
The Effectivity of Butanol Fraction of Calophyllum Nodosum as
Antiviral Drug to Dengue Virus Serotype 2 In Vitro
Syifa Salsabila
1
, Nabilla Calista
1
, Hidayati Desti
2,3
, Beti Ernawati Dewi
2,3
1
Undergraduate Student, Medical Faculty Universitas Indonesia
2
Department of Microbiology, Medical Faculty Universitas Indonesia-Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital Jalan Pegangsaan
Timur no 16, Jakarta, , Indonesia.
3
Infectious Disease and Immunolgy Research Center, Indonesian Medical Education and Research Institute, Jalan Salemba
Raya no 6, Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Antiviral drug, Butanol fraction of Callophylum nodosum, Dengue virus serotype 2
Abstract: Dengue fever still has a high incidence rate especially in Indonesia. Until now, there is no dengue antiviral
therapy found. Researches to develop dengue antiviral from herbal sources had been done. One of the
potential plants as dengue antiviral is Calophyllum nodosum which is known to have antimicrobial activity.
This study to evaluate the antiviral effects of butanol fraction of Calophyllum nodosum on DENV-2 activity
with Huh-7-it cells as host cells and also to evaluate minimal inhibitory concentration. Antiviral capability
was measured by 50% cytotoxic concentration (CC
50
) values and 50% inhibitory concentration (IC
50
)
values. The IC
50
value showed the effect of extract inhibition and was obtained from the focus assay of
DENV after treated with serial concentrations of extract (80, 40, 20, 10, 5 and 2.5 μg/mL). The CC
50
value
showed the effect of cytotoxic extract and resulted from MTT assay using concentrations of 640, 320 , 160,
80, 40, 20, and 10 μg /mL. The selectivity index (SI) value was ratio of CC
50
and IC
50
. The IC
50
, CC
50
and
SI value of butanol fraction of Calophyllum nodosum was 5.6 μg/mL, 1181 μg/mL and 210.9, respectively..
Statistical analysis showed significant differences between control group and treatment group on focus
assay and MTT assay. It can be concluded that the butanol fraction of Calophyllum nodosum had strong
antiviral effect with low cytotoxic effects.
1 INTRODUCTION
Dengue virus (DENV) infection is serious health
problem in the world, including Indonesia. DENV is
transmitted to humans by infected female Aedes
aegypti or Aedes albopictus.
1
There are four
serotypes of dengue virus (DENV 1-4) that manifest
with similar symptoms
2,3
DENV infection cause
various clinical manifestation range from
asymptomatic to severe cases such as Dengue
Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF) and Dengue Shock
Syndrome (DSS). Both DHF and DSS can cause
fatal cases and can lead to death of the patients.
4
When DENV infect to human, only few hours after
infection, tens of thousands of copies of viral
molecules are produced from a single viral
molecule, leading to severe cases to death. Despite
the availability of a dengue vaccine, improvements
in case management to reduce the risk of severe
dengue are still needed.
The prevention of DENV infection and better
treatment have been developing. Prevention usually
directed to the DENV vector control. In other hand,
for DENV patient management usually given
supportive care. DENV infection is self limiting
disease, but there are patients with severe disease
4
.
Improvements in case management to reduce the
risk of severe dengue are still needed. Current
approaches are entirely supportive care in the form
of judicious fluid replacement and close clinical
monitoring during the critical phase of illness.
4
Up
to now, there is no specific antiviral drug to DENV
even there were association between higher viremia
levels and severe dengue. Development of antiviral
drug to DENV may help for better treatment of
DENV patients. The development of dengue
antiviral drugs is still in progress. At present, the
development of antiviral drug to DENV medications
leads to sources of herbal medicines
5
. The source of
these herbal medicines is widely discovery because
Salsabila, S., Calista, N., Desti, H. and Dewi, B.
The Effectivity of Butanol Fraction of Calophyllum nodosum as Antiviral Drug to Dengue Virus Serotype 2 In Vitro.
DOI: 10.5220/0009843100002406
In Proceedings of BROMO Conference (BROMO 2018) - Symposium on Natural Product and Biodiversity, page 1
ISBN: 978-989-758-347-6
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1

of the possibility of having low side effects and
abundant in nature. Genus of Calophyllum have
been widely used as traditional herbal medicines in
the tropic area.
