
The Influence of Monetary Instrument toward Money Demand M2
under Dual Banking System in Indonesia Period 2015-2018
Imam Haryadi and Vinny Kurniati
Islamic Economics Department, Faculty of Economics and Management, University of Darussalam Gontor, Indonesia
Keyword: Dual Banking System, Monetary Instruments.
Abstract: Money demand holds an important role in monetary policy’s behaviour in overall economic activities.
Moreover, Bank Indonesia use monetary instrument which transform to dual banking system. This research
has purpose to analyze the influence of monetary instruments toward money demand M2 under dual banking
system and to know the monetary instrument more stable and faster in influencing money demand M2 under
dual banking system. The data used in this research was secondary data earned from Indonesia Banking
Statistics (SPI), Sharia Banking Statistics (SPS), Indonesian Financial Statistic (SEKI) and Financial Service
Authority (OJK). using the time series data from January 2015 till December 2018. In order to achieve the
purpose, this research used Vector Autoregression/Vector Error Correction Model. The research concluded
that the influence of monetary instruments toward M2 under dual banking system are significant. Based on
VECM result, conclude that Islamic monetary instruments are more significant influenced than conventional
one toward M2. based on IRF result, conventional monetary instrument more stable and faster than Islamic
monetary instrument which FASBI and SRR more stable and faster than FASBIS and SRRISL in influencing
money demand M2. But, SBIS is more stable and faster than SBI to influence Islamic M2 and increase
economic growth.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to the law No. 10 1998 Indonesia has
operating dual banking system. It is due to the fact
that monetary policy has practiced dual system which
monetary stability be the same purpose of them and
become the most important targets. There are the
different principle of taking profit between dual
banking system, distribution of fund in conventional
bank based on interest rates. On the contrary, Islamic
bank did not based on interest rate for taking the
profit.
In addition, the inflation would give the effect in
reducing effectiveness monetary policy especially,
for influencing money demand
, money instability and
purchasing power of money. Moreover, this
decreasing, would effect to demand for holding
money or saving money. Conceptually, the inflation
volatility is the result one of the highest growth of
money supply.
Whereas, Bank Indonesia as monetary authority,
maintain the money stability by optimizing monetary
operation in money market and strengthen the
monetary policy by stabilizing monetary instrument
in financial system. Commonly, there are the
monetary instruments through conventional banking
system such as Open Market Operation (OMO),
discount rate and reserve requirement. While, Islamic
banking system, bank Indonesia used reserve
requirement (SRR), Open Market Operations and
Standing Facilities.
The different concept between Islamic bank and
conventional bank for getting the profits which
influence the money demand M2 under dual banking
system. Then, this paper will compare the monetary
instruments in every bank.
Actually, those instruments are influenced by
interest rate and interest rate negatively correlated to
the money demand and income positively correlated
against money demand. This describes that the
influence of interest rate, because the Government
conducts the monetary contraction, interest rate will
be raised which cause increasing on monetary
instruments such as SBI, FASBI and SRR. From here
the Government wants to decrease money demand
and money supply in the community. It will slow the
economic growth.
46
Haryadi, I. and Kurniati, V.
The Influence of Monetary Instrument toward Money Demand M2 under Dual Banking System in Indonesia Period 2015-2018.
DOI: 10.5220/0010114600002898
In Proceedings of the 7th ASEAN Universities International Conference on Islamic Finance (7th AICIF 2019) - Revival of Islamic Social Finance to Strengthen Economic Development Towards
a Global Industrial Revolution, pages 46-51
ISBN: 978-989-758-473-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

The Islamic financial system operates PLS system
in executing monetary operation. Islamic monetary
instruments are not different as conventional
monetary instrument, but Islamic financial system use
SBIS and FASBIS which have several differences to
SBI and FASBI. Hence, the researcher specifies the
following research model:
Md = f (SRR, SBI, FASBI) (1)
MdISL = f (SRR, SBIS, FASBIS) (2)
The differences between the two models is
opportunity cost variable in holding money for each
model. Opportunity cost for conventional M2 model
is the interest rate and for Islamic M2 model is the
return sharia (Figure 1).
