. Both anthropometric and
metabolic measurements having been carried out
because physical activities are usually classified in
terms of their mutually dependent biomechanical and
metabolic aspects, as well as their intensities and
durations. Therefore, not only body composition
should be assessed but also other potential sources of
change in energy expenditure during lifting activities,
through activation levels of major muscles groups. By
assessing the energy expenditures while lifting, the
prescribed energy intake will be examined to
determine the energy balance status and then
accordingly adjusted (i.e., in terms of macro-and
micro-nutrients) for a more suitable dietary intake.
For accurate measurement of energy expenditure and
outcome assessment, accelerometer-, heart rate-,
electromyography-, or calorimetric-based devices
have been used to collected data related to diverse
energy expenditure components.
2.1.2 Assessment and Monitoring of
Biomechanics Features
To maintain consistence in each lift while enhancing
performance, weightlifting biomechanics have been
analysed following qualitative, quantitative, and
predictive approaches, as well as combinations of
them (Ho et al., 2014). Quantitative approaches have
been toward kinetics and kinematics of barbell and
weightlifter body, mainly trying to classify barbell
trajectory, identify optimal lifting technique, quantify
barbell parameters, joint angle, and applied force. In
so doing, it required several devices such as motion
capture systems, force plates, and EMG, as well as
several and different method of analysis.
Having already defined the motivation for
addressing issues related to the weightlifting TDC
cycle, the following general competence questions
were formulated to be answered by the ontology and
so, limiting the ontology scope:
1) Did the athlete properly lift the barbell?
2) Did the athlete’s body move accordingly
during exercises phases?
3) Was the athlete well-served in terms of
macronutrients and micronutrients according
to the training protocol specificity?
4) Did the rhythmic execution reflect an efficient
snatch technique?
The rhythmic execution, should be understood as the
definition presented by Ho et al. (2014) i.e., the
coordination movement of the weightlifter-barbell
system for an efficient and effective lift.
Figure 2: Weightlifting TDC-cycle OWL- and Rule-
Knowledge-based System.
In Figure 2, each actor plays a fundamental role in
the assessment task. The Reasoning and Knowledge
Base layer encompasses three non-overlapping
sublayers. The four perspectives are defined as
follows. (i) Task Fact Base (FB) encloses task related
instances. The Athlete creates its profile by inserting
relevant personal data whereas the Training Manager
and Lab Technician are in charge of updating the
Modelling Weightlifting “Training-Diet-Competition” Cycle Ontology with Domain and Task Ontologies
209

knowledge base with training data, respectively,
providing qualitative and quantitative assessments.
(ii) Reasoning and Knowledge Base (KB) is
composed of all available knowledge over which the
reasoning is performed. The Task FB input is used as
a trigger to start the inference process, which is based
on SWRL rules whereas the output of that process is
given as a series of axioms, representing detailed
results with practical, human readable data. (iii) Task
Rules comprises all SWRL rules created to infer
knowledge from training related instances. These
rules may be created or updated by several experts
from different domains. (iv) Domain Knowledge Base
refers to the application-independent axioms, which
can be updated to better cope with improvements in
the understanding of applicable fields. Knowledge
bases are implemented as ontologies, which were
divided into assertion axioms (i.e., Fact base; FB)
and terminological axioms (i.e., Concepts and
Attributes; CA) to illustrate the interaction of both
areas in the global architecture. Each KB and
respective rules were created using Protégé and its
plug-ins.
2.2 Modelling and Design of the
Weightlifting Domain Ontology
To obtain a deep understanding of aspects and concrete
entities comprising the weightlifting TDC cycle, repe-
titive collaboration meetings were organized between
athletes, coaches, biomechanist and nutritionist along
with electronics and software engineers. The following
design artefacts express ontologies in the weightlifting
TDC-cycle knowledge -based system i.e., TDC-
Ontology = (CA, CV, FB, R, A):
2.2.1 Concepts and Attributes (CA)
Different concepts in the TDC-Ontology have been
divided into four main knowledge sets: training,
biomechanics, nutrition, and problem solving,
complemented with an athlete profile concept as
nearly all observation and measurement are around
athlete's activities. The first three sets correspond to
domain ontology which identifies general concepts
and their relations in the field of weightlifting, while
the fourth one is part of the task ontology.
