
Using DBpedia Categories to Evaluate and Explain Similarity in Linked
Open Data
Houcine Senoussi
Quartz Laboratory, EISTI, Cergy, France
Keywords:
DBpedia, DBpedia Categories, Linked Open Data, Similarity Measure, Semantic Web.
Abstract:
Similarity is defined as the degree of resemblance between two objects. In this paper we present a new
method to evaluate similarity between resources in Linked Open Data. The input of our method is a pair of
resources belonging to the same type (e.g. Person or Painter), described by their Dbpedia categories. We
first compute the ’distance’ between each pair of categories. For that we need to explore the graph whose
vertices are the categories and whose edges connect categories and sub-categories. Then we deduce a measure
of the similarity/dissimilarity between the two resources. The output of our method is not limited to this
measure but includes other quantitative and qualitative informations explaining similarity/dissimilarity of the
two resources. In order to validate our method, we implemented it and applied it to a set of DBpedia resources
that refer to painters belonging to different countries, centuries and artistic movements.
1 INTRODUCTION
DBpedia (Lehmann et al., 2015) is one of the most
important semantic datasets freely accessible on the
web. It contains structured knowledge extracted from
Wikipedia. To define RDF triples, Dbepdia uses its
own vocabulary
1
, RDF
2
, RDFS
3
and OWL vocabula-
ries and other ontologies such that Dublin Core Me-
tadata Intitiative
4
(dcmi), Skos
5
and Foaf
6
.
DBpedia uses many thousands predicates to des-
cribe resources but all these predicates don’t have the
same importance. For example, on the french version
of Dbpedia
7
we have 208796
8
(resp. 3352) articles be-
longing to the type Person (resp. Painter). These arti-
cles use 2887 (resp 345) predicates, but only 13 (resp.
14) predicates are used in 99% of the articles and only
18 (resp. 21) predicates are used in 80% of the arti-
cles. Only these common predicates can be used to
compare resources. dcterms:subject is one of these
few predicates. Its values are DBpedia categories and
1
http://dbpedia.org/ontology/
2
https://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns
3
https://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema
4
http://dublincore.org/documents/2012/06/14/dcmi-
terms/
5
https://www.w3.org/2009/08/skos-reference/skos.html
6
http://xmlns.com/foaf/spec/
7
http://fr.dbpedia.org/
8
Retrieved April 28, 2017
it is intended to define the topics of the resources.
Categories contain all important information
about a resource. For example, when the article is
about a novel, they give us all information about it
(author, date, language, genre, ...). Therefore, catego-
ries contain all elements we need to compare two re-
sources and to measure their similarity/dissimilarity.
Similarity is defined as the degree of resem-
blance between two objects (Meymandpour and Da-
vis, 2016). According to Tversky (Tversky, 1977) it
serves to ”classify objects, form concepts and make
generalizations”. Many methods to evaluate simila-
rity have been presented by researchers. An overview
of these methods can be found in (Meng et al., 2013)
and (Meymandpour and Davis, 2016). In this article,
we present a new method for evaluating and explai-
ning similarity between objects. These objects are re-
presented as sets of Dbpedia categories.
The rest of this paper is organised as follows. In
section 2 we describe DBpedia categories and their
organization. Section 3 summarizes the motivation of
this work and its contributions. Sections 4, 5 and 6
give a detailed description of our method. In section
7 we present our experimental results. Section 8 des-
cribes related work. We conclude in the section 9.
Senoussi, H.
Using DBpedia Categories to Evaluate and Explain Similarity in Linked Open Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0006939001170127
In Proceedings of the 10th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2018) - Volume 2: KEOD, pages 117-127
ISBN: 978-989-758-330-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
117

2 DBpedia CATEGORIES
There are two main types of categories : administra-
tive categories and content categories. Administrative
categories are used to organise the Wikipedia project.
They are non-semantic categories. The content cate-
gories are used to group articles dealing with the same
subject. In other words, two Wikipedia articles belong
to the same category if they share some property : e.g.
Leonardo da Vinci, Raphael and Michelangelo belong
to the 16th-century Italian painters.
Some categories are called container categories :
they are intended to be populated entirely by subcate-
gories. Other categories can contain only articles or
both sub-categories and articles. We call the former
pure categories and the latter mixed categories.
Given what we have summarized above, Dbpe-
dia categories are organised using two graphs. The
first one is a bipartite graph GS=(R, C, ES), where
R is the set of all resources, C the set of categories
and ES the set of edges defined by the predicate dc-
terms:subject. The second one is an acyclic directed
graph GB=(C, EB) where EB is the set of edges defi-
ned by the predicate skos:broader. For two categories
cat1 and cat2, we have cat1 skos:broader cat2 if cat1
is a sub-category of cat2. We notice that in this graph
about 13% of the vertices are isolated. The majority
of these vertices correspond to date categories. We
also have a little number of sinks (vertices without in-
coming edges). About 50% are sources (vertices wit-
hout incoming edges). These vertices represent pure
categories.
3 MOTIVATION AND
CONTRIBUTION
Our aim in this work is to define a similarity measure
for linked data that simulates as well as possible hu-
man notion of similarity. Given how humans evaluate
the similarity between objects, such a measure must
have at least the two following properties :
1. Be able to detect hidden commonality : let us
for example consider two paintings defined by the
following sets of features : P1 = {Author=Claude
Monet, Creation Year= 1914, Museum=Mus
´
ee
de l’Orangerie} and P2={Author=Auguste Re-
noir, Creation Year= 1911, Museum=Petit Pa-
lais}. These two paintings don’t have common
features. A standard feature-based similarity me-
asure will conclude that their similarity is equal to
0. However, they have an important commonality
: both of them were painted by french impressi-
onist painters, were created about 1910, and are
on display in a parisian museum. We call that a
’hidden’ commonality.
2. To give different weights to features depending
on their ’obvious’ importance : let us for example
consider the following objects : P1 = {..., Aut-
hor=Claude Monet, Category=Vandalized works
of art,...} and P2={..., Author=Claude Mo-
net,...} and P3={..., Category=Vandalized works
of art,...}. According to a standard feature-based
similarity measures, the similarity between P1
and P2 is equal to the similarity between P1 and
P3 because the two pairs of paintings have the
same number of common features and the same
number of different features. But in the defini-
tion of a painting the feature ’Author=’ is ob-
viously more ’important’ than the feature ’Cate-
gory=Vandalized works of art’. Therefore, in a
’good’ similarity measure, contribution of the for-
mer feature should be more important than that of
the latter.
