
Exploring the Intention to Use Mobile Learning in Higher Education
Risma Nur Anissa, Tusyanah, Rediana Setiyani, Fentya Dyah Rahmawati, and Ashomatul Fadlilah
The Faculty of Economics, Universitas Negeri Semarang, Sekaran Campus, Semarang, Indonesia
Keywords: Students’ Perception, Personal Innovativeness, Mobile Learning.
Abstract: The transition to mobile devices and ubiquitous computing technology in education provides an
unprecedented opportunity to help instructors influence ively deliver learning materials to learners anytime
and anywhere (Cheng, 2013). The objective of the study is to determine the influence of students 'perception
and personal innovativeness on students' intention to use mobile learning. It is a quantitative research. The
variables of the study are students' perception, personal innovativeness, and intention to use mobile
learning. The population of this research are Accounting students in the sixth semester at Unversitas Negeri
Semarang. The samples of the research are 89 respondents taken by using simple random sampling
technique and data are collected by questionnaires. Then, data are analyzed by descriptive analysis and
multiple regression analysis with SPSS 21 application. The result of multiple regression analysis showed
that simultaneously, social proof (X1) and purchase intention (X2) have significant influence on students'
purchasing decision (Y) for 58.1% . Meanwhile, partially, the influence of students’ perception (X1) and
personal innovativeness (X2) on intention to use mobile learning (Y) are 22% and 25% respectively. Thus,
the model of the study is Y = 2.254 + 0.299X1 + 0.626X2 + e. The personal innovativeness variable shows
a higher influence than the students’ perception. It is understandable that personal innovativeness is more
likely to trigger concrete behavior to try new things about technology, as Lopez-Nicolas et al. (2008) argues
that personal innovativeness in the use of information technology reflects a desire to try new technologies.
1 INTRODUCTION
The rapid development of the digital age today
modifies various human activities including teaching
and learning techniques in education institutions.
Almost everyone today already has a mobile device
in his or her hand. In Indonesia, as per January 2018,
the population of mobile device users reaches 177.9
million users, with penetration rate reaching 67%
(bisnis.co, 2018). It is also used by educators and
students in supporting the learning process. The
transition to mobile devices and ubiquitous
computing technology in education provides an
unprecedented opportunity to help instructors deliver
learning materials to learners anytime and anywhere
(Cheng, 2013).
Then, m-learning is defined as a form of
electronic learning (e-learning) which specifically
uses mobile devices to deliver the learning content
and support (Brown, 2005; Muyinda, 2007; Cheng,
2013). In addition, mobile learning can be seen as a
mobile or wireless device application for learning on
the go (Park, 2011; Chaka and Irene, 2017). Digital
mobile devices such as cell phones, PDAs, and
smartphones are often used for the educational
purposes. The use of mobile digital technology is the
core of a dynamic and growing research flow known
as mobile and ubiquitous learning. The two concepts
are highly interconnected (Pimmer, Magdalena, and
Urs, 2016).
Mobile technology and applications have
grown rapidly and widely developed for m-learning.
Today, there are few studies to ascertain whether m-
learning has the potential to attract more learners or
not. Therefore, a deeper understanding on the factors
which influence the learner’s intention to use m-
learning in a mobile-based interactive learning
environment is essential to be done.
Furthermore; Technology Acceptance Model
(TAM) is one of the most widely applied models in
various domains related to IT acceptance study
(Lindsay et al., 2011; Wu, 2011). ; Maditinos et al.,
2013; Cheng, 2013), and it can be used as a basis for
the research model of this study. To enhance the
power of TAM explanation, it must first include the
perspective of intrinsic motivation to expand its
function (Davis et al., 1992; Lee et al., 1999; Cheng,
2013), and it can then be integrated with innovation
Nur Anissa, R., Tusyanah, ., Setiyani, R., Dyah Rahmawati, F. and Fadlilah, A.
Exploring the Intention to Use Mobile Learning in Higher Education.
DOI: 10.5220/0009015600002297
In Proceedings of the Borneo International Conference on Education and Social Sciences (BICESS 2018), pages 11-15
ISBN: 978-989-758-470-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
11
diffusion theory to overcome compatibility (Chen et
al., 2002; Wu and Wang, 2005; Tan and Chou;
2008; Tung and Chang; 2008; Ryu et al., 2009;
Cheng , 2013). Thus, a hybrid model is developed to
explore the learners’ intentions for using m-learning.
