
Optimizing Students’ Speaking and Critical Thinking
through Students’ Reflective Practice in Socratic Circle
Speaking
Woro Kusmaryani
1
, Bachrudin Musthafa
2
and Pupung Purnawarman
2
1
Department of English Education, Universitas Borneo Tarakan, Tarakan, Indonesia
2Department of English Education, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Bandung,
Indonesia
Keywords: Speaking Skill, Critical Thinking, Reflective Practice, and Socratic Method
Abstract: We investigated students’ reflective practice after Socratic circle speaking which is purposed to optimize
students’ speaking and critical thinking skill. Critical thinking cannot be separated from speaking skill.
Students’ reflective practice can help the teacher in revising teaching method, materials, classroom
management, etc. This research used descriptive qualitative design which collected documents, observation,
and interview as the data. This research was done in Speaking class at Third semester students of Borneo
University Tarakan. The data was analysed qualitatively. The result shows that students’ reflexive practice
could optimize students’ speaking and critical thinking. Speaking result shows that 23% in Excellent category,
26% in Good category, 38% in Fair category, 13% in Weak category, and 0% in Poor category. Critical
thinking result shows that 13% in Critical Thinking level 4, 36% in Critical Thinking level 3, 38% in Critical
Thinking level 2, 13% in Critical Thinking level 1, and 0% in Critical Thinking level 6 and 5. In interview,
the researcher found that teaching quality and students’ learning improved and they could prepare themselves
related to their speaking skill and critical thinking. There were some obstacles faced such as; time consuming
in analysing students’ reflection, redesigning the lesson plan and material selection.
1 INTRODUCTION
EFL speaking skill is the most difficult and gives
challenges to the students because of its fundamental
aspects in communicating and learning the language
(Alaraj, 2017). (Luoma, 2004) explains the hearth of
foreign language learning is students able to speak
and use it. The students can personalize, make self-
image, know the world’s knowledge, give reasons
and show their thoughts. The students can give their
performance orally about their ability in foreign
language. Developing students’ speaking skill is not
easy and it takes time to work with the speaking
competence. There are many things that the students
need to know such as; English phonology, the use of
vocabularies appropriately, and fluently translate the
words in English from their first language.
Thornbury (2005) adds in speaking the students
must be interactive and they have to co-operate with
their speaking partner by using speaking turn
management. Speaking is done in real situation and
time where we have limited time to work with the
detail. In this case, to make the students fluent in
speaking, they need to memorize the lexical. It cannot
be denied that the students face obstacles in learning
speaking skill. Speaking skill is a complex skill and
this skill needs other skills and other supported
knowledge. Finally (Akbari, 2015) identifies the
problems in teaching and learning EFL
speaking
skill.
There are seven problems with five crucial parts in
education system such as; the teacher, the students,
the material, teaching method, and assessment.
Curriculum and policy also influence and become the
sub-component of the problems.
Empirical studies in speaking also found that the
students face speaking obstacles such as; lack of
vocabulary, grammar mistake or error, not fluent in
speaking, incorrect pronunciation, listening problem,
Kusmaryani, W., Musthafa, B. and Purnawarman, P.
Optimizing Students’ Speaking and Critical Thinking through Students’ Reflective Practice in Socratic Circle Speaking.
DOI: 10.5220/0008215800002284
In Proceedings of the 1st Bandung English Language Teaching International Conference (BELTIC 2018) - Developing ELT in the 21st Century, pages 201-209
ISBN: 978-989-758-416-9
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
201

shy to speak in front of public, afraid to express their
opinion, low self-confidence, make hesitation, have
problem in other skills, afraid in making mistake, less
effort, and less practice (Ansari, 2015), unacceptable
thought or desire, limited background knowledge of
certain topics, passive in participating, and mother
tongue influence their speaking (Tuan & Mai, 2015),
and it can be classified into two factors (internal and
external). Internal factors are some things which
come from the inner side of the students when they
learn English such as; how old, attitude and
behaviour, willingness, knowledge, perception, and
mother tongue. External factors are some things
which come from the outer side of the students such
as; syllabus, civilization or society, state, and
enthusiasm (Rico, 2014).
Chaney & Burk (1998) explain that in speaking
we develop meaning by using symbols verbally or not
with many kinds of situations and share its meaning
to others. In second language teaching and learning,
speaking skill becomes very important since long
time ago speaking has been underestimated by
English teachers by giving the students drills such as;
repeating the teacher and dialogue making. It is
totally different nowadays that the purpose of
speaking is the ability to communicate where the
students can express their ideas based on situation in
which social and cultures influence their perspectives.
We need to provide appropriate activities which can
be implemented in ESL and EFL classroom where the
students can improve their speaking skill based on
teacher’s experience and background in teaching
speaking.