In addition to these two essential properties, we want
our similarity measure to have some other nice pro-
perties : to be intuitive, data type-independent and
dataset-independent, and its results are easily explai-
ned.
To the best of our knowledge, no one of the known
methods has all these properties (see section 8).
The main contributions of this paper can be sum-
marized as follows :
1. Defining a unified representation of LOD resour-
ces using weighted DBpedia categories.
2. An intuitive algorithm that uses categories’ graph
to measure similarity between resources.
3. The output of this algorithm is not limited to the
similarity measure but contains qualitative ele-
ments explaining it.
4 PROBLEM FORMALIZATION
• Given two DBpedia resources belonging to the
same type, our objective is to measure their si-
milarity and give an explanation to this simila-
rity/dissimilarity.
• A resource is described by its categories and each
category is assigned a weight.
• As input we have two resources represented by
their categories and their weights. In other words
each resource is described by a set of couples
R={(c
i
, w
i
)} where c
i
s are categories and w
i
s are
real numbers such that
∑
w
i
=1.
KEOD 2018 - 10th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
118

• To measure similarity between R1={(c1
i
, w1
i
)}
and R2={(c2
i
, w2
i
)} we need a function compu-
ting the ’distance’ between categories. Let us call
dist such a function.
• We use dist to compute first the distance bet-
ween each pair (c1
i
, c2
j
), then the distance bet-
ween each category c and the other resource, and
finally the distance between the two resources.
• The desired output contains 3 levels. The level
0 contains couples {(c1, c2) ∈ R
1
× R
2
} such that
c1 is close to c2. These categories explain resour-
ces’ similarity. This level also contains categories
which are not close to other categories. These ca-
tegories explain dissimilarity between the two re-
sources. The level 1 contains a 1-dimension table
summarizing the level 0 content. The top level
contains a measure of the similarity between the
two resources.
5 DISTANCE BETWEEN
CATEGORIES
The predicate skos:broader is a particular case of the
’is-a’ relation. This relation has been extensively stu-
died and we know ((Rada et al., 1989)) that in this
case the shortest path length between categories de-
fines a semantic distance. We call dist this semantic
distance and we compute it using the following algo-
rithm :
• Input : The graph GB, the two categories c
1
and
c
2
, An integer DEPTH MAX and a ’big’ integer
INF.
• Output : the integer value dist(c
1
, c
2
).
• Starting from c
1
and c
1
explore the graph GB
using a breadth-first traversal. Limit the graph ex-
ploration to a depth DEPT H MAX .
• If we find a common ancestor cc : dist(c
1
, c
2
) =
length(c
1
→ cc)+length(c
1
→ cc).
• Else : dist(c
1
, c
2
) = INF.
In the following we will take INF=2 ∗
DEPT H MAX + 1. It results that dist(c
1
, c
2
) ∈
{0, ..., 2 ∗ DEPT H MAX +1}.
5.1 Particular Case of Isolated
Categories
Some categories are isolated vertices in the graph GB.
Il follows that if we apply the general definition of
the distance between categories we will have : For
each isolated category c
d
, for each category c 6= c
d
,
dist(c
d
, c) = INF.
In this work, we considered more speci-
ally birth and death categories (YYYY births and
YYYY deaths) that we find in resources belonging to
the type Person. These categories are processed as
follows :
1. The distance between two birth (resp. death) ca-
tegories is the number of generations between
them. If this number of generations is greater than
2 ∗DEPT H MAX we consider that the distance is
INF. In this work we take GEN=25.
2. For each other category c the distance between a
birth (resp. death) category and c is equal to INF.
6 DISTANCE BETWEEN
RESOURCES
Given two resources R1={(c1
i
, w1
i
)} and
R2={(c2
i
, w2
i
)}, we compute the distance
dist(R1,R2) between them as follows :
1. For each pair (c1
i
, c2
j
) compute the distance d
i j
=
dist(c1
i
, c2
j
).
2. For each category c1
i
compute the distance
between c1
i
and the resource R
2
defined by
dist(c1
i
)=dist(c1
i
, R2)=min
j
(d
i j
).
3. For each category c2
j
compute the distance
between c2
j
and the resource R
1
defined by
dist(c2
j
)=dist(c2
j
, R1)=min
i
(d
i j
).
4. When computing the latter distances we define the
set T as follows :
• T ={(c, dist(c), c
0
)} where c is a category of R1
or R2, and dist(c)=dist(c, c
0
), in other words c
0
is a category that minimizes the distance bet-
ween c and the categories of the other resource.
5. Define the 2 ∗ DEPTH MAX +2-size table tab as
follows :
• tab[i] = cumulated weight of categories whose
distance to the other resource is equal to i.
6. dist(R1, R2) =
∑
i
(i ∗tab[i])/
∑
i
tab[i]
This distance is comprised between 0 and INF=2 ∗
DEPT H MAX + 1. We can normalize it if we want
to compare distances computed with different values
of DEPT H MAX. Similar resources have low values
of dist. Dissimilar ones have values close to INF.
To explain similarity/dissimilarity of the two re-
sources, we use :
Using DBpedia Categories to Evaluate and Explain Similarity in Linked Open Data
119

1. the set T : If the d value of a triplet {(c, d,c
0
)}
is low, categories c, c
0
and their common succes-
sor cs explain similarity. If d is high, c explains
dissimilarity.
2. the table tab : This table summarizes the con-
tent of T . Its left cells (lowest indexes) contain
the cumulated weights of similar elements and Its
right cells (highest indexes) contain the cumulated
weights of dissimilar elements.
6.1 Algorithm
• Input :
– Two resources R1 and R2 defined by
R1={(c1
i
, w1
i
)} and R2={(c2
i
, w2
i
)}.
– Two integers DEPT H MAX , GEN.
• Output :
– T : the set of triplets {(c, d, c
0
)}.
– tab : the 2 ∗ DEPT H MAX + 2 table.
– dist(R1, R2) : the similarity measure.
1. Intialize T to
/
0 and tab to {0, ..., 0}.
2. Clean R1 and R2 :
• Remove administrative categories.
• Remove categories which are super-categories
of other categories in the same resource.