Based on the above explanation, the main purpose of
this study is to examine students’ perceptions and
personal innovativeness on students’ intention to
use mobile learning.
Most studies on mobile learning show the
positive influence. Students begin to accept mobile
technology as a new learning tool, the consequences
of this acceptance affecting their learning
achievements both directly and indirectly (Shin and
Minseok, 2015). It is supported by the research
results of Nassuora (2013) which shows that the rate
of students’ enrolment towards mobile learning in
Saudi Arabia is quite high. However, empirical
evidence supporting the widespread application of
learning with mobile learning in higher education
settings is limited. (Anissa et al., (2017) showed
there is a significant difference of students’ skills in
producing text between classical class and blended
learning (combination of face-to-face and online
delivery methods). Hwang and Tsai (2011) report
that high-education students are the most frequently
researched targets for mobile learning, particularly
in meta-analysis. Most of the studies included
reported positive learning outcomes. Cheng (2013)
reports that Perceived usefulness (PU), perceived
ease of use (PEOU), perceived pleasure (PE), and
compatibility can play an important role in
influencing the learner's intent to use m-learning.
The student's perception seems to be quite
instrumental in choosing the use of mobile learning.
It is supported by research Wong et.all., (2015)
which reveals that students prefer to use mobile
devices than desktops to access the internet. So the
hypothesis is:
H1 Student's perception has a significant
influence on students’ intention to use mobile
learning.
Besides perception, personal innovativeness
also takes part in the use of mobile learning.
Personal innovativeness is reported to moderate the
influence s of PU, PEOU, and compatibility on the
intent to use m-learning (Cheng, 2013). Individuals
with higher levels of personal innovation tend to be
more confident in new technologies (Lewis,
Agarwal, & Sambamurthy, 2003). Personal
innovativeness stifles the impact of one’s decision
on the perception of mobile adoption. Thus;
individuals with innovations are more anticipated to
generate more positive thinking for new IT (Lopez-
Nicolas et al., 2008). A different story is reported by
Tan, et.al, (2014). They find that personal
innovativeness does not affect behavioural intention
to use mobile learning. Related to this, the
hypothesis is:
H2 Personal innovativeness has a significant
influence on intention to use mobile learning.
Then, the antecedent of attitude construction is
the belief of attitude. Confidence in attitudes comes
from TAM. TAM argues that there is a causal
relationship between perceived ease of use, benefit
perception, the desire to use the new system, and the
intention of using the system (Davis, 1989; Teo,
2009; Cheon et.al., 2012). The study included two
such perceptions (i.e. ease of use and usefulness) as
a perception of mobile learning usage. Personal
innovativeness in the domain of information
technology as an individual tendency that, in
general, is associated with positive beliefs about the
use of technology (Lewis, Agarwal, &
Sambamurthy, 2003). Rogers's theory of the
diffusion of innovation holds that individual beliefs
are increasing about new technologies by
synthesizing information from multiple channels,
including mass media and interpersonal channels.
Individuals with higher personal innovation are
expected to develop a more positive belief of target
technology (Rogers, 1995). The study also wants to
examine the simultaneous influence of students’
perception and personal innovativeness on intention
to use mobile learning.
H3 Students' perception and personal
innovativeness simultaneously influence the
intention to use mobile learning.