The importance of language learning success is
teaching speaking which can give the students ability
to communicate effectively in school or out of school,
their real life in society. Teaching speaking covers the
linguistic aspects such as; phonology, morphology,
syntax, semantic, etc. The students can use those
skills in speaking by seeing social context, listeners,
condition, and the issue, arrange the idea based on
logic meaning steps, function the language to show
value and judgement, and they can speak fluently and
confidently.
Interaction is the key in speaking which linguists
and ESL/EFL teachers concern on. The purpose is to
teach the language communicatively and
collaboratively by seeing speaking as real life
communication. The use of this method to ESL/EFL
learners will give chance to the students to
communicate the target language. Classroom
environment needs to be adjusted to give the students
real life situation to communicate and stimulate
speaking through authentic activities and also
meaningful task that can be done collaboratively in
groups.
The development of classroom interaction is
very important in teaching speaking skill at
language courses. Speaking studies are similar to the
other studies which use language in the field of
interdisciplinary. The study is related to the
understanding
of
psycholinguistic
and internal factors
which influence the production of speech, the
structure, interpretation, and the involvement of
process and the way to develop these aspects. A
description of the characteristics of speaking in a
foreign language can be approached from different
angles, but typically it is conceptualized in terms of
two interrelated facts, that is various types of
knowledge that learners possess and their expertise in
adeptly using the knowledge in real communication
(Pawlak, 2011). Richard (2008) explains that the
priority in ESL and EFL learning is the students can
master the speaking skill. As the consequence, the
students tries to assess their process in learning
language effectively based on quantity and quality of
their speaking to see the improvement of their
speaking.
There are three aspects of primer sources
problem-makers. The first is communicators focus on
speaker and listener. The second is message. The last
is the context or situation and condition
(Jamshidnejad, 2011). Communicative language
teaching is said to be one of the latest pedagogic
approach which is based on the principles of
motivation enforced learning. Khan (2013) says that
communicative language teaching incorporates the
idea of interaction considering it as essential element
of the whole process and output. The total interaction
in meaning which the students depend on and
participate will influence the success of acquisition in
target language. Of course, the contribution in
developing students’ system comes from language
input which is integrated to language output. Kanuka,
Rourke, & Laflamme (2007) add that arguments,
discussions, and debates are some communicative
activities which can be used by the students to achieve
their higher order thinking. The students are
introduced to conceptual issue and problems which
lead them to share their opinion to others, assess the
information to solve the problems, make self-
reflection and investigate their understanding which
cover their needs and make them get new
interpretation toward real life issues. Marie & Rohan
(2011) underline that interactional competence is
what students must have. The students have to co-
construct conversation with the other students’
interaction in various events and show their
BELTIC 2018 - 1st Bandung English Language Teaching International Conference
202
understanding in pragmatics by using syntax talk
which involves paralinguistic, gesture, body
language, proxemics, kinesics, and gaze where the
purpose is social or institutional purpose which focus
on joint management with co-participants in the
system of turn taking and the roles are adopted from
appropriate interaction. The comprehension and
practice in designing and responding turns coherently
and in manner sequent, displaying comprehension
and commonly fixing the communication which is
treat or breakdown. Presenting relevant empathy and
engagement as well as completing the action socially
where the goals are interaction condition and social
or institutional.
The other thing which also important to be
considered besides speaking is critical thinking. As
teachers and communicators, it becomes their
responsibility to create proper atmosphere which can
improve students’ critical thinking. The students must
be motivated in asking questions to go beyond facts
rather than memorization of knowledge. Teachers
must remain open to have ideas, opinions, and beliefs
questioned critically by the students. The students
must be prepared to accept corrective critique of their
efforts.
Everyone knows the importance of critical
thinking. It cannot be separated from many aspects of
people’s life. Paul (1993) says that critical thinking is
valuable not only in school but also in the world
beyond school as well. Nowadays we see many
people in modern society face obstacles in thinking
critically to solve their daily problems. We need to
learn how to think critically because we face different
character of people and trapped in the condition
which force us to make tough decisions or choices.
Critical thinking skill gives everyone a chance to
make wise decision and choices toward the problems.