Discount rate and moral suasion is not discussed
in this research. The researcher using instruments
OMO (Open Market Operation) SRR, FASBI and
FASBIS
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Monetary instruments is Bank Indonesia instruments
which have influenced to the operational target in a
direct or indirect target. These instruments used by
Bank Indonesia through monetary instruments to
change profit-sharing ratio and the high currency
value through SBI and other securities transaction
(Daisy, 2010). There are other monetary instrument
such as open market operation, reserve requirement,
discount facility dan moral suasion.
From these several monetary instruments,
Ascarya (2002) differ into three types: 1) According
to operational target, divided into direct and indirect
instrument, 2) According to orientation in financial
market, divided into market oriented and non-market
oriented, 3) According to discretion. Generally, the
direct instrument is a non-market oriented and the
discretion in central bank as monetary authority.
While indirect instrument is a market oriented or a
non-market oriented and discretion in central bank.
different
from the characteristics of the system of
Figure 1: Theoretical Framework.
revenue sharing. Interest rates may be determined at
any time by the banking authorities and its nominal
movement can be seen by the public.
Meanwhile, Hasanah et.al (2008) explains that the
characteristics of the system of interest is very
Thus, its movement can lead to speculative
activities. In contrast, the nisbah is set and its value
remains valid throughout the contract. Meanwhile,
the returns will follow the actual business. In a profit-
sharing system (sharia return), profits will be shared
as well as the loss will also be shared. Therefore,
profit-sharing system will ensure the fairness and
neither party will be harmed. In Islamic banking,
profit-sharing system can be shaped as wadha
contract, musharaka, mudharaba.
Moreover, Ahmad Kaleem explains the demand
for Islamic monetary instruments in
case of dual banking system. It also demonstrates the
validity and effectiveness of these instruments for
monetary policy purposes. Apart from this Islamic
bank is also not allowed to issue securities involving
interest like long and short-term bonds, debentures
and preference shares. Currently, Islamic banks on its
liability side of their balance sheet are based on four
main sources of funds. This includes shareholder’s
funds, current, saving and investment accounts.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This study used quantitative and comparative
research. Other side, this research used the time series
data, then it would cause the data not stationer which
show the failure in forecasting economy. This
condition called by spurious correlation which cause
to false regression. So, the problem solving is Vector
Auto Regression (VAR)/Vector Error Correction
Model (VECM).
Where in the VAR model all variables are treated
as endogenous variables. Then the VAR equation
model for conventional monetary instruments can be
written as follows:
(3)
Then, if the data are stationary at first difference
and having one co-integration, the next process is
performed using the error correction method. Then
the VECM equation model for conventional
monetary instruments can be written as follows:
The Influence of Monetary Instrument toward Money Demand M2 under Dual Banking System in Indonesia Period 2015-2018
47
(4)
While, VAR equation model for Islamic monetary
instruments can be written as follows:
(5)
Because the data is stationary at frist difference
between variables and there are co-integration among
VAR models and the test will continue to VECM
models. VECM equation model for Islamic monetary
instrument can be written as follows:
(6)
4 RESULT DISCUSSION
4.1 Unit Root Test and Co-integration
Test
This method used to perform stationary test data
using ADF test by 5% significance level. On the
contrary, when the probability t-statistic higher than
5% significance level, it would conclude non
stationary data. Roots unit test is done at the level
until the first difference level.
The all variables are
not supposed to be stationary at the level. Therefore,
unit root test needs to be continued on the first
difference level (Table 1).
Table 1: Summary of Root Test.
From information above, it can be concluded that
all variables have the same order of integration or it
is called as co-integration. Co-integration among
variables show based on trace method, see from a
trace-statistic value greater than the critical value
which indicated there are co-integration on the model.
Based on co-integration test, shows that there is at
least one co-integration on a 5% significance level.
Conventional M2 and Islamic M2 both have one co-
integration (Table 2).
Table 2: Co-integration Test.
4.2 VECM Estimation
After the co-integration test, it is known that M2
model and M2ISL model have the co-integration,
then it can be extended to the VECM phase. At this
step, the result of VECM will be used to determine
the long-term and short-term relationships between
variables of research. The variable is called
significant in influencing other variables when the
value of t-statistics higher than t-table on rank 1.96 (t
statistic > 1.96) (Table 3).
Table 3: Summary of VECM Estimation.
Based on the VECM results, in the conventional
model there is an error term amount 0.277016 and
shows that the error need to be corrected by the model
27%. The adjustment required to reach the stability
condition (1/0.277016) is 3 months. While, in Islamic
model there are an error term amount 0.075989 and
show that the error needs to correct by the model 7%.
