
Discrete Mathematics’ Textbook Development based on
Multiple Intelligences
Sunyoto Hadi Prajitno and Erlin Ladyawati
Mathematics Education Department, University of PGRI Adi Buana Surabaya,
Jl. Ngagel Dadi III-B No. 37, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Discrete Mathematics, Multiple Intelligences, Textbook Development
Abstract: The purpose of learning Discrete Mathematics is to improve students' abilities to organize reasons or
develop intelligence. However, students learning outcome is still low. One of the students’ weaknesses of
mastering Discrete Mathematics is that it is difficult to understand the lesson that involves less students'
logical thinking. For that reasons and many obstacles in learning discrete mathematics, so the researcher
develops discrete mathematics textbook based on multiple intelligences. The problem statement of this
research is "How to increase Multiple Intelligence of University of PGRI Adi Buana of Surabaya’s student
using Discrete Mathematics textbook that was developed?". The Multiple Intelligence developed only
limited to 3 intelligences: linguistic intelligence, logical mathematical intelligence, and visual spatial
intelligence. The development of teaching materials is based on a modified 4D model consisting of four
stages: definitional, design, development, and disseminate phases. To know the learning progress based on
multiple intelligences, the researcher develops some problems containing applied of discrete mathematics.
The problem is given to students before using textbooks that have been developed and after using textbooks.
The results of the research are linguistic intelligence increased by 78%, logical mathematical intelligence
increased by 80.13% and visual spatial intelligence increased by 67.47%.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the things that also become an obstacle for
students in learning mathematics is the approach and
way of organizing learning material in higher
education due to the teacher's point of view. In the
learning process, the lecturer must be able to
conduct a conducive learning atmosphere, so that he
is able to pay attention to several variables in
learning such as teaching methods, learning
conditions and learning outcomes. There are many
characteristics of students such as background,
gender, learning style, interests, talents and
intelligence (intelligence). On some occasions
lecturers sometimes do not provide enough
motivation and applications when they will give a
certain subject matter because they know that the
material to be taught generically is definitely very
important for students. Especially for intelligence, it
is generally defined as the ability to understand
information that forms knowledge and awareness.
Intelligence is the ability of students to think
abstractly and logically so that they can adapt to new
situations. According to Gardner (2003) there are
seven types of student intelligence and then
developed into eight by Lazear (2004), namely
linguistic intelligence, mathematical logic, space-
dimension (visual-spatial), music, kinesthetic,
interpersonal, intrapersonal, and intelligence.
naturalist. Intelligence does not improve but can be
developed.
The theory of intelligence proposed by Gardner
(2003) is known as the theory of multiple
intelligences. Each individual has eight intelligences,
but the level is different, depending on which type of
intelligence is more dominant. Intelligence plays an
important role in achieving student success. The
multiple intelligence theory proposed by Gardner
(2003) can help lecturers to maximize student
learning outcomes by utilizing the type of
intelligence held by students.
Learning in Discrete Mathematics courses has a
strategic position to develop students' reasoning
abilities and can be seen as an exercise to organize
reason or develop intelligence. However, conditions
in the classroom indicate that student learning
222
Hadi Prajitno, S. and Ladyawati, E.
Discrete Mathematics’ Textbook Development based on Multiple Intelligences.
DOI: 10.5220/0008519702220227
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mathematics and Islam (ICMIs 2018), pages 222-227
ISBN: 978-989-758-407-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

outcomes from Discrete Mathematics subjects are
unsatisfactory. One of the constraints of students in
mastering Discrete Mathematics is that students find
it difficult to understand the lesson because the
learning process does not involve students to think
critically about the problems given by the lecturer.
Another obstacle in the process of learning Discrete
Mathematics is the limited learning resources,
references, books, modules and teaching materials
that are easily understood by students. In fact,
Discrete Mathematics material is books that use
foreign languages. From the problems described
earlier, students were not motivated to learn Discrete
Mathematics. So, thinkers think that it is necessary
to develop a learning resource for Discrete
Mathematics. Compound intelligence is one of the
keys to teaching students to solve non-routine
problems. Multiple intelligences are important
because they will be an important component in
developing students' analytical skills and critical
abilities.
