
The Analysis of Exposure Economic on the Value of
Manufacturing and Mining Industry
Isma Dewi Br Panjaitan
1
, Isfenti Sadalia
1
and Khaira Amalia Fachrudin
1
1
Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan -Indonesia
Keywords: Economic Exposure, Firm Size, Market to Book Ratio, Quick Ratio, Export Ratio, Debt to Asset Ratio,
Earning Variability, Hedging, Value of Company
Abstract: Economic exposure is a measure of change in exchange rates that effect the company’s value as measured in
the present value as measured in the present value of cash flows that aims to maximize shareholder wealth.
The purpose of this research is to find out and analyze the effect of the economic exposure of manufacturing
and mining company. The independent variables of research are firm size, market to book ratio, quick ratio,
export ratio, debt to asset ratio, earning variability and hedging against value companies with economic
exposure as intervening variable in Manufacturing and Mining Industry. This research is a statistical study
of associative. Method of data collection is done through study of documentation. The Population of this
research is the Manufacturing and Mining industries that are listed in the Indonesia Stock Exchange in
accordance with the specified criteria as much as 171 companies consisting of 132 manufacturing company
and 39 mining companies. Methods of data analysis used is using path analysis software with E-views 7.0.
The research of the first substructure is show firm size, market to book ratio, quick ratio, export ratio, debt
to asset ratio, earning variability and simultaneously hedging exposure to economics in Manufacturing and
Mining companies. The export ratio partially positive and significant effect against the economic exposure.
The second substructure result show firm size, market to book ratio, quick ratio, export ratio, debt to asset
ratio, earning variability, hedging and economic exposure simultaneously affect the company’s value in
manufacturing and mining companies. Partially only debt to asset ratio and earning variability which have
positive and significant influence to company value. Economic exposure is not an intervening variables the
influence of firm sixe, market to book ratio, quick ratio, the export ratio, debt to asset ratio, earning
variability and hedging against the value of the company.
1 INTRODUCTION
The rapid development process of the world
economy has increased the relationship of
interdependence and sharpened world business
competition. This international trade activity not
only benefits producers but as a means of meeting
unlimited consumer needs. Moreover, at this time it
will take effect and the system of the Asean
Economic Community (MEA) will take place which
supports international economic activities.
This greatly affects the income and expenditure
of companies that use foreign currencies in export or
import transactions. The fluctuation of the rupiah
exchange rate against the USD also affects stocks
(Hudiwinarti, 1998) In addition, the actions of
foreign investors who use shares as a means to take
advantage of currency speculation also influence the
value of these shares so that the value and
performance of the company is affected by foreign
exchange rates (Kuncoro, 2000). According to
(Faisal, 2001) there are three types of exposures
caused by changes in exchange rates, namely
economic translation and economic transaction.
Translation and transaction exposure are explained
in accounting calculations defined by the book value
of assets and liabilities nominated in foreign
currencies. While economic exposure is the
sensitivity of a company's value to changes in
exchange rates.
According to (Bodnar, a professor from John
Hopkins University), economic exposure is the total
impact of changes in a macroeconomic variable on
the company's market value, where changes in
exchange rates will affect the nominal value of
contracts in future contracts which will affect cash
flows company.
Researchers
who have carried out research on
Panjaitan, I., Sadalia, I. and Fachrudin, K.
The Analysis of Exposure Economic on the Value of Manufacturing and Mining Industry.
DOI: 10.5220/0009509806230627
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 623-627
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
623

economic exposures such as the (Pritamani, Shome
dan Singal, 2004) study prove that the company's
total economic exposure is negatively related to the
level of stock returns, these variables are proxied as
variables needed for hedging.
(He dan Ng, 1998) use the Quick Ratio variable
as a determinant of the level of economic exposure
faced by a company. Quick Ratio is a proxy variable
to reduce the level of hedging carried out by the
company. Other variables, namely Debt to Equity
Ratio, can be proxied as a variable needed for
hedging purposes.