Although thinking in the language dictionary
means the process of thinking about something, ideas
or opinions about something, intelligent and able to
think seriously about things, but the interpretation
about thinking by psychologists were different. The
interpretation about thinking changed from time to
time. Reinard (1991) explains critical thinking
requires deliberate and careful efforts relate to
proposition before making a decision. What a person
has in mind is from information which already
evaluated thoughtfully such as the width of issue in
our proposition before decision is made. Many option
to react on the issue such as; acceptance, rejection, or
suspend judgement based on proposition in people’s
mind. Scientific attitude is needed in thinking
critically and push the existing issue to go to decision
making. At last, arguments lead to the judgement
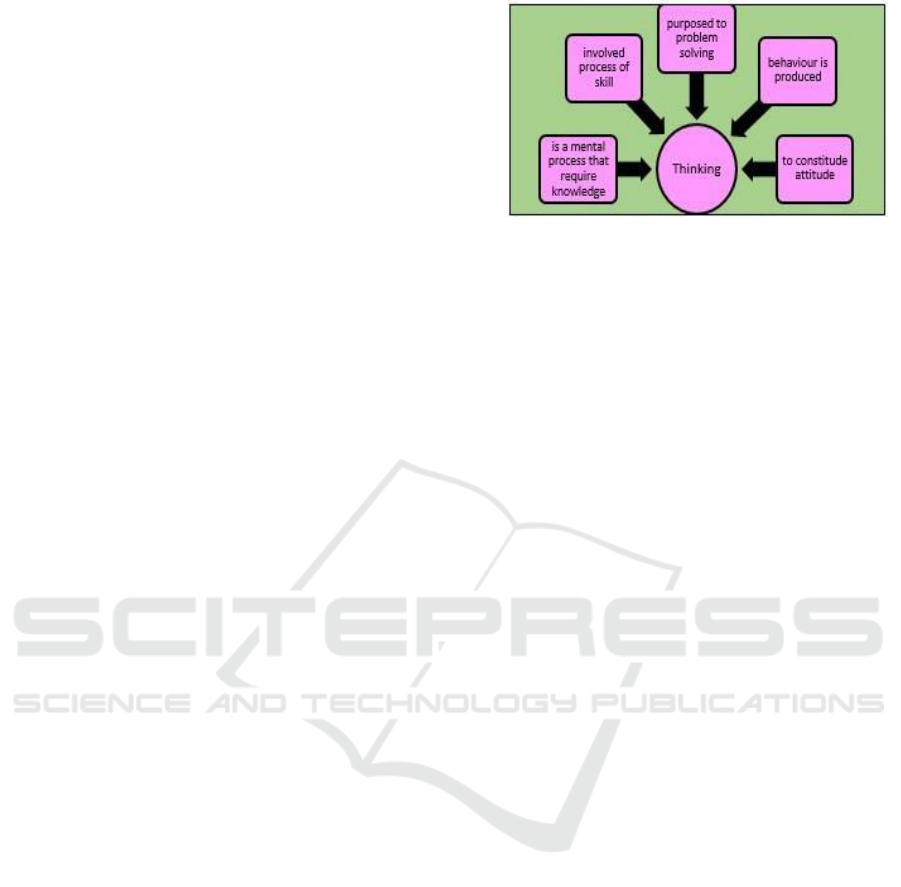
Figure 1: Concept of thinking (Phillip, 1997)
Thinking is a mental process in people’s brain,
processes the information collected then gives
interpretation
about it and functions to solve problems
and makes decisions also produces behaviour and
constitutes attitude (Phillip, 1997).
The term “critical” is taken from two Greek words
etymologically from “kriticos” is the skill in
considering the decision from the conclusion which is
sensible and “kriterion” is the quality or criteria
which can be used to measure the ideas. It can be said
that etymologically the development of discerning
judgement is based on standards. It is relevant to
Webster’s dictionary “characterized by careful
analysis and judgement” and the gloss follow it,
“critical – in its strictest sense – implies an attempt at
objective judgement so as to determine both merits
and faults”. The implementation of thinking, the
concept of critical thinking is clearly thinking which
focus on the decision or the conclusion after assessing
the criteria appropriately in the purpose of
determining the truth which worth, value or merit the
issue. Elder (2007) in Paul & Elder (2008) define
critical thinking as the ability to reason which is
guided oneself in thinking with discipline that reach
the quality of thinking in the highest position fair-
mindedly. It will allow people critically and
consistently think in a rational way, able to give
reason and empathy. Intellectual equipment is used to
help people think critically in assessing and analysing
the concepts and principles where people’s thinking
skill is improved. From the explanation above, it can
be seen that critical thinking uses standard of thinking
and process in higher order thinking not only to solve
problems and make decision but also give
interpretation to the given information.
In education field critical thinking is very
important to be taught and implemented. Critical
thinking skill is developed from knowledge and
guidance to understand written information. It builds
and fluids based on their knowledge. It is not just
memorize knowledge and comprehend the lesson
without asking the questions. Critical thinking gives
opportunity to the students to think critically by
Optimizing Students’ Speaking and Critical Thinking through Students’ Reflective Practice in Socratic Circle Speaking
203
making hypotheses questions, finding alternative
hypotheses, and assessing the hypotheses based on
the facts found. We do not say that memorizing fact
is not good. Memorization can help students to solve
their problems, use their logic, give argument and
clear the confusion.
