
The Design of E-Learning System to Support Academic
W
ri
t
i
ng
Skills
for Engineering Students of Vocational Higher E
du
c
at
i
on
Dita Lupita Sari
1
, Choirun Niswatin
2
1
Teknik Informatika, Politeknik Kota Malang, Jl.Tlogowaru, Malang,
Indon
e
s
ia
2
Teknik Telekomunikasi, Politeknik Kota Malang, Jl.Tlogowaru, Malang,
Indon
e
s
ia
Keywords: E-Learning, System Design, Academic Writing, English.
Abstract: Engineering students seem to have a great potential to globally disseminate their research. However, their
low proficiency in English skills, particularly academic writing becomes their major obstacle. In response to
that problem, this paper proposes the design of e-learning system encouraging their ability improvement in
doing so. The design of e learning is called Waterfall and it is applied as a method of software
development. It has 5 phases namely: communication, planning, modeling, construction and
deployment. This paper discusses its process including: communication, planning and modeling.
Modeling phase is visualized through DFD (Data Flow Diagram). This system is operated by three
different actors namely administrators, teachers, and students. Their roles are different. Administrator
refers to the users who manage all the management system. While the teachers manage the content
of e-learning, the students can access the learning materials, quizzes, as well as the template of abstract.
1 INTRODUCTION
The ability of writing skills particularly among
academician tends to show low quality. In line with
this, several studies show that students’ ability
in writing skill including their critical thinking
through writing is poor (Setiyaningsih, 2008)).
Buchori (2001) highlighted that poor writing skills
remained a common problem to numerous students.
In the same line, Alwasilah (2003) pointed out that
the ability of writing skill of universities alumni is
categorized in low level. This is signposted by the
process of writing a final assignment, such as thesis
or dissertation. Their final assignments frequently
have still got the errors even they had been
revised by their supervisors. These errors occur
mostly in linguistic matters covering orthography,
linguistics, and logical writing (Soewandi, 1992).
The problem of poor writing skill ability
occurs in Indonesian language, and it gets worse
when it comes to English as a foreign language.
This is worrisome because English proficiency pins
down very demanding in globalization era
nowadays for it is an international language.
Therefore, a study investigating writing skill could
be beneficial for university student for future life in
wider scope.
The curriculum of education in Indonesia sets
the English as a mandatory course which is
taught in elementary school or early junior high
school. However, the students’ proficiency is still
far. To be proficient in English means that they
have to learn four skills covering listening,
speaking, reading, and writing. The latter is
considered as the lowest level of proficiency. As a
matter of fact, the students’ ability tends to low
although they are formally taught writing skills
earlier in lower education level of schools before
enrolling the university (Waloyo, 2017). On the
contrary, language learners who study English have
been given writing skills as one of the cores of
curriculum. Because it is one of the four skills that
should be accomplished (Yamin, 2009). Hence, the
difficulties are possible to be overcome to achieve
the competency.
On the other hand, non-English learners face
bigger problem. The writing skills do not
become the main core of non-English field of
Sari, D. and Niswatin, C.
The Design of E-Learning System to Support Academic Writing Skills for Engineering Students of Vocational Higher Education.
DOI: 10.5220/0008221400002284
In Proceedings of the 1st Bandung English Language Teaching International Conference (BELTIC 2018) - Developing ELT in the 21st Century, pages 547-555
ISBN: 978-989-758-416-9
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
547

studies, engineering for example. As a result, when
the engineering students write the academic writing
using English, they obviously find some obstacles.
The research which encompassed the engineering
students as the object of the research found that
their writing skills are the lowest than other three
English skills; listening, speaking and reading (Xu,
2012). It can be concluded that the ability of
Indonesian scholars in English academic writing
is still poor, particularly those whose the
background of study is not English.
The low level of English proficiency
particularly academic writing has been pointed out
as the cause of the low number of international
publication. In fact, the percentage of Indonesian
contribution is only 0.0012% in the whole world
international publication. Paradoxically, this number
is the lowest number compared to other Asian
countries, i.e. Philippines (0.035%), Malaysia
(0.064%), Thailand (0.086%) and Singapore
(0.179%). The number becomes considerably lower
than European developed countries, i.e. France
(5.6%), Germany (7.2%), Greta Britain (7.9%),
Japan (8.2%), and United State of America (30.8%).
