
The Effect of Work Culture, Personality, Leadership and Trust on
Employee Commitment at PT Astra Agro Lestari Tbk on Indonesia
Pandapotan Sitompul
1
, Suparno Eko Widodo
1
, R. Madhakomala
1
and Hamidah
1
1
Universitas Negeri Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Employee Commitment, Work Culture, Personality, Leadership and Trust
Abstract: The objective of research is to study the effect of work culture, personality, leadership and trust on
employee commitment. The process of research carried out at the private company it has used case study
methode. The samples of research were 105 employee at the private company that were selected in a simple
random sampling. The results of finding are: (1) there is a positively direct effect of work culture on
employee commitment, (2) there is a positively direct effect of personality on employee commitment, (3)
there is a positively direct effect of leadership on employee commitment (4) there is a positively direct
effect of trust on employee commitment (5) there is a positively direct effect of work culture on trust, (6)
there is no a positively direct effect of personality on trust, (7) there is a positively direct effect of leadership
on trust. Referring to these findings, the researcher could conclude that employee commitment is positively
affected by work culture, personality, leadership and trust. Therefore, to maintain employee commitment,
the organization has to apply the work culture, personality, leadership and trust. Finally, it should be
concluded that work culture, personality, leadership and trust should be considered in generating the
employee commitment.
1 INTRODUCTION
Employee commitment is a measure of the
willingness of employees to stay together a company
in the future. There are three general behavioral
indicators of employee commitment, namely (1)
there is willingness to help colleagues complete
organizational tasks, (2) unite their activities and
priorities to achieve larger organizational goals, (3)
choose needs appropriate organizations rather than
following some professional interests.
According to Colquitt et al., employee
commitment is defined as desire of employees to
continue to be members of the organization.
Employee commitment affects whether employees
endure being members of organizations or going to
pursue other jobs. Employees who are not
committed to the organization have self-withdrawal
behavior, namely a set of actions that employees
show to avoid behavioral work situations that
usually trigger out of the organization (Colquitt et
al., 2009).
Inanlou & Ahn's research from Ewha Womans
University, South Korea with the title Impact of
Organizational Culture on Employee Commitments:
Role of Mediation in Human Resource Development
in Korean Companies: Commitment of workers is an
important to increase employees’ accomplishment.
The rationale is the following. When what the
employee feels part of the organization, such
identification immediately contributes to fostering
high degree commitment and innovation. Therefore,
we expect organizational culture will enhance
commitment of employees (Inanlou & Ahn's, 2017).
Based on the opinions above, worker
commitment is important to improve employee
performance. The rationale is as follows. When
employees feel that they are part of an organization,
such identification immediately contributes to
encouraging high-level commitment and innovation.
Therefore, it is expected that the organizational
culture will increase employee commitment.
Bartholomew et al. in his research entitled
Personality Characteristics and Employee Affective
Commitment: Nigeria Experience mengatakan, “It
was explained that there is a significant positive
898
Sitompul, P., Widodo, S., Madhakomala, R. and Hamidah, .
The Effect of Work Culture, Personality, Leadership and Trust on Employee Commitment at PT Astra Agro Lestar i Tbk on Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0009510808980905
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 898-905
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

relationship between the five personality
characteristics and affective commitment”
(Bartholomew et.al., 2016). Based on this
explanation opinion, it was revealed that there was a
positive and significant relationship between the five
aspects of personality traits with affective
commitment.
Porter stated: Organizational commitment has
evolved from the past until now as a multi-
dimensional construction to understand why
employees remain or leave the organization.
Transformational leadership has been studied in a
limited way as an antecedent to organizational
commitment, and the results of this study provide
consistent results (Porter, 2015).
Based on the above opinion, organizational
commitment has progressed from the past until now
as multi-dimensional construction to understand the
reasons why employees survive in the organization
or leave the organization. Transformational
leadership has been studied in a limited way as an
antecedent for organizational commitment, and the
results generally provide consistent results.
Njoroge et al., stated: Management literature is
awash with evidence suggesting that organizational
commitment is associated with variables of great
importance for organizational efficiency and
success. Transformational leadership is an important
antecedent of organizational commitment (Njoroge
et.al., 2015).
Based on the statement above, there is a lot of
research in management that shows that
organizational commitment is associated with
variables that are very important for the purpose of
efficiency and success of the organization.
Transformational leadership is an important
antecedent of organizational commitment.