There are many ways to optimize students’
speaking and critical thinking. This paper tries to
present the research result in optimizing students’
speaking and critical thinking through students’
reflective practice in Socratic circle speaking.
Reflective practice is a process where learners
consider the incidents
critically
in their learning based
on their background and continuously process as self-
reflection. This concept is proposed by Schon (1987)
who says that reflective practice consider students’
own background in implementing what they know
into practice thoughtfully and the professionals in the
discipline will coach this. His argument shows that
the goal of learning is to prepare the students facing
the world where practice should be appropriate to the
fast changing world by filling the knowledge through
professional training model. Reflection will give the
students and the novice opportunity to develop and
improve themselves by practicing the reflection itself.
There are so many concepts of word “reflection”
based on its context. Meditation of thought is
commonly used to define it. In education especially
learning context, Rowntree (1988) explains reflection
as serious self-conversation or critically think about
the subjects, the methods, and learning tasks after the
class over. The steps are preparation, learning
process, and the reflection. Fade (2005) explains that
in reflection we need to describe, assess our ideas,
opinions, point of views or perspectives, the theories
which support, and the process of learning. It is
divided into three categories. The first is prospective
reflection which focus on seeing forward. The second
is spectative reflection which focus on seeing what
we are doing now. The third is
retrospective
reflection
which focus on seeing back after learning. Reflection
task will help the students to evaluate their activities
during learning process such as the material which
related to reality context. The reflection is done
personally and the evaluation comes from one’s
individual. Every student has different evaluation on
what they noticed, concerned, focused, and did in the
class. The reflection gives the students chance to
assess what they got in learning process.
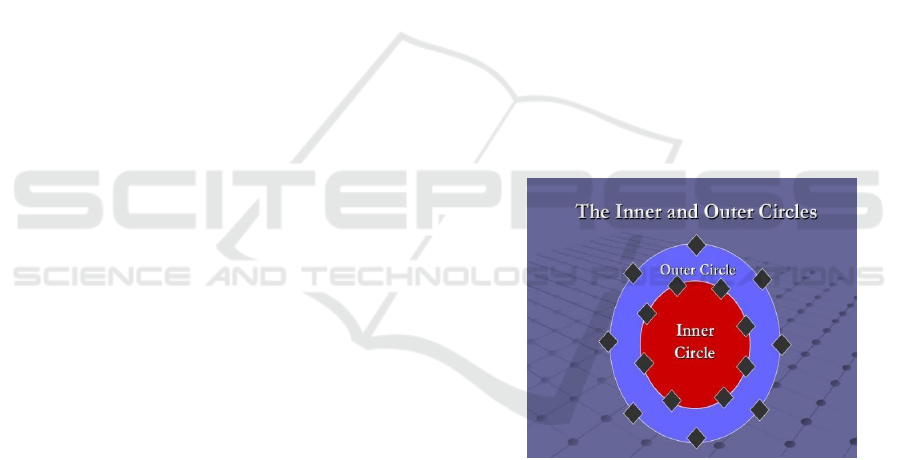
Socratic circle speaking means that in
optimizing students’ speaking and critical thinking,
the teacher used Socratic Method in the form of
Socratic circle speaking. The concept of Socratic
Method is familiar among professional educators
especially teaching methodologies in legal studies.
Socrates focused on continuous questions to find the
truth or what we call as a dialectic method of inquiry
(Pang, 2008). Schiller (2008) says that the students’
learning can be encouraged by using a method
which has guided question pedagogy, using
dialogue and refutation to make the students
assess their understanding critically about certain
issues. Fahim (2012) understands that organized
series and systematic questions are what Socrates
proposed to make students assess their thinking and
avoid the students to make wrong concepts and
conclusion. Socratic questioning method is far from
memorizing information from textbook in teaching.
Philosophically this method aims to optimizing
students’ thinking where the students are asked with
no definitive answer so the students keep thinking to
evaluate the given issue. Socrates thought that
teaching the students were not effective by lecturing
method. Socratic seminars are proposed to evaluate
students’ knowledge and comprehension related to
the given issue about people or others which lead to
students’ understanding the thoughts by continuously
asking question. The students’ reasoning can be
stimulated to be more rational and logic (Byrne,
2011).
Figure 2. Socratic circle concept
Socratic questioning method is also can be said as
transformative learning, the process where creative
composition is brought to the opposites. The
individual is created socially during it is generated.
The teaching and learning process includes person
from group community. The main focus in this
process is a deep understanding from the students
individually or collectively (Formenti & Dirkx,
2014). The implementation of Socratic questioning
method can be done in good environment classroom
which accompany the students to get knowledge and
make them critically think about the material given
and they can create positive and constructive manner
engagement with other students (Bodinet, 2016).
