
Identified Physical Settings Determinants of Public Activities in the
Sidoarjo City Square
Muhamad Ratodi
1
, Qurrotul A’yun
1
, Oktavi Elok Hapsari
1
, and Rita Ernawati
1
1
Department of Architecture, Universitas Islam Negeri Sunan Ampe, Jl. A.Yani 117, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Physical setting, Public activities, Green open space, City square
Abstract: Physical environment settings are believed to be able to influence public activity patterns by facilitating the
interaction between physical spatial space with its users. As one of the public green open areas and main civic
activities points, the Sidoarjo City Square also has a variety of user activity patterns, which are both suitable
and unsuitable to its design purposes. This article attempts to identify the physical settings determinants that
affect public space activities in Sidoarjo Square. Behavior mapping and time budget techniques were used to
collect data and analysis was conducted through data tabulation. The study identified at least five physical
settings factors that influence the Sidoarjo Square user activities, including shaded spaces, sitting and relaxing
areas, plazas, pedestrian paths and artificial lighting.
1 INTRODUCTION
The provision of green open space in Indonesia is
regulated through Law No. 26 of 2017, which
requires a minimum of twenty percent of the city to
be public open space. A good public open space must
be able to function and be used by the community to
gather, interact, and move safely and comfortably
(Siahaan, 2010).
In reality, there was a significant reduction in
the number of public open spaces in urban areas due
to public open land conversion into urban
infrastructure (Dwiyanto, 2009). This condition will
certainly lead to a decline in the quality of urban
public open spaces in Indonesia where they serve an
important function by contributing to the quality of
life of urban citizens (Ostermann, 2010).
The decline of the quality of public open
spaces is often encountered as common problems
arise, such as the lack of seating and gathering places,
visually poor entrance accesses, dysfunctional
features, winding paths, dead zones and unreachable
bus stop locations (Siahaan, 2010).
This phenomenon was also found in the district
of Sidoarjo. As with other cities in Indonesia, the
existence of the city square as a public open space has
also become a feature of urban spaces (Nas, 1986),
including Sidoarjo. Sidoarjo City Square, as the only
open public space in the area, also experienced
problems related to the quality of its public open
space. (Bilqisa, 2014) in her research stated that the
comfort of Sidoarjo Square users was still not well-
optimized due to the various economic and
recreational activities that take place there and have
not been facilitated by a good physical settings
arrangement. A good physical settings arrangement in
an area is believed to be able to influence the
activities and social behaviour of its users (Rapoport,
2016). Understanding user requirement activities will
help designers set up appropriate public facilities
(Courage and Baxter, 2005). This article will attempt
to identify the various factors that affect the physical
settings of Sidoarjo Square’s user activities.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
A qualitative approach was used to ensure the
sharpness of the research analysis, objectivity, and
systematicity in obtaining accuracy in interpretation.
We used direct observation techniques in addition to
behavioral mapping and time budget techniques to
map user behavior related to the physical settings of
Sidoarjo Square.
The purposive sampling technique was also used
to determine the observation subject, which was
observed during five different time periods for five
consecutive days (Sunday to Friday). Data analysis
Ratodi, M., A’yun, Q., Hapsari, O. and Ernawati, R.
Identified Physical Settings Determinants of Public Activities in the Sidoarjo City Square.
DOI: 10.5220/0008906100002481
In Proceedings of the Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference (BEST ICON 2018), pages 49-53
ISBN: 978-989-758-414-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
49
was carried out through the data coding stage and data
interpretation to obtain a research conclusion.