In this study, researchers developed what needed
to be done to solve the problem was to develop
teaching materials that could increase multiple
intelligence. Double intelligence is one of the keys
to teaching students to solve non-routine problems.
Double intelligence is important because it will be
an important component in developing students'
analytical and critical skills.
Based on the description above, we will present a
research article on the subject matter "How does the
increase in Multiple Intelligence of PGRI Adi Buana
Surabaya University students after using the results
of the development of textbooks on Discrete
Mathematics courses?". Multiple Intelligence
developed is limited to 3 intelligences, namely:
linguistic intelligence (linguistic intelligence),
mathematical logic intelligence (logical
mathematical intelligence), and spatial visual
intelligence (visual spatial intelligence).
2 BASIC THEORY
2.1 Discrete Mathematics Textbooks
Based on Wikipedia (2010), the definit ion of a
textbook is a manual of instruction in any branch of
study. Textbooks are produced according to the
demands of educational institutions. (accessed on
July 9th, 2018 on
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Textbook).
Textbook is a book used in teaching and learning
activities that contain teaching materials based on
the curriculum applied. In this study the teaching
materials produced is a textbook. The textbook is a
basic knowledge base and used as a learning tool
and is used to accompany lectures and independent
learning (Kurniawan, 2014 and Suroso, 2004).
The textbook in this study is the result of module
development of the research in the first year. This
teaching material as an educational process
supporter and implementation of the material as an
exercise. The teaching materials development is
done based on a systematic process so that the
validity and reliability of teaching materials can be
guaranteed. There are several factors that can affect
the quality of teaching materials and should always
be considered in the development process of
teaching materials, namely content, scope, legibility,
language, illustration, covering and packaging. The
quality of instructional materials is highly dependent
on the accuracy in implementing of these factors in
developing teaching materials.
2.2 Multiple Intelligences
Based on Gardner's research there are eight different
human intelligences of the students, then the other
researchers was added two more intelligences, so
that on the last research explained, there are 9
intelligences owned by the students. The following
explanation will be briefly described the ten
intelligences.
1. Verbal/linguistic Intelligence
This intelligence is an intelligence related to the
ability of the students in speech, writing, and
how to express oneself in words. The ability in
using language, poetry, stories, grammar,
symbolic thinking, is the expression of this
intelligence.
2. Logical-Mathematical Intelligence
Logical-mathematical intelligence is often called
scientific thinking, including deductive and
inductive thinking. This intelligence is a linear
brain intelligence that is activated when a person
faces a new problem or challenge and tries to
solve it.
3. Visual-Spatial Intelligence
Visual intelligence is the intelligence related to
drawing, painting, using charts and maps, and
searching for different places/route. Other
expressions of this intelligence are visual art,
navigation, viewability space, architecture, chess
games. The visual-spatial intelligence is related
to the senses of view and imagination. The
Discrete Mathematics’ Textbook Development based on Multiple Intelligences
223

students with the visual-spatial intelligence start
their work by describing something in their head
and then redrawing it into a medium of paper, a
computer, or something.
4. Body/Kinesthetic Intelligence
The Body/kinesthetic intelligence is the ability to
control the body to do the activity and to express
feelings. The expression of this intelligence is
Dancing, sports games, clowns, pantomimes,
typing, and others.
5. Musical/Rhythmic Intelligence
Rhythmic intelligence involves the ability of the
students to recognize and to use rhythm and tone,
and sensitivity to sounds. In over the world,
music and ritmik can be changed the human
awareness.
6. Intrapersonal Intelligence
Interpersonal intelligence is the ability to
understand the condition of the other people and
to make a good relationship. In other hand,
Interpersonal intelligence can be described as the
ability of the people to understand oneself, such
as feelings, thinking processes, self-reflection,
intuition, and spiritual.
7. Naturalistic Intelligence
Naturalist intelligence is mostly owned by
environmentalists. A countryside resident can
recognize the signs of the environmental change
by looking at natural phenomena.
8. Spiritualist Intelligence
Spiritual intelligence is mostly belonged to the
clergy. This intelligence related to the
relationship between humans and their God.
