
Information Technology Adoption in Islamic Higher Education
Institutions in Indonesia
Yusuf Amrozi
1,2
, Mujib Ridwan
1
, and Eni Purwati
1
1
Department of Information System, Sunan Ampel State Islamic University, Surabaya, Indonesia
2
Department of Management, Airlangga University, Surabaya, Indonesia
1
Department of Technology, Sunan Ampel State Islamic University, Surabaya, Indonesia
1
Faculty of Islamic Education, Sunan Ampel State Islamic University, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: IT Adoption, Organizational Capabilities, SCA, NU University.
Abstract: Business in the higher education sector in Indonesia, especially in the environment of private Islamic higher
education, has been showing a significant increase. The winner is largely determined by the business strategies
designed, supported by organizational resources, rarity, difficulty to imitate the product, and difficulty to
substitute the product, in order to create a sustainable competitive advantage. According to the existing
research, support for ERP (enterprise resource planning) information system plays an important role in
realizing organizational capabilities towards a sustained competitive advantage (SCA). This research focused
on the extent of information technology adoption to encourage Islamic higher education institutions—
especially NU Universities—to realize a competitive advantage in order to win the competition. The results
show that IT Adoption did not have any significant effect on Organizational Capabilities and Sustained
Competitive Advantage, but Organizational Capabilities had a significant effect on Sustained Competitive
Advantage. Implications of the research findings will be discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Higher education institutions in Indonesia, especially
the private ones which are based on Islamic religion
and fostered by the Ministry of Religious Affairs,
show a significant increase in number, now
numbering more than 6,000 (Directorate of Islamic
Higher Education–Ministry of Religious Affairs,
2017). The development of higher education amid
competition is largely determined by the business
strategies designed, supported by the management of
rare, valuable, hard-to-imitate resources, creating a
sustainable competitive advantage (Barney, 1991).
Porter (2008) explains that a competitive advantage
basically develops from a value that can be created by
a company for its buyers and exceeds the cost of the
company that created it. The resources for developing
a competitive advantage are the core competencies
owned by a company or organization.
In the Indonesian context, the existence of private
universities is heavily influenced by organizations or
social groups affiliated with religious professions or
organizations. In Indonesia, the majority of the
population are Muslims. Some of them are affiliated
with religious organizations. These religious
organizations were established prior to the state of
Indonesia establishment or during the colonial period.
There are two major Islamic religious organizations
in Indonesia: Nahdlatul Ulama (NU) and
Muhammadiyah. The subjects of this research were
private Islamic universities affiliated with Nahdlatul
Ulama (Nahdlatul Ulama universities). The reason
why the researchers focused on Nahdlatul Ulama
universities is that early in its development, NU
emphasized not secular sciences, but religious
education. However, in the last 20 years, it has been
concentrating on the establishment of higher
education. For quick reference, NU is a civil
organization founded by Islamic clerics in 1926 when
Indonesia was still in the colonial period. Of the 250
million Indonesian people 90 million join this
organization. The distinct characteristic of the NU-
style Islamic religion is that it combines the Middle
Eastern Islamic values with local values prevailing in
a given period. Therefore, later in its development,
NU is known as a moderate community organization
tolerant toward other traditions, cultures, and tribes or
groups. Institutionally, NU universities are managed
326
Amrozi, Y., Ridwan, M. and Purwati, E.
Information Technology Adoption in Islamic Higher Education Institutions in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0008904100002481
In Proceedings of the Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference (BEST ICON 2018), pages 326-332
ISBN: 978-989-758-414-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

by legal entities, either foundations or legal entities of
NU associations, of 250 institutions (Data of the
National Board of Nahdlatul Ulama/PBNU, 2018).
The growing number of NU universities poses a
challenge to their management in generating
competitive advantages in order to win the market
competition. Competitive advantages can be gained
through the application of information technology
(Aggarwal, 2017). Information technology can meet
the information needs of the business world quickly,
effectively, accurately, and relevantly. In addition, to
companies, information technology has an important
role in the strategy to obtain competitive advantages.
Information technology will contribute an effect on
almost all aspects of business management and can
provide an added value if properly managed and
designed into an effective information system.
Jogiyanto (2007) argues that the information
technology system has developed very rapidly and is
seen to be quite significant in this era. In relation to
the development of higher education, Indrajit (2013)
argues that universities can utilize information
technology in three ways: by providing support for
services and administration; by using it as a teaching
aid and means of communication; and by using it for
decision-making.
