
In Vitro Dissolution Test of Bromelain Isolated from Pineapple Core
Encapsulated in Hydrogel Semi-IPN Methyl Cellulose-Chitosan
Ahmad Aly Irfan, Adinda Azkia, Achmad Buhori, Hegi Adi Prabowo, Elmira Vania, Nathasya
Humaira Adriani, and Siswati Setiasih
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Universitas Indonesia, Depok West Java,
Indonesia
Keywords: Bromelain, semi-IPN methyl cellulose-chitosan, encapsulation, dissolution, proteolytic activity
Abstract: One of many sources of bromelain is pineapple core. However, in its application as an enzyme-based oral
drug, its activity can be reduced due to interactions with gastric fluids. The isolated bromelain from the
pineapple core is encapsulated with a hydrogel semi-IPN methyl cellulose-chitosan in order to control its
release and to maintain its activity. Isolation of bromelain was conducted with several stages of
fractionation with ammonium sulfate salt and dialysis. The bromelain in semi-IPN methyl cellulose-chitosan
dissolution capability is evaluated in vitro at artificial gastric fluid pH and artificial intestine environment.
The specific activity of bromelain obtained from several purification steps shows an increment. The crude
enzymes, the ammonium sulfate fraction and the dialysis fractions have specific activity value of 22.39
U/mg, 76.73 U/mg, and 111.72 U/mg, respectively. Hydrogel semi-IPN methyl cellulose-chitosan was used
for encapsulation which has the value of crosslinking degree of 46.63% and swelling ratio of 397.59%,
respectively. Meanwhile, post loading encapsulation efficiency is 89.47%. The dissolution test results shows
proteolytic activity of bromelain can be maintained up to 2.83 U/mL in artificial pH environment. The
release rate of bromelain is relatively larger in artificial intestinal environment than artificial gastric fluid.
1 INTRODUCTION
Indonesia occupied third place in ASEAN as an
exporting country of canned pineapple with an
average contribution of 16.42% in 2009-2013
(Respati, 2016). Pineapple core is the solid waste
from pineapple canning industrial process.
Meanwhile, pineapple core is one of many source of
bromelain that can be utilized in the medical
application such as anti-platelet aggregation agents
and other therapeutic effect (Musfiroh et al., 2018,
Manzoor et al., 2016).
Bromelain is a protein-digesting enzyme, thus
the structure can be destabilized due to the pH
change. Destabilization of enzyme structure leads to
decreasing proteolytic activity of bromelain. Based
on studies with milk clotting assay method in
artificial gastric fluid, proteolytic activity of
bromelain was reduced slowly and relatively stable
only in the first 4 hours (Setiasih et al., 2018).
Castell et al. (1997) states that bromelain can be
absorbed in the human intestine without losing its
biological activity. However, in the human digestive
system, before reaching the intestine, oral
consumption of bromelain passes through the
stomach, which has very acidic environment.
Therefore, bromelain needs to be encapsulated in
order to obtain a controlled delivery release of the
bromelain enzyme.
Encapsulation slows down the release of
bromelain, stabilizes bromelain enzyme in gastric
fluid and maintains the proteolytic activity until it
reaches intestine environment. One of the materials
used for encapsulation is semi-interpenetrating
polymer network (semi-IPN) hydrogel. The
dissolution of bromelain was performed in vitro on
artificial gastric fluid (pH 1.2) for 2 hours and in an
artificial intestinal environment (pH 7.4) in the next
10 hours (Farooq et al., 2017).
Irfan, A., Azkia, A., Buhori, A., Prabowo, H., Vania, E., Adriani, N. and Setiasih, S.
In Vitro Dissolution Test of Bromelain Isolated from Pineapple Core Encapsulated in Hydrogel Semi-IPN Methyl Cellulose-Chitosan.
