
Inhibition Study of EDTA and PCMB on Purified Bromelain Activity
from Pineapple Core [Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.] Using Ion
Exchange Chromatography Column and Antiplatelet Activity Test
Nita Magfirah Ilyas
1
, Siswati Setiasih
1
and Sumi Hudiyono
1
1
Department of Chemistry, FMIPA Universitas Indonesia, Kampus UI Depok, Depok 16424, Indonesia
Keywords: Pineapple core, bromelain, purification, chromatography, kinetic study, antiplatelet.
Abstract: The aim of this research was to isolate and purify bromelain from pineapple core (Ananas comosus) through
fractionation using ammonium sulfate followed by dialysis and ion exchange chromatography.
Fractionation of bromelain with ammonium sulfate produces highest specific activity on fraction 2 (20-
50%) of 260.042 U/mg with purity level 2.548 fold compared to crude extract. Further purification by ion
exchange chromatography DEAE-sepharose and CM-Sephadex C-50 showed an increase in specific
activity, sequentially 500 U/mg with purity level 4.901 fold compared to crude extract and 729.167 U/mg
with purity level 7.150 fold compared to crude extract. The determination of kinetics parameter of purified
bromelain using LM plot gives Km and Vmax value for casein and azocasein substrate of 0.94% (w/v); 0.07
U/min and 0.87% (w/v); 0.05 U/min respectively. Bromelain fraction was inhibited competitively with
EDTA and mix-inhibition type was observed in the presence of PCMB. The addition of EDTA and PCMB
at a concentration of 0.5 ppm can decrease the activity of the enzyme up to 70%. In vitro study of
antiplatelet agent activity using human Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) revealed that the purified bromelain
show activity as an antiplatelet agent with percentage of aggregation 20.892% and percentage of inhibition
77.994%.
1 INTRODUCTION
The fifth largest pineapple producer in the world is
Indonesia (Rugayah, 2012). Bromelain is a group of
cysteine proteases found in all plant tissues of
pineapple [Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.] (Babagana,
2016). This enzyme break down a protein by
breaking a peptide bond and produce a more simple
peptide. Bromelain can be found in all parts of
pineapple plants. Stem bromelain (EC 3.4.22.32) is a
glycoprotein with isoelectric pH 9.5 and Fruit
Bromelain (E.C. 3.4.22.33) lacks carbohydrate
moiety with isoelectric pH 4.6 (Kaur, 2015).
This enzyme is used in many therapeutic
applications and was known has antithrombic effect
as antiplatelet agent that useful in cardiovascular
diseases treatment (Bhattacharya, 2008). The
benefits of bromelain is quite extensive in the field
of pharmacology and the food industry, stimulate
many researchers to learn more. Bromelain research
in pineapple has been started for a long time until
now. Various methods of isolation and purification
have been done to get the best bromelain activity
from pineapple (Neta, et al, 2012).
Various heavy metals such as mercury, cobalt,
and zinc can inhibit bromelain enzyme. In 2012,
Marshall and Golden characterized bromelain from
Morinda citrifolia (Noni) and observed that
inhibition of bromelain by HgCl2 is the non-
competitive inhibition type. (Kaur, 2015). Protease
group is inhibited by PCMB (p-
Chloromercuriobenzoate), PMSF
(Phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride), EDTA
(Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid), benzamidine, and
pepstatin A (Walsh, 2002). Several factors that can
influence enzyme kinetics are the enzymes source
and conditions such as pH or temperature
environment (Kaur, 2015).
In this research the crude bromelain was
extracted from pineapple core and purified through
several stages. We also study the kinetics behavior
in the presence of inhibitor and antiplatelet activity
test by in vitro method.
Ilyas, N., Setiasih, S. and Hudiyono, S.
Inhibition Study of EDTA and PCMB on Purified Bromelain Activity from Pineapple Core [Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.] Using Ion Exchange Chromatography Column and Antiplatelet Activity
Test.
DOI: 10.5220/0009843200002406
In Proceedings of BROMO Conference (BROMO 2018) - Symposium on Natural Product and Biodiversity, page 1
ISBN: 978-989-758-347-6
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1

2 EXPERIMENTAL
2.1 Enzyme Extract from Pineapple
Core
The pineapples that were used in this research
were obtained from Palembang, Kramat Jati Market.
