
The Effect of Work Involvement and Work Satisfaction to Employee
Turnover Intentions in Indonesia: Case Study in SCTV
Lia Amalia
1
, Agus Ramadani
1
, Deddy S. Bratakusumah
1
and R. A. Nurlinda
1
1
Economics and Business Faculty Esaunggul University
Keywords: Job Involvement, Job Satisfaction, Turnover Intention
Abstract: The purpose of this research is to bring involvement inemployees’ jobs and the company should be rewarded
as well with the feeling of satisfaction from the employees themselves. Furthermore, to acquire a sufficient
portion of job involvement from its employees, the company should put its trust to the employees. Hence, to
grant the employees with job satisfaction, the company should facilitate and provide comfortability and
opportunity for career development to accommodate the ability of its employees. This study is a descriptive
quantitative study. The method of analysis used is SEM (Structural Equation Modeling) with the employees
of PT. SCTV as the samples. The data were collected using a questionnaire, from the data, there were 150
employees of PT. SCTV who met the criteria to be selected as the respondents who would be used as the
samples of the research. In the result of the analysis part, it can be found that job involvement significantly
affects turnover intention and job satisfaction. On the other hand, job satisfaction does not significantly affect
turnover intention. The conclusion is the deeper job involvement of an employee, the smaller number of
turnover intention and the number of job satisfaction will increase.
1 INTRODUCTION
Toly (2001) mentioned that turnover intention should
be addressed as an important human phenomenon and
behavior in the life of the company from an individual
and social points of view, given that an employee
turnover intention will have a significant impact on
the company and its current employees, high turnover
intention has become a serious problem for
companies, and even some companies are frustrated
to learn that the recruitment process that has captured
qualified employees ultimately becomes useless
because the recruited employee has chosen a job at
another company. Lambert (2003) mentions that
work involvement is measured from the level of the
individual interest that provides the work in his life.
He thinks this is a person's psychological
identification with his work where an individual with
a high level of work involved will place work at the
center of his life's interest. Raziq (2014) mentions that
if employees are not satisfied with the task assigned
to them, they will beunsure of their ability. Factors
such as their rights, unsafe working conditions,
uncooperative co-workers, disrespectful bosses and
they are not considered in the decision-making
process thus causing them to feel separated from the
organization. Employee morale should be high
because it will be reflected in their performance
because,with low spirits, they will make a lower
effort to help the company.
In reducing turnover intention, a good
organization should be able to see work involvement
and job satisfaction of its employees. Simanjuntak
(2014) describes the work for employees should be so
much for them that employee engagement becomes
high and ultimately minimizes the chance of those
employees to look for other jobs. Research conducted
by Medina (2012) (variables of job satisfaction and
turnover intention) showed a negativecorrelation
between job satisfaction andlow turnover intention as
has been shown to improve productivity and
organizational performance.Tziner (2011) also found
that job involvement has an effect on job satisfaction
and that employment involvement also hasa negative
and significant effect on employee exit intention.
Lambert (2003) mentions that job involvement
negatively affects job satisfaction and turnover
intention. His study shows that the involvement to
important work influences job satisfaction and
turnover intention.
Simanjuntak’s research (2014) (variables of work
involvement and turnover intention) in the field of
Amalia, L., Ramadani, A., Bratakusumah, D. and Nurlinda, R.
The Effect of Work Involvement and Work Satisfaction to Employee Turnover Intentions in Indonesia: Case Study in SCTV.
