
Higher Order Thinking Skills of Mathematics Education Department
Students of Hasyim Asy’ari University in Solving the Problem
of Generator Function in Discrete Mathematics Lecture
Novia Dwi Rahmawati, Gunanto Amintoko, and Siti Faizah
Department of Mathematics Education, Hasyim Asy’ari University
Keywords: HOTS, Problem Solving, Discrete Mathematics
Abstract: This research aimed at describing students’ higher order thinking skills in solving the problem of generator
function. Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) in this research consisted of logic and reasoning, analysis,
evaluation, and creation skills. This research was a descriptive research by using qualitative approach.
Meanwhile, the research subject was three students of mathematics education department of Hasyim Asy’ari
University,one student with high ability, one student with medium ability, and one student with low
ability.The data collecting method used was test, scoring rubric, and interview. Then, the data validation
technique used was tie triangulation. To analyze the data, the researcher used Miles and Huberman concepts
consisting of data reduction, data interpretation, and conclusion making. The conclusion of this research
shows that one student do the skills of logic and reasoning, analysis, evaluation, and creation not very well
in solving the problem of generator function, so that, they are included in the medium level of high order
thinking skills. Next, two students cannot do the skills of logic and reasoning, analysis, evaluation, and
creation well in solving the problem of generator function, so that, they are included in the low level of high
order thinking skills.
1 INTRODUCTION
The abilities of learning, improving performance,
and reducing weaknesses belong to students with
HOTS because learning effectiveness, learning
speed, and learning ability are affected by the
thought of a person (Yee, Othman, Yunos, Tee,
Hasan, and Mohammad, 2011). Furthermore, Kings,
Goodson, and Rohani (2013) state that HOTS are
students’ ability to think not only by remembering
but also by encountering unfamiliar problems,
uncertainties, questions, or dilemmas. Moreover
Pogrow (2005) argues that students’ success can be
predicted by HOTS owned by them because by
having HOTS can make students face advanced
academic life and adult’s work and responsibility in
daily basis better.
Moore and Stanley (2010) state that Higher
Order Thinking Skill is the last three aspects of
Bloom taxonomy consisting of analysis, evaluation
and creation. According to Brookhart (2010), Higher
Order Thinking Skills cover skills of logic and
reasoning, analysis, evaluation, creation, problem
solving and judgment.
Anderson and Krathwohl (2001) say that analysis
skill in HOTS is a skill to find a problem, then it
needs to rebuild the thing becoming the problem
and identify the most important and relevant part of
the problem, next it is continued by building an
appropriate relation to the given information.
Meanwhile, evaluation skill consists of planning
how far a plan works well and criticizing to a
product or operation assessment based on external
criteria and standards. Next, creation skill in HOTS
is a skill to present the problem, finding of
alternative hypothesis needed and planning to solve
the problem given. Reasoning skill is thinking
proses and concluding in the form of knowledge.
HOTS in this researchare skills of logic and
reasoning, analysis, evaluation also creation.
Same researches deal with HOTS of student have
been conducted araund the world. Tajudin (2015)
conducted studies in mathematical knowledge and
higher order thinking skills for teaching algebraic
problem solving in Turkey. Next, Yen and Halili
260
Rahmawati, N., Amintoko, G. and Faizah, S.
Higher Order Thinking Skills of Mathematics Education Department Students of Hasyim Asy’ari University in Solving the Problem of Generator Function in Discrete Mathematics Lecture.
DOI: 10.5220/0008520402600264
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mathematics and Islam (ICMIs 2018), pages 260-264
ISBN: 978-989-758-407-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reser ved

(2015) conducted the study of effective teaching of
higher order thingking (HOT) in education.
Discrete mathematics is a part of mathematics
that studies different and separated objects.
Generally, discrete mathematics is used to count
many objects, study the relationship between finite
sets and analyze process that engages infinite steps
(Rahmawati, 2016). One material that is considered
difficult by students in discrete mathematics course
is generator function. The research that was
conducted by Podilito (2015) explains that students
have not been able to formulate the problem solving
steps correctly and systematically.
In mathematics learning, problem solving is a
way to think. It means that students cannot just rely
to what they learn to be able to solve a problem
without structured process. Even though, some
students may be able to solve the problem well, most
of them should learn how to find the reason and how
to solve the problem. Whereas according to
Rahmawati (2015), problem solving is a learning
approach that stimulates students to want to think,
analyze a problem so that it can determine its
solution. In line with this, Ersoy (2016) explains that
Problem solving plays an important role in
mathematics education since it increases the
students’ high level thinking by having self-learning.
The purpose of this research is to describe students’
HOTS in solving generator function problem based
on arranged indicators.
