
Analysis of Separation the Functions of Account Representative
to Increase Tax Revenues and Compliance of Taxpayers
A Case Study at Serpong Tax Office, Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office
and Jakarta Matraman Tax Office
Merda Listana Leonyca and Christine Tjen
Economic and Business Faculty, University of Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
merdainzaghi@gmail.com, indivara_devi@yahoo.com
Keywords: Account Representative, Compliance, Functions, Tax Revenues, Taxpayer.
Abstract: This research aimed to know the level of tax revenues and taxpayer compliance and problems that are still
encountered after the separation of Account Representative functions. Separation of this functions is done
because of the dualism of Account Representative functions in the implementation of daily tasks so that less
optimal in increasing tax revenue and taxpayers compliance. Research method used in this research is
qualitative method with case study approach in Serpong Tax Office, Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office and
Jakarta Matraman Tax Office. Data used in this research is Tax Revenues, especially form disbursement
letter of appeal issued by Account Representative and Compliance in Submission of Annual Tax Return at
2014 when the start of the implementation of the trial separation of Account Representative functions until
2016 after the separation of AR functions is implemented in all the tax office. The result of this research is
that after the separation of Account Representative functions, Tax Revenues and Compliance in Submission
of annual tax return has not increased optimally. In addition, there is still a problem faced by Account
Representative after the separation of this functions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Taxes have an important role to play in governance
as it is one of the largest sources of financing in the
State Budget. The target of tax revenues always
increase year by year, but not followed by the
percentage of tax revenues realization. Based on
Financial Report of Central Government data known
that within last ten years from 2007 to 2016, tax
revenues just once reached target in 2008 which
amounted 108.12% due to the sunset policy that
helps increase tax revenues.
Because the tax role is very important, therefore
the tax system is required in order to perform
supervision and provide good service to the
Taxpayer so that it can to increase tax revenue. Due
to the demand for increased taxpayer compliance
and tax revenues as well as other improvements in
the tax administration system, it is necessary to do
tax reform through modernization of taxation. In
2002, Directorate General of Taxes (DGT) was
performed the modernization of taxation, one of
them is forming Account Representative (AR). AR
is a front guard in the supervision and improvement
of taxpayer compliance and provision of services to
taxpayers.
Increasing the revenue target of DGT from year
to year requires the role of AR in improving
taxpayer compliance, but the demands have not been
followed by the management and structuring of good
tasks so that AR often face difficulties in the
implementation of their daily tasks. Some of these
difficulties are the number of clerical jobs that
actually dominate the main job, there is a dualism of
work where on the one side an AR must become a
taxpayer partner by providing services in carrying
out the consultation function, while on the other side
must be assertive to the Taxpayer to perform the
functions of supervisory and explore the potential of
the taxpayer in fulfilling his tax obligations. This
often leads to conflict of interest between AR and its
taxpayers. In addition, the ratio between the amount
of AR compared with the number of taxpayers who
become his responsibility has not been balanced so
that the AR work does not maximal (Rahayu and
Lingga, 2009). Therefore, it is deemed necessary to
382
Leonyca, M. and Tjen, C.
Analysis of Separation the Functions of Account Representative to Increase Tax Revenues and Compliance of Taxpayers - A Case Study at Serpong Tax Office, Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax
Office and Jakarta Matraman Tax Office.
In Proceedings of the Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study (JCAE 2018) - Contemporary Accounting Studies in
Indonesia, pages 382-391
ISBN: 978-989-758-339-1
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

separate the AR duties and functions between the
functions of consultation and service with the
supervision and explore of the potential taxpayers.
With the separation, AR is expected to work more
optimally in accordance with their respective
functions. Therefore, in accordance to the Minister
of Finance Regulation number 206.2 / PMK.01 /
2014 stated that in order to improve the good
administrative, effectiveness, and performance of the
vertical organization in DGT, it is necessary to
improve the organization and work procedures of the
vertical institution in DGT, one of the point stated in
article 61 that in Tax Office there is separation
between Section of Supervision & Consultation I
with functions of service & consultation and Section
Supervision & Consultation II, III, and IV with
functions of supervision and exploring potential
taxes. This research trying to analyze tax revenues
and taxpayer’s compliance by comparing the
conditions at the time before and after the separation
functions of Account Representative.
Based on the background of problems that have
been described, the purpose of this research are to
know the level of tax revenues and taxpayer’s
compliance with the separation of Account
Representative functions and the problems that are
still encountered after the separation of Account
Representative functions. Hopefully, it can increase
the tax revenues and taxpayer’s compliance.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Modernization of Tax Administration
System
Tax administration aims to build and maintain good
relationships with taxpayers and assist and facilitate
them in fulfilling taxation obligations. The tax
administration is responsible for reporting the
performance and achievement of organizational
objectives, including the responsibility for
overseeing taxpayer compliance and the impact of
such efforts on improving taxpayer compliance
(Alink and Kommer, 2011)
The increasing target of government revenues
and the low level of public trust in Indonesia's tax
system encourages the government to undertake
reforms in taxation.
Tax reform begins with the implementation of
Self Assessment as a tax collection system in
Indonesia. With the system, the taxpayer is entrusted
with calculating, calculates his own tax payable and
then repays and reports it to the registered Tax
Office. By providing good service to the taxpayer is
expected to be a motivation for taxpayers to pay
taxes.
