
Cross-domain & In-domain Sentiment Analysis with Memory-based
Deep Neural Networks
∗
Gianluca Moro, Andrea Pagliarani, Roberto Pasolini and Claudio Sartori
Department of Computer Science and Engineering (DISI), University of Bologna,
Via Cesare Pavese, 47522 Cesena, Italy
Keywords:
Sentiment Classification, Transfer Learning, Fine-tuning, Deep Learning, Big Data, Memory Networks.
Abstract:
Cross-domain sentiment classifiers aim to predict the polarity, namely the sentiment orientation of target text
documents, by reusing a knowledge model learned from a different source domain. Distinct domains are ty-
pically heterogeneous in language, so that transfer learning techniques are advisable to support knowledge
transfer from source to target. Distributed word representations are able to capture hidden word relationships
without supervision, even across domains. Deep neural networks with memory (MemDNN) have recently
achieved the state-of-the-art performance in several NLP tasks, including cross-domain sentiment classifica-
tion of large-scale data. The contribution of this work is the massive experimentations of novel outstanding
MemDNN architectures, such as Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) and Differentiable Neural Computer (DNC)
both in cross-domain and in-domain sentiment classification by using the GloVe word embeddings. As far as
we know, only GRU neural networks have been applied in cross-domain sentiment classification. Sentiment
classifiers based on these deep learning architectures are also assessed from the viewpoint of scalability and
accuracy by gradually increasing the training set size, and showing also the effect of fine-tuning, an expli-
cit transfer learning mechanism, on cross-domain tasks. This work shows that MemDNN based classifiers
improve the state-of-the-art on Amazon Reviews corpus with reference to document-level cross-domain sen-
timent classification. On the same corpus, DNC outperforms previous approaches in the analysis of a very
large in-domain configuration in both binary and fine-grained document sentiment classification. Finally,
DNC achieves accuracy comparable with the state-of-the-art approaches on the Stanford Sentiment Treebank
dataset in both binary and fine-grained single-sentence sentiment classification.
1 INTRODUCTION
Sentiment analysis deals with the computational tre-
atment of opinion, appraisals, attitudes, and emotions
toward entities, individuals, issues, events, topics and
their attributes (a survey is in (Liu and Zhang, 2012)).
The task is technically challenging but very useful
in practice. For instance, companies always want to
know customer opinions about their products.
When an understanding is required of whether a
plain text document has a positive, negative or neu-
tral orientation, sentiment classification is involved.
This supervised approach learns a model from a la-
belled training set of documents, then applies it to an
unlabelled test set, whose polarity (e.g. positive, ne-
∗
This work was partially supported by the project ”Tore-
ador”, funded by the European Unions Horizon 2020 rese-
arch and innovation programme under grant agreement No
688797. Thanks to NVIDIA Corporation for the donated
Titan GPU used in this work.
gative or neutral orientation) has to be found. The
typical approach to sentiment classification assumes
that both the training set and the test set deal with the
same topic. For example, a model is learnt on a set
of book reviews and applied to a distinct set of re-
views, but always about books. This modus operandi,
known as in-domain sentiment classification, guaran-
tees optimal performance given that documents from
the same domain are semantically similar. However
this approach is often inapplicable in practice, where
documents are mostly unlabelled. Tweets, blogs, fora,
comments on social networks could bear opinions, but
no information is available on whether they are po-
sitive, negative or neutral. Document categorisation
by human experts is the only way to deal with such
a problem in order to learn an in-domain sentiment
classifier, but it is infeasible with large text sets.
It would be advantageous if a model, once learnt
on a source domain, could be used to classify docu-
ment polarity in a distinct target domain. This appro-
Moro, G., Pagliarani, A., Pasolini, R. and Sartori, C.
Cross-domain & In-domain Sentiment Analysis with Memory-based Deep Neural Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0007239101270138
In Proceedings of the 10th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2018) - Volume 1: KDIR, pages 127-138
ISBN: 978-989-758-330-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
127

ach, known as cross-domain sentiment classification,
has become a hot research thread due to its practi-
cal implications. The biggest obstacle to learning an
effective cross-domain sentiment classifier is the lan-
guage heterogeneity in documents of different dom-
ains. For instance, a book could be described as in-
teresting or boring, whereas an electrical appliance
is more likely to be working or noisy. In such ca-
ses, transfer learning or knowledge transfer techni-
ques may help solving the problem. Many transfer le-
arning approaches have been attempted during the ye-
ars, including the usage of multiple classifiers in (Aue
and Gamon, 2005), measures of domain similarity in
(Blitzer et al., 2007), feature and document alignment
in (Pan et al., 2010; He et al., 2011; Zhang et al.,
2015b; Domeniconi et al., 2015b; Domeniconi et al.,
2015a; Bollegala et al., 2016), and knowledge ba-
ses in (Bollegala et al., 2013; Franco-Salvador et al.,
2015). They are generally based on dense bag-of-
words representation and often require heavy para-
meter tuning. Despite their good performance with
small-scale data (e.g. hundreds or few thousands in-
stances), standard transfer learning approaches do not
scale well with the number of features and are not the
best choice with large-scale data.
The advent of deep learning has brought a more
expressive way to encode text, named distributed re-
presentation (aka word vectors), alternative to bag-of-
words. Bag-of-words loses the ordering of words and
ignores their semantics. Distributed representation
solves these problems along with the curse of dimen-
sionality, providing a low-dimensional representation
(i.e. 300 features are often enough) wherein words
are not mutually exclusive and feature configurations
correspond to the variation seen in the observed data.
The two main model families for learning word vec-
tors are: global factorization methods, such as latent
semantic analysis (LSA) by (Deerwester et al., 1990),
and local context window methods, such as the skip-
gram and the continuous bag-of-words model by (Mi-
kolov et al., 2013), paragraph vector by (Le and Mi-
kolov, 2014), and others proposed by (Mnih and Ka-
vukcuoglu, 2013; Levy and Goldberg, 2014). Met-
hods from the former family leverage statistical in-
formation but perform bad on the word analogy task,
whereas those from the latter family are better on the
analogy task but inadequately utilise the statistics of
corpus since they train on separate local context win-
dows instead of on global co-occurrence counts.
Other than choosing the best text encoding, anot-
her aspect that affects sentiment analysis tasks as sen-
timent classification is how to deal with sequential
inputs. This problem impacts on text comprehen-
sion and allows the detection of sentiment inversi-
ons in phrases or sentences. Recurrent nets are of-
ten the best choice for tasks that involve sequential
inputs. They process an input sequence one element
at a time, maintaining a state vector in their hidden
units that implicitly contains information about the
history of all past elements of the sequence. Recur-
rent nets are very powerful, but training them is pro-
blematic because the backpropagated gradients either
explode or vanish over many time steps, as shown by
(Bengio et al., 1994). This makes recurrent neural
network unable to learn long dependencies in text.