BELTIC 2018 - 1st Bandung English Language Teaching International Conference
204
Socratic method is relevant to EFL classroom
because question-asking is one of the most common
techniques used by language teachers (Al-darwish,
2012). Socratic questioning first proposed by
Socrates, one of the great philosophers in Greek who
engaged the questions with his students in seeking the
truth by asking continuously his students and
colleagues’
perspectives which exposed contradiction
where fallacies and assumptions were proved. In this
this strategy, the method of learning is helping teacher
in relating material with real condition of the students
and supporting them to make relation between their
own knowledge with the implementation in daily
activities. With this strategy, the students are
expected to understand the importance of the study,
the advantages, and how they reach it. Socratic
questioning method is a method where questions take
place in teaching and learning. It will make the
students understand the content or issue to increase
their thinking level through their deep thinking on the
concept and value from written text. Socratic Method
pushes the students to think by continuously asking
questions and selecting the questions’ types to
develop discussion where discipline and responsible
manner intellectually are required. In learning
process, questioning is considered as teacher’s
activity to support, guide, and evaluate students to dig
information, analyse, and explore the ideas
(Copeland, 2005; Paul, 2006).
2 METHOD
Descriptive qualitative is the design of this research.
The purpose of this design is investigating the
implementation of students’ reflective practice in
optimizing students’ speaking skill and critical
thinking skill in Socratic circle speaking. The
implementation was done at English department of
Borneo University Tarakan in academic year
2017/2018..
Subject of the research was third semester
students. The researcher used closed observation. In
the observation activities, the researcher acted as non-
participant observer it means that the researcher did
not participate and interfere the process of teaching
and learning. Some aspects observed were the
implementation of students’ reflective practice in
optimizing students’ speaking skill and critical
thinking skill in Socratic circle speaking. In this
research, the researcher observed the running process
of Socratic circle speaking, analysed students’
reflection, saw the progress of students’ speaking and
critical thinking after reflection practice. The
researcher recorded the activities in the classroom. In
interview session, the researcher asked questions
which related to the implementation of students’
reflective practice.
Qualitative data analysis was used in this
research. The data was coded (open, selective,
axial) by looking for themes related to the research
focus. In analysing the data, the researcher used
Miles & Huberman (1984) interactive model for
component data analysis.
3 RESULTS
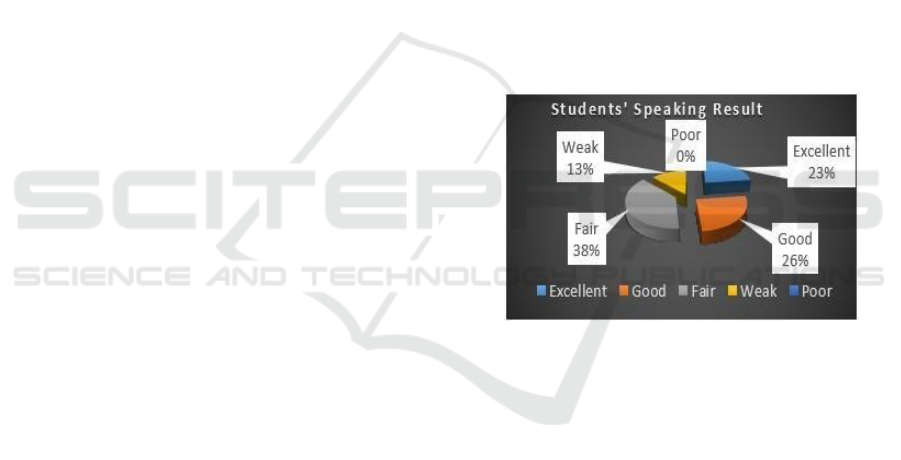
Students’ Speaking Resuls
The result shows that students’ reflexive practice
could optimize students’ speaking and critical
thinking.
Speaking
result shows that 23% in Excellent
category, 26% in Good category, 38% in Fair
category, 13% in Weak category, and 0% in Poor
category.
Chart 1. Students’ Speaking Result
Excellent category covers the criteria such as; in
fluency students are very fluent in speaking, almost
no doubt, rich in vocabularies, and perfect in voice
tone in pronouncing the words, and accent students
are in excellent and good effort at accent, in
vocabulary students are excellent in controlling the
language features and have a wide range of well-
chosen vocabulary, in grammar students do accuracy
and variety of grammatical structures, and in details
students are excellent in describing and give
additional details beyond the required.
Good category covers the criteria such as; in
fluency students are very fluent in speaking, some
doubt, looking for few words, and some words are
unheard in pronouncing the words and accent
students are in good effort at accent, in vocabulary
students are in good power in directing the language,
well space, well selected vocabularies, for grammar
students did grammatical errors in structure because
of various grammar function, and details students are
Optimizing Students’ Speaking and Critical Thinking through Students’ Reflective Practice in Socratic Circle Speaking
205

giving clear description including the information
which is required.