Rahmani & Heydari explained, “trust, in addition
to organizational commitment within the educational
organization could have a positive impact on
maintaining quality staff” (Rahmani & Heydari,
2017).
Based on the above opinion, trust in addition to
organizational commitment to educational
organizations can have a positive effect on
maintenance of quality staff / employees.
Based on research conducted by the five
researchers, it is known that organizational culture
has an impact on employees commitment,
personality influences employee commitment,
leadership impact on employee commitment and
trust affects employee commitment.
This research was conducted at PT Astra Agro
Lestari Tbk, one among the promment private
plantation companies in Indonesia. The real
conditions at the research location were employees
the private company, based on a preliminary survey
with 30 employees, it was seen that employee
commitment was still low.
Based on the background of the problem,
identification of the problem, limitation of the
problem, then formula problem of this study are as
follows: (1) Is there a direct influence of work
culture on employee commitment? (2) Is there a
direct influence of personality on employee
commitment? (3) Is there a direct influence of
leadership on employee commitment? (4) Is there a
direct influence of trust on employee commitment?
(5) Is there a direct influence from work culture on
trust? (6) Is there a direct influence of personality on
trust? (7) Is there a direct influence of leadership on
trust?
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
2.1 Employee Commitment
According to Schermerhorn, organizational
commitment is employee loyalty to the organization
(Schermerhorn et al, 2010). Thus Schermerhorn
briefly defines organizational commitment as
individual loyal to the organization. That means that
the higher a person's organizational commitment, the
higher the level of pride of being part of the
organization, because the stronger he identifies
himself with his organization. organisasinya.
According to Robbins & Judge, organizational
commitment is as strong as what an employee
identifies with the organization where he works and
his goals and wants to always be a part of a
particular organization (Robbins & Judge, 2007).
With this understanding of organizational
commitment by Robbins and Judge as the level of
identification of a person in the existence and
purpose from the organization and its willingness to
survive to be part of the organization.
Colquitt et al., said that the notion of
organizational commitment is the desire of
employees to remain a part of the organization
(Colquitt et al., 2009). According to Colquitt, et al.,
understanding of organizational commitment desire
of members in order to remain part of the
organization. Thus their opinions are in line with
previous opinions that make the aspect of defense as
the main feature in one's commitment to the
organization.
Luthans said that organizational commitment is
(1) strong will to remain a part organization, (2)
willing with all the high-level efforts on behalf of
organizational, (3) certain beliefs and can accept the
values and objectives of the organization (Luthans,
2011). For Luthans, organizational commitment
The Effect of Work Culture, Personality, Leadership and Trust on Employee Commitment at PT Astra Agro Lestari Tbk on Indonesia
899

contains a number of commitments, such as (1)
strong desire from members to survive in certain
organizations, (2) a strong willing to participate in
maintaining the organization's name, and (3) a
determination to wholeheartedly accept values and
the purpose of the organization.
Gibson said that commitment organization is a
sense of identification, loyalty, and involvement
expressed by an employee toward the organization
or unit of the organization (Gibson, 2012).
According to Gibson, understanding of
organizational commitment the identification,
loyalty, and various kinds of expressions a person
has towards his organization. Gibson also mentions
3 scope in organizational commitment, namely (1)
sense of identification with the organization's goals,
(2) a feeling of involvement in organizational duties,
(3) a feeling of loyalty for the organization (Gibson,
2012). This means, there are 3 scopes in
organizational commitment, namely (1) a sense of
identification with organizational goals, (2) feelings
of involvement in organizational tasks and (3)
feelings of loyal to the organization. Based on the
statement above, organizational commitment and
employee loyalty are how strong employees want to
stay in the organization and want to continue to
actively participate.
Based on the explanation of the concept above, it
can be synthesized that employee commitment is a
desire and loyal attitude (identification, involvement
/ attachment) that is shown by someone to the
organization by being willing and fully involved in
carrying out tasks / work in achieving organizational
goals and desires and remain as members .
The indicators are (1) emotionally bound with
organization; (2) self-identification of the
organization; (3) rational attachment to the
organization; (4) attachment due to the need for the
organization; (5) moral attachment to the
organization; and (6) loyalty to stay in the
organization.