3 DISCUSSION
Located in the heart of the city, Sidoarjo Square has
become one of the landmarks of Sidoarjo City. In the
past, the square was more often used as a shopping
location by the residents of Sidoarjo. However, the
number of street vendors grew rapidly and caused the
square to become chaotic and disorganized, which led
to the square being revitalized into a green open
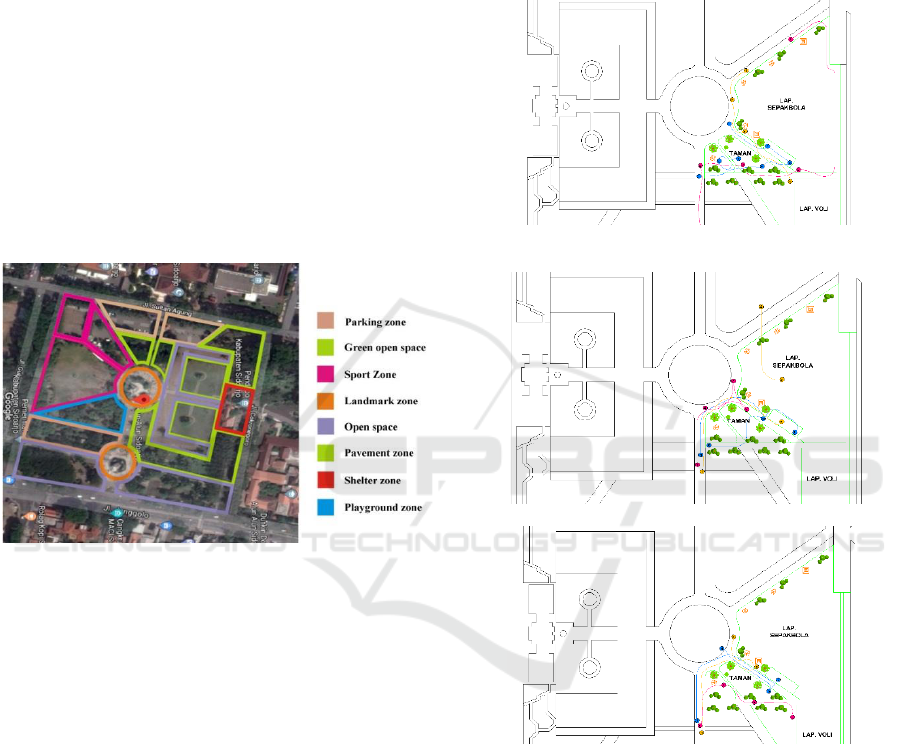
space. Broadly speaking, the activities in the Sidoarjo
Square are divided into several zones, comprising of
the sport zone, playground zone, and shelter zone (see
figure 1).
Figure 1: Zoning of the Sidoarjo square.
The next section will discuss the Sidoarjo Square
visitor movement patterns in the sports, playground
and shelter zones. We have observed the visitor
movement patterns in those zones at three different
time points: in the morning (9am), day (1pm) and
afternoon (4pm).
3.1 Movement in the sports zone
The visitor movement pattern in the sports area in the
morning tends to be more crowded in the park. This
is because the conditions around the park are shadier
and have more park seating compared to other points
in the sports area.
During the day, the movement pattern tends to
be more concentrated in parts around the Sidoarjo
monument. This condition is caused by hot
temperatures during the day at the observation site, so
visitors who have just arrived will consider where to
first sit and relax.
The visitor movement pattern in the afternoon
tends to be more crowded in the area around the
Sidoarjo monument, specifically in the gazebo and
group seating areas close to the fitness area. This
condition is most likely due to visitors preferring to
sit and relax together.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Figure 2: Visitor movement patterns in the sports zone at
(a) 9 am, (b) 1 pm, and (c) 4 pm.
The observation results in the sports zone
show that the most frequently passed points and a
large number of activities occur in the park area and
around the sports field. There were no striking
differences regarding the movement of visitors in the
morning or evening. A difference was only seen in the
age group of visitors, where there were more adult
visitors in the morning and evening who tend to visit
the sports zone just to take a break after their daily
routine.