6
Those plants have phytochemicals
such as flavonoids, xanthones, coumarin, chalcone,
benzofuran, and triterpene. Those phytochemical
have antioxidant and antimicrobial activity.
7
Calophyllum plants able to inhibit the activity of
bacteria and fungi.
8
Some species have also been
reported to have bioactivity against various viruses
such as HIV-1 virus and human leukemia HL-60
9
.
Calophyllum nodosum species also contain
phytochemicals that have antioxidant and
antimicrobial activity. This phytochemical content is
thought to have antiviral activity against dengue
virus.
8,9
.But then, the antiviral activity to DENV of
Calophyllum nodusum has not been discovered yet.
Therefore, the purpose of this study is to investigate
the effectivity of leaf extract Calophyllum nodusum
in butanol fraction as antiviral drug to DENV-2.
2 METHODS
The study was done at Department of
Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas
Indonesia. We used Huh 7 it-1 cell and DENV
serotype 2 strain New Guinea C. To evaluate
antiviral activity of Calophyllum nodusum, we used
previous method
10
with slight modification. The
serial dilution of extract at 320 µg/mL, 160 µg/mL,
80 µg/mL, 40 µg/mL, 20 µg/mL and 10 µg/mL were
used to determine inhibition of DENV replication.
To determine cytotoxic effect we used serial dilution
of extract at 640, 320 µg/mL, 160 µg/mL, 80 µg/mL,
40 µg/mL, 20 µg/mL and 10 µg/mL. DMSO as a
diluent of extract were used as negative control of
antiviral assay. The test were made in triplicate.
2.1 Determination of Half-inhibitory
Concentration
A total of 2×104 cells/well were seeded into 96-
well plate and the plate were incubated at 37°C with
5% CO2. After 24 hours, the cells were infected
with DENV-2 with MOI of 1 FFU/cell. Various
concentration of extracts ranging from 320, 160, 80,
40 20 and 10, µg/mL were added shortly afterwards.
After 2 hours of infection, a mixture of DMEM+2%
FBS and various concentration of extracts were
added with volume of 100 ul/well. The tested of
each concentration were done in triplicate. Treated
with 0.1% of DMSO were used as negative control
of antiviral treatment. Plates were further incubated
at 37°C for 3 days. Next, supernatant of viruses were
harvested and determined the titter by focus assay.
Briefly, 10-fold serial dilution of the supernatant
was inoculated onto Huh-7 it-1 cell monolayer in
triplicate wells. Absorption was carried out at 37
o
C
with 5% CO
2
for 2 hours with agitation at 30
minutes interval. Methylcellulose 1.5% overlay
medium was added to the cell and incubated at 37
o
C
with 5% CO
2
for 3 days. The infected cells were
stained according to previous study with slight
modification.
10
First, infected cells were fixed and
increased permeable for immunostaining. After cell
washing, human IgG-anti dengue were added to
each well 1/1000 and incubated at room temperature
for 1 hour. For the secondary antibody. We used
1/1000 antihuman IgG label HRP. After washed
using PBS, substrate for horseradish peroxidase
were added and cells were observed for its brownish
colour. Number of foci formed in each well
including in negative control well was counted
manually under microscope after staining. Number
of foci in each treatment well was compared to that
of negative control well to obtain percentage of
infectivity of each well. The mean value of
percentage of infectivity for each concentration
triplicate was calculated and then those values were
plotted against corresponding concentration to
generate concentration-percentage of inhibition
curve. The half-inhibitory concentration (IC
50
) was
obtained from nonlinear regression equation of
concentration-effect curves.
2.2 Determination of Half-cytotoxic
Concentration
To determine CC50, we used MTT assay as
describe in our previous study.
