Factors Analysis of Individual Childhood Affect Financial Literacy
Employee’s in Palembang
Marieska Lupikawaty
1*
, Yusleli Herawati
1
, Purwati
1
and Elisa
1
1
Department of Business Administration, State Polytechnic of Sriwijaya, Palembang, Indonesia
Keywords: individual factors in childhood, financial literacy
Abstract: This study aims to determine the factors that affect the individual childhood on an individual's ability to
manage money today, who are already working and have income. Problems arise because there is still low
level financial literacy of individual to manage money and still not good financial behavior of individuals.
Respondents are individuals aged fifteen years aboved who worked in Palembang in formal sector with total
sample of 348 people. The results of multiple linear regression showed individual education quality factors
have the greatest influence on the level of individual financial literacy, while the smallest of factors influence
the educational background of parents to the level of an individual's ability to manage money. The results of
this study can be interpreted that the educational background of parents do not give a great influence on
financial literacy. The greater influence were factor individual education quality and factor of teaching parents
at home. Suggestions for respondents as individuals who have a good level of education, already working
and may be have children at home, should provide teaching manage money to their children in order to
produce the next generation being smarter. The results of this study give little different results from several
previous studies in which the majority factors that affect individual financial literacy from a family
background, while result of this research gives statement that the greater influence to individual financial
literacy were education quality factor from employee and teaching parents in childhood.
1 INTRODUCTION
Financial Services Authority (FSA) together with the
banking industry and non-bank financial industry
(IKNB) set October as the month of financial
inclusion in Indonesia. Financial inclusion is a
program that appealed to the middle to lower use of
formal financial products and services as a means of
saving money safe, transfer, savings and loans, and
insurance. Financial Inclusion Program is expecting
the public to gain access evenly and public finance
can leverage access formal financial services than
non-formal financial services.
Financial inclusion program will be successful
when the financial literacy of individuals and
communities is also good. Financial literacy is the
ability of individuals to manage personal finances and
avoid debt at a level where private not afford to pay
(www.birmingham.ac.uk). Based on a national
survey conducted Financi al Services Authority
(2016) that there was a rise in the index of financial
literacy in Indonesia as shown in the following
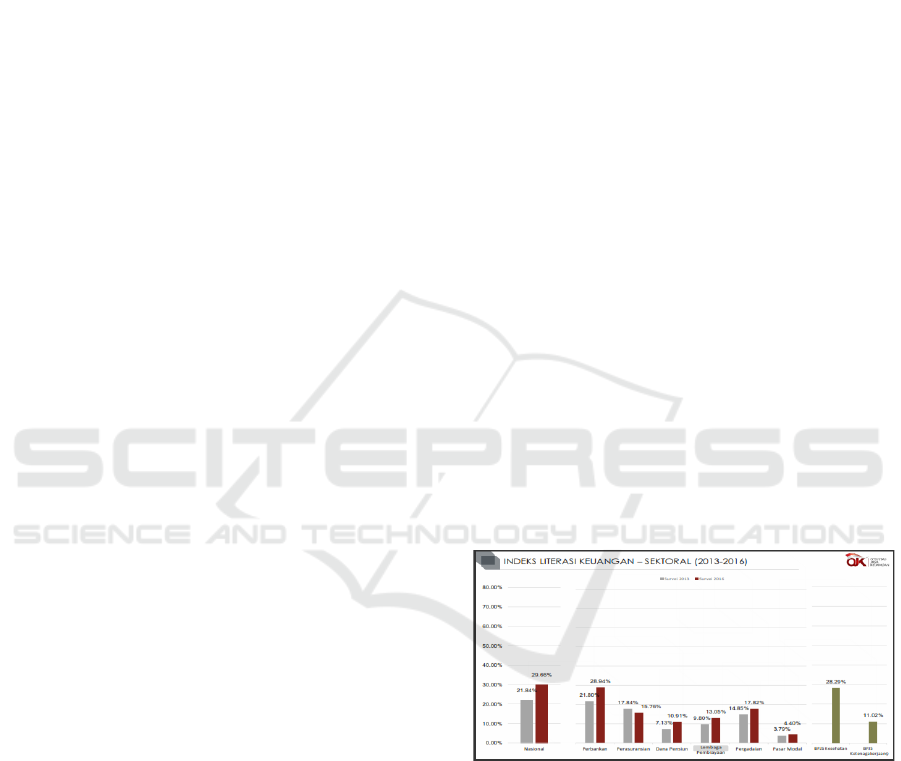
picture:
source: www.ojk.go.id
Figure 1: Financial literacy index 2013-2016
In Figure 1 above provides information that the
community banking sector has the largest financial
knowledge while the capital markets sector of society
still lacked the financial knowledge because most
small pick literacy index. In general, the financial
literacy index of the Indonesian people has increased
from the period 2013 to 2016 meaning that people
began to have the rise of financial knowledge in the
financial industry. Perhaps the question, what is the
Lupikawaty, M., Herawati, Y., Purwati, . and Elisa, .