DOI: 10.5220/0009841700002406
In Proceedings of BROMO Conference (BROMO 2018) - Symposium on Natural Product and Biodiversity, page 1
ISBN: 978-989-758-347-6
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1

2 METHODS
2.1 Isolation, Ammonium Sulfate
Precipitation and Dialysis of
Bromelain
In the cold condition, pineapple core was crushed
into juice using blender. The juice was filtered and
centrifuged at ±4 °C for 45 min with rotor spinning
at 6000 rpm (rotation per minute), the supernatant
obtained was called crude enzyme. Then, protein in
the crude enzyme was precipitated using (NH
4
)
2
SO
4
with interval concentration variation of 0-20%; 20-
50%; and 50-80%. The mixture was centrifuged at
±4 °C for 25 min and 6000 rpm. The precipitate
obtained (pellet) from each fraction was dissolved in
0.20 M phosphate buffer pH 7 solution which had
been cooled. Then, dialysis with cellophane sac in a
0.05 M phosphate buffer pH 7 with continuous
stirring at ±4 °C was done in the fraction with
highest specific activity. The dialysis buffer solution
was replaced every 2 hours and tested with BaCl
2
in
acidic condition. If there is no a white precipitate of
BaSO
4
, thus dialysis process has been completed.
2.2 Determination of Enzyme Specific
Activity
The specific activity of the enzyme was obtained by
dividing total number of the units of enzyme activity
(U) from Kunitz method with total protein (mg) of
Lowry method for each enzyme fraction (Setiasih,
2018).
(2.1)
A and B are the total proteolytic and total protein,
respectively.
2.3 Synthesis of Chitosan and Semi-
IPN Methyl Cellulose-Chitosan
Hydrogel
The synthesis of non-covalent chitosan hydrogel was
carried out by dissolving 2 g chitosan into 2% acetic
acid as much as 50 mL until homogenous. Then, the
mixture was molded and dried at 60 °C with an oven
until the hydrogel is completely dry. Furthermore,
synthesis of semi-IPN methyl cellulose-chitosan was
carried out by adding 1.33 g methyl cellulose into
the homogenous mixture of non-covalent chitosan
and stirred for 24 hours at room temperature until
homogeneous. Then the crosslinking agent as much
as 10% (w/w) to chitosan weight of glutaraldehyde
0.10 M was added to the mixture and stirred for 2
hours. Hydrogels were shaped in a molding
container and dried at 60 °C using an oven for 24
hours. Hydrogels were stored in desiccators for
further testing and characterization (Rokhade et al.,
2007).
2.4 Swelling Ratio and Degree of
Crosslinking Determination
Hydrogels were immersed in 0.20 M phosphate
buffer pH 7 at room temperature for 60 minutes, and
removal of water remains on the hydrogel surface
was conducted using filter paper. The percentage of
swelling ratio was determined by the equation
(Katime and Mendizábal, 2010):
Swelling Ratio (%)=
x100%
(2.2)
Where, m
o
and m are the weights of dry hydrogel
and swollen hydrogel, respectively. Dry hydrogel
(m
o
) weight was measured and then the hydrogel
was immersed into 2% acetic acid for 24 hours.
Then, the hydrogel was grounded and stirred at 60
°C to a fixed weight (Wg). The degree of
crosslinking was determined by the following
equation (Abdel-Mohzen et al., 2011):
Degree of Crosslinking (%) =
x 100%
(2.3)
2.5 Bromelain Encapsulation into
Hydrogel
Dried semi-IPN methyl cellulose-chitosan hydrogel
was spilled with bromelain and incubated for up to
24 hours. Then, the hydrogel was rinsed with cold
phosphate buffer pH 7. The amount of encapsulated
bromelain and encapsulated activity can be
determined by the following formula (Croisfelt et
al., 2015):
Encapsulated Bromelain = [C]
1
– [C]
0
(2.4)
Activity Loading = A
1
– A
0
(2.5)
Efficiency
(2.6)
BROMO 2018 - Bromo Conference, Symposium on Natural Products and Biodiversity
2

[C]
1
and [C]
0
are the bromelain before encapsulation
and bromelain rinsed. A
1
and A
0
are Activity before
encapsulation and activity rinsed.