3. For each couple (c1
i
, c2
j
) compute the distance
d
i j
= dist(c1
i
, c2
j
).
4. For each category c1
i
:
• compute d1
i
=dist(c1
i
, R2).
• Add w1
i
to tab[d1
i
].
• Add triplets (c1
i
, d1
i
, c
0
) such that dist(c1
i
, c
0
)
= d1
i
to T .
5. Do the same with categories c2
j
.
6. Compute dist(R1, R2) =
∑
i
(i ∗tab[i])/
∑
i
tab[i]
6.2 Defining the Weights w
i
As it is noted by Cheekula et al.((Cheekula et al.,
2015)), Wikipedia has a convention stating that the
categories of a particular article should be ordered ac-
cording to their significance in the article. We define
the weights as a function of this order. In other words
the weight w of a category c is defined by w = f (r),
where f is a decreasing or constant function, and r is
the rank of the category. We used 4 different functions
:
1. The constant function f
1
(x) =
1
n
, where n is the
total number of categories defining the resource
(figure 1 (a)).
Figure 1: Functions for the weights.
2. The affine function f
2
(x) = ax + b (figure 1 (b)).
3. The logistic function f
3
(x) =
α
1+exp(lx)
(figure 1
(c)).
4. The inverse function f
4
(x) =
β
x
(figure 1 (d)).
f
1
considers that all categories have the same impor-
tance. f
2
decreases slowly, we use it when we want to
limit difference between high weights and low weig-
hts. f
3
decreases very slowly then more rapidly, it
divides categories into 3 groups : the first one is given
a high weight, the second is given an average weight
and the last is given a low weight. f
4
decreases very
rapidly : only the very first categories are taken into
account in the evaluation of the similarity.
6.3 An Example
Let us take an example. We want to measure the simi-
larity between the two painters Raphael and Leonardo
da Vinci. We take DEPT H MAX=4 and use the affine
function to compute the weights.
1. Raphael is defined by an ordered list of 15 ca-
tegories : {Italian Renaissance painters, Italian
Renaissance architects, Mythological painters, ...,
1483 births, 1520 deaths, Death in Rome, ...}.
2. Leonardo da Vinci is defined by an ordered list of
15 categories : {Italian Renaissance painters, Ita-
lian Renaissance architects, ..., 1452 births, 1519
deaths, ..., Humanists, ..., Hydraulic engineers, ...,
Anatomists}.
3. sim(R1, R2) = 2.97 out of 2*4+1=9 : it is a high
similarity but not as high as we could expect. The
reason is that the two painters have many similar
elements and some dissimilar ones. The explana-
tion of this value is given by the set T and the table
tab.
4. The table tab is shown by figure 2. We see in this
bar chart that the weight of the distance 0 repre-
sents more than 35% of the total weight : this is
KEOD 2018 - 10th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
120
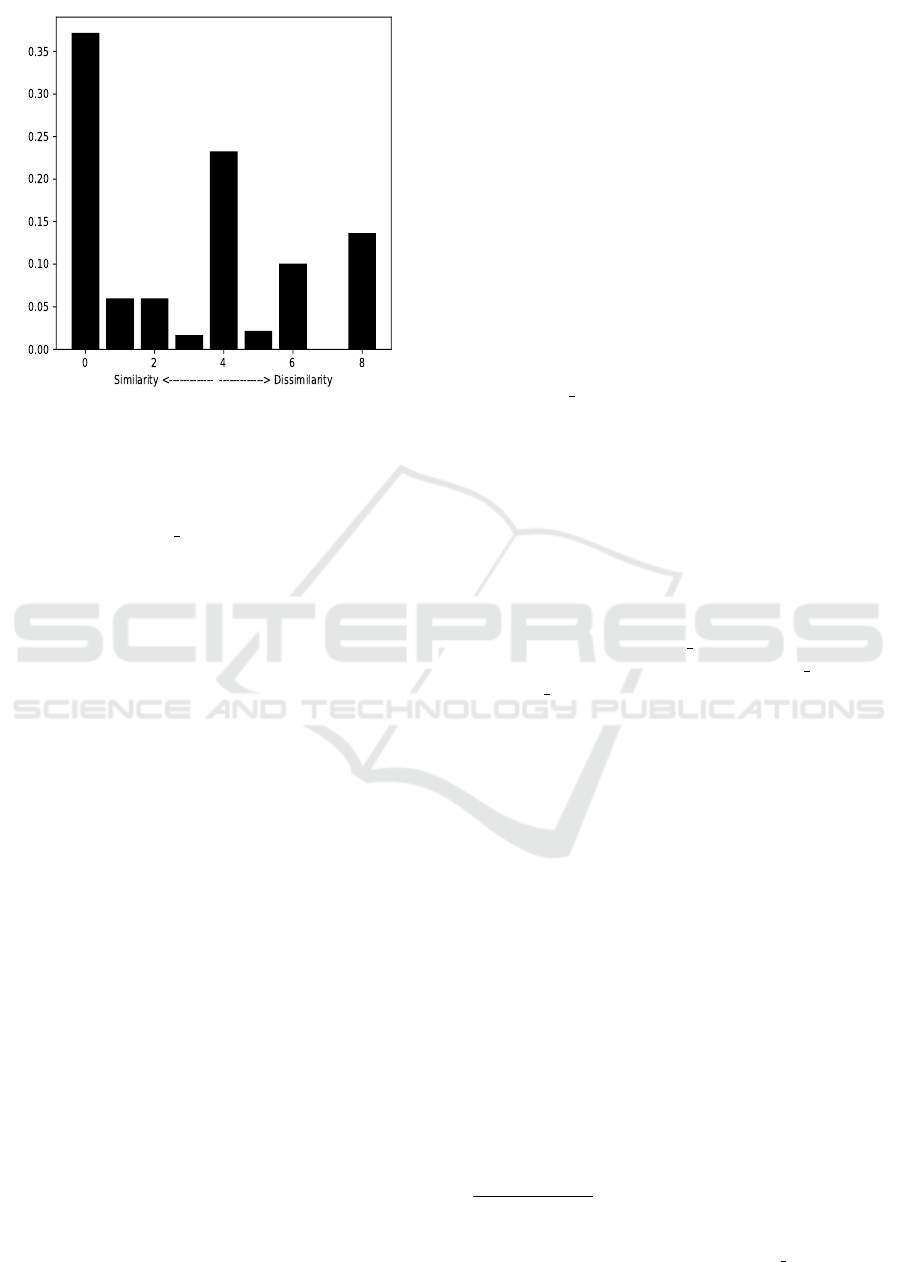
Figure 2: Raphael-Leonardo Da Vinci Similarity.
due to the important number of common catego-
ries and to their high weight. We also notice that
the right part of the figure is not empty : the dis-
tance 2∗ DEPTH MAX = 8 represents more than
10% of the total weight, ...
