
Differences of Islamic Bank Performance based on
Establishment Method: Evidence from Indonesia
Sylva Alif Rusmita
*
, Faralaily Erika Widijanto Putri, Noven Suprayogi,
and Vicky Vendy
Department of Islamic Economics, Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Airlangga,
Indonesia
Abstract. A spin-off is required when a conventional bank has a UUS that has a
minimum asset value of 50% of the total value of the parent's assets. This
readiness is measured through company performance, such as performance. This
research becomes important to prove from various kinds of establishment which
gives the best performance. The results of this study can be taken into
consideration for banks before making the move to BUS rather the company
performance is maintained and has sustainable growth. The results of this study
are of the three policies proved that the establishment method has differences,
with further tests that the BUS with the method of acquisition and merger has
better efficiency and capital adequacy compared to other methods. While
liquidity and profitability is better to use a conversion method.
Keyword: Establishment Method
∙Efficiency∙Capital Adequacy∙ Liquidity∙
Profitability
1 Introduction
Islamic banking plays an important role in economic activities. The beginning of known
Islamic banks in Indonesia is since the establishment of Bank MuamalatIndonesia in
1991. At the beginning of its establishment, the existence of Bank MuamalatIndonesia
has not received optimal attention in the national banking industry order (Antonio M.
S., 2001). According to Nuzuliah (2014), the rapid development of Islamic banking in
Indonesia was triggered by a change in Law Number 7 of 1992 concerning banking to
Law Number 10 of 1998 which allows banks to implement a dual banking system.
Conventional banks that dominate the market begin to look and open Islamic business
units. Based on this law, it is permissible to allow conventional banks to open sharia
branches or even convert themselves into banks with sharia principles in total. The birth
of the Sharia Banking Law pushed the number of BUS in 2009 to 2010 from five BUS
to 11 BUS in less than two years (Otoritas Jasa Keuangan, 2010). In 2010 to September
2018, the BUS only increased by three to 14.
Rusmita, S., Putri, F., Suprayogi, N. and Vendy, V.
Differences of Islamic Bank Performance based on Establishment Method: Evidence from Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0010598800002900
In Proceedings of the 20th Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics, Management and Accounting (MIICEMA 2019), pages 823-837
ISBN: 978-989-758-582-1; ISSN: 2655-9064
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
823

Table 1. List of Islamic Bank Establishments in Indonesia in 2018.
Bank Umum Syariah (BUS) The process of establishment
PT. Bank Aceh S
y
ariah Conversion PT Bank Aceh
PT. BPD Nusa Ten
gg
ara Bara
t
Conversion BPD NTB
PT. Bank Muamalat Indonesia Pure S
y
ariah
PT. Bank Victoria Syariah Conversion Bank Swaguna by Bank
Victoria
PT. Bank BRI S
y
ariah Acquisition Bank Jasa Artha b
y
Bank BRI
PT. Bank Jabar Banten S
y
ariah Spin off
PT. Bank BNI S
y
ariah Spin off
PT. Bank Syariah Mandiri Conversion Bank Susila Bakti by Bank
Mandiri
PT. Bank Mega Syariah Conversion Bank Umum Tugu by Bank
Me
g
a
PT. Bank Panin Dubai S
y
ariah spin off
PT. Bank Syariah Bukopin Acquisition Bank Perserikatan Indonesia
by
Bukopin
PT. BCA S
y
ariah Acquisition Bank UIB oleh BCA
PT. Bank Tabungan Pensiunan
N
asional S
y
ariah
Acquisition Bank Sahabat Purbadanarta by
BTPN
PT. Maybank Syariah Indonesia Joint Venture Maybank with Nusa
N
asional
Sumber: (Otoritas Jasa Keuangan, 2018)
UUS growth is less than the maximum compared to BUS growth. In accordance with
the Banking Law, spin off obligations must be planned and discussed in the Sharia
Division more seriously (Rustam, 2012). According to Rustam (2012), there are many
factors that cause UUS to develop less than the maximum. Some of these are inefficient
UUS operations, lack of product features developed by UUS, many UUS head office
policies that are less conducive, synergy with parents that are far from expectations,
and unsupportive working relationships. Under these conditions, the choice of spin off
must be prepared early by conventional banks. This spin off is expected to bring UUS
to become more independent and focused. Changes in conventional bank business
activities to Islamic banks have been regulated in Bank Indonesia Regulation Number
11/15 / PBI / 2009 concerning Changes in Conventional Bank Business Activities to
Sharia Banks (Bank Indonesia, 2007).
A spin-off is required when a conventional bank has a UUS that has a minimum
asset value of 50% of the total value of the parent's assets. This also applies to all UUS,
15 years after Law Number 21 Year 2008 was passed (until 2023). The provisions of
Article 68 indicate that a UUS which still has a conventional parent is ready to separate
from its parent, and become a sharia business entity. This readiness is measured through
company performance, such as financial performance and can be seen in terms of fixed
assets, third party funds, and five financial ratios, namely liquidity ratios measured by
NPF and FDR ratios, solvency ratios measured by CAR, rentability ratios measured
using ROA, and operational efficiency ratios measured using OER (Kasmir, 2008). The
effectiveness and efficiency of the company's activities are displayed in the financial
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
824

statements, and the company's goal to achieve optimal profit levels reflects the
performance of Islamic banks.
