
Model of English Teaching Materials for Police with Communicative
and Task-based Learning Approaches
Syahrial
English Education Study Program of University Bengkulu
W.R. Supratman St. of Kandang Limun, Bengkulu City 38371
Keywords: Learning Material Model, Material Development, Communicative Approach, Task-based Learning.
Abstract: The research is aimed at developing teaching material (textbook) of English for Police based on the
approach of Communicative and Task-Based Learning Approach. To achieve the goal, a model of
developmental research was adopted. The research was carried out in three steps: (1) need assessment and
curriculum analysis, (2) learning material design and development, and (3) teaching materials (textbook)
evaluation. The need assessment was carried out on the bases of the respondents’ opinions. Meanwhile,
developing and designing learning materials were based on relevant theories on effective learning material
development and empirical data. To assess effective model of learning material development, the
respondents’ opinion were elicited by questionnaires and expert judgments. After conducting several tryouts
and improvements, an affective learning material model was succefully developed. This implies that
developing and designing an effective model of learning material should be based a comprehensive
need
assessment.
1 INTRODUCTION
The police education in Indonesia, to a great extent,
has promoted the use of English in working places.
The mission is in line with the development of
network and the strengthening cooperation among
different international agencies, especially the police
agencies across the countries. To develop police
officer professionalism and to respond the global
challenges, the police education has set up English as
one of important subjects. The LEMDIKLAT POLRI
(Education and Training Institution of the Police of
The Republic of Indonesia) has formulated the
following vision: "promoting Indonesian police who
understand their identity as guard, protector, and
ministers of the society".
Police educational Language School (SEBASA
POLRI) is the only institution that provides English
language learning course for police officers on the
police boards of the Republic of Indonesia. In its
implementation, the goal for learning English which
is developing both oral and written communication
skills in English, has not been well achieved. Two
field studies held in two countries (UK and Australia)
reveal that the police officers who were SEBASA
students could not interact actively by using English.
From the observation, it was found that whole
language interaction was dominated by the translators
and tutors. Moreover, advanced activities related to
the written report also could not be succefully done
by the participants of field practice. Therefore, the
English language learning was not considered less
successful.
The results of these
observations
and studies show
that the unsuccessful of learning program was caused
by the available teaching materials has not yet been
able to support communicative competence that
includes the competencies of grammatical,
sociolinguistics, discourse and strategic that should
be owned by the students. In addition, teaching
materials that are available are not arranged based on
the needs analysis of the students, so they did not
accommodate the skills needed by the students. The
model of teaching materials that are available have
weaknesses from various aspects such as the form of
the exercise questions that were monotonous and less
diverse, the reading material information is not
adequate and not equipped with difficult glossary
words, limited exercise that support the ability of
speaking for students, lack of English expressions
(language expressions) in module, focus featured in
the materials contents are only in the form of the
understanding
of the students over the treasures word
310
Syahrial, .
Model of English Teaching Materials for Police with Communicative and Task-based Learning Approaches.
DOI: 10.5220/0008217400002284
In Proceedings of the 1st Bandung English Language Teaching International Conference (BELTIC 2018) - Developing ELT in the 21st Century, pages 310-317
ISBN: 978-989-758-416-9
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

(the vocabulary of police field). This causes
disintegrated language ability (skills) in applying
English in the field.
Other weaknesses found in the model of available
teaching materials is the weakness of time
management of learning, where the scope of the
materials that is too wide only be taught in one
meeting. The problems of the scope of the material
and the limited time allocation were
acknowledged
by
students who sometimes feel confused and difficult to
understand the lessons thoroughly. The model of
teaching materials that was rigid and less supported
the ability to talk caused the teaching-learning
process became less communicative so that on the
implementation the acquired language knowledge
often cannot be used well. As a result, in the activities
of teaching and learning, the available teaching
materials did not support students’ performance in
developing communicative language skills.
From the students’ perspective, most of them feel
really helped with the availability of the Treasury
words for police field in the available materials. But
the students feel that the benefits of language learning
that they follow are only on the stages of identifying,
recognizing and listing various objects in English
terms correctly. The students have not been able to
communicate in English with both for speaking or
writing. In addition, the discussion sessions and the
use of verbal language in the learning process is also
not adequate, in other word the time of speaking
exercise (speaking practice) is lack. These opinions
are also supported by the statement of the teachers in
SEBASA POLRI stating that the materials need to be
revised or equipped with additional teaching
materials that more advancing the students ability to
talk (speaking skill). With the
supplementary
teaching
materials then the effectiveness of the learning
process will be increased and learning goals will be
reached. Therefore, the development of an effective,
functional, meaningful and contextual learning is
needed.