2 METHODS
This research on students’ HOTS in solving the
problem is a descriptive research with a qualitative
approach. This research includes descriptive
research because the researcher just analyzes up to
description step. It is analyzing and presenting the
facts systematically (Azwar, 2007). While according
to Sugiyono (2011), qualitative research method is
research method that is used to conduct the research
about natural object condition, the researcher as a
key instrument, triangulation as the data collection
technique, inductive/ qualitative data analysis, and
the emphasize of qualitative research result on
meaning more than generalization.
This research subjects are mathematics students
having taken discrete mathematics course. They are
3 students in the semester 5 of mathematics
education department, Hasyim Asy’ari University.
So, the data of Students’ HOTS in solving the
problem achieved is expected to be able to represent
the real condition in the field. Subject selection uses
purposive sampling technique based on students’
ability determination on their midterm test, final test,
and task score given by the lecturer of generator
function. Meanwhile, the research is conducted at
department of mathematics education classroom in a
conducive condition, so that the students focus to
explain what is to be a problem in solving the
problem at the generator function in detail.
In research there must be a valid research
instrument. Before the researcher conducts research,
the researcher must make a research instrument.The
main instrument and supporting instrument are used
to get HOTS category data. The main instruments
are the researchers themselves as planners, data
collectors, data analyzers, data interpreters, and
research result reporters. Supporting instruments are
test questions, assessment rubric and interview
guidelines. Test questions are given in this research
in the form of worksheet that is done by the students
individually. It is done to find HOTS description in
solving generator function problem from the
researchers. Then the instrument is validated to the
validator. In the results of the validation test, the
researcher conducted an analysis of the results to
determine the validity level.
Data validity technique that is used in this
research is time triangulation. Data analysis
technique used in this research is Miles and
Huberman concepts; such as reduction, data
presentation and conclusion making. HOTS score
from each student is the students’ total scores gained
based on the number of reactions to the problem/
question that occur when they complete the test
question and interview. Maximum score is the
highest score of assessment rubric on every HOTS
multiplied by the number of test question, while
minimum score is the lowest score of assessment
rubric on every HOTS multiplied by the number of
test question. If the maximum and minimum score
have been gained, so the step to categorize the
HOTS in high, middle and low level is by
determining data range and dividing it into 3 parts,
so that high, middle and low class interval is got in
sequence reflecting high, middle and low level
students’ HOTS categories.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Score result gained from generator function solving
problem and interview answers, is used in
determining students’ HOTS level. From the
Students’ HOTS test and interview results covering
logic and reasoning, analysis, evaluation and
Higher Order Thinking Skills of Mathematics Education Department Students of Hasyim Asy’ari University in Solving the Problem of
Generator Function in Discrete Mathematics Lecture
261

creation aspects, the lowest and highest score are
obtained in sequence; 30 and 42. The score is used
to determine students’ HOTS level categories
presented in the table 1.
Table 1: Students’ HOTS score categories.
No
Score
Categories
1
20 ≤ skor ≤ 34
Low
2
34 ≤ skor ≤ 48
Middle
3
48 ≤ skor ≤ 62
High
The research result that is gained from 3 research
subjects is that there is no student with high level of
HOTS, one student with middle level of HOTS, who
has less ability in doing logic and reasoning,
analysis, evaluation and creation skills well in
solving generator function problem, and two
students with low level of HOTS, who cannot do
logic and reasoning, analysis, evaluation and
creation skills in solving generator function problem.
Based on interview transcript results, they can
represent middle and low level of HOTS.
3.1 Middle level of HOTS
The result based on data analysis is that a student
with middle level of HOTS is good at analysis skill
of both first and second problems; this student can
identify the main idea by stating thing known and
asked on the questions clearly, shortly and
appropriately. Next, she can give theoretical reason
in every answering step to the last answer correctly.
Additionally, she can give the similarity, difference
and usage known to answer the question correctly.
The following is the example of answer sheet from
students:
In evaluation skill of both first and second
problems, the student is able to give assessment to
the solution and method used in answering the
questions appropriately. Next, the student criticizes
the arguments appropriately to the questions. The
student is also able to recheck starting from the thing
known to the conclusion of the answer by
considering theoretical aspects of answering steps
appropriately to the questions.
In creation skill of both first and second
problems, the student can design how to answer the
questions correctly. The following is the example of
answer sheet from students:
Then, the student designs the way to answer the
question correctly by considering the first analysis
on the thing known and asked in the questions. The
student is also able to make new answering step by
combining previous answering steps logically and
theoretically on the questions. The following is the
example of answer sheet from students:
In logic and reasoning skills, both the first and
second problems, student can write the answer
content, evidence and reason, and language style
clarity effectively, well and logically in finishing the
questions.