Fair category covers the criteria such as; in
fluency students are fluent enough in speaking, doubt
sometimes, paraphrase make students unbalanced by
looking for some words and hesitating voice tone in
pronouncing, a non-native accent sometimes some
efforts, in the aspect of vocabulary students gave
adequate language control and vocabulary range is
lacking, in grammar students did errors more often
but not influence the idea and limited styles in
grammar, and in detail students give enough
explanation and add some detail information.
Weak category covers the criteria such as;
speaking is often doubt with uncomplete sentences
left, very low voice tone in pronouncing, limited and
difficult to comprehend and for native accent no
attempt, in the aspect of vocabulary students are
weak,
directing
the language and use task which is not
equal to the vocabulary used, error in grammar more
often although in simple grammar which influence
understanding, and limited details critically which is
hard for the listener to catch the point.
Poor category covers the criteria such as; in
fluency students’ speaking is not fluent, doubt and
only in short phrase memorization, hard to think how
to speak continuously, cannot be heard, in
pronouncing the words, it is limited and difficult to
know and for native accent there is no attempt, in the
aspect of vocabulary students are weak in directing
the language and the task is not fit to the vocabulary
used in speaking, in grammar students did errors more
often and influence the meaning and also limited
information which the listener cannot get the point.
Students’ Critical Thinking Result
Critical thinking result shows that 13% in Critical
Thinking level 4, 36% in Critical Thinking level 3,
38% in Critical Thinking level 2 and 13% in the first
level of critical thinking.
Chart 2: Students’ Critical Thinking Result
Critical thinking level 6 or the highest level covers
the criteria such as; facts, arguments, charts,
questions are interpreted accurately, students
recognize claim and reason in salient arguments,
agree or disagree are analysed and evaluated to give
point of view which can give explanation as
alternative of phenomena or event where the students
describe opinion and the cause fair-mindedly based
on facts that the reason in ethical judgment making.
Critical thinking level 5 covers the criteria such
as; facts, arguments, charts and questions are
interpreted accurately, identification of relevant
argument based on reason and claim in thinking the
issue in positive or negative side, assess and analyse
various points as alternative ideas to describe the
event or phenomena, describe the arguments, facts
and reasons are thought fair-mindedly.
Critical thinking level 4 covers the criteria such
as; events, people and places are described by adding
the source details, make relation to not only the
sources but also personal analytic which show
students’ basic skill in analysing, interpreting,
formulating inferences or statement which involves
multi-perspectives in literature discussion,
background knowledge and others’ perspectives are
challenged through questions and saying
understanding and guessing by giving limited facts to
think twice on others’ belief.
Critical thinking level 3 covers the criteria such
as; answer by showing events and evidence
grammatically
that makes individual connect with the
limited sources, start to give effective fact to support
opinion in literature discussion, background
knowledge, factually or literally relay to the sources
which involves limited or no fact to respond the
dualistic thoughts and demonstrate unwell
organization and uneven thinking.
Critical thinking level 2 covers the criteria such
as; misconception in facts, arguments, charts and
questions, cannot identify the argument which is
strong and relevant to the issue and fall in giving
conversation, limited justification in procedure and
result, reasons are explained rarely and also to the
facts and arguments, self-interest and preconception
are maintained by perspectives.
Critical thinking level 1 or the lowest level covers
the criteria such as; facts, arguments, charts and
questions are interpreted with bias in information on
others’ perspectives, cannot identify the counter
argument which is strong and relevant to the issue and
missed in assessing the alternative perspective and
give arguments based on wrong facts and reasons and
the claim cannot be justified in not only the procedure
or result but also closed-mindedly reasons.
BELTIC 2018 - 1st Bandung English Language Teaching International Conference
206

Students’ Reflection in Socratic Circle Speaking
Students’ speaking and critical thinking result
above are optimized by using students’ reflection in
Socratic circle speaking where the student in speaking
class used Socratic method and after class students
were asked to make self- reflection on students’
performance and content. The following pictures are
the examples of student’s self-reflection.
Figure 3. Student’s Reflection on Performance
Figure 4. Student’s Reflection on Content
Reflective assignments make students think about
the reality context based on their practice on how the
content implemented in their learning. Reflection is
very individual and personal where the opinion comes
individually. Every student will do different
reflection in noticing, observing or doing things in
teaching and learning process. The reflection gives
the students chance to evaluate what they have got in
the class. Experience is learning will give benefit to
the students by reflecting the lesson, for example in
the science class. Continuous reflection can improve
students’ performance in speaking by evaluating the
strengths and weaknesses they had, recognize their
problems and how to solve those problems for future
improvement. Their task can be done by choosing
appropriate strategy or approach based on their
learning experience especially which gives positive
result to them.
