
Servant Leadership in Indonesia Asian Games 2018 Organizing
Committee: Its Impact on Organizational Learning and Performance
Delly Mawarni Gumay
1
, Nayunda Andhika Sari
1
1
Universitas Indonesia, Jl. Margonda Raya, Pondok Cina, Beji, 16424, Depok, Indonesia
Keyword: Servant leadership, Asian Games, organizational learning, performance, Indonesia
Abstract: Asian Games 2018 has become the biggest sport event Indonesia ever hosted in years. Indonesia Asian
Games 2018 Organizing Committee (INASGOC) as the organizer Asian Games 2018 was fully responsible
and plays a key role in the success of this event. Therefore, the emergence of an effective leader is
important to ensure its performance and servant leadership is found to have strong impact on organization
learning and performance. This study aims to examine the influence of servant leadership on organizational
performance with organizational learning as the mediator in INASGOC. Data were collected by using
survey method with questionnaire distributed to 150 INASGOC employees working for the core functions.
The hypothesis was tested using multiple regressions. The result shows that Servant Leadership has a
positive impact on Organizational performance, which is fully mediated by organizational learning. This
study proves that organizational learning among INASGOC employees has a significant role to successfully
held Asian Games 2018 event.
1 INTRODUCTION
Sport organization is a social entity involved in
sports industry, goal oriented with structured activity
system and can be identified relatively (Marcu and
Buhas, 2014). One example of sports organization
that is garnering a lot of attention in Indonesia is
INASGOC which stands for Indonesia Asian Games
2018 Organizing Committee as the organizing
committee of the 2018 Asian Games. INASGOC is
fully responsible for organization performance and
the success of 2018 Asian Games event which will
we commencing in August. In order to achieve the
success of the 2018 Asian Games organization,
INASGOC needs the right leadership style to
accomplish the great responsibility given.
Servant leadership is an interesting leadership
concept to be studied for its impact (Lantu,
Pesiwarissa and Rumahorbo, 2007) and most of
leadership theories always revolve around power
and position (Zaluchu, 2011). However, that is not
the case with servant leadership which emphasizes
heavily on the ability of a leader to serve employees
in companies or organizations. In the context of
Asian games organization, servant leadership style is
a relevant leadership due to the short term and
temporary nature of INASGOC with team oriented
culture that demands positive relationship between
superiors and subordinates. Leadership style is also
considered very important in achieving
organizational goals, learning, and organizational
performance (Barling, Weber and Kelloway, 1996).
This is shown by a study conducted by Choudary,
Akhtar & Zaheer (2013) stating that servant
leadership has a positive influence on organizational
performance.
This study is interesting and noticeably distinct
from previous study by Choudary, Akhtar and
Zaheer (2013) because this study is conducted on
non-profit and sport organization, thus it is expected
to contribute fruitfully. This research is conducted in
the context of sporting events at the Indonesia Asian
Games 2018 Organizing Committee. This research is
also carried out by organizational performance
variables using indicators on Invitation Tournament
Test Event Asian Games 2018 which was held in
February 2018. Therefore, this study will analyze the
impact of servant leadership with organizational
performance on INASGOC as organizing committee
of 2018 Asian Games. This study also uses the
organizational learning variable as a mediating
variable and is carried out by survey method by
distributing questionnaires to INASGOC employees
Gumay, D. and Sari, N.
Servant Leadership in Indonesia Asian Games 2018 Organizing Committee: Its Impact on Organizational Learning and Performance.
DOI: 10.5220/0009999700002917
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Social Sciences, Laws, Arts and Humanities (BINUS-JIC 2018), pages 45-49
ISBN: 978-989-758-515-9
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
45

and conducting interviews with several leaders at
INASGOC.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Previous studies related to servant leadership,
organizational learning, and organizational
performance are used in this study.
2.1 Servant Leadership
Servant leadership focuses on others rather than
themselves and on the understanding of the role of
leaders as a servant (Greenleaf, 1977). The main
purpose of servant leadership is to serve and meet
the needs of others, which optimally must be the
primary motivation for leadership (Russell and
Stone, 2002). Servant leadership develops people,
helps them to strive and thrive (McMinn, 2001).
Servant leadership is a relationship process that
generates feedback between leaders and employees
where the leader appears as a person who serves the
needs of their employees and in turn, it makes the
person acknowledged and accepted as the leader
(Poli, 2011). There are eight leadership indicators
that use the theory of Barbuto and Wheeler (Lantu,
Pesiwarissa and Rumahorbo, 2007), which include
altruistic calling, emotional healing, wisdom,
persuasive mapping, organizational stewardship,
humility, vision, service. Taylor et al (Taylor, Pearse
and Louw, 2013) explained that initially servant
leadership is a different leadership paradigm.