The performance of Islamic banks is an important key to determine the position of
Islamic banks in the banking world. In Indonesia, the performance of Islamic banks is
measured as reported by Bank Indonesia (BI) using financial information, such as
assets, financing, pooling of funds, capital, and profitability (Bank Indonesia, 2007).
This information is also used to measure the performance of conventional banks. But
in principle there is a difference between Islamic banks and conventional banks, namely
in Islamic banks there are profit sharing principles while in conventional banks use the
principle of interest (Antonio M. S., 2001). The performance of Islamic banks can be
measured in various aspects. In this study, aspects of Islamic bank performance used
are fixed assets, third party funds, and five 24 financial ratios, namely the ratio of
operational efficiency measured by OER, liquidity ratios measured by NPF and FDR,
profitability ratios measured by ROA, and solvency ratios measured by CAR (Kasmir,
2008).
In this study, researchers wanted to further test the research conducted by Nasuha
(2012), Siswantoro (2014) dan Al Arif (2017) comparing the three policies establishing
Islamic banks. Al Arif (2017) see that spin off policies affect financial performance
using influence analysis. The difference between this research and the previous research
is that this study uses MANOVA for different tests so that it really distinguishes inter-
bank performance after changing to BUS. This research becomes important to prove
from the way of their establishment which gives the best performance. So, based on the
description above, researchers are interested in researching more about "Differences of
Islamic Bank Performance Based on Establishment Method: Evidence from Indonesia.
In this case the researchers took samples from the BUS with the three methods of
separation, namely the way of spin off, acquisition and mergers, as well as conversion,
namely BNI Syariah, BJB Syariah, BRI Syariah, Bukopin Syariah Bank, Victoria
Syariah Bank, and Aceh Syariah Bank. Analysis of financial performance in this study
was seen from four variables. The financial performance used is OER, FDR, ROA, and
CAR.
The results of this study shows that there is a significant difference among three
establishment methods of Islamic banks. Further analysis using post-hoc test indicates
that Islamic banks established through acquisition and merger method have better
efficiency and capital adequacy compared to Islamic banks established using other
methods. While in terms of liquidity and profitability, Islamic banks established
through conversion method perform better than Islamic banks established using other
methods. It suggests that Islamic banks established either using acquisition and merger
method or conversion methods have better financial performance than Islamic banks
established using pure spin-off method.
The remainder of this paper is organised as follows. The second section briefly
discusses the literature review. The third section explains the research methodology
used in the study and hypothesis development. The empirical results and analysis are
discussed in the fourth section. Lastly, conclusions are drawn in the final section with
a brief explanation of the limitations and suggestions for future research.
Differences of Islamic Bank Performance based on Establishment Method: Evidence from Indonesia
825

2 Literature Review
2.1 The Relationship between the Establishment of Islamic Banks and
Financial Performance
In Article 1 number 12 of Law No. 40 of 2007 concerning Limited Liability Companies,
the term spins off is called separation. According to the article, separation is defined as
a legal act carried out by a company to separate a business that is switched because the
law is to two or more companies or a part of the liability of the company is transferred
because it is legal to one or more companies. In addition to that, the ratification of Law
No. 21 of 2008 prompted the establishment of several Islamic banks by acquiring and
converting conventional banks to full-fledged Islamic banks. According to Adiwarman
Karim (2011), the establishment method of Islamic bank can be done through three
approaches, namely, first, acquisition and merger method. Conventional commercial
bank that already has Islamic banking unit acquires a relatively small bank and converts
it to afull-fledgedIslamic bank and then merges it with the already existed Islamic
banking unit.Second, conversion method. Conventional bank that donot havean Islamic
banking unit, acquires a relatively small bank and converts it to a full-fledgedIslamic
bank. Third, pure spin-off method. Conventional bank already has an Islamic banking
unit and then spins it off from the parent company(bank) so that an Islamic banking
unit becomesa full-fledgedIslamic bank.
Siswantoro (2014) in his article analyzes the performance of Islamic banks and
strategies after separation as an independent Islamic bank in Indonesia. The results
obtained explain that the capital injection from conventional parent banks should be
utilized optimally to increase the growth of the sharia bank resulting from the
separation. However, it must still be supported by effective management of the BUS
resulting from the separation. Hamid (2014) the results of his research related to the
impact of separation on profitability in the sharia banking industry in Indonesia,
explained that the separation policy applied to the sharia banking industry has a good
effect to increase profitability as measured by the Return on Assets (ROA) ratio. The
same is true of the research conducted Al Arif (2015) related to the separation and its
impact on third party funds in the sharia banking industry in Indonesia, the results
explain that the separation policy has a good impact on increasing the third party funds
of the sharia banking industry in Indonesia.