Training-or coaching-related ontology subset
refers to classes modelling exercises performed by
athlete, with each exercise consisting of several
phases. Basically, these concepts are used to promote
a qualitative weightlifting analysis and are mainly
represented by abstract values regarding observable
lifting performance by a coach.
Biomechanics-related ontology subset is used to
leverage a quantitative weightlifting analysis and are
represented by the ExerciseProperty concept. The
main purpose is complementing qualitative lifting
performance values with biomechanics ground values
measured during a lifting exercise phase, using
biomechanics equipment.
Nutrition-related ontology subset is also used to
leverage a quantitative weightlifting analysis and it is
modelled by the following subclasses. The Dietary
Protocol related to each workout period, the
respective NutrientPortions, and the Consumable
having nutrients. Nutritional ground values are
measured for a lifting exercise phase, using a
combination of energy expenditure measurement
equipment, prediction equations, and methods of
analysis. The DietaryProtocol concept prescribes the
receipt of nutrient portions for a specified workout
phase, the NutrientPortions concept identifies a
specific nutrient and its amount in terms of macro-
and micro-nutrients and the Consumable concept
represents the food and drink that are sources of
nutrients. In this prototype, Consumable concept are
adopted from our previous work (Tumnark et al.,
2013). However, in the future, we may consider
adopting the food concept from other available
literature in order to cover all available menus items.
2.2.2 The Controlled Vocabulary (CV)
Horizontal to concepts defined in CA, there is a list of
authorized keywords, used across both domain and
task ontology. The list contains nine subclasses and
under each of them, authorized keywords are used to
provide reference and indexing for communication
with other concepts and instances. Subclasses are the
WorkoutPhase concept defining periods for which a
dietary protocol is prescribed, which is instantiated as
authorized keywords Preworkout, Duringworkout,
and Postworkout. The DayPart concept represents
day time prescribed for weightlifting training and
dietary intake which is instantiated as authorized
keywords Morning, Afternoon, and Evening. The
Acquisition Method concept establishes methods used
to collect quantitative ground values, e.g., heart rate
monitor, motion analysis, electromyography (EMG),
or force measurement; Muscle concept defines
muscles where activity should be measured, e.g.,
VastusLateralis, Biceps Femoris, PectineusGracilis.
The AnalysisMethod concept establishes analysis
methods used for the assessment of energy
expenditure and biomechanics features from several
kinds of collected data, such as kinetics, kinematics,
and physiological. The Calibration Method concept
KEOD 2018 - 10th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
210
establishes some known methods for proper
calibration of biomechanics equipment which is
instantiated as authorized keywords OnePointCal,
TwoPointCal, and Curve FittingCal. The Resource
Type concept defines resource types used for
quantitative measurement of barbell/body kinematics
and kinetics (e.g., video camera, infrared cameras,
force plates), body composition, as well as training
resource (e.g., barbell and weight plates). The
Nutrient concept includes groups of macro- and
micro-nutrients, as standard vocabulary used in
energy expenditure assessment and dietary intake to
promote optimal health and performance across
different scenarios of weightlifting training. The
ExerciseMethod concept classifies weightlifting
training methods under Bulgarian or Russian
frameworks and principles.
2.2.3 The Fact Base as a Set of Individual
(FB)
Concepts in the domain ontology are further
elaborated and terminal concepts are described in
terms of instances. These individuals belonging to the
ontology will act as the foundations of the knowledge
base supporting the problem solving activity. The fact
base is populated by a collection of facts generated
through the elaboration of domain ontology concepts,
i.e., terminal concepts are described in terms of
instances. These instances contain measured
nutritional and biomechanics ground values as well as
observable training-related abstract values collected
by coaches which are mapped to corresponding
ground values.