(Wulandari, 2013) one of them is the mining
industry because this industry still relies on imported
raw materials. This strengthening of the exchange
rate causes local mining products to become more
expensive so that they are not competitive with
similar products from competing countries.
Based on the description of the background, the
researcher was interested in researching about
economic exposures with the title "Analysis of
Economic Exposures to Firm Values in the
Manufacturing and Mining Industry in the Indonesia
Stock Exchange". The time period examined is from
2010-2015.
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
(Kanagaraj dan Sikarwar, 2011) conducting research
under the title "A Firm Level Analysis of the
Exchange Rate Exposure of Indian Firms", this
study examined the level of foreign exchange
exposure and determinants for samples of Indian
companies. For this purpose, the relationship
between exchange rates and stock returns for a
sample of 361 non-financial companies in India with
the period April 2006 - March 2011. The study
found that only 16 percent of companies were
affected by exposure where 10 percent were
significant. Furthermore, from companies that have
significant exposure 86 percent of companies have a
negative influence by Rupee appreciation which
confirms that Indian companies are exporters.
(Susilowati, 2015) conducted a research with the
title "Rupiah Exchange Rate Exposures and Stock
Returns on Companies Listed on the Kompas 100
Index". This study aims to determine the effect of
changes in the real exchange rate index on company
stock returns. Stock return is used as a proxy for
company value. The exchange rate exposure of the
company varies depending on the management
carried out by the company. Therefore this study
also aims to analyze the influence of the level of
foreign operations and explanatory variables of the
company's hedging policy on the rupiah exchange
rate exposure faced by the company. The research
sample was focused on companies listed on the
Kompas 100 Index in the period 2009 to 2013.
Based on the selection of samples by purposive
sampling, the number of samples in this study were
43 companies. This study uses multiple linear
regression analysis as a test tool. From the multiple
linear regression test in the regression model
equation 1, the beta values of each company are
obtained which indicate the level of exposure of the
company's exchange rate. The beta value was tested
in the equation 2 regression model with the ratio of
exports, firm size, long-term debt ratio, dividend
payout ratio, quick ratio, book to market value of
equity. The results showed that changes in the real
effective exchange rate index had a significant
positive effect on stock returns. Companies that have
export activities benefit when the rupiah exchange
rate depreciates against the currencies of Indonesia's
main trading partners. Exchange rate exposure will
increase along with the increase in the ratio of
exports owned by the company. This study also
found empirical evidence that two hedging
explanatory variables namely dividend payout ratio
and long-term debt ratio affect the level of exposure.
(Nur, Binti dan Ahmad, 2015) carried out
research under the title "Foreign Exchange Exposure
and Its Determinants Among Some Listed
Companies From Selected Sectors in Malaysia".
This study analyzes the exchange rate exposures of
90 Malaysian companies in various sectors such as
the agricultural sector, consumer product sector and
industrial sectors listed on Bursa Malaysia for the
period January 2008 to December 2012. The results
of this study indicate that the agricultural sector is
more affected by exposure than the sector
consumption and industrial sector. Besides that
company size, liquidity, debt, asset turnover, profit,
diversification of currencies and diversification of
foreign subsidiaries were found to be insignificant in
explaining the factors that might influence foreign
exchange exposure.
The Model Framework in this research is below:
Source: (Kurniawati Sri Lestari & Anggraeni, 2004) (Data
processed, 2016)
Figure 1: Research Design
Eksposur
Ekonomi (Z)
Firm Size (
X
1
)
Market to Book
Ratio (X
2
)
Q
uick Ratio
(X
3
)
Export Ratio (X
4
)
Debt toAsset Ratio
(X
5
)
Earning Variability
(X
6
)
Nilai
Perusahaan
(Y)
Hedging (D
1,0
)
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
624
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This study is an associative study in which research
links two or more variables (Ginting Paham &
Syafrizal Situmorang, 2008).