Leadership at that time was dominated by the leader
centered paradigm focus that used command and
control approaches. Servant leadership brings
changes that leaders need to serve rather than be
served.
2.2 Organizational Learning
According to Robbins (2006), organizational
learning is a continuous performance development
process to face individual challenges in
organizations. It is believed that organizational
learning process can help ease the challenges of
individual work. Moreover, individual learning
process occurs when organization member goes
through understanding process of new concept
(know why), resulting in the improvement of skills
and experience to actualize the concept (know how),
thereby changing and improving organizational
value (Senge, 2006).
Studies identifiedthat the characteristics of
organizational learning are the development of a
systematic approach to problem solving to find out
what work can and cannot be done, the development
of the ability to think of things beyond
circumstances, the development of personal abilities,
the dissemination of knowledge and information in
organization, and elaboration of organizational vision
(Hodge, Anthony and Gales, 1996). The purpose of
organizational learning is to successfully adapt to
ever-changing environment, to adapt to uncertain
conditions, and to improve efficiency (Dodgson,
1993).
2.3 Organizational Performance
Wheelen and Hunger (2001) proposed the definition
of organizational performance, that the end result of
activities where selection of measures for
performance appraisal depends on the organizational
unit being assessed and the objectives achieved. The
predetermined purpose in a strategy formulation as
part of strategic management process (related to
profit, marketing audit, and cost reduction) should
be used to measure company performance when the
strategy is being implemented. Performance
indicators are quantitative and qualitative measures
describing the level of predetermined goal or target
achievement by calculating the indicator elements,
such inputs, outputs, outcomes, and impacts
(Wheelan and Hunger, 2004).
Research has proved that the impact of servant
leadership has a positive and significant effect on
organizational learning and therefore has a positive
impact on organizational performance (Choudary,
Akhtar and Zaheer, 2013). Its is also founf found
that organizational learning has a positive and
significant effect on organizational performance
(Kunartinah and Sukoco, 2010; Marlikan, 2011).
Based on the results of previous study, the
hypotheses in this study are as follows:
Hypotheses: Organizational learning mediates
the impact between Servant leadership with
Organization Performance in INASGOC
Figure 1: Research model.
BINUS-JIC 2018 - BINUS Joint International Conference
46
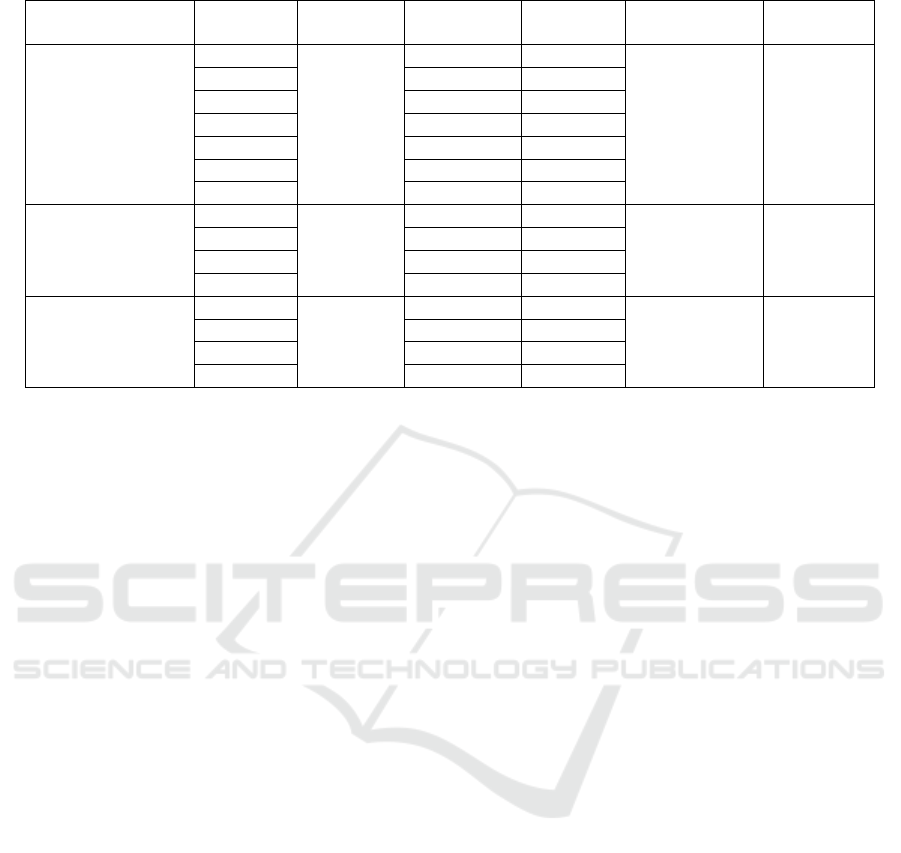
Table 1: Reliability and validity test results.