2.2 Work Culture
In simple terms, work culture look as the
implementation of cultural concepts in work or in a
group. As stated by Schein the following: The
culture of groups are now interpreted as patterns of
shared basic assumptions that groups learn when
they solve problems of adjustment with external
parties and their internal integration, that was works
well so it is considered valid because it must thaught
for new members as the right way to understand,
thing and feel in connection with the problem that
exists (Schein, 2004).
Based on the above opinion, the culture that
develops in a group or organization is basic pattern
of assumptions agreed upon, has been studied by
group members in solving problems related to
adjustments externally and internally integration.
Culture develops because it has worked well so that
it is which means valid therefore culture can taught
for new members of the organization as right way to
realize, think and feel relationships in dealing with
group problems.
According to Nawawi, understanding of work
culture is a habit that is carried out repeatedly by
employees in an organization, violations of this
practice are not strictly sanctioned, but morally
organizational behavior has agreed that these habits
are habits that must be adhered to in order to carry
out work to achieve aim (Nawawi, 2003).
Whereas according to Prasetya, the notion of
work culture is a philosophy based on the view of
life as a value that becomes traits, habits, and the
power that drives, rooted in life a community group
or organization reflected in attitudes to behavior,
ideals, beliefs, actions and opinions incarnate as
work or work (Prasetya, 2001).
So work culture is an attitude and belief and trust
from all members of organization in action that is
real or working, because it contains values that form
habits, and also is a strong encouragement.
In organizations, functions or goals of work
culture are as social glue in uniting members in
achieving organizational goals in the form of
provisions or values that must be said and done by
its members. In addition, work culture also functions
as a control over behavior of members of the
organization.
Tylor (in Ndraha), stated “Culture or civilization
from a broad ethnographic is a very complex whole
that covers beliefs, knowledge, morals, arts,
customs, laws and abilities and other habits acquired
by individuals as members society”. It cannot be
denied the opinion of Tylor. Because work culture
always involves many things, knowledge, beliefs,
art, morality, law, customs and capabilities and other
habits. All of them have their respective roles as part
of the community in an organization (Ndraha, 1997).
According to Ndraha, understanding of work culture
is a group of basic thoughts or mental programs that
can be used for improve work efficiency and human
cooperation owned by a group of people.
Based on the explanation of the concept above, it
can be synthesized that what is meant by
understanding work culture is a system of values,
perceptions, behaviors and beliefs held by each
individual employee about the meaning of work and
reflection in activities to achieve organizational
goals. The indicators are 1) Hard work, 2)
Discipline, 3) Productive, 4) Responsibility, 5)
Creative, 6) Dynamic, and 7) Mandiri.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
900

2.3 Personality
Personality is a characteristic of identifying their
tendency to behave in a certain way. This is
supported by the opinion of Schermerhorm, who
expressed the notion of personality: Personality is an
overall combination of characteristics that capture
the unique nature of individuals that is important for
understanding and helping someone as a person who
reacts and interacts with others (Schermerhorn et al.,
2010).
Shabahang & Amani stated: Personality traits or
attributes can influence the decisions and
organizational behaviors of employees. Personality
is generally known to affect the way individuals
decide and behave, many studies have examined the
relationship between personality and employee
commitment (Shabahang & Amani, 2016).
Based on the explanation above, personality
traits or attributes can influence employee decisions
and behavior. When personality variables found in
general affect in what way individuals decide and
behave, various many studies have examined the
relationship between personality factors and
employee organizational commitment.
According to Colquitt et al., the notion of
personality is:Personality refers to the structures and
propensities inside people that explain their
characteristic patterns of though, emotion and
behavior personality creaters people’s social
reputations the way they are perceived by friend,
family, coworkers and supervisors (Colquitt et al.,
2009).
Furthermore Larsen & Buss stated personality as
follows: Personality is the set of psychological traits
and mechanisms within the individual that are
organized and relatively enduring and that influence
his or her interactions with, and adaptations to, the
intrapsyhic, physical and social environments
(Larsen & Buss, 2010).
Personality is the whole way in which an
individual reacts and interact with each other
individuals, and adjusts to the environment.
Adjustment is as "a process of individual response
both behavioral and mental in an effort to overcome
the needs of self, emotional tension, frustration and
conflict, and so that there is a balance between
meeting those needs with the demands (norms) of
the environment. These characteristics are unique.
This is supported by Griffin's opinion, which says
that: “Personality is the relatively stables set of
psychological atributes that distinguish one person
from another” (Griffin & Moorhead, 2007).
Personality is defined as a combination of stable
physical and mental characteristics that give
individuals their identity.