From the aspect of operational efficiency, Al Arif et al. (2018) explained that there
is an influence between the separation policy on the level of operational efficiency as
measured by the ratio of Operational Costs to Operating Income (OER) at Islamic
Commercial Banks, where the separation policy actually reduces the level of
operational efficiency in the Islamic banking industry in Indonesia. This shows that
after the separation policy was carried out, it resulted in the Islamic banking industry
being less efficient than before the separation policy was carried out. The research
conducted by Kusumawardani, Haryanto, and Wibowo (2006) concerning the
comparison of financial performance between Islamic banks and conventional banks
before and after financial regulation and the monetary crisis and took a case study of
Bank Muamalat Indonesia and four Conventional Commercial Banks, namely BTPN
Bank, North Sumatra Bank, Domestic Bank, and American Express Bank. The results
of the analysis are based on CAREL (Capital, Assets, Rentability, Earning, Liquidity)
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
826

bank financial ratios, which are represented by financial ratio indicators namely CAR,
NPF / NPL, ROA, ROE, OER, and FDR / LDR. The independent t-test statistical
method states that there are significant differences in financial performance except the
ROE ratio. There is only one bank that has a significant impact after the financial
regulation and the monetary crisis, the North Sumatra Bank. Sharia banks represented
by Bank Muamalat Indonesia have the best NPF and FDR financial ratios. The spin off
will certainly be related to the performance of a bank, because the spin off process
requires very large operational costs and this can affect the financial performance of
course there are adjustments from the bank that makes the spin off (Kurniawan, 2016).
Based on the various results obtained, showing that in general the spin-off to
become a BUS is one of the strategies that can be taken to develop the Islamic banking
industry in Indonesia. With the change in the status of a bank to become an independent
BUS, its operational activities will become wider and more focused on activities based
on sharia principles. With wider and optimal operational activities, it is expected to
expand investment and networks, so that it will increase revenue which has an impact
on improving bank performance.
The performance of Islamic banks is seen from the aspects of fixed assets, DPK,
OER, NPF, FDR, ROA, and CAR. Based on research conducted by Nasuha (2012), on
the asset, financing, third party fund, and NPF variables experienced differences in the
performance of Islamic banks in one year after the spin off. In addition, in research
conducted by Poerwokoesoemo (2016), on the CAR, ROA, OER, and NPF variables
there are differences in the performance of Islamic banks in one year after the spin off.
In this study, measuring whether there is a difference in performance one year before
and one year after becoming a BUS. In addition to measuring how the comparison
between the performance of Islamic banks with the three policies of the establishment
of Islamic banks after becoming BUS. Based on some research that has been done, it
proves that the policy of establishing Islamic banks is related to financial performance
that occurs in a system in Islamic banks.
3 Research Method
This approach uses quantitative analysis tools with several methods such as normality
test, homogeneity test, and different test. The main objective of this study is to analyze
the differences in the four performances of six Islamic commercial banks one year after
becoming a BUS and determine the comparison of the financial performance of Islamic
banks with the pure spin off, acquisition-merger, and conversion methods after
becoming a BUS. Types and Sources of Data Data used in this study are secondary data
from quarterly financial reports from each sample bank and Financial Services
Authority (OJK) within one year after the spin off.
Differences of Islamic Bank Performance based on Establishment Method: Evidence from Indonesia
827

Table 2. List of Banks in the study Sample.
No. Sample Establishment method Annual report
1
2
3
4
5
6
BNI Syariah
BJB Syariah
Syariah BRI
Bank Syariah Bukopin
Bank Victoria Syariah
Bank Aceh S
y
ariah
spin off
spin off
Akuisisi-merger
Akuisisi-merger
Konversi
Konversi
2010 & 2011
2010 & 2011
2009
2009
2010 & 2011
2016 & 2017
3.1 Operational Variabel
The operational definition contains an explanation of the specifications of the variables
that have been identified, the measurement variables and the size scale used (Rusmita,
Sukmaningrum, and Amani (2018). The variables in this study are:
1. OER: used to measure the ability of bank management in controlling operational
costs to operating income and the smaller this ratio the more efficient operational
costs incurred by banks so that the possibility of the bank concerned in a
problematic condition is also getting smaller (Almilia, Luciana Spica and
Herdinigtyas (2005). OER of a bank can be calculated by the following formula:
OER = (𝑂𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑎t𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑙 Expenses/𝑂𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑎t𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑙 Revenue) X 100% (1)
2. Financing to Deposit Ratio (FDR): In the Islamic banking blueprint issued by
Bank Indonesia in 2002, the FDR was analogous to a Loan to Deposit Ratio
(LDR) at conventional banks. The higher the ratio gives an indication of the low
ability of the bank's liquidity concerned. According to Arifin (2009), The
following is the FDR calculation formula:
FDR = (Total financing/𝑇𝑜𝑡al third party fund) X 100% (2)
3. Return on Assets (ROA): ROA is a comparison between net income and average
assets of Zainul Arifin (2012) Zainul Arifin (2012). The greater the ROA of a
bank, the better the bank's position. According to Dendawijaya (2009), the ROA
amount of a bank can be calculated by the following formula:
ROA = (Income before tax/ average total asset) X 100% (3)
4. Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR): Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) to determine
the ability of capital needed to absorb or lose Sharia Commercial Banks The
higher the CAR, the stronger the bank to buy credit risk. According to Kasmir
(2014), the CAR amount of a bank can be calculated using the following
formula:
CAR = (𝑀𝑜𝑑𝑎𝑙/ 𝐴𝑇𝑀𝑅) X 100% (4)
3.2 Data Analysis Technique
3.2.1 MANOVA One Way
Anova Multivariate is abbreviated to MANOVA. Another name for MANOVA is
Multivariate Path Analysis. MANOVA is a statistical technique that can be used
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
828

simultaneously to explore relationships between several categories of independent
variables and two or more dependent variables. MANOVA can be used if the response
value or the dependent variable is greater than or equal to two. MANOVA is the
development of analysis of variance (ANOVA) in which to measure the average
difference for two or more dependent variables based on one or several categorical
variables that act as predictors.
