
Analysis of Degeneration Hepatosit Cell on Female Mice(Mus
musculus) Induced by Ruthab Dates (Phoenix dactylifera) Extract and
Paracetamol
Risa Purnamasari
1
, Nurul Nahdiyah
1
, Eko Teguh Pribadi
1
, Sri Hidayati
1
, Nova Lusiana
1
, Funsu
Andiarna
1
, Moch. Irfan Hadi
1
, Hanik Faizah
1
, Mohammad Yusuf Alamudi
2
1
UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, Indonesia
2
Prof Nidom Foundation, Surabaya, Indonesia
novalusiana@uinsby.ac.id, funsuliu@gmail.com, m_i_h@uinsby.ac.id, hanikfaizah@uinsby.ac.id,
myusufalamudi@hotmail.com
Keywords: Paracetamol, Ruthab Dates, Hepatosit Cell Degeneration
Abstract: Paracetamol is a drug used as an analgesic antipyretic. One of the fruits used as a hepatoprotection agent is
Dates (Phoenix dactylifera) ruthab. This study aims to determine the hepatoprotective activity of various
doses of ruthab date fruit extract against liver degeneration of female mice induced by paracetamol. This
study used a group pre-experiment with the control group and group with dosing dates of 1, 3, and 7. While
the experimental group was the group with 41.4 grams of paracetamol and the group given paracetamol and
ruthab dose dates 7. The results of this study showed that there were no significant differences in various
doses of ruthab dates extract in the pre-experimental group, although there was a decrease in the mean
degeneration score. While the results of the experimental group, namely the group with the administration of
ruthab and paracetamol dates, showed significant differences, indicating that there was a hepatoprotective
activity of rutab dates extract. The existence of these differences was thought to be due to the flavonoid content
in ruthab dates extract which acts as a hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidant.
1 INTRODUCTION
Paracetamol (PCT) is a drug commonly used to
reduce body temperature during fever (antipyretic),
and reduce pain (analgesics). Although paracetamol
is declared safe at therapeutic doses, high doses of
paracetamol can cause liver failure. The hepatoxic
effects of paracetamol are known since around 1960
(Oktiari et al, 2010).
In France, there is a study that shows the
population of DILI (Drug Induce Liver Injury) around
13.9 cases / 100,000, two people (5.9%) died and 4 of
34 (11.8%) patients were hospitalized. In Singapore,
liver transplants are even 14%. 96% of patients with
liver dysfunction are still many who are given liver
disease inducing drugs including ranitidine,
cefriaxone, and paracetamol in 2012 at Tasikmalaya
hospital (Sa'roni, 2012). Paracetamol is widely
researched to cause liver toxicity.
Liver is an organ that plays a role in the body's
detoxification and metabolic system. Liver damage
can be caused by infection or chemical intoxication.
The toxicity of the liver can be reduced by the
presence of antioxidant compounds. (Hayati et al,
2014). One of the fruits contained in the antioxidant
is ruthab dates (Phoenix dactylifera).
Ruthab dates (Phoenix dactylifera) extract
can be used as hepatoprotection because it contains
antioxidant compounds. The workings of antioxidant
compounds are bound to reactive free radicals to form
relatively unreactive free radicals.
Arem et al (2014) stated that the effect of
hepatoprotection occurred in rats (Rattus novergicus)
given dichloroacetic acid (DCA) with
hepatoprotector of dates extract (Phoenix dactylifera)
as much as 0.5 and 2 g / l. Other studies it was also
found that ruthab dates (Phoenix dactylifera) contain
fiber which has a good effect on health.
Therefore, it is important to conducted the study
in order to determine the effect of various doses
comparisons on hepatopotective activity of ruthab
palm extract (Phoenix dactylifera) and
Purnamasari, R., Nahdiyah, N., Pribadi, E., Hidayati, S., Lusiana, N., Andr iarna, F., Hadi, M., Faizah, H. and Alamudi, M.
Analysis of Degeneration Hepatosit Cell on Female Mice(Mus musculus) Induced by Ruthab Dates (Phoenix dactylifera) Extract and Paracetamol.