9. Existentialist Intelligence
Existential intelligence is often found in
philosophers. They are able to realize and aware
about the existence of himself in this world and
what the purpose of his life.
Using multiple intelligences, a lecturer can give
the opportunities for students to learn the material
based on their needs, interests, and talents. Students
will be able to show their ability to build the
characteristic and motivation in learning discrete
mathematics.
3 DEVELOPMENT OF LEARN-
ING SYSTEM
The development model that will be used to develop
learning tools in this study is the model of
Thiagarajan et al. (1974: 5-9) known as Four-D
Models (4D Model). The 4D model was chosen
because it was more systematic and suitable for
developing learning tools, but in this study,
researchers made modifications to the 4D model.
This is done because the 4D model is designed for
learning for exceptional pupils while the subject of
this research is normal / normal students. The
modifications made in this study will be explained
as follows.
Steps for Developing Textbooks
The following illustrates the flowchart of the
module development steps (figure 1).
Figure 1: 4-D Models.
4 RESEARCH METHOD
Research Location
The location where this research took place is
PGRI University Adi Buana Surabaya Campus 1
Preliminary
Analysis
Analisis Mahasisa :
1. Conseo Analysis
2. Task Analysis
Lecture Needs
Analysis
DEFINE
Preliminary data
Mulitiple intelligence
Textbook Format
Analysis
Designing Textbooks
(Draft 1)
DESIGN
Validation of
Material Expert
Revision of 1
Textbook
(Draft 2)
Readability test
Revision of 2
Textbook
(Draft 3)
Editing
Final Textbook
Report
DEVELOPE
ICMIs 2018 - International Conference on Mathematics and Islam
224
which is located at Jl. Ngagel Dadi III-B No. 37
Surabaya.
Research Variables
The population of this research were all seventh
semester Mathematics students who programmed the
Discrete Mathematics subject of the University of
PGRI Adi Buana Surabaya. The subjects of this
study were 37 students in Class A.
Data Collecting Technique
In this study, the data obtained are relating to
multiple intelligences. The data was obtained from
students who took Discrete Mathematics courses.
Multiple intelligence data is obtained by the test
sheet.
Analysis Data Technique
The collected data were analyzed descriptively using
the average answers. The results of the Multiple
Intelligence Test sheet are obtained from the number
of values of the three intelligences possessed
× 100%, (1)
where P is percentage of increasing student
achievement of each intelligence,
is data of the
respondent's initial value / score for each
intelligence question,
is data of the final score /
score of each respondent on intelligence, and N is
the number of respondents.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Examination (UAS) the subject is given a problem-
solving problem regarding the Discrete Mathematics
course. The questions given before and after the use
of textbooks are the same, consisting of 6 (six) items
with details of 2 (two) questions for linguistic
intelligence, 2 (two) questions for spatial visual
intelligence, and 2 (two) questions for logical
intelligence mathematics.
From the table 1, it can be calculated the
percentage of increase in linguistic intelligence
values as follows:
P =
× 100%
P = 78.54406 %
P ≈ 78.54%.
So, the percentage increase value for linguistic
intelligence is 78.54%.