The basis for decision making in the MANOVA One Way test is to compare the
value of F with the value of F crit (F table). If the value of F (F arithmetic)> F crit (F
table) then H0 is rejected or there is a difference. If the value of F (F arithmetic) <F crit
(F table) then H0 is accepted or in other words there is no difference (Santoso, 2003).
The basis for decision making if based on a probability or significance value is to
compare the P-value with a significance value. Because the desired level of trust is
95%, the significance level is 100-95 = 5% or 0.05. So, if the significance or probability
value> 0.05 then H0 is accepted or in other words there is no difference. If the
significance value or probability value <0.05 then H0 is rejected or in other words there
is a difference (Santoso, 2003).
According to Santoso (2003) In testing MANOVA One Way, we also need several
assumptions that must be met just like ANOVA, namely:
1. The population to be tested is normally distributed.
2. All samples are independent.
3. There is a variance of the populations to be tested.
4. The samples tested are not related to each other.
The MANOVA One Way hypothesis:
H0: There is no significant difference in BUS financial performance with the three
methods of establishing Islamic banks.
H1: There is a significant difference in BUS financial performance with the three
methods of establishing Islamic banks
3.2.2 Post Hoc
Post hoc test is used to examine differences in financial performance and policy
establishment before and after becoming a BUS, in addition to finding out which is
better. In the post hoc test if the data has the same variance as evidenced in the
homogeneity variance test where the probability value> 0.05, then the post hoc test can
be performed by selecting one of the options in equal variances assumed, namely LSD.
If the data is proven to have a different variance as evidenced in the variance
homogeneity test where the probability value <0.05, the post hoc test can still be
performed by selecting one of the tests in equal variance not assumed, namely howell
games (Trihendradi, 2009). If the significance level> 0.05 then there is no significant
difference, whereas if the significance <0.05 then there is a significant difference. In
addition, the post hoc test results table will show the * (star) symbol in the mean
difference column to make it easier to indicate significant differences (Trihendradi,
2009). The positive mean difference value means that it indicates that the variable is
the best (Hidayat, 2010).
Differences of Islamic Bank Performance based on Establishment Method: Evidence from Indonesia
829
Fig. 1. Teknik Analisis Data.
4 Result and Analysis
4.1 Homogenitas Test
The MANOVA test as inferential statistics (parametric statistics) requires normal
distribution of data and homogeneity of variance / covariance of dependent variable
data. Homogeneity test aims to test whether the dependent variable has the same
variance in each category of independent variables. The results of the MANOVA
homogeneity test can be seen in Table 3 below:
Table 3. Uji Homogenitas MANOVA.
Variable Sig.
OER 0,321
FDR 0,071
ROA 0,165
CAR 0,001
Sumber: Uji SPSS 22 (data diolah)
Sharia bank performance can be said to be homogeneous if the data meets the
assumption of homogeneity with a significance value> 0.05, otherwise if the data has a
significance value <0.05 then it is said that the data variants are not the same or
heterogeneous. Based on the homogeneity test in Table 4.19 it can be obtained that the
OER, FDR, and ROA variables have homogeneous data, because the significance level
of the two banks is> 0.05.
While the CAR variable has a significance level <0.05, then the data can be said to
be variable data variants in the three methods of separation are not the same. The results
of the variance-covariance homogeneity test were not met, but the multivariate
normality test for the above case was met. However, analysis can still be continued for
MANOVA calculations using MANOVA testing decisions. So it can be concluded that
MANOVATestandPostHoc
spinoff:
BNISyariah
BJBSyariah
akuisisiandmerger:
BRISyariah
BankSyariahBukopin
konversi
BankVictoriaSyariah
BankAcehSyariah
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
830

the four variables consisting of OER, FDR, ROA, and CAR can be continued by
conducting a hypothesis test that is the One Way MANOVA test.
4.2 MANOVA One Way Test
MANOVA One Way is used to see the effect of predictor variables on response.
MANOVA in this study is used to compare the four dependent variables of each bank
grouped based on the method of establishing Islamic banks. After analysis, the results
of the One Way MANOVA table are obtained as follows:
Table 4. Uji MANOVA One Way.
Tests of Between-Subjects Effects
Source
Dependent
Variable
Type III Sum
of Squares
Df Mean Square F Sig.