DOI: 10.5220/0009952427632769
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Recent Innovations (ICRI 2018), pages 2763-2769
ISBN: 978-989-758-458-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
2763

herbal medicine industry showed work involvement
has a negative and significant influence on employee
turnover intention. Previous researches on job
involvement, job satisfaction, and turnover intention
have been done a lot, but those researches are not
jointly tested in one research, and the object of the
researches conducted are not within the field of a
television company, namely PT. SCTV. So the
authors perceive that we still need to grow more
understanding on job involvement, job satisfaction,
and turnover intention and the authors put this idea
into suggestions for the next research object. Based
on the above research gap, the purpose of the research
to be achieved is to explain the effect of job
involvement and job satisfaction on turnover
intention.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Work Involvement
Noe, Hollenbeck, Gerhart and Wright (2011) describe
employment engagement as the extent to which
people identify themselves with their work. People
with high levels of job involvement consider their
work to be an important part of their lives. Liau and
Lee (2009) argue that employment involvement in
this modern economic era in particular also
contributes to the overall availability of human
resources. Cohen (2003) defined job involvement as
the internalization of values about the good of the job
or the importance of work for one's worth. Job
involvement as a level of the extent to which a
person's work performance affects his self-esteem
and the extent to which a person psychologically
identifies himself with his job or the importance of
work in his total self-image. Robbins (2003) argues
that work involvement is the level at which a person
relates himself, participates in it and assumes its
performance is important for its value. Employee
engagement is a participatory process that uses the
entire capacity of workers and is designed to
encourage increased commitment to the success of
the company. Yekty (2006) explains that job
involvement can show the integration of employees
to the company because the more an employee united
with the work, the more involved the employee will
be and he/she will want to spend more time in
his/herwork.
2.2 Work Satisfaction
Raziq (2014) explains job satisfaction as the
emotional orientation that employees have for their
roles to perform in the workplace. Job Satisfaction is
an important component of employee motivation and
encouragement for better performance. Ardana
(2012) states one of the causes of dissatisfaction in
work is employee unsuitability to work. Lack of job
training for employees can cause job mismatch.
Working training basically must be done by a
company considering no one can perform a task or
work well if it is not learned first. Jimad (2011)
explains job satisfaction is the biggest factor affecting
employees' intention to leave or stay in the company.
Job satisfaction is defined as a "security feeling" or
sense of security of employees to work both regarding
socio-economic (salary and social security) and
psychological perspectives, like getting the
moreadvanced opportunity. Fathoni (2006) says job
satisfaction is an emotional attitude that is fun and it
is able to make an employee lovehis/her job. This
attitude is reflectedthroughwork morale, discipline,
and work performance. This satisfaction is enjoyed in
work, out of work, and in and out of work
combinations. Job satisfaction in work is the job
satisfaction enjoyed in employees work by obtaining
the results of work goals, placement, treatment and
atmosphere of a good working environment.
Simanjuntak (2014) said five factors encourage the
creation of job satisfaction. These factors, among
others, are challenging jobs where employees tend to
prefer jobs that give them the opportunity to use their
skills, abilities and offer diverse tasks, freedom and
feedback on how well they work. Then the rewards
where the employees want the wage system
andpromotional policies are fair and in line with their
expectations. The important thing that connects
wages and satisfaction is not the absolute amount
paid, but the existence of justice. Further working
conditions are the working environment which is very
important for employees to personal comfort and to
facilitate the task. Then colleagues where for most
employees, work also fill the need for social
interaction. Therefore, friendly and supportive
colleagues will create job satisfaction. Moreover, the
last one is the suitability of work which where a high
fit between personality and worker will make an
individual more satisfied.
2.3 Turnover Intention
Hurley (2010) states that the Turnover Intention of
employees is something that is reasonable for the
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2764

company's operations because if there is a transfer of
employees under five percent it is considered less
healthy. Employee shifting provides a dynamic
situation for a company by introducing employees
with new ideas, new abilities, and breakthroughs.
Mathis and Jackson (2009) also expressed the opinion
that Turnover Intention is a challenge faced by a
company. Work shift occurs when employees leave a
company,and its position must be replaced. Outgoing
employees can be caused by company policy or
employee's desires. Harnoto (2002) also states
Turnover Intention is the level of intensity of the
desire to get out of the company, many reasons that
cause turnover intention is the desire to get a better
job. The opinion is also relatively similar to the
opinion expressed earlier, that the intention of
turnover is basically a desire to leave (out) of the
company. Toly (2001) argues that turnover intention
is the attitude or level tendency in which an employee
has the possibility to leave the organization or
voluntarily resign from his job. Chen and Francesco
(2000) measure intentional turnover by looking at
situations within the company that are less
comfortable that cause employees to have a mind to
leave the company, the desire to look for other jobs
and the desire to leave the company in the coming
months.