The problem was solved by means of Long Short-
Term Memory Network (LSTM) by (Hochreiter and
Schmidhuber, 1997), which introduced memory cells
to store, load and forget relevant information. Re-
cently, new memory-based neural network schemas
have been proposed that achieved the state-of-the-art
in many tasks, including machine translation, graph
tasks (e.g. graph traversal, shortest path, etc.), and
question answering tasks. The rationale is to memo-
rise essential information and use it to handle sequen-
tial events and perform complex reasoning on top of
them. Sentiment analysis and classification typically
require complicated relationships to be inferred, such
as the detection of polarity shift and sarcasm. Furt-
hermore, transitive reasoning over multiple sentences
is sometimes needed to correctly identify the opinion
holder, the target, or the sentiment itself.
The contribution of this work is to investigate
with massive experiments to what extent two no-
vel memory-based deep neural network architectures
(MemDNN) perform in cross-domain and in-domain
sentiment classification, which are Gated Recurrent
Unit (GRU) by (Cho et al., 2014) and Differentia-
ble Neural Computer (DNC) by (Graves et al., 2016).
We have also combined the two MemDNN with the
use of Global Vectors (GloVe) proposed by (Pen-
nington et al., 2014) in order to allow them to le-
arn from distributed word representation, now a de
facto standard representation in deep learning. As
far as we know, only GRU has been recently ap-
plied by (Dai et al., 2017) to a cross-domain sen-
timent classification in combination with word em-
beddings for Chinese corpora. GloVe combines the
advantages of the other two major model families
in literature for learning word vectors. The unsu-
pervised information extracted by means of GloVe
model is an important first step to align heterogene-
ous domains. Binary and fine-grained (i.e. multi-
class) sentiment classifiers has been constructed for
both MemDNN architectures. Two benchmark data-
sets have been used for the experiments: Amazon Re-
views dataset
1
for document sentiment classification,
1
http://jmcauley.ucsd.edu/data/amazon/
KDIR 2018 - 10th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
128

and Stanford Sentiment Treebank, introduced by (So-
cher et al., 2013) for single-sentence sentiment clas-
sification. In-domain and cross-domain document-
level experiments have been done to assess the vari-
ation in performance by the amount of labelled data
available for training and validating the model. Re-
sults have been compared with those in (Domeniconi
et al., 2017), where we developed solutions based on
both paragraph vectors, a different text representa-
tion method, and other machine learning algorithms.
In the former paper, Paragraph Vector by (Le and
Mikolov, 2014), despite no explicit transfer learning
capability, has been shown to achieve cross-domain
accuracy equivalent to a Markov Chain method de-
veloped ad-hoc for cross-domain sentiment classifi-
cation in (Domeniconi et al., 2015b). In the latter
paper, the same Markov Chain approach has been
outperformed by GRU with random feature weig-
hts initialisation when large-scale labelled data are
available for training and validating the model. To
enhance the capability of the MemDNN sentiment
classifiers in cross-domain tasks, fine-tuning is per-
formed on a small set of labelled target instances.
Fine-tuning, along with GloVe word representation
and the ability of MemDNN in modelling relevant
sequential information, aid the inter-domain align-
ment and bring to outstanding cross-domain docu-
ment classification results. The MemDNN based clas-
sifiers have also been employed on very large data sets
(e.g. million instances), assessing their document-
level performance in an in-domain configuration. Bi-
nary and fine-grained experiments have been carried
out. The outcome has been compared with several
variants of Character-level Convolutional Neural Net-
works (CharCNN) proposed by (Zhang et al., 2015a).
DNC based classifier outperforms the state-of-the-
art in both binary and fine-grained configurations,
whereas GRU with GloVe feature weights initialisa-
tion achieves comparable performance with previous
techniques. The experimented MemDNN methods
can be applied to any text, whatever its length and
structure. For this reason, single-sentence sentiment
classification has also been performed, using Stan-
ford Sentiment Treebank as the benchmark dataset.
The accuracy of MemDNN techniques is comparable
with state-of-the-art methods in both binary and fine-
grained settings.
2 RELATED WORK
This work encompasses many research threads, inclu-
ding sentiment classification, cross-domain and trans-
fer learning, and deep learning. Relevant research ad-
vances are reviewed in this Section, and other met-
hods are mentioned throughout the paper.
2.1 Sentiment Classification
Sentiment classification consists in labelling a plain
text based on its polarity (i.e. sentiment orientation).
This task is much more difficult than text classifica-
tion by topic, because some form of discourse analy-
sis is necessary. (Pang et al., 2002) pointed out that
the phenomenon of thwarted expectations narrative is
common in documents, where an opinion holder sets
up a deliberate contrast to earlier discussion. For in-
stance, ”This film should be brilliant. It sounds like a
great plot, the actors are first grade, and the suppor-
ting cast is good as well, and Stallone is attempting
to deliver a good performance. However, it can’t hold
up”. (Turney, 2002) made a similar point, stating that
for reviews the whole is not necessarily the sum of the
parts. This is pretty obvious if we observe the previ-
ous example. In such a case, humans could easily un-
derstand the overall polarity, but it is much less easy
for a machine, unless it is able to perform discourse
analysis and to detect the polarity shift.
To cope with the complexity of sentiment classi-
fication, several methods have been attempted. (Tan
et al., 2008) and (Qiu et al., 2009) employed a dictio-
nary containing commonly used words in expressing
sentiment to label a portion of informative examples
from a given domain, in order to reduce the labelling
effort and to use the labelled documents as a training
set for a supervised classifier. (Melville et al., 2009)
exploited lexical information about associations bet-
ween words and classes, and refined them for specific
domains by means of training examples to enhance
accuracy. Other works by (Deng et al., 2014; Wu and
Gu, 2014; Domeniconi et al., 2016) proposed term
weighting schemes to foster sentiment classification.
Cross-domain comes into play when the target
domain lacks (or has few) labelled data for training a
classifier with supervision. Transfer learning techni-
ques are generally required to bridge the semantic gap
due to language heterogeneity across domains. Two
transfer learning modes have been identified by (Pan
and Yang, 2010), namely, instance transfer and fea-
ture representation transfer. In order to bridge the
inter-domain gap, the former adapts source instances
to the target domain, whereas the latter maps source
and target features into a different space. (Aue and
Gamon, 2005) made some attempts to customize a
classifier to a new target domain: training on a mix-
ture of labelled data from other domains where such
data is available, possibly considering just the features
observed in target domain; using multiple classifiers
Cross-domain & In-domain Sentiment Analysis with Memory-based Deep Neural Networks
129

trained on labelled data from diverse domains; inclu-
ding a small amount of labelled data from the target.
(Blitzer et al., 2007) discovered a domain similarity
measure that fosters domain adaptation. (Pan et al.,
2010) introduced a spectral feature alignment techni-
que, where domain independent terms helps aligning
domain specific terms into the same clusters. These
clusters form a latent space that improves the clas-
sification of the target domain. Apart from this, ot-
her algorithms have been proposed in (Zhang et al.,
2015b; Domeniconi et al., 2015b; Domeniconi et al.,
2015a) to transfer the polarity of features from the
source domain to the target domain by using dom-
ain independent features as a bridge. (He et al., 2011)
modified the topic-word Dirichlet priors and exten-
ded the joint sentiment-topic model by adding prior
words sentiment. Polarity-bearing topics have been
used to perform feature and document expansion so
as to align domains. (Bollegala et al., 2013) sugge-
sted the adoption of a thesaurus containing labelled
data from the source domain and unlabelled data from
both source and target domains. (Bollegala et al.,
2016) modelled cross-domain sentiment classification
as embedding learning, and discovered that a good
objective function should capture geometric proper-
ties in the unlabelled documents of both source and
target domains. These unsupervised properties are
even more important than considering common featu-
res that occur in both domains and than setting label
constraints to the source domain documents.
