
Blood Glucose Levels in Students with Stress
Muhammad Zulfikar Karim Chan
1
, Isra Thristy
1*
1
Faculty of Medicine, University of Muhammadiyah Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Stress, Blood glucose
Abstract: Stress can occur at any lecture level, especially at the initial level. This is in line with previous research
which states that, there is increased stress in the first-year students due to changes in learning systems in
previous education. The purpose of this research is to know the blood glucose level on students with
stress. The type of this research is descriptive using cross sectional design, as many as 24 respondents.
Based on levels of glucose to stress levels, the normal group (without stress), whole blood glucose
levels within normal limits (100%) ie 7 of 7 respondents. For the mild stress group, there was a normal
glucose level of 11 people (78.5%) and high glucose level of 3 people (21.4%). In the moderate group, 3
respondents had high blood glucose level (75%) and only 1 respondent had blood glucose level in
normal range (25%). While in the heavy stress group found all respondents with high blood glucose
levels (100%). Conclusion, the highest stress level found was mild stress and the higehest blood glucose
levels were found to be normal glucose levels.
1 INTRODUCTION
Stress is a condition caused by transactions between
individuals and the environment that leads to a
perception of the distance between the demands
derived from the situation with the resources in the
biological, psychological and social systems of a
person. Stress occurs due to unbalanced between the
desired expectations of individuals with events that
occur, both physical and spiritual desires.
(Sukadiyanto, 2010)
The incidence of stress is still
high and varies greatly in various groups in
Indonesia. The results of basic health research
(Riskesdas) in 2007 showed that 11.6% of
Indonesians aged 15 years and over experienced an
emotional mental disorder. At Riskesdas in 2013,
that figure shows a decline to 6%. The results of the
study at the assembly taklim in South Jakarta
showed that the prevalence of stress reached 13.3%.
(Besral, et al, 2015)
Holahan mentioned the type of stress that is
divided into two parts, namely Systemic stress and
Psychological stress. Systemic stress is defined as a
non-specific response of the body to the demands of
the environment. Psychological Stress occurs when
individuals encounter stressful environmental
conditions as a threat that strongly challenges or
exceeds their coping ability. (Noviyan M, 2007)
There are other things that can trigger stress,
such as feelings of anxiety about the outcomes
achieved, unbalanced activity, self-stress, a
condition of uncertainty, anxiety, guilt, an
emotionally thirsty soul, and socioeconomic
conditions. According to Subramanian, in Student
there are many other factors that can also trigger
stress, such as: environment, academic, work
competition, interpersonal relationship, and way of
thinking of student also can make stress to student.
Usually if students experience stress will arise such
as: feeling of solitude, lack of sleep, anxiety, and
high hesitations. And if this stress continues to have
a negative effect on health, personality, social
interaction and academic achievement of students.
(Subramaniam V, 2010, Pathmanathan V, et al, 2013)
Stress can occur at any lecture level, especially at
the initial level. This is in line with previous
research which states that, there is increased stress in
the first-year students due to changes in learning
systems in previous education. (Pathmanathan V, et
al, 2013, Mahfar M, et al, 2007)
Continuous stress can affect stress hormones.
Adrenaline, cortisol which is a stress hormone will
rise in number and will affect the homeostasis
system. The hormone affects the sympathetic
nervous system and raises the heart rate and blood
pressure. This is in accordance with subramaniam
research which states that, there is a stress
relationship on Students with high blood pressure at
the time of the exam. In addition, cortisol has a
metabolic effect that increases blood glucose
Chan, M. and Thristy, I.
Blood Glucose Levels in Students with Stress.