2.2 Account Representative
One form of tax reform is by the establishment of
AR in the Large Taxpayer Tax Office. In accordance
with the Minister of Finance Decree number. 98 /
KMK.01 / 2006 concerning AR in Tax Office that
has Implemented Modern Organization, that has
been assigned AR who take the task in the field of
taxation intensification through the provision of
guidance / consultation, analysis and supervision of
taxpayers. According to KMK 98 / KMK.01 / 2006,
AR is an officer appointed in each Section of
Supervision and Consultation at Tax Office which
has implemented Modern Organization. In the early
modernization of tax administration in 2002, AR
acts as liaison officer of Taxpayer Office Taxpayer
in communicating taxpayers' obligations and rights
in the field of taxation (Hutagaol, 2007)
In other countries, for example on the Internal
Revenue Service (IRS) there are tax officers who
have functions such as AR in the DGT that perform
compliance monitoring performed by the Tax
Compliance Officer. In carrying out its functions,
the main task of a Tax Compliance Officer is to
ensure that the taxpayer has paid taxes correctly. In
addition there are also tax officers with functions in
providing services and consultation to taxpayers
conducted by Contact Representative. In carrying
out its functions, the main task of a Contact
Representative is to help taxpayers in consultation
about taxation either by phone or face to face
directly.
2.3 Tax Revenues
Tax revenue is the largest contributor to government
revenues. Tax revenues is the dominant source of
government financing for both routine and
development expenditures (Suryadi, 2006). In
general, tax revenues can be grouped into routine
and extra-effort revenues. Routine revenues mean
revenues that come from paying periods that is
usually obtained without any extra-effort by
Account Representative, because the income will
certainly receive every month, but still require strict
supervision. Revenue of extra-effort activities
requiring more effort that is derived from the
disbursement Letter of Appeal or Letter of Request
Explanation of Data or Information (SP2DK)issued
Analysis of Separation the Functions of Account Representative to Increase Tax Revenues and Compliance of Taxpayers - A Case Study at
Serpong Tax Office, Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office and Jakarta Matraman Tax Office
383
by AR, examination, collection of tax receivables
and extensification of taxation activities.
As mentioned above, that one of the tax revenues
from the extra-effort activities is derived from the
disbursement Letter of Appeal or Letter of Request
Explanation of Data or Information issued by AR if
found any data about the property (tax potential) of
the Taxpayer who has not been reported in the
Annual Tax Returns. In terms of supervisory
functions, AR will oversee tax payments from
taxpayers primarily from routine revenues. While
the explore potential taxes is done through
intensification activities by maximizing the data of
existing taxpayers from reporting data of Tax
Return, tax payments, data from third parties and
direct observation results in the field.
According to Rahayu (2010), there are several
factors in optimizing the government revenue
through tax collection, that is:
1. Clarity, certainty, and simplicity of tax laws and
regulations.
2. Government policy in implementing tax laws.
3. Appropriate tax administration system.
4. Service.
5. Awareness and understanding of citizens.
6. Quality of tax officer (intellectual, skill,
integrity, high moral).
2.4 Compliance of Taxpayers
It cannot be denied that compliance is a major
problem faced by all income authorities, for example
the IRS in the United States difficulties in estimating
tax income (James and Alley, 2004). Similarly in
Indonesia, where the low compliance of taxation is
still a problem in tax administration in Indonesia.
Even people prefer to pay more to get a product and
avoid taxes than to pay less. This non-compliance is
called as a "tax gap". Tax gap can be used to
measure the performance of a country's tax income,
that is how far the tax authorities are able to make
the taxpayers obedient to carry out tax obligations in
accordance with applicable tax provisions. The
increased ability of the tax authorities to access the
data and increase the voluntary compliance of the
Taxpayer is one way of reducing the existing tax
gap.
According to Nowak in Zain (2005) taxpayer’s
compliance is defined as a climate of awareness and
compliance fulfillment of tax obligations, where
taxpayers understand all the provisions of tax laws
and regulations, can fill out the tax form clearly and
completely, calculate correctly the amount of tax
payable as well pay them on time. While Nurmantu
in Rahayu (2010) defines compliance taxation as a
condition in which the taxpayer to fulfill obligations
and implement taxation rights. According to
Nasucha in Rahayu (2010), Taxpayer compliance
can be identified
from:
1. Compliance to register
2. Compliance to report the Tax Return
3. Compliance to calculate and pay the tax payable
4. Compliance to pay the tax arrears
Tax administration in Indonesia still needs to be
improved in the hope of providing better service to
Taxpayers so that Taxpayers are motivated to meet
their tax obligations. Good administration is also
marked by the imposition of strict sanctions for
taxpayers who attempt to smuggle their taxes. In
addition, taxpayer’s compliance will also increase if
they get a good consulting service.
Table 1 : Previous Research
Researchers Title of the
research
Result of
research
Basalamah,
Anies Said
M. et
al.(2016)
Separation of
AR Functions
for Better
Service and Tax
Revenue.
Research Object
is Serpong Tax
Office.
there is an
increase in
service quality
after the
separation of
functions but
there are still
elements that
need to be
improved
Janson
Nicholas
Samosir
(2015)
Evaluation of
Taxpayer
Compliance and
Tax Receipts
Before and
After Trial
Arrangement of
Duties and
Functions of
AR at Medan
Timur Tax
Office
There is no
significant
difference in
taxpayer
compliance and
tax revenues
between before
and after the
trial of
structuring tasks
and functions
AR
JCAE Symposium 2018 – Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study
384

3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Research method used in this research is qualitative
method with case study approach in Serpong Tax
Office, Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office and Jakarta
Matraman Tax Office. Creswell (2014) states that
qualitative research is an approach to explore and
understand the meaning of individuals or groups that
are perceived as a social or humanitarian problem.