Corrected
Model
OER 27809.471
a
2 13904.735 131.716 .015
FDR 3224.462
b
2 1612.231 4.806 .019
ROA 86.775
c
2 43.388 5.263 .014
CAR 6176.829
d
2 3088.415 23.448 .000
Intercept OER 308520.586 1 308520.586 113.828 .000
FDR 32270.830 1 32270.830 96.204 .000
ROA .810 1 .810 .098 .757
CAR 30654.198 1 30654.198 232.730 .000
METODE OER 27809.471 2 13904.735 5.130 .015
FDR 3224.462 2 1612.231 4.806 .019
ROA 86.775 2 43.388 5.263 .014
CAR 6176.829 2 3088.415 23.448 000
Error OER 56918.497 21 2710.405
FDR 7044.240 21 335.440
ROA 173.125 21 8.244
CAR 2766.028 21 131.716
Total OER 393248.553 24
FDR 42539.531 24
ROA 260.710 24
CAR 39597.055 24
Corrected
Total
OER 84727.968 23
FDR 10268.702 23
ROA 259.900 23
CAR 8942.857 23
a. R Squared = .328 (Adjusted R Squared = .264)
b. R Squared = .314 (Adjusted R Squared = .249)
c. R Squared = .334 (Adjusted R Squared = .270)
d. R Squared = .691 (Adjusted R Squared = .661)
Differences of Islamic Bank Performance based on Establishment Method: Evidence from Indonesia
831

Based on the table above, it can be seen in the method row. Where there are four more
lines, namely OER, FDR, ROA, and CAR. That explains that each row shows a
different test result of one variable, namely the method of each dependent variable.
From the results above, it can be seen in the Sig. (significant if the Sig. value <0.05),
the first variable, OER, indicates a significance level of 0.015. These results indicate a
significance level of less than 0.05 which means the initial hypothesis was rejected,
which indicates a significant difference between the three policies establishing Islamic
banks after becoming a BUS.
The second variable, FDR, shows a significance level of 0.019. These results
indicate a significance level of less than 0.05 which means the initial hypothesis was
rejected, which indicates a significant difference between the three policies establishing
Islamic banks after becoming a BUS. The third variable, ROA, shows a significance
level of 0.014. These results indicate a significance level of less than 0.05 which means
the initial hypothesis was rejected, which indicates a significant difference between the
three policies establishing Islamic banks after becoming a BUS.
The last variable, CAR, shows a significance level of 0,000. These results indicate
a significance level of less than 0.05 which means the initial hypothesis was rejected,
which indicates a significant difference between the three policies establishing Islamic
banks after becoming a BUS. The conclusion of the MANOVA One Way test
conducted on the four variables taken into account in Islamic banks after becoming a
BUS in this study shows that all variables have significant differences in the three
policies establishing Islamic banks.
4.3 Post Hoc Test
Once it is known that there are differences between the three policies, a post hoc test
will then be performed to find out which variables are different. Post hoc test results
can be seen in the following table.
It is known from the table below that the variance of the OER, FDR, and ROA
variables are the same, so the post hoc test used is the LSD test. For CAR variables use
the games-howell test. It is said that there are differences in the performance variables
of Islamic banks, which are based on the policy of establishing Islamic banks if they
have a star sign (*) and have a significance <0.05. The best method is shown with a
positive mean difference (Hidayat, 2010).
In this study, for the difference in the OER variable, there is a significant difference
in the acquisition-merger method with the conversion method with a significant value
of 0.005 and has a mean different 82.2688, so it can be concluded that the OER on the
acquisition-merger is higher than the conversion.
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
832
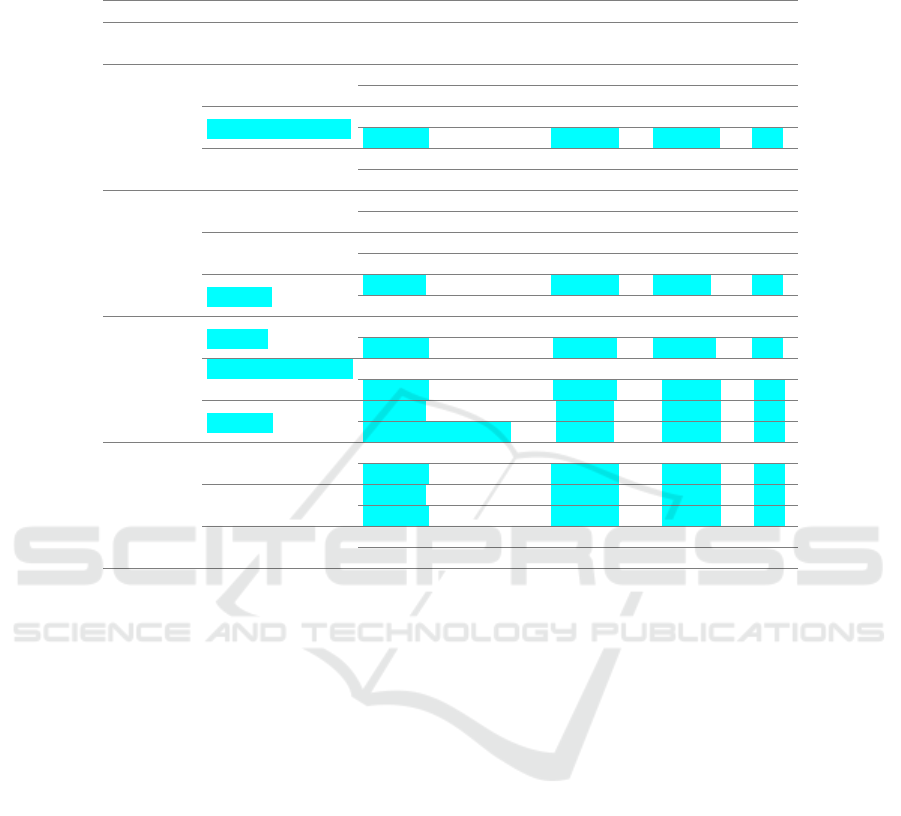
Table 5. Post Hoc Result.