3 HYPOTHESIS
Faslah (2010) found that job involvement had a
negative and significant effect on employee
outsourcing and work involvement was able to make
employees work together well. Similarly, Sumarto
(2009) found that high employee involvement proved
to be able to increase job satisfaction and able to damp
turnover intention of the employee. According to
Blau and Boal (1989) in Kartiningsih (2007) work
involvement in practice related to the level of
absenteeism, the application rate of stop working and
the will to participate in teams or working groups. If
the level of work involved is not addressed, it will
result in high absenteeism and high turnover intention
(Robbins and Caulter, 2007). From the results of this
study, it shows that there is significant influence
between work involvement on turnover intention at
PT. SCTV.
From the above description the authors propose a
hypothesis:
H1: The greater the employee's involvement in his
work the lower the turnover intention.
Nasution (2009) mentioned job satisfaction proved to
have a significant influence on the employee's desire
to get out. Ayodogdu and Asikgil (2011) found that
job satisfaction negatively and significantly affects
the employee's desire to leave the company. The
negative relationship between job satisfaction with
leaving out intentions means that if employment
satisfaction increases, it decreases employee’s desire
to leave the company. Handoko (2006) in
Simanjuntak (2014) job satisfaction affects employee
turnover and absenteeism. The company can expect
that if job satisfaction increase, employee turnover
and attendance decrease. Employees will not be easy
to leave the company and then look for opportunities
in other companies. From the results of this study,it
showsthat there is significant influence
between job
satisfaction on turnover intention at PT. SCTV.
From the above description the authors propose a
hypothesis:
H2: The more satisfied the employee towards his
work the smaller the turnover intention.
Khan and Nemati (2011) and Putri (2010) found that
job involvement had a positive effect on job
satisfaction. Sumarto (2009) got the result that high
employee involvement proved to be able to increase
job satisfaction and able to dampen the intention of
the employeeto leave out. Makvana (2008) mentioned
that employees with high levels of job involvement
showed high levels of job satisfaction. Brown (1996)
in Mantler and Murphy (2005) observed that people
with high work involvement tend to be satisfied with
their work and have a high commitment to their
careers, profession, and their organization. From the
results of this study, it showsthat there is significant
influence between work involvement and job
satisfaction at PT. SCTV.From the above description
the authors propose a hypothesis:
H3: The greater the employee's involvement in the
company, the greater the employee's job satisfaction
with the company
The Effect of Work Involvement and Work Satisfaction to Employee Turnover Intentions in Indonesia: Case Study in SCTV
2765

4 METHODS
Analysis method in this research uses Structural
Equation Modeling (SEM) method. The sampling
process was performed using the Maximum
Likelihood Estimation (MLE) technique, which was
an effective sampling technique for samples ranging
from 100 to 420 samples (Ferdinand, 2002). Data
measurement method uses a Likert scale with scale
interval one to ten. The aspects studied job
involvement, job satisfaction and turnover intention.
Research started in August 2017 with quantitative
descriptive analysis research method by adopting a
causality model to see the relationship between
variables. This research conducted on permanent
employees of PT.SCTV with a sample of 150
respondents. Analysis results are then interpreted, and
the last step was concluded and given suggestions.
4.1 Measurement
In this research, there is one exogenous variable that
is the turnover intention and two endogen variables
that arejob involvement and employee job
satisfaction. Measurement of turnover intention
variable appliesthe dimensions of Chen and
Francesco (2000) whose dimensions consisted of the
thought of exit, the desire to seek other vacancies, and
the desire to leave the organization in the coming
months. Employment involvement variable uses the
dimensions of Lodahl and Kejner (1985) consisting
ofa large indicator of expectations for work, high
emotional involvement in work, a great sense of
responsibility for work, preparedness for duty, pride
in employment, and ambition for mobilityover
mobility. Employee job satisfaction adapts the
dimensions of Luthans (2006) consisting of salary,
promotional opportunities, peer relationships,
supervision, and work environment. Furthermore,
from the measurement dimensions presented in the
form of questionnaires, we tested the validity and
reliability. Confirmatory Factor Analysis does the
validity test by looking at Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin
Measure of Sampling (KMO) and Measures of
Sampling Adequacy (MSA). In this test, the value
obtained must be greater than 0.5 which means that
the factor analysis is appropriate or appropriate for
use, and can be further processed (Malhotra, 2004).