2.2 Deep Learning
The advent of deep learning has dramatically impro-
ved the state-of-the-art in several research areas, such
as speech processing and recognition, visual object
detection, video, audio, and natural language proces-
sing, and many other domains like drug discovery and
genomics, as pointed out by (LeCun et al., 2015). The
first issue to face when analysing a plain text is how to
deal with sequential data. This problem is even more
essential to detect sentiment orientation, because of
the presence of sarcasm, negations, and the phenome-
non of thwarted expectations narrative. Bag-of-words
text representation, where the presence (or the fre-
quency) of terms into documents is encoded in a term-
document matrix, is intrinsically unable to handle se-
quential inputs. Word ordering is lost and word se-
mantics is ignored, since context is not taken into ac-
count. Another big issue of the bag-of-words model is
dimensionality, because each term is a feature of the
model, resulting in very sparse term-document matri-
ces. Feature selection techniques attenuate the pro-
blem and let data be processed, but relevant informa-
tion can be lost during this process.
Alternative to the bag-of-words model are distri-
buted text representations. Words are mapped into
low-dimensional vector spaces, where features, cal-
led word vectors, capture most of the variation obser-
ved in data. A feature in the newer space incorporates
the characteristics of several features in the original
space. (Mikolov et al., 2013) introduced the conti-
nuous bag-of-words (CBOW) model, a local context
window method derived from the neural network lan-
guage model by (Bengio et al., 2003). In CBOW, a
projection layer is shared among words so that their
vectors get projected (e.g. averaged) into the same
position. The model is trained by building a log-
linear classifier with k future and k history words as
input, where the training criterion is to correctly pre-
dict the current word. In the same work, the skip-
gram model is also proposed, where the current word
is used as input to a log-linear classifier with continu-
ous projection layer to predict words within a certain
range before and after the current word itself. Follo-
wing the same idea of word vectors, (Le and Mikolov,
2014) proposed an approach to learn paragraph vec-
tors. Every paragraph vector is mapped into a unique
vector, then averaged or concatenated to word vec-
tors to predict the next word in a given window size
(i.e. context). In spite of capturing semantic and syn-
tactic regularities, local context window methods for
distributed word representation typically fail in mo-
delling global statistics and properties. (Pennington
et al., 2014) advanced a global log-bilinear regression
model to solve this lack. Their GloVe model utili-
ses the benefits of count-based methods like LSA by
(Deerwester et al., 1990), while simultaneously cap-
turing the meaningful linear substructures prevalent in
local context window methods.
Along with the distributed word representation
models, several deep learning architectures have been
proposed that brought to a dramatic improvement in
sentiment classification. (Dos Santos and Gatti, 2014)
proposed a deep convolutional neural network that
jointly uses character-level, word-level and sentence-
level representations to perform sentiment analysis of
short texts. (Socher et al., 2013) introduced Recur-
sive Neural Tensor Networks (RecNT N) for single-
sentence sentiment classification. Its recursive struc-
ture makes RecNT N able to capture polarity shifts in
sentences. The experiments have been carried out
on Stanford Sentiment Treebank, which became a
benchmark for single-sentence sentiment classifica-
tion. It turned out that RecNT N improves the state-
of-the-art in both binary and fine-grained configura-
tions. RecNT N has been outperformed by the Dy-
namic Memory Network (DMN) by (Kumar et al.,
KDIR 2018 - 10th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
130

2016), which naturally captures position and tempo-
rality by processing input sequences and questions,
forming episodic memories, and generating relevant
answers. The memory and input modules of the ori-
ginal technique have been improved later by (Xiong
et al., 2016). (Tang et al., 2015) introduced Gated Re-
current Neural Networks to learn vector-based docu-
ment representation, showing that the underlying mo-
del outperforms the standard Recurrent Neural Net-
works in document modelling for sentiment classifi-
cation. (Zhang and LeCun, 2015) applied temporal
convolutional networks to large-scale data sets, sho-
wing that they can perform well without the kno-
wledge of words or any other syntactic or semantic
structures.
Despite the success of deep nets, few work has
been done on transfer learning and cross-domain sen-
timent classification so far. The Stacked Denoising
Autoencoder, introduced in (Vincent et al., 2010),
was used by (Glorot et al., 2011) to extract domain-
independent features without supervision that act as
a bridge between heterogeneous domains. In (Do-
meniconi et al., 2017), we showed that labelled data
from multiple domains encoded by means of para-
graph vectors help transfer learning and cross-domain
sentiment classification.
3 DEEP LEARNING ADVANCES
This section describes the main features of the deep
learning advances combined in this work to break
through cross-domain sentiment classification.
3.1 Gated Recurrent Unit
Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU), proposed by (Cho et al.,
2014), is an evolution of Long Short-Term Memory
(LST M), a neural network architecture provided with
a memory mechanism that allows storing and retai-
ning information through long time sequences. GRU
adds a mechanism that makes each recurrent unit
adaptively able to capture dependencies of different
time scales. While LST M is composed of three gates
(i.e. input, output, and forget), GRU only has two ga-
tes, such as update and reset (figure 1). The update
gate rules the unit activation, by deciding how much
information will be moved from the previous hidden
state to the current one. Any information in the hid-
den state that becomes irrelevant later on is dropped
via the reset gate. As each hidden unit has separate
reset and update gates, it will learn to capture depen-
dencies over different time scales.
Figure 1: A schematic representation of GRU.
GRU with randomly initialised feature weights
has shown promising results in cross-domain sen-
timent classification with large-scale data. When
enough training instances are available, the align-
ment of heterogeneous domains is achieved thanks to
memory units, which are automatically able to cap-
ture and preserve domain-independent information,
despite no explicit transfer learning mechanism.
3.2 Differentiable Neural Computer
Differentiable Neural Computer (DNC), introduced
by (Graves et al., 2016) as the evolution of Neural Tu-
ring Machines (NT M) by (Graves et al., 2014), is one
of the most innovative MemDNN techniques. Dif-
ferently from previous MemDNN architectures (e.g.
GRU), where the memory mechanism was internal
to the network, DNC uses an external memory to re-
present and manipulate complex data structures. The
neural network can selectively address the external
memory, both to read from and write to it, allowing
iterative modification of memory content. This makes
DNC able to learn complex tasks from data, such as
finding the shortest path or inferring the missing links
in graphs, and answering synthetic questions desig-
ned to emulate reasoning in natural language. Figure
2 shows the basic behaviour of a DNC. It uses diffe-
rentiable attention mechanisms to define weightings,
which represent the degree to which each memory lo-
cation is involved in a read or write operation. The
functional units that determine and apply the weig-
htings are called read and write heads.
Figure 2: A schematic representation of DNC.