Therefore, this developmental research was done
on the basis idea to present a model of teaching
materials with the main characteristics of using
communicative and Task-based Learning approaches
to create meaningful learning process and suitable
with the needs on the field. The model of teaching
materials selected becomes the focus of research
because it is the main learning resources in the
learning process which will determine the direction
of the system and the purpose of the lesson. The
objective wanted to be achieved is communicative
competence in line with the demands of the use of
English for police officers in the days of now so that
the basic principles and the purpose of English
language learning are implemented.
The focus of this research is how the model of
English teaching materials English for Police with
communicative approach and Task-based Learning
is. It is answered by the procedure of developmental
research and the procedures of developmental
teaching materials. The procedures or steps of
developmental research includes the needs of
materials teaching English for Police according to the
instructor and learners in language school for police,
the available and unavailable material used in
language school for police, design model of English
materials English for Police that is compatible with
the needs of the students in SEBASA POLRI, decency
model of materials English for Police with
communicative
approach and Task-based Learning in
SEBASA POLRI, teachers’ and students’ perception
against the model of materials English for Police with
communicative approach and Task-based Learning
developed and the results of field tests of teaching
materials English for Police with Communicative
approach and Task- based Learning developed.
Teaching materials is a lesson that is packaged as
teaching materials to be served in the learning
process. The relationship between teaching materials
and the competencies is the teaching materials will
affect the quality of class interaction and the use of
the target language. A good material must support
substantially that covers the common vision against
the achievement of the purpose/ competency,
materials, and indicators of success. Its rendering
result is also arranged systematically, methodological
underpinnings and with the needs of the students. A
good material also meets the criteria of presentation
that covers: have high reading level, an interesting
presentation of physical formats and teaching
materials.
English for Police is one form of the development
of English special purpose which points on fulfilling
language in the field of certain work. English for
Police emphasizes on providing English and its using
in the context of police. The translation covers
vocabulary in the scope of the police, contextual
reading text theme of law enforcement and crime,
model conversation with the topic of the daily police
task, simple expression in daily conversation in the
world of the police and various knowledge of the use
of English in the police. A big scope of teaching
materials English for Police emphasizes the
achievement of learning goals include the
development of writing skill in form of police report
which is the record of witnesses’ statements, the
recording of evidence; the ability to speak includes
the ability to ask questions in an interview;
Model of English Teaching Materials for Police with Communicative and Task-based Learning Approaches
311

vocabulary such as collocation, connotation and
words registered; and grammar which is the accuracy
of the use of language orally and written effectively
in both the time of education and in the context of
work (Basturkmen, 2010).
The development of materials independently
intended to produce the quality and effective teaching
materials in increasing students understanding. In
fact, the development of teaching materials is the
selection process, adaptation and creation of teaching
materials based on specific benchmark. Hamalik
(2003) explained that some of the principles that need
to be noted in the arrangement of teaching materials
or material learning including cover the principle of
relevance, consistency and adequacy.
In the development of teaching materials, various
principles put forward by the experts. According to
Widodo and Jasmadi (2008), teaching materials
must be adjusted with the followings; and expected to
change
prioritizing
learning itself. Teaching materials
should also be in accordance with the needs and
characters
of learning that is listed
clearly
the learning
aims itself. The last one is teaching material must
contain materials in detail, both for training and
learning activities as well as load evaluation as a tool
to measure the success of learning.
The same thing was expressed by Tomlinson
(2011) in the development of teaching materials and
its relevance in the achievement of second language:
teaching materials can provide the impact that
means, advancing the principles of ease to understand
by learners, can develop a sense of students’
confidence, relevant and useful for learners. Teaching
materials also should be able to generate curiosity of
learners, provide adequate information about the
topics being taught so that the learners become
ready to study. Further development of English
language teaching materials must show the actual use
of language, describes the attention of learning
through language symptoms, and gives the
opportunity for learners to use the target language.