Furthermore, according to Creswell that this study
involves questions and procedures, data, data
analysis is built inductively and then the authors
make interpretation of meaning over the data. The
case study was chosen because to answer three
conditions: "how" or "why" questions, the least
supervision of an event, and to focus on real-life
phenomena (Yin, 2009). Serpong Tax Office was
chosen as the object of research because it is one of
Tax Officer pilot project at the time of trial of
separation of AR functions which will be compared
with Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office and Jakarta
Matraman Tax Office. This research is different
from the previous research because the object of
research is not only one of Tax Office which become
the pilot project, but also compared with other Tax
Office that have implemented the separation of AR
functions and to see tax revenue and taxpayer
compliance and problems still encountered after the
separation of AR functions.
Data used in this research are primary data and
secondary data. Primary data obtained from
interviews and questionnaires with related parties to
obtain an overview of the implementation of policy
arrangement of tasks and functions of Account
Representative through the separation of Account
Representative functions. The interview was
conducted to Section Head of Institutional Design
Development - Directorate of Internal Compliance
and Transformation of Apparatus Resources, Head
of Supervision & Consultation Section I and IV
Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office, and Head of
Supervision & Consultation Section I and II Jakarta
Matraman Tax Office. While the questionnaires
distributed to Account Representative Jakarta Duren
Sawit Tax Office and Jakarta Matraman Tax Office.
Secondary data obtained through data in the form of
compliance data and tax income, especially from the
realization of disbursement of appeal by the
Taxpayer. In addition, secondary data can also be
obtained through documents, journals, articles and
other data related to the arrangement of tasks and
functions of Account Representative.
Serpong Tax Office was chosen as the research
object because it is one of Tax Office which became
the pilot project during the trial of separation of
Account Representative functions. Serpong Tax
Office was formed in 1994 with working area
covering four districts namely: Pondok Aren,
Pamulang, Serpong and Ciputat.
Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office was established
in accordance with the Minister of Finance
Regulation Number 55/PMK.0 / 2007 dated May 31,
2007, commencing operation on October 2, 2007
based on the Decree of the Director General of
Taxes No. KEP-86 / PJ / 2007 dated 11 June 2007.
The working area of Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office
covers 7 village namely: Pondok Bambu, Duren
Sawit, Malaka Jaya, Pondok Kelapa, Pondok Kopi,
Malaka Sari and Klender.
In accordance with the Decree of the Director
General of Taxes No. KEP-86 / PJ / 2007 dated June
11, 2007, then on July 3, 2007 Jakarta Matraman
Tax Office started to operate. The Working Area of
Jakarta Matraman Tax Office covers Matraman Sub
District consisting of 6 Village namely: Pisangan
Baru, Utan Kayu Utara, Utan Kayu Selatan, Kebon
Manggis, Pal Meriam, and Kayu Manis.
4 ANALYSIS
As has been explained earlier that tax income comes
from regular and extra-effort revenues. Regular
revenues come from revenues where we do not need
to excessive effort, the tax income will be obtained.
While the revenues from extra-effort activities, more
efforts are needed in order to increase tax income.
The following graph shows the data of overall tax
revenues, disbursement SP2DK and compliance
submission of Annual Tax Returns of Serpong Tax
Office, Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office and Jakarta
Matraman Tax Office. Then will be described the
analysis and discussion of overall tax revenues as
well as reveue from disbursement SP2DK which is
one source of revenues from extra effort in 2014
until 2016. The discussion of SP2DK can also be
seen from the development of the number of SP2DK
publishing along with the nominal amount of tax
potential listed in SP2DK. Meanwhile, what is
meant by compliance here is compliance in
submission of Annual Tax Return by taxpayer with
year of delivery 2014 until 2016. As mentioned
before, that taxpayer compliance can be identified
one of them as compliance in submitting Tax
Return. Therefore, the limitation of this research is
only submission of Annual Tax Return.
Analysis of Separation the Functions of Account Representative to Increase Tax Revenues and Compliance of Taxpayers - A Case Study at
Serpong Tax Office, Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office and Jakarta Matraman Tax Office
385
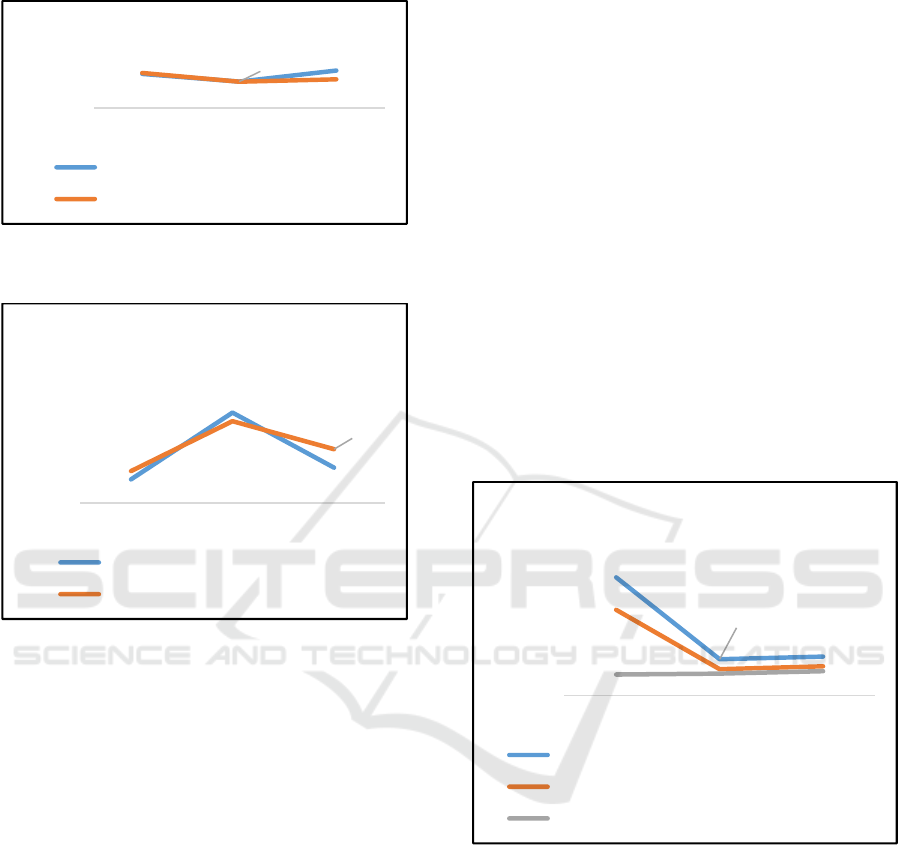
4.1 Serpong Tax Office
Graph 1 Target and Realization of Revenues Serpong Tax
Office (2014 -2016)
Graph 2 Potential and Realization of SP2DK
Disbursement Serpong Tax Office (2014 - 2016)
Based on the graph 1 and 2, it can be seen that
the acceptance of Serpong Tax Office in the year
when the trial of separation of AR functions 2014
reached 103.02% as well as SP2DK disbursement in
2014 that exceeded the potential targeted in SP2DK.