Some factors affecting the low number of
Indonesian contribution in global publication are
likely the low level of English academic writing in
terms of standardized English as well as the
ungrammatical tenses (Adnan & Zifirdaus, 2005).
Poor academic writing is credited to the most
students’ opinion that learning to writing
academically is very difficult (Susanti, 2003). It is
more difficult and challenging than other skills like
listening, speaking and reading. According to
(Oshima & Hogue (2006), academic writing is
difficult, indeed.
The result of preliminary survey which involved
engineering students at Polytechnic in Malang
found the difficulties on academic writing in
particular writing abstract for their final assignment.
It showed that they were confused how to construct
the words into sentence (70%). Other obstacles were
grammar (15.7%) and followed by vocabulary
(14.3%). The findings of the preliminary survey
was that it is required a great effort to write
standardized abstract. The students might
intensively consult to the lecturers, English lectures
(38%), and two lectures as their final assignment
supervisors (31.5). They needed to see them
more than 3 times (56.1%) at least until they felt
confident that their abstract was good.
Consequently, these are time consuming for their
lectures and required their efforts as well.
Furthermore, they still need translation application
though (87%).
A preliminary study showed that the
respondents need the learning aids to enhance their
ability to support their academic writing. Learning
aids ease lecturers’ efforts to supervise them
particularly in their busy time for other agendas
such as, preparing and evaluating teaching
materials, undertaking and disseminating research
projects, and etc. Therefore, this research aims to
design e-learning system as it is perceived that
such medium could improve the ability of
academic writing. A study conducted on Faculty
of Letters UPI in particular Germany department
indicates that e-learning is more effective to
improve students’ ability in Germany writing
academic. Findings show that those who use e-
learning achieve better result than those who use
conventional learning (Permana, 2013). In the same
line, an empirical data from nursery students at
Akademi Keperawatan Aisyiyah Bandung-
Indonesia showed that the use of e-learning
effectively increased their ability in academic
writing particularly medical record documentation
(Yualita, 2011) Thus, this research design e-
learning system aiming to improve the academic
writing ability for students who study
engineering at diploma 3 program. It is expected
that they are able to increase their ability in
academic writing and lessen the lectures’ work
when guiding them to produce good academic
writing.
2 LITERATURE
REVIEW
2.1 E-Learning
One of the important roles of technology in
education is e-learning. The words of e-learning
derived from two words i.e. 'e' which stands for
electronic and learning. E-learning is the activity
of learning process using electronics as the main
BELTIC 2018 - 1st Bandung English Language Teaching International Conference
548

media (Wena, 2010). It is online learning using
internet and intranet requiring a specific media
to display learning materials-course materials and
frequently asked questions. In addition, it still
needs the media to communicate for exchanging the
information among teachers and learners as the
users (Riyanto and Prasojo, 2011). Meanwhile,
Markwell (2003) define e-learning as the
instruction conveyed through computer using CD-
ROM, internet or Intranet employing the following
features:
a. Consisting of contents which are relevant to the
goal of learning.
b. Using instructional method such as
examples and exercises to support the learning
process.
c. Using media communication, such as words and
pictures to deliver the contents and methods.
d. Building knowledge and skills leading to the
goal of learning for individual or teamwork.
In conclusion, e-learning is the media of learning
delivered by electronic media providing learning
facilities in terms of learning materials, questions,
as well as information exchange requiring by
teachers and learners.
(Siahaan, 2002, p. 9) points out that the function
of e-Learning is supplement, complement, and
substitution. It is explained as follows:
a. Supplement
E-Learning is called a supplement when learners
freely have the options to use it. There is no
obligation for them to access it. However, for those
who do so seem to have more additional knowledge.
b. Complement
E-learning becomes a complement when the
learning materials in e-learning aimed to complete
the learning materials in the class room. It means
that e-learning serves as the reinforcement or
remedial media for the students when commonly
attending the class. E-learning also becomes
enrichment particularly for those students who are
considered as fast learners in a class room are
given the opportunity to access e- learning
materials which are specifically designed for them.
This e-learning aims to review all the materials
given by the teachers in classroom.