When in the process of learning, teaching materials
should also be able to pay attention to the positive
effects of the lessons, accommodate differences in
learning style, different learners, provide time
attitude calm on the sidelines of the matter, and able
to maximize learning potential by improving
intellectual, aesthetics and emotional involvement.
On the other hand, teaching material cannot be too
controlling the way the exercise is delivered by
providing opportunity to the students to give
feedbacks.
Maley also reveals the principle of the
development of teaching materials which include: (1)
stimulate and develop students’ motivation, both
through the intrinsic interest in thematic and other
techniques used; (2) prepare students with an
authentic English; (3) offer students various
suitability of achievement level of the work done on
the same teaching materials; (4) allow teachers to
specifically separate and select teaching materials in
specific group; (5) make students responsible for
independent learning the best possible; (6) integrate
language skills; (7) advance category communicative
function without ignoring the grammatical problem;
& (8) teaching materials must have a mean (Maley
and Grellet, 1980).
Of all the principles of the development of
learning materials that have been expressed above are
all in synergy with the exposure of teaching materials
that accentuate academic knowledge with attention to
the social aspects of empties on applying language
integrated with communicative competence.
Elements of the context of learning, diversity of
matter, students’ characters, students’ attitude toward
materials and the impact of materials to the
achievement of the students is becoming an important
consideration in developing an appropriate teaching
material, in line and able to achieve the goal of
learning itself.
The concept of ‘communication competencies’
was introduced firstly by Hymes as a critic to
Chomsky. Hymes (1972) stated that Chomsky’s
language competencies more intended to individual
capacity in developing grammatical system
(linguistic competence) (Stern et al., 1983). Hymes
emphasized sociolinguistic competence as a
fundamental concept in teaching communicative
language. These both experts emerge a number of
communicative competence models. The models
have similar concept but have different development
in detail description of communicative competence.
Model of communicative competence refers to
Canale and Swain, Canale, Bachman and Palmer, van
Ek, Celce-Murcia, and Dornyei and Thurell. Celece-
Murcia, Dornyei and Thurell made a model which is
enclosing the previous models. Model of
communicative competence presented by Celce-
Murcia, Dornyei & Thurell (1995) is described as a
pyramid consisting of a cycle and is surrounded by
circles. The cycle in the pyramid covers discourse
competence, and three pyramids, that is sociocultural
competence, linguistic competence, and action
competence. The cycles rounded the pyramid are
strategy competencies, which have potential
inventory skills that are able for a competent speaker
strategically to negotiate the message and solve
matters or compensate the lacks of others
competencies. The frame shows that discourse
competency as the core.
BELTIC 2018 - 1st Bandung English Language Teaching International Conference
312

The theory of language learning underlying the
communicative approach can be composed of some
of the basic principles of the communicative, they are
the activities that involve real communication which
can encourage learning, the task principle are
activities where language is used to perform the duty
means that can encourage learning and meaningful
principles. It is a principle stating that a meaningful
language for learning can enhance the process of
learning language. Learning activities also involve
various activities with the main purpose involving
students in communication, information sharing,
negotiations meaning and interaction.
The last learning element that is also a factor that
must be noted in the communicative approach is the
role of the teaching materials that affect the quality of
the classroom interaction and language usage.
Teaching materials has a major role to support the use
of teaching materials
communicatively.
The materials
focus on the ability of interpretation, expression and
negotiation, the ability to understand, relevant and the
desire for exchanging information rather than using
the forms of grammatically and the main point
according to Freeman (2013) teaching materials
taken from an authentic language samples or found in
the daily use of the language could be taken from the
use of language in real communication.
In addition, communicative approach has a
meaning that language learning is an approach of
Task Based Learning (TBL). TBL approach is
advancing learning activities in tasks that students
must complete the target language as the appliance or
the instructional language (Skehan, 1996). The
activities that the students do in the classroom of TBL
illustrate the problems found in daily life and
advancing language meaning usage in completing
each issue. In the task-based learning the students as
often as possible may be presented with the target
language with the aim to be able to directly observe
the target language usage, make the hypothesis of
understanding individually to discuss the target and
as the end objective of practicing the use of the target
language. The role of teachers in the TBL approach is
not dominant but very important in helping students
distinguish and perception of target language, help
students improving, clarifying and deepening the
perception of the target language. In addition, all the
understanding achieved by the students is by trying
out directly the target language so it is well known by
the term of tasks-based learning adheres to the system
of language learning by doing.