Based on the description of the concept above, it
can be synthesized that personality is a pattern of
behavior and a unique way of thinking that
determines one's adjustment to the environment,
with the following indicators: conscientiousness,
extraversion, agreeableness, emotion stability,
openness to experience.
2.4 Leadership
Colquitt et al. define leadership or leadership is the
use of strength and influence in directing followers'
activities to achieve goals (Colquitt et al., 2015). For
them leadership is about a person's ability to use
strength and influence on his followers to want to
carry out their activities to achieve desired goals.
Stoner and Freeman say that leadership or
leadership is art in coordination and motivating
individuals and group to achieve the desired end
(Stoner & Freeman, 1995). For them leadership is
art in coordination and encouraging individuals or
groups in achieving the expected goals. So,
leadership means the process of how leaders are
imaginatively governing, directing, guiding or
influencing others in choosing and achieving certain
goals.
Dlamini, said “transformational leadership
occurs when the leader motivates, inspires and
intellectually encourage subordinates with
charismatic behavior and employees follow the steps
in achieving organizational goals” (Dlamini, 2017).
This means transformational leadership occurs when
leaders motivate, inspire and intellectually stimulate
subordinates to behave in charismatic ways and
employees follow rules in achieving organizational
goals.
By exposing the concept above, it can be
synthesized that what is meant by leadership is a
person's actions in influencing and directing a person
or group of people by recognizing, supporting,
training or developing, motivating or inspiring,
fostering good relations, protecting and giving
feedback to subordinates to be willing to work
together in achieving goals set by the organization.
The indicators of leadership are (1) leadership
actions in influencing and directing; (2) leadership
clarity in delegating tasks; (3) ways to guide and
establish and reinforce organizational policies; (4)
how to guide its members in carrying out the
organization's vision and mission; (5) how to
provide input or advice in implementing policies; (6)
activities in working both personally and in groups.
2.5 Trust
Trust is important in the organization, because
without trust there may not be a harmonious
relationship between leaders and subordinates.
Experts try to define trust based on their conditions
and points of view.
The Effect of Work Culture, Personality, Leadership and Trust on Employee Commitment at PT Astra Agro Lestari Tbk on Indonesia
901

McShane and & Glinow said that trust refers to
positive expectations one person has toward another
person in situations involving risk (McShanes &
Von Glinow, 2008). For McShane & Von Glinow,
trust refers to a person's positive expectations of
others in which there is certainly a risk. Trust means
betting on trust in a person or group of people. It is
also a reciprocal activity. That is, to get the trust of
others, someone must also do it to others.
Employees will take sides and be responsible for
working with institutions / companies, if the
employees put trust in their leaders.
Sureyya said “organizational trust is considered
as the most important element for the organizational
productivity and commitment” (Sureyya, 2017).
This means that organizational trust likened to the
most important element for productivity and
organizational commitment.
Luthans expressed a different opinion, “Trust is
relationships make companies farmore reliant on
each other” (Luthans, 2011) or trust is a relationship
that depends on each other. Can be interpreted that
trust is built by the existence of mutually bound
relationships between one person and another.
Based on the explanation of the concept above, it
can be synthesized that trust is a willingness and
positive expectation given to a person or group of
authorities on the basis of mutual respect and respect
based on interpersonal relationships in the hope of
obtaining positive results also from those who are
authorized.
The indicators of trust are (1) assignment of
tasks, (2) completion of tasks, (3) team
cohesiveness, (4) effective communication, (5) idea
development, (6) justice, (7) responsibility , (8)
support, (9) consistency, and (10) mutual respect.
In summary the above theoretical framework can
be described in the following scheme:
Figure 1 Theoretical Framework Between Research
Variables
Research Hypothesis
Based on the formulation of problem and the
theoretical framework, the research hypothesis can
be formulated as follows:
1. There is direct effect of work culture on
employee commitment
2. There is direct effect of personality on employee
commitment
3. There is a direct effect of leadership on employee
commitment
4. There is a direct effect of trust on employee
commitment
5. There is a direct effect of work culture on trust
6. There is a direct effect of personality on trust
7. There is a direct effect of leadership on trust.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This research was carried out for 1.5 years, starting
in December 2016 until May 2018. In accordance
with the problems and research objectives to be
achieved, this research method uses a survey with a
path analysis approach. The target unit in this study
is the middle managerial level employee of the
private company. The sample characteristics are (1)
managerial employees at the middle manager level;
(2) middle level manager employees who have
worked in a plantation for a minimum of 5 years of
work; (3) middle level manager employees with
positions as head of department.