The job engagement scale consists of 5 questions, and
there are only 3 valid questions, the job satisfaction
scale consists of 6 questions and only 4 valid
questions,and the turnover intention scale consists of
3 questions,and they are all valid. Test reliability
value of Alpha Cronbach is greater than> 0.6 which
means reliable (Anindita and Hasyim, 2009), which
can be said operational-operational organizational
climate involvement, training and employee
performance can be said as a reliable data collection
tool in research. The next stage, our data was
analyzed by using SEM analysis method. SEM can
explain the complex association of variables as well
as the direct or indirect effects of one or several
variables on other variables (Hair, 2008).
5 RESULT
Our research focuses on the influence of job
involvement, job satisfaction, and intention turnover
where the results show that of the three hypotheses it
was obtained two data supporting the hypothesis and
one data was not supporting the hypothesis or not all
hypotheses are accepted, as we have done SEM
testing. It can be seen in Figure 2 as follows:
Figure 2
Path Diagram T-Value
Based on Figure 2 the T-Value Path Diagram above
which is a hypothesis in this study is presented in the
following structural equation.
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2766
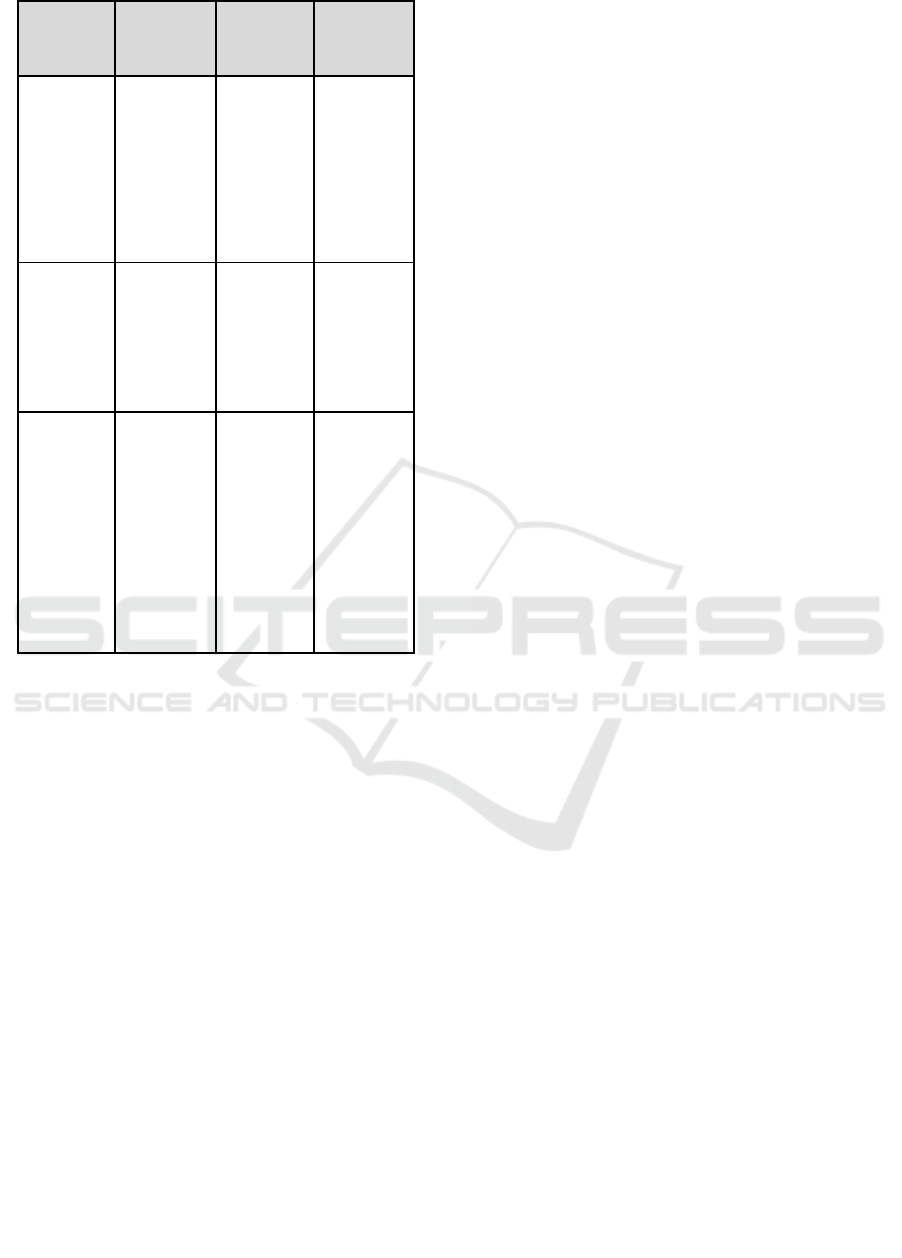
Hypothesis
Statement
Hypothesis
T
Value
Value
Description
Hypothesis
Statement
Hypothesis
T
Value
Value
Description
H
1
The greater
the
employee's
involvement
in his work,
the lower
the
employee
turnover
intention
2,84
The data
support the
hypothesis
H
2
The more
satisfied
employees
to their
work the
smaller the
turnover
intention.
-0.36
The data do
not support
the
hypothesis
H
3
The greater
the
employee's
involvement
in the
company,
the greater
the
employee's
job
satisfaction
with the
company.
10.96
The data
support the
hypothesis
In the result of the first hypothesis testing (H1), it
was found that the result of the analysis support H1
hypothesis that employee engagement would lower
turnover intention of the employee which equals to
2.84. This shows that turnover intention is influenced
by good work involvement. Like the better the
involvement of work within the company, the lower
the turnover of employee intention will be. This result
is reinforced by previous research conducted by Blau
(1889) in Robbins (2003) which found that high
levels of work involvement have been found to be
related to lower absenteeism and lower stopping