On the other hand, for students who are felt as
slow learners, e-learning turns into remedial
program. They get the difficult to understand the
learning materials in class room. Therefore, they
could access e- learning materials which are
particularly designed for them. Such e-learning
purposes to make slow learners easier to
understand the materials given by the teachers in
class room
c. Substitution
Universities in developed countries offer the
alternative learning models to their learners. The
objective of this model provides students’ flexibility
to manage their time to learn in their daily
activities. There are three models, i.e. 1) fully face
to face meeting in a class room just like
ordinary learning process (conventional class); 2)
partial models which mean that learning process
through conventional class and internet; and 3) full
internet.
In this research, the development of e-learning
aims to provide complement functions to support
the process of learning academic writing. There are
some components which should be taken into
account when developing the e-learning. Therefore,
e-learning could run well. These following three
components may develop e-learning (Wahono,
2007):
a. Infrastructure of e-learning
The infrastructure is the main devices used to run
the e-learning program such as personal computers
(PCs), computer networks, internet, and multimedia
application. Teleconference is also part of it when it
provides synchronous learning through
teleconference.
b. System and application of e-learning :
The system of software application is virtualized the
conventional learning process. This includes how to
manage class activity, create learning materials or
content, conduct forum discussion, assess learning
process, carry out the online examination, and other
features relate to classroom management. Those
software systems often called Learning
Management System (LMS). There are many
LMSs in open source that is simply operated.
What is more there are free of charge.
Content or materials of e-learning
The content or learning materials will be put in
The Design of E-Learning System to Support Academic Writing Skills for Engineering Students of Vocational Higher Education
549

Learning Management System LMS). It is in
Multimedia-based Content (interactive multimedia
content) or Text- based Content (as a common
printed books or references. These should be
put in storage system in LMS. The content is
easily operated by the user in anytime and in
anywhere.
An important component of infrastructure is
software of e-learning. One of the e-learning
software which plays the important role is Learning
Management System (LMS). LMS is a set of
solution designed to deliver, track, report and
manage the learning materials, monitor the progress
and interaction of the learners as well. LMS is a
software application for teaching and learning
process, such as running administration, filing
documents, creating report of learning process via
online connected to internet. The content or learning
materials are provided online web-based and
accessed through internet. In other words, LMS is
an application to make the learning process deliver
automatic and virtual electronically (Wahono,
2007). It provides features to meet the needs of
users in learning process. Currently, there are many
types of LMS embedded with the specific
features as required application.
LMS consists of materials in multimedia (texts,
animation, video, and sound) version serving as a
supplement and enrichment for learners’ aptitude.
LMS offers innovative learning system covering
information technology particularly virtual-based
through online learning web, multimedia, and video
conference. LMS web-based learning enables to
be developed dynamically or commonly known
as a dynamic e-learning (Munir, 2010). In general,
LMS is able to (Setiyo, 2013):
a. Upload and share the materials: LMS
provides the features to make the learning
materials easier to share. Course tutors will
upload learning materials as designed syllabus.
The materials could be in the form of main
topic of the materials, notes, articles, quizzes,
assessment, etc.;
b. Carry out forum and chat: Forum and
online chatting are a dialogue or conversation
between tutors and their students synchronously
or asynchronously (forum and emails). The
forum and chat allow the learners to write their
comments and discuss them with their classmates.
c. Create Quizzes and surveys: Online quizzes and
surveys let the learners present a quick score. This
instant grading is very good to get the learners’
direct responses to their achievement and
understanding of the learning materials;
d. Gather and review assignment: The result of
evaluation on learning achievement provides the
score to the learners automatically and online.
e. Record grades: LMS enables to monitor and record
the learners’ achievement automatically.
In the design of e-learning system conducted in this
research refers to the concept of LMS as above.
2.2 Academic Writing
Academic writing is a part of writing skill that
follows particular rules and format referring to
academic circumstances. The certain rules
and format differ the academic writing to
personal writing, such as writing on Blogs, writing
on walls of Facebook walls or articles in
newspapers and magazines. Swales & Christian
(2017) outline that academic writing is one of
writing products that should pay attention much to
readers, goal, organization, style, plot, and layout.