Multiple Comparisons
Dependent
Variable
(I) METODE (J) METODE
Mean
Difference(IJ)
Std. Error Sig
OER Spin Off
Akuisisi dan Merge
r
-29.3800 26.03077 .272
Konversi 52.8887 26.03077 .055
Akuisisi dan Merger
Spin Off 29.3800 26.03077 .272
Konversi 82.2688* 26.03077 .005
Konversi Spin Off -52.8887 26.03077 .055
Akuisisi dan Merge
r
-82.2688* 26.03077 .005
FDR Spin Off
Akuisisi dan Merge
r
-16.8964 9.15751 .079
Konversi -28.2085* 9.15751 .006
Akuisisi dan Merger
Spin Off 16.8964 9.15751 .079
Konversi -11.3121 9.15751 .230
Konversi
Spin Off 28.2085* 9.15751 .006
Akuisisi dan Merge
r
11.3121 9.15751 .230
ROA Spin Off
Akuisisi dan Merge
r
.9812 1.43562 .502
Konversi -3.4525* 1.43562 .025
Akuisisi dan Merger Spin Off -.9812 1.43562 .502
Konversi -4.4338* 1.43562 .006
Konversi
Spin Off 3.4525* 1.43562 .025
Akuisisi dan Merge
r
4.4338* 1.43562 .006
CAR
Spin Off
Akuisisi dan Merge
r
-23.7763* 5.73837 .000
Konversi 15.2075* 5.73837 .015
Akuisisi dan
Merger
Spin Off 23.7763* 5.73837 .000
Konversi 38.9838* 5.73837 .000
Konversi
Spin Off -15.2075* 5.73837 .015
Akuisisi dan Merge
r
-38.9838* 5.73837 .000
Sumber: Hasil SPSS 22 (data diolah)
Furthermore, for the difference in the FDR variable, there is a difference in the pure
spin off method with the conversion method because it has a significance <0.05 or equal
to 0.006. Between pure spin off and conversion methods have a mean difference of
28,2085. This shows that the FDR with the conversion method is higher than the pure
spin off method.
ROA variable differences are found in all separation methods. Pertaman there is a
difference in the conversion method with the pure spin off method, with a significance
of 0.025 and a mean different of 3.4525. Based on the mean difference between
conversion and pure spin off, the conversion ROA is higher than pure spin off. Secondly
there are differences in the conversion method with the acquisition-merger method with
a significance of 0.006 and mean different 4.4338. Based on the mean different number
between conversion and merger acquisition, the conversion ROA is higher than merger
acquisition. Meanwhile between merger-acquisition and pure spin-off is not significant.
Based on post hoc analysis data, the conversion method has the highest ROA.
For differences in CAR variables, there are differences in all separation methods,
with significance <0.05 and positive. First, between pure spin off and conversion with
a significance value of 0.015 and mean different 15.2075. This means that the CAR on
the pure spin off method has a higher CAR than Conversion. Second, the acquisition
and merger method with pure spin off has a significance of 0,000 and a mean different
of 23.7763, meaning that the CAR on the acquisition and merger method is higher than
Differences of Islamic Bank Performance based on Establishment Method: Evidence from Indonesia
833

pure spin off. Third, the method of acquisition and merger with conversion has a
significance of 0,000 and a mean different of 39.9838, meaning that the CAR on the
acquisition and merger method is higher than conversion. If the three methods are
sorted, the highest CAR is acquisition and merger, then CAR with pure spin off method
and the last CAR is the conversion method.
The conclusion of the post hoc test conducted on the four variables taken into
account in Islamic banks after becoming a BUS in this study shows that:
1. OER acquisition and mergers are the highest compared to conversions
2. FDR conversion is higher than pure spin off
3. ROA conversion method is higher than merger acquisition and pure ROA
4. The highest CAR is acquisition and merger, then CAR with pure spin-off method
and finally CAR on the conversion method.
5 Analysis
Based on the results of the MANOVA One Way test of Operational Income Operational
Costs (OER), Financing to Deposit Ratio (FDR), Return on Assets (ROA), Capital
Adequacy Ratio (CAR) of Islamic banks after becoming BUS, there are significant
differences between the three establishment policies Islamic Bank.
Judging from the results of the post hoc test, the OER variable on the acquisition
and merger methods has a higher OER than the conversion. OER is a reflection of
efficiency ratio, the higher the OER, the more inefficient the company shows. A high
OER indicates inefficiency between operating costs and revenue. Based on the financial
statements 1 year after becoming a Sharia OER Commercial Bank, acquisition and
mergers are the highest compared to conversions. Inefficient OER could be due to the
Bukopin Syariah NPF increasing in the first year after becoming a BUS and added to a
fall in return. Declining returns could be due to bad financing, according to Indrajaya,
(2019) the accumulation of non-performing financing in economic activities financed
by banks may cause problems for the continuity of bank operations, which if it exceeds
certain limits has the potential to stop bank activities.
