
Analysis and Design of Internal Control on Revenue Cycle in Order
to Optimize Enrollment Fees Collection in Non-Profit Organization:
Case Study on ABC Foundation
Ceicilia Astri Hartanti
and Malik
Magister of Accounting, Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
ceicilia.astri@gmail.com,
\
malik01277@gmail.com
Keywords: Agency Theory, Competitive Advantage, Information Technology, Internal Control, Non-Profit
Organization, Revenue Cycle, Value.
Abstract: Information technology utilization could promote more efficient business process. However, if it is not
supported by adequate internal control activities, management will lose control its operational activities.
Fraud, loss of trust from stakeholders, and reputation declining are risks that must be borne due to the lack
of internal control. By using a qualitative approach with a case study approach at ABC Foundation, a non-
profit organization in education industry, this study aims to analyse and design the internal control activities
in its new student admission business process. The research was conducted by observation, series of
interviews with its management, and analysis on the internal documents. The results show that there are
some weaknesses on procedures in optimizing its billing process which due to lack of procedures’
adjustment to current business processes and unstructured implementation of internal control activities. It
impacts the balances of accounts receivable and the value of the recorded income being inaccurate and the
number of complaints from the parents of students due to inappropriate billing amount. Therefore, this study
provides recommendations for improvements in company’s financial administration procedures and internal
control activities that can be applied to solve existing problems while improve company’s performance and
reputation.
1 INTRODUCTION
This research is aim to analyse the internal control
on non-profit organisation engaged in educational
services in Indonesia. Even though there are no
regulations required the non-profit entity in
Indonesia should have an internal control system,
Jeffrey (2008) writes that a strong internal control
system creates a separate competitive advantage for
an entity regardless of whether the entity is profit-
oriented or non-profit. An entity that has strong
internal control will be able to respond to
encountered risks faster and better (Jeffrey, 2008).
Strong internal control system will also maximize
the value delivered to customers, since it is part of
entity’s value chain. It also can be view as part of
management’s strategic plan to achieve company’s
target performance (Mawanda, 2008).
Porter (1985) explained that competitive
advantage grows out of value a firm is able to create
for its buyers that exceeds the firm's cost of creating
it. Value, as explained by Porter (1985), is what
buyers are willing to pay. Value also described as
price-quality ratio of a product (Lindič and Silva,
2011). In the education industry, the value offered
by education providers will affect parents in
deciding where their children will be enrolled in.
Consumer loyalty towards a product will
increase when the value received by consumers are
deemed to be greater than the cost incurred. This
becomes important as part of a company's marketing
strategy, especially in the education industry that
relies on its marketing strategy through word of
mouth. Jiewanto, Laurens, and Nelloh (2012) in his
research explains that the excellent quality of service
from an educational institution will have a positive
impact on the consumer's satisfaction and image of
the educational institution, and it will also increase
the intention of its customers to disseminate
information or provide good testimonies based on
their experience.
In Indonesia, Law Number 20 of 2003 on
National Education System, Article 53 stipulates that
338
Hartanti, C. and Malik, .
Analysis and Design of Internal Control on Revenue Cycle in Order to Optimize Enrollment Fees Collection in Non-Profit Organization (Case Study on ABC Foundation).
In Proceedings of the Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study (JCAE 2018) - Contemporary Accounting Studies in
Indonesia, pages 338-347
ISBN: 978-989-758-339-1
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

the provider and /or formal education units shall be
non-profit educational legal entities. Although non-
profit principled, it does not mean that a non-profit
entity can override the internal controls in its
operations. The internal control is posited to be used
to address agency cost by mean ensuring
information efficiency between principal and agent
(Namazi, 2013).
The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of
the Treadway Commission (COSO) (2013) defines
internal control as a process influenced by the
entity’s board of directors, management, and other
personnel, designed to provide reasonable assurance
regarding the achievement of objectives in the
categories of effectiveness and efficiency of
operations, reliability of reporting, and compliance
with applicable law and regulations.
The Association of Certified Fraud Examiners
(ACFE) (2016) in its publication explains that lack
of internal control is one of the biggest factors
causing fraud within an organization. Furthermore,
ACFE (2016) in the research also found that fraud
occurred in organizations operating in the education
industry is largely associated with assets
misappropriation. A total of 25% of frauds are
related to skimming in which incoming payment is
stolen from an organization before it is recorded on
the organization's books and records.
Based on research conducted on 27,495 public
charities from 1999 to 2007, some of the causes of
internal control issues in public charities are poor
financial conditions, growing organizations, and
complex or small organizations (Petrovits,
Shakespeare and Shih, 2011). This research also
concluded that the disclosure of a problem in
internal control negatively affects the support from
the next donors. Synder, Andersen, and Zuber
(2017) in their paper stated that based on research
conducted by the Association of Certified Fraud
Examiners (ACFE) in 2014, an estimate losses
suffered by non-profit entities due to fraud has
reached 5% of their annual income or about US
$108,000. The magnitude of these losses does not
take into account the impact of reputation damage
and the loss of public trust towards the entity’s
performance, which will undermine income in the
short term.
Burtseva, Vokina and Schneider (2015)
explained that the continuity of an educational
institution business depends on its ability to identify
risks. Implementation of this task required the
involvement of employees who work in internal
control functions within the organization.