5. The set of triplets T = {(Italian Renaissance pain-
ters, Italian Renaissance painters, 0), (Italian Re-
naissance architects, Italian Renaissance archi-
tects, 0), (1483 births, 1452 births, 1), (1520 de-
aths,1519 deaths, 0), (Mythological painters, Re-
ligious painters, 4), (Death in Rome, People of the
Republic of Florence, 5), ...}.
7 EXPERIMENTAL
RESULTS-EVALUATION
There are two main kinds of methods to evaluate
computational measures of similarity. The first is
correlating these values with those of human judg-
ments(Resnik, 1995). The second is application-
oriented evaluation : for example, the similarity me-
asure is included in a recommender system ((di Noia
et al., 2012), (Meymandpour and Davis, 2016)) and
the predictions of this system are compared to actual
users’ behaviour. In this work, we chose to validate
our method by showing that it simulates human no-
tion of similarity. For that, we conducted several in-
dependent series of experiments. In the one we pre-
sent in this paper, we use our similarity measures to
rank resources with respect to their similarity with a
given resource, then we compare the obtained results
to those given by a human group.
7.1 Experimental Setting
The dataset we used in our experiments is the french
version of DBpedia
9
. This dataset can be queried
via its SPARQL endpoint
10
. The DBpedia resources
we considered refer to painters belonging to different
countries, centuries and artistic movements.
To implement our method we used Python pro-
gramming language and its package Sparqlwrapper.
The first task accomplished by our programs is to ex-
tract the set of categories of each resource and clean it
by removing administrative categories and categories
which are super-categories of other categories. These
sets are then completed by adding the rank of each
category.
For the next steps we need to choose the value(s)
of DEPT H MAX. Both the accuracy of our mea-
sures and the time efficiency of our programs de-
pend on the value of this parameter. In these expe-
riments we chose these values empirically. For that,
we started by trying a large set of values (between
2 and 10) and observed the categories lists obtained
in each level and changes in the measures obtained.
We then noticed that starting from the level 4, cate-
gories are too general and/or not too correlated with
the considered resources. We also noticed that si-
milarity measures change very little when we incre-
ase the value of DEPT H MAX . Considering this,
in all our experiments we used DEPT H MAX=2 or
DEPT H MAX=3. Generality of categories and their
correlation with resources can be precisely measured
using respectively information content and related-
ness. For example, table 1 presents a short example
giving average relatedness between the DBpedia re-
source
´
Edouard Manet
11
and the categories met when
exploring the graph starting from this resource. In
this evaluation, relatedness value is between 0 for the
very weakly correlated pairs resource/category (e.g
Manet and Cultural anthropology) and 5 for the very
highly related ones (e.g Manet and French Impressio-
nist painters).
7.2 Application to Ranking
In this series we evaluated our results by correlating
our similarity values with those of human judgments.
For that we formed two groups : the first was compo-
sed of 10 engineering school teachers and the second
was composed of 10 graduate students. We gave the
list of 12 painters shown in table 2 to every member
of these groups and asked them to rate similarity for
9
http://fr.dbpedia.org/
10
http://fr.dbpedia.org/sparql
11
http://fr.dbpedia.org/resource/
´
Edouard Manet
Using DBpedia Categories to Evaluate and Explain Similarity in Linked Open Data
121

Table 1: Average relatedness/level.
Level 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Avg. Relatedness 2.75 2.22 1.61 0.75 0.26 0.13 0.08 0.03 0.03 0.03
each pair of painters on a scale from 0 (no similarity)
to 4 (very high similarity). We computed the 4 simi-
larity measures (constant, affine, logistic and inverse)
between each pair of painters. Then for each pain-
ter, we rank the 11 other painters with respect to their
similarity with this painter. It follows that for each
painter P we have 6 rankings : RT (resp. RS) is the
ranking wrt average value of similarity measures ra-
ted by the teachers (resp. students) group. RC (resp.
RA, RL and RI) is the ranking wrt the values calcu-
lated by our programs in the constant (resp. affine,
logistic and inverse) case. We compute Spearman’s
rank correlation coefficient ((Saporta, 2011), chapter
6) between RT and RS, then between RT and the 4
computational rankings.
Table 2 presents the URIs of resources used in this
series. Table 3 contains a detailed example : the simi-
larity measures (columns T*) and the corresponding
rankings (columns R*) for the painter Claude Mo-
net
12
.
The table 4 contains the spearman coefficient for
each painter and for each pair of rankings, the best
value (column BestV) of this coefficient among our 4
cases, the case in which we obtain this value (column
BestF) and the probability to have a Spearman coef-
ficient greater than the best value we obtained. This
table shows that :
1. The Spearman coefficients we obtain in the best
case vary from 0.47 and 0.97. Those between the
two human rankings vary from 0.52 and 0.93.
2. The probability to have better correlation (last co-
lumn) is equal to 17% in one case (The painter
Henri Matisse) and smaller or equal to 5% in all
the other cases.
3. In all but two cases, we obtain the best correlation
with a method taking into account the weights (af-
fine, logistic or inverse).
Using these three remarks we can conclude that our
approach simulates very well the human notion of si-
milarity and that giving the right weights to categories
in the description of a resource is essentiel for simila-
rity measure accuracy.
12
http://fr.dbpedia.org/resource/Claude Monet
7.3 Similarity Measure Considered as a
Random Variable
According to G. Saporta ((Saporta, 2011), chapter 2),
Laplace-Gauss distribution is usually used to describe
”distribution of measurement errors around the ”true
value””. Given two objects, similarity measure va-
lues, rated by humans or calculated by algorithms,
can be seen as approximations of the ”true value” of
the similarity between these two objects. Errors in
these approximations are due to subjective judgments
or lack of knowledge. In this section we state the fol-
lowing hypothesis : ”Similarity measure between two
objects can be represented by a random variable follo-
wing the normal distribution”. To test this hypothesis
we use two properties of the normal distribution : Its
skewness s is 0 and its kurtosis k is 3. Considering
this, we split our hypothesis into two ones :
1. H
0
: s = 0; H
1
: s 6= 0.
