
Risk Factors Fall in the Elderly at Panti Werdha Sejahtera
Banjarbaru
Meilya Faridka Indah
1
and Rudi Hartono
2
1
Public Health Faculty, Universitas Islam Kalimantan, Jl Adyaksa No 2 Kayu Tangi Banjarmasin, Kalimantan Selatan,
Indonesia.
2
Engineering Faculty, Universitas Lambung Mangkurat, Jl Ahmad Yani KM. 35 Banjarbaru, Kalimantan Selatan,
Indonesia
Keywords: anthropometry, spatial design, elderly, fall risk, safety
Abstract: Spatial design influences human behaviour conducting activities within. These influence includes attitude,
action, psychological condition, safety feeling, and lenience in doing activities. Anthropometry is essential
in spatial design. The objective of this study is to define the impact of incorrect anthropometric spatial
design on elderly fall risk, to know identify accident level occurring as result of incorrect anthropometric
spatial design, and to provide spatial design solution appropriate for elderly safety. This study is designed as
a qualitative descriptive study with whole 110 habitants of Panti Sosial Tresna Werdha “Budi Sejahtera”
population. Purposive sampling method is used with consideration on the elderly’s ability to respond in
communication. Data are analysed using descriptive statistic method. The spatial design of Panti Sosial
Tresna Werdha “Budi Sejahtera” does not fully accommodate safety factors for elderly. This is supported by
the frequence fall accidents happened there, espesially female elderly. The spatial design should pay more
consideration on safety factors for the elderly by taking inhabitants’ anthropometric characteristics into
consideration.
1 INTRODUCTION
One indicator of the success of Health Development
in Indonesia is the increasing Life Expectancy Age.
In National Medium Term Development Plan,
Rencana Pembangunan Jangka Menengah Nasional
(RPJMN) 2014 Life Expectancy Age was expected
to increase from 70.6 years in 2010 to become 72
years in 2014. As a result of the increasing age of
life expectancy, the age structure of the population
will change.
Nowadays, Indonesia is included in top five of
countries with highest number of elderly, which
reaches 18.1 millions in 2010 or 9.6% of the total
population. National Development Agency, Badan
Pembangunan Nasional (Bappenas) predicted that
the number of elderly will be doubled in 2025
reaching 36 millions (BPS, 2009). International data
by the U.S Census Bureau indicates that the number
of elderly in Indonesia shows significant growth. In
2007, the number of elderly was 18.96 millions and
became 20.54 millions in 2009. it is predicted that in
2025 the number will reach 27 millions. This
increasing Life Expectancy Age is indicated by the
increasing number of he population who reached age
60 years or above (Balitbang Kemenkes RI, 2013).
The increasing number of elderly rises several
problems. When a person reaches the age of elderly,
he or she will experience degradation of biological,
physiological, psychological, and spiritual
conditions. These degradation create some health
problems for elderly. One of the problems is the
increasing fall risk. It has been reported that more
than one third of elderly who reached age 65 or
more experienced fall every year. One of every three
cases was recurrence (Gai et al, 2010).
Health effort for elderly is complete basic health
effort. This includes enhancement, preventive,
curative, and rehabilitative health (Darmojo, 2009).
In Indonesia, approximately 30-50% elderly who
reached age 65 years or more ecperienced fall every
year (Probosuseno, in Widuri, 2010). Tuti’s study
(2013) shows that in Panti Sosial Tresna Wredha
Unit Abiyoso, Pakem, Sleman, Yogyakarta, from 46
elderly being observed 52,2% had experienced fall.
Tuti (2013) indicates that risk factor of falls are age
618
Indah, M. and Hartono, R.
Risk Factors Fall in the Elderly at Panti Werdha Sejahtera Banjarbaru.
DOI: 10.5220/0009024900002297
In Proceedings of the Borneo International Conference on Education and Social Sciences (BICESS 2018), pages 618-621
ISBN: 978-989-758-470-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
and gender, mainly happened in the age group of 75-
90 years (55%), and happened to male (58,8%) more
than female.
Based on interview with polyclinic officers of
Panti Werdha “Budi Sejahtera” Banjarbaru, it can be
indicated that fall accident in elderly is quite high.
Hartono and Indah (2012) states that the result of
anthropometric study on the inhabitants of Panti
Sosial Tresna Werdha “Budi Sejahtera” shows that
there are some significant gaps between the result of
the study on body proportion of the elderly from the
standard stated in Minister of Public Works
Regulation Peraturan Menteri Pekerjaan Umum
Number: 30/PRT/M/2006. Minister of Public Works
Regulation Number: 30/PRT/M/2006 contains the
standard of accessibility for environment and
building. Accessibility factors include safety,
easiness, function, and independence for building
users to be able to do activities within. The problem
in this study is derived from this condition: is fall
experienced by the elderly resulted from spatial
design that does not considere the anthropometric
characteristics of the inhabitants.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
The study is conducted in Panti Sosial Tresna
Werdha “Budi Sejahtera” located in Jl. A. Yani Km.