Yayasan ABC (the Foundation) is an entity that
operates as a provider of educational services.
Currently, there are 1,300 registered students in 6
school branches under the management that located
in Jakarta, Tangerang Selatan and Surabaya. In the
near future, the management also plans to open 2
(two) new school branches outside of Jakarta. With
this expansion plan, the management targets an
increase in the number of students to more than
50%.
Since 2014, the Foundation implements a web-
based application as a tool for new student
admission. Then, in order to improve the company's
internal control and to support the Foundation's
expansion plan, by mid-2017, the board decided to
centralize most of the school's supporting activities.
With changes to the organizational structure and
the way of work, there is the risk that Foundation’s
financial statements could not provide the reliable
information to decision makers. Errors of numbers
presented can occur due to intentional or accidental
elements. Based on the results of interviews between
the researcher and the Finance Division team, the
Foundation's accounting team is facing several
problems that arise in the Foundation's revenue
cycle, especially in admission process, such as:
1. Discrepancies are found between the balance of
accounts receivable in the financial statements
with the list of students who still have
outstanding balance;
2. Total income from new students enrolled
recorded in the income statement for the period
ended in 31 December 2016 has a significant
fluctuation compare to prior period, which was
difficult to explain.
3. Prospective parents are complaining because the
registration fees they have been charged with are
inconsistent to the information provided
beforehand.
The problem raised may be indicated there are
some weaknesses on company’s accounting
information system, especially related to its internal
control system. This research will analyze current
condition of internal control system on ABC
Foundation revenue cycle, especially related to its
new student’s admission process. This study does
not just extend the current finding of the effect of
internal control system to company’s financial
performance and its going concern, but also propose
a recommendation to improve company’s financial
administrative procedures and internal control
activities that can be applied to solve existing
Analysis and Design of Internal Control on Revenue Cycle in Order to Optimize Enrollment Fees Collection in Non-Profit Organization
(Case Study on ABC Foundation)
339

problems. The value delivered to its consumer and
company’s reputation also expected to be improved.
2 LITERATUR REVIEW
2.1 Agency Theory
Agency theory postulates that as a contract
under which principal (founders) engage agents
(managers) to perform services on their behalf
(Jensen and Meckling, 1976). This theory, assumes
that agents have more information than principals
which lead to asymmetric information and adversely
affect the principals’ ability to monitor whether their
interest are being properly served by agents (Adams,
1994). It also premiss that principals and agents act
rationally to use the nexus of contract to maximise
their own wealth. By adapting the agency theory, the
principals can design and implementing effective
control mechanism. One of this role is to ensure
informational efficiency by using accounting
information in establishing control system (Namazi,
2013). It also provides a delegate model to explain
why control is important, thus it should be exerted in
entity (Namazi, 2013).
2.2 Porter’s Theory
Competitive advantage grows out of value a firm is
able to create for its buyers that exceeds the firm's
cost of creating it (Porter, 1985). There are 3 (three)
generic strategies to company gain the advantage,
i.e. company offer unique value to its consumers,
company sets out to become lower cost producer,
and company decide to serve segmented market.
The strategy chosen then is reflected in the series
of activities in delivering the value to the consumers,
namely value chain (Porter, 2015). Value is
explained as what buyers are willing to pay (Porter,
2015). One of activities in value chain is related to
firm infrastructure which accounting information
system is under its activities. Internal control is one
of accounting information system component
(Romney, 2015). Therefore, better internal control in
organization could promote better company’s value
chain and increase value delivered to its customers.
2.3 Internal Control
The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the
Treadway Commission (COSO) (2013) defines
internal control as a process, effected by an entity’s
board of directors, management, and other
personnel, designed to provide reasonable assurance
regarding the achievement of objectives in the
categories of effectiveness and efficiency of
operations, reliability of reporting, and compliance
with applicable law and regulations. Romney (2015)
defines it as the process implemented to provide
reasonable assurance that the following control
objectives are achieved, in such as safeguard assets,
provide accurate and reliable information, and
prepare financial reports in accordance with
established criteria. Therefore, it can be concluded
that internal control is a process that is interrelated,
designed and effected by the entity’s management in
order to achieve operational effectiveness, financial
reporting reliability, and compliance with
regulations and applicable law.
There are five component on COSO Framework
component, i.e. control environment as the
foundation, risk assessment as a dynamic and
iterative process, control activities as the series of
actions established by policies and procedures,
information and communication, and monitoring
activities as ongoing and separate evaluations
process (COSO, 2013).
Internal control has become a requirements to
organizations to achieve either its business
objectives or financial performance, including in
education institution (Mawanda, 2008). Any internal
control weaknesses, especially on control
environment component, accounting policies and
procedures, or control design, will have negative
impact on company’s performance (Lai, Li, Lin,
Wu, 2017). It will also lead to unreliable financial
data that may impact to accuracy of financial
forecast (Clinton, Pinello, and Skaife, 2014).
Therefore, it is imperatives for organizations, either
profit or non-profit oriented, to assess, design,
develop and monitor its control system. It will turn
allows the organizations to operate effectively
(Maguire, 2014).
