
Investigation on the Damaged Factors of Paving Asphalt Pavement
Chunhua Hu and Qiuhai Chen
Hubei University of Technology, Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China
Keywords: Pavement, Asphalt, Shearing force, Vertical deformation.
Abstract: Pavement has been a technical difficulty in road engineering. This paper compares the two pavement
schemes of modified asphalt mixture pavement and pouring asphalt pavement. Through the finite element
method simulation analysis, considering the influence of different parameters, we explore the relationship
between the stress value and deformation under different conditions. The analysis results show that
longitudinal shear stress is an important factor to destroy the road surface and affect the traffic.
1 INTRODUCTION
For a long time, road pavement has always been an
international research difficulties.Road pavement
materials not only greatly affected the normal use of
roads and the transportation function, but also plays
an extremely important role in traffic safety. In the
study of road pavement, the key problem lies in the
small surfacing layer stiffness and large
deformation, which requires good deformation of
asphalt pavement structure layer. At the same time,
the stress condition of the pavement is complex,
affected by temperature, in a larger horizontal shear
stress, the pavement layer shear displacement and
damage, appear easily affect the use and the traffic.
According to incomplete statistics, each year more
than billion yuan for the study of the road, of which
more than 35% is used in the pavement. At the same
time, the government to coordinate the area highway
construction in west China, the implementation of
the western traffic construction projects of science
and technology research has achieved fruitful
results.
2 PAVEMENT STRUCTURE AND
CHARACTERISTICS
Road pavement mainly refers to a layer of asphalt
mixture on the road surface layer, passing through
the asphalt mixture layer to transfer the force to the
lower base. Although it is based on the actual need
to choose different structure layer, but whatever the
form of pavement, generally can be divided into two
categories, namely waterproof (sometimes called
rust) system and body shop system (Wen, 2003).
The pavement plan is different from the actual
project. In the present stage, the asphalt pavement is
mainly modified with asphalt concrete and pouring
asphalt concrete (Ding, 2002). And the composition,
function and construction method of these two kinds
of pavement materials are very different from each
other.
2.1 Modified asphalt mixture paving
layer
In the early stage, due to lack of understanding of
modified asphalt mixture and pavement, there are
many diseases such as rutting, crack and passage in
road use. With the progress of materials and
technology, the comprehensive performance has
been improved greatly. The process of the paving
scheme is becoming more and more mature, and the
construction technology is simple, and it is used in
the municipal highway with small area and no
special requirement.
2.2 Casting asphalt concrete
The casting type asphalt concrete originated in
Britain, the main way of application of the pavement
in commonwealth countries .After the introduction
of our country, according to China's national
conditions, to adjust and optimize the structure and
material, formed the casting type pavement typical
structure. The scheme is the most commonly used in
our country, and the life is more than 12 years,no
matter from the late construction quality and
396
Hu, C. and Chen, Q.
Investigation on the Damaged Factors of Paving Asphalt Pavement.
In 3rd International Conference on Electromechanical Control Technology and Transportation (ICECTT 2018), pages 396-399
ISBN: 978-989-758-312-4
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved

reliability maintenance. Compared with similar
schemes, it has obvious advantages, but also has its
corresponding faults, high temperature stability, easy
to form in at high temperature rut.
3 ANALYSIS OF STRESS
CHARACTERISTICS OF
ASPHALT PAVEMENT
Safety is the first requirement, we are in use in the
process of building surfacing with good
performance is the important guarantee of safe
driving vehicles, but a lot of road traffic within a
few years pavement layer occurs the problem such
as cracks, deformation, seriously affected the normal
use of roads and dramatically reduces the
transportation capacity.
Under the action of driving load, there are two
main ways to damage the pavement layer: first, the
internal damage is caused by the shear stress inside
the pavement layer, which causes the shear failure of
the paving layer. External damage mainly because of
pavement layer and layer panel joint surface
between the cohesive force is insufficient, weak
ability to resist horizontal shear, so prone to shear
displacement in horizontal direction, the final
package, goes on, beat on the pavement, as well as
the aging situation (Xu, 2002).
In this paper, based on the finite element
software ANSYS calculation, analysis of modified
asphalt mixture surfacing and the casting type
asphalt layer of internal force, when the maximum
shearing stress state, at the same time, considering
pavement changes related parameters, vehicle status
and level on the stress caused by different factors,
such as stress changing.