Whereas Islamic banks with conversion methods (Bank Victoria Syariah and Bank
Aceh Syariah) have the most efficient OER compared to others. At Bank Victoria
Syariah and Bank Aceh Syariah, in one year there was an increase in return so that the
efficiency ratio could be reduced by 1 year after becoming a Sharia Commercial Bank.
Table 6. Islamic Bank Efficiency Average.
No. Sample Spin-off method OER Ratio
1
2
BNI Syariah
BJB S
y
ariah
Murni spin off
Murni spin off
87.03
86.51
Rata-rata 86.77
3
4
BRI Syariah
Bank S
y
ariah Bukopin
Akuisisi-merger
A
kuisisi-mer
g
e
r
90.095
112.503
Rata-rata 101.229
5
6
Bank Victoria Syariah
Bank Aceh Syariah
Konversi
Konversi
86.64
83.3525
Rata-rata 84.9963
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
834

Whereas the FDR variable conversion method is higher than the pure spin off method,
in other words the pure spin off method has a smaller spin off.
Table 7. Sharia Bank Liquidity Average.
No. Sample Spin-off method FDR Ratio
1
2
BNI Syariah
BJB S
y
ariah
Murni spin off
Murni spin off
14,7558
34.6622
Rata-rata 24.7009
3
4
BRI Syariah
Bank S
y
ariah Bukopin
Akuisisi-merger
A
kuisisi-mer
g
e
r
36.5119
13.2717
Rata-rata 24.8918
5
6
Bank Victoria Syariah
Bank Aceh Syariah
Konversi
Konversi
2.0951
76.1125
Rata-rata 39.1038
FDR is a reflection of bank liquidity, the conversion method has the highest FDR on
average compared to pure spin-off, meaning that Islamic banks which through
conversion tend to provide more financing than Islamic banks with other methods.
However, in the conversion method Bank Victoria Syariah has the lowest FDR, while
Bank Aceh Syariah has the highest FDR.
At Bank Victoria Syariah can be said to have the best liquidity due to low FDR, the
financing data of Bank Victoria Syariah decreased within 6 months after the spin off,
this could be due to the process of adjusting contracts and contracts. This conversion
method converts conventional banks to sharia banks directly so that contract and
contract adjustments are needed to be in accordance with sharia. Aside from low
financing, depositors of Bank Victoria Syariah continue to increase, this also triggers
the liquidity of Bank Victoria Syariah in the worst position.
Bank Aceh Syariah has the lowest liquidity among others. Funding in the sharia
scheme has actually begun since 2004. After the conversion, the liquidity of Bank Aceh
Syariah did not experience significant changes and changes in the contract and contract
of the Bank did not experience many difficulties because Bank Aceh had sharia branch
offices (not UUS) before the change. FDR also tends to be stable and does not
experience liquidity problems, when viewed from the NPF it tends to go down and
ROA also increases.
The greater the financing provided, the more benefits will be obtained. Based on
various results obtained, it shows that the policy of establishing a bank to become a
Sharia Commercial Bank (BUS) is one of the business strategies that can be taken to
develop the sharia banking industry. If based on Post hoc test data and average data,
the one with the highest ROA is the conversion method. Bank Aceh Syariah which
tends to have a stable and increasing ROA. Bank Victoria Syariah also has an ROA
which shows the increase after becoming a Sharia Bank. In the BRIS after Spin off
BRIS decreased ROA. While what happened at Bukopin Syariah Bank, ROA has
increased every 3 months but runs very slowly, so that within 1 year after the spin off
it has only shown positive ROA before 3 months in a row having negative ROA.
CAR is a ratio that reflects the ratio of capital adequacy in providing funds used to
overcome the possibility of risk. The highest CAR is acquisition and merger, then CAR
Differences of Islamic Bank Performance based on Establishment Method: Evidence from Indonesia
835

with pure spin-off method and finally CAR on the conversion method. In the CAR ratio,
the Post hoc test results show that there are significant differences between all methods
of separation of Islamic banks and of the three methods, the acquisition and merger
have the most different CARs. Islamic banks resulting from the acquisition and merger
experience a very striking difference because in the merger process, if the assets being
merged are assets that are not good then it will add to the burden of risk-weighted assets
according to risk. But it could also be considered better because after becoming a BUS,
Islamic banks get a large injection of funds from their parent bank. Then from the
merger process there is a merging of capital between merged banks.
However, this separation policy is not the final goal of the development of the
Islamic banking industry, many things need to be prepared related to the separation of
Islamic business units to become Islamic banks. According to Tubke (2004) there are
several factors that influence the process of establishing an Islamic bank. First, factors
related to business activities. In this factor, related to company size and business sector
differences between the parent company and its subsidiary companies. Second, factors
related to the organization and management of the company. Third, factors related to
relationships and support. There are three patterns of relationships that might be created
between a parent company and a subsidiary that makes a separation, namely market-
relatedness, product-relatedness, and technology-relatedness. Fourth, the transfer factor
or transfer in the form of transfer of experience from the parent company to its
subsidiary companies. Fifth, factors related to motivation. Finally, factors related to the
business environment.