From the graph above it is known that the realization
amount of SP2DK disbursement is Rp.80.86 Billion
with initial potential amount of Rp.59.84 Billion.
The realization of SP2DK disbursement becomes
one of the factors of achieving revenues exceeding
100%. However, in 2015, the decrease of revenues
target due to Serpong Tax Office experienced the
breakdown of Tax Office with Pondok Aren Tax
Office in October 2015. While the nominal value of
SP2DK potential is increased by Rp.229.44 Billion
with the realization of Rp.207.55 Billion. The
increase in SP2DK nominal value is due to an
increase in the number of SP2DK issued due to the
increase of Account Representative Controlling
efforts in the potential exploring. Acceptance in
2015 of Rp.2,826.27 Billion or 99.44% of the target
revenues of Rp.2,842.27 Billion. Target revenues
increased again in 2016 to Rp.4,035,58 Billion with
realized revenues of 3,089.13 or only 76.55% of the
target revenues. However, the nominal value of
SP2DK is decreased by Rp.89.60 Billion with the
realization of Rp.136.36 Billion. This decrease is
due to the Amnesty Tax program in the middle of
2016, so that the focus of Account Representative
Supervision at that time was split between exploring
potential by appealing to taxpayers to utilize Tax
Amnesty program. Therefore, in the middle of 2016,
Account Representative's task of is more focused on
Tax Amnesty activities. Based on SP2DK reception
and disbursement data above, during the
implementation of the Account Representative
functions separation trial, the realization of SP2DK
disbursement may exceed the potential value in
SP2DK. Similarly, when the separation of Account
Representative functions started to be applied in all
Tax Office, there has been a significant increase in
SP2DK in both quantity and potential value, but it
has not been followed by significant increase of
SP2DK disbursement realization.
Graph 3 Submission of Annual Tax Return Serpong Tax
Office (2014 - 2016)
While based on compliance data seen from the
graph 3, it is known that in 2015 there was a
decrease in the number of taxpayers who must
submit annual tax returns to 59.282 taxpayers from
193,206 taxpayers in 2014. This decrease is due to
the cleansing data from the Head Office of DGT
which aims to improve master file taxpayer in order
to realize the orderly administration of taxation and
the formation of relevant data and relevant
information and taxpayer related. Cleansing of data
is done by eliminating positions on double Taxpayer
Identification Number, taxpayer who has no tax
3.668,65
2.842,27
4.035,58
3.779,48
2.826,27
3.089,13
0,00
5.000,00
2014 2015 2016
Target and Realization of Revenue
Target of Revenue (Billion Rp)
Realization of Revenue (Billion Rp)
59,84
229,44
89,60
80,86
207,55
136,36
0,00
100,00
200,00
300,00
2014 2015 2016
Potential in SP2DK and
Realization of SP2DK Disbursement
Nominal in SP2DK (Billion Rp)
Realization of SP2DK (Billion Rp)
193.206
59.282
63.622
140.074
42.979
47.717
34.245
35.773
39.789
0
50.000
100.000
150.000
200.000
250.000
2014 2015 2016
Submission of Annual Tax Return
Taxpayers must submit Annual Tax Return
Target of Annual Tax Return
Realization of Annual Tax Return
JCAE Symposium 2018 – Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study
386
transaction in the last 3 (three) years consecutively
or against Taxpayer Identification Number with non-
effective status in the last 5 (five) years. The target
of sum the Annual Tax Return in 2015 is 42,979
taxpayers with a delivery rate of 72.5%. Realization
of Annual Tax Returns in 2015 is 35,773 taxpayers
or reaches 83.23% of the target ratio, an increase
over the previous year. In 2016 there is an increase
of the number of registered taxpayers to 98,312
taxpayers with the number of taxpayers who are
required to submit the annual tax returns 63,622
taxpayers. The target of submission the Annual Tax
Return is increased to 47,717 taxpayers with a
delivery rate of 75%. While the realization of 39,789
taxpayers or reach 83.39% of the target ratio. Based
on these data, the separation of Account
Representative functions in 2015 can improve the
compliance of Annual Tax Returns if compared to
the year of trial although the realization is still below
the target ratio.