Factors Analysis of Individual Childhood Affect Financial Literacy Employee’s in Palembang.
DOI: 10.5220/0009152100002500
In Proceedings of the 2nd Forum in Research, Science, and Technology (FIRST 2018), pages 37-42
ISBN: 978-989-758-574-6; ISSN: 2461-0739
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved
37

purpose of government in an effort to increase
financial literacy.
This government program certainly has a purpose
and benefits. The goal is critical to economic and
financial stability of the country, while its benefits as
quoted from the OECD report (2013) of moving the
risk from the government and corporate employers to
individuals, increasing individual responsibility when
there are changes in the market and the economy,
raising the bids comprehensive financial products and
services and increasing demand on financial products
and services. The economic situation and the market
are always changing. Economic uncertainty is very
important to observe the policies of individual
financial decisions. The ability to make money policy
is the basis for today's prosperity and our future.
Personal financial planning is a process to manage
finances in achieving the satisfaction of individual
economies.
There are several factors an individual has a good
level of financial literacy as quoted by the DIW Berlin
(2015) is the educational background of parents,
teaching parents in managing money, economic
education in schools, the quality of education, and
experience managing money as a child. The level of
financial literacy that can either be a positive
influence on the individuals financial behavior.
The purpose of this study is to determine the
factors that affect the individual as a child on the
financial literacy of individuals today who are already
working and have income. The benefits of this
research that gives an idea of the level of the
individual's ability to manage money as an employee
in Palembang and to provide input for the individual
to manage personal finances are the basis for the well-
being of today and the future.
2 REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Financial literacy is often referred to as personal
financial education is an individual's ability to
manage personal finances and avoid debt at a level
where private is not afford to pay
(www.birmingham.ac.uk).
Definition from Huston (2010) personal financial
literacy is the ability to read, analyze, manage and
communicate about the personal financial condition
that affect material well being. It includes the ability
to discern financial choices, discuss money and
financial issues without (or despite) discomfort, plan
for the future and respond competently to life events
that affect everyday financial decisions, including
events in the general economy.
Potrich, Vieira and Kirch (2015) gives the
conclusions of some previous studies that financial
literacy is synonymous with financial literacy or
financial education. Financial literacy is defined by
Chen and Volpe (1998) is as the knowledge to manage
finances in decision-making. Chen and Volpe using
four financial aspects of the individual with the
description of Remund (2010) there are:
1. general knowledge; planning process and
financial control of individual or family unit
2. save and borrow ; savings in the bank that can be
done in the form of savings, time deposits,
certificates of deposit and current accounts
3. insurance; one form of risk control is done by
controlling/transfer of risk from one party to
another party
4. investment; a form of revenue allocation is done
today to make a profit at a later date could exceed
current investment capital.
Based on the description of several previous
studies it can be concluded that financial literacy is an
individual's knowledge and ability to read financial
condition and manage personal finances.
3 METHODOLOGY
Data collection method used in this research is using
interviews, questionnaires and literature review.
Questionnaires used research instrument to make a
measured data, is called scale. Type of scale that used
in this research is interval, a measured data that have
range and have a meaning (Ferdinand, 2014).
