
Sales of Life Insurance Products in Indonesia:
InsurTech and Traditional Insurance Agents
Debrina Ferezagia
1
1
Insurance and Actuary Departement, Vocational Education Program, Universitas Indonesia
Keywords: Technology, Insurance, Agent, Competencies
Abstract: This study aims to overview life insurance market development in industry 4.0. It also attempts to examine
the utilization of insurance technology and what competencies must be owned by insurance agents. The
authors collected literature on insurance technology, which is used in Indonesia. Then, the author
interviewed 15 respondents who often use the insurTech application to see what factors influence the
response of the portal. The data found is processed using descriptive statistical methods. Based on the
results, the insurance market has implemented the “4.0”. Insurance sales distribution in Indonesia with the
hybrid method is to combine the internet and face to face. Futuready has a portal with attractive, user-
friendly, complete product sales, whereas the online portal provides complete premium simulation, namely
Cekpremi. Insurance agents are still needed as an intermediary between customers and the insurance
industry. The competencies of insurance agents are knowledgeable of law/regulation, skills in implementing
codes of ethics, knowledge of life insurance, knowledge of products, skills/expertise of marketers, and
personal development. This paper contributes to marketing insurance management. The use of InsurTech in
the insurance marketing process will increase, but currently, InsurTech will not replace the role of the
insurance agent.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today, there are massive changes in the world
industry, as well as in the insurance industry sector.
The industrial revolution 4.0 has an impact on the
sustainability of the consistency of an industry. The
factors that determine changes in the insurance
market are increased risk, technological
development, information asymmetry, changes in
generation and their social norms (Millennial
generation or Y). This generation is the future client
of the insurance company and others. In addition,
technology development (eg Big Data analytics,
Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence,
autonomously controlled technical facilities (cars,
drones), connected sensors) also became the trigger
factors for the need for life insurance market
development (KLAPKIV, Lyubov et al., 2017).
Thus, the insurance industry is required to be able to
survive the industrial revolution 4.0.
In Indonesia, the insurance industry is still not
proliferating. Other countries experience the same
thing. Moaradi (2015) has examined the factors that
have caused the development of the insurance
industry to be difficult, namely at the level of
insurance sales services. One of the factors that
caused the insurance industry to reach the right level
of insurance services became difficult was that the
sales network was inefficient, growth failure was
hampered, and the sales network was a presence in
the insurance market. (Moradi, 2015).
In addition, three main factors cause people to
invest in low self-insurance: namely, the availability
of insurance, insurance features, and behaviour
characteristics of individual agents (Mol, Botzen, &
Blasch, 2018). These factors are a significant
concern for the insurance industry in Indonesia. The
development of the insurance industry, especially in
the marketing system, is focused on two dominant
things: how to market and who the marketer is.
Further, there are technological-supported
innovations in the insurance industry that are
combined with technological finance. This insurance
technology is often referred to as “InsurTechs.” The
advantage is offering more straightforward products
and a more efficient customer experience, which
serves an increasingly evolving generation towards
Ferezagia, D.
Sales of Life Insurance Products in Indonesia: InsurTech and Traditional Insurance Agents.
DOI: 10.5220/0010029700002967
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE 2019) - Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable 4.0 Industry, pages 59-63
ISBN: 978-989-758-530-2; ISSN: 2184-9870
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
59

the millennium generation (Shanique, Manager, &
Ford, 2017).
However, InsurTech has not been able to
develop a stand-alone business model. It still
requires licensed support staff in marketing
insurance. Human capital (Human Capital - HC) of a
company is part of capital intellectual (intellectual
capital) owned by the company, which together with
financial capital (financial capital) can provide
market value (market value) for the company
(Wibawa, 2010). InsurTech, combined with a
marketing agency, is expected to be able to reduce
the weaknesses of insurance technology that has not
been able to stand alone in developing the model.
In Indonesia, an intermediary between insurance
companies and customers is one of them using agent
services to market insurance products. The thing that
is of concern is how to use agent service that is able
to market insurance products appropriately. In
Taiwan, to improve the ethical behaviour of
insurance agents, the Financial Supervisory
Commission (FSC) in Taiwan has issued
“Regulations Governing Insurance Lawyer
Supervision”. Insurance agents fail to comply with
regulations (Tseng, Kang, & Chung, 2010). This
condition is a concern for the insurance industry
agency department to develop human capital.
