
Spiritual Well-Being and Depression of Indonesian Adults with
Diabetes Mellitus
Nunung Febriany Sitepu
1
, Febriani Khairunisa Pohan
2
1
Department of Medical Surgical Nursing, Faculty of Nursing, University of Sumatera Utara, Jalan Prof. T. Maas, Kampus
USU, Medan, Indonesia
2
Undergraduate Program of Nursing Study, Faculty of Nursing, University of Sumatera Utara, Jalan Prof. T. Maas,
Kampus USU, Medan, Indonesia
Key Words: Spiritual Well-being, Depression and Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract: Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease characterized by increased blood sugar levels. Complementary
complaints arising from chronic complications experienced and complex diabetes management can affect
the patient's physiological and psychological conditions. One psychological disorder that can arise is
spiritual well-being and depression. The spiritual well-being of the situation that underlies satisfaction in life
and the ability to express relationship with the creator is called His spiritual prosperity. Psychological
changes such as anxiety and depression experienced by people with diabetes mellitus can adversely affect
the development of diabetes mellitus. This study aims to determine the description of spiritual well-being
and depression in diabetes mellitus patients at primary health care center. This research is a descriptive
study conducted on 52 respondents with purposive sampling technique, data collection using spiritual
wellbeing scale and PHQ-9 questionnaires and statistic by descriptive analysis. Based on the results of the
study and a description of the discussion in this study it can be concluded that diabetes mellitus patients
have a high spiritual wellbeing of 48 people (92.3%) and experienced mild depression as many as 26 people
(53.8%). The high spiritual wellbeing because respondents still have hope, that hope is a multi-dimensional
concept that provides comfort as long as individuals experience life-threatening situations. Activities need
to be made to stimulate patients to care about mental health and physical health, such as screening the health
condition of people with diabetes mellitus at the primary health care center.
1 INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a degenerative disease,
which is predicted to continue to increase in
prevalence. According to WHO in 2011, diabetes
mellitus is one of the most common diseases
suffered by people worldwide for degenerative
diseases. The prevalence of diabetes mellitus in
adult populations around the world is expected to
increase by 35% in two decades and contract 300
million adults by 2025. The biggest part of this
increased prevalence will occur in developing
countries (Gibney, 2009). Based on the data from
the International Diabetes Federation (2014) that the
prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) in 2011 was
366 million sufferers and increased in 2013 to 382
million sufferers with the notion that 46% of
sufferers did not realize that they had been
conditioned diabetes mellitus (IDF, 2014). North
Sumatra Province is one of the provinces with the
highest prevalence of diabetes mellitus in Indonesia
with a 2.3% prevalence diagnosed by doctors based
on symptoms, this makes North Sumatra Province
one of the top 10 provinces with the highest
prevalence of diabetes mellitus in Indonesia
(Ministry of Health, 2014). In 2012, the city of
Medan included the largest number of patients with
diabetes mellitus, which continued to increase in
number. Based on data obtained from the Medan
City Health Office in 2012, the highest number of
cases after hypertension was diabetes mellitus. Until
2012 there were 10.347 people with diabetes
mellitus who went to 39 health centers in the city of
Medan. These data show that diabetes mellitus
patients in Medan City are very high (Medan City
Health Office, 2012).
250
Sitepu, N. and Pohan, F.
Spiritual Well-Being and Depression of Indonesian Adults with Diabetes Mellitus.
DOI: 10.5220/0008397100002442
In Proceedings of the Aceh International Nursing Conference (AINC 2018), pages 250-254
ISBN: 978-989-758-413-8
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Primary health care center in Indonesia has a DM
clinic with 1.010 visits and a total of 115 patients.
This shows that DM patients at the DM clinic at the
primary health care center often tend not to carry out
outpatient treatment routinely according to the
prescribed schedule. DM Clinic Health Center of
Community of Health is the first DM clinic in
Medan, DM primary health care center often
established in 2008 and is one of the hopes of the
Medan City Health Office to prevent an increase in
DM cases and all complications of DM. One of the
supporters of spiritual resources is the fulfillment of
spiritual wellbeing. Spiritual well-being is stated by
Ellison (1983) that the conditions underlying
satisfaction in his life and the ability to express His
relationship with the creator are called His spiritual
prosperity. Also affirmed by the National Interfaith
Coalition on Aging (NICA) in Washington
proposing spiritual wellbeing as an affirmation of
life in establishing a special relationship with God,
oneself, society and the environment by nurturing
faith, integrity to be together in personal peace
(Fisher, 2009).