Respond from respondent can be measured with
intervally scaled data with two extreme category,
there are strongly disagree to strongly agree (1-10).
The population in this study are individuals who
work in the formal sector in Palembang. The reason
is (i) priorities that require the ability to manage
finances individuals are those who already have a
salary income and non-salary, (ii) individuals who
work in the formal sector usually graduated from
university level because to look at factors level of
individual financial literacy and have a good quality
education.
Type of data is secondary data and is sourced from
Central Bureau of Statistic Palembang City (2015).
The study population are employee in Palembang
whose age of fifteen years above in the formal sector
with amount as 661192, with a sample size of 348
people. The sampling method using simple random
sampling method in which every element of the
FIRST 2018 - 2nd Forum in Research, Science, and Technology (FIRST) – International Conference
38

population has an equal chance to be selected as the
sample (Puspowarsito, 2008).
Technical analysis of data using multiple linear
regression, by the following equation:
FL = a + b
1
PE + b
2
PT + b
3
EE + b
4
EQ + b
5
Exp + e
Information:
PE = parents educational background
PT = parents teaching
EE = Economic Education
EQ = Quality of education
Exp = Experience managing money
FL = individual financial literacy
Test the hypothesis in this study conducted on
statistical hypothesis using t test and F test with
significance level 0. 05, while the hypothesis are:
H
0
: there is no a significant influence between
independent variables to dependent variable
H
1
: There is a significant influence between parental
background variables to variable individual
financial literacy
H
2
: There is a significant influence between the
variables of teaching parents to variable
individual financial literacy
H
3
: There is a significant influence between the
variables of economic education of the
individual against individual financial literacy
variables
H
4
: There is a significant influence between the
variables of education quality of the individual
against individual financial literacy variables
H
5
: There is a significant influence between the
variables of individual experience managing
money against individual financial literacy
variables
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Here are the results of the technical analysis of the
data with regression:
Table 1: t-Test and F-test
Var iabl es B T Significant*
Constants 35.323 5.676 0,000
The
educational
background of
p
arents (PE)
0,365 2,092 0,037
Teaching
Parents (PT)
.737 2.208 0,028
Economic
education (EE)
.688 3.679 0,000
Education
quality (EQ)
1.957 3.649 0,000
Experience
managing
money (Exp)
.480 2,853 0,000
F = 19.728 0,000
Source: results of data processing, 2018
*) Significant at the 0.05 level
FL = 35.323 + 0,365PE + 0,737PT + 0,688EE +
1,957EQ + 0,480Exp
4.1 Partial Test
Table 1 was the results with multiple linear regression
analysis showed that all independent variables a
significant and positive influence on the variable,
where: Constants means that without any influence of
factors of childhood, the financial literacy of
respondents in the amount of 35.323
H
0
: there is no a significant influence between
parental background variables to individual financial
literacy variable
H
1
: There is a significant influence between parental
background variables to variable individual financial
literacy
Result from Table 1 indicate that PE has sig 0,037
< 0,05 it means parental background variables
influences significant to financial literacy. Formal
educational background of parents influence the
financial literacy of respondents is 0.364. This may
imply that the respondents felt the parental education
does not too influence the respondents in managing
money. Education background of respondents parents
are not of from college graduates.
H
0
: there is no a significant influence between
teaching parents variables to individual financial
literacy variable
H
2
: There is a significant influence between the
variables of teaching parents to variable individual
financial literacy
Result from Table 1 indicate that PT has sig 0,028
< 0,05 it means teaching parents variables influences
significant to financial literacy. Teaching parents
affect the financial literacy of respondents is 0.737.
Factors Analysis of Individual Childhood Affect Financial Literacy Employee’s in Palembang
39

This may imply that parents in the direction and
teaching in childhood about managing money plays a
sizable and more remembered by the respondents
until now as employee.