Therefore, it is necessary to support ERP
(enterprise resource planning) information systems,
such as academic information systems, which can
play a real role in realizing organizational capabilities
toward a sustained competitive advantage (SCA). The
early view of the research target (NU Universities) in
relation to the adoption and use of information
technology, according to the vision, is how to become
excellent universities in the national and local
contexts to be able to compete with other universities,
especially Islamic universities, in Indonesia.
Meanwhile, the vision of IT utilization is how IT is
able to support the universities’ operational
performance. In fact, based on preliminary
observations, some technological mastery and
environmental problems were found, requiring more
in-depth research.
This research focused on how far the adoption of
ERP information technology encourages private
higher education institutions to realize competitive
advantages that can empower them to win the
competition eventually. This research was conducted
quantitatively at NU universities as private
universities in Indonesia which had adopted
information technology.
Some studies have been carried out by several
researchers, for example, one by Miranda et al. (2016)
on the adoption of ERP technology at non-profit
organizations such as higher education organizations.
The results of the study show that process factors and
administrative service innovations that used
technology could effectively reach organizational
goals. The connection with our research is that at NU
universities, the adoption of information technology
is relatively new. Meanwhile, Abugabah, Sanzogni,
and Alfarraj (2015) examined the impact of the
implementation of ERP information systems in
universities. The results of the study indicate that the
quality of the system adopted at a university, the
suitability of the role of technology, and the quality
of information were the most important factors in the
university’s performance. Another study was
conducted by Melitski and Gavin (2010), which was
about technology adoption and organizational culture
in public organizations. The study found that there
was a relationship between individuals’ perception of
organizational culture and their willingness to adopt
a technology.
None of the related research that we have
described above studied other factors besides the use
of technology, for example, an organization’s
capabilities to improve its performance. Therefore,
the addition of the factor organizational capabilities is
expected to be a differentiator from previous studies
in relation to factors of technology adoption in higher
education.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 IT Adoption
Adoption is a person's new behavior in accordance
with the background of knowledge, awareness, and
attitude towards excitement or stimuli (Notoatmodjo,
2003). Adoption may essentially be interpreted as the
process of accepting an innovation and/or changing
good behavior in the form of knowledge (cognitive),
attitude (affective), and skill (psycho-motoric) after
receiving the "innovation" received by a target
community. In this context, "adoption" refers to the
stage at which technology is accepted and preferred
to be used by an individual or organization.
Technology adoption basically aims to raise
human awareness of learning technology, with a
technology being utilized, applied, and adopted to
improve the quality of learning in all aspects of life.
As Prawiradilaga (2012) says, the existence of
technology in education permits the programming of
education, thus an educational process can be
organized and detailed. This includes a technology
model that is intentionally created to facilitate the
learning process to achieve educational goals.
According to the explanation above, it can be seen
that the adoption of an information technology is the
Information Technology Adoption in Islamic Higher Education Institutions in Indonesia
327

release of an idea (innovation) until it is accepted and
implemented by someone so that it becomes a
behavior which is a combination of knowledge
(cognitive), attitude (affective), and skills
(psychomotor) in using information technology. In
the context of technology adoption and organizational
environment changes, Aggarwal (2017) points out
two influencing factors, namely inducement to adapt
and difficulty of adaptation.
2.2 Organizational Capabilities
An organizational capability is defined as the ability
of a company to mobilize both tangible and intangible
resources in order to perform tasks or activities to
improve its performance (Amit and Schoemaker,
1993; Grant, 1991; Teece et al., 1997). Helfat and
Peteraf (2003) define it as an organization’s ability to
coordinate a series of tasks to utilize organizational
resources to achieve its ultimate goal.
Organizational capability is very important for an
organization to solve organizational problems
effectively. Sampurno (2011) describes capabilities
as representing a set of integrated sources used to
carry out important activities. The ability is integrated
into the knowledge (capability) and skills of workers
or individuals in the company or organization.
Furthermore, Sampurno (2011) explained that
organizational capability is the capacity of an
organization to place and utilize resources to fulfil its
desires and achieve expected outcomes.
Organizational capability requires a variety of
individual skills that are integrated with technology,
equipment, and various other resources.
According to Teece (2017), organizational
capabilities go through three processes, namely
sensing, seizing, and transforming. Meanwhile,
Gurkan (2015) states that a collaboration can take
place in two ways: strategy development and
implementation as well as continuous improvement
process.