The total population of employees and at the
same time as an affordable population are 143
people. To determine sample size, researchers used
Slovin's formula technique. The level of precision is
set at 0.05 or 5% of the total population of 143
middle level employees, a sample of 105 people is
obtained.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Descriptive Statistic
The data of this research were obtained from
respondents of the Head of Education (middle
manager) as many as 105 (one hundred and five)
people who filled in the statement items in
accordance with the instrument consisting of 5 (five)
variables, including: 3 (three) independent variables:
Work Culture (X1), Personality (X2), Leadership
(X3), 1 (one) intervening variable: Trust (X4), and 1
(one) dependent variable: Employee Commitment
(X5).
A summary of the results of basic statistical
calculations of all variables can be seen in the table
below:
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
902

Table 1: Statistic Description
4.2 Basic Assumption Test
Normality test
Table 2: Normality Test
From the above output we see in the
Kolmogorov-Smirnov column and it can be seen that
the significance value for Work Culture (X
1
),
Personality (X
2
), Leadership (X
3
), Trust (X
4
),
Employee Commitment (X
5
) is 0.200. Because the
significance for all variables is greater than 0.05, it
can be concluded that data population is Work
Culture (X
1
), Personality (X
2
), Leadership (X
3
),
Trust (X
4
), Employee Commitment (X
5
) with normal
distribution.
Linearity Test
Table 3: Linearity Test X
5
-X
1
From the output above, the linearity test results
can be seen in ANOVA Table output. It can be seen
the significance value of Linierity is 0,000. Because
the significance is less than 0.05, the variable
between employee commitment and work culture
has a linear relationship.
Table 4 Linearity Test X
5
-X
2
From the output above, the linearity test results
can be seen in ANOVA Table output. It can be seen
the significance value of Linierity is 0,000. Because
the significance is less than 0.05, there is a linear
relationship between employee commitment and
personality variables.
Table 5: Linearity Test X
5
-X
3
From the output above, the linearity test results
can be seen in ANOVA Table output. It can be seen
the significance value of Linierity is 0,000. Because
the significance is less than 0.05, between employee
and leadership commitment variables there is a
linear relationship.
Table 6: Linearity Test X
5
-X
4
From the output above, the linearity test results
can be seen in ANOVA Table output. It can be seen
the significance value of Linierity is 0,000. Because
the significance is less than 0.05, between the
variables of employee commitment and trust there is
a linear relationship.
Table 7: Linearity Test X
4
-X
1
The Effect of Work Culture, Personality, Leadership and Trust on Employee Commitment at PT Astra Agro Lestari Tbk on Indonesia
903
From the output above, the linearity test results
can be seen in ANOVA Table output. It can be seen
the significance value of Linierity is 0,000. Because
the significance is less than 0.05, there is a linear
relationship between the variables of trust and work
culture.