Spiritual well-being is an integrated aspect of
humanity as a whole which is characterized by
meaning and hope. Spiritual health or well-being is a
sense of harmony that is close together between
oneself and others, nature and with the highest life.
This sense of harmony is achieved when one finds a
balance between the values, goals and belief systems
of individuals with their relationships within
themselves and with others. This belief is often
rooted in the person's spirituality. Throughout the
life of an individual may be spiritual will grow more
so that individuals become more aware of the
meaning, purpose and value of life (Ellison, 1983).
Spirituality gives a broad dimension to a holistic
view of humanity. The definition of spirituality or
dimension of spirituality will be unique and different
for each individual. Individual definitions of
spirituality are influenced by their own culture,
development, life experiences and ideas about life.
The spiritual dimension seeks to maintain harmony
or harmony with the outside world, trying to answer
or gain strength when facing emotional stress,
physical illness, or death, which is a force that arises
beyond human strength. Depression is a serious
mental disorder characterized by feelings of sadness
and anxiety. This disorder will usually disappear
within a few days but can also be sustainable which
can affect daily activities (National Institute of
Mental Health, 2010).
According to WHO, depression is a mental
disorder characterized by the appearance of
symptoms of decreased mood, loss of interest in
something, feelings of guilt, sleep disturbances or
appetite, loss of energy, and decreased concentration
(World Health Organization, 2010). Depression is a
mood disorder with sadness, feeling alone, low self-
esteem, despair, usually accompanied by signs of
psychomotor retardation or sometimes agitation,
withdrawal and physiological disorders such as
insomnia and anorexia (Kaplan, 2010). Depression
is a mood disorder characterized by loss of feeling of
control and subjective experience of severe
suffering. Mood is an internal emotional state that
permeates a person (Kaplan, 2010).
Psychological changes such as anxiety and
depression experienced by people with diabetes
mellitus can adversely affect the development of
diabetes mellitus. The prevalence of depression may
be higher in DM patients who have multiple
complications. Depression in DM patients is often
undetectable, and depression is a major barrier to
effective diabetes management.
The purpose of this research is to find out the
description of spiritual well-being and depression in
diabetes mellitus patients at the Primary Health Care
Center Indonesia.
2 METHODS
The time of this research was conducted in January -
June 2018. Sampling technique in this study uses
non probability sampling. Inclusion of the criteria
specified in the study are diabetes mellitus patients
who got treatment frequently at health care centers,
DM patients ≥2 years old, can read and write, can
communicate as well, the sample in this study were
52 patients with diabetes mellitus, data collection
using spiritual well-being scale and PHQ-9
questionnaire, statistic by descriptive analysis
.
3 FINDINGS
Based on the research that has been done, the
following are the results of respondent characteristic,
their spiritual well-being and their level of
depression.
The results on patient characteristics obtained
data that female patients were 26 people (50.0%)
and male sex as many as 26 people (50.0%). Other
patients, 18 people (34.6%). Most patients were 41-
60 years old as many as 27 people (51.9%). The
Spiritual Well-Being and Depression of Indonesian Adults with Diabetes Mellitus
251
majority of respondents who were the subject of this
study had a long history of suffering from 6-10 years
of diabetes mellitus as many as 34 people (65.4%).
The majority of other respondents' jobs were 24
people (46.2%). Furthermore, data on the spiritual
well-being of the respondent presented in table 2.