Crude enzyme was prepared by making pineapple
core puree using 0.2 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.0 at
4°C and then filtered. The filtrate had been
centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 20 minutes at 4°C. The
supernatant obtained from each sample was crude
bromelain extract. The crude bromelain was stored
in a refrigerator to be used as a source of enzyme.
2.2 Fractionation of Enzyme with
Ammonium Sulfate
Fractionation of crude bromelain was done by
using ammonium sulfate at different range of
concentration (0-20%, 20-50%, 50-80%). About 150
ml of crude enzyme extract was put in a beaker glass
which was placed in a salt ice bath. The crude
enzyme was slowly added by ammonium sulfate (0-
20%) with constant stirring using a magnetic stirrer.
After the addition of salt was completed, the stirring
process had been continued for 20 minutes. The
solution was then allowed to settle overnight in the
refrigerator. The solution was centrifuged (6000
rpm) for 20 minutes at 4
o
C and the precipitate was
dissolved in 0.2 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.0.
2.3 Dialysis
The enzyme solution was put into a cellophane bag.
The cellophane bag was then immersed in a solution
of 0.05 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.0. The dialysis
was taken place at 4°C using ice salt bath by
constant stirring. The buffer was changed for every 2
hours.
2.4 Protein and Enzyme Activity Assay
Lowry method is used to determine the protein
concentration. The enzymatic activity assay was
perfomed by Kunitz method using casein as
substrate at 37°C for 30 minutes. The enzyme was
inactivated by adding 3 ml of 5% TCA. The solution
then had been incubated in ice water bath for 30
minutes.
2.5 Kinetics Studies
2.5.1 Determination of Kinetics Parameter
Kinetic parameters (Km: Michaelis-Menten constant
and Vmax: maximum velocity) were determined
from Lineweaver Burk Plot between the enzyme
activity at optimum pH and temperature.
2.5.2 The Effect of EDTA and PCMB on
Bromelain Activity
The absence and presence of EDTA (0,1; 0,3 and 0,5
mM) and PCMB (0,1; 0,3 and 0,5 mM) were used to
assay the bromelain activity. Km and Vmax were
calculated using Lineweaver Burk plot.
2.6 In vitro Antiplatelet Activity Test
The antiplatelet activity test of the enzyme
bromelain fraction was carried by Born method. The
absorbance of the sample solution was measured
before and after the addition of aggregators.
Aggregators that used was ADP (Adenosine
Diphosphate 5'). Samples that tested were crude
enzymes and enzyme fractions obtained from each
stage of purification with the highest specific
activity. Aspirin was used as a positive control and
distilled water is used as a negative control.
In the sample tubes containing enzyme sample
(70 ml), was added PRP (Platelet Rich Plasma) (560
ml) and saline water and then shaken with a vortex
(low speed). The solution was incubated for 2 min at
37 °C. The absorbance of the solution was measured
by a spectrometer at a wavelength of 600 nm. Once
measured, the solution was added by 70 ml of ADP
and incubated for 10 min at 37 °C, subsequently re-
measured the absorbance. For the control solution is
done the same way, but the sample solution is
replaced with distilled water (negative control) and
asetosal 1 mg / ml (positive control). Calculation of
antiplatelet action can be seen from the percentage
inhibition of platelet aggregation and presentation of
aggregation that occurs. Calculation of percentage
inhibition were also performed to determine how
large the inhibition of platelet aggregation in each
solution (Moriyama, 2009).
BROMO 2018 - Bromo Conference, Symposium on Natural Products and Biodiversity
2

3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Purification of Bromelain from
Crude Extract by Ammonium
Sulfate Precipitation
Crude bromelain extract from pineapple core has
been purified by fractionation using ammonium
sulfate, followed by dialysis. Crude enzyme
obtained from pineapple core have a specific activity
of 102.018 U/mg protein. The next stage to purify
crude enzyme was the fractionation method using
ammonium sulfate with different of range
concentrations produced enzyme fractions that have
different proteolytic activity and protein content
(Table 1). Fraction 2 of pineapple core has higher
proteolytic activity than fraction 1 and 3.