21.700 Kelurahan Landasan Ulin Tengah
Banjarbaru. This study is conducted in several
stages: preparation, data collection, analysis, and
data synthesis. The population is all 110 inhabitants
of Panti Werdha “Budi Sejahtera”. Purposive
sampling methode is used to choose 83 samples that
have good abilities to respond in communication.
The variables in the study are respondents
characteristics: anthropometric characteristics, age,
gender, and physical conditions, respondents fall
risk characteristics: fall history and fall location and
spatial design of the facilities.Data collection
technique is applied as follows: Primary Data, These
data includes anthropometric characteristics, fall
risk, and spatial design. Anthropometric
characteristics and spatial design data are collected
through direct observation and direct measure. Fall
risk data is collected from health record and
interview with both inhabitants and polyclinic
officers. Secondary Data, These data include age and
health condition of the inhabitants. They are
collected from polyclinic record. The analysis is
conducted by tabulation and percentage calculation
then being analyzed using qualitative descriptive
method.
3 RESULT
From 83 samples of 110 inhabitants of Panti Werdha
“Budi Sejahtera, there are 46 males and 37 females.
Age distribution can be seen in the following table:
Table 1. Respondents’s age group
Age Group Total Percentage
60 - 65 year 23 28%
66 - 70 year 15 18%
71 - 75 year 21 25%
76 - 80 year 13 16%
More than 80 year 11 13%
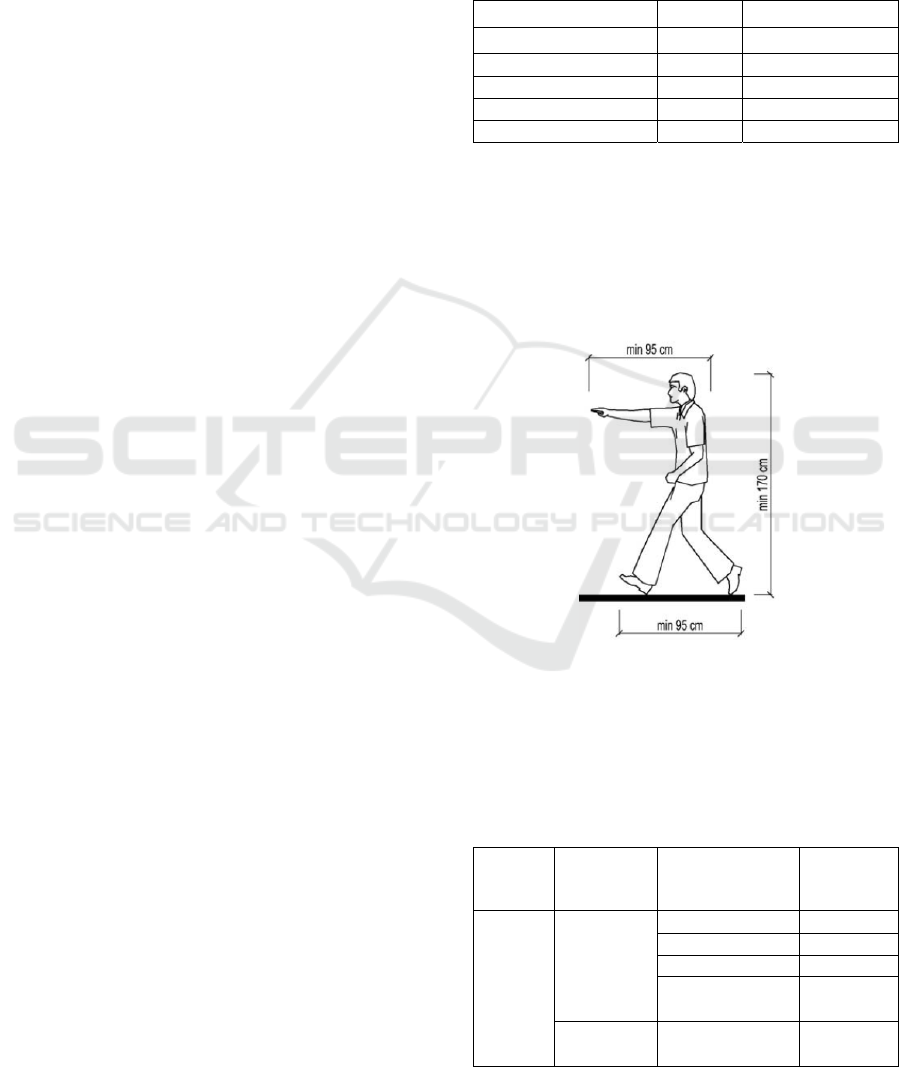
The result of anthropometric measure shows that the
average height of respondents is different to the
average height of Indonesian which is 170 cm as
indicated in Minister of Public Works Regulation
Number : 30/Prt/M/2006 on Facility Technical
Guidelines and Accessibility in Building and
Environment page 13 as followed:
Figure 1. Average height according to standard
The result of anthropometric measure show that the
average height of male respondents is 149.6 cm and
138.9 cm for female residents. The result of the
measure is shown in following table:
Table 2. Result of respondents’ anthropometric measure
Gender Body
Position
Part being
Measured
Average
Result
(cm)
Male Standing
Up
Height 149,6
Hand fist height 65
Chest 32,5
Ability to lift up
foot
11,7
Sitting Height 94,8
Risk Factors Fall in the Elderly at Panti Werdha Sejahtera Banjarbaru
619

Squatting Knee Height 39,3
Female Standing
Up
Height 138,9
Hand fist height 59,2
Chest 35,3
Ability to lift up
foot
11,6
Sitting Height 66,6
Squatting Knee Height 35,1
Based on interview and confirmed by polyclinic
record, between 2015 – 2016 there were 31 cases of
fall. This means 15-16 accidents every year or 1.3
accidents per month. From the accidents, 11 cases
(35%) involved male respondents, and 20 cases
(65%)involved female respondents. There 9
respondents who experienced recurrence, the
following table shows fall accidents related to age
group.
Table 3. Fall accidents based on age group
Age Group Total
Case
Percentage
compared to