DOI: 10.5220/0008906600002481
In Proceedings of the Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference (BEST ICON 2018), pages 99-102
ISBN: 978-989-758-414-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
99
hepatoprotection activity of ruthab date fruit (Phoenix
dactylifera) on liver histology of female mice (Mus
musculus) induced by paracetamol.
2 METHOD
2.1 Making Ruthab Dates (Phoenix
dactylifera) Fruit Extract
Making ruthab dates (Phoenix dactylifera) fruit
extract with the following steps, ruthab dates
(Phoenix dactylifera) with 250 grams of wet weight
cut into small pieces in an oven for 3 days at 60 ° C
(Nurdiana, 2009). Then a dry weight of 150 grams
was produced. Macerated with 2 times 300 ml of
methanol for 6 days and every 3 days the extract was
filtered (Simanjuntak et al, 2014). After that, it is
evaporated using a rotary evaporator with a
temperature of 50° C for approximately 30 minutes
(Qorriaina, 2015). Then extract is put into a vial
bottle.
2.2 Making Paracetamol Dosage
The making of paracetamol dosage conducted
through several steps as follow:
a. Toxic dosage of paracetamol in human are 10-
15 grams (put of median point is 13 grams)
b. Convention factor from human to mice (Mus
musculus) are 0,0026
c. Weight of mice (Mus muculus) are 25-30 grams
(put of median point is 28 grams)
d. Dosage of mice 20 grams
grams x 0,0026 = 0,0338.
e. Dosage of mice (Mus msculus)
28
20 x 0,0338
= 0,04732 gr
2.3 Research Design
This research is a laboratory experimental research
with the research design used is a completely
randomized design (CRD) with 6 treatment groups
divided into 2 large groups and 5 repetitions namely:
a. Experimental group
K (-): Injection with 0.2 ml Aquades.
P1: Injected with ruthab dates (Phoenix
dactylifera) extract with a dose of 1 ml as much
as 0.2 ml.
P2: Injected with ruthab dates (Phoenix
dactylifera) extract with a dose of 3 dates as
much as 0.2 ml.
P3: Injected with ruthab dates (Phoenix
dactylifera) extract with a dose of 7 dates as
much as 0.2 ml.
b. Experiment group
K (+): Injected with paracetamol with a dose of
41.4 as much as 0.2 ml.
P4: Injected with paracetamol with a dose of
41.4 grams as much as 0.2 ml and ruthab dates
extract with a dose (best of the preexperiment
group) of 0.2 ml.
2.4 Surgery
Surgery in this study was carried out on the 16th day
after treatment. Surgery is performed on paraffin
blocks and using surgical instruments. After that the
liver organ that has been taken is made histological
incision
2.5 Presentation of Data
The presentation of the data in this study using the
scoring method of the degree of liver damage on this
examination was carried out according to the
modified Knodell (2000) and Klopfleisch (2013)
method, where the degree of damage of each sample
was determined by summing all scores of
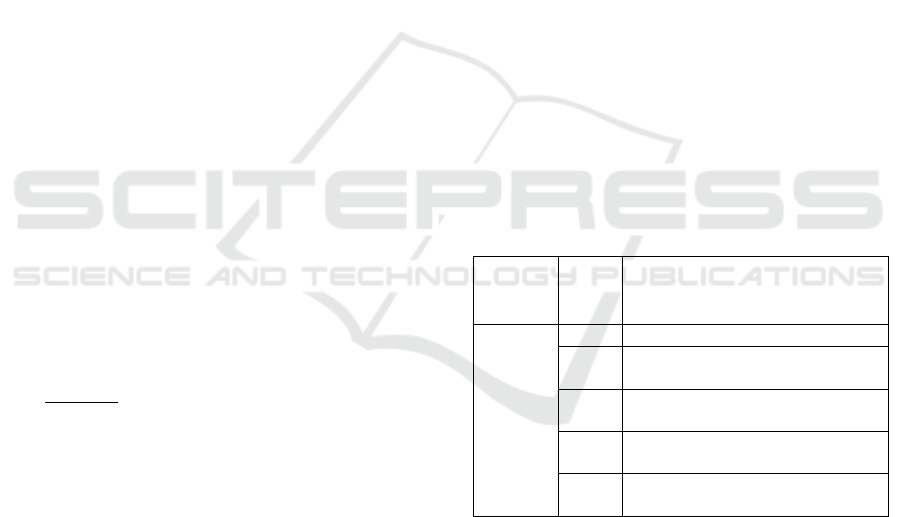
histopathologic lesions as in Table 1.