2.3 Sustained Competitive Advantage
According to Schermerhorn (2011), a competitive
advantage is the ability to do something so well that
one outperforms competitors. Kotler and Armstrong
(2015) define competitive advantage as an advantage
over competitors obtained by offering value to
consumers, either through lower prices or by
providing more benefits that support higher price
revenues. David (2010) describes competitive
advantage as a situation where a company can do
something and other companies cannot or has
something their competitors want.
Grant (2011) proposes five steps to achieve
competitive advantages through the company's
resources:
1. Identifying and classifying resources that can
affect the strengths and weaknesses of the
company.
2. Combining the strength of the company with
the specific capabilities of the company.
Company capability (commonly referred to as
core competence) is everything that the
company can do very well. When the
capability/competency is superior to its
competitors’, it becomes a special competence
for the company.
3. Assessing the potential benefits of the
resources and the potential capabilities the
company has to be able to gain benefits
generated and to achieve a sustainable
competitive advantage.
4. Selecting strategies that can well exploit the
company's resources and capabilities to
achieve external opportunities.
5. Identifying resource gaps and invest in
transforming weaknesses into strengths.
Competitive advantages in this research can be
measured by three indicators proposed in Tuan and
Yoshi’s research (2010):
1. Cost strategy, measured by emphasizing cost
reduction through process innovation in the
operating system business, investment in
machinery, and increase in employee
productivity and operations.
2. Quality strategy, measured through product
quality, strict quality control, fulfilment of
customer needs, and handling of customer’s
product requirements.
3. Innovation strategy, measured by the level at
which the company strives to introduce new
products, emphasis in the innovation in the
production process, and engagement in new
marketing.
Barney (1991) explains that, based on Resource
Base theory, a competitive advantage needs to be
sustainable (sustained competitive advantage). In his
opinion, there are five pre-requisites for the creation
of a sustainable competitive advantage. The company
must have organizational resources which are (a)
valuable, (b) substitutable, (c) imitable, and (d) rare.
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
328

3 RESEARCH METHODS
In this study, data were collected using questionnaires
and analysed quantitatively. This research is
categorised as causal research because one variable as
an independent variable was related to another
variable as a dependent variable. According to
Sugiyono (2014), a causal relationship is a
relationship in which independent variables
(affecting variables) are related to a dependent
variable (influenced variable).
Population is an area of generalization consisting
of objects or subjects that have the quality and
characteristics set by researchers to be studied and
from which conclusions are drawn (Sugiyono, 2014).
The population in this study consisted of all of the 250
Islamic private higher education institutions in
Indonesia which were affiliated with Nahdlatul
Ulama. The sample used consisted of NU universities
spread across East Java and outside East Java, such as
those in Central Java, West Java, Jakarta, Sumatera,
Kalimantan, and Sulawesi. Nonetheless, the majority
of members of NU and NU universities were more
likely to be spread in East Java province. The analysis
unit was institutional (one questinnaire for each
campus). There were 52 validated questionnaires.
3.1 Hypotheses
H1 : IT Adoption has a significant effect on
Sustained Competitive Advantage.
H2 : IT Adoption has a significant effect on
Organizational Capabilities.
H3 : Organizational Capabilities have a significant
effect on Sustained Competitive Advantage.
3.2 Operational Definition
3.2.1 IT Adoption (X
1
)
IT Adoption is the release of an idea (innovation)
until it is accepted and implemented by someone so
that it becomes a behavior which is a combination of
knowledge (cognitive), attitude (affective), and skills
(psychomotor) in using information technology. The
indicator of the variable IT Adoption, according to
Aggarwal (2017), are the following:
1. Inducements to adapt
In this context, researchers operationalized into
five things, namely: encouragement of IT
acceptance from organizational culture,
organizational conditions, internal drive to
adopt IT, and encouragement from external
stakeholders.
2. Difficulty of adaptation
In this context, researchers operated into three
things, namely: resistance of the organizational
culture in adopting IT, organizational resource
conditions, and the absence of external
stakeholders who help adopt IT.
3.2.2 Organizational Capabilities (X
2
)
Organizational Capabilities are the capacity of an
organization to place and utilize resources to fulfil its
desires and achieve expected outcomes. The
indicators of the variable Organizational Capabilities,
according to Teece (2017) and Gurkan (2015), are as
follows: (a) Sensing; (b) Seizing; (c) Transforming;
(d) Strategy of Development & Implementation; and
(e) Continuous Improvement Process.
