
A Comparative Study of the Antimicrobial Activity of Wild (Tualang)
Honey and Artificial Honey Against Methecillin-resistant
Staphylococcus Aureus, Streptococcus Pneumoniae and Klebsiella
Pneumoniae
May Florence Dela Cruz Bacayo
1
, Shazwan Fahmi Shafi
1
, Wong Charng Choon
1
, Santosh Fattepur
1
,
Kiran Chanabasappa Nilugal
1
, Jiyauddin Khan
1
, Fadli Asmani
1
, Eddy Yusuf
1
1
School of Pharmacy, Management and Science University, 40100 Shah Alam Malaysia
Keywords : Tualang honey, Artificial honey; Antimicrobial activity.
Abstract : Antimicrobial agents are becoming less effective due to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant microbes, thus
the discovery of alternative antimicrobial agents are urgently needed. Honey is believed to have antimicrobial
activity and are used in traditional medicine as skin healing dressing for wound. To find an alternative
substance as a substitute for the current antimicrobial agent for the three strains of microbes and to make a
comparison between the antimicrobial activity of the wild (Tualang) honey and the artificial honey. The 50 %
(w/v) of honey were diluted using double dilution method and are tested for its antimicrobial activity using
disc diffusion method with Ampicillin as a standard antibiotic for Streptococcus pneumoniae, Gentamycin for
Klebsiella pneumonia and Vancomycin for Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aurues as positive control.
The MIC and MBC were determined. Based on the results obtained from the disc diffussion assay, it shows
that wild (Tualang) honey has antimicrobial activity at a concentration of 10 % (w/v) for MRSA and S.
pneumoniae while at 25 % (w/v) for K. pneumoniae. Meanwhile it need 100% (w/v) concentration of artificial
honey to shows its antimicrobial activity. Wild (Tualang) honey was recorded as the most potent honey
against S. pneumoniae, in which a dilution of 10% (w/v) was required to inhibit the growth and kill S.
pneumoniae colony at 20% (w/v). The concentration of 20% (w/v) was required to inhibit MRSA and 25%
(w/v) to kill MRSA. Meanwhile, the highest concentration were required to inhibit K.pneumonia at 50% (w/v)
and no bactericidal effect were recorded. The comparative study between Tualang honey and Artificial honey
gives a promising result that the Tualang honey has a highest antimicrobial activity against MRSA, Klebsiella
pneumoniae, Sterptococcus pneumoniae compared to the Artificial honey.
1 INTRODUCTION
Honey is a natural syrup which have a complex
function of physicochemical properties (color, flavor
and texture), mainly determined by their botanic and
geographic origins. Honey is a concentrated aqueous
solution of glucose (31%) and fructose (39%). It
contains free amino acids at a level of 1%, pollen
being one of their sources. Proline, which might
originate from bees, is the prevalent amino acid and
makes up 50–85% of the amino acid fraction (White,
1975). Organic acids are present in honey at low
concentrations (<0.5%) and it is related to the color,
flavor and physico-chemical properties of the honey,
such as pH, acidity, and electrical conductivity.
Organic acids chelate metals can synergistically
enhance the antioxidant action of phenolic
compounds (Gheldof, Wang & Engeseth, 2002).
Moreover, acetic acid and ethanol can be used as
fermentation indicators and formic acid as an
indicator for the treatment of Varroa infestation
(Calderone, 2000).
It was used as a wound treatment that are
non-responsive to conventional therapies, such as
diabetic ulcers, and wounds infected with
antibiotic-resistant bacteria. There were countless
studies that recount the antimicrobial activity of
honey against microbes. (Dunford C, Cooper R,
Molan P, et al, 200)
With the emergence of antibiotic-resistant
microbial strains, such as Methicillin-resistant S.
aureus that can cause difficult-to-treat wound
Bacayo, M., Shafi, S., Choon, W., Fattepur, S., Nilugal, K., Khan, J., Asmani, F. and Yusuf, E.
A Comparative Study of the Antimicrobial Activity of Wild (Tualang) Honey and Artificial Honey Against Methecillin- resistant Staphylococcus Aureus, Streptococcus Pneumoniae and Klebsiella
Pneumoniae.