Cross-domain & In-domain Sentiment Analysis with Memory-based Deep Neural Networks
131

In the original work, DNC has only been applied
to small-scale tasks. However, (Graves et al., 2016)
pointed out that DNC should be able to seamlessly
acquire knowledge and take advantage of exposure
to large data sources. This consideration, along with
the ability of memory mechanisms to capture inter-
domain relationships, makes DNC suitable for cross-
domain sentiment classification.
3.3 GloVe Word Representation
Global Vectors (GloVe) is a log-bilinear regression
model that have been proposed by (Pennington et al.,
2014) to learn distributed word representation. Alike
other methods for learning vector space representa-
tion of words, GloVe is able to capture fine-grained
syntactic and semantic regularities in an unsupervi-
sed fashion, just using vector arithmetic, and solves
the data sparsity problem of dense bag-of-words mo-
dels. GloVe combines the advantages of global ma-
trix factorization and local context window methods:
as the former, it efficiently leverages statistical infor-
mation by training only on the nonzero elements in
a word-word co-occurrence matrix; as the latter, it
achieves great performance on word analogy, simi-
larity and named entity recognition tasks. The unsu-
pervised information extracted by means of distribu-
ted word representation fosters the alignment of he-
terogeneous domains ; for this reason, we argue that
GloVe can be promising to initialise the feature weig-
hts that MemDNN architectures will use.
4 DATASETS
In this Section the benchmark datasets for document-
level and single-sentence classification respectively
will be introduced. Amazon Reviews corpus
2
has
been used for the former task, whereas Stanford Sen-
timent Treebank
3
for the latter. Both are widely used
benchmarks for sentiment analysis.
4.1 Amazon Reviews Corpus
Amazon Reviews corpus is a collection of Amazon
reviews about different domains. Each domain con-
tains a list of English reviews, which include both the
plain text and a score from 1 (i.e. very negative) to
5 (i.e. very positive). In binary sentiment classifi-
cation, reviews with rating > 3 have been conside-
red as positive, reviews with rating < 3 as negative,
2
http://jmcauley.ucsd.edu/data/amazon/
3
https://nlp.stanford.edu/sentiment/code.html
while reviews with rating = 3 have been discarded as
they are ambiguous and could express a neutral senti-
ment orientation. On the other hand, all the 5 classes
have been taken into account in the fine-grained set-
ting. Data from 4 domains have been used for the
experiments: Books (B), Movies (M), Electronics (E)
and Clothing-Shoes-Jewelry (J) have been chosen for
a matter of comparison with the state of the art.
4.2 Stanford Sentiment Treebank
Stanford Sentiment Treebank (SST) is a dataset of la-
belled sentences that was introduced by (Socher et al.,
2013). SST is built on a corpus of movie review ex-
cerpts, composed of 11,855 sentences, half of which
are positive and half negative. The sentences are par-
sed with the Stanford parser by (Klein and Manning,
2003) into 215,154 syntactically plausible phrases.
Each phrase is annotated by 3 human experts into 5
possible categories, namely negative, somewhat ne-
gative, neutral, somewhat positive and positive. Simi-
larly to Amazon Reviews corpus, neutral phrases are
discarded in binary classification.
5 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
This Section illustrates the experiments that have
been performed. The first assesses to what extent
the amount of labelled data available for training
the model affects its performance in both in-domain
and cross-domain document sentiment classification.
Then the impact of fine-tuning on cross-domain is
evaluated, with appropriate comparison with the state
of the art. In the third experiment, in-domain docu-
ment sentiment classification is performed on large-
scale data, in order to evaluate the scalability of
MemDNN techniques and their potential feasibility
in big data scenarios. The last trial assesses whet-
her MemDNNs can be successfully applied to single-
sentence sentiment classification.
Accuracy of the classifier (i.e. the percentage of
correctly classified instances) has been measured for
each single test, averaging results on 10 randomly
chosen training-test partitions to reduce the variance,
(i.e. the sensitivity to small variations in the training
set), but always keeping the classes balanced.
5.1 The Impact of Training Data
The first experiment checks to what extent the amount
of labelled training data affects MemDNN perfor-
mance. Na
¨
ıve Bayes (NB), Markov Chain (MC), Pa-
ragraph Vector (PV ) and Gated Recurrent Unit with
KDIR 2018 - 10th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
132

randomly initialised feature weights (GRU
rand
) have
already been taken into account in (Domeniconi et al.,
2017). For a matter of comparison, source-target par-
titions of three different orders of magnitude have
been tested, preserving 80%-20% as the source-target
ratio, and balancing positive and negative examples.
The small-scale data set has 1,600 labelled instances
as the training set and 400 unlabelled instances as the
test set; the medium-scale 16,000 and 4,000; and the
large-scale 80,000 and 20,000 respectively.
Figure 3 shows the in-domain performance of the
various techniques, averaged on the 4 domains con-
sidered (detailed results have not been reported due
to space reason). As pointed out by (Domeniconi
et al., 2017), deep learning approaches usually do
not perform well when few training data are avai-
lable. That is the reason why MC outperforms the
proposed MemDNN techniques with small-scale data.
However, GRU and DNC outperform the other ap-
proaches. GRU with feature weights initialised by
GloVe achieves a higher accuracy with respect to
GRU
rand
whose features have been initialised with
random weights. Increasing the amount of labelled
training data, DNC obtains astonishing performance.
Its accuracy is 90.08% with medium-scale data, mea-
ning that 16,000 training examples are enough for the
memory mechanism of DNC to capture relevant in-
formation. The same does not hold for GRU, whose
performance does not increase considering medium-
scale data. However, in opposition to their trial, GRU
already achieves comparable performance with MC in
the medium-sized data set. Considering large-scale
data, the accuracy of DNC continues to grow, rea-
ching 91.24%. This outcome makes it interesting to
evaluate to what extent DNC performance can incre-
ase. For this purpose, an in-domain test with a huge
dataset will be shown later in 5.3. Finally, it may be
noted that GRU performance improves as well. A re-
asonable explanation is that the memory mechanism
of GRU is automatically able to decide which infor-
mation is relevant to classification, if trained with a
large amount of data.
The cross-domain evaluation of the same techni-
ques can be seen in figure 4. The plot displays accu-
racy averaged on each of the 12 source-target confi-
gurations of the 4 domains considered. The first out-
come that catches the eye is that DNC dramatically
outperforms all the other techniques regardless of the
dataset size. It is remarkable that DNC exceeds by
more than 9% the accuracy of MC, which is a non-
deep method that was specifically developed by (Do-
meniconi et al., 2015b) to accomplish both transfer le-
arning and sentiment classification. The reason of this
outcome resides in several combined factors that lead
Small-scale Medium-scale Large-scale
65
70
75
80
85
90
95
Dataset size
Accuracy (%)
NB P V MC
GRU
rand
GRU DN C
Figure 3: Average in-domain accuracy over the 4 domains.
Small-scale Medium-scale Large-scale
60
65
70
75
80
85
90
Dataset size
Accuracy (%)
NB P V MC
GRU
rand
GRU DN C
Figure 4: Average cross-domain accuracy over the 12
source-target combinations of the 4 domains.
to semantic comprehension of text. The first factor is
the usage of distributed representation to encode text.