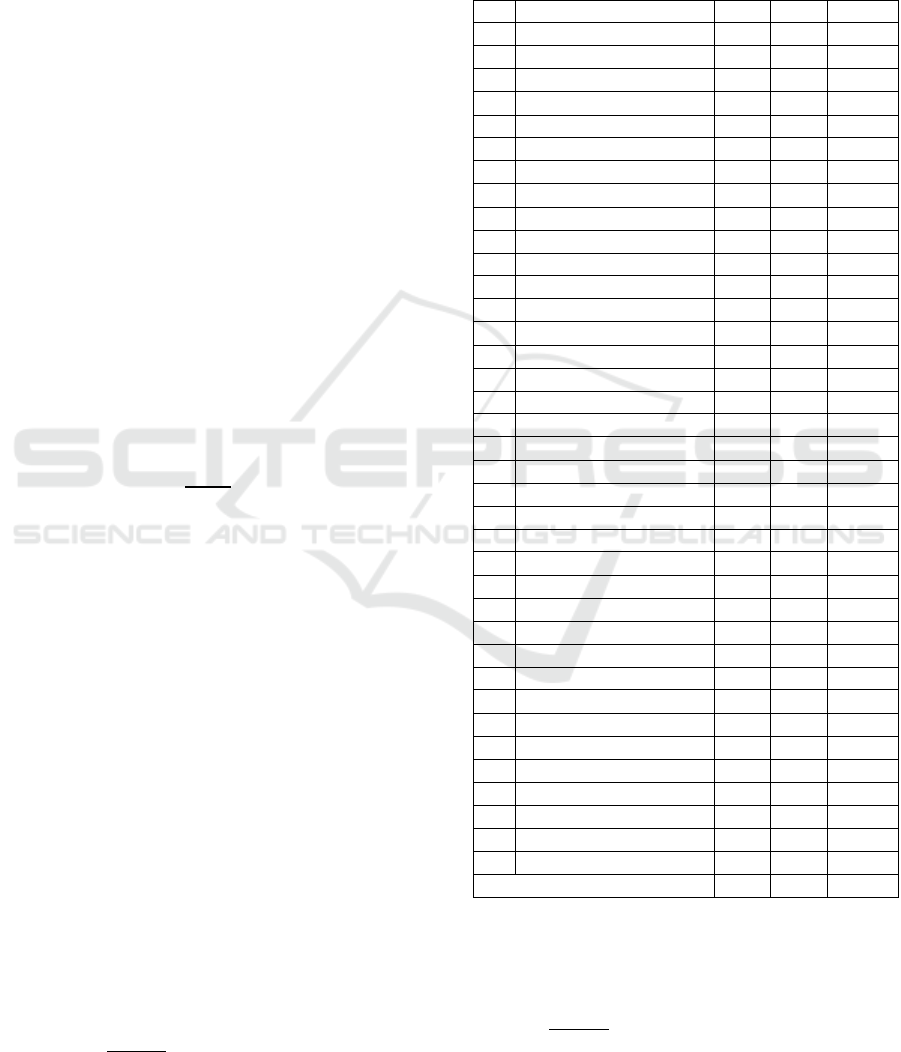
Table 1: Multiple Intelligences student test results for
Linguistic intelligence
No
Subject Name
-
1
Shilvia Putr iPradana
49
90
41
2
Ike Yuniarsih
46
88
42
3
Ruri Dwi Suciyanti
46
90
44
4
Jiwanti Mahmudah
47
92
45
5
Alifah Nur Aini
60
90
30
6
Afrian Kurniawan
61
92
31
7
Dwi Mardiana
47
92
45
8
Lidia Concita
61
86
25
9
Winda Paramita
47
94
47
10
Wahyu Ningtias
48
89
41
11
Wahyudi Edo Awanda
61
88
27
12
Ina Triana
46
86
40
13
Paskalia Mediayana
62
88
26
14
Maria G Jehabut
46
85
39
15
Mira Dewi Damayanti
47
90
43
16
Febry Fitria Pratiwi
48
86
38
17
Nurul Laili Karimah
60
86
26
18
Rosita Dewi
45
90
45
19
Erma Adiningsih
61
86
25
20
Emmanuel Mahardhika
47
84
37
21
Yulin Pratiwi Suwarno
46
85
39
22
Dinik Nofiah Ningrum
42
85
43
23
Shinta Dewi Suparno
47
90
43
24
Sulimah
46
88
42
25
Apriliani Ayuningtyas
44
88
44
26
Siti Nur Azizah
58
92
34
27
Nur Azizatun Ni`Ma
20
85
65
28
Dina Mustafidah
40
86
46
29
Hana' Fairuz Mufidah
45
85
40
30
Annisa Zuhrotul
45
87
42
31
Siti Asmaul Azizah
62
88
26
32
Mega Rahayu
47
94
47
33
Santi Dwi Lestari
59
88
29
34
Miftakhul Hidayah
43
85
42
35
Vida Ayu Amaliya
43
90
47
36
Lulu Eka Oktaviani
42
80
38
37
Deny Triyanto
63
94
31
Average
49.3
88.1
38.7
From the table 2, it can be calculated the
percentage of increase in logis mathematic
intelligence values as follows:
P =
× 100%
P = 80.12862 %
Discrete Mathematics’ Textbook Development based on Multiple Intelligences
225

P ≈ 80.13%.