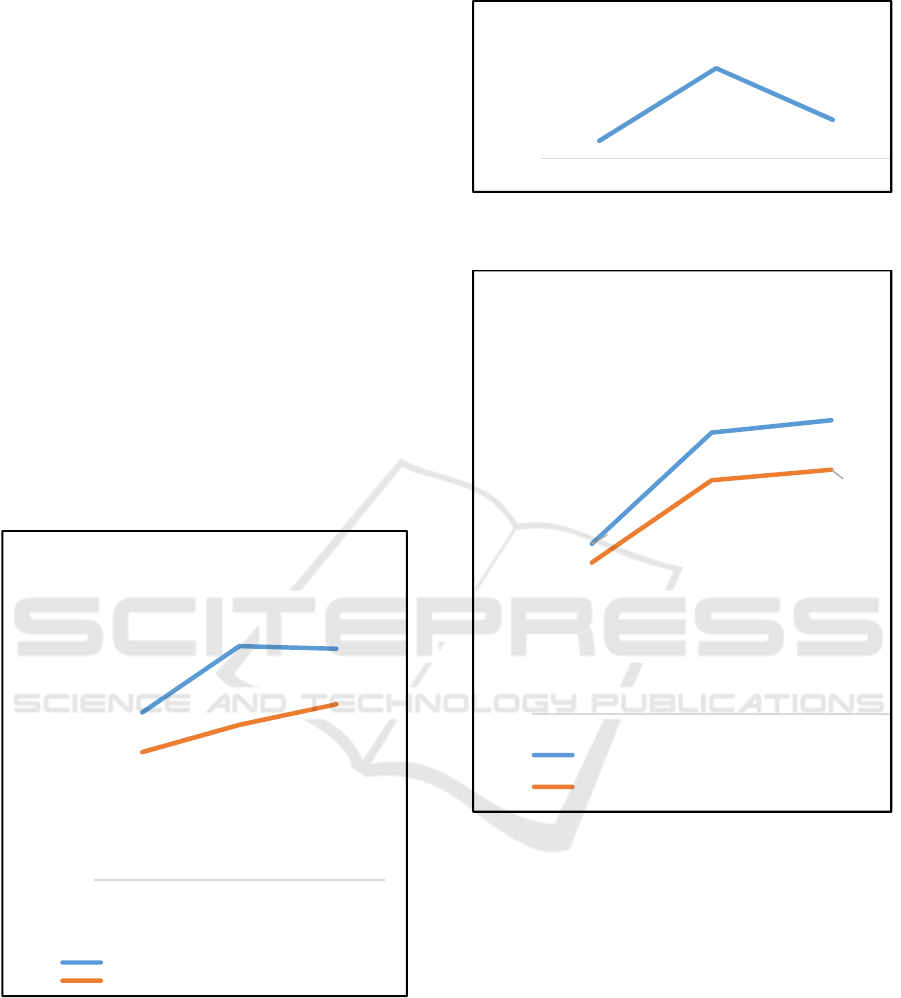
4.2 Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office
Graph 4 Target and Realization of Revenues Jakarta
Duren Sawit Tax Office (2014 -2016)
Graph 5 Number of SP2DK issuance Jakarta Duren Sawit
Tax Office (2014 - 2016)
Graph 6 Potential and dan Realization of SP2DK
Disbursement Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office (2014 -
2016)
Based on the graph of data of Jakarta Duren
Sawit Tax Office, from 2014 to 2016, the
achievement of Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office has
not reached 100%. In 2014 the realization of
revenues of Rp.900.60 Billion or reach 76.35% of
the target. Then in 2015 the target of revenues
increased by Rp.1,646.30 Billion with the realization
of Rp.1,092.60 Billion or only reached 66.37%,
down compared to the previous year. In 2016,
revenues target decreased to Rp.1.627,30 Billion
with the realization of Rp.1,237.19 Billion or reach
76% of the target, experiencing an increase in
achievement over the previous year.
1.179,59
1.646,30
1.627,97
900,60
1.092,60
1.237,19
0,00
400,00
800,00
1.200,00
1.600,00
2.000,00
2014 2015 2016
Target and Realization of Revenue
Target of Revenue (Billion Rp)
Realization of Revenue (Billion Rp)
959
4.942
2.109
-
2.000
4.000
6.000
2014 2015 2016
Number of SP2DK issuance
38,11
63,03
65,83
33,91
52,37
54,74
0,00
10,00
20,00
30,00
40,00
50,00
60,00
70,00
2014 2015 2016
Potential in SP2DK and
Realization of SP2DK Disbursement
Target of Revenue (Billion Rp)
Realization of Revenue (Billion Rp)
Analysis of Separation the Functions of Account Representative to Increase Tax Revenues and Compliance of Taxpayers - A Case Study at
Serpong Tax Office, Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office and Jakarta Matraman Tax Office
387
As well as the number of SP2DK publishing in
2014 amounting to 959 SP2DK with the amount of
potential in SP2DK in 2014 of Rp.38.11 Billion with
realization of SP2DK disbursement of Rp.33.91
Billion. Then in 2015 SP2DK publishing increased
dramatically to 4,942 SP2DK with the amount of
potential in SP2DK of Rp.63.03 Billion with the
realization of Rp.52,37 Billion. The increase of
SP2DK issuance is mainly due to the separation of
Account Representative functions, so Account
Representative Supervision focuses their work more
on exploring of tax potential. However, by 2016 the
number of SP2DK issuance has decreased to 2,109
SP2DK with the increase of potency amount in the
amount of Rp.65.83 Billion with the realization of
Rp.54,74 Billion. This decrease occurred because of
Amnesty Tax Program in the middle of 2016. Based
on the data of SP2DK disbursement and realization
of the above disbursement, when the separation of
Account Representative functions started to have
been applied in all Tax Office, there was a
significant increase to SP2DK both the amount and
the potential value, but not followed by the
significant increase of SP2DK disbursement
realization.
Graph 7 Submission of Annual Tax Return Jakarta Duren
Sawit Tax Office (2014 - 2016)
In 2014 the number of taxpayers registered on
Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office as much as 145,492
taxpayers. While the number of taxpayers who must
submit the Annual Tax Return is 86.978 taxpayers.