DOI: 10.5220/0009842900002406
In Proceedings of BROMO Conference (BROMO 2018) - Symposium on Natural Product and Biodiversity, page 1
ISBN: 978-989-758-347-6
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1

infections, honey has again caught the attention of
medical researchers. Scientists had first reported the
ability of honey to treat infections caused by
microbes in the late 1800s, but with the advent of
antibiotics in the early 1900s, the scientific interest in
honey decreased. (Fry DE, Barie PS, 2001)
The aim and objective of this study is to
determine the antimicrobial activity of honey against
MRSA, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Streptococcus
pneumoniae which can be an alternative to the
existing antimicrobial agent. It is so that the case of
antimicrobial resistance will reduce significantly.
This study is also to compare antimicrobial activity
of the wild (Tualang) honey and artificial honey.
Thus comparing also the antimicrobial activity of
wild (Tualang) honey, artificial honey and the
standard antibiotics.
2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Preparation of Media
38g of MHA is dissolved into 1 liter of saline water
and the solution is stirred homogenously. The agar
solution is then autoclaved for 2 hours and poured
into the petridish until the height is not more than
5mm keeping the petridish dry. The pH of the
Mueller-Hintom medium should be maintained at 7.2
to 7.4 at room temperature and keep in the incubator
set to 37°C prior to use . (Mm & Fatema, 2009)
2.2 Minimum Inhibitory
Concentration (MIC)
The 50% w/v was prepared by diluting 10 g of honey
in 20 ml of Mueller Hinton broth and the two-fold
dilution of the honey solution in Mueller Hinton
broth were prepared. Ten sterile tubes were labeled
each and placed in a test tube rack. Tube 1 with 1 ml
of honey solution was labeled as the honey control
and tube 8 was labeled as growth control. 1 ml of
Mueller Hinton broth was added to test tube 1 to 4.
Using a sterile micropipette, take 1 ml from tube 1
and transfer to tube 2 and thoroughly mixed. 1 ml
again was transferred from tube 2 to tube 3. This
process was repeated until tube 4 except for growth
control tube. Using fresh micropipette for each
dilution. The last tube received no honey solution and
was served as growth control then add 20% (4g in 20
ml), 15% (7.5g in 50 ml), 10% (1g in 10 ml), and 5%
(2.5 in 50 ml) in test tube 5 to 8 respectively. Each
tube was inoculated including the growth control
except honey control with 1 ml of the culture of
respective organism. The tubes were incubated at
37°c for 24 hours. The tubes were examined for
growth and were determined the MIC of the tested
antibiotics, which is bacteriostatic for the test
organism. The tubes were examined for visible
growth (cloudy) and was recorded growth as (+) and
no growth as (-).
2.3 Minimum Bactrialcidal
Concentration (MBC)
The MBC test was used to determined the lowest
concentration needed to kill the bacteria. MBC was
perform after MIC test. Each honey dilution with no
bacteria growth from the mic test was determined.
For each honey solution that has no growth was
incubated onto Mueller Hinton agar plate. It was
spread evenly and incubated at 37°c for 24 hours.
MBC were determined by minimum concentration
that allowed less than 1% of bacterial growth.(
Fakruddin,M., 2013)
BROMO 2018 - Bromo Conference, Symposium on Natural Products and Biodiversity
2

Figure 3: (a) Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and (b) Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) (Yilmaz, 2012)
2.4 Disc Diffusion Assay for
Determination of Zone of
Inhibition
The antimicrobial activity of the diluted honey
concentration is tested by disc diffusion susceptibility
method . The Mueller-Hinton Agar (MHA) plate is
used as the agar plate for the bacterial culture because
it gives a good result in batch to batch reproducibility,
it is low in of sulfonamide, trimethoprim and
tetracycline inhibitors. (Zainol, Mohd Yusoff, &
Mohd Yusof, 2013) Tualang and artificial honey
were prepared by double dilution method from 100%
concentration until 6. 25% of the concentration is
diluted with distilled water. A sterile swab is used to
spread the suspension of the pure culture on one side
face of the agar plate. The honey solution and
standard antibiotic is applied to the opposite side face
of the agar plate and distilled water was employed as
negative control. The agar plate was incubated for 24
hours at a temperature of 37°C. The size of the zone
of inhibition were measured using a metric ruler. The
larger zone of inhibition represents the antimicrobial
activity.