Romney (2015), in his book, stated that revenue
cycle is exposed some of the risks, i.e. inaccurate
order, invalid order, uncollectible accounts, loss of
customers, shipping errors, failure to bill, billing
errors, posting errors in accounts receivable, theft of
cash and cash flow problems. Those risks can be
mitigated by implemented control activities, such as
restriction access to master data, segregation of
duties, aging A/R preparation, reconciliation
between sales order, bill-of-lading, and invoice,
proper authorization, and system configuration.
Romney (2015) also explained that those internal
controls activities perform preventive, detective, or
corrective functions.
JCAE Symposium 2018 – Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study
340

3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Research Methods
This research is a descriptive qualitative research
which is used to gaining a deep understanding to
make a conclusion of the pattern or phenomenon
that occurs (Wahyuni, 2015). The data obtained and
processed are not numerical, but instead flowcharts
and interview results, as well as observations
(Wahyuni, 2015). In this study, the phenomenon to
be analysed is the design of ABC Foundation
internal control system.
This research using case study approach on 1
(one) research object. The object of this research is
ABC Foundation, an entity engages as education
service providers. The foundation was selected as
the place to conduct the research because, in general,
there is limited access to financial information of a
non-profit entity.
Considering the main purpose of conducting this
research this research utilized primary data sources
that are directly obtained from the Finance division
and Sales division of the Foundation. Data collection
techniques used in this research is observation of
usage of web-based application system, interviews
with finance and sales division, and with the finance
director as the management’s representative, as well
as analysing the company’s internal documents.
The observation will conducted on one branch of
the school owned by the Foundation. This
consideration was taken because the particular
school branch has the most number of students
compared to other school branches. Income recorded
by the school branch by 31 December 2016 reached
88% of the total income recorded by ABC
Foundation. Of the total income accounted for by the
school's branches, 19% of them came from the
enrolment of new students. In addition, another
consideration is that, since it was decided to
centralize in July 2017, business processes
uniformity between branches of the school. Hence,
the results of this research will be utilized and
implemented in other branches or could be a
blueprint to be used by the management when they
are opening another branch.
3.2 Data Analysis
This research will use the data obtained to analyse
ABC Foundation control environment, risk
assessment process and internal control practices in
new student’s admission process at ABC
Foundation. The analysis will produce information
on the conformity of internal control practices in the
field with the existing procedures. This research will
also develop a framework to adjust internal control
activities therein. The results of interviews,
observations, and analysis of the company’s internal
documents will generate an overview of operational
activities in the field as well as system development
plans that will form the basis for the preparation of
the internal controls adjustment framework.
3.3 Scope of Research
In order to make this research focused, the scope of
this study will be limited to analysis until
designation of internal control activities on revenue
cycle which is related to new student’s admission
activities.
4 RESEARCH OUTCOME
4.1 Control Environment
Company’s code of conduct has been communicated
regularly to all employees. In its notarial deed also
stated duties and responsibilities of Foundation’s
organ, i.e. founder, controller, and management.
Foundation’s financial statements regularly
reviewed and presented to controller and founder as
part of management’s accountability. Its
organisation structure has been developed to
represent each function and line of command. Each
employee also has key performance indicator which
related to admission and students retention ratio.
Company also give appreciation to employee who
has more than 10 service years.
Even though company has communicated its
code of conduct regularly, ABC Foundation has no
internal audit division or whistle blowing system as
a tool to mitigate fraud risk. Management rely on
supervisor review for any code of conduct violation.
4.2 Risk Assessment
In general, based on interview with Finance
Director, ABC Foundation has neither risk
assessment tool nor risk control matrix. She stated
that new student’s admission process is exposed low
risk of skimming, since all the cash receipt
transactions was done directly through company’s
bank account. ABC Foundation is also exposed low
environment significant changes risk, since better
government support and people awareness on
education.
Analysis and Design of Internal Control on Revenue Cycle in Order to Optimize Enrollment Fees Collection in Non-Profit Organization
(Case Study on ABC Foundation)
341
4.3 Control Activities
In the company’s web-based application system, the
prospective parents will register independently if
they want their children enrolled in ABC School.
There are 3 (three) division involved in the
admission process, i.e. sales, finance, and academic
division.
During the research, researcher identify that
there are some threat on the admission process.
Furthermore, researcher paired it to internal control
activities to mitigate the risk. The activities will
classified by its functions, i.e. preventive, detective,
or corrective actions. And at the end, based on
observation and interviewing process, researcher
assess whether the finance and sales team do the
activities.