3.2 Low Level of HOTS
The result based on data analysis is that students
with low level of HOTS in analysis skill of both first
and second problem, the two students have not been
able to identify the main idea by stating the thing
known and asked on the questions clearly, shortly
and appropriately. Next, they are not able to give
similarity, difference, and usage known to answer
the questions correctly. The following is the
example of answer sheet from students:
ICMIs 2018 - International Conference on Mathematics and Islam
262

In evaluation skill of both the first and second
problems, they are also not able to give evaluation
on the solution and method used in answering the
questions correctly. But, they criticize the argument
the questions correctly. Then students also are not
able to recheck the answer from the start to the
conclusion by considering theoretic al aspect of
answering steps correctly to the questions.
In creation skill of both the first and second
problems, they cannot design how to answer the
questions appropriately. The following is the
example of answer sheet from students:
Next, the students are not able yet to design the
way by considering the first analysis on the thing
known and asked of questions. They cannot make
new answering steps by combining previous
answering steps logically and theoretically on the
questions.The following is the example of answer
sheet from students:
In logic and reasoning skill of both the first and
second problems, the students cannot write the
answer content, evidence and reason, as well as
language style clarity effectively, well and logically
to answer the questions.
The test and interview results show that there is
correlation between analysis, evaluation, and
creation skills. Creation skill is affected by analysis
and evaluation skills. So, the requirement for the
students to be able to do creation is if the students
have been able to do the analysis and evaluation
skills at first. This is in line with Anderson’s
opinion in A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and
assessing: A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy of
Educational Objectives (2001), creation as the
highest part of cognitive domain.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the research result, the research
conclusions are as follows:
First, the student with middle level of HOTS is
able to identify the main idea, analyze an argument,
and show the usage of the thing known to answer
some questions, so she has quiet good analysis skill.
She is also able to give assessment to the solution
and methods used and recheck the questions, it
means that the student has quite good evaluation
skill. The student also can design how to answer and
show well to the questions. Thus, it can be said that
she has good creation skill. While on their logic and
reasoning skill, the student can write the answer
content, evidence and language style clarity
logically, well and effectively.
Second, the students with low level of HOTS
have less ability in identifying the main idea,
analyzing the arguments, and showing the usage of
the thing known to answer some questions, so they
do not have good analysis skill. The students also
have less ability in giving assessment to the solution
and method used also rechecking to the questions, so
they do not have good evaluation skill. The students
also are not able to design how to answer and show
well to the questions, so they have less good creation
skill. While on their logic and reasoning skill, the
students have less ability in writing the answer
content, evidence and language style clarity
logically, well and effectively.
This research was conducted in Hasyim Asy’ari
University which still has few students so that it is
suggested to do the research with more research
subjects because the more subject collection, the
Higher Order Thinking Skills of Mathematics Education Department Students of Hasyim Asy’ari University in Solving the Problem of
Generator Function in Discrete Mathematics Lecture
263
more possible to describe HOTS on students in
solving generator function problem.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported in part by the Beginner
Lecturer Research under grant DRPM Ristekdikti.
REFERENCES
Azwar, S., 2007. Metode Penelitian. Yogyakarta: Pustaka
Pelajar.
Anderson, L.W., and Krathwohl, D. R., 2001. A Taxonomy
for Learning, Teaching, and Assessing: A Revision of
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives. New
York: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc.
Brookhart, S. M., 2010. How to Assess Higher-Order
Thinking Skill in Your Classroom. Alexandria: ASCD.
Ersoy, E., 2016. Problem Solving and Its Teaching in
Mathematics. Journal of New Horizons in Education.
6 (2), 79-87
King, F. J., Goodson, L., & Rohani, F., 2013. Higher
Order Thinking Skills. [online] [12 April 2017]
http://www.cala.fsu.edu/files/higher_order_thinking_s
kills.pdf
Podilito, A. S., 2015. Deskripsi Kemampuan Pemecahan
Masalah Matematika Mahasiswa Pendidikan
Matematika dalam Mata Kuliah Matematika Diskrit
Materi Fungsi Pembangkit. Unpublished Article.
Gorontalo: Pendidikan Matematika Universitas Negeri
Gorontalo.
Pogrow, S., 2005. HOTS revisited: A Thinking
Development Approach to Reducing the Learning Gap
after Grade 3. Phi Delta Kappan, 87, 64-75.
Moore, B., & Stanly, T., 2010. Critical thinking and
formative assessments. Larchmount, NewYork: Eyeon
Education, Inc.
Rahmawati, N. D., 2016. Peningkatan Kualitas
Pembelajaran Matematika Diskrit melalui Problem
Based Learning pada Mahasiswa Semester IV Prodi
Pendidikan Matematika Universitas Hasyim Asy’ari.