2. H
0
0
: k = 3; H
0
1
: k 6= 3.
To test these two hypotheses we use the fact that
for N size samples from a normal distribution we
have(Bob
´
ee and Robitaille, 1975) :
1. s follows a normal distribution with an ex-
pectation ms=0 and a variance std
2
(s) =
6N(N−1)
(N−2)(N+1)(N+3)
2. k follows a normal distribution with an ex-
pectation mk=3 and a variance std
2
(k) =
24N(N−1)
2
(N−3)(N−2)(N+3)(N+5)
It follows that we can accept the null hypotheses H
0
and H
0
0
with type 1 error α = 5% if we have :
−1.96 ≤
ˆs
std(s)
≤ 1.96 and −1.96 ≤
ˆ
k−3
std(k)
≤ 1.96
where ˆs and
ˆ
k are the sample’s skewness and kurtosis.
We applied this normality test to all our pairs of
painters (66). The samples we used were obtained
by merging for each pair the values proposed by the
teachers’ group and those proposed by the students
group : thus, we had 20 observations for each test.
The normality test has been accepted for 49 pairs of
painters and rejected for the 17 others (both H
0
and
H
0
0
have been rejected for 15 pairs, H
0
has been re-
jected for the 2 others). For each one of these 49
pairs we wanted to measure how close are our 4 simi-
larity measures to the ”true value” (the mean m of the
normal distribution). For that we calculated the value
KEOD 2018 - 10th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
122
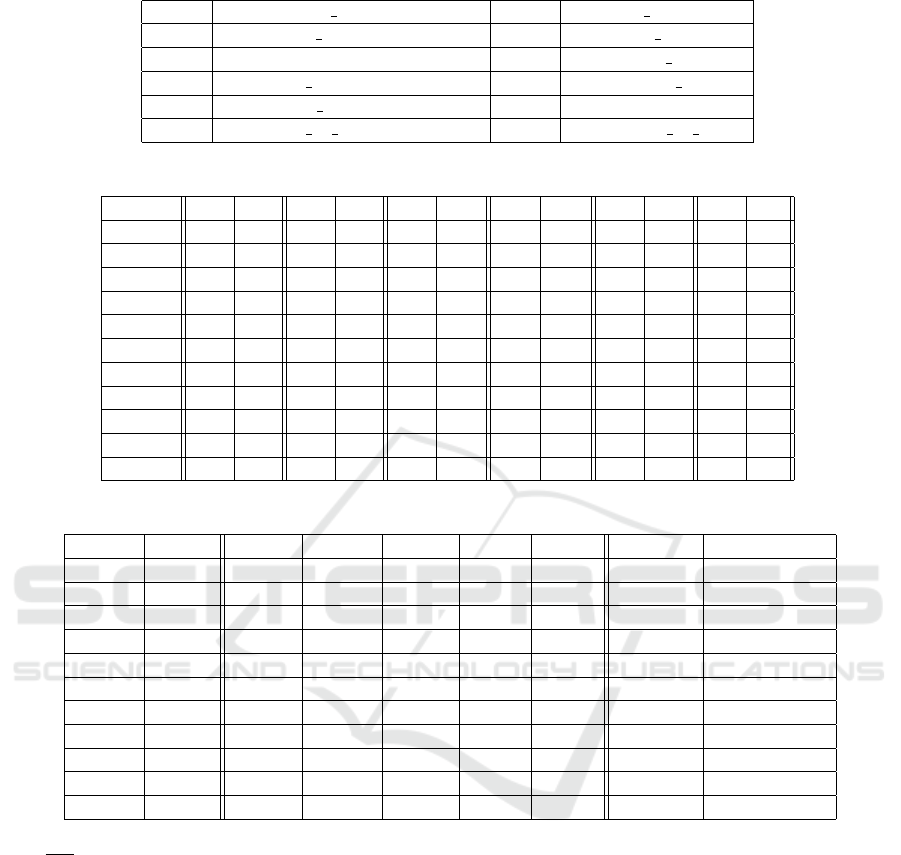
Table 2: Resources URIs.
DAL dbo:Salvador Dal GAU dbo:Paul Gauguin
MAN dbo:douard Manet MAT dbo:Henri Matisse
MCA dbo:Michel-Ange MON dbo:Claude Monet
PIC dbo:Pablo Picasso REN dbo:Auguste Renoir
RPH dbo:Raphal (peintre) TIT dbo:Titien
TLT dbo:Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec VNC dbo:Lonard de Vinci
Table 3: Similarity and rank for Claude Monet.
Painter ST RT SS RS SC RC SA RA SL RL SI RI
DAL 4.3 10 3.2 5 5.4 6 4.9 6 4.2 6 4.4 6
GAU 3.0 3 1.8 3 3.5 3 3.1 3 3.1 3 2.6 3
MAN 2.2 2 1.6 1 2.7 1 2.4 1 2.3 2 1.9 1
MAT 3.6 5 3.4 7 4.1 5 3.9 5 3.4 4 3.5 5
MCA 4.0 7 4.4 9 6.5 8 6.3 10 5.9 10 5.7 9
PIC 3.8 6 3.2 6 6.1 7 5.6 7 4.8 7 4.5 7
REN 1.6 1 1.7 2 3.2 2 2.7 2 2.1 1 2.0 2
RPH 4.1 9 4.4 10 6.5 9 6.2 9 5.6 8 5.7 10
TIT 4.0 8 4.3 8 6.6 11 6.5 11 6.3 11 6.3 11
TLT 3.2 4 2.9 4 3.8 4 3.5 4 3.6 5 3.1 4
VNC 4.3 11 4.5 11 6.5 10 6.1 8 5.6 9 5.1 8
Table 4: Spearman coefficients.
