
'Batang' as a Domestic Space –
The Manifestation of Sustainability in
the Riverside Settlement Culture in Banjarmasin
Dahliani
1
, Purwantini Setijanti
2
, I. Soemarno
2
, Muhammad Faqih
2
, Arina Hayati
2
1
Doctoral Student in Department of Architecture, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember, Surabaya
2
Lecturer in Department of Architecture, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember, Surabaya
Keywords: The Use of Domestic Space, Batang, Riverside Culture
Abstract: Riverside settlement is the start of the development of river cities in Indonesia. At this time the cities’
growth has shifted from river-based to land-based. This condition raises the question of whether riverside
settlements still have connectedness to the river for daily activities as the manifestation of a riverside
culture. This research used a qualitative method with case studies on riverside settlements in Banjarmasin,
such as Panglima Batur and Kampung Kenanga settlements. The focus of the observations was on the daily
activities carried out by residents on some elements of the settlements, namely batang and its connection
with the dwellings. Based on this research, riverside functioned not only as a "looked-on space" but also a
"used space"; there was an active relationship between the river, settlement, and dwellers that materialized
from domestic activities. Daily activities conducted by the inhabitants were the most specific forms of
culture that could be seen in the built environment. In this case, the riverside culture was visible through the
existence of batang and its use. Through this batang, the sustainability of the riverside culture in riverside
settlements can be maintained.
1 INTRODUCTION
The city of Banjarmasin is known as the "City of
Thousand Rivers"; it is flowed by many rivers, large
and small. This natural condition of being
surrounded by many rivers created a culture of
living by the riverside. The riverside culture is a
form of daily life of people who depend on the river
for their way of life and behavior (Nurfansyah,
2006). According to Saleh (1984), this is triggered
by the existence of the river as a main transportation
route, so the population is concentrated along the
river. It can be seen from the existence of
settlements in the form of houses on stilts along the
river or in the form of lanting houses that float on
the river.
Different cultures will produce different
dwellings (Lawrence, 1983, Lang, 1987).
Residential place is the social-cultural expression
implied through its domestic activities. Activity is
the reflection of people's desires, attitudes, and
knowledge of the world as a place of residence
(Lang, 1987). Activities connect them (occupants)
with the environment to process and change the
nature in settling in an environment as a cultural
embodiment based on an understanding of what is
known, thought, and viewed by individuals about the
world and the values that are formed and developed
in the community (Sangalang and Adji, 2014).
Activities can be seen from the daily behavior of
residents interacting with their environment.
Behavior is one of the factors that influence the
relationship between residents and the environment
in which they live. In addition, there are also
influences from culture, environmental conditions,
and outside influences (Hirsan, 2011).
In order to achieve sustainable settlements, one
aspect that needs to be considered is culture. Culture
is an important part of human-centered development,
so culture is used as an aspect of the realization of
sustainable development (referring to the World
Commission on Culture and Development/WCCD,
1996). The most specific cultural breakdown is an
activity that can be studied through the built
environment (Rapoport, 2005). The values held by a
society and the material objects it uses are cultural
Dahliani, ., Setijanti, P., Soermarno, I., Faqih, M. and Hayati, A.
Batang’ as a Domestic Space – The Manifestation of Sustainability in the Riverside Settlement Culture in Banjarmasin.
DOI: 10.5220/0008904300002481
In Proceedings of the Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference (BEST ICON 2018), pages 11-19
ISBN: 978-989-758-414-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
11

elements that embody its way of life (Knox and
Pinch, 2010). A culture that is realized through the
way of life of everyday residents as a community
can support the sustainability of settlements. This is
especially the case for the culture that can show the
relationship between residents and their environment
based on specific environmental conditions such as
the state of being on the banks of rivers.
The existence of a river will affect the use of
domestic space as a place for daily activities. One of
the elements of riverside settlements is batang. A
batang is a vernacular building built by a
community to accommodate daily activities directly
related to the river. A batang is a material object in
settlements as a cultural element of riverside. The
existence of batang in riverside settlements is
currently decreasing because it is considered by
some to provide a less attractive view of the
riverside. Therefore, through the study in this article,
it is hoped that it can contribute to the importance of
batang as a domestic space, which is a cultural
element in settlements that can manifest the cultural
sustainability of riverside settlements.