These insurance agents are workers who are
externalized (i.e., not under company ownership).
Therefore, corporate investment in the loyalty of
agents and agents in serving their companies is very
relevant (Galunic et al., 2019). Therefore, education
and training programs are needed to improve the
knowledge, expertise, and professionalism of agents
in order to have high competence and integrity in
providing the best service to their customers. It has
also been developed a premise that insurance is
“influenced by the public interest,” because it has “a
range of influences and consequences outside and
different from ordinary business in the commercial
world” (Helfand et al.,2017). Strict regulation of this
insurance agent occurs in Indonesia.
In accordance with Minister of Finance
Regulation in Indonesia, Insurance Companies that
conduct marketing through Insurance Agents must
provide continuous education and training to
Insurance Agents in order to be able to carry out
professions with high competence and integrity.
Human capital is an investment asset that varies
significantly between individuals. This investment
shows a significant advantage of insurance (Krebs,
Kuhn, & Wright, 2017). The same thing also
mentions that human resource management is
essential for effective performance and assessment
that will guarantee an increase in employee
performance and sustainability for the achievement
of organizational goals. (Chukwuka & Nwakoby,
2018).
The author further emphasizes that how to
achieve marketing success that synergies between
insurTech and competent agents, both collaborate
very well. InsureTech success depends on wise use
while the success of insurance agents focuses on
higher levels of individual competence (Amodu,
Alege, Oluwatobi, & Ekanem, 2017). So that the
goals of insurance companies to increase profits and
corporate accountability will be fulfilled. (Crick,
Jenkins, & Surminski, 2018).
2 LITERATURE REVIEWS
2.1 Insurance Technology
One of the drivers of socio-economic change, digital
technology plays a significant role. Technology
creates enormous potential for new ways to inform
people (Lee, 2008; Porter and Heppelmann, 2014;
McAfee and Brynjolfsson, 2012). At the same time,
existing IT infrastructure enables new forms of
trade, which can lead to innovation through
platform-based interaction and systemic value
creation (Lusch and Nambisan 2015). This change
provides an opportunity for insurance companies to
enter a new phase of digital insurance (Nicoletti
2016).
The potential of digital technology for innovation
in the insurance industry is quite significant (Eling
and Lehmann, 2018). This potential includes the
implementation of new forms of online marketing
and sales activities (Seitz, 2017). The implications of
digital technology for the insurance industry are
mainly related to online distribution channels
(Garven 2002; Dumm and Hoyt 2003), particularly
concerning their consequences for insurance agents
(Eastman et al. 2002), Kaiser 2002 customer
orientation) and Meyer and Krohm 1999
regulations).
In addition, older data processing systems in
companies are seen primarily as a means of
increasing efficiency, and a new generation of
digital technology is expected to improve market
dynamics and competition. Due to higher
transparency, lower transaction costs and a more
extensive range of online platforms are needed
(Schulte-Noelle 2001; Taylor 2001).
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
60

2.2 Agents Insurance
Related to the success of insurance determined by a
marketer (agent), agents are people, who are bound
by insurance companies who act to find customers,
negotiate policy provisions, and serve policyholders.
In an insurance practice, an agent may be appointed
by the insurer. The assignment can be a half-day or a
full day’s assignment. An agent has to disseminate
the correct information about insurance practices to
explain to the public how important it is to have an
insurance policy, fill out an application form for
people who are interested in buying a policy, in this
case, the agent will explain the policies and terms
and conditions before the buyer signs the application
form. Agents can also help serve payments from
policyholders and maintain good relations between
the perpetrators and policyholders, one of the factors
that influence between service companies and
consumers are the services performed by agents as
part of human resources that offer products directly
to the public or consumers. Without the role of the
agent, the prospect of having difficulty obtains
insurance services. For individual companies, if the
insurance agent does not play an optimal role, sales
productivity will be low (Juwono, 2010).
In an insurance company, a salesperson provides
direct interviews to consumers carried out by an
agent. According to M. Wahyu Prihartono (2010),
agents are the spearhead of the success of achieving
organizational goals. Nowadays, agents are very
instrumental in the current new product offering in
Islamic insurance. Moreover, they provide services
in offering protection services to the financial needs
of both individuals and groups, both health and
property needs. These services are provided to
consumers in order to be successful and satisfying.