The target of delivering the Annual Tax Return is
63,059 taxpayers with a target ratio of 72.5%.
Realization of Annual Tax Returns as much as
50,101 taxpayers or reach 79.45% of the target ratio.
In 2015 the number of registered taxpayers increases
to 152,309 taxpayers, but there is a decrease in the
number of taxpayers who must submit annual tax
returns accompanied also with a decrease in the
annual tax return targets. According to Section Head
of Supervision & Consultation Section IV Jakarta
Duren Sawit Tax Office, the decline in the target is
due to the cleansing of data of taxpayers by the DGT
Head Office. Based on that, then in 2015 the target
of submission of Annual Tax Returns to 60,247
taxpayers and target ratio of 72.5% while the
submissing of Annual Tax Return increased by
53,452 taxpayers or reached 88.72% of the target
ratio.
Meanwhile, there is a significant increase in the
number of registered taxpayers in 2016, one of
which is because there are several programs of the
DKI Jakarta Provincial Government for the lower
and lower middle class which require having
Taxpayer Identification Number. So that the number
of taxpayers registered in Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax
Office increased to 161.183 taxpayers with the
number of taxpayers who must submit annual Tax
Return of 86.650. The target of annual Tax Return
submission is 64,988 and the target ratio is 75%.
Realization of Annual Tax Return submission
increased to 54,801 taxpayers or reached 84.33% of
the target ratio, a decrease over the previous year.
Based on these data, the separation of Account
Representative functions can improve the
compliance of Annual Tax Return, although the
realization is still below the target ratio.
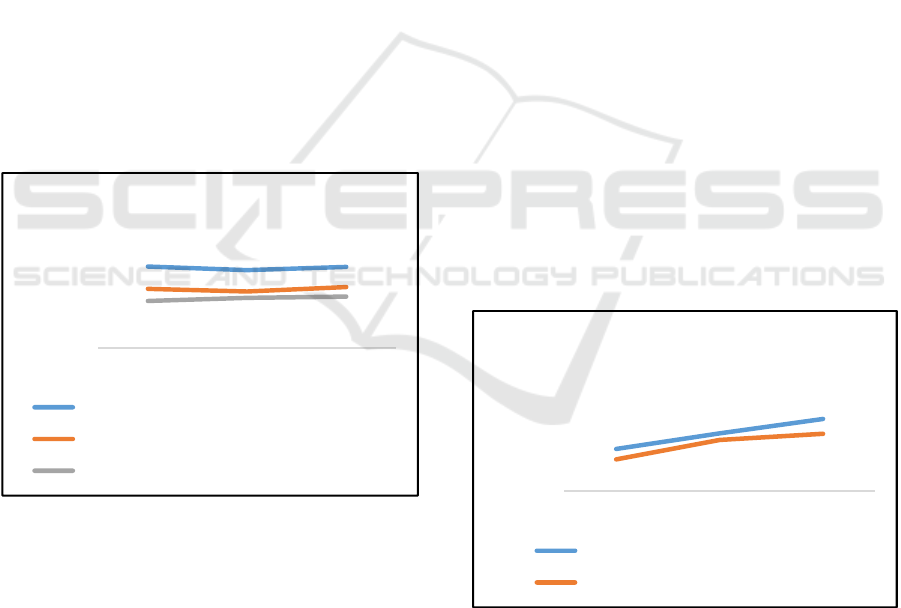
4.3 Jakarta Matraman Tax Office
Graph 8 Target and Realization of Revenues Jakarta
Matraman Tax Office (2014 -2016)
86.978
83.099
86.650
63.059
60.247
64.988
50.101
53.452
54.801
-
50.000
100.000
2014 2015 2016
Submission of Annual Tax Return
Taxpayers must submit Annual Tax Return
Target of Annual Tax Return
Realization of Annual Tax Return
641,12
877,60
1.097,19
482,44
777,64
871,77
0,00
500,00
1.000,00
1.500,00
2014 2015 2016
Target and Realization of Revenue
Target of Revenue (Billion Rp)
Realization of Revenue (Billion Rp)
JCAE Symposium 2018 – Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study
388
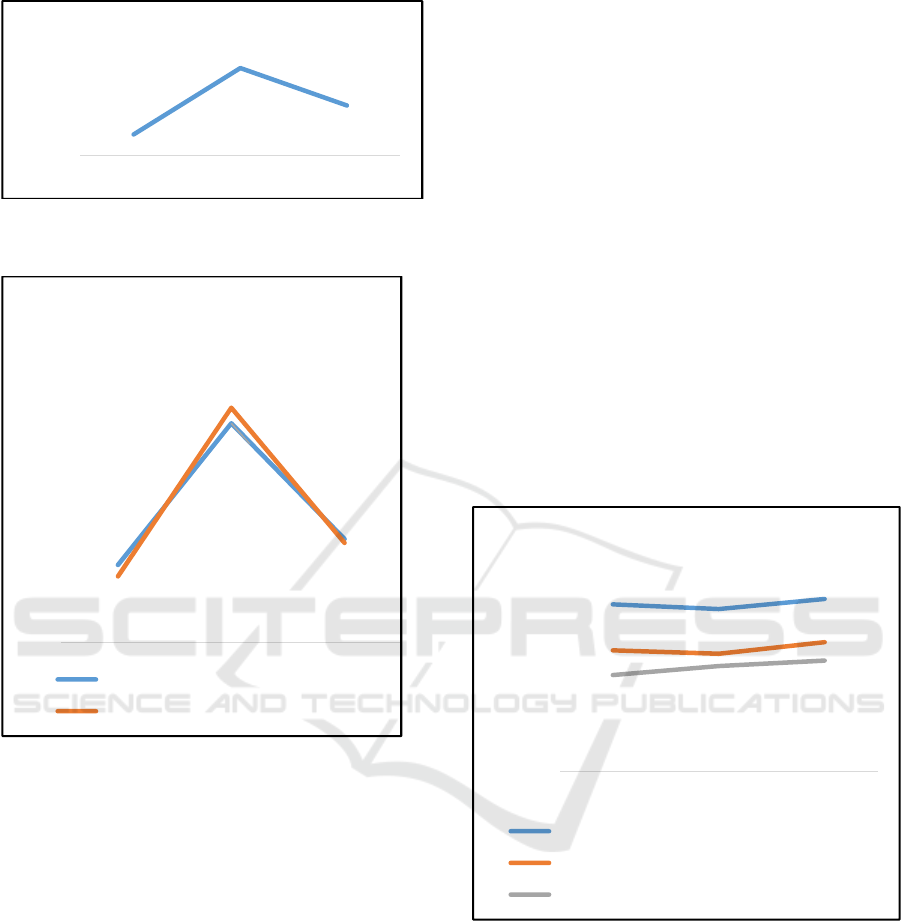
Graph 9 Number of SP2DK issuance Jakarta Matraman
Tax Office (2014 – 2016)
Graph 10 Potential and Realization of SP2DK
Disbursement Jakarta Matraman Tax Office (2014 - 2016)
Based on the data of Jakarta Matraman Tax
Office, in 2014 the revenues target of Rp.641.12
Billion with the realization of Rp.482.44 Billion or
reach 75.25%. Likewise in 2015 the target of
Rp.877.60 Billion with the realization of Rp.777.64
Billion or up 88.6%, an increase in percentage of
achievement compared to the previous year. In 2016
the revenues target of Rp.1079.19 Billion with the
realization of Rp.871.77 Billion or reached 79.45%,
decreased percentage of achievement compared to
the previous year.
Similarly with Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office,
SP2DK publishing in Jakarta Matraman Tax Office
in 2015 increased drastically to 3,727 SP2DK
compared to 2014 which only published as many as
891 SP2DK. The increase of SP2DK issuance is also