Table 1: Purification of Crude Enzyme by using Ammonium Sulfate
Fraction
Volume
(mL)
Total
Specific
Activity
(U/mg)
Purity
Level
(Fold)
Activity
(
U
)
Protein
(
m
g)
Fraction 1
(
0-20%
)
7.1 122.356 0.818 149.465 1.465
Fraction 2
(20-50%)
11 223.116 0.858 260.042 2.548
Fraction 3
(
50-80%
)
4 32.4 0.532 60.902 0.596
Leftove
r
186 306.9 8.556 35.869 0.351
Table 2 shows that the specific activity before
and after dialysis. The fraction 2 from the pineapple
core after dialysis has the highest specific activity.
This is because in dialysis some proteins that has
molecular weight less than bromelain can pass
through the cellophane membrane. The specific
activity of bromelain from pineapple core is 381.287
U/mg protein with a purity level of 3.737 fold to the
crude enzyme extract.
Table 2: The Result of Dialysis on Bromelain Enzyme
Fraction
Volume
(mL)
Total
Specific
Activity
(U/mg)
Purity
Level
(Fold)
Activity
(U)
Protein
(mg)
Fraction 2
Before Dial
y
sis
8 223.116 0.858 260.042 2.548
Fraction 2
After Dial
y
sis
11 208.450 0.546 381.287 3.737
3.2 Bromelain Fractionation with Ion
Exchange Chromatography
Columns
Ion exchange chromatography column is an
advanced stage to purified bromelain. In this
research, the reversible interaction between charged
molecules and a resin which has the opposite charge
of the protein molecules will be affected by the
eluent through the column. This method is called
stepwise gradient elution (gradient method and
elution rise). If the ion charge of protein molecules
was same with resin’s ion charge, then the molecules
weren’t bound and eluted out first. The molecules
that have different ion charge interacted with the
resin in different strengths, then it required eluent
that has a gradually concentration to release protein
molecules bound from the resin. The resin that used
as the stationary phase in the column is a DEAE
(diethylaminoethyl) Sepharose (anion exchange
resin). Here are the values of proteolytic activity
against fraction number can be mapped in the form
of chromatograms and had 5 peak proteins (Figure
1).
Inhibition Study of EDTA and PCMB on Purified Bromelain Activity from Pineapple Core [Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.] Using Ion
Exchange Chromatography Column and Antiplatelet Activity Test
3

0
1
2
3
4
0
0, 25
0, 5
0, 75
1
0 102030405060708090100110120
Proteolytic