Variable Item KMO
Factor
Loadin
g
Valid
Cronbach’s
Alpha
Reliability
Servant
Leadership
SL2
0.699
0.592 Valid
0.724 Reliable
SL4 0.602 Valid
SL5 0.724 Valid
SL6 0.796 Valid
SL7 0.634 Valid
SL8 0.691 Valid
SL9 0.808 Valid
Organizational
Learning
OL1
0.689
0.657 Valid
0.742 Reliable
OL2 0.684 Valid
OL3 0.736 Valid
OL4 0.678 Valid
Organizational
Performance
OP1
0.763
0.839 Valid
0.863 Reliable
OP2 0.706 Valid
OP4 0.750 Valid
OP5 0.800 Valid
3 METHODOLOGY
This study is a causal study because it aims to
examine the causal relationship or causality between
servant leadership and organizational learning with
organizational performance. The method used is a
survey by distributing questionnaires to INASGOC
employees. However, interview was also conducted
in building the items for organizational performance
as well as to confirm the survey results. In this
study, the researchers used non-probability sampling
and specifically purposive sampling which means a
person or an object is taken as a sample because the
researchers believe that the person possesses the
information needed for the study (Malhotra, 2007).
Specifically, this study collected samples of the I, II,
and III deputies of INASGOC employees who has a
direct contact with INASGOC's leaders and
deputies, this was intended to obtain samples of
respondents who already have enough experience in
organizing at INASGOC and understand the
leadership style from leaders in this organization.
The sample of each deputy is 50 respondents and the
total respondents are 150 people.
To measure all servant leadership and
organizational learning variables, researchers used
measurements from the results of a study review of
journals which were then summarized by Choudary,
Akhtar and Zaheer (2013) totaling 18 questions.
Organizational performance variables will be
measured by the measurement results that have been
modified by researchers because the context of the
2018 Asian Games implementation has different
success indicators compared to previous studies that
have success indicators of profit oriented
organizations. The question modification process is
carried out by conducting interviews with three
Deputy Heads. In this study, statistical tests that will
be used are multiple regression statistical methods
and mediation analysis on SPSS software (Statistical
Package for the Social Science) 24.0 to perform
primary data processing.
4 FINDINGS
4.1 Reliability and Validity
The researchers distributed questionnaires to 150
respondents divided into 3 deputies which are I, II,
and III deputies in random departments of the
deputies. Table I shows the results of reliability and
validity Main-Test of questionnaire results
distributed to 150 respondents within INASGOC.
Based on Table 3, it can be concluded that the
indicator items that have been determined as reliable
and valid are 15 items, where these items are ready
to be included in the linear regression test. Items that
are reliable and valid from servant leadership are
items SL2, SL4, SL5, SL6, SL7, SL8, SL9, from
organizational learning are OL1, OL2, OL3, OL4,
and from organizational performance are OP1, OP2,
OP4, and OP5.
Servant Leadership in Indonesia Asian Games 2018 Organizing Committee: Its Impact on Organizational Learning and Performance
47

Table 2: Multiple regression test results.
Independent Variable Dependent
Variable
Sig R Square Standardized
Coefficient Beta
Notation
Servant Leadership Organizational
Performance
0.002 0.063 0.250 C
Organizational
Learning
0.000 0.080 0.283 A
Servant Leadership dan
Organizational Learning
Organizational
Performance
0.135 0.295 0.108 c’
0.000 0.503 B
4.2 Multiple Regression
Based on multiple regression test results (Table 2),
no servant leadership impact on organizational
performance was found due to the significance level
of 0.135> 0.05, but there was servant leadership
impact on organizational performance if mediated
by organizational learning with a significance level
of 0.000 from servant leadership on organizational
learning and from organizational learning on
organizational performance.
Furthermore, direct effect c' of 0.108 which is
smaller than c = 0.250 was found which means that
servant leadership impact on organizational
performance is reduced and not significant (p-value
>0.05) after multiple regression tests on all
variables. INASGOC needs the role of strong
organizational learning, as in the OL1 indicator
which has the highest mean value of 4.19 which
indicates INASGOC absorbing and using new and
relevant knowledge that provides competitive
advantage and is explained in OL3 which is the
highest loading factor of 0.736 indicating the
progress of INASGOC which was influenced by the
new study on INASGOC itself. From this, it can be
concluded that without organizational learning,
leaders at INASGOC will find it difficult to
influence organizational performance. As for some
examples of organizational learning that has been
applied by INASGOC, the role of leaders in
providing information and guiding the work of their
employees, this is in accordance with the words of
one of the employees at INASGOC.