rates. Similarly, Sumarto (2009) found that high
employee engagement proved to decrease employee
turnover intention.While Faslah (2010) found that job
involvement had a negative and significant impact on
employee intentions.
Results of testing the second hypothesis (H2),
found that the analysis does not support the
hypothesis H2 of which valueis -0.36. This shows that
turnover intention is not influenced by job
satisfaction. The lower the job satisfaction of
employees the higher the turnover intention of
employees working on SCTV. Job satisfaction on
permanent employees of PT. SCTV is so low that it
impacts turnover intention, this is not in accordance
with the statements of Kuruuzum et al. (2009) and
Sharagay and Tziner (2011) who found that job
involvement had a positive effect on job satisfaction
on employees.
Nasution (2009) which mentions job satisfaction
proved to have a significant influence on the desire of
employees to leave their job. However, in research
conducted by Ayodogdu and Asikgil (2011), it was
found that job satisfaction negatively and
significantly influence the employee's desire to leave.
The negative relationship between job satisfaction
and out-of-pocket intentions means that if a person's
job satisfaction increases, it further decreases his
desire to leave the company. Satisfaction is a form of
feeling that someone has more value for his company.
When employees feel satisfaction in their jobs,
employees will expect the company to meet whatever
is needed by them and whether they receive adequate
facilities or not. Jimad (2011) says job satisfaction is
the biggest factor that affects employees' intention to
leave or stay afloat in the company. The authors find
that job satisfaction does not affect the turnover
intention. This may be caused by several things,
according to the authorsthis can occur because the
form of satisfaction given is sufficient in accordance
with the level of ability of employees. Another thing,
employees feel that it is enough to be trusted to do the
job well. The last one according to the authors is
because employees feel that the important thing that
can make them survive is not job satisfaction from the
company alone, it could be from the work
environment or the compensation and benefits they
earn which is enough to be able to meet their life
needs. Result of testing of the third hypothesis (H3),
found that result of analysis support hypothesis H3
that is good employee engagement will make
employees’ job satisfaction bigger or equals to 10.96.