total
Respondent
s
Percentage
compared to
number of
elderly in age
group
60 - 65 year 14 45% 61%
66 - 70 year 2 6% 13%
71 - 75 year 6 19% 29%
76 - 80 year 3 10% 23%
More than
80 year
6 19% 55%
Table 3 shows that fall accidents occur mostly in the
age group of 60-65 year (61%) and the age group of
more than 80 year (55%). It is interesting that fall
accidents mostly occur in the youngest age group.
One factor that influences it is the fact that most
respondents within the youngest age group have
lived in the facility for not a long time. Thus, they
are still in the process of adapting to the
environment of the facility.
Fall can happen anywhere. Fall accidents mostly
occurred in toilet (65%), followed by dish washing
room (26%). The following table shows the location
of fall accidents in Panti Werdha Budi Sejahtera.
Table 4. Location of fall accidents
Location
N
umber of
Acciden
t
Percentage
Toile
t
20 65%
Dish washin
g
roo
m
8 26%
Bedroo
m
2 6%
Terrace 1 3%
The result of direct observation on spatial design of
the facility shows, the height of steps from outside to
the terrace is 25 cm, floor is covered with smooth-
textured ceramics. It is slippery not only when it is
wet, hand-railing inside building is 80 cm high,
while railing outside building along pedestrian way
is 90 cm high, the floor in the toilet is very slippery
and not well-maintained. The difference between the
floor peil and closet peil is 30 cm. The height of
water tank is 80 cm, the floor of dish washing room
is made of smooth-textured wood. Some parts are
covered with mould. Thus it is very slippery,
especially when it is wet. The height of the water tap
is 70 cm.
4 DISCUSSIONS
This study indicates that most fall accidents occurred
in area related to water, namely toilet and dish
washing room. The slippery condition of the floor is
the main cause of fall accidents.
Toilets are covered with ceramics that are not
abrasive enough. Thus, the slipperiness increases
when it is wet. The difference of main room floor
peil with toilet floor peil is about 5 cm. There is no
different floor texture and color. This increases the
fall risk since there is no texture and color difference
for clue of different peil height. With the sippery
condition of toilet floor, toilet users will have to
experience the slipperiness without warning of
different texture and color of the floor. It is
suggested that toilet floor uses more abrasive tiles
with contrast color different form those of the main
room. The different of floor peil of the toilet and
main room is suggested to be 2 cm. This to avoid
tripping.
The difference between toilet floor peil and the
closet peil is 30 cm. It is different from the standard
that states 15 – 19 cm. Anthropometric study of the
respondents shows that the ability for respondents to
lift up their feet is 11,64 cm for female and 11,71 cm
for male. The peil difference of 30 cm makes it
difficult for respondents to use closet and
unsupportive to their physiological condition. Even
the standard height of 15 – 19 cm is not supportive.