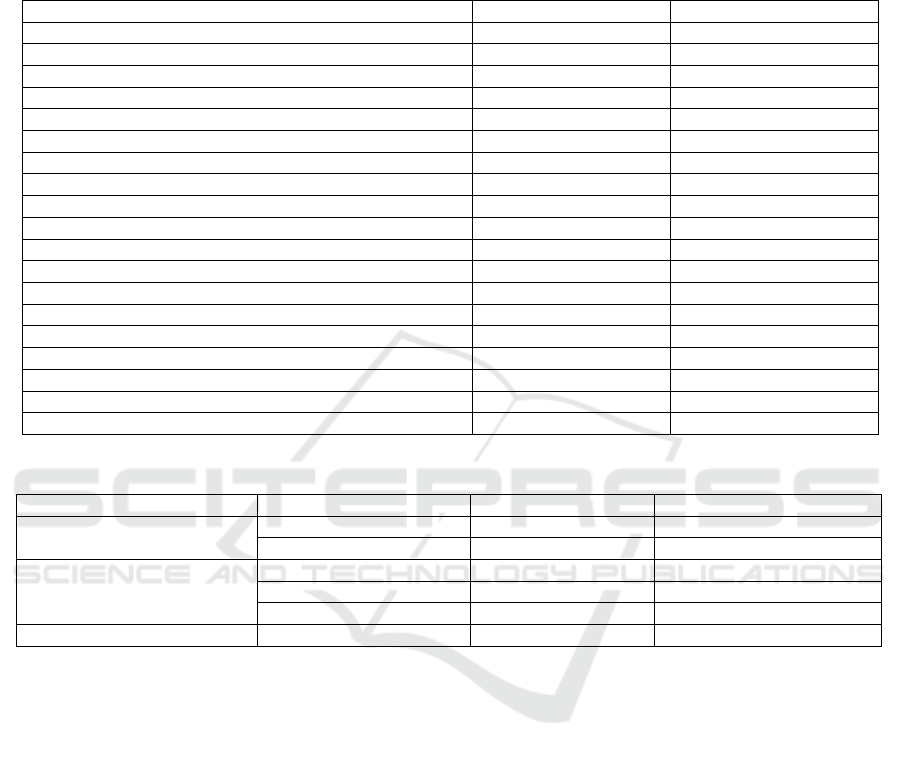
Table 1: Respondent characteristics (N=52).
Characteristics Frequency Percentage (%)
Sex
Male 26 50
Female 26 50
Race
Javanese 14 26.9
Bataknese 15 28.8
Sundanese 5 9.6
Others 18 34.6
Age (years)
21-40 20 38.5
41-60 27 51.9
61-80 5 9.6
Duration of diabetes (years)
6-10 34 65.4
11-15 17 32.7
16-20 1 1.9
Occupation
Government employee 7 13.5
Non-Government employee 12 23.1
Table 2: Respondent’s level of spiritual well-being and depression (N=52).
Level Frequency Percentage (%)
Spiritual well-being
Medium 4 7.7
High 48 92.3
Depression
Minimum 20 38.5
Mild 28 53.8
Moderate 4 7.7
Total 52 100
Spiritual well-being as shown in table 2, the
majority of diabetes mellitus patients have a high
spiritual welfare of 48 people (92.3%). According to
researchers, high spiritual well-being in patients
shows that patients have a hope of spiritual
strengthening in the patient According to Utama
(2015) the spiritual well-being of patients before
heart surgery approaches the highest value. From the
results of this study it can be concluded that spiritual
well-being is in the high category, this is influenced
by the age of respondents who are generally in
middle age and elderly. The results of the study
found that the majority of diabetes mellitus patients
in Primary Health Care Center had a high spiritual
wellbeing of 48 people (92.3%).
Based on the results of research on depression in
patients with diabetes mellitus data obtained that at
least 20 people depression (38.5%), mild depression
as many as 28 people (53.8%), moderate depression
as many as 4 people (7.7%).
4 DISCUSSION
According to Nugroho's opinion (2008), most of the
spiritual level in an elderly person has increased,
where the elderly are more organized in living their
daily spiritual lives. Research by Ellison (1983) that
the middle age group and the elderly have and
provide more time for religious activities and try to
understand religious values which are believed to be
a response to individual awareness in living religious
life. This can happen because the patient feels a
meaningful relationship with God through prayer
and the emergence of hope, strength in healing the
disease. This is supported by Eom( 2011) personal
communication with God can provide strength, hope
and is part of trust. This is evidenced in patient
statement that "I believe that God loves me and
cares about me. According to Chandler, Cynthia K,
Holden, Janice Miner, &Kolander, Cheryl. (1992
AINC 2018 - Aceh International Nursing Conference
252

(2004), hope is a multi-dimensional concept that
provides comfort as long as individuals experience
life-threatening situations.
Hope is energy that can give individuals
motivation so that they help patients overcome life
pressure. Improving spiritual welfare also occurs
because the patient feels his life is prosperous and
God is watching what happens to him and there is a
meaningful belief in his life. This is also supported
by McEvoy (2005) that spiritual beliefs will create a
sense of self so that it can provide a purpose and
meaning in life and gain a positive outlook and
surrender to the disease that is natural.
This is in line with Gray (2006), that spiritual
well-being will create spiritual health. Individuals
get spiritual health by finding a balance between
values, goals, beliefs and relationships in themselves
and others. The spiritual well-being that has been
explained above illustrates the need for meaning
from life, whether it is from the creator or the
individual effort de Wildman, (2012) that existential
spiritual well-being is a process of how individuals
respond to themselves and their lives. An existential
welfare indicator of a good individual is that the
individual can interpret the purpose of life and feel
peaceful in his life.