Presently, the growth of Banjarmasin city has
shifted from river-based to land-based. The riverside
is more geared towards the development of a more
public riverfront. This condition raises the question
of whether riverside settlements still have
connectedness to the river for daily activities as the
embodiment of a river culture.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 The Culture of Living
Culture concerning various ways of human life is
reflected in the patterns of action and behavior
(Poerwanto, 2008, Daeng, 2008). Culture can be
seen in three forms (Koentjaraningrat, 1985). First, it
can be seen in the form of complex ideas, values,
norms, rules, and so on. Second, it can be seen in the
form of complex patterned activities of human
beings in a society. Third, culture can also be seen in
the form of objects of human works; through this
form, culture can be studied architecturally as the
result of human relationships with the environment
in a built environment, including the use of space in
a settlement. In the use of domestic space, a
community’s values, the activities undertaken by
residents, and the buildings, spaces, and elements in
it as objects of human creation are observable.
Humans’ activities reflect the desires, attitudes,
and knowledge of their world as their place of
living, so how environment is addressed tends to be
different to every person. This is influenced by their
society and culture (Lang, 1987). Rapoport (2005)
describes in detail the relationship between culture
and activities that can be seen in a built
environment. He describes culture to be more
concrete, so it can be understood in the built
environment. Culture is defined as a way of life
consisting of values, ideals, images, schemata,
meanings, norms, standards, expectations, rules,
lifestyles, and activity systems. All aspects of culture
will be realized in the built environment in the form
of space organization, time, meaning, and
communication. Built environment is the
embodiment of a system of activities. It is a cultural
landscape. Built environment is composed of fixed
elements, semi-fixed elements, and non-fixed
elements. Through this explanation, the
implementation of culture in a built environment
becomes clearer and easier to study.
The processes of culture, environment, and
psychology take place in an interconnected system.
These three are related to mental activities (seeing,
hearing, smelling, interpreting, believing, and
behaving) and behavioral activities (what people do
and how they act) towards their environment
(Altman and Low, 1992). Culture is a process in
which people create meanings to give themselves a
sense of identity. Place is a manifestation of human
culture (Cohen, 1994 in Ujang and Zakariya, 2015).
Environmental variations can also reflect the cultural
complexity that distinguishes one group from
another. Ways of life, symbols, meanings and
cognitions, and sustainability are accepted as
specific norms to a particular group. In a pluralistic
society, culture plays an important role in
determining its identity that influences the character
and identity of the places it inhabits (Ujang and
Zakariya, 2015).
2.2 Domestic Space and Domestic
Activities
The word domestic comes from the Latin word
"domesticus", which means home and house or
household. Domestic space is found in home, house,
and yard for the relationships between human with
their residence, both inside and outside the house in
everyday contexts (Briganti and Mezei, 2012). The
existence of domestic space can be understood from
the existence of space elements in the form of
furniture, tools, and appliances arrangement as the
main marker (Schlyter, 1991, Hanson, 1998).
Equipment in this space can show the functions for
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
12

everyday activities, for example, living room, dining
room, sleeping room, study room, and kitchen
(Oseland, 1999). Domestic activity indicates the
relationships between human and their living space
in everyday contexts (Monteiro, 1997; Collignon,
2010). Domestic space as a place of daily activities
directly responds to human needs and wants. Every
human being forms a domestic space in accordance
with his/her will to get the best conditions for his-
/herself.
Monteiro (1997) divides the activities in
domestic space into three groups: 1) integrated
activities, which are various activities that can be
done in one space; 2) rooted activities, which are
restricted and inflexible activities consisting of only
one type of activity function that depends on specific
equipment/furniture in the room, for example,
cooking in the kitchen, bathing in the bathroom; and
3) loose activities, which are activities that are
flexible—it can be done anywhere in the house and
can be associated with other activities. Residents
have the freedom to use the space to meet their
activity requirements. One space can be used for
various activities, and certain activities can take
place in any space.