This attitude is a commitment to work and is needed
to be always practised consistently. Therefore, the
agent must have knowledge about insurance.
In dealing with prospective policyholders, an
agent is required to be able to maintain trust. The
agent is the one who plays a role in providing
services by bringing the vision and mission in
marketing insurance to the community. This act can
be understood by comparing the problems faced by
consumers in buying insurance policies. Consumers
can receive valuable assistance from agents when
the loss occurs. An agent will help consumers by
providing data regarding losses received and will be
a defender if it turns out the company does not want
to admit the loss. Besides that, agents will be able to
help consumers make overall plans (Juwono, 2010).
3 METHODOLOGY
This research will discuss the hypothesis about the
existence of InsurTech and the competencies that
must be possessed by an insurance agent. To answer
this hypothesis, researchers are looking for
supporting data. The data used in this study comes
from secondary data primary data. Researchers are
looking for information about the existence of
InsurTech in Indonesia. Then the author interviewed
15 users of the insurance market portal to find out
about people’s preferences for the portal.
Descriptive statistics will analyze the data.
Furthermore, the method used is a literature study of
competencies that must be possessed by agents
through sharing relevant information sources and
government regulations.
4 DISCUSSIONS
4.1 InsurTechs
Indonesia, there is a real opportunity for innovative
technology to shape the future of emerging
insurance markets in the region. As markets become
globalized, individual capabilities or functions in the
value chain (i.e. the modular economy) are
becoming increasingly portable between markets.
Any InsurTech predicated upon a solution-driven
business model supported by product, geographic
and financial agnosticism is likely to be replicable in
other markets. While Emerging Asia may be in its
early stages of growth and development, the region
has effectively served as an incubator for Insurance
Technology that ultimately ends up transforming
more developed markets currently controlled by
traditional incumbents. Distribution in Indonesia
markets and relatively low demand for cover have
prevented the penetration of innovative products in
many markets. The proliferation of hand-held smart
technology and digital awareness among consumers,
coupled with increased demand, however, has begun
to change the landscape.
Online insurance product selling portal in
Indonesia, namely Cermati, Asuransi88.com,
Cekpremi, Futuready, DuitPintar.com, Pasarpolis,
Premiro, RajaPremi. Tokopedia insurance, Cekaja,
PasarPolis, RajaPremi, aturDuit. The researcher
interviewed 15 respondents to compare the four best
online stores in Indonesia, namely Asuransi88,
Tokopedia Insurance, CheckPrime, and Futuready.
Factors that influence online sales include attractive
Sales of Life Insurance Products in Indonesia: InsurTech and Traditional Insurance Agents
61
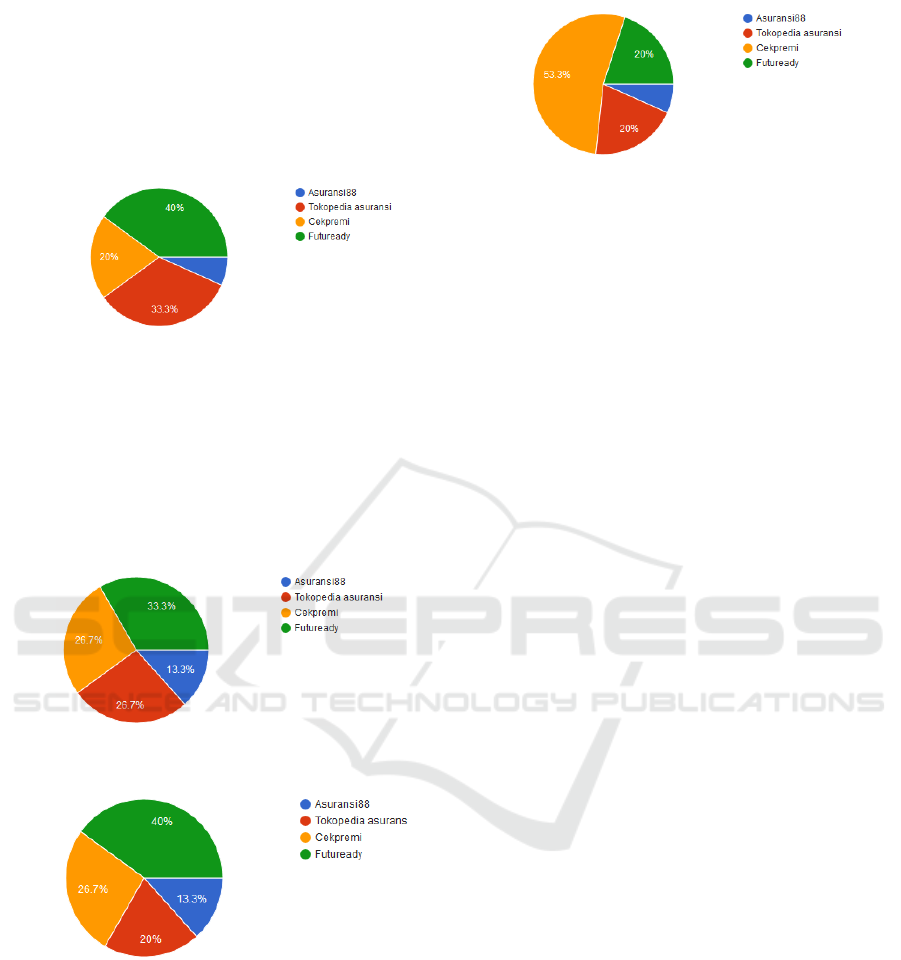
appearance, user-friendliness, the complete product
information, and explicit premium simulations.
Based on interviews, 40% of respondents liked
Futuready as a provider of online insurance products
with the most attractive portal display, while the
portal that had an unattractive appearance was
Asuransi88.