The principle of TBL is advancing tolerance
toward the mistake made by the students during
learning activities. A comprehensive input is very
much appreciated. Target language used as the media
or instructional language must facilitate interaction of
students and vary in order to accommodate dip
reversed of active and passive students. It must also
be noted the meaning of tasks and activities which is
based on the selection of teaching materials
appropriate to the age of students. Learning activities
are also designed to improve and maintain the
motivation of students’ learning (Nunan, 2006).
TBL approach is considered a positive effect and
in line with the communicative competence that want
to achieve. The Advantage found in TBL approach is
the existence of the established real communication
which will be integrated with the four language skills
culminated in the smooth (fluency) and the accuracy
of the language usage (accuracy).
2 RESEARCH METHOD
This research aims to develop teaching materials of
English for Police applied in Language School
(SEBASA) Police. They are to improve
communicative competence among the students. The
model of teaching materials produced in the present
study was based on the result of the situational
analysis and need assessment focusing on the
communicative approach and Task-based Learning.
The research adopted a procedure as suggested by
Borg and Gall (1983). They divided the
developmental research into the following steps: (1)
researching and collecting information; (2) planning;
(3) developing early forms of products; (4) field
testing; (5) revising the last product; (6)
disseminating and implementation (Borg and Gall,
1983).
In addition, model developmental research will
produce model of teaching materials. The
development of the teaching materials model is using
the principles suggested by Tomlinson (2011)
consisting of: (1) identification of need/problem, (2)
exploration areas of need/problem, (3) contextual
realization, (4) pedagogical realization, (5) physical
production, (6) use of material by students, (7)
evaluation. Thus, the merger of these two
development models will produce the realization of
the development of the teaching materials model as
described in the following chart.
Model of English Teaching Materials for Police with Communicative and Task-based Learning Approaches
313
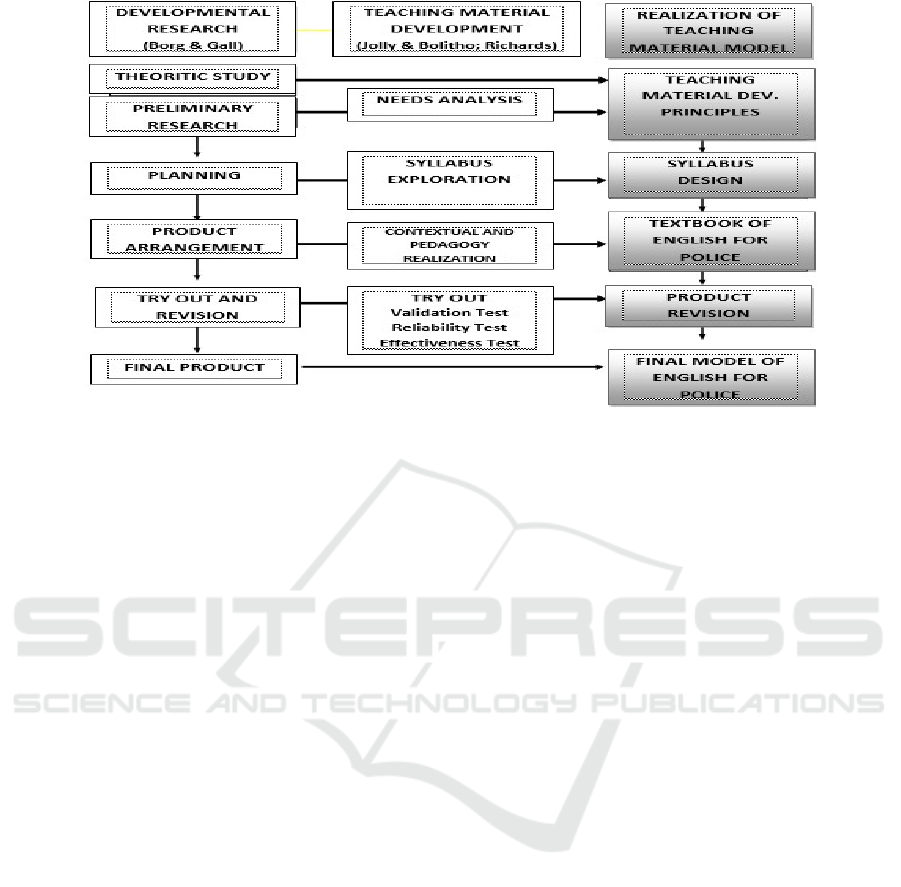
Figure 1: The framework of the development of English teaching material model for Police.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Developing a model of English teaching material
appropriate with and supporting to language
learning in SEBASA POLRI begins with need
assessment carried out to the students and teachers.