6 Conclusion
The core objective of this study is to empirically examine whether there is a significant
difference among three establishment methods of Islamic banks, namely acquisition
and merger method, conversion method and pure spin-off method. Afterwards, this
study seeks to test which establishment method that gives the best financial
performance of Islamic banks. This study uses the sample of all 6 spin-off Islamicbanks
in Indonesia for the period of one year after spin off.
This study found that the conversion method is superior in efficiency, liquidity and
profit compared to other methods. As for the solvency capability of the acquisition and
merger method, the highest position. From the findings of this study, it can be seen how
the differences in the performance of Islamic banks of the three Islamic banking
establishment policies. In addition, it is hoped that this research can provide information
and considerations before implementing the Islamic banking establishment policy. In
addition, without changing the theme of this study, it is recommended that future
studies be able to use more samples and use different methods. So it can be known to
increase the validity of the results of the study.
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
836

References
Adiwarman Karim. 2011. “BANK ISLAM : Analisis Fiqih Dan Keuangan.” In Edisi Keempat,.
Almilia, Luciana Spica and Herdinigtyas, Winny. 2005. “ANALISIS RASIO CAMEL
TERHADAP PREDIKSI KONDISI BERMASALAH PADA LEMBAGA PERBANKAN
PERIODA 2000-2002.” Jurnal Akuntansi dan Keuangan.
Al Arif, M. Nur Rianto. 2015. “Impact of Spin-Off Policy on the Asset Growth on Indonesian
Islamic Banking Industry.” Journal of Islamic Economics Banking and Finance.
———. 2017. “Spin-off and Market Share in the Indonesian Islamic Banking Industry: A
Difference in Difference Analysis.” Management and Marketing.
Al Arif, M Nur Rianto, Nachrowi D Nachrowi, Mustafa Edwin Nasution, and T.M. Zakir
Mahmud. 2018. “Evaluation of the Spinoffs Criteria: A Lesson from The Indonesian Islamic
Banking Industry.” IQTISHADIA.
Arifin, Zainul. 2009. Manajemen Bank Syariah. Tangerang: Azkia Publisher.
Bank Indonesia. 2007. Peraturan Bank Indonesia No.9/17/PBI/2007 Tentang Sistem Penilaian
Tingkat Kesehatan Bank Umum Berdasarkan Prinsip Syariah. Jakarta.
Dendawijaya, Lukman. 2009. Manajemen Perbankan. Jakarta: Ghalia Indonesia.
Hamid, Abdul. 2015. “The Impact of Spin-Off Policy To The Profitability On Indonesian Islamic
Banking Industry.” Al-Iqtishad: Jurnal Ilmu Ekonomi Syariah.
Hidayat, Aziz Alimul. 2010. Metode Penelitian Kesehatan Paradigma Kuantitatif. Surabaya:
Health Books Publishing.
Indrajaya. 2019. “Determinan Non-Performing Financing Pada Bank Umum Syariah Di
Indonesia.” Jurnal Ekonomi dan Bisnis Islam (Journal of Economics and Business Islamic)
5(1): 68–81. https://e-journal.unair.ac.id/JEBIS/article/view/13180/7847.
Kasmir. 2014. PT. Raja Grafindo Persada jakarta Bank Dan Lembaga Kuangan Lainnya.
Kurniawan, Zulfa Ahmad. 2016. “Perbandingan Kinerja Keuangan Bank Umum Syariah
Sebelum Dan Sesudah Spin Off Unit Usaha Syariah.” IEF Trisakti.
Kusumawardani, Deni, Tri Haryanto, and Wisnu Wibowo. 2008. “Tingkat Kesehatan Dan
Efisiensi Bank Perkreditan Rakyat Jawa Timur.” Majalah Ekonomi.
Nasuha, Amalia. 2016. “Dampak Kebijakan Spin-off Terhadap Kinerja Bank Syariah.” Al-
Iqtishad: Journal of Islamic Economics.
Otoritas Jasa Keuangan. 2010. Laporan Keuangan Perbankan. www.ojk.go.id.
———. 2018. Statistik Perbankan Syariah. www.ojk.go.id.
Poerwokoesoemo, Atman. 2016. “KINERJA BANK KONVENSIONAL PASCA SPIN OFF
UNIT USAHA SYARIAH.” Jurnal Keuangan dan Perbankan.
Rusmita, Sylva Alif, Puji Sucia Sukmaningrum, and Zata Atikah Amani. 2018. “Early Warning
System for Sharia Insurance Companies in Indonesia and Malaysia at 2013-2015 Periode.”
Rustam, Bambang Rianto. 2012. “Spin Off UUS Agar Cepat Tumbuh.”
http://www.infobanknews.com.
Santoso, Singgih. 2003. Mengatasi Berbagai Masalah Statistik Dengan SPSS Versi 11.5. Jakarta:
Gramedia Pustaka Utama.
Siswantoro, Dodik. 2014. “Analysis of Islamic Bank’s Performance and Strategy After Spin-off
as Islamic Full-Fledged Scheme in Indonesia.” Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences.
Trihendradi, Cornelius. 2009. Step by Step SPSS 20 Analisis Data Statistik. Yogyakarta: Penerbit
Andi.
Zainul Arifin. 2012. “Dasar-Dasar Manajemen Bank Syariah.” Pustaka Alvabet.
Differences of Islamic Bank Performance based on Establishment Method: Evidence from Indonesia
837