In particular, we used GloVe for word representation
of both GRU and DNC. As pointed out by (Penning-
ton et al., 2014), GloVe combines the advantages of
the other two model families in literature for learning
word vectors, namely factorization methods and lo-
cal context window methods. This means that GloVe
also inherits the benefits of PV , which is able to dis-
cover hidden relationships between semantically si-
milar words. The unsupervised information extracted
by GloVe aids the alignment of heterogeneous dom-
ains. The second factor is the memory mechanism
of DNC. Once enough training data are available,
MemDNN architectures are automatically able to cap-
Cross-domain & In-domain Sentiment Analysis with Memory-based Deep Neural Networks
133
ture domain-independent information and preserve it
in memory. The third factor are deep neural networks.
In particular, DNC is one of the most powerful mecha-
nisms to emulate reasoning and inference problems in
natural language. The combined effect of these three
factors led to a dramatic improvement of the state of
the art in cross-domain sentiment classification. DNC
turns out to be 9% more accurate than MC. Compa-
ring in-domain and cross-domain results, it could be
noted that the accuracy of DNC is perfectly aligned
by looking at small-scale data, whereas cross-domain
performance is slightly worse by increasing the da-
taset size. Apart from the astonishing performance of
DNC, careful readers can note the behaviours of GRU
and GRU
rand
respectively, which probably are even
more interesting. As expected, GloVe initialisation
of feature weights leads to a substantial increasing
of accuracy with small-scale data, which jumps from
66.30% of GRU
rand
to 74.14% of GRU. Comparing
in-domain and cross-domain experiments, we can see
the combined effect of GloVe distributed word repre-
sentation and GRU memory mechanism. The former
plays a key role to align heterogeneous domains when
few labelled data are available as the training set. The
latter is automatically able to extract relevant inter-
domain concepts as the amount of labelled training
data increases.
5.2 Fine-tuning of MemDNNs
The second experiment aims to assess whether fine-
tuning affects MemDNN performance. Fine-tuning
is the practice of using a labelled sample of target
instances to refine a model previously learnt on the
source domain. The sample is usually small (e.g.
hundreds instances) for two main reasons. On the one
hand, if a large set of labelled instances was available,
it would be advisable to learn an in-domain sentiment
classifier rather than a cross-domain one. On the other
hand, if a large set of labelled instances was not avai-
lable, the only alternative would be to let a team of hu-
man experts pre-classify some instances. Manual ca-
tegorisation becomes infeasible when many instances
are required to be labelled. Therefore, fine-tuning on
a small sample of labelled target instances is generally
a good trade-off between its cost and the expected
improvement of performance. To further investigate
the performance, we have experimented fine-tuning
by using 250 and 500 examples respectively.
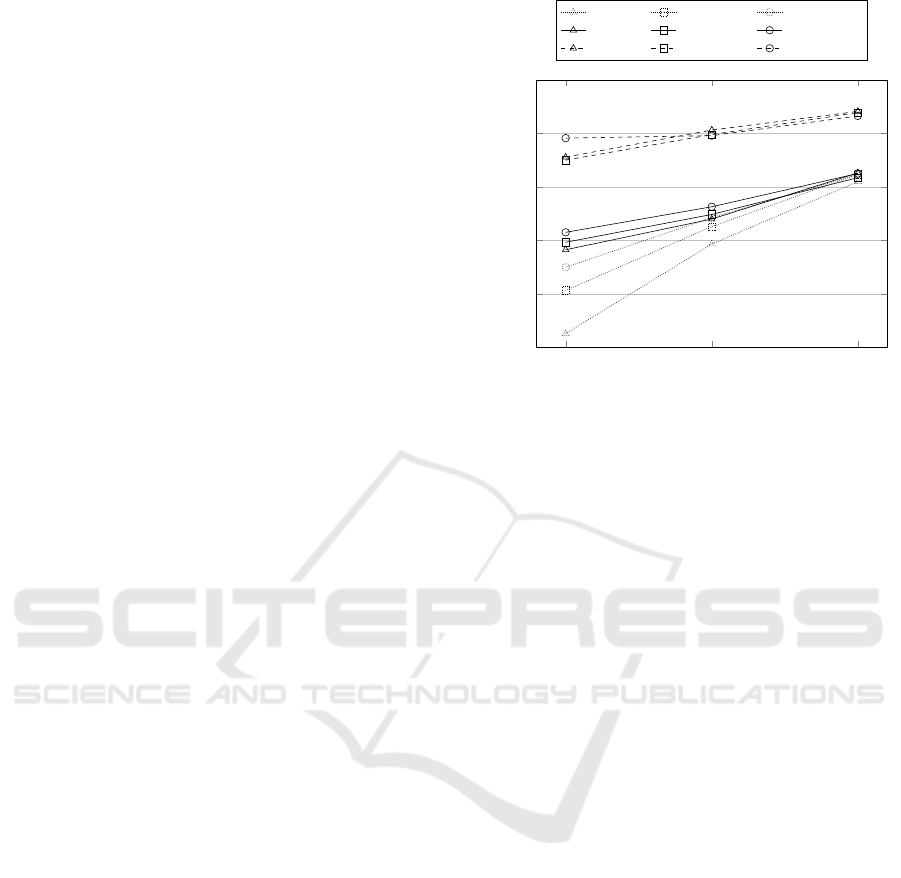
Figure 5 shows the effect of fine-tuning on
MemDNN architectures. GRU takes a slight advan-
tage of fine-tuning. With reference to small-scale
data, accuracy increases from 74.14% to 74.84%
using 250 target instances to 75.77% using 500 tar-
Small-scale Medium-scale Large-scale
65
70
75
80
85
90
Dataset size
Accuracy (%)
GRU
rand
GRU
rand
250
GRU
rand
500
GRU GRU
250
GRU
500
DN C DN C
250
DN C
500
Figure 5: Average cross-domain with fine-tuning accuracy
over the 12 source-target combinations of the 4 domains.
The subscripts 250 and 500 represent the number of labelled
target instances utilised for fine-funing.
get instances. It deserves to be noted that GRU per-
formance is more affected by GloVe feature weights
initialisation than by fine-tuning. In fact, GRU wit-
hout fine-tuning outperforms GRU
rand
500
. As dataset
size increases, the contribution of fine-tuning diminis-
hes, until eventually vanishing with large-scale data.
A different behaviour is observed for DNC. Fine-
tuning only impacts on accuracy when performed on
500 target instances with reference to the small-scale
dataset. It is quite obvious that, when few training
data are available, even a small sample can conside-
rably affect performance. GRU is a clear proof of this
behaviour. However, DNC
250
does not lead to a per-
formance improvement. The reason is that DNC is
a very robust technique, almost unaffected by noise.
The attention mechanism to address the external me-
mory makes DNC less sensitive to noise than GRU,
whose memory units are internal to the network. As
a consequence, DNC is less prone than GRU to al-
tering memory content. In other words, it is unli-
kely that DNC stores irrelevant information in me-
mory. 250 target instances are not relevant enough
for DNC and are considered as noise by the network.
The same considerations apply to experiments with
medium-scale and large-scale data, where both 250
and 500 target instances do not affect performance.