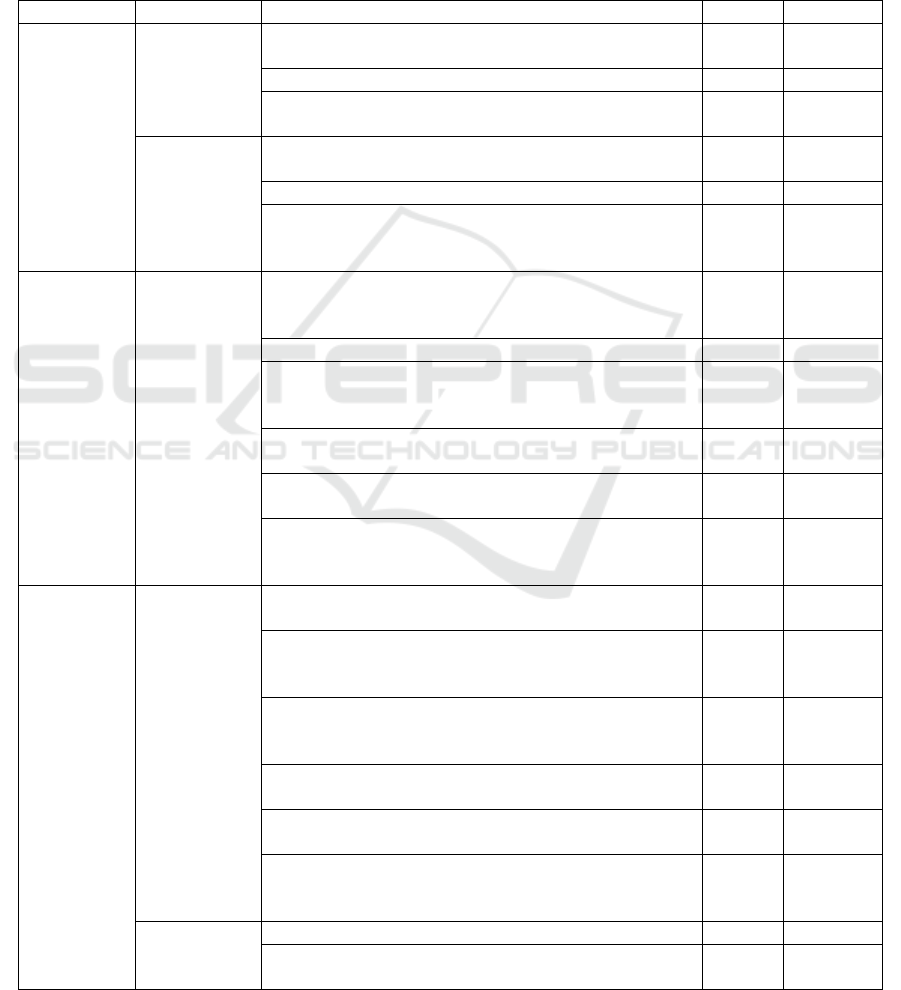
Table 1: Risk and Internal Control Activities on Admission Process.
Process
Risk
Internal Control Activities
P/D/C
*)
Checklist
Registration
Invalid order
Registration can only process through admission system,
including if the parents is Foundation’s employee.
P
√
Sales team verify validity of registration data.
P
√
Access limitation to student information in academic
system.
P
√
Loss of
customer
Record and resolve complaints from customers in a
timely manner
C
√
Follow up unpaid invoice exceed the due date.
P
√
Cancel registration process if the parent does not response
our follow-up actions properly or settle the enrolment bill
before maturity date.
P
√
Billing
Billing error
System configuration to automatically identify discount
criteria, based on employee ID, or e-mail address, or
student ID.
P
×
System configuration to automatically enter pricing data
P
×
Do proper socialization to sales and finance team related
to enrolment fee, early bird price, and instalment
mechanism before admission period started.
P
√
Access limitation to pricing data, only can be accessed by
Finance Manager.
P
√
Access limitation to employee data, only can be accessed
by HRD Manager.
P
√
Proper authorization and documentation up to GM
Marketing and Sales level to approve special enrolment
fee discount.
P
×
Failure to bill
Registration can only process through admission system,
including if the parents is Foundation’s employee.
P
√
Reconcile number of new students enrolled per academic
year between finance division and sales division
periodically.
D
×
Instalment application should be documented properly, in
written documentation, between parents and school
(approved by Finance Director).
P
√
Prepare manual register of the name of parents, name of
students, and the enrolment fee instalment value.
P
√
Develop integrated system to issued enrolment fee
instalment invoice automatically.
P
×
Reconcile of enrolment fee instalment invoice issued to
manual register of outstanding enrolment fee instalment,
periodically.
D
×
Uncollectible
account from
the enrolment
Prepare aging account receivable.