This indicates that job involvement is influenced
by good job satisfaction. This result is reinforced
from previous studies conducted by Makvana (2008)
who found that employees who have high levels of
job involvement indicate a high level of job
satisfaction. Brown (1996) in Mantler and Murphy
(2005) also add that people with high work
involvement tend to be satisfied with their work and
have a high commitment to their careers, professions
and organizations.
Diefendorff et al. (2006)state that Job
involvement is an important factor in other work-
related attitudes such as job satisfaction. People with
high working involvement will focus most of their
attention on their work so that they become totally
immersed and enjoy the job. This is a person's belief
in his job and a function of how much work can
The Effect of Work Involvement and Work Satisfaction to Employee Turnover Intentions in Indonesia: Case Study in SCTV
2767

satisfy one's desires. The results of this study are in
line with this and support the results of researches
Khan & Nemati (2011) and Princess (2010) who
found that job involvement positively affect job
satisfaction.
5.1 Managerial Implications
This study discusses the factors that influence work
involvement, job satisfaction, and good turnover
intention in PT. SCTV. In an organization, employees
are important aspects and assets that must be
maintained and cared for because the employee is the
driver of all the processes that exist within the
organization. Therefore, it is important for an
organization to create comfortable conditions, respect
each other, provide opportunities and employment
opportunities to all employees and sufficient
circumstances so that employees will feel happy in
working and eventually have a high commitment.
Because basically with the involvement and high
satisfaction of employees, the results expected by the
organization will also be better. Managerial
implications that can be suggested are the company
can increase employment to the employees in
PT.SCTV, the company must also be able to convince
and provide opportunities for all employees to work
and trust each other against their colleagues. Because
in this industry all work is very specific and when the
program runs employees will all be combined into a
solid team in running all of their duties. Basically, this
company must really understand the needs of
employees not only materially but also
psychologically for each of its employees so that such
employee can play an active role in his work. The
company should design new standard operating
procedures (SOP) to ensure the level of satisfaction
with the values of employee work. SOP is important
in implementing all stages of work on the employees
of PT. SCTV, because the SOP, of course, can make
uniformity of all programs in the implementation of
the work so that the lack of possible coordination can
make mistakes in the work itself.
The company also needs to facilitate and provide
comfort as well as able to provide more career
opportunities to the employees in order to develop
their skills to reduce employee turnover intention
from the company. The issue which, of course, affects
the improvement of employee satisfaction is rewards
and relationship with the management. The
management can increase the rewards for employees
‘achievement. In addition to maintaining
relationships with employees, it is also important to
manage employee job satisfaction and continue to
increase it. It can be done by holding a family
gathering and the like. The management can also
provide motivation and give direction so that
employees grow the feeling of having the company
and generate personal commitment to achieving
common goals with the management. A comfortable
working environment will also make employees feel
comfortable in the workplace and can continue to
improve employee performance in the company.
5.2 Limitations of Research
This study has some limitations that can be
considered for further research. This research uses
questionnaires as a measuring tool to save time and
energy. However, the questionnaires have usual
limitations are,i.e. dealing with the filling ofthe
question. One of those limitations is the authorsmust
spend quite a long time towait for the respondents to
filling in the questionnaires because if they are not
observed there will be the possibility thatthe
respondents do not fill in the question based on their
truth condition or just fill them all based on ideal
conditions expected by them instead of the actual
conditions that are happening.This can cause the
measurement used does not describe the variables
significantly. Also, there are limitations of variables
in this study which only discuss job involvement, job
satisfaction and turnover intention.
5.3 Suggestions for Further Research
Based on the above explanation we can put forward
some suggestions that can be given to permanent
employees of PT. SCTV for the sake of progress in
all television programs and progress of the company.
The authors hope that presumably as employees, they
can give the good value of work and maintain good
cooperation in order to get maximum result of their
work and to be able to be more creative in presenting
more broadcasted programs to the society so that
society will find those things (entertainment
programs) are positive for their everyday life.