Research result conducted by Lerch, Bilics, &
Colley (2006) is similar to this research where
effective learners are influenced by their ability to
think critically, self-evaluation on their learning, and
metacognitive thinking in their reflective practice.
Students can analyse their problems, challenges, and
obstacles in learning to find alternative solutions
where they can optimize their skill.
Reflective practice is a process of deep
evaluation on teaching and learning which already
done (Herod, 2002). It is totally different with non-
reflective learning which focuses on memorization
of material without stimulating students’ critical
thinking. The purpose of reflective learning is the
engagement among the teacher, the students, the
material, teaching method, learning assessment, and
classroom management to achieve the language
target guiding the students’ knowledge and
experience meet the real situation. The learning
concept is connected to their schoolwork through
reflection. Students’ experience replace where the
task is just material memorization.
There are many aspects of teaching and
learning which can be connected to make both the
teacher and the students realize their strengths and
weaknesses in order to achieve the effectiveness in
teaching and learning. In education field,
experience teaches us. We grow the personal
reflection based on experience which develop our
skill more cognizant. Continuous reflection will
make the teacher realize and recognize the strengths
and weaknesses of his/her teaching. It also makes
the teacher evaluate teaching to find alternative
solution and final decision for the future.
Situational analysis will help teacher develop
his/her teaching skill. Decision making is the end
of this reflection and it requires critical thinking
skill
Meaningful teaching and learning process can
be done by designing reflective practice which
covers clear and realistic purpose to give reflection
a chance to improve the quality of teaching and
learning. The structured reflection has
opportunity to transform reality learning from
learning task (Amulya, 2003). Continuous
reflection can be done daily, weekly, to biweekly
or after finishing each lesson unit where the focus is
evaluate teaching and learning activities regularly.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Students’ reflective practice can optimize students’
speaking and critical thinking in Socratic circle
speaking. The key point of reflection is willingness
from both teacher and the students to evaluate their
strengths and weaknesses and also the quality and
effectiveness of teaching and learning process.
Optimizing Students’ Speaking and Critical Thinking through Students’ Reflective Practice in Socratic Circle Speaking
207

Problems in teaching and learning process can be
solved by the teacher through continuous
reflection. The quality of teaching and learning can be
evaluated by recognizing the strengths and
weaknesses of preparation, process, assessment,
material selection, teaching method, etc. the teacher
can avoid and anticipate what will happen to the next
teaching.
Reflection
can help teacher not only to solve
problems in teaching but also improve the quality of
his/her teaching. Reflection also helps students to
optimize their learning. Reflective practice makes the
students evaluate critically what they learned which
can improve their skill in speaking and critical
thinking. Reflective practice will motivate the teacher
and the students to do self-correction in teaching and
learning.
EFL speaking skill should focus on bringing real
life context in teaching and learning process. It can be
done by designing appropriate curriculum or syllabus
which can explore functional speaking and express
ideas toward global issues. The students can talk their
opinions, arguments, data or evidence, clarification,
viewpoints or perspectives implications and
consequences until questioning the given issues. The
students are guided to improve fluency, aware on
pronunciation, enrich vocabulary, well-arranged
structure or grammar, and provide detail information
relate to issue being discuss in the class.
Philosophically, critical thinking is defined as
cognitive skill which is very complex and focus on
problem solving where innovation and intellectual
consideration are required. In critical thinking people
evaluate the information they got quantitatively and
qualitatively to the end of new perspectives and belief
to be used to problem solving and decision making.
REFERENCES
Moore, R., Lopes, J., 1999. Paper templates. In
TEMPLATE’06, 1st International Conference on
Template Production. SCITEPRESS.
Smith, J., 1998. The book, The publishing company.
London, 2
nd
edition.
Akbari, Z. (2015). Current Challenges in Teaching /
Learning English for EFL Learners : The Case of
Junior High School and High School. Procedia -
Social and Behavioral Sciences, 199, 394–401.
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.07.524
Alaraj, M. M. (2017). EFL Speaking Acquisition :
Identifying Problems , Suggesting Learning
Strategies and Examining Their Effect on Students ’
Speaking Fluency. The International Journal of Social
Sciences and Humanities Invention, 4(1),3215–
3221. http://doi.org/10.18535/ijsshi/v4i1.05
Al-darwish, S. (2012). The Role of Teacher Questions and
the Socratic Method In EFL Classrooms in Kuwait.
World Journal of Education, 2(4), 76–85.
http://doi.org/10.5430/wje.v2n4p76
Amulya, J. (2003). What is reflective practice? Retrieved
September 3, 2017, from www.learningfor
innovation.com
Ansari, M. S. (2015). Speaking Anxiety in ESL / EFL
Classrooms : A Holistic Approach and Practical
Study. International Journal of Educational
Investigations, 2(4), 38–46.