Domestic space as an area for domestic activity
shows the relationship between humans and their
environment. The existence of activities is
determined by four components: the existence of the
subject, the existence of activities, and the existence
of places in association with time. There are various
domestic activities that can be done indoors and
outdoors. The type of domestic activity to be used in
this study is based on the classification of activities
undertaken by Monteiro (1997), Ahrentzen (1989),
and Kisnarini (2015) as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Classification of Domestic Activities
Household Chores
Extended Chores
a. Washing clothes
b. Drying clothes
c. Ironing
d. Storing clothes
e. Cleaning/maintaining the
house
f. Cooking preparation
g. Cooking
h. Washing dishes
a. Shopping
b. Working
c. Playing with
children
Passive Leisure
Interactive Leisure
a. Watching TV
b. Reading books
c. Listening to music/radio
d. Relaxing
a. Talking
b. Receiving guests
c. Playing
d. Playing a musical
instrument
e. Doing a hobby
f. Going for a walk
Private Needs
Communal Needs
a. Bathing
b. Sleeping
c. Praying
d. Studying
e. Personal care
f. Childcare/babycare
g. Resting
a. Drinking together
b. Eating together
c. Togetherness with
family
d. Celebration
e. Religious
meetings
3 RESEARCH METHODS
This research used a qualitative research method
with a phenomenology approach, which looks at the
research object in the natural context.
Phenomenological research emphasizes, to a greater
extent, people's experience at where they are. The
focus of this research was the existence of residents
who used batang as domestic space.
The study was conducted in the city of
Banjarmasin in a settlement on the banks of
Martapura River. The selected locations were
Panglima Batur and Kampung Kenanga. Both
villages were categorized as old villages.
The data required were in the form of primary
data, which were data on batang types and
placement in the settlement, activities carried out in
the batang, semi-fixed and non-fixed supporting
elements, types of actors, time of activities, and
occupants’ reasons for using batang. Data collection
was carried out by in-depth interviews with batang
users and field observations, which were conducted
directly in the field where activities were carried out
by batang users.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Batang as a Vernacular Building on
a Riverside Settlement
Vernacular architecture is also called architecture
without architect. A vernacular building reflects the
habit of community life; it is built due to the desire
to adjust to natural conditions. The community has
the autonomy in construction to fulfill its functions.
The riverside community makes the batang adjusted
to the condition of the site where the building is
located, which is on the banks of the river.
Batang is an unroofed rectangular construction
located on the bank of a river. Its dimensions variy
from 1 m x 1 m to 3 m x 4 m. Based on the
construction, there are two types of batang, namely
Batang’ as a Domestic Space – The Manifestation of Sustainability in the Riverside Settlement Culture in Banjarmasin
13
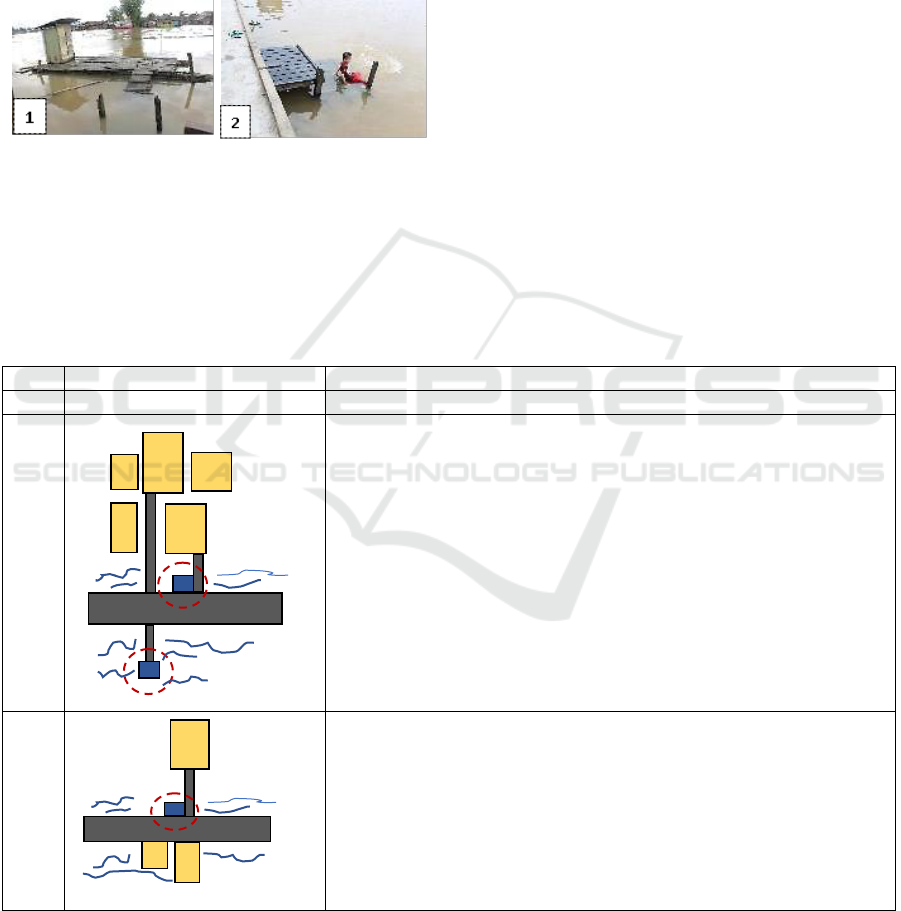
batang lanting and batang panggung (platform).