Besides, academic writing must present strong
argumentation as the state of the art unifying the
whole passage. Academic writing is classified into
several types (Phil, 2010):
a. a. Summary
Occasionally, reading summary lets readers’ choice
catch the main idea of the whole passage. The
summary is a typical brief text taken from written-
scientific works such as books, articles, journals,
research, etc. The goal of writing summary is to
convey the most prominent idea from a text to
readers and to present the concise explanation
providing by the robust argumentation to support
the main idea (Friedman, 1989). A summary
consists of the main idea of the background,
point of view, argumentation supported with the
details of justifications, methods (if it is a research),
and conclusion linked back to the conceptual
background without providing analysis,
interpretation, and evaluation (Friedman and
Steinberg, 1989). In general, a summary is 750-
BELTIC 2018 - 1st Bandung English Language Teaching International Conference
550

1000 words length (Phil, 2010). The summary of
books or research will significantly help students
when they prepare to write their assignment on
scientific works such as paper, thesis or dissertation.
Students tend to refer the summary of any types of
written-scientific works to support their own
writing, particularly writing critical review.
b. Critical Review
A critical review is thought writing which is more
complicated than a summary. A critical
review requires the ability to analysis texts as
the authors’ point of view, thesis, organization
techniques, and summary. The purpose of writing
critical review is to provide the evaluation on
quality of writing. There are two essential
questions to evaluate a critical review. The former is
‘is the information is objectively presented?’ The
latter is ‘is the authors’ opinion fair and reasonable
(Phil, 2010).
The organization of critical review covers
introduction, summary, critics, and conclusion. The
content of introduction of critical review is similar
to a common introduction of other written-scientific
works. Whereas, its summary provides the point
of view, main ideas, and authors’ conclusion.
Critics presents the evaluation of the importance
of writing elements such as topics, actuality,
length, authors’ objective, data interpretation, detail
explanation and authors’ practical ideas. The
conclusion of critical review gives the evaluation to
references. The average of critical review length is
around 1000-1500 words (Phil, 2010).
c. Essay
Essay is one of the academic writings that students
are most familiar with. Every semester, not a few
lecturers require their students to write an essay.
Hence, the ability to write essay is demanding for
students. Regardless numerous definitions on
what essay is, the acceptable organization
comprises introduction, body of the content, and
closing or conclusion. The average length of essay
is about 2500-3000 words with the proportions
around 10-20%, 60-70%, 15-25% for each part
respectively
(Phil, 2010)
d. Final Project
Any program of higher educational levels requires
students to write paper as their final assignment,
thesis or dissertation. The main differentiation of
final assignment in each level of program lies on
the depth of discussion and the number of words
count. Each institution has particular rules and
format for each type of final assignment. However,
the average number of words from academic books
from universities around the world is about (Phil,
2010).
Bachelor dissertation: 15.000-25.000 words
Master dissertation: 30.000-40.000 words
Doctoral dissertation: 80.000-100.000 words
Any types of written-scientific works
aforementioned above, whether it is summary,
critical review, essay, or final assignment require
abstract as a part of its paper. Abstract is short
cut for readers to get the main ideas of the whole
paper. Abstract is about 250-300 words for the
average length (Phil, 2010). There are 9 types of
abstract, i.e.: informative, indicative, informative-
indicative, critics, mini, sideways, basics, statistics,
or numeric, and authors’ abstract (Basuki, 1989).
The aim of abstract is: 1) to complete the part of
writing which will be published in journals, or
magazines letting the readers inform about the
articles that are going to be published; 2) to share
the information to library visitors that there are
documents that they need; 3) to help the readers to
gain the information that they need faster for
carrying out the research, supporting teaching
matters, or updating the up-to-date facts about
science and knowledge which are suitable to their
background field of study; 4) to hinder the language
problems (Sophia, 2002).
2.3 Waterfall Design Model
Waterfall model is a classic model to build software
in a systematic method. The real name of this model
is linear sequential model (LSM). It is well-known
for classic life cycle either or waterfall method.