5.3 Large-scale Classification
The third experimentation is an in-domain sentiment
classification task with a very large data set. This
trial let us assess to what extent MemDNN archi-
tectures with GloVe feature weights initialisation are
KDIR 2018 - 10th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
134

suitable as sentiment classifiers in big data scena-
rios. Moreover, MemDNN architectures can be com-
bined with many other sentiment classification techni-
ques, in particular several variants of Character-level
Convolutional Neural networks (CharCNN), propo-
sed by (Zhang and LeCun, 2015) and empirically ex-
plored in (Zhang et al., 2015a). For result compa-
rison purposes, two very large data sets have been
constructed. The former deals with binary in-domain
sentiment classification, where the goal is to distin-
guish positive from negative instances. The latter
aims to predict the full score assigned to instances
(i.e. from 1 to 5). So it is a fine-grained in-domain
sentiment classification task. The binary dataset con-
tains 1, 800, 000 training samples and 200, 000 testing
samples for each polarity sentiment. The fine-grained
contains 600,000 training samples and 130, 000 tes-
ting samples for each of the five classes. In both da-
tasets, samples have been taken in equal proportion
from the 4 domains considered. Differently from the
previous experiments, review title has also been con-
sidered, together with review content.
Table 1: In-domain accuracy on very large datasets con-
structed from Amazon Reviews corpus. Binary and fine-
grained refer to 2-class and 5-class in-domain sentiment
classification respectively. CharCNN variants are prefixed
with Lg. or Sm..
Model Binary Fine-grained
BoW 90.40% 54.64%
BoW T f -Id f 91.00% 55.26%
n-grams 92.02% 54.27%
n-grams T f -Id f 91.54% 52.44%
Bag-o f -means 81.61% 44.13%
LST M 93.90% 59.43%
Lg. w2v Conv 94.12% 55.60%
Sm. w2v Conv 94.00% 57.41%
Lg. w2v Conv. T h. 94.20% 56.25%
Sm. w2v Conv. T h. 94.37% 57.50%
Lg. Lk. Conv 94.16% 54.05%
Sm. Lk. Conv 94.15% 56.34%
Lg. Lk. Conv. T h. 94.48% 57.61%
Sm. Lk. Conv. T h. 94.49% 56.81%
Lg. Full. Conv 94.22% 59.11%
Sm. Full. Conv 94.22% 59.12%
Lg. Full. Conv. T h.
94.49% 59.46%
Sm. Full. Conv. T h. 94.34% 59.47%
Lg. Conv 94.49% 58.69%
Sm. Conv 94.50% 59.47%
Lg. Conv. T h. 95.07% 59.55%
Sm. Conv. T h. 94.33% 59.57%
GRU 94.07% 59.55%
DNC 95.51% 61.45%
Apart from the several variants of CharCNN, re-
sults have also been compared with other methods, in-
cluding Long Short-Term Memory networks (LST M),
Bag-of-means by (Lev et al., 2015) and some Bag-
of-words (BoW ) based configurations. Careful rea-
ders can find further details on these methods along
with their parameters in (Zhang et al., 2015a). Table
1 shows the accuracy of MemDNN methods and the
state-of-the-art techniques. GRU achieves compara-
ble performance with the other methods. In particu-
lar, it is slightly more accurate than LST M. This is
not surprising, since GRU is an evolution of LST M,
but both have a built-in memory mechanism. On the
other hand, DNC outcome is astonishing. It outper-
forms all the other techniques with reference to both
binary and fine-grained datasets. Fine-grained accu-
racy is almost 2% higher than the previous methods.
This difference in accuracy is significant in a multi-
nomial classification problem, where predicting the
correct class is challenging. To the best of our know-
ledge, it is the first time that a method achieves accu-
racy higher than 60% on Amazon Reviews corpus in
fine-grained sentiment classification.
5.4 Single-sentence Classification
While the previous experiments deal with docu-
ment sentiment classification, the last one focuses on
single-sentence sentiment classification. The bench-
mark dataset used is Stanford Sentiment Treebank
(SST). According to the work by (Socher et al., 2013),
8,544 sentences are used as the training set, 1, 101 as
the validation set, and 2, 210 as the test set. Plenty of
techniques have been applied to SST in the last few
years. (Socher et al., 2013) presented Recursive Neu-
ral Tensor Networks (RecNT N) in the same work they
introduced SST, and compared their algorithm on SST
with Na
¨
ıve Bayes with unigram features (NB), Na
¨
ıve
Bayes with unigram and bigram features (BiNB),
Support Vector Machine with unigram and bigram
features (SV M), Recursive Neural Networks (RNN)
by (Socher et al., 2011) and Matrix-Vector RNN
(MV -RNN) by (Socher et al., 2012). (Kalchbrenner
et al., 2014) proposed Dynamic Convolutional Neu-
ral Network (DCNN), comparing its performance on
SST with Max Time-Delay Neural Networks (Max-
T DNN) by (Collobert and Weston, 2008), and a Neu-
ral Bag-of-Words (NBoW ) model. (Dos Santos and
Gatti, 2014) introduced Character to Sentence Con-
volutional Neural Network (CharSCNN) and applied
it to SST. A variant of CharSCNN has been trained
by using word embeddings only (SCNN). Other two
variants of the previous, referred as CharSCNN ph.
and SCNN ph., have been trained by exploiting also
phrases representation in addition to sentence repre-
sentation. (Kim, 2014) experimented some variants of
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN-rand, CNN-
static, CNN-non-static, CNN-multichannel) on SST.
(Le and Mikolov, 2014) applied to SST logistic re-
Cross-domain & In-domain Sentiment Analysis with Memory-based Deep Neural Networks
135

gression on top of their Paragraph Vector PV for dis-
tributed word representation. Finally, Multiplicative
Recurrent Neural Network (DRNN) by (Irsoy and
Cardie, 2014), Constituency Tree-LSTM (CT -LST M)
by (Tai et al., 2015), and Dynamic Memory Network
(DMN) by (Kumar et al., 2016) have also been app-
lied to SST.
Table 2: Accuracy achieved by the compared methods on
SST. Binary and fine-grained refer to 2-class and 5-class in-
domain sentiment classification respectively.
Model Binary Fine-grained
NB 81.80% 41.00%
BiNB 83.10% 41.90%
SV M 79.40% 40.70%
RecNT N 85.40% 45.70%
Max-T DNN 77.10% 37.40%
NBoW 80.50% 42.40%
DCNN 86.80% 48.50%
RNN 82.40% 43.20%
MV -RNN 82.90% 44.40%
SCNN 82.00% 43.50%
CharSCNN 82.30% 43.50%
SCNN ph. 85.50% 48.30%
CharSCNN ph. 85.70% 48.30%
CNN-rand 82.70% 45.00%
CNN-static 86.80% 45.50%
CNN-non-static 87.20% 48.00%
CNN-multichannel 88.10% 47.40%
PV 87.80% 48.70%
DRNN 86.60% 49.80%
CT -LST M 88.00% 51.00%
DMN 88.60% 52.10%
GRU 84.13% 45.89%
DNC 85.22% 46.78%
Table 2 shows the comparison between the
MemDNN architectures and the mentioned methods.
GRU and DNC achieve comparable performance in
both binary and fine-grained configurations. The
accuracy of DNC is just about 1% higher than the
accuracy of GRU. They perform similarly to most
of the other techniques, but are not definitely the best
methods for single-sentence sentiment classification.