3.2.3 Sustained Competitive Advantage (Y)
Sustained Competitive Advantage (SCA) is an
advantage over competitors that is obtained by
offering values to consumers, either through lower
prices or by providing more benefits that support
higher price revenues. The indicators of the variable
Sustained Competitive Advantage, according to
Barney (1991), are as follows: (a) Rarity; (b)
Substitutability; (c) Imitability; and (d) State of Being
Valuable.
In the context of this research, the four SCA
indicators above were transformed into higher
education performance that could be operationalized
better, namely (a) SCA implications for the
performance of college, (b) institutional reputation,
(c) graduates' achievements, and (d) product
knowledge.
3.3 Data Collection Technique
The method used by the researchers in this research
was a survey method using questionnaire. According
to Sugiyono (2014), questionnaire is a data collection
technique that is carried out by giving a set of written
statements to respondents to be responded to. A
Likert scale was used. The variables measured by the
Likert scale were re-elaborated into sub-variables,
which were reinterpreted into components that could
be measured.
Information Technology Adoption in Islamic Higher Education Institutions in Indonesia
329
3.4 Data Analysis Technique
The analysis technique chosen to analyze the data and
test the hypotheses in this study was Structural
Equation Model (SEM). To answer the hypotheses,
Partial Least Square (PLS) was used. Calculations
were carried out using Smart Partial Least Square
(PLS) following Ghozali (2012) due to the multi-lane
shape and model used in the form of reflective. The
calculations were performed using Smart PLS
because this study had a multi-lane, formative,
reflective relationship.
4 DATA ANALYSIS
The analysis used structural model testing to specify
the relationship between research variables. In some
references it is referred to as the inner model. The
results of the suitability analysis of the structural
model built show that the overall model was
"relevant" to explain the variables studied and their
relationship between each other. The Q2 value
calculated was 0.579. It exceeded the critical limit of
0.5, and, thus, the structural model was declared
suitable and appropriate.
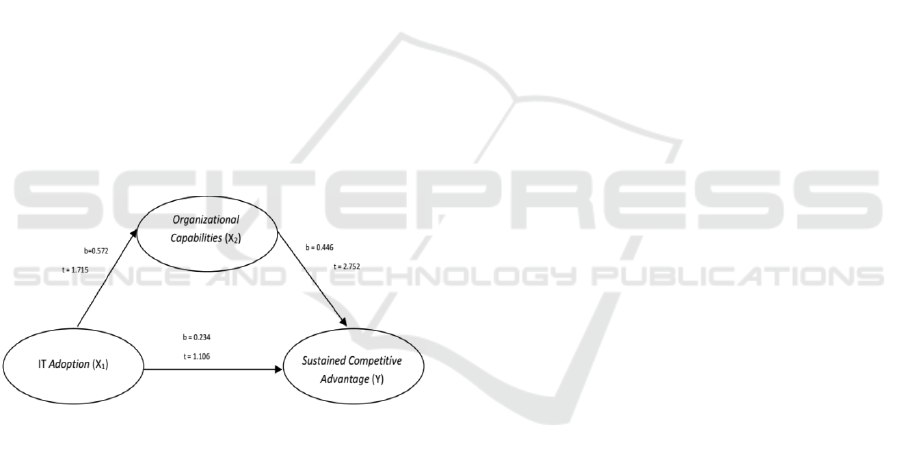
Figure 1: Research findings
The exogenous variables studied in the inner
model were IT Adoption and Organizational
Capability, while the endogenous variable was
Sustained Competitive Advantage. The results of the
inner weight shown in Figure 1 above shows that the
variable Sustained Competitive Advantage was
influenced by the variables IT Adoption and
Organizational Capabilities, while the variable
Organizational Capabilities was influenced by the
variable IT Adoption following the equation below:
Y = 0.234 X
1
+ 0.446 X
2
X
2
= 0.572 X
1
The effect of the variable IT Adoption on the
variable Organizational Capabilities had an R
2
score
of 0.328, which indicates a "weak" model.
Meanwhile, the effect of the variables IT Adoption
and Organizational Capabilities on the variable
Sustained Competitive Advantage had an R
2
score of
0.373, which indicates a "moderate" model.