This research was conducted in the
Manufacturing and Mining Industry on the
Indonesia Stock Exchange. The observation period
from 2010 to 2015 was examined on the official
website www.idx.co.id. The planned time to conduct
the study was October 2015 to September 2016.
The population of 132 Manufacturing Industry
companies and 39 Mining Industry companies.
4 RESULTS
The following is a summary of the test results of the
significance of the simultaneous influence as
follows:
Table 1: Test for the Significance of Simultaneous
Influence for Equation I Structure and Substructure II for
the Manufacturing and Mining Industry.
The following is a summary of the results of the
partial effect tests as follows:
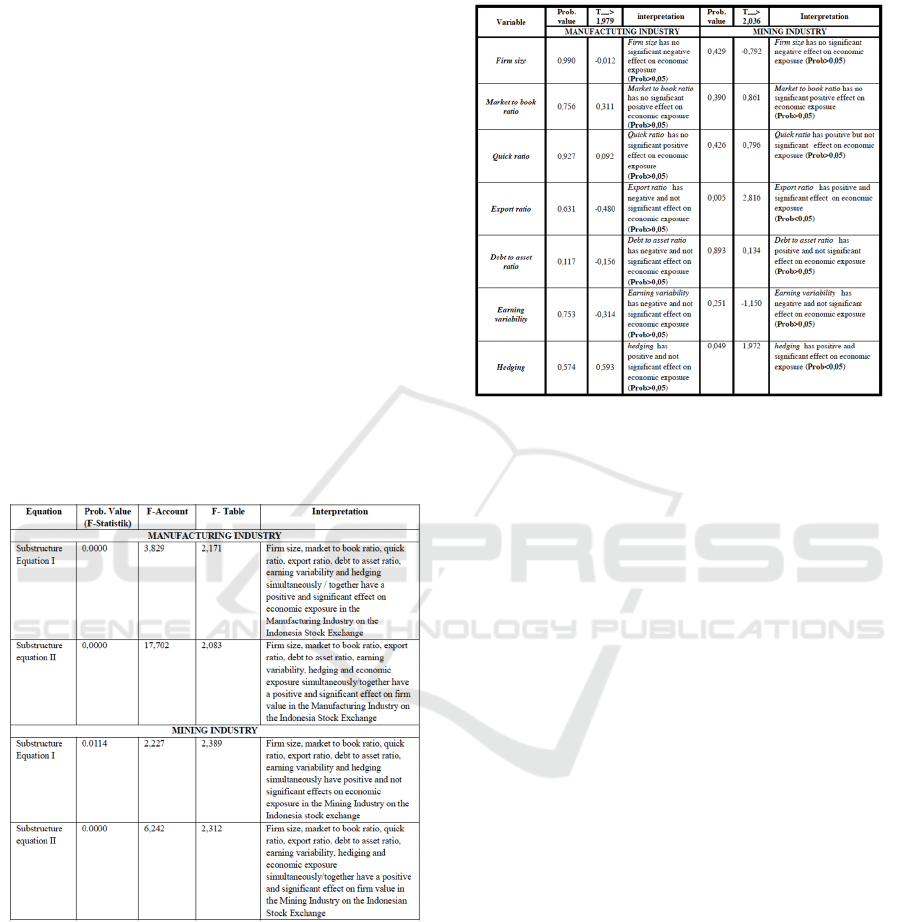
Table 2: Test the Significance of Partial Influence with
Probability Value (Sig.) For Equation I Structure in
Manufacturing and Mining Industry.