Bodinet, J. C. (2016). Pedagogies of the Futures : Shifting
the Educational Paradigms. Springer - European
Journal of Futures Research, 4(21), 1–12.
http://doi.org/10.1007/s40309-016-0106-0
Byrne, G. (2011). Using Socratic Circles to Develop
Critical Thinking Skills. Journal of Practically
Primary, 16(2), 13–16.
Chaney, A. L., & Burk, T. L. (1998). Teaching Oral
Communication in Grades K-8. Boston: Allyn &
Bacon.
Copeland, M. (2005). Socratic Circles: Fostering Critical
and Creative Thinking in Middle and High School.
Portland, MN: Stenhouse.
Fade, S. (2005). Learning and assessing through reflection:
A practical guide. Retrieved September 3, 2017,
from university of ulster
Fahim, M. (2012). Fostering Critical Thinking through
Socrates ’ Questioning in Iranian Language Institutes.
Journal of Language Teaching and Research,
3(6), 1122–1127.
http://doi.org/10.4304/jltr.3.6.1122-1127
Formenti, L., & Dirkx, J. (2014). A Dialogical Reframing.
SAGE Journal of Transformative Education, 12(2),
123–133. http://doi.org/10.1177/1541344614554508
Herod, L. (2002). Glossary of terms. Retrieved September
3, 2017, from www.nald.ca
Jamshidnejad, A. (2011). An Innovative Approach to
Understanding Oral Problems in Foreign Language
Learning and Communication. Journal of Academic
and Applied Studies, 1(1), 3–21.
Kanuka, H., Rourke, L., & Laflamme, E. (2007). The
Influence of Instructional Methods on the Quality of
Online Discussion. British Journal of Education
Technology, 38(2), 260–271.
http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2006.00620.x
Khan, I. A. (2013). Speaking Skills and Teaching
Strategies : the Case of an EFL Classroom.
Educational Technology Journal, 58, 14557–14560.
Lerch, C., Bilics, A., & Colley, B. (2006). Using reflection
to develop higher order processes. In American
education research association.
Luoma, S. (2004). Assessing Speaking. UK: Cambridge
University Press.
Marie, A., & Rohan, B. (2011). Using Conversational
Analysis in the Second Language Classroom to Teach
Interactional Competence. SAGE Journal of Language
BELTIC 2018 - 1st Bandung English Language Teaching International Conference
208

Teaching Researc, 15(4), 479–507.
http://doi.org/10.1177/1362168811412878
Miles, M. B., & Huberman, A. M. (1984). Qualitative
data analysis: A source book of new methods.
Newbury Park, CA: SAGE Publications Ltd.
Pang, K. (2008). Sophist or Socratic Teaching Methods in
Fostering Learning in US Graduate Education. The
International Journal of Learning, 15(6), 197–201.
Paul, R. W. (1993). Critical Thinking: What every person
needs to survive in a rapidly changing world (J.
Willson). Santa Rosa, CA: Foundation for Critical
Thinking.
Paul, R. W. (2006). Thinker’s Guide to the Art of Socratic
Questioning. Santa Rosa, CA: Foundation for
Critical Thinking.
Paul, R. W., & Elder, L. (2008). The Miniature Guide to
Critical Thinking: Concepts and Tools. California: The
Foundation for Critical Thinking.
Pawlak, M. (2011). Speaking and Instructed Foreign
Language Acquisition. Bristol, Bufalo, Toronto:
Multilingual Matters.
Reinard, J. C. (1991). Foundation of Argument: Effective
communication for critical thinking. Dubuque, Iowa:
WM. C Brown Publisher.
Richard, J. C. (2008). Teaching Listening and Speaking:
From Theory to Practice. USA: Cambridge
University Press.
Rico, L. J. A. (2014). Identifying Factors Causing
Difficulties to Productive Skills among Foreign
Language Learners. Open Writing Doors Journal,
11(1), 65–86.
Rowntree, D. (1988). Learn how to study: A realistic
approach (3rd edition). London: Macdonald & Co.Ltd.
Schiller, N. (2008). Finding a Socratic Method for
Information Literacy Instruction. Routledge Journal of
College & Undergraduate Libraries, 15(1-2), 39–56.
Schon, D. (1987). Educating the reflective practitioner.
San Fransisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Thornbury, S. (2005). How to Teach Speaking. UK:
Pearson, Longman.
Tuan, N. H., & Mai, T. N. (2015). Factors Affecting
Students’ Speaking Performance at Le Thanh Hien
High School. Asian Journal of Educational Research,
3(2), 8–23.
Optimizing Students’ Speaking and Critical Thinking through Students’ Reflective Practice in Socratic Circle Speaking
209