D
×
Reconcile of enrolment fee instalment invoice issued to
manual register of outstanding enrolment fee instalment,
D
×
JCAE Symposium 2018 – Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study
342
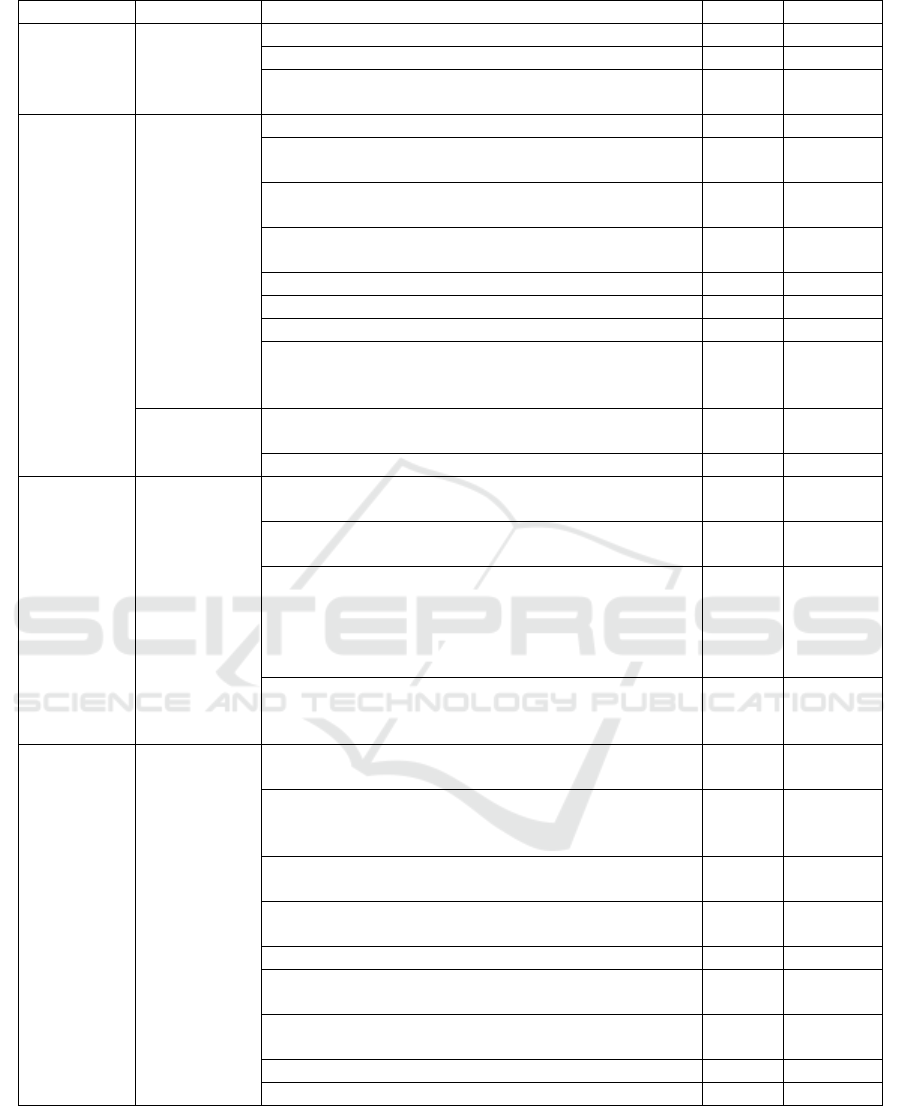
Process
Risk
Internal Control Activities
P/D/C
*)
Checklist
fee
instalment.
periodically.
Follow up receivables aged more than 30 days.
P
√
Close access to admission system if the student or sibling
still has unpaid invoice.
P
√
Cash receipt
Theft of cash
Cashier prohibited to receive payment in cash.
P
√
Socialization and persuade parents to utilize payment
channel via virtual account or, if any, payment gateway.
P
√
Segregation of duties between cashier and the person who
do accounting record.
P
√
Daily reconcile between EDC machine transactions
listing to bank statement.
D
√
Do bank reconciliation periodically and in timely manner.
D
√
Investigate long outstanding account receivables.
D
×
Pre-numbered payment receipt form.
P
√
Develop payment receipt system that can’t be edited or
cancelled by the cashier without the supervisor's
authorization.
P
√
Cash flow
problem
In cooperation with banks to provide credit card
instalment facility.
P
√
Prepare cash flow budget
P
×
Providing
service
Provide
services to
students who
have unpaid
enrolment fee
bill.
Close access to admission system if the student or sibling
still has unpaid invoice.
P
√
Ensure payment of the enrolment fee instalment
completed before the beginning of school year.
P
√
In case of the enrolment fee instalment schedule
exceeding the stipulated period, proper authorization and
documentation from Finance Director and/ or HRD
Director (if the parent is Foundation’s employee) is
needed.
P
√
Reconcile payment of the enrolment fee instalment to
invoice amount and manual register of outstanding
enrolment fee instalment, periodically.
D
√
Accounting
record
Revenue
recorded and
balance of
account
receivable at
the end of
period is
inaccurate.
Ensure to record the invoice issued to accounting
information system through Account Receivable menu.
P
√
If invoice recorded to accounting information system in
batch, do batch total check and compared to computer
generated total, to ensure no data missing out.
P
√
Reconcile accounts receivable sub-ledger to general
ledger at the end of month.
D
×
Reconcile total invoice amount issued to revenue
recorded at general ledger at the end of month.
D
×
Do bank reconciliation in timely manner and periodically.
D
√
Daily reconcile between EDC machine transactions
listing to bank statement.
D
√
Accounting manager perform analytical review of
revenue amount recorded periodically.
D
√
Send monthly statement to parents.
D
×
Investigate long outstanding account receivables.
D
×
*) P = Preventive, D = Detective, C = Corrective.
Analysis and Design of Internal Control on Revenue Cycle in Order to Optimize Enrollment Fees Collection in Non-Profit Organization
(Case Study on ABC Foundation)
343
4.4 Discussion
Based on the results of observations and interviews
conducted, this research concluded that there are
some weaknesses in internal control activities in the
process of admission of new students in the ABC
Foundation. The weaknesses are compared to related
control objectives. The weaknesses are shown in the
table below.