Table 1. histopathologic scoring
Form of
Lesion
Score
Information
DEGENER
ATION
0
Degeneration does not occur
1
If degenerative changes < 25%
from all fields of view
2
If degenerative changes 26 – 50%
from all fields of view
3
If degenerative changes 51 - 75%
from all fields of view
4
If degenerative changes >76%
from all fields of view
2.6 Data Analysis
Liver cell scores that experienced degeneration in
liver histology incision of mice (Mus musculus) in the
form of nominal ordinal data scale, comparative test,
and will be processed using SPSS 21.0 application.
Based on the scale of the data, the test used was Chi-
Square test both in the pre-experimental group and
the experimental group because the sample in this
study consisted of 2 samples or more and were
independent (independent), then included in the non-
parametric test
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
100

3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The results of observations of cell nucleus undergoing
degeneration in the pre-experimental group can be
seen in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Mean Scores of Liver Degeneration Pre
Experimental group
From Figure 1 it was found that there was no
difference in scores on the mean score of liver
degeneration on the administration of various doses
of ruthab dates (Phoenix dactylifera L.). According to
the chi-square test, the data in this pre-experimental
group had an α value of 0.420 where α> 0.05. In this
case it can be concluded that H0 is accepted that there
is no difference between the degeneration change
score and the ruthab palm extract (Phoenix dactylifera
L.) which has been given.
Although according to the test, it showed that
there is no effect between necrosis, paracetamol, and
palm ruthab (Phoenix dactylifera L.) extract dates, but
in Figure 1 there is a decrease in the mean score of
degeneration changes. This is due to the presence of
flavonoid compounds in the ruthab palm fruit extract
(Phoenix dactylifera L.).
This compound is widely known as
hepatoprotection and is closely related to the
prevention of the emergence of several diseases such
as liver disease (Bandy, 2009). According to
Midlleton (2007), flavonoids are active compounds
included in the type of antioxidant intermediates that
act as hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidants.
Flavonoids are compounds that act as antioxidants.
The antioxidant mechanism of flavonoids is to
capture ROS directly, prevent regeneration of ROS
and can indirectly increase the antioxidant
antioxidant cellular antioxidant enzymes.
Flavonoids are the most effective compounds as
scavanger reactive species, such as super dioxide,
peroxyl radicals, and peroxinitrite by transferring H +
atoms (Bandy, 2009). The prevention of the
formation of ROS by flavonoids is done in various
ways, namely inhibiting the action of the enzyme
xanthine oxidase and Nicotinamide Adenine
Dinucleotide Phosphate (NADPH) oxidase, and
chelating metals (Fe2 + and Cu2 +) so as to prevent
redox reactions that can produce free radicals (Bandy,
2009). Whereas for the second 15 days, the
experimental group, the results of the observation of
necrosis change scores can be seen in Figure 2 below.
Figure 2. Mean Scores of Liver Degeneration
Experimental Group
Chi-square test results show that the value of
α in this experimental group is 0.05 where α = 0.05.
In this case it can be concluded that H0 is rejected,
namely there is a difference in the score of
degeneration changes, paracetamol, and ruthab dates
extract (Phoenix dactylifera) that have been given.
In Figure 2 shows that there is an increase in
the graph from the score 2.2 towards the number 2.6.
This is because the p4 group had previously been
induced with paracetamol. Therefore, it can increase
the average score of degeneration. Cheville (1976)
states that fat degeneration occurs because cells
experience oxygen deficiency and food substances.
Oxygen deficiency and these food substances
can interfere with the process of energy formation, so
protein synthesis decreases, which eventually the cell
is unable to form proteins.
According to Carlton and Mc Gavin (1995),
there are two reasons that cause the liver to be
susceptible to toxins. First, the liver receives 89% of
the blood supply from the portal vein that drains
blood from the gastrointestinal system. The substance
of toxic substances including plants, fungi, metals,
minerals, and other chemicals absorbed into the portal
is transported to the liver. Second, the liver produces
enzymes that have the ability to biotransform various
kinds of exogenous and endogenous substances that
are eliminated by the body.