A c tiv ity
(U /m L)
Protein
Absorbance
(2 8 0
nm )
Fraction
Number
Pr otein
(280
nm) Prot eolytic
Activity
(U/mL)
Figure 1: Anion exchange chromatography DEAE – Sepharose Chromatogram. SP: protein absorption peak (280 nm); AP:
proteolytic activity peak.
The value of proteolytic activity, protein content and specific activity at this stage of purification by ion-
exchange chromatography column in Table 3.
Table 3: Results of Purification Phase by Ion Exchange Column Chromatography with DEAE-Sepharose
Fraction
Volume
(mL)
Total
Specific
Activity
(U/mg)
Purity
Level
(Fold)
Activity
(U)
Protein
(mg)
AP1
(13-20)
40 13.320 0.612 21.764 0.213
AP2
(
36-55
)
100 28.300 0.110 257.272 2.521
AP3
(
59-80
)
110 143 0.286 500 4.901
AP4
(82-89)
40 44 0.272 161.764 1.585
AP5
(
92-115
)
70 56 0.224 250 2.450
Further purification, the bromelain fraction was
purified by ion exchange chromatography CM
(carboxymethyl)-Sephadex C-50 (cation exchange
resin). Here are the values of proteolytic activity
against fraction number can be mapped in the form
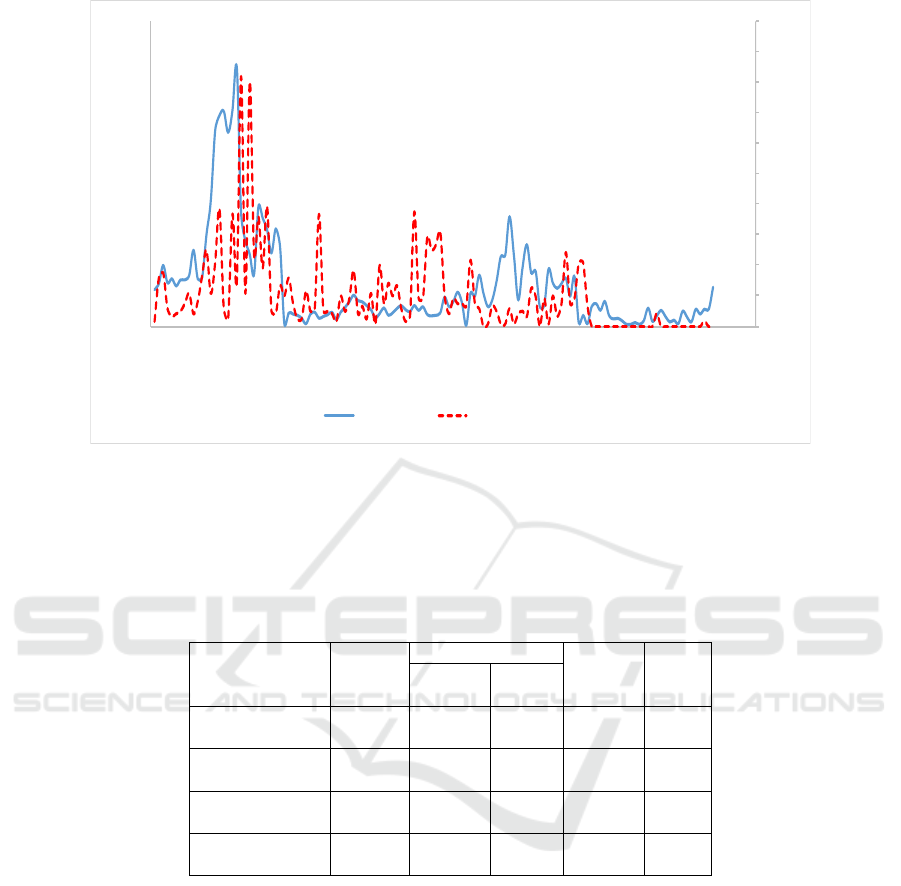
of chromatograms and had 4 peak proteins (Figure
2).
BROMO 2018 - Bromo Conference, Symposium on Natural Products and Biodiversity
4
0
0,2
0,4
0,6
0,8
1
1,2
1,4
1,6
1,8
2
0
0,05
0,1
0,15
0,2
0,25
0,3
0,35
0,4
0,45
0,5
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 1 20 130 140
Proteolytic
A c tiv ity
(U /m L)
Protein
Absorbance
(2 80
nm )
Fraction
Number
Protein
280
nm Proteolytic
Activity
(U/mL)
Figure 2: Cation exchange chromatography CM–Sephadex C-50 Chromatogram. SP: protein absorption peak (280 nm); AP:
proteolytic activity peak.
The value of proteolytic activity, protein content and specific activity at this stage of purification by ion-
exchange chromatography column in Table 4.
Table 4: Results of Purification Phase by Ion Exchange Column Chromatography with CM–Sephadex C-50
Fraction
Volume
(mL)
Total
Specific
Activity
(U/mg)
Purity
Level
(Fold)
Activity
(
U
)
Protein
(
m
g)
AP1
(16-27)
60 35 0.048 729.167 7.150
AP2
(
32-47
)
80 10.667 0.240 44.444 0.435
AP3
(
53-67
)
75 7.500 0.450 16.67 0.163
AP4
(88-100)
65 1.083 0.104 10.417 0.102
3.3 Kinetics Studies
3.3.1 Determination of Kinetics Parameter
Kinetic parameters (Km and Vmax) were
determined from Lineweaver Burk Plot between the
enzyme activity at optimum pH and temperature in
Figure 3 and 4.