The adjustment required to reach the stability
condition (1/0.075989) is 13 months. From this
explanation, conclude that the Islamic model need
more times than conventional.
While, money demand M2 conventional in the
long term showed the significant correlation between
variables. SBI had negatively correlated toward
conventional M2 with coefficient -0.067994, which
means increasing SBI by one per cent would trigger
the decline to M2 by -0.067994 per cent. On the
Test
ADF Prob ADF Prob
M2 -0.347276 0.9093 -7.746453
0.0000
Stationary
M2ISL -0.442398 0.892 -3.0059
0.0427
Stationary
SBI -1.59791 0.4755 -4.251412
0.0015
Stationary
SBIS -1.577392 0.4859 -5.0871
0.0001
Stationary
FASBI -2.003262 0.2844 -9.429407
0.0000
Stationary
FASBIS -2.619637 0.0962 -6.557681
0.0000
Stationary
SRR -1.32294 0.6113 -8.280907
0.0000
Stationary
SRRISL -1.13741 0.6932 -7.922341
0.0000
Stationary
Augmented Dickey-Fuller
VARIABLES
Level first difference
Note
None * 68.73692 0.0002 None * 49.28524 0.0365
At most 1 29.35191 0.0562 At most 1 9.415262 0.9876
At most 2 10.55512 0.2404 At most 2 3.507152 0.9392
At most 3 1.308699 0.2526 At most 3 0.080677 0.7764
M2IS L M2
Hypothesized No.
Of CE(s)
Trace
Stat istic
Prob.**
Hypothesized No.
Of CE(s)
Trace
Stat istic
Prob.**
Variables Coefficient T-Statistic Variables Coefficient T-Statistic
SBI -0.067994
-2.40326
SBIS 0.072545
2.77159
FASBI 1.003219
4.50062
FASBIS 0.079495
2.92258
SRR -1.442787
-2.70387
SRRISL -0.637239
-25.9177
CointEq1 -0.277016 -3.07945 CointEq1 -0.075989 -0.48727
D(M 2(-1)) -0.418997
-2.23523
D(M 2ISL(-1)) -0.399005 -1.88453
D(M 2(-2)) -0.201427 -1.14298 D(M2ISL(-2)) -0.16707 -0.91693
D(SBI(-1)) 0.001279 0.1116 D(SBIS(-1)) -0.092833 -1.43093
D(SBI(-2)) 0.012795 1.18346 D(SBIS(-2)) 0.083996 1.34172
D(FASBI(-1)) 0.019478 1.63439 D(FASBIS(-1)) -0.019796 -0.74899
D(FASBI(-2)) -0.001664 -0.17272 D(FASBIS(-2)) -0.024069 -0.96362
D(SRR(-1)) -0.042317 -0.61071 D(SRRISL(-1)) -0.156775 -1.62165
D(SRR(-2)) 0.070875 1.0195 D(SRRISL(-2)) -0.056821 -0.66523
LO NG TERM
SHORT TERM
LO NG TERM
SHORT TERM
7th AICIF 2019 - ASEAN Universities Conference on Islamic Finance
48

contrary, SBIS had positive influence on Islamic M2
Islam with t coefficient of 0.072545, which means
when SBIS increased by one per cent it will trigger an
increase in Islamic M2 by 0.072545 per cent.
Moreover, FASBI had a significant impact of
conventional M2 with the coefficient 1.003219,
which means when FASBI increased by one per cent,
it would trigger the increase of conventional M2 by
1.003219 per cent. While, FASBIS had positive
correlated on Islamic M2 with coefficient of
0.079495, which means when FASBIS increased by
one per cent it will trigger increase in Islamic M2 by
0.079495 per cent.
Whereas, SRR variable in conventional banking
had negatively correlated toward conventional M2
with coefficient -1.442787 per cent, which means
when SRR increased by one per cent, it would trigger
a decline in conventional M2 by -1.442787 per cent.
Moreover, SRRISL negatively correlated to Islamic
M2 by coefficient -0.637239, which means when the
level SRRISL increases by one per cent it will trigger
a decrease on Islamic M2 of -0.637239 per cent.