Another thing that can affect is that culture in
Indonesia is very thick with doctrine and puts
forward a relationship with God in spiritual
improvement. This is in accordance with the opinion
of Bredle et al., (2011) that spiritual well being
based on religious doctrine is more visible than
based on the ex-Depression in patients with diabetes
mellitus is a complex condition, where the known
etiology is still very lacking. But many factors
influence the occurrence of depression. Depression
is also a risk factor of the most important
psychological aspects in patients with diabetes
mellitus that can reduce the quality of life of
patients. This can occur because related to serotonin.
In the neurons the presence of serotonin that binds to
serotonin receptors can activate chemical signals
that are believed to affect a person's psychological
function (regulation of mood, sexual desire, sleep,
appetite) (Bredle and Jason M,2011).
Depression in DM patients is the result of the
fact that someone diagnosed with DM will
experience (Paloutzian, R., Bufford, R., & Wildman,
A. 2012) a pattern of life and the danger that
threatens they life ( This is as stated by depression is
expected in 2020 to be the second most common
cause of disability. Based on the results of the study,
there was also a correlation between the occurrence
of depression and age, which reminded health
workers of the importance of examining all factors
related to aging and not only paying attention to one
aspect. Depression screening in the elderly will help
diagnose depression in the elderly better and be able
to provide needed care (Singh, Padmanabhan &
Arora, Pratap (2010). Elderly people aged 85 and
older are more susceptible to depression than other
age groups. Elderly patients with DM often have to
deal with a variety of health problems and various
complex health check schedules. In addition, the
patient's family and elderly patients will find it
difficult to differentiate the decline in the physical
condition of the patient whether it is physiologically
due to old age or due to the progression of DM
complications experienced by the patient Eom, et.all
(2011) that disease is a life threatening condition.
For that disease is often a source of depression that
is very high, and people who are suffering from a
disease that does not understand what is experienced
and treatment. On the other hand, diabetes and
depression can be said to be a couple who often
appear.
5 CONCLUSION
Based on the results of the study and a description of
the discussion in this study it can be concluded that
diabetes mellitus patients have a high spiritual
welfare of 48 people (92.3%) and experienced mild
depression as many as 26 people (53.8%). The high
spiritual welfare because respondents still have
hope, that hope is a multi-dimensional concept that
provides comfort as long as individuals experience
life-threatening situations.
REFERENCES
Bredle, Jason M., 2011. Spiritual well-being as a
component of health-related quality of life: the
functional assessment of chronic illness therapy—
spiritual well-being scale (FACIT-Sp). Journal
Religions 2, 7794;
Chandler, Cynthia K, Holden, Janice Miner, & Kolander,
Cheryl., 1992. Counseling for spiritual wellness: theory
and practice. Journal of Counseling and Development.
November/December 1992. Volume 71
Ellison C.W., 1983. Spiritual well-being:
conceptualization and measurement. Journal of
Psychology & Theology, 11, 330–34
Eom, S.Y. et al. (2011). “Evaluation of Stress in Korea
Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Using the Problem
Areas in Diabetes-Korean Questionnaire”. Diabetes
and Metabolism Journal.35:182-187.
Spiritual Well-Being and Depression of Indonesian Adults with Diabetes Mellitus
253

Fisher, J., 2009. Perkembangan dan Aplikasi Kuesioner
Spiritual Well-being SHALOM. Religions, Volume 1,
105-121.
Fisher J., 1999. Helps to fostering students’ spiritual
health. International Journal of Children’s Spirituality
vol 4, no 1. 1999
Gibney, M.J., et al., 2009. Gizi kesehatan masyarakat.
Jakarta: EGC
International Diabetes Federation. Weight loss surgery
reduces diabetes risk. (Online). 2014. www.idf.org
Retrieved on 12 November 2017
Singh, Padmanabhan, Arora, & Pratap., 2010. Antecedents
of individual well-being. Journal Vision: The Journal
of Business Perspective 2010 14: 191
World Health Organization (WHO)., 2014. Definition,
diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its
complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classifications of
diabetes mellitus. Geneva: Department of Non-
communicable Disease Surveillance.
World Health Organization. 2010. Depression.
http://www.who.int/en. Retrieved on 4 November
2017.
AINC 2018 - Aceh International Nursing Conference
254