So, the percentage increase value for logis
mathematic intelligence is 80.13%.
Table 2: Multiple Intelligences student test results for
Logis Mathematic intelligence.
No
Subject Name
-
1
Shilvia Putri Pradana
34
82
48
2
Ike Yuniarsih
47
72
25
3
Ruri Dwi Suciyanti
37
70
33
4
Jiwanti Mahmudah
30
72
42
5
Alifah NurAini
42
76
34
6
Afrian Kurniawan
46
80
34
7
Dwi Mardiana
40
76
36
8
Lidia Concita
43
76
33
9
Winda Paramita
39
74
35
10
Wahyu Ningtias
54
72
18
11
Wahyudi Edo Awanda
49
74
25
12
Ina Triana
46
78
32
13
Paskalia Mediayana
47
72
25
14
Maria G Jehabut
36
70
34
15
Mira Dewi Damayanti
40
78
38
16
Febry Fitria Pratiwi
49
68
19
17
Nurul Laili Karimah
54
82
28
18
Rosita Dewi
47
80
33
19
Erma Adiningsih
18
76
58
20
Emmanuel Mahardhika
55
74
19
21
Yulin Pratiwi Suwarno
41
78
37
22
Dinik Nofiah Ningrum
40
75
35
23
Shinta Dewi Suparno
43
74
31
24
Sulimah
44
70
26
25
Apriliani Ayuningtyas
39
68
29
26
Siti Nur Azizah
56
75
19
27
Nur Azizatun Ni`Ma
17
64
47
28
Dina Mustafidah
35
82
47
29
Hana' Fairuz Mufidah
38
80
42
30
Annisa Zuhrotul
43
82
39
31
Siti Asmaul Azizah
54
75
21
32
Mega Rahayu
40
82
42
33
Santi Dwi Lestari
51
80
29
34
Miftakhul Hidayah
36
78
42
35
Vida Ayu Amaliya
40
74
34
36
Lulu Eka Oktaviani
39
80
41
37
Deny Triyanto
46
82
36
Average
42.0
75.7
3.36
From the table 3, it can be calculated the
percentage of increase in visual-spasial intelligence
values as follows:
P =
× 100%
P = 67.47487%
P ≈ 67.47%
So, the percentage increase value visual-spasial
intelligence is 67.47%.
Table 3: Multiple Intelligences student test results for
visual-spasial intelligence.
No
Subject Name
-
1
Shilvia Putri Pradana
46
92
46
2
Ike Yuniarsih
61
80
19
3
Ruri Dwi Suciyanti
36
87
51
4
Jiwanti Mahmudah
44
74
30
5
Alifah Nur Aini
45
70
25
6
Afrian Kurniawan
60
82
22
7
Dwi Mardiana
39
84
45
8
Lidia Concita
46
82
36
9
Winda Paramita
35
72
37
10
Wahyu Ningtias
55
72
17
11
Wahyudi Edo Awanda
63
75
12
12
Ina Triana
48
72
24
13
Paskalia Mediayana
61
72
11
14
Maria G Jehabut
39
70
31
15
Mira Dewi Damayanti
44
72
28
16
Febry Fitria Pratiwi
45
80
35
17
Nurul Laili Karimah
55
72
17
18
Rosita Dewi
60
82
22
19
Erma Adiningsih
17
70
53
20
Emmanuel Mahardhika
43
60
17
21
Yulin Pratiwi Suwarno
45
74
29
22
Dinik Nofiah Ningrum
39
75
36
23
Shinta Dewi Suparno
44
74
30
24
Sulimah
63
80
17
25
Apriliani Ayuningtyas
39
64
25
26
Siti Nur Azizah
63
72
9
27
Nur Azizatun Ni`Ma
22
74
52
28
Dina Mustafidah
36
80
44
29
Hana' Fairuz Mufidah
40
82
42
30
Annisa Zuhrotul
47
80
33
31
Siti Asmaul Azizah
53
80
27
32
Mega Rahayu
38
80
42
33
Santi Dwi Lestari
54
78
24
34
Miftakhul Hidayah
36
83
47
35
Vida Ayu Amaliya
48
74
26
36
Lulu Eka Oktaviani
36
80
44
37
Deny Triyanto
46
82
36
Average
45.7
76.5
30.8
Discussion
Multiple intelligence theory suggests that everyone
has several levels of intelligence and has their own
intelligence profile, Mahmot et al., 2014, in
Maharani (2015). This intelligence profile is in the
form of 8 intelligences that have been initiated by
Gardner (2003), namely linguistics, logic-
ICMIs 2018 - International Conference on Mathematics and Islam
226

mathematical, visual-spatial, kinesthetic, music,
interpersonal, intrapersonal, and naturalist. The
intelligence discussed in this study is only three
intelligences, namely linguistic intelligence,
mathematical logic intelligence, and spatial visual
intelligence. Linguistic intelligence is the ability to