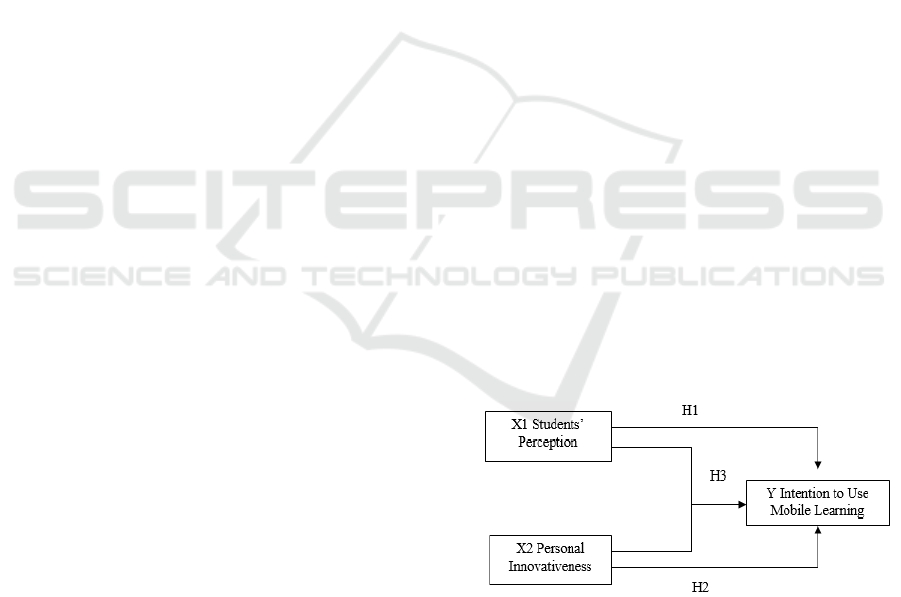
Based on above description, the study proposed
the theoretical framework as presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Theoretical Framework
2 METHODS
This research is conducted at the Faculty of
Economics, Universitas Negeri Semarang. In the
learning, the combination of learning in the
classroom and the use of mobile learning began to
BICESS 2018 - Borneo International Conference On Education And Social
12

be combined in several courses. The population of
the study are Accounting students; they are 118
students. It used the simple random sampling which
took 89 students as the samples.
It used the primary data using questionnaires. In
this questionnaire, the students’ perception, personal
innovativeness and intention to use mobile learning
variables are measured by the likert items (1=
"strongly disagree" - 4= "strongly agree"). The items
chosen to measure variables adapted from previous
researches. Data are then analyzed by descriptive
statistics and multiple linear regression tests. In the
statistical analysis is supported by the Statistical
Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 21.0.
before being analyzed, the data confirmed its
validity and reliability. Tables 1 and 2 show the
validity. Furthermore, the data are tested to ensure
there is no classical assumptions that accompany it.
After that, data are analyzed by using multiple linear
regression which will be described below.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Reliability Testing
Reliability relates to the consistency of a
measure (Heale & Twycross, 2015). A study is said
to be reliable if it has Cronbach’s alpha> 0.70
(Nunnally, 1994).
Table 1. Realibility Analysis
Variable No. of
Items
No. of
the
Delete
Items
Cronba
ch's
Students’
Perception
9 0 0.872
Personal
Innovativeness
4 0 0.854
Intention to Use
Mobile Learining
6 0 0.849
Based on the table above, it shows that the
students’ perception (X1) has a Cronbach's by 0.872.
Personal innovativensess has Cronbach's 0.854. And
intention to use mobile learning has Cronbach's for
0.849. It means that all the instruments of the study
are reliable.
3.2 Construct Validity
Validity is defined as the extent to which a
concept is accurately measured in a quantitative
study (Heale & Twycross, 2015). Validity is tested
by comparing item scores to total score with
correlation analysis. The research instrument is said
to be valid if it has significance <0.05. Table 3.2.
shows the results of validity testing.
Table 2. Correlation
Items Pearson
Correlati
on
Sig. (2-
tailed)
Students’ Perception
Using mobile learning
improves the learning process
.747 .000
Using mobile learning make
my study better
.692 .000
Mobile learning is useful for
the learning process
.740 .000
Using mobile learning is
effortless
.585 .000
Using mobile learning is easy
to be understood
.716 .000
Mobile learning is easy to use .754 .000
Using mobile learning is
interesting
.686 .000
The process to use mobile
learning make me study
happily
.637 .000
I often use mobile learning .760 .000
Personal Innovativeness
When I know something new
regarding the technology, I
will learn how to use it
.816 .000
I am interested to the new
technology
.851 .000
I am not worried to try the
new technology
.846 .000
I like making experiments
with technology
.821 .000
Intention to Use Mobile
Learning
I will use mobile devices to
support my study
.809 .000
I will use mobile learning for
my study in the future
.832 .000
I will use mobile learning in
every occasion that I have
.663 .000
I will install aplication which
support my study
.754 .000
I am ready to receive the
learning material from my
lecturer through mobile
devices
.765 .000
I am ready to do the task or
quiz from my lecturer
through mobile learning.
.705 .000
Based on the correlation table above, it shows
that all the instruments in the study are valid,
because they have significance <0.05.