5 CONCLUSIONS
1. Based on the results of the study of economic
exposure analysis on the value of the company in
the manufacturing and mining industries on the
Indonesian stock exchange, it can be concluded
that: Firm size, market to book ratio, quick ratio,
export ratio, debt to asset ratio and earnings
variability simultaneously have a positive and
significant effect on economic exposure in the
manufacturing and mining industries in the
Indonesian stock exchange;
2. Firm Size, market to book ratio, quick ratio,
export ratio, debt to asset ratio, earnings
variability and economic exposure
simultaneously have a positive and significant
effect on firm value in the manufacturing and
mining industries in the Indonesian stock
exchange;
3. Economic exposure is not an intervening variable
(intermediary) capable of mediating the
influence of firm size, market to book ratio,
quick ratio, export ratio, debt to asset ratio,
earnings variability, and hedging of firm value in
manufacturing and mining industries on the stock
exchange Indonesia;
4. There are differences in the influence of firm
size, market to book ratio, quick ratio, export
ratio, debt to asset ratio and earnings variability
on economic exposures that do hedging and no
The Analysis of Exposure Economic on the Value of Manufacturing and Mining Industry
625

hedging in the manufacturing and mining
industries in the Indonesian stock exchange;
5. There is a difference in the influence of firm size,
market to book ratio, quick ratio, export ratio,
debt to asset ratio and earnings variability on the
value of the company through economic
exposure to hedging and non-hedging in the
manufacturing and mining industries in the
Indonesian stock exchange.
6 SUGGESTION
Based on the conclusions from the results of the
research as stated earlier, the suggestions that can be
given are as follows
1. The firm size of the manufacturing and mining
industry companies can be seen from the
research results that firm size has a positive and
significant impact on the value of the company.
There is a good idea for the company to control
its firm size if it wants to develop the company
even more in the international trade arena. the
greater the firm size of the company, the greater
the risk of being exposed to economic exposures
because the company carries out international
trade cooperation with foreign companies and the
inflow of cash and assets in foreign currencies
will increase, so the management of the company
must be able to cast a watch on the movement of
the rupiah the company does not carry out
policies in hedging, the company will be at
greater risk of being exposed to economic
exposure which will result in a decrease in the
value of the company.
2. In this study, the market to book ratio has a
positive but insignificant effect on firm value and
economic exposure for the manufacturing and
mining industries, this might occur if at the time
of the year examined some of the company's
conditions were not good because economic
movements in the country were experiencing a
crisis so that the company's ability to increase its
growth rate is very difficult. Moreover, people's
purchasing power is declining, which makes the
sale of production from the manufacturing
industry very bad, as well as companies that do
certain materials to make their products by
importing raw materials from other countries, of
course, the cost of production costs will be
impact on the sale of these products. So that
manufacturing and mining companies can take a
way by carrying out various promotional
strategies in increasing sales to cover large
operational costs so as not to have a significant
impact on the company's growth.
3. In this study more quick ratios have a negative
and insignificant impact on economic exposure
but there are also those that have a negative and
significant impact on the value of the company in
the mining industry. of course this is very
worrying for some companies because it is how
well the company fulfills its obligations, this has
a negative impact on exposure because if the
amount of assets or cash in foreign currencies is
very risky when they want to make liabilities to
other companies. This can be anticipated by
carrying out hedging policies when conducting
work agreements, so that the value of sales or
purchases of raw materials that we do are not
subject to increases or decreases in the exchange
rates of these currencies.
4. The mining industry must pay more attention to
the export ratio and continue to monitor its
progress so that it is still in good condition and
under control because the export ratio is a
variable that influences economic exposure and
also affects the value of the company. Where in
maintaining stability, companies engaged in the
mining industry must better understand and
master the techniques of using derivative
instruments such as SWAP and Hedging, where
hedging is a variable that plays an important role
in economic exposure for companies that
conduct international trade. But in this study
hedging has no significant effect on economic
exposure in the manufacturing industry only in
the mining industry hedging has a positive and
significant effect on economic exposure and on
the value of the company through economic
exposure. Mining is more significant because
Indonesia is rich in natural products in the form
of mining materials such as gold, aluminum,
coal, nickel and so on. However, some
companies have not directly processed it into
finished goods and have chosen to export raw
materials and re-import after being semi-finished
goods so that mining more often applies hedging
policies to protect the value of export sales and
import activities from their mining products.