Waterfall lets the steps of sequence run orderly. In
other words, the first step should be perfectly
finished then continued to the second step and so on
(Permana, 2015). Conversely, it could not run steps
randomly or in parallel way. This model is
categorized into a generic software model in
software engineering (SE) which is proposed by
The Design of E-Learning System to Support Academic Writing Skills for Engineering Students of Vocational Higher Education
551

Winston Royce in around 1970. This model is
underestimated as an out-of-date type, but it tends
to be widely used in SE. In short, this model
applies the systematic method as the following
sequences:
1. Communication (Project Initiation &
Requirements
Gathering)
Setting the need requirement by conducting
communication or interview with the users is the
starting point to develop the software. Need
requirement is the first step to collect the
predominant information beforehand to meet the
users’ goal of developing software. The result of
this need requirement is an initial project covering
analysis of the users’ problem, collecting required
data, defining features and determining function of
the software. Searching relevant information from
other references such as journals, articles, and
internet is also required to collect supporting data
2. Planning (Estimating, Scheduling, Tracking)
The next step is planning to outline of technical
works that are going to do such as: predicting the
risks including force- major, providing resources to
create the system, determining the outcomes,
scheduling the standard operating system containing
what are going to do, and tracking time line of the
working process of the system.
3. Modeling (Analysis & Design)
This step is designing and modeling the
architecture system focused on data structure design,
software architecture, interface display, and
algorithm program. It is aimed to fully understand
the framework of description on what to be done.
4. Construction (Code & Test)
This step is translation process from design
into code or particular language that is readable
by machines. After coding finished, the system and
code are tested. This aims to detect the errors and to
fix them afterwards.
5. Deployment (Delivery, Support, Feedback)
This step is implementing the software application
to customers, maintaining software periodically,
fixing software, evaluating software, developing
software linked back to the customers’ feedback to
make sure that the system works properly and
develops as the determined function.
3 METHOD
3.1 Data Collection
Before designing and building a software system,
depth analysis on functional requirement is required
to meet the users’ demands. This study utilized
interview and questionnaire to collect the data from
end-users.
The first step to determine the functional
requirements of e-learning system is to conduct a
preliminary survey. This survey aims to investigate
the problems encountered by students in academic
writing, particularly writing abstract of final
assignment. The survey was conducted by
distributing questionnaires to students of
engineering at Polytechnic in Malang, Indonesia.
There were two types of the participants; 1) students
who were writing abstracts in English for their
final assignment; 2) alumni who have graduated
for 2 years maximum. The result of questionnaire
is used to support data in interview
process.
Interviews involved the lecturers of English
course supported by the result of preliminary
survey. The results of the interview became a
general overview of the solution for solving the
problems encountered by the students which was
collected in the preliminary survey from the English
lectures’ point of view. In addition, these results
turned into the basis for determining the list of
functional requirements of e-learning system.
The list of system functional requirements then
should be tested to meet the needs of the users.
3.2 System Design
This research discussed about the process of
communication, planning and modeling. The
sequences of the waterfall are:
1. Communication (Project Initiation and
Requirements Gathering)
The initial step of the waterfall is building
communication with the end-users known as the
system requirement. Two types of instrument were
applied to attain system requirement. The former
was questionnaires which were distributed to
students of engineering at Polytechnic in Malang.
BELTIC 2018 - 1st Bandung English Language Teaching International Conference
552
The latter was interviews involving lecturers of
English course at Polytechnic in Malang.
2. Planning (Estimating, Scheduling, Tracking)
Planning is the second step of waterfall sequence
covering four main divisions: 1) data collection; 2)
interviews; 3) analysis and design of the system,
and 4) system development and tests. Data
collection was the only division engaging the field
assistants who are familiar with informatics to
make easier to collect data. The researcher
was the person-in-charge to conduct the remaining
divisions but the last one required a programmer to
help the researcher.
3. Modeling (Analysis & Design)
Data Flow Diagram (DFD) was used to design
system. The system is divided into 2 sub-systems.
The first is a subsystem which relates to academic
writing. Whereas, the final sub system relates to
English grammar.
4 FINDING AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Data Collection Result
The preliminary survey found that the most
common problems encountered by students in
academic writing were the difficulties in arranging
standard abstract. The difficulties lie on composing
words into sentences as well as the abstract format
(70%). The next problem was grammar constraints
(15.7%) and vocabulary (14.3%). This
preliminary data was useful to lead the interviews
involving the lecturers of English course.