4.3 Impluse Response Function
Impluse Response Function shows the conventional
M2 responded to shocks from other variables. The
shocks of SRR variables have positively responded
by conventional M2 for overall of the forecast. In the
third period, the shocks of SRR for one standard
deviation led an increase of conventional M2 for
0.000983 standard deviations, but this is not
permanent because the decline continued during the
fourth period until the ten a period. Those responses
began to stable from the tenth period to until the end
of the forecast.
On the contrary, the shock of FASBI has
negatively responded by conventional M2 for overall
the forecast. Shocks of FASBI for one standard
deviation will trigger a decline conventional M2 by -
0.002273 standard deviations, but this is not
permanent because it has increased in the fifth period
until ninth period. The repons of conventional M2
began to stable in eleventh period which is indicated
by the coefficient of -0.00108 standard deviations.
While, the shock of SBI has positively responded
by conventional M2 for the overall forecast. On the
fourth period, the shock of SBI for one standard
deviation will trigger an increase the conventional M2
by 0.000451 standard deviation. Increasing of
conventional M2 responce has occurred from the fifth
period until the ninth period and getting stable in the
fourteenth period and indicated by 0.000847 until the
end of the forecast (Figure 2).
Figure 2: IRF of Conventional M2 Model.
Moreover, Impluse Response Function for
Islamic model is Uneven. the second period until the
end of forecast Islamic M2 has negatively responded
to a shock from SRRISL variables. The shock of
SRRISL for one standard deviation can lower Islamic
M2 by -0.0018 standard deviation, but this did not
happen continuously because Islamic M2 has
positively responded in the next period. In the sixth
period shocks of SRRISL for one standard deviation
would an increase Islamic M2 by 0.0047 and will be
stable in twentieth period.
Meanwhile, the Islamic M2 had negatively
responded to shocks of FASBIS variable for the
overall forecast. In the third period, the shock of
FASBIS for one standard deviation led to decrease
the Islamic M2 by -0.0047 standard deviation. But
this is not permanent because it would increase until
the eighth period. The response would be stable from
the fifteenth period until the end of the forecast.
Moreover, Islamic M2 variable had positively
responded to the shock of SBIS variable in the first