0
1
2
3
4
K(-) P1 P2 P3
Average Degeneration Score
2
2.2
2.4
2.6
2.8
K (+) P4
Average Degeneration Score
Analysis of Degeneration Hepatosit Cell on Female Mice(Mus musculus) Induced by Ruthab Dates (Phoenix dactylifera) Extract and
Paracetamol
101

4 CONCLUSIONS
In this study it can be concluded that in the pre-
experimental group there was no difference in the
various doses of ruthab dates extract (Phoenix
dactylifera), but there was an average reduction in
damage scores. Whereas in the experimental group
there were differences between the groups given
paracetamol and the combination of ruthab dates
(Phoenix dactylifera) and paracetamol
REFERENCES
Arem, Amira., Fatma Ghrairi., Lamia Lahouar., Amira
Thouri., Emna Behija Saafi., Amel Ayed., Mouna
Zekri., Hanen Ferjani., Zohra Haouas., Abdelfattah
Zakhama., Lotfi Achour. (2014). Hepatoprotective
activity of date fruit extracts against dichloroacetic
acid-induced liver damage in rats. Journal of
functional foods, 9 (1): 119-130
Bandy. (2009). Evaluasi Penggunaan Parasetamol
Intravena pada Pasien Anaka Rawat Inap di RSUD
Mas Amsyar Kasongan Kalimantan Tengah. Drug
Use Evaluation, 1 (2): 422-426
Hayati, T. Armansyah TR., Amalia Sutriana., Dwinna
Aliza., Henni Vanda., Erdiansyah Rahmi. (2014).
Aktivitas Hepatoprotektif Ekstrak Etanol Daun
Kucing kucingan (Acalypha indica L.) pada Tikus
Putih (Rattus Novergicus) yang Diinduksi
Parasetamol. Jurnal Ilmiah Ilmu-Ilmu Peternakan,
13 (6): 292-298.
Klopfleish, Robert. (2013). Multiparametric and
semiquantitative scoring systems for the evaluation
of mouse model histopathology - a systematic
review. BMC Veterinary Research, 1 (1): 1-6.
Knodell. (2000). Comparison of three algorithms used to
evaluate adverse drug reactions. American Journal of
Health-System Pharmacy , 43 (7) 1709-1714.
Middleton. (2007). Formulation and Application of a
Numerical Scoring System for Assessing
Histological Activity in Asymptomatic Chronic
Active Hepatitis. Hepatology 1981, 1(5): 431–43.
Nurdiana. (2009). The Effect of 17-Estradiol on Rat
Adrenergic Receptor Density and Vascular Smooth
Muscle Contractility. Jurnal Kedokteran
Brawijaya, 26 (2): 1-10.
Oktiari, Sri., Cyla Willa Pebriandini., Helmi Arifin. (2010).
Uji Aktivitas Hepatoprotektor Ekstrak Daun Sukun
(Artocarpus) Atlitis (Palinson) terhadap Kerusakan
Hati yang diinduksi CCL
4.
Prosiding seminar
nasional dan workhop
,
1 (1) 77-84.
Qorriana, Rofiatul., La Choviya Hawa., Rini Yulianingsih.
(2015). Aplikasi Pra Perlakuan Microwave Assisted
Extraction (MAE) Pada Ekstrak Daun Kemangi
(Ocimum sanctum) Menggunakan Rotary
Evaporator (Studi Pada Variasi Suhu dan Waktu
Ekstraksi). Jurnal Bioproses Komoditas Tropis, 3
(1): 32-38.
Sa’roni. (2012). Pengaruh Pemberian Buah Pepaya (Carica
papaya) terhadap Kadar Enzim Transminase GOT-
GPT dan Gambaran Histologi Hepar Mencit(Mus
musculus L.) yang Diinduksi Karbontetraklorida
(CCl4). Skripsi. Jurusan Biologi. Fakultas Sains
dan Teknologi. UIN Maulana Malik Ibrahim.
Malang.
Simanjuntak, Lidya., Chairina Sinaga., Fatimah. (2014).
Ekstraksi Pigmen Antosianin dari Kulit Buah Naga
Merah (Hylocereus polyrhizus). Jurnal Teknik
Kimia, 1 (1): 1-5.
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
102