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
50
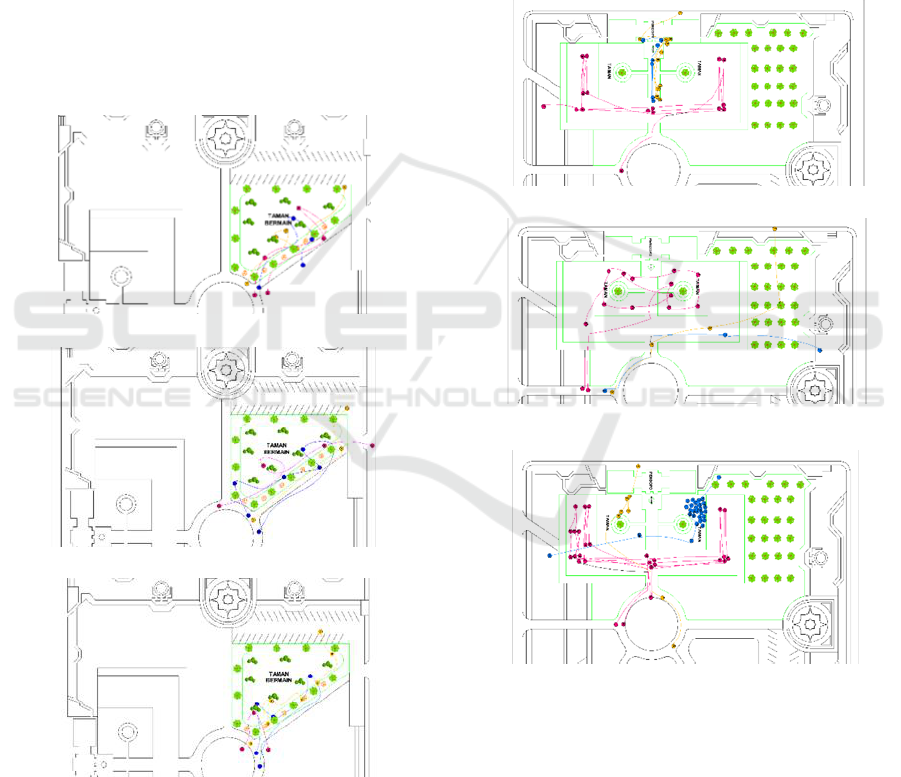
3.2 Movement in the playground zone
The visitor movement pattern in the children's
playground zone in the morning tends to be more
crowded in the children's playground area. The cool
morning atmosphere encourages visitors to take their
children to play or just watch the children's
playground. During the day, the visitor movement
pattern in this area tends to be more concentrated
around the children's playground and seating area
near the shady trees. The scorching heat of the sun
encourages visitors to rest in a shady spot, but tends
not to use the play equipment. Whereas in the
afternoon, the movement of visitors also tends to be
concentrated around the children's playgrounds and
seats close to the shade of the trees. Visitor activities
were dominated by recreational activities as well as
watching over their children play.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Figure 3: Visitor movement patterns in the playground
zone at (a) 9 am, (b) 1 pm, and (c) 4 pm.
From the observation results in the playground
zone, it can be seen that the children's playground and
seating areas were the most frequently passed points
where most activities were conducted.
3.3 Movement in the shelter zone
The visitor movement pattern in the shelter zone in
the morning tends to be concentrated around the plaza
area. The cool morning atmosphere encourages
visitors to do various physical activities such as
walking, jogging, doing gymnastics etc. The grass
tends to be moist due to dew, which causes visitors to
be reluctant to step on it. During weekdays, the
pavement on the side of the field was often used for
exercise and morning jogging. These activities were
generally carried out by middle-aged to elderly men.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Figure 3: Visitor movement pattern in the shelter zone at (a)
9 am, (b) 1 pm, and (c) 4 pm.
During the day, the visitor movement pattern at
the plaza area tends to be less crowded than in the
morning, where this area was often traversed by
visitors. This was because the area did not have an
adequate shade, so visitors tended to look for other
shady locations. In the afternoon, the movement
pattern of visitors tends to become more crowded
around the plaza and park. This area was not only
Identified Physical Settings Determinants of Public Activities in the Sidoarjo City Square
51
used for sitting, the green grass area was very popular
among children and adolescent visitors for playing
football. The plaza area was also used for certain
community activities, such as the photography,
dance, and automotive communities. Conducive
weather conditions also encourage visitors to be more
active in this area.
3.4 Identifying the relationship between
physical settings and visitor activities
From the observation results, we attempted to analyze
the correlation between the physical settings variables
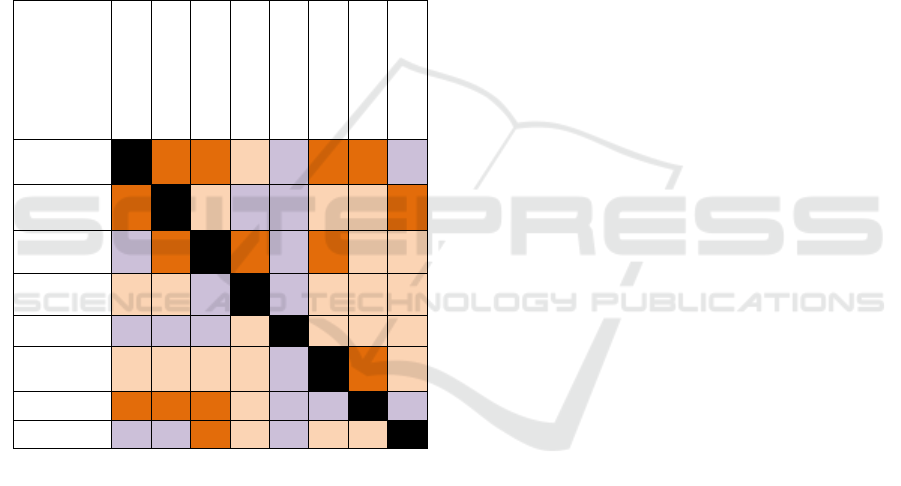
with user activities utilization (see Table 1 below).