DOI: 10.5220/0008790700530056
In Proceedings of the 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences (SKIC-MHS 2018), pages 53-56
ISBN: 978-989-758-438-1
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
53
concentration by using protein and fat stores. So
there is an increase in stored glucose, amino acids,
and fatty acids available for use when necessary, for
example under stress. (Kadir A, 2010)
Glucose is one of the simplest monosaccharides
that has the C6H12O6 molecular formula. Glucose
serves as the fuel of most living things. The
breakdown of carbohydrates produces
monosaccharides and disaccharides, with the
greatest result being glucose. Through glycolysis
and the citric acid cycle, glucose is oxidized to form
CO2 and water, producing an energy source in the
form of ATP. (Ekawati ER, 2012)
Normal levels of glucose in blood are
<126mmHg at the time of fasting and <200mmHg
add random glucose levels. If there is an increase in
blood sugar levels in the body, it is called
hyperglycemia. If the state of hyperglycemia is very
dangerous for the body. Has symptoms of
polyphagia, polydipsia, weight loss, polyuria and
other symptoms. The state of chronic hyperglycemia
can cause damage to organs, especially the eyes,
kidneys, heart, nerves and blood vessels. (Suci M,
2015)
2 METHOD
The type of this research is analytic descriptive by
using cross sectional design. Cross-sectional
research is an option because the study was
conducted at one time and only one time, no follow-
up. This research was conducted in April 2017 until
December 2017 and the location of the research was
conducted at the Faculty of Medicine, University of
Muhammadiyah Sumatera Utara. Population is the
whole of all variables concerning the problem under
study. The population of the research is the medical
faculty students of University of Muhammadiyah
Sumatera Utara in the first semester of academic
year 2017 - 2018 who will take the test. The sample
assessed in this research is the medical faculty
students of University of Muhammadiyah Sumatera
Utara who are included in the inclusion criteria. The
number of samples required in this study was 24
people. The last step of this research is to analyze
data. Data analysis is done gradually and done
through computerization process. This study used
univariate analysis. This analysis is used to provide
an overview of the research data. The data will be
presented in the form of descriptive statistics.
3 RESULT
The gender characteristics of the respondents
consisted of the same two groups between the 12
men (50%) and the 12 women group (50%).
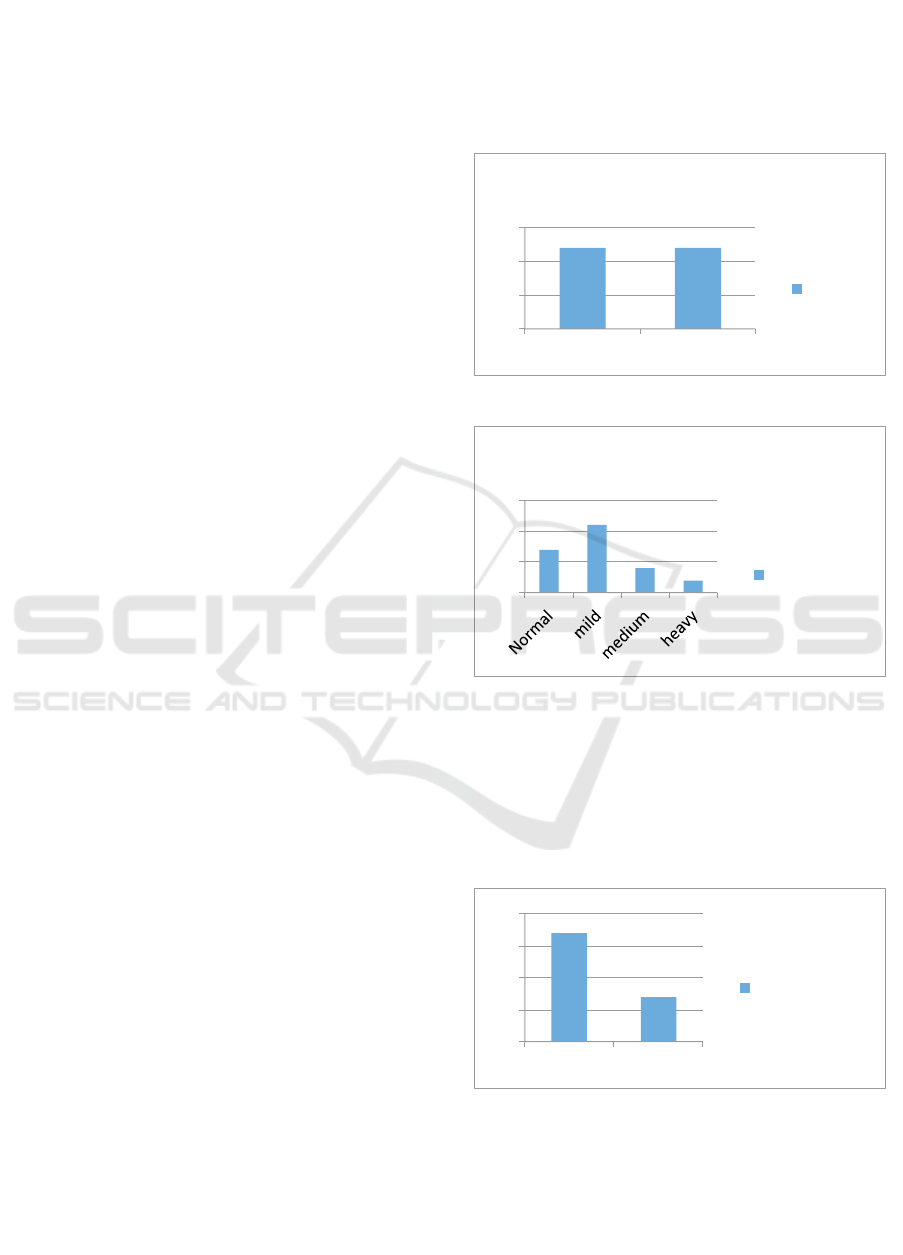
Figure 1. Characteristic of gender
Figure 2. Characteristic of stress level
Characteristic of stress level, it was found that there
were 4 stress level on respondent with the most
group in mild stress group were 11 people (46%),
normal group with 7 people (29%), medium stress
group with 4 people (17%) and smallest group on
the heavy stress of 2 people (8%).