3.1 The influence of variation of each
parameter of asphalt concrete pavement
on the stress of pavement layer
In this paper, the influence factors of stress mainly
consider the thickness and elastic modulus of
pavement layer. In the design process of pavement,
an important index is to select the corresponding
structural layer according to the actual situation of
material and grade composition, and determine its
thickness (Luo, 1999). It is mainly due to the
particularity of asphalt concrete and the
non-uniqueness of asphalt concrete modulus. In the
process of development, asphalt concrete materials
are more and more functional, and different
materials are different in terms of modulus and
intensity. Secondly, even if the asphalt concrete
material is the same, the difference of temperature
and the time of loading will also affect the elastic
modulus. The change of elastic modulus will cause
the force change of the whole structure, and even to
another completely different stress equilibrium state.
And for the same material, because the modulus
changes with the temperature, the strength of the
material changes.
3.2 Relationship between thickness and
stress of pavement layer
In order to analyze the relationship between the
thickness of the modified asphalt mixture and the
structural stress, this paper uses the thickness of the
surface layer of 3cm, 5cm, 7cm, 9cm, 11cm,13cm
and 15cm.
(1) In the process of continuous change in the
thickness of the surface layer, the variation of the
main stress, normal stress and shear stress in the
surface layer is shown in table 1, and the
relationship curves of each stress and thickness are
shown in FIG. 1:
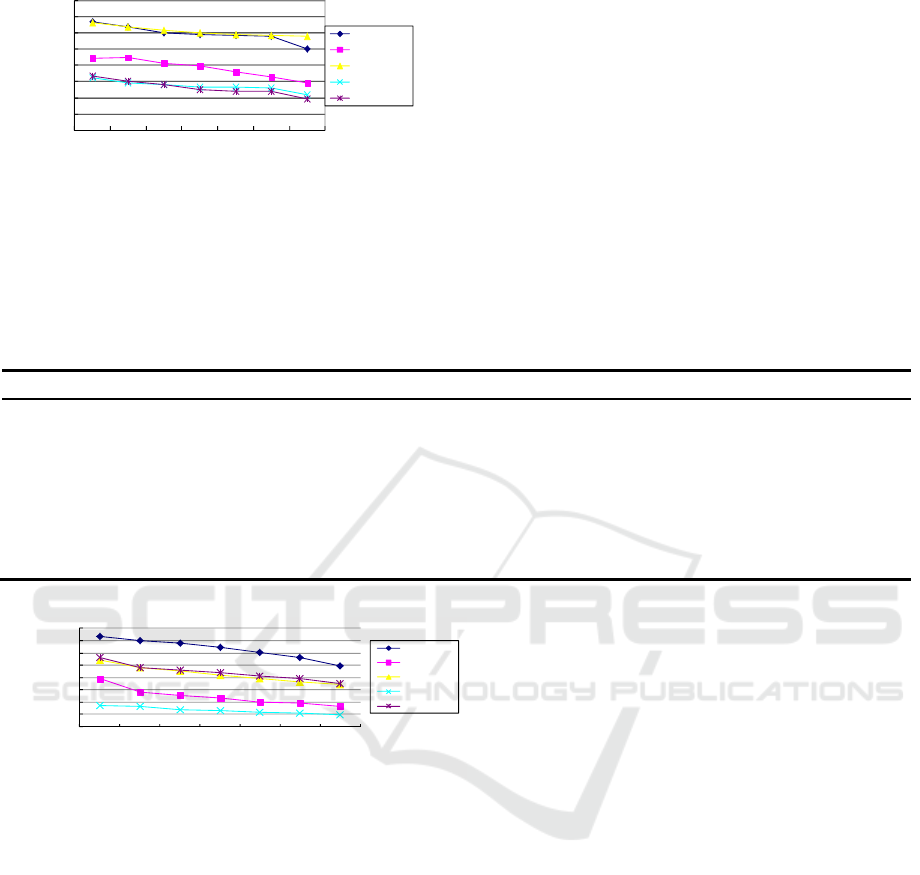
Table 1: variation of stress with thickness of modified asphalt mixture.