Table 1: The relationship between physical settings in
influencing visitor activities
Shading area
Sitting points
Outdoor Lighting
Accessibility
Sanitation
Food facili
ties
Park
Plaza
Shading
area
**
*
**
*
**
*
**
*
**
*
*
Seating
points
**
*
**
*
*
**
**
**
*
Outdoor
Lighting
*
**
*
**
*
*
**
*
**
**
Accessibilit
y
**
**
*
*
**
**
**
Sanitation
*
*
*
**
**
**
**
Food
facilities
**
**
**
**
*
**
*
**
Park
**
*
**
*
**
*
**
*
*
*
Plaza
*
*
**
*
**
*
**
**
remarks:
* : weak influence
** : sufficient influence
*** : strong influence
From the results of the analysis, it can be seen
that the visitor activity of Sidoarjo Square was more
likely to be influenced by spatial factors (such as
shading areas and plazas) and supporting elements
and facilities such as seating, accessibility, outdoor
lighting and food facilities.
4 CONCLUSION
From the analysis results it is concluded that there
were at least four physical settings that were found to
be the public activities determinants in the Sidoarjo
Square, which include shaded areas, relaxation and
resting spaces, the plaza setting, and visitor
accessibility. Shaded area has become the most
important element in shaping visitor behavior,
considering that many Sidoarjo Square users
preferred to engage activities in shady areas. Seating
was the second most important element; however the
usage of the park benches in Sidoarjo Square was also
influenced by the location and shade patterns of the
seating areas. Meanwhile, the existence of the plaza
as the center of activity was the third most important
element considering the very large plaza area and
high frequency of activities conducted there
compared to other areas. The characteristics of the
square users were also varied and came from all age
groups.
Accessibility was the fourth most important
element in Sidoarjo Square. This is due to the
pedestrian pathway in Sidoarjo Square becoming a
gathering point for visitors to conduct various
activities such as sitting, resting, and holding
meetings among communities. There are also a
number of vocal points in this pedestrian area, such
as the Sidoarjo Monument and Jayandaru Monument,
which have become photo spots for visitors.
REFERENCES
Bilqisa, C.C., 2014. Kebijakan Pemerintahan Kabupaten
Sidoarjo Dalam Penataan Pedagang Kaki Lima
Di Alun-Alun Sidoarjo.
Courage, C., Baxter, K., 2005. Chapter 4 - Setting Up
Facilities For Your User Requirements Activity,
in: Courage, C., Baxter, K. (Eds.), Understanding
Your Users, Interactive Technologies. Morgan
Kaufmann, San Francisco, pp. 106–141.
https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-155860935-
8/50034-8
Dwiyanto, A., 2009. Kuantitas dan Kualitas Ruang Terbuka
Hijau Di Permukiman Perkotaan. TEKNIK 30,
88–92.
https://doi.org/10.14710/teknik.v30i2.1861
Nas, P., 1986. The Indonesian city: studies in urban
development and planning. Foris Publications.
Ostermann, F.O., 2010. Digital representation of park use
and visual analysis of visitor activities.
Computers, Environment and Urban Systems,
GeoVisualization and the Digital City 34, 452–
464.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2010.0
5.007
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
52

Rapoport, A., 2016. Human Aspects of Urban Form:
Towards a Man—Environment Approach to
Urban Form and Design. Elsevier.
Siahaan, J., 2010. Ruang Publik: Antara Harapan dan
Kenyataan. Bulletin Tata Ruang 3.
Identified Physical Settings Determinants of Public Activities in the Sidoarjo City Square
53