think in the form of words, use language to express,
and appreciate complex meanings. Logic-
mathematical intelligence is the ability to count,
measure, and consider a proposition and hypothesis,
and complete the operations of numbers. Visual-
spatial intelligence is a way of looking at certain
projections and the capacity to think in three
dimensions. This intelligence allows one to explore
imagination, for example modifying the shadow of
an object by performing a simple experiment.
The application of the third theory of intelligence
is one of which can be fulfilled through textbooks.
In a learning that uses certain instructional materials
must pay attention to the specifications or
qualifications of changes in attitudes and behaviors
so as to be expected. The textbooks used must also
be right on the target. Educators should also know
the purpose of the learning so that the objectives of
learning must be formulated so clearly. Because
teaching that has no direction and purpose will be
difficult to be processed and understood by students.
The implementation of textbooks that apply
Multiple Intelligence can be observed through
learning outcomes tests. In this study teaching
materials were prepared based on Multiple
Intelligence and based on Thiagarajan's theory
(Thiagarajan, 1974) that applies step 4D in product
development, namely define, design, and
development, this research was carried out and
obtained results. Based on the test results before and
after using textbooks as a learning guide, the results
obtained from the percentage increase in linguistic
intelligence was 78.54%, for mathematical logic
intelligence was 80.13%, and for mathematical logic
intelligence was 67.47%.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study are textbooks on
Discrete Mathematics courses based on Multiple
Intelligence. Test results before and after using
textbooks as a learning guide showed that the
percentage increase for linguistic intelligence was
78.54%, for mathematical logic intelligence was
80.13%, and for visual-spatial intelligence was
67.47%.
REFERENCES
Gardner, Howard, 2003. Multiple Intelligences after
Twenty Years. Paper presented at the American
Educational Research Association, Chicago, Illinois,
April 21.
Kurniawan, H., Arifin, M., Sakti, W., and Fuady, M. J.,
2014. Pengembangan Buku Pintar Metode
Pembelajaran Kooperatif Berbantuan Augmented
Reality pada Smartphone Studi Kasus Mahasiswa
Pendidikan Fakultas Tekni Universitas Negeri
Malang. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Teknologi
Informasi dan Komunikasi (SEN TIKA), ISSN: 2089-
9813.
Lazear, David, 2004. Multiple Intelligence Approaches to
Assessment: Solving the Assessment Conundrum.
Crown House Publishing.
Maharani, R., 2015. Model Pembelajaran Berbasis Teori
Multiple Intelligences: Pembelajaran Kooperatif
dengan Pendekatan Saintifik pada Pembelajaran
Matematika. Jurnal Inovasi Pendidikan dan
Pembelajaran Matematika, 1(1), 11–24.
Suroso, 2004. Penulisan Buku Ajar Perguruan tinggi.
Disampaikan pada Pelatihan Penulisan Buku Sekolah
Alkitab Baptis. 29 Nov-1 Des 2004. STBI.
Thiagarajan, S., Semmel, D. S., and Semmel, M. I., 1974.
Instructional Development for Training Teachers of
Exceptional Children: A Sourcebook. Leadership
Training Institute/Special Education, University of
Minnesota.
Discrete Mathematics’ Textbook Development based on Multiple Intelligences
227