The data analysis on questionnaire and
interview determined a list of functional
requirements of e-learning systems. The functional
system should provide:
a. Theory framework of academic writing.
b. Quizzes to improve the understanding of
academic writing.
c. Grammar matters such as tenses, synonym,
antonyms, paraphrasing, etc. to support the
grammatical sentences in abstract
composition.
d. Quizzes on grammar matters.
e. Templates for organizing abstract composition
to minimize the errors when writing abstract.
f. Print menu after finishing writing abstract on
a given template
g. Login feature for each user to provide
security service
4.2 System Design
The e-learning system was designed using DFD
(Data Flow Diagram). The main system of the e-
learning is divided into 2 sub-systems as explained
previously; 1) English grammar sub-system; and 2)
academic writing sub-system. The former subsystem
contained grammar matters commonly found on
abstract composition and exercises to support
writing grammatical sentences, such as tenses,
antonyms, synonyms, and paraphrasing. The latter
contains conceptual framework on abstract
composition. The academic sub-system also
provides a template menu to help the users organize
abstract composition. This menu attempts to
diminish the common errors on abstract format.
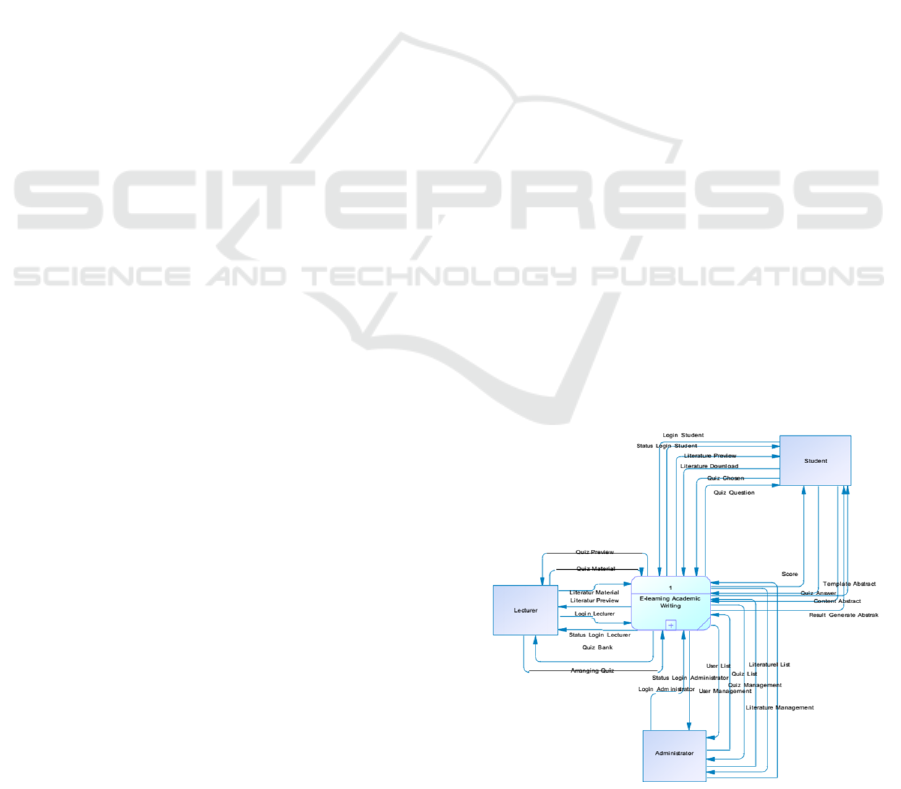
The e-learning system allows users’ permission
into 3 types of users, i.e.: 1) administrators, 2)
students, and 3) lecturers. The user administrators
are users who have responsibility to set up the
entire of e-learning system and confirm all e-
learning registries. This type of users is the persons
who are appointed by language centre at
Polytechnic in Malang. User students are users who
flexibly access all contents of e-learning, quizzes,
generate, and print abstract as well from given
template. They could be students from all over
Indonesia who are registered in DIKTI FORLAB
and have successfully registered on this e-learning
system. User lecturers are the lectures who run the
main materials as the contents of e-learning. These
users are the lectures who have been registered
and have permission to access e-learning
application from the administrators.