period until the fourth period. The shock of SBIS for
one standard deviation would trigger an increase in
Islamic M2 to 0.0013 standard deviations. But this is
not permanent because the next period Islamic M2
had negatively responded until the end of the forecast.
The shock of SBIS in the fifth period for one standard
deviation would trigger a reduce the Islamic M2 by -
0.0004 standard deviations and would be stable in
twelve period (Figure 3)
Figure 3: IRF of Islamic M2 Model.
-0,0030
-0,0020
-0,0010
0,0000
0,0010
0,0020
1
8
15
22
29
36
43
50
57
64
71
78
85
92
99
SBI SRR FASBI
-0,0100
-0,0050
0,0000
0,0050
0,0100
1
7
13
19
25
31
37
43
49
55
61
67
73
79
85
91
97
SBIS SRRISL FASBIS
The Influence of Monetary Instrument toward Money Demand M2 under Dual Banking System in Indonesia Period 2015-2018
49
4.4 Forecasting Error Variance
Decomposition
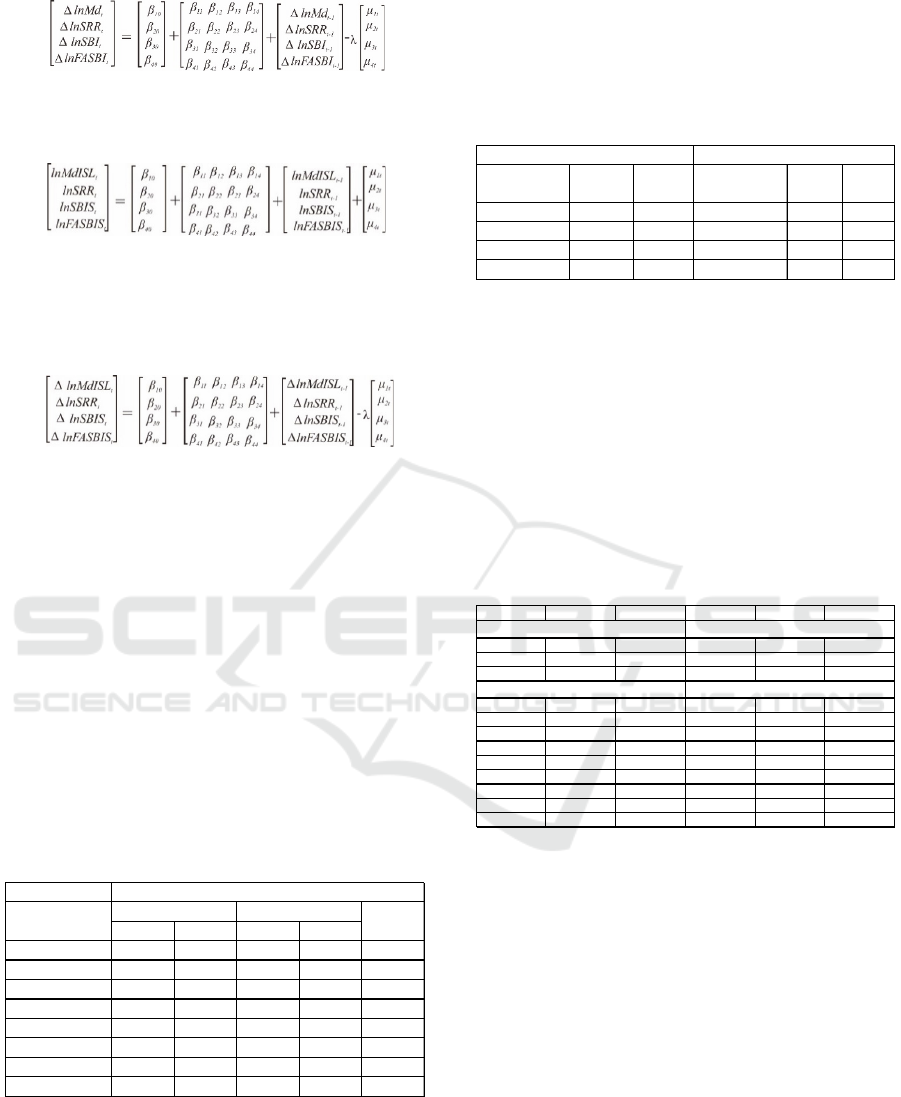
The conventional M2 model on the first period was
influenced by conventional M2 variable itself by 100
per cent. Meanwhile, the effect of variable
conventional M2 decreased to 58.96 per cent in 100
th
period. The results of FEVD indicate the information
that conventional M2 can be explained by variables
SRR, FASBI and SBI by 0.00 per cent in the first
period.
Furthermore, conventional M2 can be explained
by the variable SRR by 4.92 per cent in 100
th
period.
This show that SRR has the smallest influence and
contribution to the conventional M2. Results of
FEVD provides information that SBI had influenced
by 14.11 per cent in the 100
th
period. While the
influence of FASBI amounted 21.99 per cent in the
100
th
period. Meanwhile, FASBI has significant
influence and contributing to the conventional M2
(Figure 4).
Figure 4: Forecasting Error Variance Decomposition of
Conventional M2 Model.
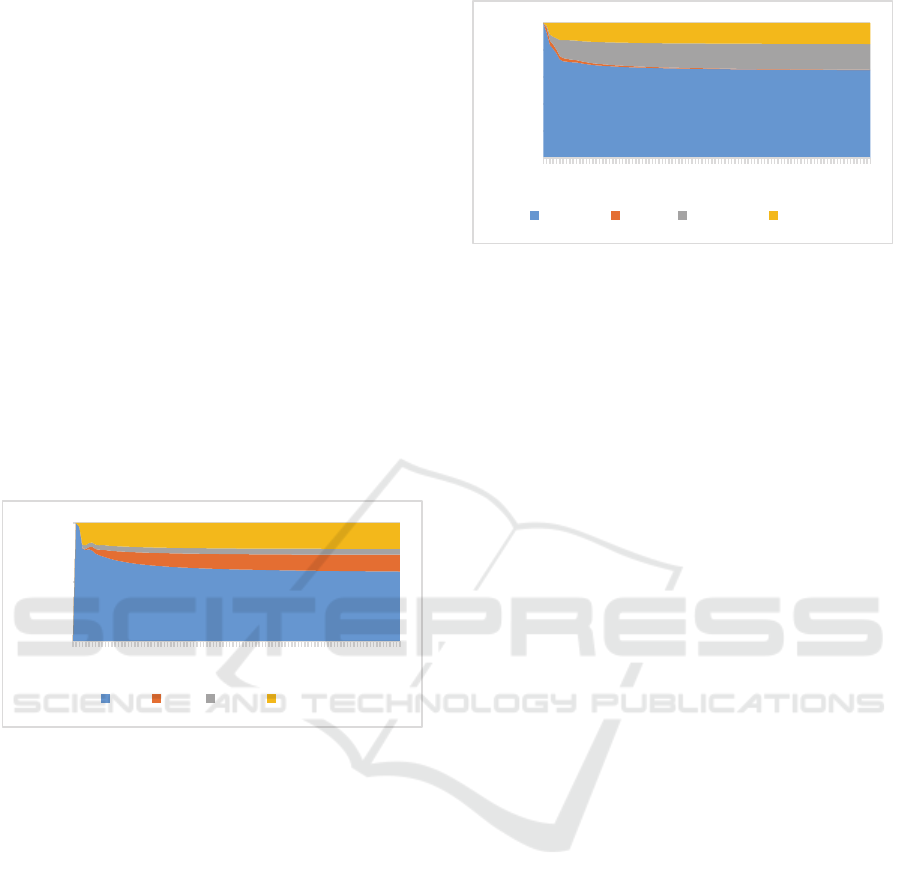
Moreover, FEVD for Islamic M2 in the first
period was affected by Islamic M2 itself by 100 per
cent. However the influence of Islamic M2 decreased
to 65.12 per cent in the 100
th
period. Furthermore,
from results FEVD it can be seen that the information
could be explained by the Islamic M2 such as
SRRISL, FASBIS and SBIS with 0.00 per cent in the
first period.
Furthermore, Islamic M2 can be explained by the
variable SBIS with 0.27 per cent in the 100
th
period.
In addition, the results of FEVD provide information
that FASBIS influenced by 15.61 per cent during the
100
th
period. while SRRISL was influenced by 18.98
per cent in the 100
th
period. This indicates that the