Batang lanting has a floating construction made of
logs, bamboos, or plastic drums. Meanwhile, batang
panggung has a pole construction made of galam
wood or ironwood that is plugged into the ground.
The batang’s floor is made of sparsely-arranged
ironwood. The structure and materials of a batang
show that it is a vernacular construction.
Figure 1. Batang lanting with a floating bamboo
construction (1) and batang panggung with an ironwood
construction (2)
4.2 Placement of Batang at Dwelling
Subiyakto (2005) states that the characteristics of
riverside settlements in Banjarmasin are as follows:
“The house is built as a house on stilts rights on the
riverbank or some of the posts are in the water.
Sometimes it can be a lanting house floating on the
water on the riverbank. In the same case they also
built a places of worship such as mosque or langgar.
Aside from that, there are also lanting or batang for
bathing, washing and latrine. Lanting and batang
function like docks, a place to unload and upload
items from boats or ships. It is a place for people to
make sale transactions with boats peddlers. It is also
a place to tether boat.”
Historically, the above text indicates that
‘batang' is located on the bank of a river, stands
alone, and exists in a similar manner as other
dwellings that are located by the river (lanting
houses and houses on stilts). It serves as a bath,
laundry, and latrine, as well as a dock for boat and
passenger and a boat tether.
The laying of a batang in subsequent
developments is not only done along the bank of a
river as a stand-alone construction, but related to
dwellings on the riverside. The laying of a batang
can be seen in the following table 2.
Table 2. Placemnet of Batang at Dwelling
No.
Placement of Batang
Description
1
2
3
1.
A. The batang panggung is situated in front of a group of dwellings after a
public titian (walkway). The dwellings on the riverside settlement are
grouped based on marital relationships called bubuhan (family cluster).
Each of these bubuhan will have a single communal batang.
Historically, batang has existed since the first house in the bubuhan
group was built (grandfather or great-grandfather) and has survived
until now.
B. The batang panggung is situated in front of the dwelling directly
connected to the terrace. This new batang is built to facilitate the
activity of the occupants. The inhabitants feel that it takes a great
distance to use the family batang (bubuhan). Except during low tide,
residents will use family-owned batang.
2.
The batang panggung is situated in front of the dwelling at the end of the
private titian. It is private, but can be used by neighbors. The dimensions of
the batang range from 1 m x 1 m to 1 m x 1.5 m. On the banks of the river
there are dwellings.
A
B
A
B
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
14

1
2
3
3.
The batang panggung is directly connected to the public titian (walkway).
Usually, this happens in areas that have abrasion, so it does not require a
long walkway to reach the water at low tide. It is private (owned by a house
on the land), but it can be used by others. The dimensions of the batang
range from 1 m x 1 m to 2 m x 3 m.
4.
The batang panggung is directly connected to the riverbank behind a
dwelling (A) and next to another dwelling (B). It is a private property, but
the batang adjacent to the dwelling (B) can be accessed by neighbors in
need. The dimensions of the batang range from 1 m x 1 m to 2 m x 3 m.
5.