Moreover, the company should give more
opportunity to its employees to be able to give
ideas,and insights and develop new innovation that
can help the success of the company.
This study is still very limited because it only
examines the extent of the influence of job
involvement, job satisfaction and turnover intention.
More researcheson the analysis of job involvement,
job satisfaction affecting turnover intention arestill
possible to be further developedin the future. Thus,
future researches are suggested to add new variables
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2768

such as organizational commitment, organizational
culture, leadership, work stress and work
environment that can influence turnover intention
which are of course should be tailored to the object of
the researches.
REFERENCES
Ardana, I Komang, Ni Wayan Mujiati, I Wayan Mudiartha
Utama. 2012. Human Resource Management.
Yogyakarta: Graha Ilmu.
Blau, G.J. (1889). Using Job Involpmentand
organizationalcommitment interactively to predict
turnover. Journal of management, 15,115-127.
Brown, S. P. (1996). A Meta-Analysis and Review of
Organizational Research on Job Involvement.
Psychological Bulletin, 120 (2), 235-255.
Chen, Z. X. & Francesco, A. M. 2003. The relationship
between the three components of commitment and
employee performance in China. Journal of Vocational
Behavior, 62: 490-510. Faslah, Rony. 2010. "The
Relationship Between Work Involvement with
Turnover Intention On Employees". Journal of
Management & Entrepreneurship. Vol VIII, No. 2.
Hair., Anderson., Tatham., And Black. (2008).
Multivariate. Data Analysis Fifth Edition USA.
Prentice Hall International Inc
Handoko, T. H. (2001). Personnel and Human Resources
Management, Second Edition.Yogyakarta: BPFE.
Hasyim and Rina Anindita. 2009. "The Basic
Principles of Marketing Research Methods" .Edition
First. Jakarta; UIEU-University Press.
Hisham, Achmad. (2009). Application of Structural
Equation Modeling Method With LISREL 8.54.
(Second Edition). Jakarta: Data Processing Consultant
Statistics And Data
Processing.http://cpratanto.blogspot.co.id/2015/01/ket
erlibatan-kerja-job-involvement.html
Khan, K. & Nemati, A. R. 2011. Impact of Job
Involvement on Employee Satisfaction: A Study Based
on Medical Doctors Working at Riphah I nternational
University Teaching Hospitals in Pakistan. African
Journal.
Lambert, E. (2008). The impact of job involvement on
correctional staff. Professional Issues in Criminal
Justice, 3 (1), 57-76.
Luthans, F. 2006. Organizational Behavior 10th. Indonesia
Edition. Yogyakarta: Andi Publisher.
Makvana, S. M. (2008). A Study of Job Involvement and
Work Satisfaction Prevailing Among Employees of
Engineering and Pharmaceutical Organizations.
Journal of the Institute of Productivity and
Management. 2 (2), 9-12.
Mathis Robert L. and John H. Jackson. 2009. Human
Resource Management. Edition 10. Jakarta: Salemba
Four.
Putri, H. A. 2010. The Influence of Job Engagement on
Employee Job Satisfaction At PT. Garuda Indonesia
Airways Medan. Essay. University of Sumatera Utara
Medan
Raziq, Abdul. "Impact of Working Environment on Job
Satisfaction". 2014, Prague, Czech Republic Robbins
and Judge. 2003. Organizational Behavior. Jakarta: PT.
Index Group Gramedia.
Simanjuntak, Naomei ;. "Analysis of the Influence of Job
Engagement and Job Satisfaction On Turn Over
Intention Employees (Study At PT Njoja Meneer
Semarang). Essay. Semarang: Diponegoro University
(2013).
Sumarto. 2009. Improving Commitment and Satisfaction
to Drop Out Intent. Journal of Management and
Entrepreneurship, 11 (2), pp: 116-125.
Toly, A. A. 2001. Factor Analysis Affecting Turnover
Intention on Staff of Public Accounting Firm. Journal
of Accounting and Finance. Vol. 3, No. 2.
The Effect of Work Involvement and Work Satisfaction to Employee Turnover Intentions in Indonesia: Case Study in SCTV
2769