Painter RT,RS RT,RC RT,RA RT,RL RT,RI BestV BestF P(|r|>BestV)
GAU 0.73 0.7 0.65 0.77 0.66 0.77 Logistic 1%
MAN 0.52 0.5 0.56 0.65 0.48 0.65 Logistic 4%
MAT 0.87 0.44 0.44 0.46 0.47 0.47 Inverse 17%
MCA 0.65 0.81 0.82 0.8 0.79 0.82 Affine 0.5%
MON 0.83 0.76 0.76 0.76 0.76 0.76 All 1%
PIC 0.93 0.67 0.81 0.84 0.92 0.92 Logistic 0.03%
REN 0.65 0.64 0.6 0.57 0.57 0.64 Constant 5%
RPH 0.77 0.65 0.68 0.73 0.77 0.77 Inverse 1%
TIT 0.6 0.8 0.81 0.84 0.81 0.84 Logistic 0.4%
TLT 0.59 0.93 0.97 0.93 0.91 0.97 Affine 0.00002%
VNC 0.69 0.69 0.68 0.62 0.55 0.69 Constant 3%
u = |
x−m
σ
| for each similarity x. The table 5 contains
a summary of these values.
We conclude from this summary that, in average,
between 52% and 62% of similarity values are furt-
her from the ”real value” than our measures. We also
notice that the best results are obtained when we take
into account the weights of the categories in the re-
sources’s description.
7.4 Concluding Remarks
In the previous subsections we presented experiments
we conducted to validate our approach. The results
of these experiments show that our approach approx-
imates well the human notion of similarity applied to
complex objects : linked data resources. In all our
experiments, the best results have been obtained with
logistic or inverse weight functions. This fact proves
the importance of weights in the description of com-
plex objects and that similarity value depends mainly
on the most important features (categories). To com-
plete this conclusion, let us note that during our expe-
riments, we have been faced with some characteristics
of DBpedia content and ontology that have limited the
precision of our programs. These characteristics can
be summarized as follows :
• Missing information (1) : We often noticed diffe-
rences between Wikipedia articles’ categories and
those of corresponding DBpedia resources. DB-
pedia is not up to date.
• Missing information (2) : In some Wikipedia arti-
cles, obvious categories are missing. This is cer-
Using DBpedia Categories to Evaluate and Explain Similarity in Linked Open Data
123
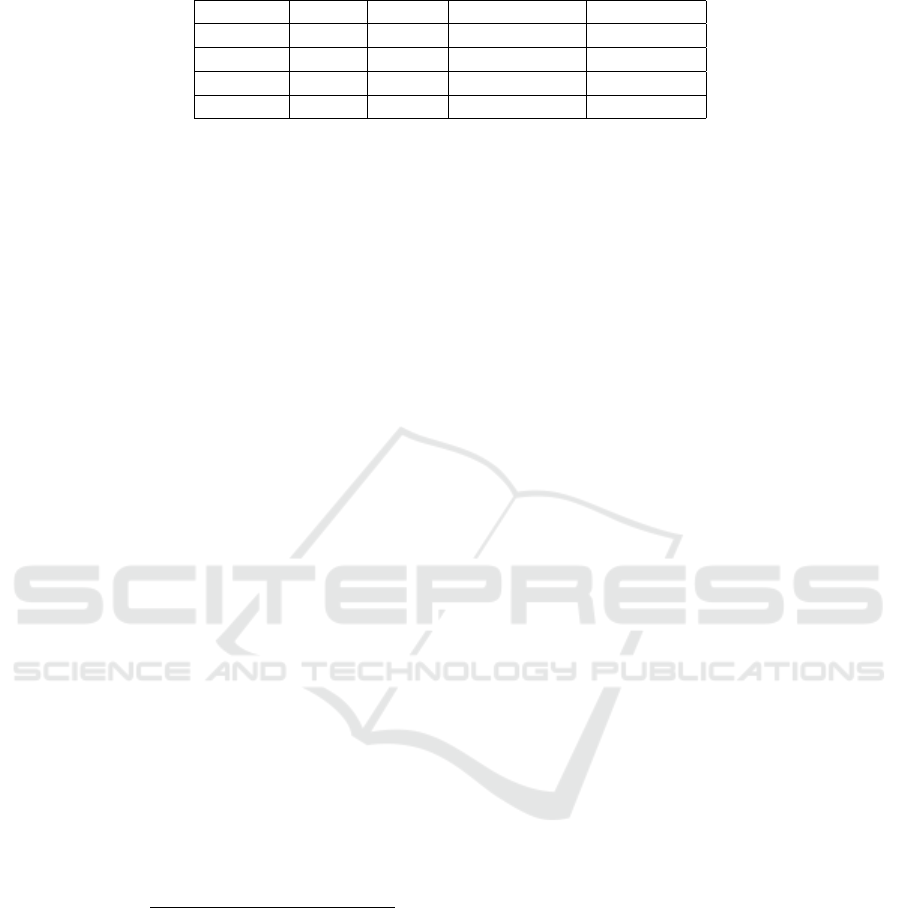
Table 5: Position of the similarity measures in the normal distribution.
min(u) max(u) av=average(u) P(|X| > av)
Constant 0.03 1.57 0.65 0.52
Affine 0.05 1.45 0.58 0.56
Logistic 0.05 1.29 0.49 0.62
Inverse 0.03 1.70 0.51 0.61
tainly due to the fact that it is crowdsourced.
• ”Shallow” schema(Gunaratna et al., 2011) : For
example, there is no difference between Adminis-
tration categories and Content categories. During
the graph exploration we were obliged to remove
the former manually.
• Some information can not be extracted from Wi-
kipedia, e.g. the order of categories within resour-
ces. We were obliged to add them manually.
8 RELATED WORK
Several works aimed to define a similarity measure
for complex objects and more specially for linked data
resources. In the following we present these works
and qualitatively compare them to ours.
• (Meymandpour and Davis, 2016) : A linked data
resource r is defined by a set of features F
r
repre-
senting its outgoing and incoming relations. Out-
going (resp. incoming) relations correspond to
RDF triples in which the resource is the subject
(resp. the object). The information content IC( f )
of a feature f is defined, as is well known in In-
formation theory, as a decreasing function of its
relative frequency. The information content of a
set of a features (a resource, the intersection or the
difference of two resources) is defined as the sum
of the information content of its features. The si-
milarity of two resources r and s is defined by the
following formula :
sim(r, s) =
IC(F
r
∩ F
s
)
IC(F
r
∩ F
s
)+IC(F
r
− F
s
)+IC(F
s
− F
r
)
Several important differences can be noticed be-
tween this work and ours. We use exclusively
categories, which in general summarize well the
important properties of the resources, while they
use all resources’ properties. Unlike ours, this
work doesn’t take into account hidden commona-
lities. We explicitly assign a weight to each fea-
ture while they consider that importance of featu-
res are related to their information content. Cha-
racterizing importance of a feature by its informa-
tion content doesn’t correspond to human judg-
ment (to which we want to correlate our similarity
measures) : for example, among the properties of
the resource representing the painter Claude Mo-
net, 19th century French painter is 35 times more
frequent than People with cataractes. Therefore,
the information content of the former is much lo-
wer than that of the latter. But, when measuring
similarity of Claude Monet with any other person,
human will give much more importance to the first
property. Let us note to finish this comparison that
information content of features is indirectly taken
into account in our similarity measure since in our
category graph exploration the more specific cate-
gories (higher information content, e.g. French
Impressionist painters) are met before more ge-
neral categories (lower information content, e.g.