Figure 1: DFD Level 0
The Design of E-Learning System to Support Academic Writing Skills for Engineering Students of Vocational Higher Education
553
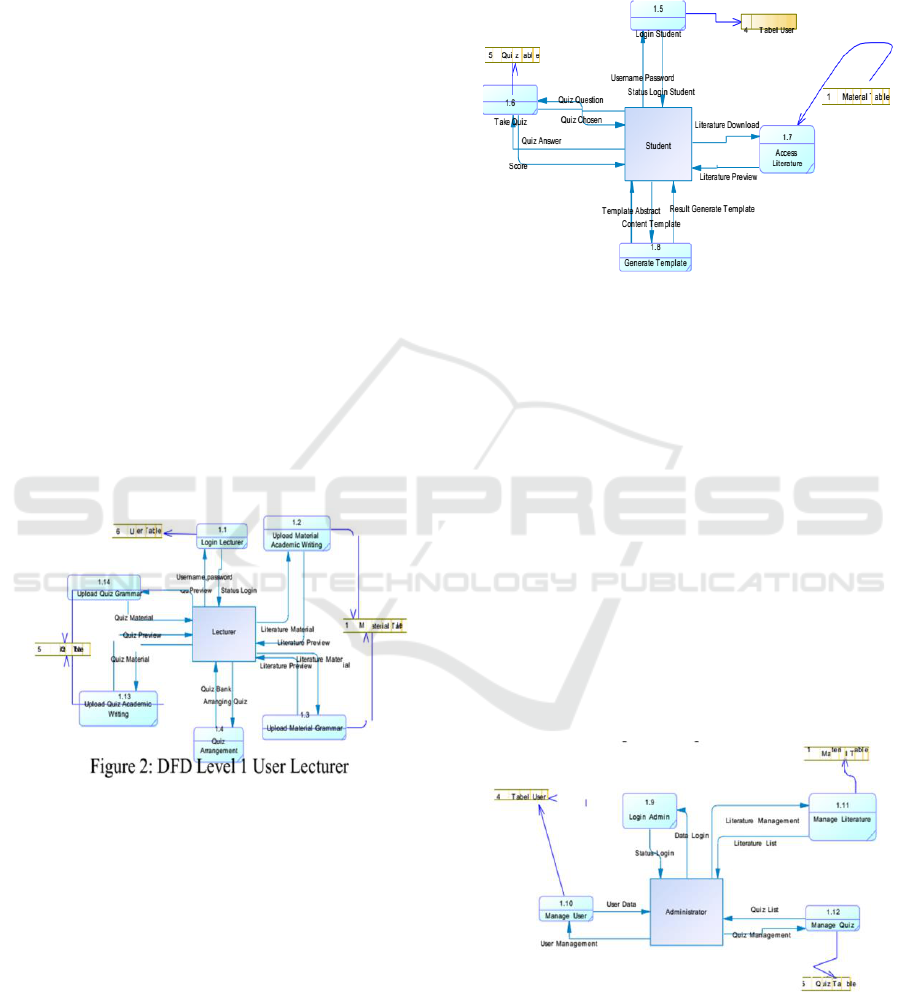
There are six processes that responsible by user
lecturer. The description of the user activity of the
lecturer is shown by DFD Level 1 in Figure 2.
a. Login Lecturer
The only users who could login this menu is the
lecturers who have already been registered to e-
learning system by entering their usernames and
passwords.
b. Upload learning materials
on academic writing
Lecturers are able to upload the main content of
academic writing, particularly writing abstract
serving as the learning materials.
c. Upload grammar materials
Lecturers upload grammar matters to support
learning materials particularly tenses, synonyms,
antonyms, paraphrase, etc.
d. Upload Quiz Academic Writing
Lecturers are allowed to upload quizzes on
academic writing particularly abstract composition
for final assignment.
e. Upload Quiz Grammar.
Lecturers upload the quizzes on grammar matters,
such as tenses, synonyms, antonyms, paraphrase, etc.
f. Quiz Arrangement
Lecturers design and modify the quizzes from
questions bank.
There are four processes that can be accessed by
user student. The description of the user activity of
the student is shown by DFD Level 1 in Figure 3.
a. Log in Student
This activity is only accessed by students who
had already been registered to e-learning system by
entering the username and password.
b. Access
Literature
Students are able to access e-learning materials
particularly the theory on academic writing as well
as grammar
c. Take Quiz
Students are allowed to take quizzes on academic
writing and grammar. This system lets them know
the instant score after submitting their quizzes.
d. Generate Template
Students are permitted to input the text of abstract
content into abstract template and easily print and
generate the text of abstract in certain format.