2.2.4 Relationship between Classes (R)
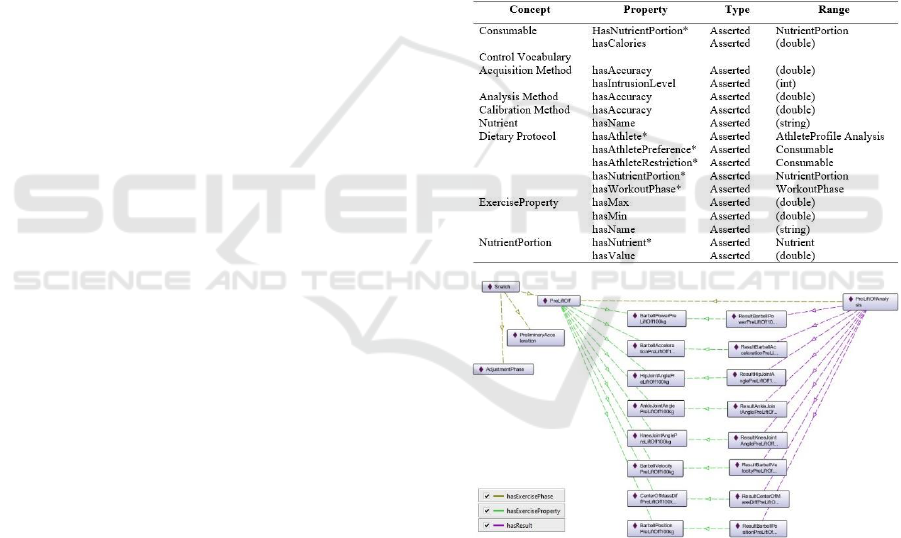
Excluding the data properties presented in Table 1,
the remaining relationships (i.e., among classes) are
constructed as object properties. Figure 3 displays
some individuals that represent the analysis of a phase
of the Snatch exercise. The Snatch exercise individual
is related to five phases/six positions by the object
property hasExercisePhase and, for the Firstpull
phase (Liftoffposition), there are some Exercise
Property individuals where each is related to a Result
individual that belongs to an individual of the
PhaseAnalysis concept, called LiftoffAnalysis.
2.3 Engineering the Task Ontology
To solve specific weightlifting TDC-cycle problems
as previously formulated through competency
questions, the task ontology will use the conceptual
structure of the domain ontology expressing the
semantic knowledge of biomechanics, nutrition, and
training dimensions of the TDC-cycle, while defining
other concepts’ constituent properties to describe the
problem solving structure. Basically, (i) property
values of known facts or unknown knowledge are
defined to separate asserted properties from inferred
ones, (ii) the corresponding domain and range of
properties are asserted, and then, (iii) Semantic Web
Rule Language (SWRL) rules supported by Sematic
Query-Enhanced Web Rule Language (SQWRL) are
created for reasoning about individuals on FB and so,
addressing the insufficient expressivity of ontologies
in properties association and operation required by
the formulated competency questions.
Table 1: Data properties of each concept presented on the
domain ontology.
Figure 3: Some individuals and their associated object
properties.
Generically, the problem solving structure
consists of two main groups: nutrition analysis and
training analysis (i.e., addressed both in terms of
qualitative and quantitative analysis, being the latter
achieved through biomechanics analysis) according
to Figure 1 and also the aforementioned competency
questions. Therefore, some concepts that constitute
the problem solving structure are:
Modelling Weightlifting “Training-Diet-Competition” Cycle Ontology with Domain and Task Ontologies
211

The AthleteProfileAnalysis concept contains 9
properties, being 8 asserted properties and 1 inferred
from rule EEE (Exercise Energy Expenditure).
The PhaseAnalysis concept contains 8 properties.
6 are asserted properties and 2 are inferred properties,
which are used for the evaluation of an exercise's
phase. (see rule analyse).
The ResourceAnalysis concept contains 5
asserted properties and 1 inferred property that
represents the accuracy of the resource. It is inferred
using rule topResources.