This is probably due to the absence of a specific me-
chanism to take sentence syntax into account, and
to the small amount of training data, which is an
obstacle to GRU and DNC performance. Just look
at the in-domain experiment on Amazon Reviews 3,
where they have been outperformed by Markov Chain
with small-scale data. Somebody might argue that
SST have 8, 544 instances, but we should not forget
that they are single-sentences, not whole and usually
longer reviews (i.e. documents) as in the Amazon
dataset. The best algorithm turns out to be DMN,
which performs better than all the other techniques
in both binary and fine-grained configurations. This
is not surprising, since DMN includes a memory me-
chanism to store and preserve relevant information
through time and has also been proved to work well
with single-sentences in (Kumar et al., 2016).
6 CONCLUSIONS
This work has investigated with massive experiments
to what extent novel memory-based neural networks
(MemDNN) perform in cross-domain and in-domain
sentiment classifications. We have combined the ad-
vances of MemDNN together with word embeddings,
a de facto standard in deep learning, along with fine-
tuning on target instances to investigate whether they
are able to outperform ad-hoc cross-domain solutions.
Among the deep memory-based methods, we expe-
rimented Differentiable Neural Computer and Gated
Recurrent Unit. The former is one of the most inno-
vative deep learning techniques. Its ability to address
and manage an external memory makes DNC able to
emulate reasoning and inference problems in natural
language. The latter is a different kind of MemDNN,
since its memory mechanism is part of the network
structure. GloVe distributed word representation has
been used in combination with both MemDNN archi-
tectures.
Experiments on Amazon Reviews corpus show
that DNC with GloVe word representation drama-
tically outperforms state-of-the-art techniques for
cross-domain sentiment classification. Transfer le-
arning from the source to the target domain is sup-
ported by distributed word representation with small-
scale datasets, as proved by the comparison between
GRU and GRU
rand
, and by memory mechanisms as
the dataset size increases. MemDNN techniques take
advantage of large-scale data to align heterogene-
ous domains. Fine-tuning on a small sample of tar-
get instances is more useful to GRU than DNC, as
the latter is more robust and less sensitive to noise.
Both techniques have been compared with state-of-
the-art methods on two very large datasets, built on
the same Amazon Reviews corpus, for in-domain do-
cument sentiment classification. DNC with GloVe
feature weights achieves new state-of-the-art perfor-
mance both in binary and fine-grained classification
tasks. Finally, DNC and GRU achieve comparable
performance with many techniques in single-sentence
in-domain sentiment classification on Stanford Senti-
ment Treebank. Small-scale training data and the ab-
sence of a mechanism to deal with sentence syntax are
probably the reasons that prevent DNC from reaching
the state-of-the-art performance.
KDIR 2018 - 10th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
136

REFERENCES
Aue, A. and Gamon, M. (2005). Customizing sentiment
classifiers to new domains: A case study. In Procee-
dings of recent advances in natural language proces-
sing (RANLP), volume 1, pages 2–1.
Bengio, Y., Ducharme, R., Vincent, P., and Jauvin, C.
(2003). A neural probabilistic language model. Jour-
nal of machine learning research, 3(Feb):1137–1155.
Bengio, Y., Simard, P., and Frasconi, P. (1994). Learning
long-term dependencies with gradient descent is diffi-
cult. IEEE transactions on neural networks, 5(2):157–
166.
Blitzer, J., Dredze, M., and Pereira, F. (2007). Biographies,
bollywood, boom-boxes and blenders: Domain adap-
tation for sentiment classification. In Proceedings of
the 45th annual meeting of the association of compu-
tational linguistics, pages 440–447.
Bollegala, D., Mu, T., and Goulermas, J. Y. (2016). Cross-
domain sentiment classification using sentiment sen-
sitive embeddings. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge
and Data Engineering, 28(2):398–410.
Bollegala, D., Weir, D., and Carroll, J. (2013). Cross-
domain sentiment classification using a sentiment sen-
sitive thesaurus. IEEE transactions on knowledge and
data engineering, 25(8):1719–1731.
Cho, K., Van Merri
¨
enboer, B., Gulcehre, C., Bahdanau, D.,
Bougares, F., Schwenk, H., and Bengio, Y. (2014).
Learning phrase representations using rnn encoder-
decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv pre-
print arXiv:1406.1078.
Collobert, R. and Weston, J. (2008). A unified architec-
ture for natural language processing: Deep neural net-
works with multitask learning. In Proceedings of the
25th international conference on Machine learning,
pages 160–167. ACM.
Dai, M., Huang, S., Zhong, J., Yang, C., and Yang,
S. (2017). Influence of noise on transfer learning
in chinese sentiment classification using gru. In
2017 13th International Conference on Natural Com-
putation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery
(ICNC-FSKD), pages 1844–1849. IEEE.
Deerwester, S., Dumais, S. T., Furnas, G. W., Landauer,
T. K., and Harshman, R. (1990). Indexing by latent
semantic analysis. Journal of the American society
for information science, 41(6):391.
Deng, Z.-H., Luo, K.-H., and Yu, H.-L. (2014). A study of
supervised term weighting scheme for sentiment ana-
lysis. Expert Systems with Applications, 41(7):3506–
3513.
Domeniconi, G., Moro, G., Pagliarani, A., and Pasolini,
R. (2015a). Cross-domain sentiment classification via
polarity-driven state transitions in a markov model. In
International Joint Conference on Knowledge Disco-
very, Knowledge Engineering, and Knowledge Mana-
gement, pages 118–138. Springer.
Domeniconi, G., Moro, G., Pagliarani, A., and Pasolini, R.
(2015b). Markov chain based method for in-domain
and cross-domain sentiment classification. In Kno-
wledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Kno-
wledge Management (IC3K), 2015 7th International
Joint Conference on, volume 1, pages 127–137. IEEE.
Domeniconi, G., Moro, G., Pagliarani, A., and Pasolini, R.
(2017). On deep learning in cross-domain sentiment
classification. In Proceedings of the 9th Internatio-
nal Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Kno-
wledge Engineering and Knowledge Management.
Domeniconi, G., Moro, G., Pasolini, R., and Sartori, C.
(2016). A Comparison of Term Weighting Schemes
for Text Classification and Sentiment Analysis with a
Supervised Variant of tf.idf, pages 39–58. Springer In-
ternational Publishing, Cham.
Dos Santos, C. N. and Gatti, M. (2014). Deep convolutional
neural networks for sentiment analysis of short texts.
In COLING, pages 69–78.
Franco-Salvador, M., Cruz, F. L., Troyano, J. A., and Rosso,
P. (2015). Cross-domain polarity classification using
a knowledge-enhanced meta-classifier. Knowledge-
Based Systems, 86:46–56.
Glorot, X., Bordes, A., and Bengio, Y. (2011). Domain
adaptation for large-scale sentiment classification: A
deep learning approach. In Proceedings of the 28th
international conference on machine learning (ICML-
11), pages 513–520.
Graves, A., Wayne, G., and Danihelka, I. (2014). Neural
turing machines. arXiv preprint arXiv:1410.5401.