It deals with (1) teaching materials, (2) method of
learning and teaching, (3) expected language skills,
(4) language content, (5) teaching materials
relevant to the existing labor field, (6) aspects
complementing the students’ motivation (7)
students’ learning strategy preference,and (8) the
teachers’ opinion towards the existing teaching
materials.
The need assessment was conducted by
distributing the questionnaires to the respondents.
A number of respondents (76%) stated that the
existing teaching materials were not authentic yet
and compounded the students in developing
language skills in the labour filed. On the other
hand, language and the explanation used in the
teaching materials can be easily digested and
motivate students’ learning. In respect to the model
of teaching and learning, of 56% respondents
expressed that the teaching process mached with
the teaching materialsl however, the teachers tend
to use less interactive methods of teaching.
Most respondents (63%) were found to be in the
beginning level It means that they are still low in
their ability. It was proven from the mistakes made
by the respondents when translating a short text into
English. They also realized that they were difficult
to correctly understand, respond, and communicate
with the native speakers.
The result also showed their difficulties to
understand English grammar, and pronunciation,
and their limited space to practice English in the
classroom. From the questionnaires, it can be
concluded that in general the students’ needs for
materials were capable to synergy in integrating
students’ language skills. Furthermore, the result of
questionnaires was used as the guideline draft of
English language learning model that is compatible
with the needs and capabilities of SEBASA POLRI
students.
The results of the analysis to the existing
textbook show the following findings: (1) the order
in each unit of learning in the book is allegedly not
through analysis of a logical or appropriate learning
with the fact of the development of the competence;
(2) In general the order of learning in one unit is
arranged by considering the variation of topics that
must be presented in each unit, like listening,
reading, speaking, writing, literature, and grammar,
and (3) the order always uses the same pattern,
namely: started with reading text with the general
theme as, environment, events, communication,
hobbies, moral and others that are then continued
by learning basic competencies.
The arrangement of such learning could be said
to meet the aspects of the diversity of the topics or
teaching materials but less attention to the aspects
of learning in line with a competency. One unit of
learning in the text books analyzed was not a unified
whole but a collection of the topics. The
BELTIC 2018 - 1st Bandung English Language Teaching International Conference
314

competencies
given separately in the form of the
topic which is not logically arranged in the chapter
would be obstructionist police students in
developing competency.
Teaching materials currently used is still based
on structural approach which stresses more on
grammatical aspects. Teaching materials for police
students is supposed to be more focused on the
development of language skills in accordance with
the tasks of the police. Therefore, the basis
development of teaching materials in this research
that refers to the communicative and tasks-based
approach becomes important as a step in improving
the quality of teaching materials of SEBASA
POLRI.
To identify and to collect the teachers’ and
students’ perception of SEBASA POLRI toward
the model of English material for Police based on
communicative competence and tasks-based, this
study used an open questionnaire containing essay
tasks regarding with: (1) the availability of the
material presented; 56% of respondents answered
the materials were very helpful and increased
knowledge and English language expression
provided that it can be used in the daily work; (2)
the teachers’ and students’ interest in using the
developed teaching materials; 87% of respondents
answered the display of colorful materials and
exercises did not cause
boredom
and the language
used is easy to understand; (3) activities presented in
the teaching materials make the students easy to
develop language skills; 45% of respondents
answered the activities provided are various and
interesting since the ability to Communicate is low
so the language acquisition does not run smoothly ;
(4) the diversity of activities encourages students to
be active, 70% of respondents answered that various
learning activities did make students bored and
busy to complete; (5) language skills taught also
includes all langage skills, 100% of respondents
answered that the materials practice all language
skills but portion of writing exercises is too little (6)
the influence of the materials that in accordance
with the working field, 52% of respondents
admitted to become more confident to use English
at work.