Inhibition Study of EDTA and PCMB on Purified Bromelain Activity from Pineapple Core [Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.] Using Ion
Exchange Chromatography Column and Antiplatelet Activity Test
5
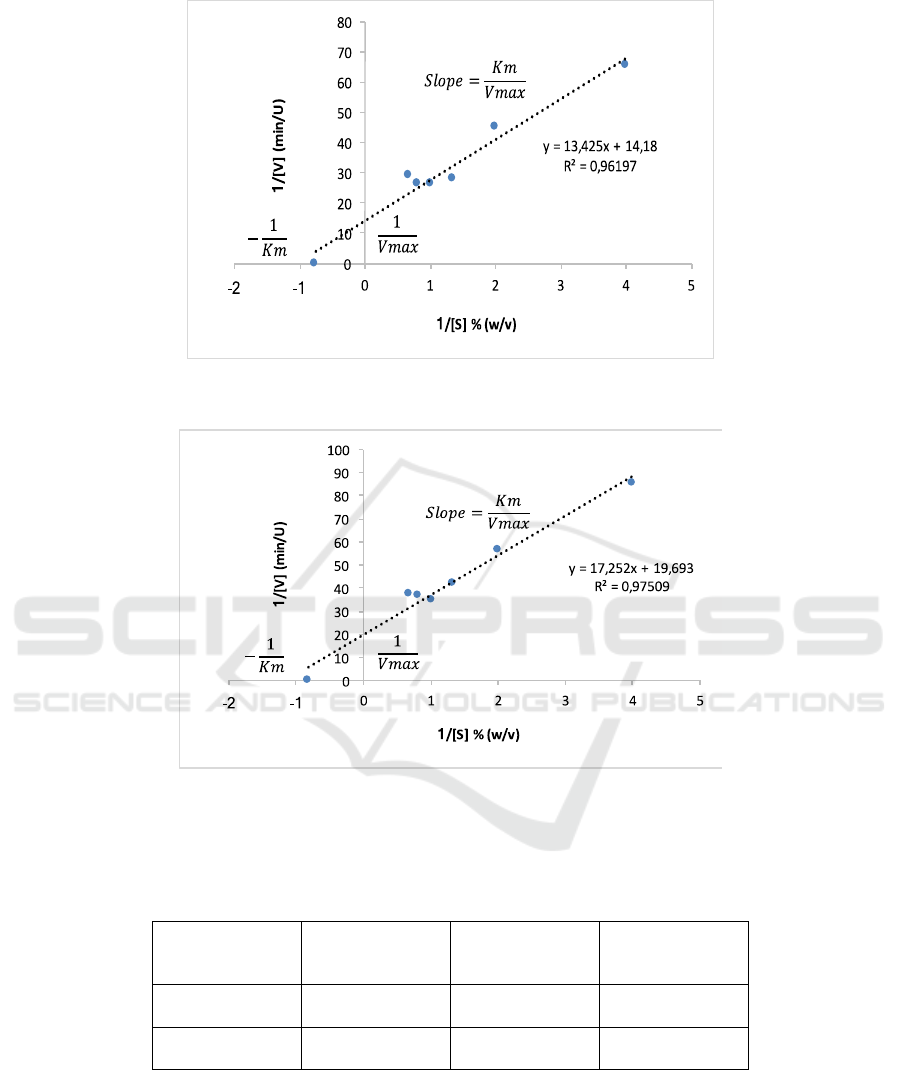
Figure 3: Lineweaver Burk Plot for the Hydrolysis of Casein by Purified Bromelain.
Figure 4: Lineweaver Burk Plot for the Hydrolysis of Azocasein by Purified Bromelain.
The value of Kinetics Parameter and Proteolytic Activity Bromelain on Casein and Azocasein in Table 5.
Table 5: Kinetics Parameter and Proteolytic Activity Bromelain on Casein and Azocasein.
Substrate
Proteolytic
Activity
(
U/mL
)
Km
(%)
Vmax
(U/min)
Casein 1.133 0.94 0.07
Azocasein 0.866 0.87 0.05
Based on these data, the value of Km fraction of
bromelain on casein and azocasein is relatively same
and low. A low Km bromelain on casein and
azocasein indicate that the Enzyme-Substrate
complex is good with a high affinity between
bromelain to both substrates. Several factors that can
influence enzyme kinetics are the enzymes source
and conditions such as pH or temperature
environment (Kaur, 2015).