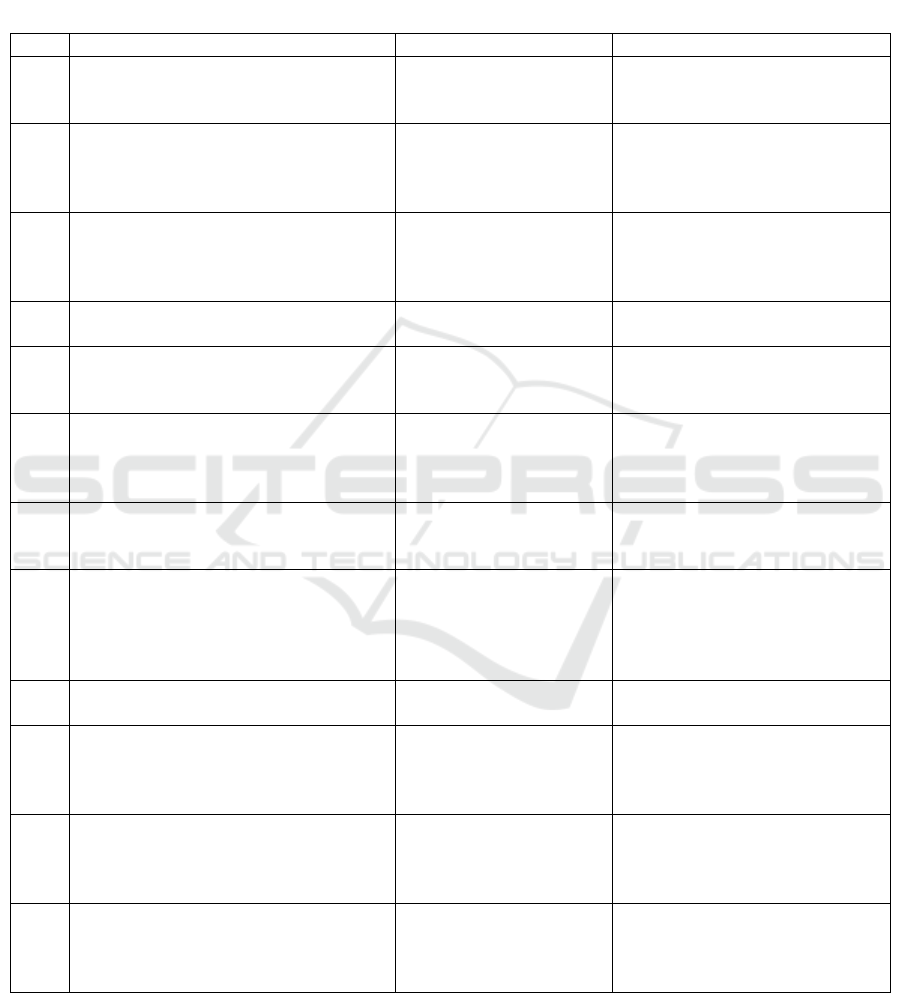
Table 2: Proposed Addition of Internal Control Activities of Admission Process.
No
Internal Control Activities
Risk
Control Objectives
1
Prepare aging account receivable.
Uncollectible account
from the enrolment fee
instalment.
As management’s tool to monitor
outstanding receivables.
2
Reconcile of enrolment fee instalment
invoice issued to manual register of
outstanding enrolment fee instalment,
periodically.
Failure to bill;
Uncollectible account
from the enrolment fee
instalment.
To detect unbilled enrolment fee
instalment in timely manner.
3
System configuration to automatically
identify discount criteria, based on
employee ID, or e-mail address, or
student ID.
Billing errors.
To avoid error during identification
process.
4
System configuration to automatically
enter pricing data
Billing errors.
To avoid error or fraud in enter
pricing data.
5
Proper authorization and documentation
up to GM Marketing and Sales level to
approve special enrolment fee discount.
Billing errors.
To prevent total discount amount is
larger than budgeted amount.
6
Reconcile number of new students
enrolled per academic year between
finance division and sales division
periodically.
Failure to bill.
To ensure all students enrolled
have settle all enrolment fee bill.
7
Develop integrated system to issued
enrolment fee instalment invoice
automatically.
Failure to bill.
To ensure completeness of
enrolment fee instalment invoice
issuance
8
Investigate long outstanding account
receivables.
Theft of cash;
Revenue recorded and
balance of account
receivable at the end of
period is inaccurate.
To detect skimming practice.
9
Prepare cash flow budget
Cash flow problems
To ensure company cash flow
stability
10
Reconcile accounts receivable sub-ledger
to general ledger at the end of month.
Revenue recorded and
balance of account
receivable at the end of
period is inaccurate.
To ensure accuracy and
completeness of account receivable
balance at the end of period.
11
Reconcile total invoice amount issued to
revenue recorded at general ledger at the
end of month.
Revenue recorded and
balance of account
receivable at the end of
period is inaccurate.
To ensure accuracy and validity of
revenue recorded during the
period.
12
Send monthly statement to parents.
Revenue recorded and
balance of account
receivable at the end of
period is inaccurate.
To ensure accuracy, completeness
and existence of account receivable
balance at the end of period.