Figure 1: The most interesting appearance.
Based on the results of interviews, user-friendly
information is one of the factors that affect the sale
of a product through the web. As many as 33.3% of
respondents answered Futuready as a portal with
easy use of features. Likewise, the complete product
information, available at Futuready, with the results
of interviews of 40% of respondents
Figure 2: User-Friendly.
Figure 3: The complete product information.
This result is different from the previous results
that FutureReady is very popular. This finding is
different from the results of interviews about
premium simulations. Of the four insurance portals,
Cekpremi has a premium summarization feature
from various insurance companies. Prospective
buyers of insurance products can compare premium
prices from various insurance companies, so that
prospective buyer can make their choices easily and
quickly.
Figure 4: Displaying premium simulations.
4.2 Competencies of Agents
The task of the Agency Department is essential to
maintain the quality of an insurance agent, such as
maintaining the quality of education and training. In
addition, an insurance agent is also required to be
skilled, intelligent, competitive and have high
business ethics. Moreover, do not forget to serve
with heart, understand life insurance products that
are needed most by their customers and master the
techniques / good marketing cycle. This service is
part of the attitude of professionalism to be better
prepared in facing free-market competition. For this
reason, education and training programs are needed
to increase the knowledge, expertise, and
professionalism of agents to have high competence
and integrity in providing the best service to their
customers. The attitude from insurance agents is also
a consideration of customers in purchasing a
product. Therefore, it can be concluded that the
competencies that need to be owned by an insurance
agent are knowledge, skills, and Personal
Development.
The knowledge that must be known by agents
including Product Knowledge, Customer Protection,
Know Your Customer / KYC, Laundering / AML
Anti Money, Law / Regulation on Insurance,
Knowledge of Insurance Law, Knowledge of
Investment Law, Underwriting, Claims, Investment.
Skills that an agent needs to have are Techniques for
Prospecting; identifying, selecting & approaching
the prospect, Closing Sales, Techniques for
exploring personal market strategy and selling,
Services after sales; long term relationship with
customer, Leadership, Effective communication.
Personal Development that must be owned by an
agent is the way to behave/speak/ dress, Personality,
Agency Code of Ethics.
In accordance with Minister of Finance
Regulation (PMK) No. 152 of 2012 Article 67a and
Financial Services Authority Regulation (POJK) No.
2 of 2014 Article 74 that, Insurance Companies that
conduct marketing through Insurance Agents, must
provide continuous education and training to
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
62

Insurance Agents in order to be able to carry out
professions with high competence and integrity.
SE No. 267 / AAJI / 2015 dated 17 December
2015 concerning the Implementation of the CPD
Program. The CPD program is an ongoing education
and training program. The aim is to increase the
knowledge and expertise/skills of the
agents/marketers so that they can carry out their
profession with high competence and integrity, and
can provide the best service to their customers.