10
MTT assay that
quantified the percentage viability of Huh-7 cells
after treated with a certain concentration of extract
compared with DMSO 0.1%) as negative control. In
96 well flat-bottom plates (Corning, USA), cell were
added as much as 2 × 10
4
cells/well and incubated at
37
o
C with 5% CO
2
for 24 hours. Then, the cells were
treated with various concentration of extract ranging
from 640, 320, 160, 80, 40, 20, 10 , 5 and 2.5 µg/mL
and were then incubated at 37
o
C with 5% CO
2
. After
48 hours of incubation, 20μL of 3-(4,5-
Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)- 2,5-diphenyltetrazolium
bromide (MTT) (Promega) salt solution was added
into each well and incubated for 4 hours according
to the manufacturer’s instruction. Theoretical
percentage toxicity of each concentration was
determined by dividing the mean blanked sample
optical density (ODs) by the mean blanked control
BROMO 2018 - Bromo Conference, Symposium on Natural Products and Biodiversity
2
ODs for each sample. The resulting percentage
toxicity values of each concentration that was tested
in triplicate was calculated for its mean and standard
deviation and then the mean percentage was plotted
to corresponding concentration to generate
concentration-mean percentage of viability curve. A
nonlinear regression equation was derived from the
curve to calculate the half-cytotoxic concentration
(CC
50
) of each extracts.
2.3 Data Analysis
Mean difference of percentage of cytotoxicity
and infectivity between treatments group and
negative control was analysed using One-way
ANOVA using SPSS version 23 with p value less
than 0.05 (p<0.05) considered as statistically
significant difference. The value of CC
50
and IC
50
were determined using simple arithmetical
calculation on regression equations obtained from
concentration-percentage of viability and
concentration-percentage of inhibition. Then,
selectivity index for each extract was derived from
the ratio of CC
50
to IC
50.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Percentage of DENV Infectivity
and IC
50
Value
After treated with extracts, the percentage of
DENV infectivity in Huh 7it-1 was decrease
significantly (Table 1). Addition of extract to
DENV-2 at concentration of 40ug/mL and more,
showed no DENV-2 in the focus assay with
significantly different (Table 1), Decrease of extract
concentration caused an increase of DENV
infectivity. This results showed that butanol fraction
of Calophyllum nodosum had antiviral activity to
DENV-2. The infectivity value was then used to
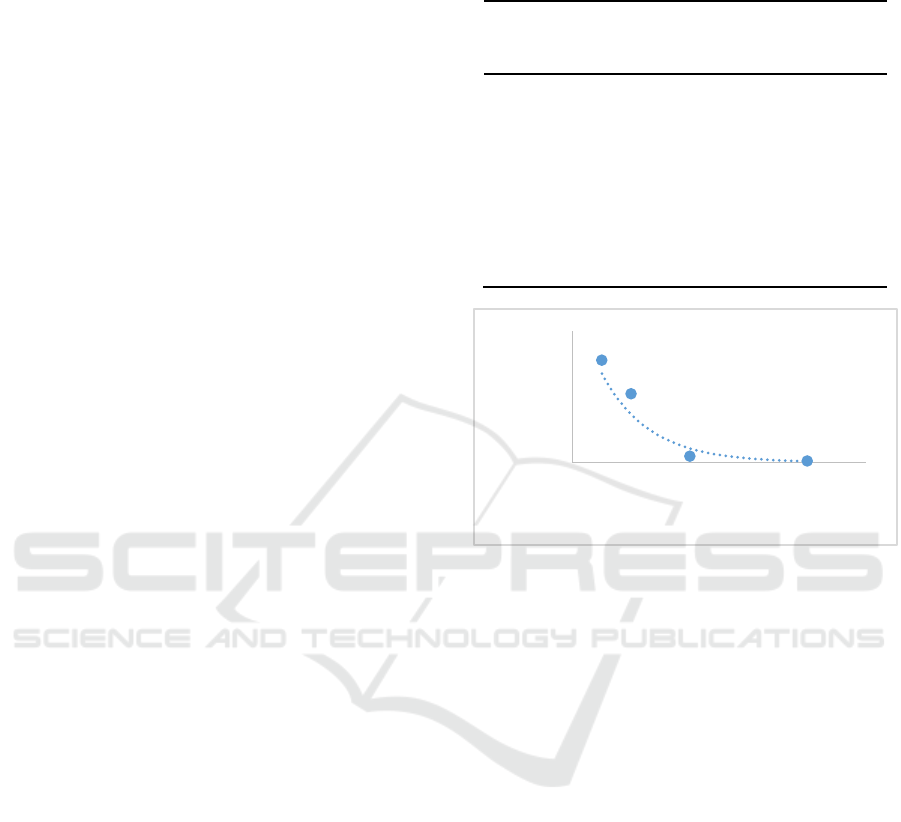
figure out an exponential regression and then to
determine IC
50
. Based on the equation, the IC
50
value was 5.6 µg/mL (Figure 1.) with R
2
of 0.927.