4.1 Hypothesis testing
The first hypothesis in this study was not proven true
because the results of the data analysis show a t value
of 1.106, which was smaller than 1.96. Thus, it can be
said that IT Adoption had no significant effect.
However, it had a positive direction toward Sustained
Competitive Advantage. The positive relationship
that occurred indicates that better IT Adoption would
be increasingly able to improve Sustained
Competitive Advantage at a value of 0.234.
The second hypothesis in this research was not
proven true because the results of the data analysis
show a t value of 1.715, which was smaller than 1.96.
Thus, it can be said that IT Adoption had no
significant effect but had a positive direction toward
Organizational Capabilities. The direction of the
relationship between the two variables was positive,
which means that better IT Adoption would be able
to increase Organizational Capabilities at a value of
0.572.
The third hypothesis in this research was proven
true because the results of the data analysis show a t
score of 2.752, which was greater than 1.96. Thus, it
can be said that Organizational Capabilities had a
significant influence on Sustained Competitive
Advantage. The direction of the relationship between
the two variables was positive, which means that
better Organizational Capabilities would be able to
improve Sustained Competitive Advantage at a value
of 0.446.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The results of the data analysis show that IT Adoption
had no significant effect but had a positive direction
toward Sustained Competitive Advantage. With a t
score of 1.106, which was smaller than 1.96, it can be
explained that an increase in Sustained Competitive
Advantage could not necessarily be formed through
good IT Adoption. The effect of IT Adoption on
Sustained Competitive Advantage was positive,
which shows that the better IT Adoption, the greater
the Sustained Competitive Advantage.
The findings in this study indicate that IT
Adoption had an important role in enhancing the
Sustained Competitive Advantage of private Islamic
higher education institutions in Indonesia. Thus, if the
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
330

universities want to improve their Sustained
Competitive Advantage, it is critical to pay attention
to IT Adoption. This is relevant to Aggarwal’s
research (2017), which shows that IT Adoption
played an important role in realizing organizational
performance, which in the context of this research
was Sustained Competitive Advantage.
The results of the analysis also show that IT
Adoption had no significant effect but had a positive
direction toward Organizational Capabilities. With a
t value of 1.715, which was smaller than 1.96, it can
be explained that an increase in Organizational
Capabilities might not be formed through good IT
Adoption. The influence of IT Adoption on
Organizational Capabilities was positive, which
indicates that better IT Adoption would be able to
improve Sustained Competitive Advantage.
The findings of this study prove that IT Adoption
played an important role in increasing Organizational
Capabilities. In other words, the organizational
capabilities of a higher education institution could be
formed with good IT Adoption. Therefore, if it wants
to increase its organizational capabilities, it is
necessary for it to pay attention to IT adoption. This
result is in line with the research conducted by Azim
and Sattar (2011), which proved that IT adoption
affects organizational capabilities.
The results of the analysis also prove that
Organizational Capabilities had a significant
influence on the Sustained Competitive Advantage of
private universities as evidenced by a t score of 2.752,
which was greater than 1.96. Thus, it can be explained
that an increase in Sustained Competitive Advantage
could be formed by good Organizational Capabilities.
The influence of Organizational Capabilities on
Sustained Competitive Advantage was positive,
which shows that the higher the Organizational
Capabilities possessed, the greater the Sustained
Competitive Advantage.
The findings in this study prove that
Organizational Capabilities played an important role
in improving the Sustained Competitive Advantage
of private universities. In other words, Sustained
Competitive Advantage of private universities could
be formed by the Organizational Capabilities of the
private universities. Wang and Ang (2004) revealed
that Sustained Competitive Advantage is generated
by organizational capabilities that are measured by
reducing costs, quality, and innovation. Tuan and
Yoshi (2010) explain that Organizational Capabilities
are the skills or expertise of employees or intangible
resources such as reputation or culture.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTIONS
The researchers concluded the following: (a) in the
case of this study, IT Adoption did not have any
significant effect on Sustained Competitive
Advantage; (b) IT Adoption had no significant effect
on the Organizational Capabilities of private Islamic
higher education institutions; and (c) Organizational
Capabilities had a significant effect on Sustained
Competitive Advantage. It is recommended that the
next research should explore why IT Adoption has no
significant influence on SCA and Organizational
Capabilities. It is also necessary to conduct
comparative studies on different research objects, for
example, public universities with different cultures
and resource conditions.