The batang lanting is directly related to the public titian. It exists only in
Panglima Batur, with dimensions of 3 m x 4 m. It is used by some residents
together even though they are not of the same family group (bubuhan). The
group is based on RT limits.
6.
The terrace of the lanting house is used as batang by residents and
neighbors around. The porch is 1 m wide. It is used by neighbors
during low tide as they cannot use the batang panggung, whereas
lanting house will follow the tides of river water.
7.
The batang panggung is directly connected to the dock. It is
originally used to tether a boat, but it is also used by residents for
other activities.
Source: field observations
4.3 Batang as Domestic Space
The original function of batang is as a place for
bathing, washing, latrine, docking, and boat
tethering. Bathing and washing are the most
frequently performed domestic activities in the
batang. It is rarely used as latrine because the
residents already have toilets at their houses,
although some of the houses do not have any and the
owners must go to batang.
In subsequent developments, as an element of
riverside settlements, batang can also be used by
residents for a variety of domestic activities. This is
presented in the following table.
A
B
Batang’ as a Domestic Space – The Manifestation of Sustainability in the Riverside Settlement Culture in Banjarmasin
15

Table 3. The use of space for domestic activity on the batang
No.
Group of
Activity
Type of
Activity
Actors
Time
Photo
1
2
3
4
5
6
1.
Household
Chores
Washing
clothes
Women
Young women
Men
05.00–10.00
16.00–18.00
According to the needs
At high tide
Washing
dishes
Women
Young women
Men
08.00–10.00
16.00–8.00
According to the needs
At high tide
Washing the
ingredients
Women
Young women
08.00–10.00
16.00–18.00
According to the needs
At high tide
2.
Extended
Chores
Shopping
Women
Men
07.00–09.00
3.
Passive
Leisure
Relaxing
Women
Men
Teens
Children
09.00–11.00
14.00–16.00
4.
Interactive
Leisure
Chatting
Women
Men
Teens
05.00–11.00
16.00–18.00
Playing
Children
15.00–18.00
Doing
a hobby
(fishing)
Men
Young men
Children
09.00–13.00
5.
Private
Needs
Bathing
Men
Women
Teens
Children
05.00–09.00
16.00–18.00
Source: field observations
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
16

In the Panglima Batur area, there are batang
lanting that serve the public. The main thing that is
done by the residents is the domestic activity.
Occupants on land and riverside feel more
comfortable doing domestic activities such as
washing clothes and bathing in batang than at home
(even though they have already been connected to a
water supply network from PDAM). Often times,
they also wash food ingredients in the batang and
then rinse them with clean water at home. They
revealed that doing activity on the batang gives
them more space (3 m x 4 m for batang lanting and
1 m x 1.5 m to 2 m x 3 m for batang panggung). In
the batang they can use water more freely than they
can at home. In addition, they can meet their
neighbors, greet each other, and talk with each other
there. Batang lanting and batang panggung are not
only useful as domestic space, but also useful as a
socializing space between neighbors while doing
activities.
In the mid-morning and afternoon, the batang
lanting and batang panggung are quiet from the
service activity. At this time it is used by fathers for
fishing and by mothers for relaxing while
babysitting (bringing toddlers with them to see the
river). Users of the batang lanting and batang
panggung are not only residents who have a house
on the riverbank, but also residents who have homes
on the mainland. This indicates that the river has an
appeal to the domestic activity of the inhabitants, not
only for the water supply, but also for the cool
scenery.
In the Kampung Kenanga area, the batang are
positioned along the walkway (titian). Each batang
is owned by a house on the opposite side of the titian
parallel to the batang. This house is the main house,
then several houses are developed to the left, right,
front, and back of the main house. These houses are
inhabited by children, grandchildren, and relatives
(one family cluster/bubuhan), so one batang is used
by one family cluster. Residents use the batang
panggung for domestic activities based on family
ownership. Usually, at high tide, one family cluster
will use the batang together for bathing and
washing, but other people (not the same bubuhan)
may use this batang.
4.4 The Cultural Manifestation of the
River on the Batang
Daily activities reflect the way of life as a cultural
manifestation. Domestic activities carried out daily
by occupants in riverside settlements embody the
culture of riverside communities. This domestic
activity is related to household activities carried out
inside and outside of a dwelling. Batang is a fixed
element contained inside and outside the dwelling.