Thickness(cm)
σ1(Mpa) σx(Mpa) σz(Mpa) τxy(Mpa) τyz(Mpa)
3 0.6695 0.4459 0.6643 0.3216 0.3356
5 0.6385 0.4471 0.6355 0.2899 0.3043
7 0.5987 0.4143 0.6159 0.2829 0.2806
9 0.5876 0.3987 0.5998 0.2673 0.2525
11 0.5839 0.3597 0.5902 0.2643 0.2412
13 0.5789 0.3312 0.5832 0.2613 0.2388
15 0.5013 0.2896 0.5799 0.2195 0.1932
Investigation on the Damaged Factors of Paving Asphalt Pavement
397
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
3579111315
Stress
Thickness
σ1(Mpa)
σx(Mpa)
σz(Mpa)
τxy(Mpa)
τyz(Mpa)
Figure 1: The relationship between stress and
thickness
From table 1 and figure 1, it can be seen that in a
certain range, the greater the thickness of the
modified asphalt mixture pavement layer, the lower
the stress value in the asphalt concrete surface layer.
It can be seen that the thickness of pavement layer is
beneficial to the internal stress of the surface layer.
The longitudinal and vertical stress decreases, and
the transverse damping is larger. The transverse
shear stress decreases with the same thickness, and
the transverse shear stress is less than the
longitudinal shear stress.
(2) The main stress, normal stress and shear
stress vary with thickness as shown in table 2, and
the variation curve of relevant stress values and
pavement thickness is shown in FIG. 2.
Table 2: the value of the stress changes with thickness of asphalt concrete pavement.
Thickness(cm)
σ1(Mpa) σx(Mpa) σz(Mpa) τxy(Mpa) τyz(Mpa)
3 0.7369 0.3912 0.5437 0.1744 0.5593
5 0.6998 0.2846 0.4778 0.1621 0.4796
7 0.6801 0.2565 0.4553 0.1403 0.4611
9 0.6415 0.2312 0.4172 0.1279 0.4368
11 0.6032 0.2003 0.3889 0.1174 0.4098
13 0.5622 0.1933 0.3658 0.1076 0.3922
15 0.4936 0.1644 0.3422 0.0958 0.3503
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
3579111315
Stress
Thickness
σ1(Mpa)
σx(Mpa)
σz(Mpa)
τxy(Mpa)
τyz(Mpa)
Figure 2: The relationship between stress and
thickness
It can be seen from the above curve that in a
certain range, the longitudinal and transverse shear
stresses of the castable asphalt concrete pavement
are inversely proportional to the thickness. When the
stress is reduced, the decrease of longitudinal shear
stress is less than that of transverse shear stress. It
can be seen that increasing the thickness of the
pavement layer has a weak influence on the shear
stress. In practical application, the thickness of the
pavement layer should not be too large.
Other conditions by the above analysis we can
see that the same circumstances, with the gradual
increase of surfacing layer thickness, modified
asphalt mixture surfacing in lateral shear stress
change is higher than the change of shear stress in
the casting type concrete pavement layer. From table
1 you can see in table 2 casting type concrete
pavement layer of longitudinal shear stress is
significantly higher than the same conditions of
modified asphalt layer of longitudinal shear stress,
and modified asphalt pavement layer transverse and
longitudinal shear stress values gap is smaller.
4 CONCLUSION
On the basis of finite element simulation, the stress
analysis of pavement layer is carried out. The
maximum shear stress in two pavement layers and
the maximum vertical deformation of the pavement
layer are compared. Analyze the relationship
between these variables and draw the following
conclusions:
(1) Through the simulation analysis, it is shown
that the longitudinal shear stress is mainly used to
control the strength of the pavement when subjected
to both horizontal and vertical forces. Therefore,
longitudinal shear stress is the main factor that
damages the pavement layer, and is also the key
factor in traffic design.
(2) The stress in pavement layer is inversely
proportional to the thickness of asphalt layer in the
process of continuous change of pavement layer
ICECTT 2018 - 3rd International Conference on Electromechanical Control Technology and Transportation
398

thickness. The vertical deformation of asphalt
surface is proportional to the thickness of asphalt.
REFERENCE
Wen jingyun, research and destruction analysis of asphalt
concrete pavement [D]. Tianjin: hebei university of
technology, 2003, 10~25.
Ding qingjun, wang chuzhou, huang shaolong. Design of
pavement layer materials [J]. Journal of wuhan
university of technology.2002.24 (4).55~58.
Xu wei, li zhi, zhang xiao-ning. Experimental study on the
mechanical properties of concrete pavement bonding
layer system [J]. Journal of Harbin architecture
university. 2002,35 (4) :127.
Luo lifeng, zhong Ming, huang cheng. Summary of
concrete pavement [J]. Foreign highway, 1999, 19
(3): 23-26.
Investigation on the Damaged Factors of Paving Asphalt Pavement
399