Table 1 : Percentage of DENV-2 infectivity after treated
with various concentration of Calophyllum nodosum
.
Concentration
(µg/ml)
Percentage of
infectivity
p Value
(mean% ± SD)
80
0.0 ± 0.0
0.034
40
0(0 - 2.9)
0.043
20
3.9 ± 4.5
0.046
10
41.8 ± 20.7
0.046
5
62.2 ± 17.1
0.046
02.05
52.5(37.9 - 52.5)
0.043
DMSO
99.1(99.1 - 102)
Figure 1. Exponential regression graph of DENV-2
infectivity after treated with serial concentration
Calophyllum nodosum
3.2 Cytotoxicity and CC
50
Value
The cytotoxicity of butanol fraction of
Calophyllum nodosum was determined by MTT
assay. In MTT assay, the absorbance value of the
test well divided by the absorbance value of the
DMSO control, times 100% to determine the cell
viability value. After treated with concentration
more than 80 ug/mL, the viability of cell slightly
decreased but no statistically different (Table 2).
From the data, increasing of concentration of extract
caused a decrease in the cell viability (Table 2).
There was an abnormality data at concentration of
320 µg/mL. Treated with 320 ug/mL of butanol
fraction of Calophyllum nodosum the cell viability
decreased rapidly in excess of 640 ug/mL. It may
due to a laboratory error. The mean cell viability
values were then translated into a graph with a linear
regression to determine CC
50
(Figure 2). The CC
50
value of butanol fraction of Calophyllum nodosum
was 1,181 ug/mL with R
2
of 0.567.
y = 99,794e
-0,123x
R² = 0,9275
0,0
20,0
40,0
60,0
80,0
0 10 20 30 40 50
Mean Infectivity
Extract Concentration (µg/mL)
The Effectivity of Butanol Fraction of Calophyllum nodosum as Antiviral Drug to Dengue Virus Serotype 2 In Vitro
3
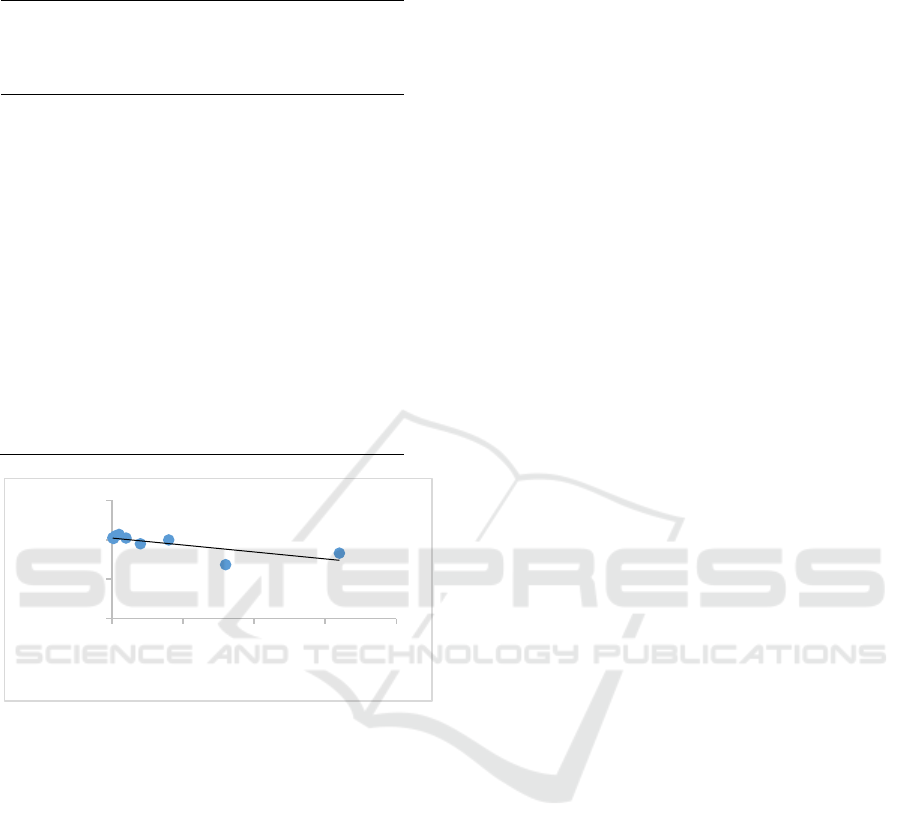
Table 2 :The percentage of cell viability after
treated with various concentration of extract.