The Indonesian Life Insurance Association
(AAJI) continues to strive to maintain public trust by
recruiting highly qualified and licensed marketing
personnel. Head of AAJI Communication
Department Nini Sumohandoyo said that the number
of licensed life insurance marketers in the first
quarter of 2019 increased 0.4% to 595,192 people,
compared to 592,913 people in the previous year, of
which 90.3% of the marketers came from channels
agency.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the study, it can be stated that
insurance marketing in Indonesia is done online and
face to face. Online insurance product selling portal
in Indonesia, namely Cermati, Asuransi88.com,
Cekpremi, Futuready, DuitPintar.com, Pasarpolis,
Premiro, RajaPremi. Tokopedia insurance, Cekaja,
PasarPolis, RajaPremi, aturDuit. Futuready has a
portal with attractive, user-friendly, complete
product sales. Whereas the online portal provides
complete premium simulation, namely Cekpremi.
Insurance sales are not only done online, but an
agent is still needed. This is because life insurance
products are personal and more complex compared
to insurance. Competencies that must be possessed
by an agent can be grouped in knowledge, skills, and
Personal Development.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The researcher thanked the Insurance laboratory,
Vocational Education Program for their support in
completing this paper.
REFERENCES
KLAPKIV, Lyubov et all. 2017. Technological
innovations in the insurance industry. Journal of
Insurance, Financial Markets & Consumer Protection
No. 26 (4/2017). rf.gov.pl/join/wp-
content/uploads/2018/01/RU26-5.pdf
Shanique, B., Manager, C., & Ford, H. (2017). By
Shanique (Nikki) Hall, CIPR Manager, (March), 22–
28.
Moradi, M. (2015). Examining of Life Insurance
Improvement and Marketing : A Case Study in Iranian
Insurance Industry, 2(9), 258–266.
Krebs, T., Kuhn, M., & Wright, M. (2017). Review of
Economic Dynamics Under-insurance in human
capital models with limited. Review of Economic
Dynamics, 25, 121–150.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.red.2017.02.008
Chukwuka, E. J., & Nwakoby, N. P. (2018). Effect of
Human Resource Management Practices on Employee
Retention and Performance in Nigerian Insurance
Industry, (April).
Wibawa, Brata. 2010. Mengukur Kontribusi Human
capital terhadap tujuan perusahaan. Binus Business
Review.
journal.binus.ac.id/index.php/BBR/article/download/1
084/951
Helfand, B. R. D., Bagley, C., Ballen, R. G., Ballon, I. C.,
Barry, H. V, Baumgarten, J. A., Connor, M. O. (2017).
JO U R N A L O F Executive Managing Editor.
Amodu, L., Alege, P., Oluwatobi, S., & Ekanem, T.
(2017). The Effect of Human Capital Development on
Employees ’ Attitude to Work in Insurance Industry in
Nigeria, 2017. https://doi.org/10.5171/2017
Tseng, L., Kang, Y., & Chung, C. (2010). The insurance
agents ’ intention to make inappropriate product
recommendations Some observations from Taiwan
life. https://doi.org/10.1108/JFRC-03-2015-0014
Crick, F., Jenkins, K., & Surminski, S. (2018). Science of
the Total Environment Strengthening insurance
partnerships in the face of climate change – Insights
from an agent-based model of flood insurance in the
UK. Science of the Total Environment, 636, 192–204.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.239
Mol, J. M., Botzen, W. J. W., & Blasch, J. E. (2018).
Behavioral motivations for self-insurance under
different disaster risk insurance schemes. Journal of
Economic Behavior and Organization.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2018.12.007
Galunic, D. C., Anderson, E., Science, S. O., Feb, N. J.,
Galunic, D. C., & Anderson, E. (2019). From Security
to Mobility : Generalized Investments in Human
Capital and Agent Commitment From Security to
Mobility : Generalized Investments in Human Capital
and Agent Commitment, 11(1), 1–20.
Juwono, Stephen B. 2010. Agen Asuransi Wajib Ikut
Lisensi Lanjutan.
https://keuangan.kontan.co.id/news/agen-asuransi-
wajib-ikut-lisensi-lanjutan. Diakses 12 November
2018.
Sales of Life Insurance Products in Indonesia: InsurTech and Traditional Insurance Agents
63