The recapitulated comparison percentage
between assessment of materials and teaching
materials models with positive and negative
dichotomy shows that teaching materials model is
more effective (87,89%) compared to the existing
materials or the newly used by SEBASA POLRI
students (25,24%). The formulation of the
hypothesis to the interests of this test is as follows:
"the average scores of the questionnaire of teaching
materials development results is higher than the
average score of the teaching materials which is not
the result of development"
The value in the table t with degree of freedom
(Indonesia Recorded Its 94) 3, shows that the value
of t
to rank the significance of 0.05 is 2.4 and equal
significance 0.01 is 4.5. Thus, the ratio of t or t count
(6.4) is greater than t tables, even to ( 0.01), it can
be concluded that there is a significant difference
between the developed teaching materials model
and the existing teaching materials.
The value in the t table with degree of freedom
(Indonesia Recorded Its 94) 14, shows that the
value of t to rank the significance of 0.05 is 1,761 and
equal significance 0.01 is 2,624. Thus, the ratio of
t or t count is greater than t table, it can be
concluded that there is a significant difference
between the test results before using the teaching
materials model with the test results after using the
teaching materials model. This means that the
developed teaching materials model is effectively
used.
Table 1: Comparison of the Suitability Test Results of Two Models with t-test.
Average
The Previous Model
(N=4)
Average
Developed Model
(N=4)
T
T-table
=0.05
=0.01
52.8 106,8 6.4 2.4 4.5
Model of English Teaching Materials for Police with Communicative and Task-based Learning Approaches
315
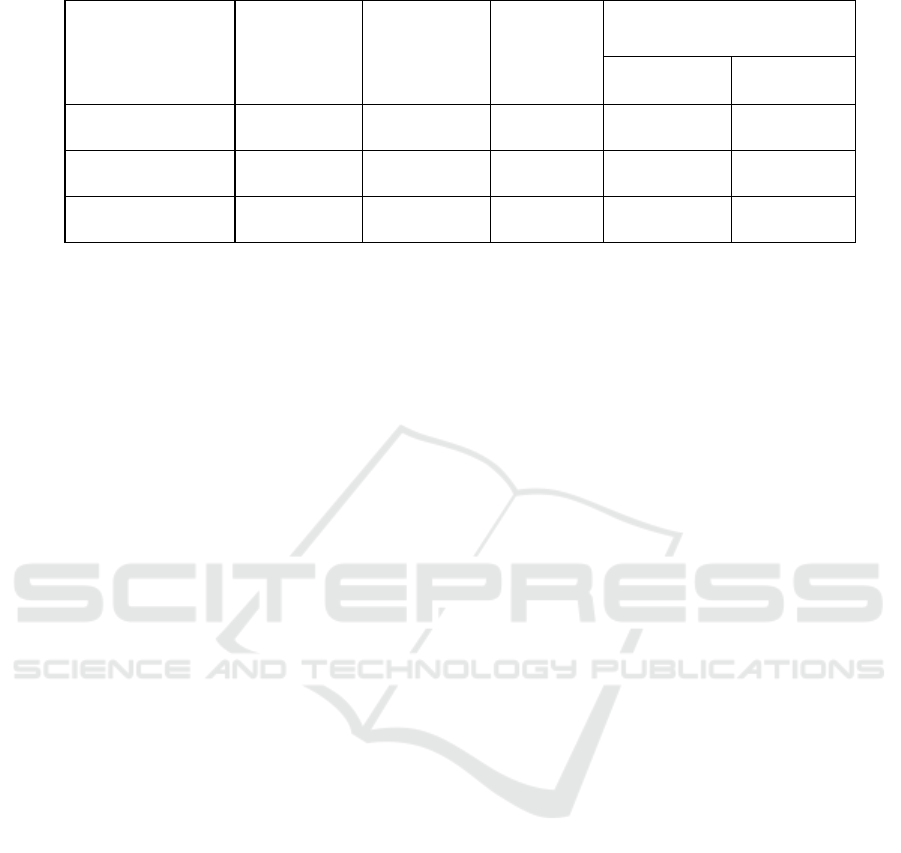
Table 2: Test Results the Effectiveness of the Teaching Materials with t-test.