“For me there is a lot of organizational learning
that can be gained here, even though this
organization is actually private but we have to
follow government regulations or civil servant style.
The example of learning that we get is that we know
a lot of new things about the procurement of goods
and the bureaucratic process and many others. I
would need two days to explain them all.”
(H, member of Broadcast Department)
This shows that the learning process at
INASGOC must be as comprehensive as possible,
starting with how the leader organizes and
coordinates his employees. This greatly helps
employees to achieve organizational performance
targeted by INASGOC.
5 CONCLUSION
In this study, organizational learning variables fully
mediate a relationship between servant leadership
and organizational performance. This means that
organizational learning fully mediates between
servant leadership style on organizational
performance. In other words, organizational learning
is very influential on the performance of employees
at INASGOC, because INASGOC is a temporary
organization that has new employees and not all
employees are experienced workers, therefore
organizational learning is of great important in this
organization. This study also provides an
opportunity for INASGOC to examine
organizational performance at the 2018 Asian
Games event and to make improvements to the
organization learning process that occurs within the
organization to improve the final performance of the
2018 Asian Games
.
REFERENCES
Barling, J., Weber, T. and Kelloway, E.K. (1996) ‘Effects
of transformational leadership training on attitudinal &
financial outcomes: A field experiment’, Journal of
Applied Psychology, vol. 81, pp. 827-832.
BINUS-JIC 2018 - BINUS Joint International Conference
48

Choudary, A.I., Akhtar, S.A. and Zaheer, A. (2013)
‘Impact of transformational and servant leadership on
organizational performance: a comparative analysis’.
Journal of Business Ethics, vol. 116, pp. 433-440.
Dodgson, M. (1993) Technological Collaboration in
Industry. London: Routledge.
Greenleaf, R. (1977) Servants Leadership: A Journey Into
The Nature Of Ligitimate Power And Greatness. New
York: Paulist Press.
Hodge, B.J., Anthony, W.P. and Gales, L.M. (1996)
Organization Theory: A Strategic Approach. New
Jersey: Simon and Schuster Company.
Hunger, J.D. and Wheelen, T.L. (2001) Essentials of
Strategic Management. 2
nd
Edition. New York:
Prentice Hall.
Kunartinah and Sukoco, F. (2010) ‘Pengaruh Pendidikan
dan pelatihan pembelajaran organisasi terhadap kinerja
dengan kompetensi sebagai mediasi’, Jurnal Bisnis
dan Ekonomi, vol. 17, pp. 74-84.
Lantu, D., Pesiwarissa, E. and Rumahorbo, A. (2007)
Servant Leadership The Ultimate Calling to Fulfill
Your Life’s Greatness. Yogyakarta: Gradien Books.
Malhotra (2007) Marketing Research: An Applied
Orientation. 5th edition. New Jersey: Pearson
Education, Inc.
Marcu, V. and Buhas, S.D. (2014) ‘Sports organizations-
management and science’, Procedia – Social and
Behavioral Sciences, pp. 678 -682.
Marlikan, M. (2011) ‘Pengaruh pembelajaran organisasi
dan motivasi kerja terhadap kinerja karyawan koperasi
syariah’, Jurnal Manajemen Bisnis, vol. 1, pp. 57-64.
McMinn, M.R. (2001) Care For The Soul: Exploring The
Intersection Of Theology And Psychology. Downers
Grove, IL: InterVarsity Press.
Poli, W.I. (2011) Kepemimpinan Stratejik, Pelajaran dari
Yunani Kuno Hingga Bangladesh. Makasar:
Universitas Hasanuddin.
Robbins, S.P. (2006) Perilaku Organisasi. Jakarta: Indeks
Gramedia
Russell, R.F. and Stone, A.G. (2002) ‘A review of servant
leadership attributes: developing a practical model’,
The Leadership & Organization Development Journal,
vol. 23, pp. 145-57.
Senge, P.M. (2006) The Fifth Discipline: The Art and
Practice of the Learning Organization. New York:
DoubledayCurrency.
Taylor, S., Pearse, N. and Louw, L. (2013) ‘Development
of a philosophy and practice of servant leadership
through service opportunity’. 9
th.
European Conference
on Management Leadership and Governance.
Wheelan, T.L. and Hunger, D.J. (2004) Strategic
Management and Business Policy. 9th Edition. New
Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Zaluchu, S. (2011) Kepemimpianan Yesus: Model Servant
Leadership. [Online]. Available at:
http://parokihkytegal.wordpress.com/2011/12/23/kepe
mimpinan-yesusmodelservant-.
Servant Leadership in Indonesia Asian Games 2018 Organizing Committee: Its Impact on Organizational Learning and Performance
49