2.6 In Vitro Release Study of
Bromelain
In vitro release study was carried out by adding a
bromelain encapsulated in semi-IPN hydrogel into a
container containing 10 mL buffer solution of pH
1.2 at a temperature of 37 °C, stirred at a rotational
speed of 100 rpm. After 2 hours, a hydrogel was
transferred into 10 mL phosphate buffer of pH 7.4 to
a total of 12 hours. Then the release solution was
tested for activity by Kunitz method and protein
content by Lowry method.
2.7 Hydrogel Characterization
Chitosan hydrogel, semi-IPN chitosan-methyl
cellulose and encapsulated bromelain in semi-IPN
methyl cellulose-chitosan were characterized using
FT-IR instrumentation, and optical microscope.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Isolation, Ammonium Sulfate
Precipitation and Dialysis of
Bromelain
Proteolytic activity of isolation product of bromelain
was determined by Kunitz method with modification
at its optimal condition (pH 8; 37 °C; 30 min). In
this method casein was used as substrate, where
casein will be dispart into tyrosine and measured by
UV-Vis. Meanwhile, the total protein content was
determined by the Lowry method. The principle of
this method is to sharpen the colors produced on the
Biuret method. After reacting with the Biuret
reagent, the system was added with
phosphomolibdate-phosphotungstate reagent.
Reduction-oxidation reactions will occur at the
tyrosine and tryptophan groups of proteins.
Bromelain is further purified to enhance its
specific activity by ammonium sulfate precipitation.
Ammonium sulfate precipitation method works by
using the salting out principle, in which the salt will
be solvated by the solvent so that the interaction
between proteins is stronger and forming aggregates
(pellets) with low solubility. After precipitation, the
dialysis process was done to remove the content of
excess salt. Dialysis works by the principle of
diffusion, in which smaller molecules of the
membrane pores will go out to a buffer whose
concentration is lower than the buffer to dissolve the
bromelain pellets. Data of total proteolytic activity
and total protein content of bromelain can be seen in
Table 1.
Based on these data, it can be seen that from each
stage of purification causes an increase in the
specific activity of bromelain. The highest specific
activity was found in dialysis fraction of bromelain
(F2D) with value of 111.72 U/mg, with purity level
5 times its crude enzyme, and yield percentage of
39.81%.