3 DATA ANALYSIS
The data obtained from different formulations will be
analyzed by Mean, Standard deviation and one-way
analysis of variance (ANOVA) procedure using
the Statistical Package for the Social Science (SPSS)
program (IBM SPSS Statistics 22.0).
When there is a statistically significant difference,
a post-hoc Tukey test will be then conducted to detect
the differences among the pairs. A statistically
significant difference is considered at p < 0.05.
4 RESULTS
Several evaluation tests were conducted in order to
determined the effectiveness of Tualang honey and
artificial honey against sample bacteria which is disc
diffussion test, Minimum Inhibition Test and
Minimum Bactericidal Test.
From the result obtain, it shows that Tualang
Honey has antimicrobial activity against MRSA and
S. pneumoniae at lowest concentration of 10 %(w/v),
while against K. pneumoniae at concentration 25
%(w/v). It means that Tualang honey has quite potent
antimicrobial activity against MRSA and S.
pneumoniae as it only need 10 %(w/v) concentration.
Meanwhile, K. pneumoniae has higher resistance
compare to MRSA and S. pneumoniae as it need 25
%(w/v) of Tualang honey to shows its antimicrobial
activity.
A Comparative Study of the Antimicrobial Activity of Wild (Tualang) Honey and Artificial Honey Against Methecillin- resistant
Staphylococcus Aureus, Streptococcus Pneumoniae and Klebsiella Pneumoniae
3
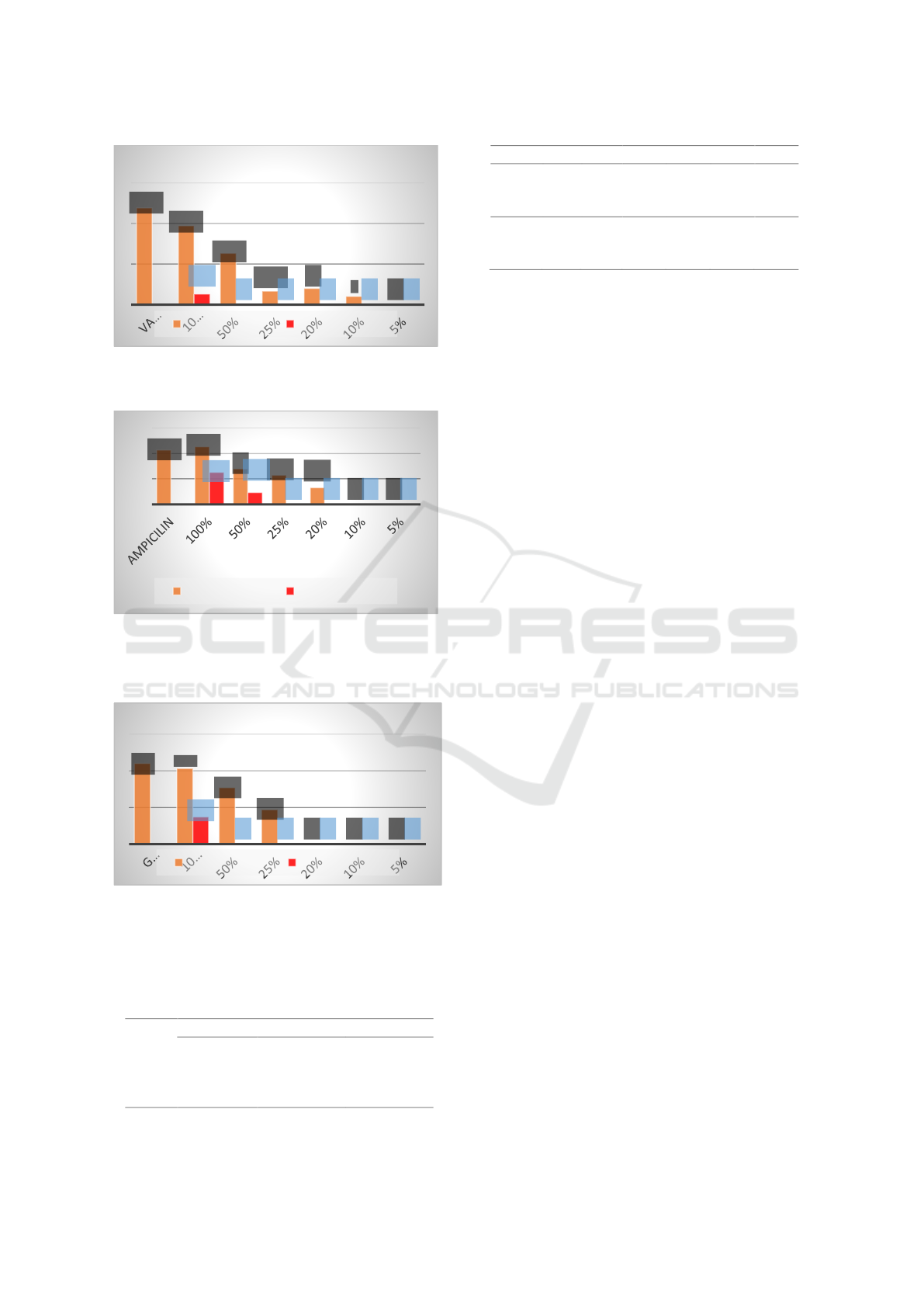
Figure 2: Zone of Inhibition for MRSA against Tualang
Honey, Artificial Honey and Positive Control.
Figure 3: Zone of Inhibition for Streptococcus pneumoniae
against Tualang Honey, Artificial Honey and Positive
Control.
Figure 4: Zone of Inhibition for Klebsiella pneumoniae
against Tualang Honey, Artificial Honey and Positive
Control.
Table 1: MIC and MBC values of Tualang honey and
artificial honey.
Honey
Sample
MIC & MBC %(w/v)
Methicillin
Resistence
Streptococcus
Aerus (MRSA)
Streptococcus
pneumoniae
Klebsiella
pneumoniae
MIC
MBC
MIC
MBC
MIC
MBC
Tualan
g
Honey
20
25
10
20
50
>50