The results of the study have the following
managerial implications: (a) for private Islamic
universities to be able to improve their sustained
competitive advantage, especially in terms of
organizational resources optimisation, it is necessary
to pay attention to cost efficiency strategies, quality
strategies, and innovation strategies (Tuan and Yoshi
(2010), and (b) a higher education institution can
improve its sustained competitive advantage through
IT adoption, in combination with the formulation of
appropriate strategies to encourage the performance
of organizational capabilities.
REFERENCES
Aggarwal, et al. 2017. Adaptive Capacity to
Technological Change: A
Microfoundational Approach. Strategic
Management Journal, 38: 1212–1231.
Abugabah, Sanzogni, Alfarraj, 2015. Evaluating the
impact of ERP systems in higher education,
The International Journal of Information and
Learning Technology, Vol. 32 Iss 1 pp. 45 -
64 http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/IJILT-10-
2013-0058
Armstrong, Kotler, 2015. Marketing an Introducing
Prentice Hall twelfth edition. England:
Pearson Education, Inc.
Azim, M., Ali, A., and Sattar, J. 2011. Factors
influencing adoption of information
technology based banking services (a case
study of pakistan). IEEE Computer Society,
45-50
Information Technology Adoption in Islamic Higher Education Institutions in Indonesia
331

Barney, J. B. 1991. Firm Resources and Sustained
Competitive Advantage. Journal of
Management 17: 99–120.
David, Fred R. 2010. Strategic Management: A
Competitive Advantage Approach, Concepts
and Cases (13th Edition). Prentice Hall
International, London.
Ghozali, I. 2012. Aplikasi Analisis Multivariate
dengan Program IBM SPSS. 20. Semarang:
Undip.
Grant, R. M., 2011. The Resource - Based Theory of
Competitive Advantage: Implications for
Strategy Formulation. California
Management Review. 33 (3). Pp. 114-135
Gurkan, I. G., & Bititci, Umit Sezer., 2015.
Understanding Organizational Capabilities
and Dynamic Capabilities in the Context of
MicroEnterprises: A Research Agenda.
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences.
DOI: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.11.371
Indrajit, Richardus Eko, 2013. Menilai Kesiapan
Kampus dalam Menerapkan Teknologi
Informasi dan Komunikasi, Presented on
https://www.academia.edu/14370907/Menil
ai_Kesiapan_Kampus_dalam_Menerapkan
_Teknologi_Informasi_dan_Komunikasi?a
uto=download
Jogiyanto. 2007. Sistem Informasi Keperilakuan.
Yogyakarta: Andi.
Melitski, David Gavin, Joanne Gavin, 2010.
Technology adoption and organizational
culture in public organizations,
International Journal of Organization
Theory & Behavior, Vol. 13 Issue: 4,
pp.546-568, https://doi.org/10.1108/ IJOTB-
13-04-2010-B005
Miranda, et al. 2016. Technology Adoption in
diffusion of innovations perspective:
introduction of an ERP System in a non-
profit organization, RAI Revista de
administracao e inovacao 13 (2016) 48—57.
Notoatmodjo, S. 2003. Pendidikan dan Perilaku
Kesehatan. Rineka. Cipta. Jakarta.
Prawiradilaga. 2008. Mozaik Teknologi Pendidikan.
Jakarta: Kencana Prenada Media Group.
Sampurno. 2011. Manajemen strategi. Gadjah Mada
University Press: Yogyakarta
Schermerhorn, J. R. 2011. Organizational behavior.
New Jersey: Prentice Hall Inc.
Sugiyono. 2014. Metode penelitian kuantitatif,
kualitatif, dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Teece, David J., 2017. Dynamic Capabilities and
(Digital) Platform Lifecycles, in Jeffrey
Furman , Annabelle Gawer , Brian S.
Silverman , Scott Stern (ed.)
Entrepreneurship, Innovation, and Platforms
(Advances in Strategic Management,
Volume 37) Emerald Publishing Limited,
pp. 211 – 225
Tuan, N. P., dan Yoshi, T. 2010. Organisational
capabilities, competitive advantage and
performance in supporting industries in
Vietnam. Asian Academy of Management
Journal, Vol. 15, No. 1, 1–21
Wang, C. K.,dan Ang, B. L. 2004. Determinants of
venture performance in Singapore. Journal
of Small Business Management, 42(4), 347–
363.
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
332