Figure 2. Linear regression graph of concentration-
mean percentage of Huh7it-1 cells viability after
treated with Calophyllum nodosum.
3.3 Selectivity Index (SI) Value
The selectivity index of butanol fraction of
Calophyllum nodosum was 210.9 based on IC
50
and
CC
50
value.
4 DISCUSSION
Specific antiviral drug to DENV was not avalable
yet. Indonesia has variety of herbal medicine that
can be developed as antiviral drug to DENV.
Calophyllum genus is known to have antimicrobial
properties that can inhibit bacterial, fungal and viral
activity. The phytochemical properties of the
Calophyllum genus are flavonoid, kumarin and
xanthone. Flavonoids have strong antioxidant,
antimicrobial and antiviral activity. Flavonoid from
other plant also contain lots of flavonoids and have
the ability to inhibit viruses including DENV.
11
Several studies on the antiviral effect of
Calophyllum on dengue virus have been carried out
and showed that Calophyllum extract had an
inhibitory effect on dengue virus activity which was
significant with a relatively small cytotoxic effect.
12,13
Similar result was found in this study. Butanol
fraction of Calophyllum nodosum showed antiviral
activity with IC
50
of 5.6 µg/mL.
Host cell viability trend was stay with numerous
test, even we increased the concentration of the
extract (Table 2). From the linear regression, the R
2
value was 0.567 (Figure 2), this indicate that no
strong correlation between extract concentration and
cell viability. The lowest of R
2
value in this study
may due to no cytotoxic effect at the highest
concentration used in this study. The CC
50
value is
1181.1 µg/mL. We suggested for next cytotoxic
assay to use butanol fraction of Calophyllum
nodosum at concentration more than 1,000 ug/mL.
The development of antiviral drug to treat DENV
infection leads to sources of herbal medicines
5
. The
development of small molecule anti-DENV drugs
has been a slow process. To date, only four small
molecule anti-DENV drugs such as chloroquine ,
celgosivir balapiravir and UV-4B9 already move to
Phase I or Phase II clinical trials.
14
But some of
them with remains unclear out come or
achieved the required safety profile, but did not reduc
e viral load as expected,
15,16
Furthermore, the clinical
trial of the α-glucosidase inhibitor was terminated at
Phase I.
14
Pre-clinical and clinical research into
anti-DENV drugs is still underway, and many
lessons can be learned from the previous studies. In
future, we are bound to overcome the challenges,
and expect our ongoing work to yield a potent anti-
DENV therapy.
In this study, we used DENV-2 NGC. The
promising anti-DENV drugs are anticipated to
inhibit all serotypes of DENV, in the next study we
will use all serotype of DENV. The antiviral drug to
DENV remain challenges. The inhibition of all
serotypes, as well as antibody dependent
enhancement phenomenon observed during DENV
infection, complicates the investigation of anti-
Dengue drugs such as if a patient was re-infected by
a heterotypic virus, the antibodies created previously
would become severe. Moreover, in laboratory
testing, the limited availability of animal models has
hampered of antiviral drug to DENV development.