Graves, A., Wayne, G., Reynolds, M., Harley, T., Da-
nihelka, I., Grabska-Barwi
´
nska, A., Colmenarejo,
S. G., Grefenstette, E., Ramalho, T., Agapiou, J.,
et al. (2016). Hybrid computing using a neural
network with dynamic external memory. Nature,
538(7626):471–476.
He, Y., Lin, C., and Alani, H. (2011). Automatically ex-
tracting polarity-bearing topics for cross-domain sen-
timent classification. In Proceedings of the 49th An-
nual Meeting of the Association for Computational
Linguistics: Human Language Technologies-Volume
1, pages 123–131. Association for Computational Lin-
guistics.
Hochreiter, S. and Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term
memory. Neural computation, 9(8):1735–1780.
Irsoy, O. and Cardie, C. (2014). Modeling compositionality
with multiplicative recurrent neural networks. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1412.6577.
Kalchbrenner, N., Grefenstette, E., and Blunsom, P. (2014).
A convolutional neural network for modelling senten-
ces. arXiv preprint arXiv:1404.2188.
Kim, Y. (2014). Convolutional neural networks for sentence
classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1408.5882.
Klein, D. and Manning, C. D. (2003). Accurate unlexicali-
zed parsing. In Proceedings of the 41st annual meet-
ing of the association for computational linguistics.
Kumar, A., Irsoy, O., Ondruska, P., Iyyer, M., Bradbury, J.,
Gulrajani, I., Zhong, V., Paulus, R., and Socher, R.
(2016). Ask me anything: Dynami memory networks
for natural language processing. In International Con-
ference on Machine Learning, pages 1378–1387.
Le, Q. and Mikolov, T. (2014). Distributed representations
of sentences and documents. In Proceedings of the
Cross-domain & In-domain Sentiment Analysis with Memory-based Deep Neural Networks
137

31st International Conference on Machine Learning
(ICML-14), pages 1188–1196.
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., and Hinton, G. (2015). Deep lear-
ning. Nature, 521(7553):436–444.
Lev, G., Klein, B., and Wolf, L. (2015). In defense of word
embedding for generic text representation. In Inter-
national Conference on Applications of Natural Lan-
guage to Information Systems, pages 35–50. Springer.
Levy, O. and Goldberg, Y. (2014). Linguistic regularities in
sparse and explicit word representations. In Procee-
dings of the eighteenth conference on computational
natural language learning, pages 171–180.
Liu, B. and Zhang, L. (2012). A survey of opinion mining
and sentiment analysis. In Mining text data, pages
415–463. Springer.
Melville, P., Gryc, W., and Lawrence, R. D. (2009). Sen-
timent analysis of blogs by combining lexical know-
ledge with text classification. In Proceedings of the
15th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Kno-
wledge discovery and data mining, pages 1275–1284.
ACM.
Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., and Dean, J. (2013).
Efficient estimation of word representations in vector
space. arXiv preprint arXiv:1301.3781.
Mnih, A. and Kavukcuoglu, K. (2013). Learning word
embeddings efficiently with noise-contrastive estima-
tion. In Advances in neural information processing
systems, pages 2265–2273.
Pan, S. J., Ni, X., Sun, J.-T., Yang, Q., and Chen, Z. (2010).
Cross-domain sentiment classification via spectral fe-
ature alignment. In Proceedings of the 19th internati-
onal conference on World wide web, pages 751–760.
ACM.
Pan, S. J. and Yang, Q. (2010). A survey on transfer le-
arning. IEEE Transactions on knowledge and data
engineering, 22(10):1345–1359.
Pang, B., Lee, L., and Vaithyanathan, S. (2002). Thumbs
up?: sentiment classification using machine learning
techniques. In Proceedings of the ACL-02 con-
ference on Empirical methods in natural language
processing-Volume 10, pages 79–86. Association for
Computational Linguistics.
Pennington, J., Socher, R., and Manning, C. (2014). Glove:
Global vectors for word representation. In Procee-
dings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in
natural language processing (EMNLP), pages 1532–
1543.
Qiu, L., Zhang, W., Hu, C., and Zhao, K. (2009). Selc:
a self-supervised model for sentiment classification.
In Proceedings of the 18th ACM conference on Infor-
mation and knowledge management, pages 929–936.
ACM.
Socher, R., Huval, B., Manning, C. D., and Ng, A. Y.
(2012). Semantic compositionality through recursive
matrix-vector spaces. In Proceedings of the 2012 joint
conference on empirical methods in natural language
processing and computational natural language lear-
ning, pages 1201–1211. Association for Computatio-
nal Linguistics.
Socher, R., Pennington, J., Huang, E. H., Ng, A. Y., and
Manning, C. D. (2011). Semi-supervised recursive au-
toencoders for predicting sentiment distributions. In
Proceedings of the conference on empirical methods
in natural language processing, pages 151–161. As-
sociation for Computational Linguistics.
Socher, R., Perelygin, A., Wu, J., Chuang, J., Manning,
C. D., Ng, A., and Potts, C. (2013). Recursive deep
models for semantic compositionality over a senti-
ment treebank. In Proceedings of the 2013 conference
on empirical methods in natural language processing,
pages 1631–1642.
Tai, K. S., Socher, R., and Manning, C. D. (2015). Im-
proved semantic representations from tree-structured
long short-term memory networks. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1503.00075.
Tan, S., Wang, Y., and Cheng, X. (2008). Combining learn-
based and lexicon-based techniques for sentiment de-
tection without using labeled examples. In Procee-
dings of the 31st annual international ACM SIGIR
conference on Research and development in informa-
tion retrieval, pages 743–744. ACM.
Tang, D., Qin, B., and Liu, T. (2015). Document mo-
deling with gated recurrent neural network for senti-
ment classification. In EMNLP, pages 1422–1432.
Turney, P. D. (2002). Thumbs up or thumbs down?: se-
mantic orientation applied to unsupervised classifica-
tion of reviews. In Proceedings of the 40th annual
meeting on association for computational linguistics,
pages 417–424. Association for Computational Lin-
guistics.
Vincent, P., Larochelle, H., Lajoie, I., Bengio, Y., and
Manzagol, P.-A. (2010). Stacked denoising autoen-
coders: Learning useful representations in a deep net-
work with a local denoising criterion. Journal of Ma-
chine Learning Research, 11(Dec):3371–3408.
Wu, H. and Gu, X. (2014). Reducing over-weighting in
supervised term weighting for sentiment analysis. In
COLING, pages 1322–1330.
Xiong, C., Merity, S., and Socher, R. (2016). Dynamic me-
mory networks for visual and textual question answe-
ring. In International Conference on Machine Lear-
ning, pages 2397–2406.
Zhang, X. and LeCun, Y. (2015). Text understanding from
scratch. arXiv preprint arXiv:1502.01710.
Zhang, X., Zhao, J., and LeCun, Y. (2015a). Character-
level convolutional networks for text classification. In
Advances in neural information processing systems,
pages 649–657.
Zhang, Y., Hu, X., Li, P., Li, L., and Wu, X. (2015b).
Cross-domain sentiment classification-feature diver-
gence, polarity divergence or both? Pattern recog-
nition letters, 65:44–50.
KDIR 2018 - 10th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
138