Table 8: Linearity Test X
4
-X
2
From the output above, the linearity test results
can be seen in ANOVA Table output. It can be seen
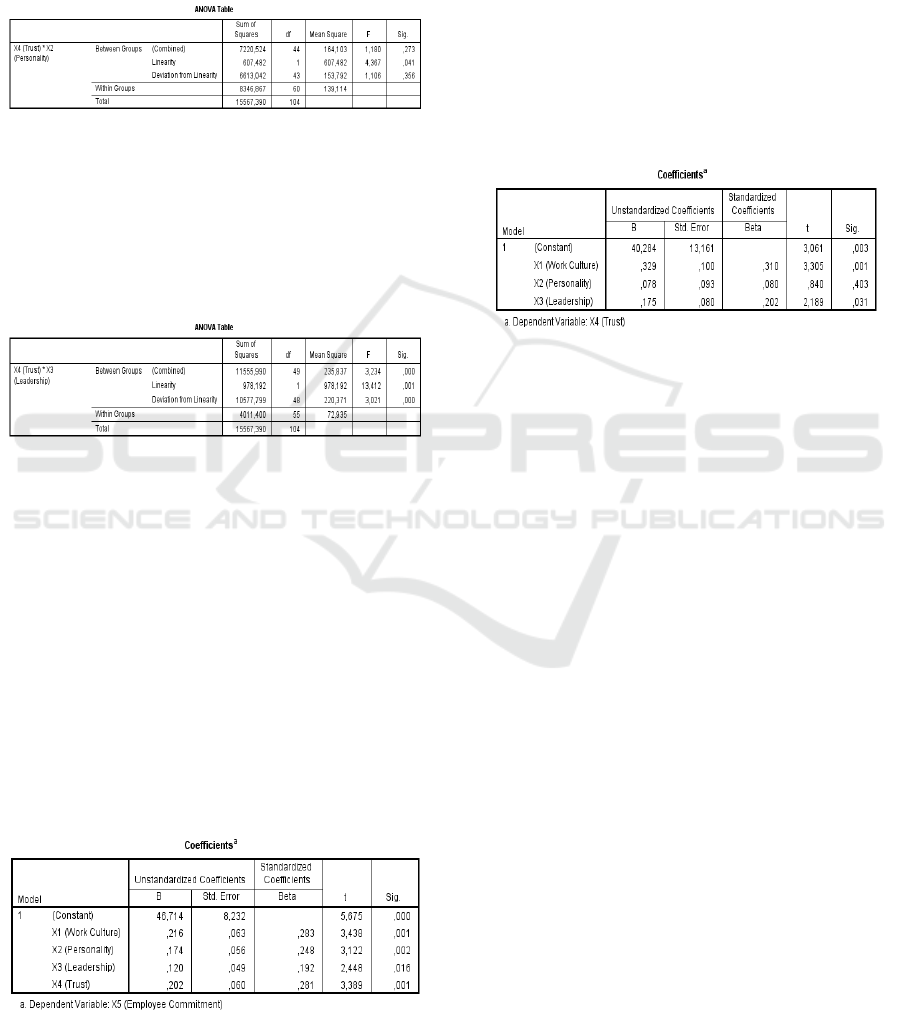
the significance value at Linierity is 0.041. Because
the significance is less than 0.05, there is a linear
relationship between the variables of trust and
personality.
Table 9: Linearity Test X
4
-X
3
From the output above, the linearity test results
can be seen in ANOVA Table output. It can be seen
the significance value in linearity is 0.001. Because
the significance is less than 0.05, between the
variables of trust and leadership there is a linear
relationship.
4.3 Multiple Regression Analysis
Multiple regression analysis to determine the effect
of Work Culture (X
1
), Personality (X
2
), Leadership
(X
3
), Trust (X
4
) on Employee Commitment (X
5
)
using the SPSS 22 Program obtained the following
output:
Table 10: Multiple Regression Structure 1
From the table above, it can be seen: (1) Work
Culture (X
1
) influences Employee Commitment
(X
5
), where sig = 0.001> 0.05, (2) Personality (X
2
)
influences Employee Commitment (X
5
), where sig
value = 0.002> 0.05 (3) Leadership (X
3
) influences
Employee Commitment (X
5
), where the sig value =
0.016> 0.05 (4) Trust (X
4
) influences Employee
Commitment (X
5
), where the sig value = 0.001>
0.05.
Multiple regression analysis to determine the
effect of Work Culture (X
1
), Personality (X
2
),
Leadership (X
3
) on Trust (X
4
) using the SPSS 22
Program obtained the following output:
Table 11: Multiple Regression Structure 2
From the table above, it can be seen: (1) Work
Culture (X
1
) influences Trust (X
4
), where sig =
0.001> 0.05, (2) Personality (X
2
) does not affect
Trust (X
4
), where value sig = 0.403> 0.05 (3)
Leadership (X
3
) influences Trust (X
4
), where the sig
value = 0.031> 0.05.
The results of this research, in line with the opinion
of Schein (2004) who said that work culture
influences employee commitment, Shabahang &
Amani (2016) study which said there was a
personality influence on employee commitment,
Dlamini (2017) research said that there was an
influence of leadership on employee commitment
and the opinion of Sureyya (2017) who said there
was an influence of trust in employee commitment.
5 CONCLUSION
Based on the analysis, the findings in this study are
as follows: (1) there is a positive direct effect of
work culture on employee commitment, meaning
that if the work culture increases, it is predicted that
employee commitment will increase, (2) there is a
positive direct effect personality towards employee
commitment, meaning that if the personality
increases, it is predicted that employee commitment
will also increase, (3) there is a positive direct effect
of leadership on employee commitment, meaning
that if leadership increases then employee
commitment is predicted to increase, (4) there is a
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
904

positive direct effect of trust on employee
commitment, meaning that if trust increases, it is
predicted that employee commitment will also
increase. (5) there is a positive direct effect of work
culture on trust, meaning that if the work culture
increases, it is predicted that trust will also increase.