The ideal height should be 10 cm. This poor
condition is worsen by the unavailability of hand-
railing. Hand-railing should be installed with the
height of 35 cm around the closet and 55 cm and 70
cm around the toilets. These heights are in
accordance with the anthropometric measure.
Water tank’s height is 80 cm. It is not supportive to
the respondents’ physiological ability. Based on thi
BICESS 2018 - Borneo International Conference On Education And Social
620

study, the height of hand fist in standing up position
is 59,23 cm for females and 64,95 cm for males. It is
suggested that the height of water tank is maximum
70 cm. For lavation, the height of water tank should
be 35 cm in accordance with the height of squatting
position. Thus, the water tank is divided into two
parts, the one with the height of 70 cm for bathing
needs and the other one for lavation with the height
of 35 cm.
The floor of dish washing area is made of soft-
textured wood planks. Some parts are covered with
mould. Thus, it is slippery. This poor condition is
worsen by the unavailability of hand-railing for
users to hold. It is suggested that the floor covering
should be made of concrete block which has more
abrasive surface. The floor color should be made
contrast to the color of back terrace floor as a clue
for different floor peils. The different of floor peil of
the terrace and dish washing area is suggested to be
2 cm. The height of water tap is already in
accordance to the anthropometric study which is 70
cm. Hand-railing should be installed with the height
55 cm and 70 cm around the dish washing area.
Hand-railing inside building is 80 cm high, while
railing outside building along pedestrian way is 90
cm high. According to standard, hand railing should
be installed doubled with the height of 65 cm and
80 cm. The result of anthropometric study requires
the hand railing installed with the height of 55 cm
and 70 cm supportive to the height of hand fist in
standing position 64.95 cm for male and 59.23 for
female.
The height of steps from outside to the terrace is 25
cm. it is not in accordance with the standard that
requires the height of 15-19 cm. The standard itself
is not supportive to the physiological condition of
the respondents who have the ability to lift up their
feet only for 11,64 cm female and 11,71 cm for
male. Thus, it is suggested that the height of the
steps are not more than 10 cm.
Fall accidents mostly occurred inthe age group of
60-65 year and more than 80 year. It cannot be
concluded that fall risk increase by the increasing of
age as stated by Tuti (2009). Tuti (2009) finds that
fall accidents occur mostly in the age group of 75-
90 years (55%). Tuti also indicated that fall
accidents more likely happen to male (58.8%) rather
than female. This study shows different result. Fall
accidents are more likely to occur among female
(65%). rathen than male.
5 CONCLUSIONS
It can be concluded that anthropometric study shows
that the average height of respondents is under the
average of Indonesian according to standard. Human
anthropometry plays an essential role in spasial
design. In this case of study, government standard
cannot be applied to the spatial design of fasilities in
Panti Werdha Budi Sejahtera.
This study also shows that most fall accidents in
Panti Werdha Budi Sejahtera are related to slippery
floor, the existence of water, and hand railing
factors, both unavailability and its installment that is
not in accordance with the anthropometric condition
of respondents. The correct decision of flooring
materials can help the safety of the inhabitnts in a
building. Abrasive surface can prevent falling.
Applying different floor color on surfaces with
different peils can halp users to be more aware of the
difference of floor peil. Hand railing is essential
factor in spatial design to support accessibility and
safety for elderly. It is shown that anthropometric
consideration in spatial design is influential to
elderly’s fall risk.
REFERENCES
Ikegami, R., D. G. Wilson, J. R. Anderson, and G. J.
Julien. 1990. “Active Vibration Control Using
NiTiNOL and Piezoelectric Ceramics,” J. Intell.
Matls. Sys. & Struct., 20(2):189-206.
Mitsiti, M. 1996. Wavelet Toolbox, For Use with MALAB.
The Math Works, Inc., pp. 111-117.
Inman, D.J. 1998. “Smart Structures Solutions to
Vibration Problems,” in International Conference on
Noise and Vibration Engineering, C. W. Jefford, K. L.
Reinhart, and L. S. Shield, eds. Amsterdam: Elsevier,
pp. 79-83.
Margarit, K. L. and F. Y. Sanford. March 1993. “Basic
Technology of Intelligent Systems,” Fourth Progress
Report, Department of Smart Materials, Virginia
Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg.
Hoffer, R. and D. Dean. 1996. “Geomatics at Colorado
State University,” presented at the 6
th
Forest Service
Remote Sensing Applications Conference, April 29-
May 3, 1996.
Risk Factors Fall in the Elderly at Panti Werdha Sejahtera Banjarbaru
621