The ExercisePropertyAnalysis concept contains 2
asserted properties and another property that is either
asserted or inferred, to represent the evaluation of the
result. When inferred, this evaluation maps to rules
evaluateMax, evaluateMin, and evaluateMinMax.
The TrainingDayAnalysis concept contains 9
properties, where 3 are asserted and 6 are inferred.
The exercise energy expenditure (EEE) is inferred by
the rule EEE. The total energy needed (TEN) and the
resting metabolic rate (RMR) are inferred by rules
TENmale or TENfemale. The energy intake is inferred
by the rule EI while the difference between consumed
and energy needed is mapped to the Rule balance.
One property was used to report dietary problems of
the training day, which is inferred from rules
evaluateNutrientsMax and evaluateNutrientsMin.
Three of these concepts are combined to form a
complete biomechanics and nutrition analysis chain,
being the core of the problem solving structure.
Starting with the ExercisePropertyAnalysis, this
concept analyses the individual biomechanics
characteristics of an exercise which are mapped to the
ExerciseProperty concept. Then, PhaseAnalysis
focuses on several phases of each exercise and
provides a broader analysis of the biomechanics of an
exercise. Lastly, TrainingDayAnalysis encompasses
the analysis of nutrition for a full training day of
multiple exercises.
3 RESULTS
All the 11 inferred properties of the Task Ontology
require semantic rules that relate facts and, thus, are
able to infer new knowledge. In order to answer all
the competency questions, SWRL-based rules and
SQWRL queries have been used. Although SWRL is
built on the same description logic foundation as
OWL-DL, it provides strong formal guarantees when
performing inference. It has considerably more
expressive power than OWL alone, particularly when
dealing with complex interrelationships between
OWL individuals or when reasoning with data values
(Dhingra and Bhatia, 2015). In this study, SWRL
rules operate over the instances of the ontology and
are expressed as a chain of atoms that, if all hold true,
a consequence is produced. SQWRL queries work
similarly to the SWRL rules but they are used for
retrieving knowledge from the ontology instead of
creating it. Also, query's result needs to be manually
added to the ontology. Overall, 9 rules and 3 queries
were created and these can be separated into three
broad categories: Biomechanics, Nutrition, and
Resource reliability.
3.1 Developing Semantic Rules
Due to the space limitations, only some of the drafted
SWRL rules are described in detail.
Biomechanics/Coaching Rules
1) evaluateMinMax used for the evaluation of an
exercise and it starts by evaluating if each of its
properties are within a considered favorable range. It
verifies whether the value of an exercise property's
result is within the specified range, and in case of
being true, it causes the result to receive a positive
evaluation denoted by the word "OK". Breaking
down the rule, it starts by obtaining an Exercise
PropertyAnalysis individual called r (1) and its value
(2) using the r's hasValue data property. Then it
obtains, through the hasExerciseProperty object
property, the ExerciseProperty individual p (3) and,
like before, its min and max values (4-5) are retrieved
using the hasMin and hasMax data properties,
respectively. After obtaining all the necessary values,
the rule then checks if the result's value is within the
exercise property's range (6-7) and it asserts r's
evaluation as "OK" (8).
Rule: evaluateMinMax
ExercisePropertyAnalysis(?r)
(1)
^ hasValue(?r, ?v)
(2)
^ hasExerciseProperty(?r, ?p)
(3)
^ hasMin(?p, ?min)
(4)
^ hasMax(?p,?max)
(5)
^swrlb:greaterThanOrEqual(?v,
?min)
(6)
^swrlb:lessThanOrEqual(?v, ?max)
(7)
-> hasEvaluation(?r, "OK")
(8)
2) evaluateMin/evaluateMax are used to evaluate if
the value of the result is below the minimum or above
the maximum. It uses the ExerciseProperty's name to
be easily identifiable, as this evaluation will be later
used for the overall examination of the exercise.
3) analyse examines if the exercise was not properly
executed by checking if there are any unsuccessful
results and so, reporting all associated problems.