Based on the above proposed table, researcher
conclude that the problems occurred in Foundation
admission process was due to lack of control
activities during billing process. Thus the control
objectives did not met. Finance team never do
reconciliation number of new students enrolled per
academic year between finance division and sales
division. The reconciliation also not done between
JCAE Symposium 2018 – Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study
344
total invoice amounts issued to revenue recorded at
general ledger at the end of month. They also never
reconcile accounts receivable sub-ledger to general
ledger at the end of month. There are also some lack
of control on instalment of enrolment fee billing and
its payment. As a result, management can’t state that
the account receivables balance and revenue
recorded at the end of year is complete, exist,
accurate, and valid.
In addition, since the verification procedures to
identify whether the potential new students are
entitled to a discount was done manually by sales
team, there are some failure risk to identify the
entitled students. Therefore, some of prospective
parents complain about the billing amount.
Based on the table 2, this research then re-
describes the second enrolment fee billing process
that occurs in the new students admission step with
the addition of internal control activity proposal in it.
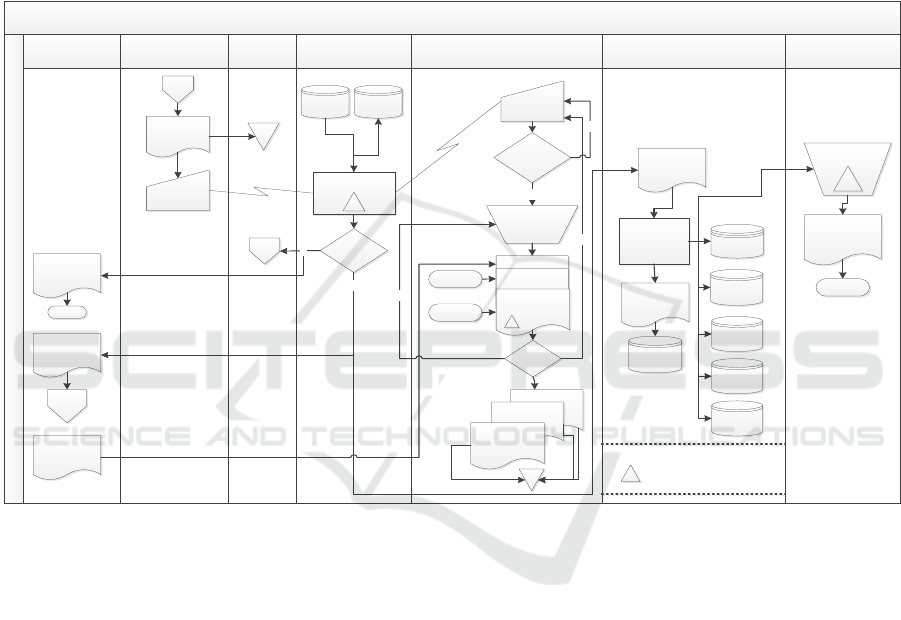
Second Enrollment Fee Billing Process
Parent Academic Divison Admission System FTA Operation Staff Accounting Staff
Accounting
Manager
Sales
Phase
Discount Voucher
Employee Discount
Memo
B
Admission Test
Result
Terminal
Admission System
Terminal – Pilih
Nilai Tagihan
Discount or
Installment?
Installment Request
Approval
Collect
supporting
document
Y
T
Pricing Data Quota Data
A
Second
Enrollment Fee
Invoice
A
Second
Enrollment Fee
Invoice
GL Update
General
Ledger
Account
Receivable
Data
Sales Data
Second
Enrollment Fee
Invoice
Email
Total Enrollment
Fee Revenue &
Analysis
Management
Unearned
Revenue
Data
A
Accepted?
C
Y
Y
T
Not Accepted
Result Letter
T
Finish
Discount Voucher
Management
HRD
Complete?
Discount Voucher
Employee Discount
Memo
Installment
Request Approval
Y
T
5
Report
Preparation
2, 6,
10, 11
3,4
Legenda Simbol
Internal control activities as per Tabel 2.
Installment
Data
Figure 1: Second Enrolment Fee Billing Process
5 CONCLUSIONS
This research was conducted to evaluate the internal
control activities in the revenue cycle in order to
optimize enrolment fees collection within ABC
Foundation. Based on the outcome of the research, it
was found that the problems experienced by ABC
Foundation’s financial division were caused by the
lack of a reconciliation process between the number
of students enrolled and the invoice value billed to
parents according to the finance division and the
sales division. In addition, the reconciliation process
between the value of revenues and account
receivables recorded in the ledger with the related
sub-ledger has not been done consistently and
structurally. The lack of control activities has
resulted in the management losing control of the
value of income recorded in the financial statements.
In addition, the above mentioned causes a number of
complaints from the parents due to frequent errors in
issuing the bill.
5.1 Research Limitations
This research only covers revenues sourced from the
enrolment of new students. In the future, other
researchers may conduct research on other sources
of income that are not included within the scope of
this research.
5.2 Recommendations
Based on the conducted research, here are
suggestions for improvements that can be
implemented by the company and the next research:
Analysis and Design of Internal Control on Revenue Cycle in Order to Optimize Enrollment Fees Collection in Non-Profit Organization
(Case Study on ABC Foundation)
345

1. For ABC Foundation, based on the deficiency in
the process of enrolment of new students, it is
necessary to improve the administrative
procedures of school finance along with the
addition of internal control activities in the form
of data reconciliation between related divisions
in the revenue cycle. Formal improvement of
this procedure is expected to facilitate the
management in enforcing existing regulations
consistently and structurally. In addition, given
the growing number of transactions and the
company's plans to continue to expand, it is
better if the Foundation perform a cost-benefit
analysis to build an integrated registration and
billing system that facilitates payment through
instalments. This is necessary to improve the
efficiency of the company's operational
activities and improve services for its
customers.