BROMO 2018 - Bromo Conference, Symposium on Natural Products and Biodiversity
6
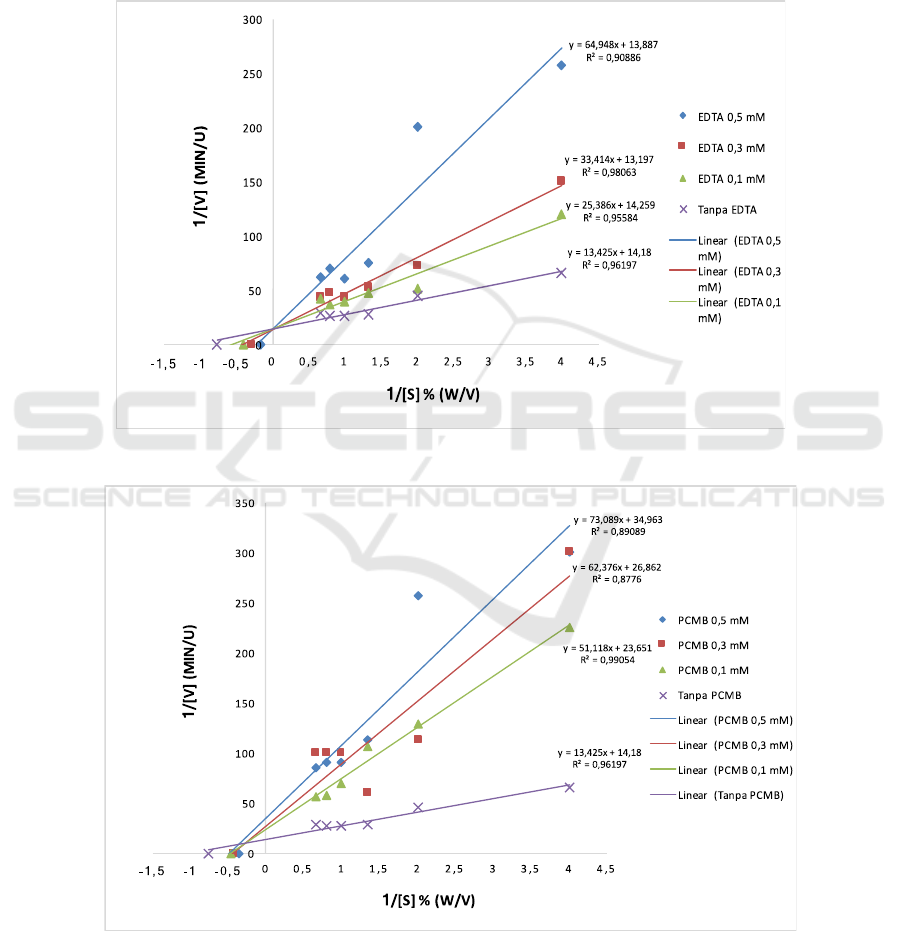
3.3.2 The Effect of EDTA and PCMB on
Bromelain Activity
The absence and presence of EDTA (0,1; 0,3 and 0,5
mM) and PCMB (0,1; 0,3 and 0,5 mM) were used to
assay the bromelain activity. Lineweaver Burk plot
in the presence of EDTA and PCMB were used to
calculate Km and Vmax (Figure 5 and 6). Bromelain
fraction was inhibited competitively with EDTA and
mix-inhibition type was observed in the presence of
PCMB.
Figure 5: Lineweaver Burk Plot for the Hydrolysis of Casein in the Presence of EDTA (0,1; 0,3; 0,5 mM).
Figure 6: Lineweaver Burk Plot for the Hydrolysis of Casein in the Presence of PCMB (0,1; 0,3; 0,5 mM).
.
Inhibition Study of EDTA and PCMB on Purified Bromelain Activity from Pineapple Core [Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.] Using Ion
Exchange Chromatography Column and Antiplatelet Activity Test
7
The value of Kinetics Parameter and Inhibition Percentage Bromelain by EDTA and PCMB in Table 6.
Table 6: Kinetics Parameter and Inhibition Percentage Bromelain by EDTA and PCMB
[I]
mM
Inhibitor (I)
EDTA PCMB
Km
(
%
)
Vmax
(
U/min
)
%Inhibition
Km
(
%
)
Vmax
(
U/min
)
%Inhibition
0 0.940 0.070 - 0.940 0.070 -
0.1 1.780 0.070 33.824 2.000 0.040 22.059
0.3 2.532 0.075 39.706 2.322 0.030 61.765
0.5 4.676 0.072 55.882 2.900 0.020 70.588
The addition of EDTA and PCMB at a concentration of 0.5 ppm can decrease the activity of the enzyme up
to 70%. Bromelain belongs to the cysteine protease containing thiol groups. PCMB is an organic compound
that reacts through a mercury-sulfur affinity with a sulfhydryl group in peptides, proteins and other molecules.