variable SRRISL has higher influence and
contribution to the Islamic M2 (Figure 5).
Figure 5: Forecasting Error Variance Decomposition of
Islamic M2 Model.
5 CONCLUSSION
Some the goals of this research are as follow, first, to
analyze empirically the influence of monetary
instrument toward M2 under dual banking system.
Second, to know which one monetary instrument
more stable and quicker in influencing M2 under dual
banking system
Empirically, the influence of monetary
instruments toward M2 under dual banking system
are significant. Based on VECM result, it can be
concluded that Islamic monetary instruments has
more significant influence than conventional one
toward money demand M2. This reality is the result
of the prohibition of interest rate in the Islamic
financial system. On the contrary, the conventional
financial system used interest rate channel and that
cause the negative impact and economic instability.
Based on the IRF result, the conventional
monetary instrument more stable and faster than
Islamic monetary instrument which FASBI and SRR
more stable and faster than FASBIS and SRRISL in
influencing money demand M2. But, SBIS is more
stable and faster than SBI. The shock of SBIS will be
responded negatively by Islamic M2 in 12
th
period.
While, SBI will responded positively by conventional
M2 and stable in 14
th
period. SBI will increase
inflation and shock while SBIS will decrease inflation
but increase economic growth.
REFERENCES
Ascarya, 2002. Monetary Policy Transmission Mechanism
Under Dual Financial System In Indonesia: Interest-
Profit Channel. International Journal of Economics,
Management and Accounting 22, No. 1
Daisy, Ebrinda. 2008, Analisis Pengaruh Social Values
Terhadap Permintaan Uang Islam di Indonesia, Skripsi
0%
50%
100%
1
8
15
22
29
36
43
50
57
64
71
78
85
92
99
M2 SBI SRR FASBI
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
100%
1
8
15
22
29
36
43
50
57
64
71
78
85
92
99
M2ISL SBIS SRRISL FASBIS
7th AICIF 2019 - ASEAN Universities Conference on Islamic Finance
50

Fakultas Ekonom dan Mabagement, Institut Pertanian
Bogor
Hasanah, Heni. 2008. Demand For Money And Monetary
Stability Under Dual Financial System In Indonesia.
Third Islamic Banking, Accounting and Finance
Conference. Malaysia
Kaleem, Ahmad. Modeling Monetary Stability Under Dual
Banking System: The Case of Malaysia. International
Journal of Islamic Financial Services, Vol. 2 No. 1
The Influence of Monetary Instrument toward Money Demand M2 under Dual Banking System in Indonesia Period 2015-2018
51