Unpublished Article. Universitas Hasyim Asy’ari
Jombang. Indonesia.
Rahmawati, Novia D. 2015. Profil Siswa SMP dalam
Pemecahan Masalah yang Berkaitan dengan Literasi
Matematis Ditinjau dari Adversity Quotient (AQ).
Unpublished Thesis. Surakarta: Postgraduate Program
Universitas Sebelas Maret. Indonesia.
Sugiyono, 2011. Memahami Penelitian Kualitatif.
Bandung: Alfabeta.
Tajudin, N. M., 2015. Mathematical Knowledge and
Higher Order Thinking Skills for Teaching Algebraic
Problem Solving. Proceeding of Socioint 15-2nd
International Conference on Education, Social
Sciences and Humanities, Istambul, Turkey, pp. 26-35.
Yee, M. H, Othman, W., Yunos, J., Tee, T. K., Hassan, R.,
& Mohammad, M. M., 2001. The Level of Marzano
Higher Order Thinking Skills among Technical
Education Students. International Journal of Socia
Science and Humanity, 1(2), 121-125.
Yen, T. S & Halili, S. H., 2015. Effective Teaching of
Higher-Order Thinking (HOT) in Education. Journal
of Distance Education and e-Learning. 3(2), 41-47.
APPENDIX
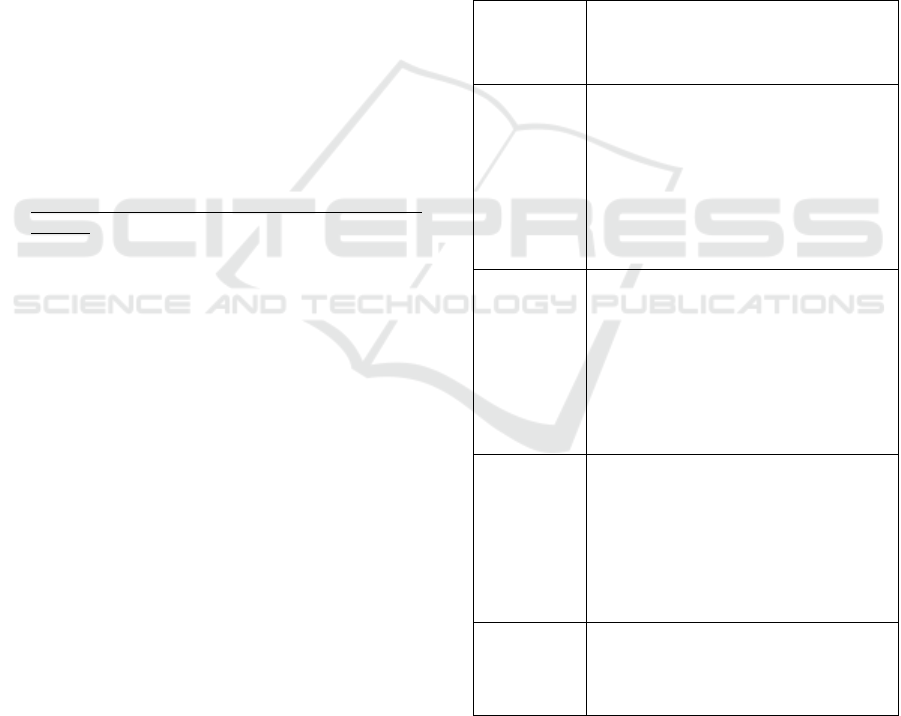
Indicators to measure students' high-order thinking
skills can be seen in the following table:
Component
of High level
thinking skill
Indicator of high-level thinking skills
in solving problems
Analysis
1. Students are able to identify the main
ideas by stating things that are known
and asked about the questions clearly,
concisely, and precisely.
2. Students provide theoretical reasons for
each step of the work until the final
answer is correct.
3. Students provide similarities, differences
and uses of things that are known to
answer questions correctly.
Evaluation
1. Students provide an assessment of the
solutions and methods used in
answering questions correctly.
2. Students criticize the argument correctly
on the question
3. Students re-check starting from the
things that are known to the conclusion
of the answer by paying attention to the
theoretical aspects of the work steps
right on the question.
Creation
1. Students design work methods to
answer questions correctly.
2. Students design ways by considering the
initial analysis in terms of known and
asked questions.
3. Students make a new step in the process
by combining the previous work steps
logically and theoretically into the
problem
Logic and
reasoning
1. Students write the content of the
answers, evidence and reasons and
clarity of the language style effectively,
well and logically in solving the
problem.
ICMIs 2018 - International Conference on Mathematics and Islam
264