Table 1: Bromelain Activity from each Purification Process
Sample
Volume (mL)
Total
Specific
Activity
(U/mg)
Purity
(times)
% Yield
Proteolytic
Activity (U)
Protein
(mg)
Isolation Process
Pineapple Core
Juice
150
275.00
23.28
11.82
-
-
Crude Enzyme
65
256.75
11.47
22.39
1
100
Ammonium Sulfate Precipitation
F1 (0-20%)
5.4
59.31
1.05
56.34
2.52
23.10
F2 (20-50%)
11.1
137.09
1.79
76.73
3.43
53.39
F3 (50-80%)
3.4
9.01
0.59
15.38
0.69
15.19
F4 (remaining)
55
2.75
4.94
0.56
0.03
2.01
Dialysis
F2D
12
102.20
0.92
111.72
5.00
39.81
In Vitro Dissolution Test of Bromelain Isolated from Pineapple Core Encapsulated in Hydrogel Semi-IPN Methyl Cellulose-Chitosan
3
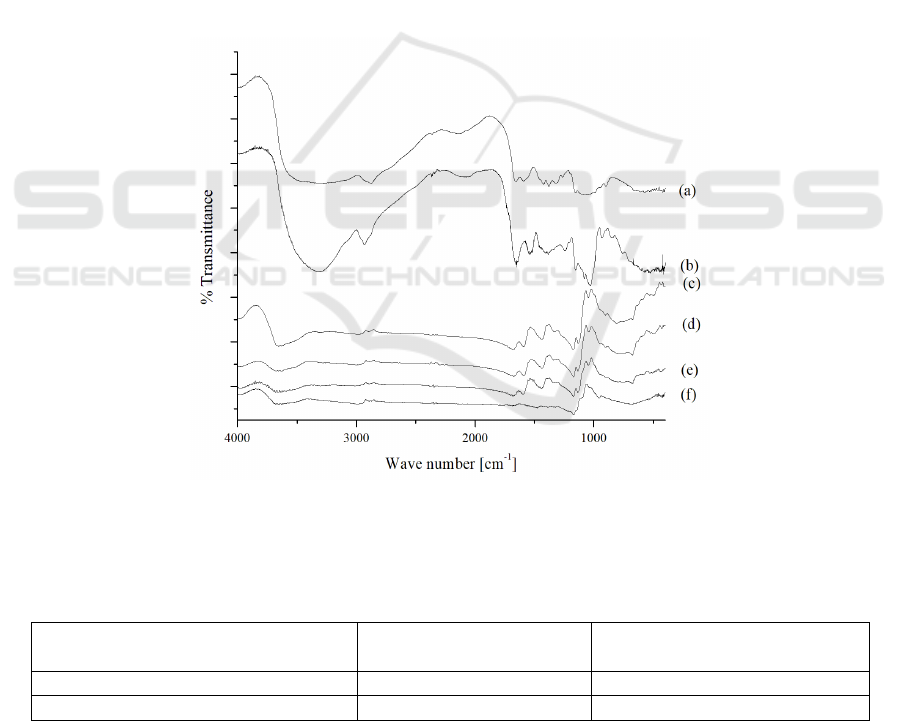
3.2 Semi-IPN Methyl Cellulose-
Chitosan Hydrogel
Visually, semi-IPN methyl cellulose-chitosan
hydrogel has brown color, in contrast to its control
(chitosan non-covalent) that has yellow color. FTIR
characterization of bromelain, chitosan powder and
hydrogel were shown in Figure 1. FTIR spectrum of
powder chitosan can be seen in Figure 1a, where
there is a wide band of uptake at 3568-3003 cm
-1
for
N-H and O-H which overlap each other.
Furthermore, at the wave number of 1653 cm
-1
there
is an absorption for C=O amide stretch of residual
acetyl in chitosan. Furthermore, the N-H stretch of
the primary amine was identified at 1592 cm
-1
and
the C-O-C bridge at 1037 cm
-1
. FTIR spectrum from
bromelain showed several absorption bands for C-N
stretch bands at wave number 1540 cm
-1
, absorption
band with strong intensity for C=O stretch (amide)
at 1653 cm
-1
, at 2933 cm
-1
for C-H stretch and at
wave number 3317 cm
-1
for N-H stretch (Figure 1b).
The difference between the two hydrogels (Fig. 1c
and d) lies in the intensity of the C = N imine band
uptake at the wave number 1596 cm
-1
. The imine-
absorbing bands arise because of a Schiff base
occurs from a crosslink reaction.
The physical parameters of semi-IPN methyl
cellulose-chitosan hydrogel were compared with
non-covalent hydrogels (as control) to ensure that
crosslinking with glutaraldehyde have been
successfully performed. Physical parameters test
including the determination of swelling ratio and
degree of crosslinking. The test results of hydrogel
physical parameters are presented in Table 2. The
semi-IPN hydrogel has a higher crosslinking degree
and relatively smaller swelling. This indicates that
the crosslink reaction has reacted well. Visual
appearance of hydrogel has been shown at Figure 2.