In this batang various domestic activities are carried
out, including not only household core activities
such as washing clothes, washing dishes, and
cleaning food, but also other domestic activities like
passive recreational activities such as leisure, active
recreational activities (e.g., talking, playing, doing
hobbies (fishing)) and private activities (e.g.,
bathing).
Domestic activities carried out on the riverside
are not only those directly related to the river itself
in the form of domestic service activities (bathing
and washing), but also those related to the
atmosphere of the riverbank. Activities can include
sitting for relaxing while looking at the river,
chatting, fishing, and playing. The existence of a
river supports the residents to use riverside batang
as their activity space. This indicates that the
riverside is not just a "used space", but also a
"looked-on space". There is an active relationship
between the river, inhabitants, and activities. River
functioned as a site with batang as a place of activity
for the residents of riverside settlements.
The domestic activities carried out in the batang
are not performed alone. Usually they are performed
together with other residents (neighbors) while they
are greeting and talking with each other. In this way
relationships are established. One domestic space in
the neighborhood is used together and alternated by
all residents of the settlement. As Koentjaraningrat
(1979) points out, most Indonesians engage in
activities outside the dwelling while talking with
neighbors and enjoying the atmosphere, and they do
not covet a life of solitude (privacy). If bathing and
relaxing are a private activity in the Western culture,
it is not the case in the culture of riverside
settlements. Communal life and togetherness in
conducting domestic activities become the main
characteristics of the society. The community
members appreciating the way of life together,
engage in interactions largely, and cooperate with
their neighbors (Kontjaraningrat, 1979).
The private batang on the riverbank (limited by
the public titian) have been experiencing a shift in
meaning. Based on the historic and settlement
patterns of the riverbanks, the riverbanks are
occupied by houses on the land facing the river and
parallel to the batang. Batang serve as docks and
areas for conducting domestic services (bathing,
washing dishes, and washing clothes). Every house
has this batang. In the present development, these
batang are legally private property, but in perception
Batang’ as a Domestic Space – The Manifestation of Sustainability in the Riverside Settlement Culture in Banjarmasin
17

of other occupants, they are public property. Owners
give freedom for anyone to use it. They are used by
not only the neighbors by the riverbanks, but also by
residents on land.
It is similar with personal batang located in front
of the house (side by side with the house or side by
side with private titian). It can be used by anyone
who needs it without the permission of the owner.
The private batang is changed to public property.
Residents do not give restrictions, so anyone can use
it. The value of "basamaan" (sharing) adhered to by
settlers is strong, so there is no conflict in the use of
domestic space together, especially in the domestic
space associated with the river.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Batang is a riverside settlement element that
supports the domestic activities of residents. Based
on the construction, batang are divided into two
types: batang lanting (floating construction) and
batang panggung (pole construction). Based on its
relation to shelter, batang panggung are divided into
4 (four) types, namely 1) batang located in front of
family cluster (bubuhan) adjacent to the public titian
(walkway), 2) batang located in front of the
dwelling at the end of the private titian or in front of
the terrace, 3) batang that are directly adjacent to the
public titian, and 4) batang that are directly related
to dwellings, situated in the back or side of the
dwelling. There is another type of batang that is
directly related to the dock. Batang lanting are
divided into 2 (two) types, namely 1) batang lanting
that is connected to the public titian and 2) terrace
lanting houses that serve as a batang.
The cultural manifestation through domestic
activities in the batang shows the following:
a. active connection between rivers, occupants, and
activity;
b. riverbank functions as a “used space” and a
“looked-on space”; and
c. the value of “basamaan” (togetherness) held by
residents of riverside settlements when
conducting domestic activities.
This research indicates that the existence of the
batang is indispensable in the sustainability of
riverside culture in riverside settlements.
REFERENCES
Ahrentzen, Sherry. 1989. Space, Time, and Activity in The
Home: A Gender Analysis. Journal of
Environmental Psychology (1989) 9, hal 89-100.
Altman, I., Low, S. 1992. Place Attachment. Plenum
Press. New York.
Briganti, Chiara., Mezei, Kathy. 2012. The Domestic
Space Reader. University of Toronto Press.