KEOD 2018 - 10th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
212

Nutrition Rules
4) EEE calculates the Exercise Energy Expenditure
based on the formula EEE = METs * 0.0175 * Weight
* Duration.
Rule: EEE
TrainingDayAnalysis(?tda)
^ hasPhaseAnalysis(?tda, ?pa)
^ hasResult(?pa, ?r)
^ hasExercisePhase(?pa, ?ep)
^ EPDuration(?p)
^ hasExerciseProperty(?r, ?p)
^ hasValue(?r, ?d)
^ hasTrainingDay(?tda, ?td)
^ hasAthlete(?td, ?a)
^ hasWeight(?a, ?w)
^ hasExerciseRoutine(?td, ?er)
^ hasExercise(?er, ?e)
^ hasExercisePhase(?e, ?ep)
^ hasMET(?e, ?m)
^ swrlb:multiply(?v0,"0.0175"^^
xsd:float, ?m)
^ swrlb:multiply(?v1, ?v0, ?d)
^ swrlb:multiply(?v2, ?v1, ?w)
˚ sqwrl:makeBag(?b, ?v2)
^ sqwrl:groupBy(?b, ?tda)
˚ sqwrl:sum(?s, ?b)
-> sqwrl:select(?tda, ?s)
5) femaleTEN calculates the RMR and the amount of
energy needed (TEN) by an athlete.
6) balance compares the energy intake with the
amount of energy needed to calculate the energy
difference.
7) EI is used to calculate the necessary energy intake
for a training day.
8) evaluateNutrinetsMin evaluates the athlete's
nutrients intake for each workout phase. In this case,
it evaluates if the intake is below the recommended
level and reports a problem.
Resource Reliability Rule
9) topResources retrieves all the resources for each
type in descending order of accuracy.
Rule: topResources
ResourceAnalysis(?res)
^ hasResourceType(?res, ?rt)
^ hasMethod(?res, ?m)
^ hasAccuracy(?m, ?ac)
˚ sqwrl:makeBag(?b, ?ac)
^ sqwrl:groupBy(?b, ?rt,?res)
˚ sqwrl:max(?max, ?b)
-> sqwrl:select(?rt,?res,?max)
3.2 Evaluation of the Knowledge
Representation
To illustrate the reasoning process, a simple test case
was inserted in Protégé. The athlete had to perform a
full Snatch lift, while monitoring numerous
biomechanical variables. To accomplish that, six
instances of PhaseAnalysis were created along with
several phase related sensor results. These values,
which are ExecisePropertyAnalysis instances (Figure
4), were linked to the analysis instance via the
hasResult object property.
Figure 4: Snatch, its six phases and all associated exercise
property analysis instances.
Figure 5: Rule based evaluation of Transition phase and
Turnover phase of Snatch.
Upon comparison of the results with exercise
ranges (domain knowledge), Pellet, which was the
chosen reasoner, inferred the existence of 2 values out
of bounds in the third phase of the exercise as
presented in Figure 5. The value of thigh angle and
knee joint angle were above maximum value and the
exercise was not declared as compensated by The
training manager. So, the evaluation was reported as
"failed". It means that there were errors in lifting's
technique of this athlete regarding the movement of
thigh and knee and it was not approved by an expert.
On the right side of the same figure, is presented a
different case, i.e., the analysis of the fifth phase. The
system generated no problems because it was
manually reported as being compensated by the
Training Manager. In this case, even there was an
error in lifting's technique of an athlete, it was
approved quantitatively by an expert.
Modelling Weightlifting “Training-Diet-Competition” Cycle Ontology with Domain and Task Ontologies
213

4 CONCLUSIONS
This study demonstrated the use of Ontology Web
Language (OWL) and SWRL to semantically model
the whole weightlifting TDC-cycle, bringing together
related knowledge subdomains, while modeling the
synergy among them. Nutritional, biomechanics, and
coaching/training facts were combined with SWRL
rules representing rhythmic execution and energy
balance to infer athlete’ lifting performance.