Exploring the Intention to Use Mobile Learning in Higher Education
13
3.3 Regression Analysis among
Variables
Table 3. Simultaneous Test Result (F Test)
ANOVA
a
Model Sum of
Squares
df Mean
Square
F Sig.
Regression
516.011 2 258.005 61.996 .000
b
Residual
357.899 86 4.162
Total
873.910 88
a. Dependent Variable: IUtotal
b. Predictors: (Constant), PItotal, SPtotal
Based on the ANOVA table or F table, they
indicate that the calculated F value of 61,996 with a
significance of 0.000. Because of the significance
0.000 <0.05 then the regression model can be used
to predict students’ perception (X1) and the personal
innovativeness (X2) simultaneously influences
intention to use mobile learning.
3.4 Partial Test (t test)
All the variables of this study are significant.
The probability of significance of independent
variables; students’ perception (X1) and personal
innovativeness (X2) are more than 0.05.
Table 4. The Result Analysis of Multiple Linear
Regression
Model Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standa
rdized
Coeffi
cients
t Sig.
B Std.
Error
Beta
(Constant) 2.254 1.483 1.520 132
SPtotal .299 061 .413 4.884 .000
PItotal .626 .117 .451 5.331 .000
The model formed from the analysis is Y =
2.254 + 0.299X1 + 0.626X2 + e. It means that:
1. Constant = 2.254, if the independent variables
are constant or 0 then the average of intention
to use mobile learning is 2.254.
2. Coefficient X1 (Students’ Perception) = 0.299,
it means that if students’ perception variable
increased by 1 point while personal
innovativeness is 0, it would lead to an increase
of intention to use mobile learning for 0,299.
3. Coefficient X2 (Personal Innovativeness) =
0.626, it means that if personal innovativeness
increased by 1 point while students’ perception
variable is 0; it would lead to an increase of
intention to use mobile learning for 0,626.
3.5 Coefficient Determination Test
(R2)
Table 5. The Result of Simultaneous Determination
Coefficient
Model Summary
b
Model R R
Square
Adjusted
R
Square
Std. Error
of the
Estimate
Durbin-
Watson
1 ,768
a
,590 ,581 2,04001 2,176
a. Predictors: (Constant), PItotal, SPtotal
b. Dependent Variable: IUtotal
Based the Model Summary, the Adjusted R
Square is 0,581 (58.1%). It means that 658.1%
variable on intention to use mobile learning can be
explained by two independent variables, students’
perception and personal innovativeness. While the
rest (100% -58.1%), i.e. 41.9% are explained by
other variables not examined.
Table 6. The Calculation Result Coefficient of
Determination of Partial
Model t Sig. Correlations Collinearity
Statistics
Zero-
order
Parti
al
Part Tolera
nce
VIF
(Constant) 1.520 .132
SPtotal 4.884 .000 .675 .466 .337 .665 1.504
PItotal 5.331 .000 .691 .498 .368 .665 1.504
From the table above, it can be seen that the
partial correlation value of Student Perception (X1)
is 0.466, so the influence of Student Perception (X1)
on Intention to Use Mobile Learning (Y) is equal to
(0.4662 x 100%) or 22%. Then, the partial
correlation of Personal Innovativeness (X2) is 0.498;
the influence of Personal Innovativeness (X2) on
Intention to Use Mobile Learning (Y) is (0.4982 x
100%) or 25%.
Then, from the hypotheses, we can state that:
H1: Student's perception has a significant influence
on intention to use mobile learning. The
hypothesis is accepted.
H2: Personal innovativeness has a significant
influence on intention to use mobile learning.
The hypothesis is accepted.
BICESS 2018 - Borneo International Conference On Education And Social
14

H3: Simultaneously, students' perception and
personal innovativeness have a significant
influence on intention to use mobile learning.
The hypothesis is accepted.
The results show that students' perception and
personal innovativeness can be the determinants of
intention to use mobile learning. This result is in line
with the results of a study from Lopez-Nicolas et al.
(2008) which states that Perceived of usefulness and
perceived ease of use have significant influence on
the behavioral intention to use mobile learning by
45% and 17%. Individuals with higher levels of
personal innovation tend to be more confident in
new technologies (Lewis, Agarwal, &
Sambamurthy, 2003).