Figure 1: FTIR Spectra a) chitosan powder, b) bromelain, c) chitosan non-covalent hydrogel, d) semi-IPN methyl-cellulose
chitosan hydrogel, e) semi-IPN methyl cellulose-chitosan hydrogel after encapsulation, f) semi-IPN methyl-cellulose
chitosan hydrogel after in vitro release study
Table 2: Result of Swelling Ratio & Degree of Crosslinking Determination (n=3)
Hydrogel
Degree of Crosslinking
(%)
Swelling Ratio (%)
Chitosan non-covalent
0.50 ± 0.03
2627.58 ± 89.75
Semi-IPN Methyl cellulose-chitosan
46.63 ± 2.92
397.59 ± 8.66
BROMO 2018 - Bromo Conference, Symposium on Natural Products and Biodiversity
4

Figure 2: Visual appearance of a) chitosan non-covalent, b) semi-IPN methyl cellulose-chitosan, c) semi-IPN hydrogel
swollen, d) semi-IPN after crosslinking degree test.
3.3 Bromelain Encapsulation into the
Hydrogel
Post loading encapsulation method is chosen to
make the encapsulation process more efficient and
fewer bromelain of dialysis fraction are being used.
The post loading efficiency can be determined
indirectly by washing the encapsulated hydrogel
with phosphate buffer pH 7, the results was
tabulated in Table 3.
Furthermore, the hydrogel after encapsulation is
characterized by FTIR and the spectra was presented
in Figure 1e. From the comparison of hydrogel
absorption spectra before and after encapsulation,
bromelain does not resulting a new absorption band.
This indicates that the interaction that occurs is only
physical interactions in the form of hydrogen bonds
which is characterized by changes in intensity at
3568-3003 cm
-1
. In addition, there was also a shift of
absorption bands from 1683 cm
-1
to 1672 cm
-1
.
Table 3: Post Loading Efficiency of Bromelain into the Hydrogel
Material
Protein Content of
Encapsulated
Bromelain (µg/mL)
Proteolytic Activity of
Encapsulated
Bromelain (U/mL)
Post Loading
Efficiency
(%)
Semi-IPN methyl cellulose-chitosan
68.00 ± 3.46
8.30 ± 0.03
89.47 ± 4.56
3.4 In Vitro Release Study of
Bromelain
Dissolution is also referred as a release process that
aims to determine the protein content of bromelain
coming out of the hydrogel matrix and monitored its
proteolytic activity. The visual appearance of the
hydrogels before and after the dissolution test is
shown in Figure 3a-d.
Hydrogel after dissolution test are also
characterized using the FTIR presented in Figure 1f.
In the FTIR results, it appears that there are some
absorption bands that missing from the matrix, such
as C=N and C=O. This is due to damage to the
matrix network due to dissolution process. The
damage is also morphologically identified using the
optical microscope presented in Figure 4a and b.
Meanwhile, the encapsulated bromelain release
profile and its proteolytic activity are shown in
Figure 5a and b.
Figure 3: Visual appearance of semi-IPN methyl cellulose-chitosan hydrogels a) before and b) after encapsulation, c)
dissolution process, d) after dissolution test.
a)
d)
c)
b)
a)
d)
c)
b)
In Vitro Dissolution Test of Bromelain Isolated from Pineapple Core Encapsulated in Hydrogel Semi-IPN Methyl Cellulose-Chitosan
5

Figure 4: Morphological structure of semi-IPN methyl cellulose-chitosan hydrogels characterized by Boeco Germany
optical microscope with 45 times magnification a) before and b) after dissolution
Figure 5: In Vitro release study of bromelain, a) dissolution percentage of bromelain and b) proteolytic activity of
dissolution result.
The apparent release in the artificial gastric fluid
(29.27 ± 2.53) was smaller than in the artificial
intestinal environment (35.61 ± 5.91). In line with
this, the proteolytic activity of bromelain in the
artificial intestinal environment (2.83 ± 0.10) is also
greater than in the artificial gastric fluid (0.36 ±
0.03).