Figure 3. Characteristic of blood glucose
The characteristic of glucose content of the
respondents was found in the group with normal
glucose level as many as 16 respondents (66.67%)
and then group with high glucose level as many as 8
respondents (33.33%).
0"
5"
10"
15"
male" female"
Gender&
gender"
0"
5"
10"
15"
stress&level&
stress"level2"
0"
5"
10"
15"
20"
Normal" high"
Blood"Glucose"
SKIC-MHS 2018 - The 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences
54

Table 1. Characteristic of stress levels and blood glucose
Blood
Glucose
Stress Level
Normal
Mild
Medium
Heavy
Total
n
7
0
%
100
0
n
8
3
%
72,7
27,3
n
1
3
%
25
75
n
0
2
%
0
100
Normal
16
8
High
Total
7
100
11
100
4
100
2
100
24
In the normal group all blood glucose levels within
normal limits (100%) ie 7 of 7 respondents. In the
mild stress group, there was a normal glucose level
of 11 people (78.5%) and high glucose level of 3
people (21.4%). In the moderate group, 3
respondents had high blood glucose level (75%) and
only 1 respondent had blood glucose level in normal
range (25%). While in the heavy stress group found
all respondents with high blood glucose levels
(100%).
4 DISCUSSION
Based on the results of research conducted on 24
students semester 1 FK UMSU, it is known that as
many as 17 people (70.8%) who experience stress in
various levels. This is in line with research
conducted by Veyna (2013) shows that almost half
of the number of initial students respondents who
studied in medical school Sam Ratulangi Manado
experiencing stress that is as much as 48.4%.
(Talumewo VR, et al, 2013) Students of Medical
Faculty UMSU first semester experience the most
mild stress, is 11 people (46%), who experienced
moderate stress as many as 4 people (17%) and
heavy stress as much as 2 people (8%). The same
study conducted in Iran on medical faculty students
and the results obtained is 26.22% is mild stress,
20.5% simple stress and 14.75% are high stress.
(Marjani A, et al, 2008) Students who will take the
exam will raising the level of stressornya, especially
academic stressors. This is consistent with Lal's
study that academic pressures such as exams can add
to stressful academic stress.
12
This is also supported
by research by Virginia (1999) in Farida (2008) that
academic problems are a contributing factor to stress
the largest in medical students. (Farida A, 2008,
Legiran, et al, 2015) In addition, the target
achievement of values and academic achievement
also contributes to the potential causes of stress in
medical students. Research conducted by Yee (2013)
also shows that academic achievement is very
influential on the incidence of stress in medical
students. (Yee L Y, 2013) Although in this study is
not described in detail the causes of stress on
students but stress levels are identified based on
attitudes and emotions samples assessed using a
DASS 24 questionnaire.
Stress not only affects a person's mental but also
affects the metabolic process in a person's body, one
of his blood sugar levels. (Djakani H, et al, 2013) In
this study found that the higher the level of stress a
person, the higher the percentage also increase in
blood glucose levels. This is in line with research
conducted by Pratiwi. Stress can increase blood
glucose content because stress stimulates endocrine
organs to release ephinephrine. (Pratiwi P, et al,
2014, PEI, 2015) Another study was also conducted
on "Correlation of stress levels with elevated blood
sugar levels. This study suggests that there is a
relationship between stress levels and elevated blood
sugar levels. (Juwita, 2008) The results of the study
are consistent with the results of the current study,
which is an overview of elevated blood glucose
levels in stressful situations.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the research it can be taken
some conclusions as most blood glucose levels in
the samples obtained were normal blood glucose
levels of 17 people. The highest level of stress found
in UMSU Medical Faculty students in the first
semester who will undergo a block exam is a mild
stress level of 11 people. The most common level of
stress is an increase in blood glucose levels is a level
of heavy stress with a percentage of 100% found an
increase in blood glucose from all samples who have
severe stress.