mainly due to the separation of Account
Representative functions. However, in 2016 the
number of SP2DK publishing has decreased to 2,130
SP2DK. This decline is due to the Amnesty Tax
Program in the middle of 2016.
The amount of potential in SP2DK in 2014 is
Rp.21.36 Billion with realization of SP2DK
disbursement of Rp.18,20 Billion. In the year 2015
increase of SP2DK issuance amount followed by
increasing amount of potency in SP2DK that is
become Rp.60.51 Billion with the realization of
Rp.64.81 Billion, it exceeds the potential in SP2DK.
This became one of the contributes tax revenues
Jakarta Matraman Tax Office up to 82.58%. But in
2016 as the number of SP2DK decreases, the
amount of potential in SP2DK also decreased
drastically to Rp.28.50 Billion with realization of
SP2DK disbursement of Rp.27.46 Billion. Based on
the revenues data, then when the separation of
Account Representative functions occurs a
significant increase to SP2DK both the amount and
potential value, but not yet accompanied by
significant increase in SP2DK disbursement
realization.
Graph 11 Submission of Annual Tax Return Jakarta
Matraman Tax Office (2014 - 2016)
Based on data number of registered taxpayer
Jakarta Matraman Tax Office increase the number of
registered taxpayers every year starting from 2014
until 2016. In 2014 taxpayers registered in Jakarta
Matraman Tax Office as many as 74,797 taxpayers
with the number of taxpayers who must submit
annual tax return as much as 41.003 taxpayer. While
the target submission of Annual Income of 29.727
with target ratio of 72.5%. Realization of Annual
Tax Return submission of 23,680 taxpayers or reach
79.66% of the target ratio.
891
3.727
2.130
-
2.000
4.000
2014 2015 2016
Number of SP2DK issuance
21,36
60,51
28,50
18,20
64,81
27,46
0,00
10,00
20,00
30,00
40,00
50,00
60,00
70,00
2014 2015 2016
Potential in SP2DK and
Realization of SP2DK Disbursement
Nominal in SP2DK (Billion Rp)
Realization of SP2DK (Billion Rp)
41.003
39.865
42.324
29.727
28.902
31.743
23.680
25.881
27.225
-
10.000
20.000
30.000
40.000
50.000
2014 2015 2016
Submission of Annual Tax Return
Taxpayers must submit Annual Tax Return
Target of Annual Tax Return
Realization of Annual Tax Return
Analysis of Separation the Functions of Account Representative to Increase Tax Revenues and Compliance of Taxpayers - A Case Study at
Serpong Tax Office, Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office and Jakarta Matraman Tax Office
389

In 2015 there is a decrease in taxpayers who
must submit annual tax returns to 39,865 taxpayers,
despite an increase in the number of registered
taxpayers. Similarly with Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax
Office, this decline occurs because of the data
cleansing conducted by the Head Office of DGT.
Likewise with the number of targets submission of
annual tax returns that fell to 28,902 taxpayers.
However, there was an increase in the realization of
the Annual Tax Return of 25,881 taxpayers or
89.55% of the target ratio.
In 2016, an increase in the number of registered
taxpayers to 82,941 taxpayers with the number of
taxpayers who must submit the Annual Tax Return
of 42,324 taxpayers. Similarly, the target of Annual
Tax Returns increased to 31,743 taxpayers with a
target ratio of 75%. Realization of Annual Tax
Return submission of 27,225 taxpayers or reach
85.77% of the target ratio, decreased compared to
the previous year.