H
0
: there is no a significant influence between
economic education variables to individual financial
literacy variable
H
3
: There is a significant influence between the
variables of economic education of the individual
against individual financial literacy variables
Result from Table 1 indicate that EE has sig
0,000 < 0,05 it means economic education variables
influences significant to financial literacy. Formal
economic education affect the financial literacy of
respondents is 0.688. It can imply that respondents
recognize that economic education in schools sizable
role for respondents to manage money. This factor did
not become dominant because the background
education respondents most are not from economic
background
H
0
: there is no a significant influence between
education quality variables to individual financial
literacy variable
H
4
: There is a significant influence between the
variables of education quality of the individual
against individual financial literacy variables
Result from Table 1 indicate that EQ has sig 0,000
< 0,05 it means education quality variables
influences significant to financial literacy. The quality
of education affect the financial literacy of
respondents is 1.957. This factor affects
predominantly the respondents manage your money
on this research. This means the respondents feel that
the knowledge to manage the money due to the
quality of education they have achieved from college
graduate. The quality of education driven responden
to improve about information about managing
money. The main source they can access is through
the internet. This finding same as research from
Goetz, et al (2011) which states that the students are
more comfortable learning online through the
financial management and learning through
technology.
H
0
: there is no a significant influence between
experience managing money variables to individual
financial literacy variable.
H
5
: There is a significant influence between the
variables of individual experience managing money
against individual financial literacy variables.
Result from Table 1 indicate that Exp has sig
0,000 < 0,05 it means education quality variables
influences significant to financial literacy. Experience
managing money affects the financial literacy of
individuals amounted only 0.480. This factor is the
lowest as independent variables affect the dependent
variable. This means that most respondents do not
have the experience of managing their own money in
childhood, the respondent has not worked before
entering college so that all financial management still
arranged by the parents.
Partial test research results show the influence of
the majority which gives greater influence were
individual education quality factors and factors of
teaching parents at home. It means also that the first
education level gave major influence to respondents
financial literacy because the respondents as an
employee and have graduated from college, the
second that the factors of childhood that is teaching
from parents in the house plays an important role in
improving the financial literacy of individuals,
because respondents already fifteen years above and
already working, then it can’t be happen again so that
it becomes responsibility to respondent if they have
children to provide financial teaching better and right
for their children. Findings from Volpe, Chen and Liu
(2006) have statement that future education program
should be focus to importance individual financial.
4.2 Simultaneous Test
Simultaneous testing results indicate that all
independent variables are the educational background
of parents, teaching parents at home, economic
education of respondents, the quality of the
respondents' education and experience to manage
money significantly affect the financial literacy of
respondents. This means that factors influencing
respondents' childhood literacy rate of respondents or
knowledge and management of money from
respondents. This is consistent with previous studies
of Grohmann and Menkhoff (2015) and Chen and
Volpe (1998). The aims for literacy financial of
childhood is to create a better generation in managing
the finances of individuals. Individual financial
education being able to make good decisions for their
families, improve the economic security and life well-
being (Hilgert and Hogart, 2003).
FIRST 2018 - 2nd Forum in Research, Science, and Technology (FIRST) – International Conference
40

Benefits for individual has the ability to manage
finances, so it can take a good financial decisions for
individuals, families and even where people are
working, so the aims government's financial literacy
at macro level can be realized.
4.3 Coefficient Determination
The technical analysis used in this study is multiple
linear regression so that to see the magnitude of the
coefficient of determination used is adjusted R square
(Sarwono, 2007) which is equal to 0.268 or 26.8%.
Table 2: Coefficient of determination
R R Square Adjusted R Square
0,531 0,282 0.268
Source: processed data, 2018
Table 2 above informed that the number has the
intention that the influence of individual childhood
factors jointly affects individual financial literacy
only by 26.8%, while the factors outside the research
variable are 73.2%. These results can be interpreted
that there are still many factors from outside the
individual's childhood that affect individual financial
literacy, so this can be a further research opportunity
in looking at the influence of individual financial
literacy factors.
5 CONCLUSION
The regression results showed that the quality factor
of individual education has the greatest influence on
the level of individual financial literacy, while the
smallest influence of factors is parents' educational
background to the level of individual finance literacy.
The results of this study can be interpreted that the
educational background of parents does not have a
large influence on the level of individual finance
literacy or understanding in managing money.