Samples
Of Unit
Average
Pre-test
(n=15)
Average
Post-test
(n=15)
T Count
T table
=0.05 =0.01
Unit 1 51.7 68,7 2.9** 1,761 2,624
Unit 2 49.7 66 2.5* 1,761 2,624
Unit 3 53 62,7 3.8** 1,761 2,624
Description:
** = very significant; * = significant Ns = not significant
4 CONCLUSION AND
IMPLICATION
Refering to the discussion above, it can be concluded
that the teaching materials used in SEBASA POLRI ,
until recently, have not met the learners’ need (police
officers and the students of SEBASA POLRI).
Therefore, the
teaching materials have to
accommodate their needs and they are able to achieve
the learning goals.
The model of teaching materials English for
Police shares the following properties: giving
sufficient information and completing task,
presenting structure exrercises given in each unit,
presenting the model of text and exercises/tasks, and
creating an authentic task conducted
independently
or
in groups. The design of the developed teaching
materials model relevant to the criteria of teaching
materials of English for specific purposes is
formulated as follows: stating learning objectives and
specific needs; emphasizing its relevance to
disciplines or specific job field; presenting materials
to meet the standard of politeness with grammatical ,
lexical and language skills; stating successful
indicators (i.e. the students are able to use the target
language); using authentic materials ; fostering self-
directed learning; and putting a teacher as a learning
facilitator.
The result of test reveals that the teaching
material model is effective, using test and
questionnaires
as its parameter. The result of the t-test
for operational field tests describes that the teaching
materials model (final draft) is used effectively for
students in SEBASA POLRI. An effective model is
indicated with the results of t-test average with
significant level.
The analysis on the teachers’ and students’
perception towards the developed teaching materials
model reveals that: (1) they have a positive response
to the existing teaching materials, (2) they are
interested in using the developed teaching materials,
(3) the activities presented in the materials facilitate
the acquisition of language skills, (4) the learning
activities encourage students’ active learning, (5) all
language skills are developed, and (6) the teaching
materials are relevant to the labour field.
Developing a model of the teaching materials of
English for Police with communicative and Task-
Based Learning aproach was conducted to meet the
needs of the teaching materials relevant to the
students’ needs and the demands of the global
expectation. In addition, the present reseach brings
some implications. First, the the developed teaching
materials model can help achieve the purpose of
English learning at Language School Police. Second,
the developed teaching material model can
accommodate the students’ need. Third, the model
meets the teachers’ need for communicative teaching
materials which integrated all language skills. Forth,
it helps students who will work as police officers
develop their communicative competence. Fifth,
research on developing teaching materials of English
for Police with communicative approach and Task-
Based Learning can enrich the availability of
teaching materials.
REFERENCES
Basturkmen, H 2010, Developing courses in english for
specific purposes, Springer.
Borg, WR, Gall, MD, 1983, Educational research an
introduction, New York and London.
Celce-Murcia, M, Dörnyei, Z, Thurrell, S 1995,
'Communicative competence: a pedagogically
motivated model with content specifications', Issues in
Applied linguistics vol. 6, pp. 5–35.
BELTIC 2018 - 1st Bandung English Language Teaching International Conference
316

Hamalik, O 2003, Perencanaan pengajaran berdasarkan
pendekatan sistem, Bumi Aksara.
Hymes, D 1972, 'On communicative competence.
sociolinguistics 269293', pp. 269–293.
Larsen-Freeman, D, Anderson, M 2013, Techniques and
principles in language teaching 3rd edition-oxford
handbooks for language teachers, Oxford University
Press.
Maley, A, Grellet, F 1980, 'Making sense: reconciling ideas
and constraints in materials production', Projects in
Materials Design—ELT Documents Special, pp. 37–60.
Nunan, D, 2006, Task-based language teaching. Ernst Klett
Sprachen.
Skehan, P, 1996, 'A framework for the implementation of
task-based instruction'. Applied linguistics, vol. 17, pp.
38–62.
Stern, HH, Stern, HH, Tarone, EE, Stern, H, Yule, G 1983,
Fundamental concepts of language teaching: historical
and interdisciplinary perspectives on applied linguistic
research, Oxford University Press.
Tomlinson, B 2011, Materials development in language
teaching, Cambridge University Press.
Widodo, CS, Jasmadi, S 2008, Panduan menyusun bahan
ajar berb asis kompetensi, Jakarta, Elex Media
Komputindo.
Model of English Teaching Materials for Police with Communicative and Task-based Learning Approaches
317