Artifici
al
Honey
0
0
50
>50
0
0
5 DISCUSSION
This study was about investigating the antimicrobial
activity of Tualang and artificial honey against
MRSA, S.pneumoniae and K. pneumoniae as there are
limited studies available comparing different type of
honey. Based on the results obtained from the disc
diffussion test, it shows that Tualang honey has
antimicrobial activity at concentration of 10 % (w/v)
for MRSA and S. pneumoniae while at 25% (w/v) for
K. pneumoniae. Meanwhile it need 100% (w/v)
concentration of artificial honey to shows its
antimicrobial activity. The results shows that Tualang
honey has high antimicrobial activity against the
selected bacteria as its only need as low as 10%(w/v)
to 25%(w/v) concentration to inhibit the growth of
MRSA, S.pneumoniae and K pneumoniae. These
result were due to the two important enzymes known
to contribute to the major biological activities of
honey which are bee-origin glucose oxidase and
floral-origin catalase. These enzymes will determine
the antimicrobial activity of Tualang honey. (Zainol,
Mohd Yusoff, & Mohd Yusof, 2013).
For MIC and MBC values, Tualang honey was
recorded as the most potent honey against S.
pneumoniae, in which a dilution of 10% (w/v) was
require to inhibit and kill them at 20% (w/v). The
concentration of 20% (w/v) are require to inhibit
MRSA and 25% (w/v) to kill them. Meanwhile, the
highest concentration are require to inhibit K.
pneumoniae at 50% (w/v) and no bactericidal effect
were recorded. Overall, the bactericidal activities of
Tualang honey were recorded to be one reading
higher than their inhibitory effect. Results of artificial
honey showed that only S. pneumoniae show were
inhibited at concentration 50% (w/v) and no
bactericidal value. It also shows no MIC and MBC
value against other bacteria.The statistical analysis
showed that the antimicrobial activity of the Tualang
honey and artificial honey were significant when
compared with positive control with the P value of
<0.05 against MRSA, S.pneumoniae and
K.pneumoniae.