Moreover, these rules can be used to trigger and
classify any qualitative-quantitative lifting mismatch
as corner cases which will deserve deeper and future
quantitative analysis, both regarding nutritional and
biomechanics perspectives. Each KB and respective
rules in TDC Competency Questions Engine
Architecture were created using only Protégé and its
plug-ins, resulting into: 43 classes, 57 properties, and
29 relationships. Overall, 9 SWRL rules, and 3
SQWRL queries were created and these can be
separated into three broad categories: Biomechanics,
Nutrition, and Resource reliability.
Beside the advantages that was mentioned
earlier, coaches and athletes can be benefited from
this system in several ways such as it can help coaches
to identify errors in the technique during the lifting.
This is due to the fact that errors can be overcome by
compensatory movement and successful lift can still
be achieved. This point causes a gap between the
weightlifter’s actual performance and what the
weightlifter could potentially lift. This system could
narrow this gap and help to identify which factors
lead to efficient technique and which ones limit the
performance. In case that the FB is large enough, the
novel factors/relationships might be discovered.
In spite of the mentioned applicability of the
proposed weightlifting TDC-cycle OWL knowledge-
based system, few drawbacks have been identified to
be later tackled in the next iterated TDC-ontology:
1) Re-design the TDC-Ontology to address domain-
level modularity, as well as being more scalable.
2) Devise the integration of new concepts and
properties which will ease the modeling of corner
cases (i.e., qualitative-quantitative lifting mismatch).
3) Iteratively tune rhythmic execution SWRL rules
according to identified corner cases, biomechanics
analysis, and optimization approaches, as well as to
reference top performance athletes, both in terms of
rhythm and anthropometric features.
Furthermore, more tests should be made based not
only on open data presented and discussed in the
existing literature but also lively collected during
weightlifting training.
REFERENCES
Chi, Y. L., Chen, T. Y. & Tsai, W. T. 2015. A chronic
disease dietary consultation system using OWL-based
ontologies and semantic rules. Journal of Biomedical
Informatics, 53, 208-19.
Dhingra, V. & Bhatia, K. K. 2015. Development of
Ontology in Laptop Domain for Knowledge
Representation. Procedia Computer Science, 46, 249-
256.
Dragoni, M., Bailoni, T., Eccher, C., Guerini, M. &
Maimone, R. 2017. A semantic-enabled platform for
supporting healthy lifestyles. Proceedings of the
Symposium on Applied Computing. Marrakech,
Morocco: ACM.
Ho, L. K., Lorenzen, C., Wilson, C. J., Saunders, J. E. &
Williams, M. D. 2014. Reviewing current knowledge in
snatch performance and technique: the need for future
directions in applied research. Journal of Strength and
Conditioning Research, 28, 574-86.
Mihnea, D., Madalina, I., Mihai, D. & Stefan, T. M. The
Runner-Recommender System of Workout and
Nutrition for Runners. 13th International Symposium
on Symbolic and Numeric Algorithms for Scientific
Computing, SYNASC 2011, 2011 Timisoara, Romania.
230-238.
Muthulakshmi, S. 2015. Design and development of
ontology Based e learning system for sports Domain.
Doctoral dissertation Doctoral dissertation, Anna
University.
Nwe Ni Aung & Naing, T. T. Sports Information Retrieval
with Semantic Relationships of Ontology 3rd
International Conference on Information and Financial
Engineering, 2011. IPEDR.
Tumnark, P., Conceição, F., Vilas-Boas, J. P., Oliveira, L.,
Cardoso, P., Cabral, J. & Santibutr, N. 2013. Ontology-
based personalized dietary recommendation for
weightlifting. In: Honghua, T. & Tingting, W. (eds.)
Advances in Intelligent Systems Research. Atlantis
Press.
Zhai, J. & Zhou, K. Semantic Retrieval for Sports
Information Based on Ontology and SPARQL.
ISME’2010, 7-8 Aug. 2010 2010. 395-398.
KEOD 2018 - 10th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
214