4 CONCLUSIONS
Bromelain is successfully encapsulated in semi-IPN
methyl cellulose-chitosan hydrogel. The release rate
of bromelain in the artificial intestinal environment
is greater than in the artificial gastric fluid.
Furthermore, the activity of dissolved bromelain in
the artificial intestinal environment is greater than in
the intestinal environment. This suggests that the
activity of bromelain can be maintained up to the
intestine.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was financially supported by Program
Kreativitas Mahasiswa (PKM) 2018 with contract
number 136/SPK/KM/IV/2018 from Ministry of
Research, Technology and Higher Education of the
Republic of Indonesia.
REFERENCES
Abdel-Mohzen AM, Aly AS, Hrdina R, Montaser AS,
Hebeish A., 2011. Eco-synthesis of PVA/Chitosan
Hydrogels for Biomedical Application. J.Polym.
Environ. 19: 1005-1012.
Castell JV, Friedrich G, Kuhn CS, Poppe GE., 1997.
Intestinal absorption of undegraded proteins in men:
presence of bromelain in plasma after oral intake.
American Journal of Physiology 273(1): G139–G146.
Croisfelt F, Martins BC, Rescolino R, Coelho DF,
Zanchetta B, Mazzola PG, Goulart LR, Pessoa AJr,
Tambourgi EB, Silveira E., 2015. Poly(N-
Isopropylacrylamide)-co-Acrylamide Hydrogels for
the Controlled Release of Bromelain from
Agroindustrial Residues of Ananas comosus. Planta
Med. 81: 1719-26.
Farooq U, Khan S, Nawaz S, Ranjha NM, Haider MS,
Khan MM, Dar E, Nawaz A., 2017. Enhanced gastric
retention and drug release via development of novel
floating microspheres based on eudragit E100 and
polycaprolactone: synthesis and in vitro evaluation.
Designed Monomers and Polymers 20: 419-433.
0
10
20
30
40
50
1,2 7,4
Dissolution
Percentage (%)
pH
a)
0
1
2
3
4
1,2 7,4
Proteolytic Activity
(U/mL)
pH
b)
a)
b)
BROMO 2018 - Bromo Conference, Symposium on Natural Products and Biodiversity
6

Katime I and Mendizábal E., 2010. Swelling properties of
new hydrogels based on the dimethyl amino ethyl
acrylate methyl chloride quanternary salt with acrylic
acid and 2-methylene butane-1,4-dioic acid monomers
in aqueous solutions. Materials Sciences and
Application 1: 162-167.
Manzoor Z, Nawaz A, Mukhtar H, Haq I., 2016.
Bromelain: Methods of Extraction, Purification and
Therapeutic Applications. Brazilian Archives of
Biology and Technology 59 pp.1–16.
Musfiroh FF, Setiasih S, Handayani S, Hudiyono S, Ilyas
NM., 2018. In vivo antiplatelet activity aggregation
assay of bromelain fractionate by ethanol from extract
pineapple core (Ananas comosus [L.] Merr). IOP
Conf. Ser.: Mat. Sci. Eng. 299 (0122017): 1-4.
Respati E., 2016. Outlook nenas. Jakarta, Indonesia: Pusat
Data dan Sistem Informasi Pertanian Sekretariat
Jenderal Kementerian Pertanian 2016.
Rokhade AP, Shelke NB, Patil SA, Aminabhavu TM.,
2007. Novel Interpenetratung Polymer Network
Microspheres of Chitosan and Methylcellulose for
Controlled Release of Theophylline. Carbohydrate
Polymers, 678-687
Setiasih S, Darwis AAC, Dzikria V, Hudiyono S., 2018.
Stability test of partially purified bromelain from
pineapple (Ananas comosus (L.) Merr) core extract in
artificial stomatch fluid. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
Eng. 299: 1-7.
In Vitro Dissolution Test of Bromelain Isolated from Pineapple Core Encapsulated in Hydrogel Semi-IPN Methyl Cellulose-Chitosan
7