11,9
9,73
6,33
1,67
2
1
0
1,3
0 0 0 0 0
Tualang Honey Artificial Honey
10,7
11,3
7
5,7
3,3
0 0
6,3
2,3
0 0 0 0
Tualang Honey Artificial Honey
11
1…
7,7
4,7
0 0 0
3,7
0 0 0 0 0
Tualang Honey Artificial Honey
BROMO 2018 - Bromo Conference, Symposium on Natural Products and Biodiversity
4

6 CONCLUSION
The in-vitro comparative study of antimicrobial
activity between Tualang honey and artificial honey
against the selected gram-negative bacteria concludes
that the Tualang honey has highest antimicrobial
activity against MRSA, Streptococcus pneumoniae
and Klebsiella pneumoniae compared to artificial
honey.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The author is grateful to the research committee and
lecturers of Management and Science University,
Malaysia for providing all the needed support and
guidance to complete this project.
REFERENCES
Archer GL. Staphylococcus aureus: a well-armed
pathogen. Clin Infect Dis 1998
Article, O. (2012). Minimum inhibitory and minimum
bactericidal concentrations of boron compounds
against several bacterial strains, 42, 1423–1429.
http://doi.org/10.3906/sag-1205-83
Andrews, J. M., & Andrews, J. M. (2001). Determination
of minimum inhibitory concentrations. The Journal of
Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 48 Suppl 1, 5–16.
http://doi.org/10.1093/jac/48.suppl_1.5
Chow JW, Yu VL. Combination antibiotic therapy versus
monotherapy for gram-negative bacteraemia: a
commentary. Int J Antimicrob Agents 1999
Calderone, N.W. (2000). Effective fall treatment of Varroa
jacobsoni (acari: varroidae) with a new formulation of
formic acid in colonies of Apis mellifera (hymenoptera:
apidae) in the Northeastern United States. Journal of
Economic Entomology, 93
Chan, B. K., & Haron, H. (2016). Insights into Putative
Health Implications of Gelam ( Melaleuca cajuputi )
Honey : Evidence from In-Vivo and In-Vitro Studies.
Medical Sciences, 4(3).
http://doi.org/10.3390/medsci4010003
Chan, B. K., & Haron, H. (2016). Insights into Putative
Health Implications of Gelam ( Melaleuca cajuputi )
Honey : Evidence from In-Vivo and In-Vitro Studies.
Medical Sciences, 4(3).
http://doi.org/10.3390/medsci4010003
Dunford C, Cooper R, Molan P, et al. The use of honey in
wound management. Nurs Stand 2000;15:63– 8.
Dissemond J. Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus
(MRSA): diagnostic, clinical relevance and therapy. J
Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2009;7(6):544-51
Diep BA, Chambers HF, Graber CJ, Szumowski JD, Miller
LG, Han LL, et al. Emergence of multidrug-resistant,
community- associated, methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus clone USA300 in men who
have sex with men. Ann Intern Med 2008
Weinstein, R. A. (2001). Controlling Antimicrobial
Resistance in Hospitals: Infection Control and Use of
Antibiotics. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 7(2),
188-192
D'Agata EM, Webb GF, Pressley J. Rapid emergence of co-
colonization with community-acquired and
hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
aureus strains in the hospital setting. Math Model Nat
Phenom 2010
White JW, Subers MH, Schepartz AI(2000): The
identification of inhibine, the antibacterial factor in
honey, as hydrogen peroxide and its origin in a honey
glucose-oxidase system.
Yilmaz, M. T. (2012). Minimum inhibitory and minimum
bactericidal concentrations of boron compounds
against several bacterial strains. Turkish Journal of
Medical Sciences, 42(SUPPL.2), 1423–1429.
http://doi.org/10.3906/sag-1205-83
Zainol, M. I., Mohd Yusoff, K., & Mohd Yusof, M. Y.
(2013). Antibacterial activity of selected Malaysian
honey. BMC Complementary and Alternative
Medicine, 13(1), 129.
http://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-13-129
A Comparative Study of the Antimicrobial Activity of Wild (Tualang) Honey and Artificial Honey Against Methecillin- resistant
Staphylococcus Aureus, Streptococcus Pneumoniae and Klebsiella Pneumoniae
5