The increase in the Annual Income Tax
submission target of 9.8% in 2016 is not followed by
the realization of the Annual Tax Return which only
increased by 5.2% from 25,881 in 2015 to 27,225 in
2016. This increase occurred because of the program
Tax Amnesty. So the effect of separation of Account
Representative functions was not too visible. If the
realization is compared to the target, there is a
decrease in the percentage from 64.9% in 2015 to
64.3% in 2016. Based on these data, the separation
of Account Representative functions can improve
the compliance of Annual Tax Returns, although the
realization is still below the target ratio.
After the separation of Account Representative
functions is running still found some problems, both
from the Account Representative Service and
Account Representative Supervision. Some of these
problems are:
1. The overlapping of consultation work between
Account Representative Service and Account
Representative Supervision. Inconsistent
Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) and Job
Description and supporting applications
2. Directorate at Head Office managing Account
Representative Service still deemed
inappropriate
3. Selection of human resources that are still not in
accordance with the competence,
4. Lack of training or training provided by Head
Office or DGT Regional Offices,
5. Additional work for Account Representative
Supervision as Tax Inspector,
6. The amount of taxpayer supervised is not
proportional to the amount of Account
Representative available.
5 CONCLUSION
From the results of the analysis and discussion in
chapter 4, this research yields the following
conclusions are seen from the overall tax revenues
after the separation of Account Representative
functions in 2015 at the time of separation of AR
function has not significantly increased. Moreover in
2016 there was a decrease in SP2DK issuance due in
middle 2016 DGT launched Tax Amnesty Program.
During the Amnesty Tax Program, the DGT is intent
on socializing the program. So Account
Representative Supervision focus to issue a letter of
appeal to taxpayers to take advantage of Tax
Amnesty program. Likewise, compliance
submission Annual Tax Return has not increased
significantly. Realization of Annual Tax Return is
still below the target of Annual Tax Return.
In addition, after the separation of Account
Representative functions is still found some
problems, both experienced by Account
Representative Supervision and Account
Representative Service, both task and functions
problems, human resources and SOP or Job
Description. So that required improvement for the
achievement of tax revenues and compliance
taxpayers better.
Because the study period is limited and restricted
only from the implementation of the trial in 2014
until 2016 plus the Amnesty Tax program, so it does
not illustrate the optimization of Account
Representative functions separation. It is hoped for
further research to have longer research period and
add research object.
REFERENCES
Books:
Alink, M and Kommer,V (2011). Handbook on Tax
Administration. Netherland: IBFD.
Creswell, J. W. (2014). Research Design :
Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods
Approaches (4
th
ed.). California: SAGE
Publications, Inc.
Hutagaol, J. (2007). Taxation: Contemporary Issues.
Yogyakarta: Graha Ilmu
JCAE Symposium 2018 – Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study
390

Rahayu, S. K. (2010). Taxation Indonesia: Concepts
and Formal Aspects. Yogyakarta: Graha Ilmu
Samosir, J. N. (2015).
Evaluation of Taxpayer
Compliance and Tax Receipts Before and After Trial
Arrangement of Duties and Functions of AR at Medan
Timur Tax Office
. Medan: University of North
Sumatera
Yin, R. K. (2009). Case Study Research : Design
and Methods, 4th edition
Zain, M. (2005). Tax Management (2
nd
ed.). Jakarta:
Salemba Empat.
Journal Article:
Alley, S. J. (2004). Tax Compliance. Self -
Assessment and Tax Administration. Journal of
Finance and Management in Public Services.
Volume 2 Number 2, pp. 27 - 42.
Basalamah, et al. (2016). Separation of AR
Functions for Better Service and Tax Revenue.
Financial Economics Review Vol. 20 No. 1 April
2016.
Lingga, S. R. (2009). Influence of Modernization of
Tax Administration System to Taxpayer
Compliance. Accounting Journal Vol. 1 No. 2
November 2009, pp. 119 - 138.
Ngadiman. (2008). Modernization and Reform of
the Tax Service. MIIPS Vol 7 No. 2 September
2008, pp. 165 - 175.
Suryadi. (2006). The Causal Relationship Model of
Awareness, Services, Taxpayer‘s Compliance
and Its Effect on The Performance of Tax
Revenue: A Survey in East Java. Public Finance
Journal Vol. 4, No. 1, April 2006, pp. 105-121.
Regulations
Directorate General of Taxes. (2007). Decision of
the Director General of Tax No. KEP-86 / PJ /
2007 concerning the implementation of the
Organization, Work Procedures, and Time of
Operation of KPP Pratama and KP2KP in the
Regional Offices of DGT in the Special Capital
Region of Jakarta Other than the Regional Office
of DGT of Central Jakarta. Jakarta.
Minister of Finance Decree. (2006). Decree of the
Minister of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia
number 98 / KMK.01 / 2006 concerning Account
Representative at Tax Office that has
Implemented Modern Organization
Minister of Finance Decree. (2007). Regulation of
the Minister of Finance No. 55 / PMK.01 / 2007
concerning Amendment to Regulation of the
Minister of Finance No. 132 / PMK.01 / 2006
concerning Organization and Working
Procedures of Vertical Institutions of the
Directorate General of Taxes.Jakarta.
Minister of Finance Decree. (2014). Regulation of
the Minister of Finance No. 206.2 / PMK.01 /
2014 on the Organization and Working
Procedures of Vertical Institutions of the
Directorate General of Taxes. Jakarta.
Analysis of Separation the Functions of Account Representative to Increase Tax Revenues and Compliance of Taxpayers - A Case Study at
Serpong Tax Office, Jakarta Duren Sawit Tax Office and Jakarta Matraman Tax Office
391