London.
Collignon, Beatrice. 2010. Domestic Spaces and Cultural
Geography. Mercatanti L. (ed), 2010. Percorsi di
geografia. Tra cultura, societa e turismo.
Bologna.
Daeng, Hans. 2008. Manusia, Kebudayaan dan
Lingkungan, Tinjauan Antropologis. Pustaka
Pelajar. Yogyakarta.
Hanson, Julienne. 1998. Decoding Homes and Houses.
Cambridge University. New York
Hirsan, Fariz Primadi. 2011.Identifikasi Pola Bermukim
Masyarakat Suku Sasak di Pulau Lombok Yang
Dipengaruhi oleh Sistem Kekerabatan (Studi
Kasus : Desa Puyung, Kabupaten Lombok
Tengah). Media Bina Ilmiah, Desember 2011,
Mataram
Kisnarini, Rika. 2015. Functionality and Adaptability of
Low Cost Apartmen Space Design: A Case of
Surabaya Indonesia. ITS Press. Surabaya
Knox, Paul dan Pinch, Steven. 2010. Urban Social
Geography An Introduction. Pearson Education
Limited. England.
Koentjaraningrat. 1979. Cara Hidup Penduduk Indonesia
di Daerah Kampung. Widyapura-Habitat, Jurnal
Pusat Penelitian Masalah Perkotaan dan
Lingkungan No. 5 Tahun II 1979.
Koentjaraningrat. 1985. Kebudayaan, Mentalitas dan
Pembangunan. PT. Gramedia. Jakarta
Lang, John. 1987. Creating Architectural Theory: The
Role of Behavioral Sciences in Environmental
Design. Van Nostrad Reinhold Company. New
York
Lawrence, Roderick J. 1983. The order of things at home.
Kunapipi Volume 5 issue 2 artikel 7. University
of Wolongong. Australia
Monteiro, Circe Gama. 1997. Activity Analysis in Houses
of Recife, Brazil. Space Syntax First
International Symposium. London.
Nurfansyah. 2006. Pola Permukiman dan Orientasi
Bangunan di Tepi Sungai Jingah. Prosiding
seminar Arsitektur Permukiman Tepi Sungai:
Problema dan Solusinya. Universitas Lambung
Mangkurat.
Oseland, NA. 1990. An Evaluation of Space in New
Homes. Building Research Establishment,
Bucknalls Lane. England.
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
18

Poerwanto, Hari. 2008. Kebudayaan dan Lingkungan,
Dalam Perspektif Antropologi. Pustaka Pelajar.
Yogyakarta.
Rapoport, Amos. 2005. Culture, Architecture, and Design.
Locke Science Publishing Company, Inc.
Chicago. USA
Saleh, Idwar. 1984. Sekilas Mengenai Daerah Banjar dan
Kebudayaan Sungainya sampai dengan Akhir
Abad ke-19. Museum Negeri Lambung
Mangkurat. Propinsi Kalimantan Selatan
Sangalang, Indrabakti dan Adji, Fredyantoni F. Pengaruh
Kondisi Hunian dan Lingkungan Terhadap
Keberlanjutan Permukiman Tepi Sungai Studi
Kasus: Kampung Pahandut dan Desa Danau
Tundai di Kota Palangka Raya. Jurnal
Perspektif Arsitektur Volume 9 / No.2,
Desember 2014
Schlyter, Ann. 1991. Time series analysis A longitudinal
study of housing quality in Lusaka. Dalam:
Housing the Poor in the Developing World
Methods of Analysis, Case Studies and Policy
(Eds) A.Graham Tipple dan Kenneth G.Willis.
Routledge. London
Subiyakto, Bambang. 2005. Infrastruktur Pelayaran
Sungai Kota Banjarmasin Tahun 1900-1970.
Buletin Arkeologi Naditira Widya No. 14
Oktober 2005. Balai Arkeologi Banjarmasin
Ujang, Norsidah., Zakariya, Khalilah. 2015. Place
Attachment and the Value of Place in the Life of
the Users. Social and Behavioral Sciences 168
page 373-380, 2015.
Batang’ as a Domestic Space – The Manifestation of Sustainability in the Riverside Settlement Culture in Banjarmasin
19