French painters).
• (Ostuni et al., 2014) : Two resources are similar if
they are related to similar entities, in other words
if they share a similar neighborhood in the RDF
graph (considered as undirected). Each resource
r is represented by the subgraph G
h
(r) obtained
when performing a breadth-first search up to a
limited depth h. A feature vector representation
Φ
h
(r) is then deduced from G
h
. Φ
h
(r) is defined
as follows :
Φ
h
(r) = (w
r,e1
, ..., w
r,et
)
where e j are the edges of G
h
and w
r,e j
their weig-
hts. The weight w
r,e j
depend on the number of
edges involving e j in each level l = 1, ..., h of G
h
.
The similarity between two resources r1 and r2
is computed by taking the scalar product of the
feature vectors Φ
h
(r1) and Φ
h
(r2). This simila-
rity measure gives different weights to the featu-
res (depending as outlined by the authors on their
’occurence’ and ’locality’) and takes into account
hidden commonalities on h levels. The main dif-
ference between this work an ours is that we use a
unified representation of resources (as sets of DB-
pedia categories) and therefore we use a smaller
set of features (while capturing the same informa-
tion) and we explore the categories’ graph instead
of the whole RDF graph. We also have two dif-
ferent definitions of the feature weights : ours are
computed in function of their human defined rank.
• (Zadeh and Reformat, 2013) : Resources are des-
cribed by their RDF triples (resource, property,
value). In other words a resource is represented
KEOD 2018 - 10th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
124

by the features property=value. Properties are gi-
ven different weights reflecting their importance
in describing the resources, and grouped accor-
ding to their importance to form fuzzy sets l
1
,
..., l
n
. To define properties’ importance, the aut-
hors proceed as follows : first they discard pro-
perties not included in the Wikipedia infobox of
the resource, then they categorize the remaining
properties based on the location of their domains
in taxonomy of domains and they consider that
properties with more abstract domains are more
important. Contribution of features to the simila-
rity value are computed with respect to two layers
: the first layer correspond to common features,
the second to different values for the same pro-
perty. Contribution of each fuzzy set is computed
by averaging those of properties belonging to it.
Finally, The overall similarity value is obtained by
aggregating fuzzy sets’ contributions. Like ours,
This work takes into account hidden commona-
lities (contribution of the second layer) and con-
siders that features should have different impor-
tance (weight) in similarity assessment. However,
there are at least two main differences between the
two works. First, the authors use a definition of fe-
ature/property weights which doesn’t correspond
to human definition of importance : for example
if we consider books, the literarygenre and author
properties are very important but their domain is
not abstract. Second, exploration of the (resour-
ces’) graph for hidden commonalities is limited to
only one layer while we showed above that it is
useful to go deeper (2 or 3 levels) in the (catego-
ries’) graph.
• (di Noia et al., 2012) : The authors present
a content-based recommender system exploiting
exclusively LOD datasets. To suggest new items
to a user, this recommender system needs to com-
pute similarity value between pairs of LOD re-
sources belonging to the same type (e.g. movies).
The first step consists of computing this simila-
rity wrt each common property p (e.g. direcor,
starring, ...). For that, the two resources are re-
presented as two vectors m
1,p
and m
2,p
showing
commonalities and differences between them wrt
p. The vectors’ values are T F −IDF weights. Si-
milarity wrt p is computed as the cosine of the
angle between these two vectors. These values of
similarity are combined to compute an overall si-
milarity value according to a user profile. In this
overall similarity value, a weight α
p
is assigned
to each property representing its worth with re-
spect to the user profile. These weights are lear-
ned using two methods : a genetic algorithm or
a statistical analysis on Amazon’s recommender
system. The main difference between this simila-
rity measure and ours is that the former was spe-
cially designed for a recommender system : it is
application-dependent (e.g. the weights are com-
puted with respect to a user profile).
• (Damljanovic et al., 2012) : In the context of a se-
arch for concepts (Linked data resources) relevant
to a given set of seed/initial concepts, the authors
present a similarity measure in which they distin-
guish two kinds of links between concepts : hier-
archical links which serve to organize resources
into classes (eg rdf:type or dcterms:subject) and
transversal links (all other links). The contribu-
tion of the two types of links are computed dif-
ferently. Several variants of the distances for cal-
culating these contributions are described. This
approach was extended by (Paul et al., 2016) and
used to enrich annotated documents and evaluate
their similarity. The main differences between this
similarity measure and ours : (1) we give different
weights to categories and (2) we don’t use ”trans-
versal links” because we noticed that we have in-
formation redundancy between the two kinds of
links (properties).
• (Passant, 2010) : To evaluate similarity between
two resources, the authors measure their ”seman-
tic distance” using a function they name LDSD
(Linked Data Semantic Distance). Six versions
of LDSD are presented and compared by corre-
lating their results with human judgments. This
function rely on the number of direct and indirect,
incoming and outgoing links between resources.
A direct link between two resources r
1
and r
2
me-
ans that for some property p we have p(r
1
) = r
2
or
p(r
2
) = r
1
. An indirect link means that for some
property p we have p(r
1
) = p(r
2
) or p(r
3
) = r
1
and p(r
3
) = r
2
for some other resource r
3
. In other
words, indirect links represent common properties
of the two resources while direct links represent
relatedness between resources. Since these mea-
sures rely on the ”number” of links, all properties
are supposed to have the same importance. Since
exploration of indirect links is limited to the first
level, hidden commonalities are ignored.