y = -0,0441x + 102,09
R² = 0,5675
0,0
50,0
100,0
150,0
0 200 400 600 800
Mean Viability
Extract Concentration (µg/mL)
Concentration
(µg/ml)
Percentage of
Viability
(mean% ± SD)
p
Value
640
82.7 ± 5.2
0.05
320
68.4 ± 5.1
0.05
160
99.7 ± 11.4
0.513
80
94.7 ± 1.1
0.05
40
102.1 ± 1.1
0.275
20
106.5 ± 0.9
0.05
10
104.9 (103.6 - 105.5)
0.05
5
101.5 ± 1.7
0.275
2.5
102.4 ± 8.6
0.827
DMSO
100.0 ± 1.7
BROMO 2018 - Bromo Conference, Symposium on Natural Products and Biodiversity
4

The value of the selectivity index of Butanol
fraction of Calophyllum nodosum was 210.9. This
value was really high compare with other study such
as Psidium guajava and Carica papaya showed SI
value of 21.28 and 37.25 respectively.
17
It can be
concluded that the butanol fraction of Calophyllum
nodosum has a strong antiviral effect to DENV with
low cytotoxic effects. Further study needed to
determine by which mechanism butanol fraction of
Calophyllum nodosum inhibit DENV replication.
5 CONCLUSIONS
From this study, we concluded that IC
50,
CC
50 and
SI
value was 5.6 µg/mL, 1181.1 µg/mL, and 210.9.
Butanol fraction of Calophyllum nodosum had
strong antiviral effect against DENV-2 with low
cytotoxic effect. Furthermore, Butanol fraction of
Calophyllum nodosum can be a candidate of
antiviral drug in future.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT:
This study was supported by grant of Publikasi
Terindeks Internasional Untuk Tugas Akhir
Mahasiswa UI (PITTA) 2018 No:
0588/SK/R/UI/2018
REFERENCES
Fatima, Z., Idrees, M., Bajwa, MA., Tahir, Z., Ullah, O.,
Zia, MQ., et al. 2011. Serotype and genotype analysis
of dengue virus by sequencing followed by
phylogenetic analysis using samples from three mini
outbreaks-2007-2009 in Pakistan. BMC Microbiol.
Ross, TM. 2010. Dengue virus. Clin Lab Med, vol. 30,
pp.149–160.
Wang, E., Ni, H., Xu, R., Barrett, AD., Watowich, SJ.,
Gubler, DJ., et al. 2000. Evolutionary relationships of
endemic/epidemic and sylvatic dengue viruses. J Virol,
vol.74, pp.3227–3234.
WHO. 1997. Dengue haemorrhagic fever: diagnosis,
treatment, prevention and control. Geneva, 2
nd
edition.
Sohail, MN., Rasul, F., Karim, A., Kanwal, U., Attitalla,
IH. 2011. Plant as a Source of Natural Antiviral
Agents. Asian J Anim Vet Adv, vol. 6, no. 12, pp.
1125–52.
Bernabé-Antonio, A. 2014. Biological Importance of
Phytochemicals from Calophyllum brasiliense
Cambess. Annu Res Rev Biol, vol. 4, no. 10, pp.
1502–17.
Alkhamaiseh, SI., Taher, M., Ahmad, F., Qaralleh, H.,
Althunibat, OY., Susanti, D., et al. 2012. The
phytochemical content and antimicrobial activities of
Malaysian Calophyllum canum (stem bark). Pak J
Pharm Sci, vol.25, no.3, pp.555-63.
Hanafi, MAM. Syatna, FD., Mirawati S., Ratnasari, S.,
Dewi, BE. 2017. Antiviral Effect of Sub Fraction
Cassia alata Leaves Extract to Dengue Virus
Serotype-2 strain New Guinea C in Human Cell Line
Huh-7 it-1 3OP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental
Science 101.
Sánchez, I., Gómez-Garibay, F., Taboada, J., Ruiz, BH.
2000. Antiviral effect of flavonoids on the dengue
virus. , vol.14, no.2, pp.89-92
Saptawati, L., Febrinasari, R., Yudhani, R., Yono, H.,
Faza, A., Luthfiani, S., et al. 2017. In vitro study of
eight Indonesian plants extracts as anti Dengue virus.
Health Science Journal of Indonesia, vol. 8, no.1.
The Effectivity of Butanol Fraction of Calophyllum nodosum as Antiviral Drug to Dengue Virus Serotype 2 In Vitro
5