(6) there is no direct effect of personality towards
trust, (7) there is a positive direct effect of leadership
on trust, meaning that if leadership increases, it is
predicted that trust will also increase.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The researcher would like to thank the leaders and
staff of the PT. Astra Agro Lestari Tbk. who had
helped in the completion of this research..
REFERENCES
Colquitt, Jason A., J. A. L. and M. J. W. (2009).
Organizational Behavior: Improving Performance and
Commitment in the Workplace. New York: McGraw-
Hill Irwin.
Colquitt, J. A. et al. (2009). Organizational Behavior
Improving Performance and Commitment in the
Workplace. New York: McGraw-Hill Irwin.
Colquitt, J. A. et al. (2015). Organizational Behavior:
Improving Performance and Commitment in the
Workplace. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Dlamini, N. N. N. et al. (2017). The impact of
transformational leadership style on organisational
commitment in the hospitality industry. African
Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure, 6(3), 3.
Emecheta Bartholomew C, Hart O. Awa, O. U. (2016).
Personality Characteristics And Employee Affective
Commitment: Nigeria Experience. International
Journal of Business and Management Review, 4(6),
68–92.
Gibson, James L, E. a. (2012). Organizational Behavior:
Structure and Processes. Singapore: McGraw-Hill.
Jason A. Colquitt, J. A. L. & M. J. W. (2009).
Organizational Behavior:Improving Performance And
Commitment In The Workplace, 221.
Luthans, F. (2011). Organizational Behavior: an Evidence-
Based Approach (12th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Luthans, F. (2011). Organizational Behavior. Singapore:
McGraw-Hill.
McShanes and Von Glinow. (2008). Organizational
Behavior. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Mohammad Javad Shabahang and Malahat Amani. (2016).
The Relationship between Personality Factors and
Organizational Commitment of Iranian Primary
School Principals. International Journal of Psychology
and Educational Studies, 3(3), 50–59.
Nawawi, H. (2003). Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia.
Yogyakarta: Gadjah Mada University Press.
Ndraha, T. (1997). Pengantar Teori Pengembangan
Sumber Daya Manusia. Bandung: Rosdakarya.
Njoroge D., Gachunga H, K. J. (2015). Transformational
Leadership Style And Organizational Commitment:
The Moderating Effect Of Employee Partcipation. The
Strategic Journal of Business & Change Management,
2(6), 94–107.
Porter, J. A. (2015). The relationship between
transformational leadership and organizational
commitment in nonprofit long term care organizations:
The direct care worker perspective. Creighton Journal
of Interdisciplinary Leadership, 1(2), 68–85.
https://doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.17062:CJIL.v1i2.13
Prasetya, T. (2001). Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia.
Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
Rahmani, S. (2017). Investigating of Trust and Perceived
Organizational Support Effects on Organizational
Commitment in Educational Organizations, using
Structural Equation Modeling and Partial Least
Squares Model. International Review of Management
and Marketing, 7(2), 384–389.
Randall Larsen & David Buss. (2010). Personality
Psychology. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Ricky W. Griffin & Gregory Moorhead. (2007).
Organizational Behavior Managing People And
Organizations. New York: Houghton Mullin
Company.
Robbins, Stephen P., T. A. J. (2007). Organizational
Behavior. New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Schein, E. (2004). Organizational Culture and Leadership.
San Fransisco: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Schermerhorn et al. (2010). Organizational Behavior. New
York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Schermerhorn et al. (2010). Organizational Behavior. New
Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Stoner, J. A. . and F. E. (1995). Management. New Jersey:
Prentice Hall.
Sureyya, C. S. (2017). Role of Culture on the
Relationships between Trust, Commitment and
Corporate Citizenship. Revista de Cercetare [i
Interven]Ie Social, 59, 118–135.
Zeinab Inanlou. (2017). The Effect Of Organizational
Culture On Employee Commitment: A Mediating
Role Of Human Resource Development In Korean
Firms. The Journal of Applied Business Research,
33(1), 88.
The Effect of Work Culture, Personality, Leadership and Trust on Employee Commitment at PT Astra Agro Lestari Tbk on Indonesia
905