• (Ponzetto and Strube, 2007) : The authors use
Wikipedia categories for computing semantic re-
latedness. They consider the system of catego-
ries as a semantic network. To compute seman-
tic relatedness between a pair of words, they re-
trieve two unambiguous pages associated with the
words. For each page they extract the set of ca-
tegories the page is assigned to. They compute
the set of paths between all pairs of categories
Using DBpedia Categories to Evaluate and Explain Similarity in Linked Open Data
125

of the two pages. Once they have all the paths
they select the shortest path or path with the most
common subsumer (two kinds of measures) and
then they apply Resnik’s measure(Resnik, 1995).
Like ours, this work uses exclusively Wikipe-
dia/DBpedia categories to represent complex ob-
jects and to measure similarity between them. But
at least two important differences exist between
the two works, probably due to the different types
of objects (words versus LOD resources) : first
we explicitely assign weights to categories and se-
cond our measure combines contributions of all
categories and not only the ones corresponding to
the shortest path.
• (Fouss et al., 2005) : To measure similarity be-
tween elements of a database, authors define a
weighted undirected graph in which nodes corre-
spond to database elements (e.g. movies, people
and movie categories) and edges to links between
them (e.g. has watched). The weight w
i j
of the
edge connecting two nodes i and j is defined as
follows : the more important the relation between
elements i and j, the larger the value of w
i j
. A
Markov chain is defined in which a state is associ-
ated to each node of the graph and the probability
of jumping from a node i to an adjacent node j
is proportional to the weight w
i j
. Using this Mar-
kov chain properties, the authors show that simi-
lar resources are connected by a comparably large
number of short paths and dissimilar resources
have fewer paths connecting them and these paths
will be longer. They also show that a similarity
measure can be extracted from the pseudoinverse
of the Laplacian matrix of the graph. This method
was not designed for linked data and if we want
to adapt it we must add weights to RDF graphs’
edges, i.e. to each RDF triple’s predicate. Such
weights should represent relatedness between the
resources connected by the concerned edges. In
other words, to apply this method to linked data,
we must first compute relatedness between each
pair of resources belonging to an RDF triple. This
is not realistic.
9 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this work we aimed to define a simple and highly
correlated to human judgment similarity measure for
Linked data. We positively answered the question :
can we measure and explain semantic similarity using
exclusively DBpedia categories. But this work is a
part of a larger project in which we also deal with the
following problems :
1. To show that DBpedia categories can used for a
unified representation for all the linked data re-
sources and not only those of DBpedia.
2. To use machine learning methods to create new
categories and to assign categories to resources.
3. To give a general characterization of feature-
based similarity that the measure presented in this
paper will be a special case.
REFERENCES
Bob
´
ee, B. and Robitaille, R. (1975). Etude sur les coeffi-
cients d’asym
´
etrie et d’aplatissemnt d’un
´
echantillon,
rapport num. 49. Technical report, INRS-Eau, univer-
sit
´
e du Qu
´
ebec, Qu
´
ebec.
Cheekula, S. K., Kapanipathi, P., Doran, D., Jain, P., and
Sheth, A. P. (2015). Entity recommendations using
hierarchical knowledge bases.
Damljanovic, D., Stankovic, M., and Laublet, P. (2012).
Linked data-based concept recommendation: Compa-
rison of different methods in open innovation scena-
rio. In Proceedings of ESWC 2012, pages 24–38.
di Noia, T., Mirizzi, R., Ostuni, V. C., Romito, D., and Zan-
ker, M. (2012). Linked open data to support content-
based recommender systems. In Proceedings of 8th
International Conference on Semantic Systems, pages
1–8.
Fouss, F., Pirotte, A., and Saerens, M. (2005). A novel way
of computing similarities between nodes of a graph,
with application to collaborative recommendation. In
Proceedings of Web Intelligence 2005, pages 550–
556.
Gunaratna, K., Lalithsena, S., Jain, P., Henson, C. A., and
Sheth, A. P. (2011). A systematic property mapping
using category hierarchy and data. Technical report,
http://corescholar.libraries.wright.edu/knoesis/601.
Lehmann, J., Isele, R., Jakob, M., Jentzsch, A., Konto-
kostas, D., Mendes, P. N., Hellmann, S., Morsey, M.,
van Kleef, P., Auer, S., and Bizer, C. (2015). Dbpedia
- a large-scale, multilingual knowledge base extracted
from wikipedia. Semantic Web, 6(2):167–195.
Meng, L., Huang, R., and Gu, J. (2013). A review of se-
mantic similarity measures in wordnet. International
Journal of Hybrid Information Technology, 6(1):1–12.
Meymandpour, R. and Davis, J. G. (2016). A semantic
similarity measure for linked data: An information
content-based approach. Knowledge Based Systems,
109:276–293.
Ostuni, V. C., di Noia, T., Mirizzi, R., and Sciascio, E. D.
(2014). A linked data recommender system using a
neighborhood-based graph kernel. In Proceedings of
the 15th EC-Web, pages 89–100.
Passant, A. (2010). Measuring semantic distance on linking
data and using it for resources recommendations. In
KEOD 2018 - 10th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
126

Proceedings of AAAI Spring Symposium: Linked Data
Meets Artificial Intelligence.
Paul, C., Rettinger, A., Mogadala, A., Knoblock, C. A., and
Szekely, P. A. (2016). Efficient graph-based document
similarity. In ESWC 2016, pages 334–349.
Ponzetto, S. P. and Strube, M. (2007). Knowledge derived
from wikipedia for computing semantic relatedness.
In J. Artif. Intell., (30):181–212.
Rada, R., Mili, H., Bicknell, E., and Blettner, M. (1989).
Development and application of a metric on semantic
nets. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cyber-
netics, 19(1):17–30.
Resnik, P. (1995). Using information content to evaluate
semantic similarity in a taxonomy. In Proceeding of
14th IJCAI, volume 1, pages 448–453.
Saporta, G. (2011). Probabilit
´
es, analyse des donn
´
es et Sta-
tistique. Editions TECHNIP, Paris, 3rd edition.
Tversky, A. (1977). Features of similarity. Psychological
Review, 84(4):327–352.
Zadeh, P. D. H. and Reformat, M. (2013). Fuzzy semantic
similarity in linked data using wikipedia infobox. In
Proceeding of IFSA/NAFIPS, pages 395–400.
Using DBpedia Categories to Evaluate and Explain Similarity in Linked Open Data
127