Related to the magnitude of the influence given
by each independent variable, the personal
innovativeness variable shows a higher influence
(25%) than the students’ perception (22%). It is
understandable that personal innovativeness is more
likely to trigger concrete behavior to try new things
about technology, as Lopez-Nicolas et al. (2008)
argues that personal innovativeness in the use of
information technology reflects a desire to try new
technologies. Individuals with innovation are more
anticipated to generate more positive thinking for
new IT.
4 CONCLUSIONS
It can be concluded that simultaneously, the variable
of Students' perception (X1) and personal
innovativeness (X2) influence the intention to use
mobile learning (Y) for 58.1%. Partially, there are
two variables affecting intention to use mobile
learning, they are Students' Perception (X1) for 22%
and Personal Innovativeness (X2) for 25%.
Therefore, increasing the personal innovativeness is
needed to increase intention to use mobile learning
which will impact of one’s decision on the
perception of mobile adoption..
REFERENCES
Anissa, R. N., Utami, S., Setiyani, R., Tusyanah, Sholikah,
M., & Nurkhin, A. 2017. What’s up with whatsapp?
The contribution of blended learning through wa
group discussion for better english writing in
Indonesia. Advanced Science Letters, 23(8).
https://doi.org/10.1166/asl.2017.9517
Bisnis.co. 2018. User Mobie Device in Indonesia.
http://industri.bisnis.com/read/20180201/101/733037/
Chaka, John Gyang. Irene Govender. 2017. Students’
perceptions and readiness towards mobile learning in
colleges of education: a Nigerian perspective. South
African Journal of Education. 37(1). 1-12.
Cheng, Yung-Ming. 2013. Exploring the intention to use
mobile learning: the moderating role of personal
innovativeness. Journal of System and Information
Technology. 16(1). 40-61
Cheon, Jongpil et. al., 2012. An investigation of mobile
learning readiness in higher education based on the
theory of planned behavior. Computers and Education.
59(2012). 1054-1064.
Heale, R., & Twycross, A. 2015. Validity and reliability in
quantitative studies. Evidence-basednursing,ebnurs-
2015.
Hwang, Gwo-Jen. Chin-Chung Tsai. 2011. Research
trends in mobile and ubiquitous learning: a review of
publications in selected journals from 2001 to 2010.
British Journal of Educational Technology. 42(4).
E65-E70.
Nassuora, Ayman Bassam. 2013. Students Acceptance of
Mobile Learning for Higher Education in Saudi
Arabia. International Journal of Learning Management
Systems. 1 (1). 1-9.
Lewis, William, Ritu Agarwal. V. Sambamurthy. 2003.
Sources Of Influence on Beliefs about Information
technology use: An Empirical study Of Knowledge
Workers. MIS Quartely. 27(4). 657-678.
Lopez-Nicolas, Carolina, et all., 2008. An assessment of
advanced mobile services acceptance: Contributions
from TAM and diffusion theory models. Information
and Management. 45(2008). 359-364.
Nunnally, Bernstein, I.H. 1994. Psychometric Theory, 3rd
Edition. New York : McGraw Hill.
Rogers, E. M. Diffusion of Innovations (4th ed.), Free
Press, New York, 1995.
Mtebe, Joel S. Roope Raisarno. 2014. Investigating
students’ behavioural intention to adopt and use
mobile learning in higher education in East Africa.
International Journal of Education and Development
using Information and Communication Technology.
10(3). 4-20.
Pimmer, Cristoph. Magdalena Mateescu. Urs Grohbiel
2016. Mobile and ubiquitous learning in higher
education settings. A systematic review of empirical
studies. Computers in Human Behavior. 63 (2016).
490-501.
Shin, Wong Sug. Minseok Kang. 2015. The Use of a
Mobile Learning Management System at an Online
University and Its Influence on Learning Satisfaction
and Achievement. International Review of Research in
Open and Distributed Learning 16(3). 110-130.
Tan, Garry Wei-Han et.al., 2014. Predicting the drivers of
behavioral intention to use mobile learning: A hybrid
SEM-Neural Networks approach. Computers in
Human Behavior. 36(2014). 198-213
Wong, Kenneth et.all., 2015. Investigating Acceptance
towards Mobile Learningin Higher Education
Students. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
Exploring the Intention to Use Mobile Learning in Higher Education
15