Blood Glucose Levels in Students with Stress
55

REFERENCES
Besral, Winne W, 2015. Determinants of Stress Among
Civil Servants at Health Ministry of Indonesia.
Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Nasional.
Djakani H, Masinem TV, Mewo YM, 2013. Gambaran
Kadar Gula Darah Puasa pada Laki-laki Usia
40-59 Tahun. Jurnal e-Biomedik.
Ekawati ER, 2012. Hubungan Kadar Glukosa Darah
Terhadap Hypertriglyceridemia pada Penderita
Diabetes Melitus. Prosiding Seminar Nasional
Kimia Unesa.
Farida A, 2008. Efektivitas Pendekatan CBM (Congestive
Behavior Modification) Untuk Mengurangi Stres
Belajar Siswa SMU. Jurnal Psikologi
Psikovidya.
Juwita, 2008. Faktor-faktor yang Mempengaruhi Tingkat
Stress Kerja Perawat Psikiatri di Rumah Sakit
Jiwa Provinsi Kepulauan Bangka Belitung.
Jurnal Fakultas Ilmu Kedokteran UGM.
Kadir Akmarawita, 2010. Perubahan Hormon Terhadap
Stres. Jurnal Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas
Wijaya Kusuma Surabaya.
Legiran, Azis M Z, Bellinawati N, 2015. Faktor Resiko
Stres dan Perbedaannya pada Mahasiswa
Berbagai Angkatan di Fakultas Kedokteran
Universitas Muhammadiyah Palembang. Jurnal
Kedokteran dan Kesehatan.
Mahfar M, Zaini F, Nordin N, 2007. Analisis Faktor
Penyebab Stres di Kalangan Pelajar.Jurnal
Kemanusiaan.
Marjani A, Gharavi A M, Jahanshahi M, Vahidirad A,
Alizadeh F, 2008. Stress Among Medical
Student of Gourgan (South East of Caspian
Sea). Kathmadu University Medical Journal.
Iran.
Noviyan Mumtahinnah, 2007. Hubungan Antara Stres
dengan Agresi pada Ibu Rumah Tangga yang
Tidak Bekerja. Jurnal Psikologi Universitas
Gunadarma.
Pathmanathan V, Husada MS, 2013. Gambaran Tingkat
Stres pada Mahasiswa Fakultas Kedokteran
Universitas Sumatera Utara Semester Ganjil
Tahun Akademik 2012/2013. E-journal FK
USU.
Pathmanathan V, Husada, 2013 Gambaran Tingkat Stres
Pada Mahasiswa Fakultas Kedokteran
Universitas Sumatera Utara Semester Ganjil
Tahun Akademik 2012/2013. E-Journal FK
USU.
Perkumpulan Endokrinologi Indonesia, 2015. Konsensus
Pengelolaan dan Pencegahan Diabetes Melitus
Tipe 2 Di Indonesia. PB Perkeni.
Pratiwi P, Amatiria G, Yamin M, 2014. Pengaruh Stress
Terhadap Kadar Gula Darah Sewaktu pada
Pasien Diabetes Melitus yang Menjalani
Hemodialisa. Jurnal Kesehatan.
Subramaniam V, 2010. Hubungan Antara Stres dan
Tekanan Darah Tinggi pada Mahasiswa. Jurnal
Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Udayana.
Suci M. J. Amir, 2015 Kadar Glukosa Darah Sewaktu
pada Pasien Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2 di
Puskesmas Bahu Kota Manado. Jurnal e-
Biomedik (eBM).
Sukadiyanto 2010. Stres dan Cara Menguranginya. Jurnal
FIK Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta. Cakrawala
Pendidikan.
Talumewo VR, Pangemanan DHC, Marunduh SR, 2013
Stres Terhadap Daya Tahan Belajar pada
Mahasiswa Angkatan 2013 Fakultas Kedokteran
Universitas Sam Ratulangi. Jurnal Fisiologi
Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sam Ratulangi
Manado.
Yee L Y, 2013. Prevalence and Sources of Stress Among
Medical Students in Universiti Sains Malaysia
and Universiteit Maastricht. Education in
Medicine Journal.
SKIC-MHS 2018 - The 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences
56