5. This research is expected to be able to
complement previous research related to
economic exposures and can add references or
knowledge about economic exposure in a
subsequent scientific work by adding more
extensive independent variables.
6. This research is expected to be an input for
financial managers to pay more attention to any
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
626

company internal factors that influence the
occurrence of economic exposure in its
operational activities.
REFERENCES
Abdullah, M. Faisal (2005). Dasar - dasar Manajemen
Keuangan. Edisi Kedua. Cetakan Kelima. Malang :
Penerbitan Universitas Muhammadiyah.
Amirullah dan Widayat, (2002). Riset Bisnis. Edisi
Pertama. Yogyakarta : Graha Ilmu.
Anggraeni (2004).“The Foreign Exchange Exposure pada
Bank – Bank Go Public di BEJ”. Jurnal Ventura Vol.
7 No. 2.
Cheung, Y. W., M. D. Chinn & A. G. Pascual. (2005).
“Empirical Exchange Rate Models of the Nineteens:
Are Any Fit to Survive?”. Journal of International
Economics
El-Masry, A. A. (2006). “The Exchange Rate Exposure of
UK Non-Financial Companies: Industry Level
Analysis”. Managerial Finance, Vol. 32(2),115-136.
Faisal (2001) Manajemen Keuangan Internasional. Edisi
Pert. Jakarta: Salemba Empat.
Ginting, Paham & Syafrizal Situmorang (2008) Filsafat
Ilmu dan Metode Riset. Medan: USU Press.
Hudiwinarti, G. (1998) “Pengukuran Economic Exposure
Dan Faktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhinya Pada
Kelompok Perusahaan Barang Konsumsi Yang Go
Public Di Bursa Efek Jakarta".(Tesis). Jakarta.
Universitas Indonesia, Program Pascasarjana.
Kanagaraj, A. dan Sikarwar, E. (2011) “A Firm Level
Analysis of the Exchange Rate Exposure of Indian
Firms,” Journal of Applied Finance & Banking.
Kuncoro, M. (2000) Manajemen Keuangan Internasional:
Pengantar Ekonomi dan Bisnis Global. Edisi Kedua.
Yogyakarta: BPFE.
Kurniawati Sri Lestari & Anggraeni (2004) “Forex
Exposure Pada Berbagai Sektor Industri Yang
Terdaftar Di Bursa Efek Jakarta.” Tersedia pada:
puslit2.petra.ac.id/ejournal/index.php/nas/article/view/
17176/17124.
Nance, D. R., Clifford W. Smith, J., & Smithson, C. W.
(1993)."On The Determinant of Corporate Hedging".
The Journal of Finance, Volume 48 (1), 267-284.
Nur, W. A. N., Binti, I. dan Ahmad, W. A. N. (2015)
“Foreign Exchange Exposure And Its Determinants
Among Some Listed Companies From Selected
Sectors In Malaysia.”
Pritamani, M. D., Shome, D. K. dan Singal, V. (2004)
“Foreign Exchange Exposure Of Exporting And
Importing Firms,” Journal of Banking and Finance.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbankfin.2003.06.002.
Susilowati (2015) “Eksposur Nilai Tukar Rupiah Dan
Return Saham Pada Perusahaan Yang Terdaftar Di
Indeks Kompas 100.” Yogyakarta: Universitas Gadjah
Mada.
Wulandari, D. L. (2013) “Analisis Variabel Fundamental
yang Berpengaruh Terhadap Eksposur Ekonomi
Perusahaan Industri Komoditas Pertambangan yang
Terdaftar di Bursa Efek Indonesia Periode 2006-
2010". Fakultas Ekonomi dan Bisnis. Malang :
Univeristas Brawijaya.”
The Analysis of Exposure Economic on the Value of Manufacturing and Mining Industry
627