PCMB interacts and reacts with thiol groups in bromelain and therefore PCMB is an inhibitor that can inhibit
the reaction between bromelain and casein substrate. The interaction between cysteine protease (bromelain) and
PCMB is highly dependent on the reactivity of the thiol (-SH) group.
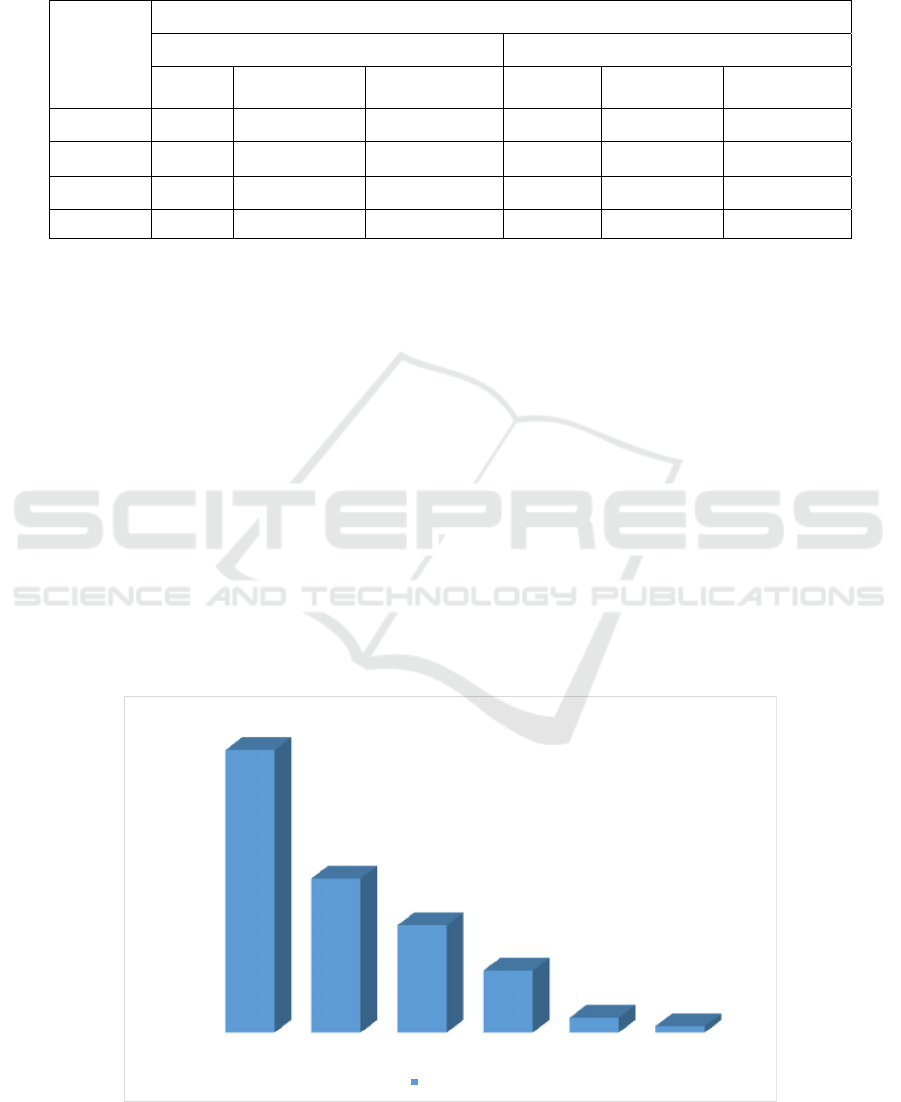
3.4 Antiplatelet Activity Test In Vitro
Antiplatelet agent activity test (in vitro) was used to
observe the value of the platelet aggregation
percentage and inhibition of platelet aggregation
percentage. Platelet aggregation (thrombosis) is the
ability of platelets to form a clot in the blood. The
percentage of platelet aggregation showed the effect
from a compound on the process of platelet clot
formation, while the percentage of inhibition of
platelet aggregation showed the ability from a
compound to inhibit the aggregation process. If the
inhibition percentage was high, it shows that the
compound was more active as well as the ability of
these compounds as antiplatelet agents. An in vitro
study using Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) with
turbidimetric method (Sathyapriya, 2012). The
platelet inhibition percentage by bromelain fraction
shown in Figure 7 and 8.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Aquadest
Dialysis DEAE-Sephar ose CM-Sephadex
Bromelain
Std Asetosal
94,939
51,772
36,100
20,892
5,031
2,22 7
%
Aggregation
Enzyme
Fraction
Figure 7: Percentage of platelet inhibition by bromelain fraction (Aggregation Percentage)
BROMO 2018 - Bromo Conference, Symposium on Natural Products and Biodiversity
8

0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Dialysis DEAE-Sepharose CM-Sephadex
Bromelain
Std Asetosal
45,469
61,976
77,994
94,700
97,655
%
Inhibition
Enzyme
Fraction
Figure 8: Percentage of platelet inhibition by bromelain fraction (Inhibition Percentage)
4 CONCLUSIONS
Bromelain was successfully purified through several
purification methods. The result of bromelain after
purified by ion chromatography exchange CM-
Sephadex C-50 gave the highest specific activity.
Bromelain fraction was inhibited competitively with
EDTA and mix-inhibition type was observed in the
presence of PCMB. The addition of EDTA and
PCMB at a concentration of 0.5 ppm can decrease
the activity of the enzyme up to 70%. All samples