Figure 3: DFD Level 1 User Student
There are four activities which could run by
user administrators. The description of the user
activity of the administrator is shown by DFD
Level 1 in Figure 4.
a. Login Admin
As previous activities of other two users’
activities aforementioned above, this activity is only
run by the user administrators by entering
usernames and passwords.
b. Manage Users
User administrators have responsibility to provide
permissions to other users who were successfully
registered and verified.
c. Manage Literature
User administrators are able to manage and set up e-
learning system
.
d. Manage Quiz
These types of users have access to manage and set
up data of quizzes.
Figure 4: DFD Level 1 User Administrator
BELTIC 2018 - 1st Bandung English Language Teaching International Conference
554

5 CONCLUSION
Based on the results of questionnaires and
interviews, it is found that students need to improve
knowledge about grammar and academic writing.
Therefore the system is divided into 2 subsystems,
subsystem English grammar and subsystem
academic writing. Users are divided into three i.e.
administrator, student and lecturer. This division is
based on entire system and makes user permissions
settings. Students can access materials and practice.
Lecturers can upload material and questions.
REFERENCES
Adnan, Z, Zifirdaus, I 2005, Merebut hati audiens
internasional: strategi ampuh meraih publikasi di
jurnal ilmiah, Gramedia Pustaka Utama, Jakarta.
Alwasilah, H 2003, Bangsa yang besar adalah
bangsa yang menulis, departemen pendidikan
nasional, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Bandung.
Basuki, S 1989, Pengantar dokumentasi ilmiah,
KesaintBlanc.
Buchori, M 2001, Pendidikan antisipatoris, Penerbit
Kanisius, Yogyakarta.
Friedman, S 1989, Writing and thinking in the social
sciences, Englewood Cliffs, N.J., Prentice Hall.
Markwell, J 2003, 'E-learning and the science of
instruction: clark, r. c., and mayer, r. e. Biochemistry
and Molecular Biology Education', vol. 31, 217a –
218. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmb.2003.494031039994
Oshima, A, Hogue, A 2006, Writing Academic English,
Pearson Longman.
Permana, P 2013, 'Efektivitas penerapan learning
management system (lms) dalam meningkatkan
kemampuan menulis mahasiswa bahasa jerman',
Allemania, vol. 2, pp. 136–151.
Phil, A, P 2010, Panduan penulisan akademik 29.
Pressmanan, R 2015, Rekayasa Perangkat
Lunak (Pendekatan Praktisi) Edisi 7 : Buku
1. Available from: http://andipublisher.com.
Riyanto, Prasojo, L 2011, Teknologi informasi pendidikan
membahas materi dasar teknologi yang wajib dikuasai
pemula ti, Gava Media, Yogyakarta.
Setiyaningsih, Y 2008, 'Peningkatan kemampuan menulis
argumentatif dan keterampilan berpikir kritis
berbahasa indonesia mahasiswa melalui model
pembelajaran berdasarkan logika toulmin 14'.
Setiyo, L 2013, 'Perancangan e-learning dengan
menggunakan learning management system (lms)',
WidyaWarta.
Siahaan, S 2002, 'Studi penjajagan tentang kemungkinan
pemanfaatan internet untuk pembelajaran di SLTA di
wilayah Jakarta dan sekitarnya', Jurnal Pendidikan
dan Kebudayaan.
Soewandi, A 1992, Linguistik terapan dan penerapannya,
Widya Dharma.
Sophia, S 2002, Petunjuk Teknis Penyusunan Sari
Karangan Ilmiah. Seri Pengembangan Perpustakaan
Pertanian, Departemen Pertanian Bogo, Bogor.
Susanti, A 2003, Pengembangan model pembelajaran
kooperatif tipe circ untuk, docobook.com.
Swales, J, Christian, F 2017, Academic writing
for graduate students: essential tasks and skills.
Wahono, RS 2007, Sistem elearning berbasis model
motivasi komunitas dan penerapannya untuk
elearning publik 15.
Waloyo, E 2017, 'The implementation of mind mapping
technique in teaching writing: a case study at man
13 jakarta', ELT echo : The Journal of English
Language Teaching in Foreign Language Context,
vol. 2, pp. 72–83.
https://doi.org/10.24235/eltecho.v2i1.1596
The Design of E-Learning System to Support Academic Writing Skills for Engineering Students of Vocational Higher Education
555