There are still many factors from outside variabel
research in the individual's childhood that affect
individual financial literacy, so this can be a further
research opportunity in looking at the influence of
individual financial literacy factors.
Suggestions for respondents as individuals who
have graduates from college, have worked and if they
have children at home, they should be provide
teaching how to manage money to their children, in
order to get a better generation in managing money.
The results of this study give slightly different results
from several previous studies where the major factors
that influence the individual financial literacy is from
family backgrounds (Grohmann and Menkhoff,
2015), namely parents' educational background and
parents' teaching managing money to their children at
home. The ability to make money policies is the basis
for our well-being present and future.
Personal financial planning is a process for
managing finances in achieving individual economic
satisfaction. This process is to control the financial
situation, because income has an allocation to meet
the needs of individuals and families today and future
needs. Furthermore, at the macro level, the goal of
long-term financial literacy from the government will
be realized and useful for the progress of the
economy’s country.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper is one part of an annual duties research in
Polytechnic State of Sriwijaya. The author would like
to thankfull with the team, students and the
institutions which has provided funding through
research grants in 2018.
REFERENCES
Central Bureau of Statistic Palembang City. 2015.
Employee in Palembang whose age of fifteen years
above. https://palembangkota.bps.go.id.
Chen and Volpe. 1998. An Analysis of Personal Financial
Literacy Among College Students. Financial Services
Review, 7(2) : 107-128. ISSN : 1057-0810. JAI Press
Inc.
DIW Berlin. 2015. Financial Literacy and Financial
Behaviour. DIW Economic Bulletin Volume 5 July, 29
2015. ISSN 0012-1304
Ferdinand. 2014. Structural Equation Modeling. Dalam
Penelitian Manajemen. Edisi 5 BP Undip-Undip Press.
ISBN : 979-9156-75-0
Goetz, et al. 2011. College-Based Personal Finance
Education : Student Interest in Three Delivery Methods.
Journal of Financial Counseling and Planning, Vol 22,
No. 1 , 2011
Grohmann and Menkhoff. 2015. Financial Literacy and
Financial Behaviour. DIW Economic Bulletin.
Hilgert and Hogart. 2003. Household Financial
Management : The Connection between Knowledge
and Behaviour. Federal Reserve Bulletin Juli 2003
Huston, S.J. 2010. Measuring Financial Literacy. Journal
of Consumer Affairs Volume 44 Issue 2
OECD. 2013. Financial Literacy Framework. PISA 2012
Assesment and Analytical Framework.
Factors Analysis of Individual Childhood Affect Financial Literacy Employee’s in Palembang
41

http://www.oecd.org/finance/financial-
education/PISA2012FrameworkLiteracy.pdf
Otoritas Jasa Keuangan. 2016. Indeks Literasi Keuangan
Sektoral. www.ojk.co.id
Potrich, Vieira and Kirch. 2015. Determinants of Financial
Literacy : Analysis of the Influence of Socioeconomic
and Demographic Variables. ISSN 1808-057x. DOI :
10.1590/1808-057x201501040
Puspowarsito. 2008. Metode Penelitian Organisasi Dengan
Aplikasi Program SPSS. Bandung:: Humaniora
Remund, D L. 2010. Financial Literacy Explicated : The
Case for a Cleaner definition in an Increasingly
Complex Economy. Journal of Consumer Affairs
Volume 44 Issue 2
Sarwono, Jonathan. 2007. Analisis Jalur untuk Riset Bisnis
dengan SPSS. Penerbit Andi : Yogyakarta
University of Birmingham. Financial Literacy Briefing 1 :
What is Financial Literacy?
https://www.birmingham.ac.uk/schools/education/rese
arch/projects/what-is-financial-literacy.aspx. accessed
February 14, 2018,
Volpe, Chen and Liu. 2006. An Analysis of the Importance
of Personal Finance Topics and the Level of Knowledge
Possessed by Working Adults. Financial Services
Review 15 (2006) 81-98
FIRST 2018 - 2nd Forum in Research, Science, and Technology (FIRST) – International Conference
42