with the highest specific activity of each stage of
purification has the ability as an antiplatelet agent.
The highest value of antiplatelet activity was from
the purest enzyme fraction that purify using ion-
exchange chromatography column with percentage
of aggregation 20.892% and percentage of inhibition
77.994%.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was funded by Penelitian
Unggulan Perguruan Tinggi (PUPT)
Universitas Indonesia 2018.
REFERENCES
Arshad, Z.I.M., et al., 2014. Bromelain: an overview of
industrial application and purification strategies.
Journal of Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:7283–7297.
Bhattacharyya, B.K., 2008. Bromelain. India:
Biotechnology and Molecular Biology. East India
Pharmaceutical Works Ltd. Vol 7(4).
Kaur, T., Kaur, A. & Grewal, R.K., 2015. Kinetics studies
with fruit bromelain (Ananas comosus) in the presence
of cysteine and divalent ions, J Food Sci Technol,
52(9), 5954–5960.
Moriyama, H. et al., 2009. Assay-guided Informatory
Screening Method for Antiplatelet Effect of
Adenosine Isolated from Malbranchea filamentosa
IFM 41300: Inhibitory Behaviors of Adenosine in
Different Solvents. Journal of Health Science; 55
suppl 1:103–108.
Neta JLV., et al., 2012. Bromelain Enzyme from
Pineapple: In Vitro Activity Study under Different
Micropropagation Conditions. Appl Biochem
Biotechnol; 168(2): 234-246.
Rugayah, Anggalia, I., Cahya, Y., 2012. Pengaruh
Konsentrasi dan Cara Aplikasi Iba (Indole Butiric
Acid) terhadap Pertumbuhan Bibit Nanas (Ananas
Comosus [L.] Merr.) Asal Tunas Mahkota. Bandar
Lampung: Jurusan Agroteknologi Fakultas Pertanian
Universitas Lampung.
Sathyapriya, E., Velpandian, V., Anbu, J. & Anjana, A.,
2012. In vitro anti platelet aggregation activity and
thrombolytic activity of Cheenalinga chendhuram.
Inhibition Study of EDTA and PCMB on Purified Bromelain Activity from Pineapple Core [Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.] Using Ion
Exchange Chromatography Column and Antiplatelet Activity Test
9

Internatioal Journal of Life Science & Pharma
Research; Vol 2: 2250-0480.
Walsh, G., 2002. Protein biochemistry and biotechnology.
John Wiley and Sons, New York, 312.
BROMO 2018 - Bromo Conference, Symposium on Natural Products and Biodiversity
10