2. For the next researchers, it is advisable to
evaluate on other business processes within the
revenue cycle of ABC Foundation, such as the
collection process of school fees or club fees.
REFERENCES
Adams, Michael B. (1994). Agency Theory and The
Internal Audit. Managerial Auditing Journal, 1994,
Vol. 9, Issue: 8, pp. 8-12. Retrieved from
https://doi.org/10.1108/02686909410071133
Association of Certified Fraud Examiners. (2016). Report
to The Nations on Occupational Fraud and Abuse
2016 Global Fraud Study.
Burtseva, K. Y., Vokina, E. B., and Schneider, O. V.
(2015). Interconnection Between Internal Control and
The Assessment of Risk of Financial Stability Loss By
Educational Institutions. Aktual'Ni Problemy
Ekonomiky = Actual Problems in Economics, (172),
410-418. Retrieved from
https://search.proquest.com/docview/1754518879?acc
ountid=17242
Commitee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway
Commission. (2013). Internal Control - Integrated
Framework Executive Summary.
Jeffrey, C. (2008). Internal control at private companies
and nonprofits. The CPA Journal, 78(9), 52-54.
Retrieved from
https://search.proquest.com/docview/212274426?acco
untid=17242
Jensen, M.C., and Meckling, W.H. (1976). Theory of The
Firm: Managerial Behavior, Agency Cost and
Ownership Structure. Journals of Financial
Economics, Vol. 3 No.3, 1976, pp. 305-60.
Jiewanto, A., Laurens, C., and Nelloh, L. (2012).
Influence of Service Quality, University Image, and
Student Satisfaction toward WOM Intention: A Case
Study on Universitas Pelita Harapan Surabaya. In
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, Volume
40, 2012, Pages 16-23, ISSN 1877-0428, Retrieved
from
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.03.155.(http://w
ww.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S187704281
2006222)
Lai, S., Li, H., Lin, H., & Wu, F. (2017). The influence of
internal control weaknesses on firm performance.
Journal of Accounting and Finance, 17(6), 82-95.
Retrieved from
https://search.proquest.com/docview/1967314575?acc
ountid=17242
Lindič, Jaka., and Carlos Marques da Silva. (2011). Value
proposition as a catalyst for a customer focused
innovation. Management Decision, Vol. 49 Issue: 10,
pp.1694-1708. Retrieved from https://remote-
lib.ui.ac.id:4611/10.1108/00251741111183834
Maguire, K. A. (2014). Best practices for nonprofits'
internal control self-assessment. Advances in
Management and Applied Economics, 4(1), 41-87.
Retrieved from
https://search.proquest.com/docview/1501427856?acc
ountid=17242
Mawanda, S.P., (2008). Effects of Internal Control System
on Financial Performance in an Institution of Higher
Learning in Uganda: A Case of Uganda Marytrs
University. Retrieved from
http://www.academia.edu/4812543/EFFECTS_OF_IN
TERNAL_CONTROL_SYSTEMS_ON_FINANCIAL
_PERFORMANCE
Namazi, M. (2013). Role of the agency theory in
implementing management’s control. Academic
Journals Vol. 5(2), pp 38-47, July 2013, ISSN 2141-
6664. Retrieved from
http://www.academicjournals.org/journal/JAT/article-
full-text-pdf/12339F31292.
Petrovits, C., Shakespeare, C., and Shih, A. (2011). The
Causes and Consequences of Internal Control
Problems in Nonprofit Organizations. The Accounting
Review, 86(1), 325-357. Retrieved from http://remote-
lib.ui.ac.id:2059/stable/2978
Porter, M. E. (1980) Competitive Strategy: Techniques for
Analyzing Industries and Competitors. New York:
Free Press.
Porter, M. E. (2015). Shared Value and Strategy. Harvard
Business School. Paper presented at Shared Value
Leadership Summit, New York.
Romney, M. B., and Steinbart, P.J. (2015) Accounting
Information System 13
th
Edition Global Edition.
England: Pearson Education Limited
Clinton, S.B., Pinello, A. S., Skaife, H.A. (2014). The
implications of ineffective internal control and SOX
404 reporting for financial analyst. Journal of
Accounting and Public Policy, Vol. 33, Issue 4, 2014,
Pages 303-327, ISSN 0278-4254,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaccpubpol.2014.04.005.
Snyder, H., Andersen, M., and Zuber, J. (2017, Maret).
Nonprofit Fraud How Good Are Your Internal
Controls?. Strategic Finance, 55-61
JCAE Symposium 2018 – Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study
346

Indonesia Government. (2003). Law of the Republic of
Indonesia Number 20 Year 2003 on National
Education System.
Wahyuni, S. (2015). Qualitative Research Method: Theory
and Practice 2nd Edition. Jakarta: Salemba Empat.
Analysis and Design of Internal Control on Revenue Cycle in Order to Optimize Enrollment Fees Collection in Non-Profit Organization
(Case Study on ABC Foundation)
347
