
RF Pulses Modelization for EMG Signal Denoising in fRMI Environment
Sofia Ben Jebara
Carthage University, Ecole Sup
´
erieure des Communications de Tunis,
COSIM Laboratory,
Route de Raoued 3.5 Km, Cit
´
e El Ghazala, Ariana, 2088, Tunisia
Keywords:
EMG Signal, fRMI, RF Pulses, HNM Model, Noise Reduction.
Abstract:
This paper deals with noise contaminating EMG signal acquired in fRMI environment. The RF pulses are
particularly addressed. Their characterization in the frequency domain allows their presentation as discrete
pulses repeated at frequencies multiple of RF pulses repetition. The Harmonic plus Noise Model (HNM) is
then used to model these pulses in the time-domain. The parameters of the model are extracted, frame by
frame, according to the principle of short time analysis. The model is validated according to two criteria: the
Segmental Signal to Noise Ratio (SSNR) and its Normalized Standard Deviation (NSD
SSNR
). Once modeled,
the estimated noise is subtracted from noisy observation of EMG signal, leading to an enhanced version.
Simulation results are given, validating the approach. In absence of ground truth, realistic situations are
simulated in order to calculate quantitative criteria. Furthermore, qualitative appreciation is given thanks to
muscular contractions profiles. Finally, the results are compared to those obtained with spectral subtraction
and comb filtering.
1 INTRODUCTION
The acquisition of EMG signals simultaneously
with brain images in functional Magnetic Resonance
Imaging (fRMI) environment offers an added value
compared to acquisition of EMG signal outside the
scanner. In fact, the combination of the two modali-
ties allows to explore the dynamics of neural activity
and to link it to muscle response to the brain com-
mand. However, these advantages come with draw-
backs like artifacts: EMG data collected during fRMI
experiments are contaminated by artifacts due to tech-
nical and physiological origins. The cross talk (elec-
trodes over an adjacent muscle pick-up a signal via
skin conduction) is one common physiological arte-
fact, the EMG signal acquisition system (driver am-
plifier, electrodes, cable movement,...) is one source
of technical artifact. In fRMI environment, the EMG
signal is affected by a supplementary noise which has
a very high level. It has two main origins: the very
high static magnetic field (of the order of Tesla, which
corresponds to thousands of times the earth’s mag-
netic field) and the ordered combination of RF and
gradient pulses designed to acquire the data to form
the image. The radio frequency pulses are emitted to
excite hydrogen nuclei for images generating while
magnetic field gradients are introduced for spatial en-
coding of the image (see for example (Hornak, 2006)
for more details).
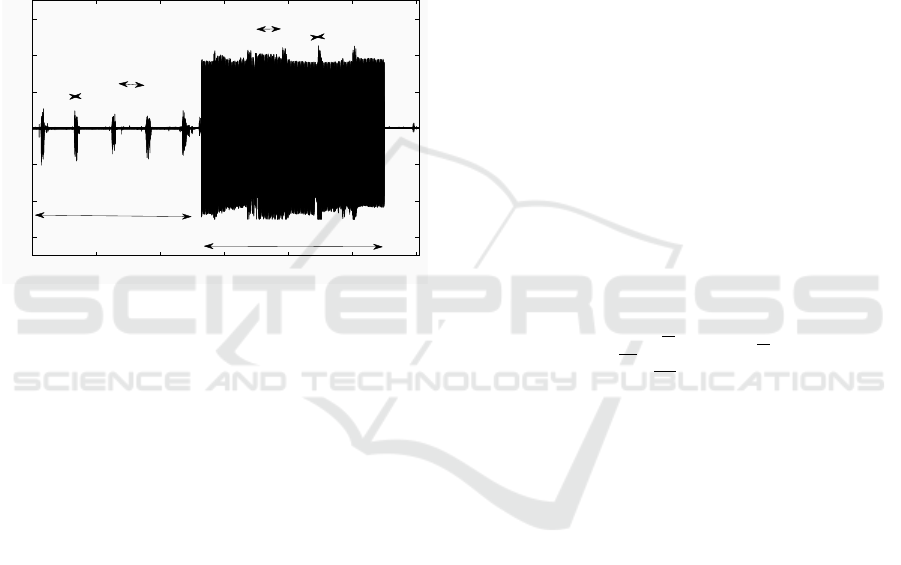
Fig. 1 shows an example of EMG data acquired in
normal conditions (outside the scanner) and in fRMI
environment (inside the scanner). Segment ’Noise
out’ (resp. ’Noise in”) corresponds to physiological
and technical noises (resp. physiological, technical
and specific fRMI noises) since there is no muscle ac-
tivity and the acquisition is carried outside (resp. in-
side) the scanner. Segment ’EMG out’ (resp. ’EMG
in’) corresponds to effective EMG signal during mus-
cle activity outside (resp. inside) the scanner. One can
notice the high level of noise due to radio-frequency
and gradient pulses. This noise completely buries the
EMG signal.
This paper aims at modelizing the RF pulses in
order to denoise EMG signals acquired in fRMI envi-
ronment. At the best of our knowledge, the mathemat-
ical modelization of fRMI noise did not attract the at-
tention of researchers, even though it is well analyzed
from a physical point of view and its origin and fre-
quency properties are well mastered (see for example
(Hoffmann et al., 2000)(Ganesh et al., 2007)(El Tatar,
2013)(Dougherty, 2010)(Garreffa et al., 2003)). In
this paper, we propose to develop an analytical model
of the RF pulses from observations when no prior in-
formation about RF pulses is available. The model
Ben Jebara, S.
RF Pulses Modelization for EMG Signal Denoising in fRMI Environment.
DOI: 10.5220/0007256401090115
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2019), pages 109-115
ISBN: 978-989-758-353-7
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
109
takes its origin from spectral characterization of noise
and leads to an Harmonic plus Noise Model (HNM).
This model will be exploited to denoise EMG signal
acquired in RMI environment.
The paper is organized as follows. Section 2 de-
scribes the RF noise in temporal and frequency do-
mains. Section 3 is devoted to HNM model expla-
nation and the algorithm to calculate its parameters.
Section 4 takes advantage of the model to reduce
noise from the EMG signal. Section 5 compares the
performances of proposed HNM model to Comb fil-
tering and Spectral Subtraction technique. Finally,
conclusions are drawn.
700 800 900 1000 1100 1200
Time (s)
-6
-4
-2
0
2
4
6
EMG
Inside the scanner
Outside the scanner
Noise in
Noise out
EMG out
EMG in
Figure 1: Temporal evolution of EMG signal before and
during image acquisition in fRMI tunel.
2 RF NOISE PROPERTIES
2.1 Data Acquisition
Participants were lying in the fRMI scanner with fore-
arm connected to bipolar electrodes (ADD208, 8-mm
recording diameter, System Inc., Santa Barbara, CA).
Surface EMG signals were recorded during a hand-
grip exercice from the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
(FDS) muscle. Simultaneously, neuro-imaging data
were acquired with an MRI system. The RF pulses
and the gradient fields are applied repetitively to ac-
quire image slices of the brain. One loop, for com-
plete brain volume scan, occurs during a time interval
called repetition time (denoted T
R
). One loop allows
to generate a sequence of images (slices). Each image
is obtained during one RF stimulation period. The du-
ration between two RF pulses T
0
is equal to the repeti-
tion time T
R
over the number of slices N: T
0
= T
R
/N.
2.2 RF Pulses Properties
To study the influence of the noise generated by RF
pulses in the EMG signal, let’s consider some exam-
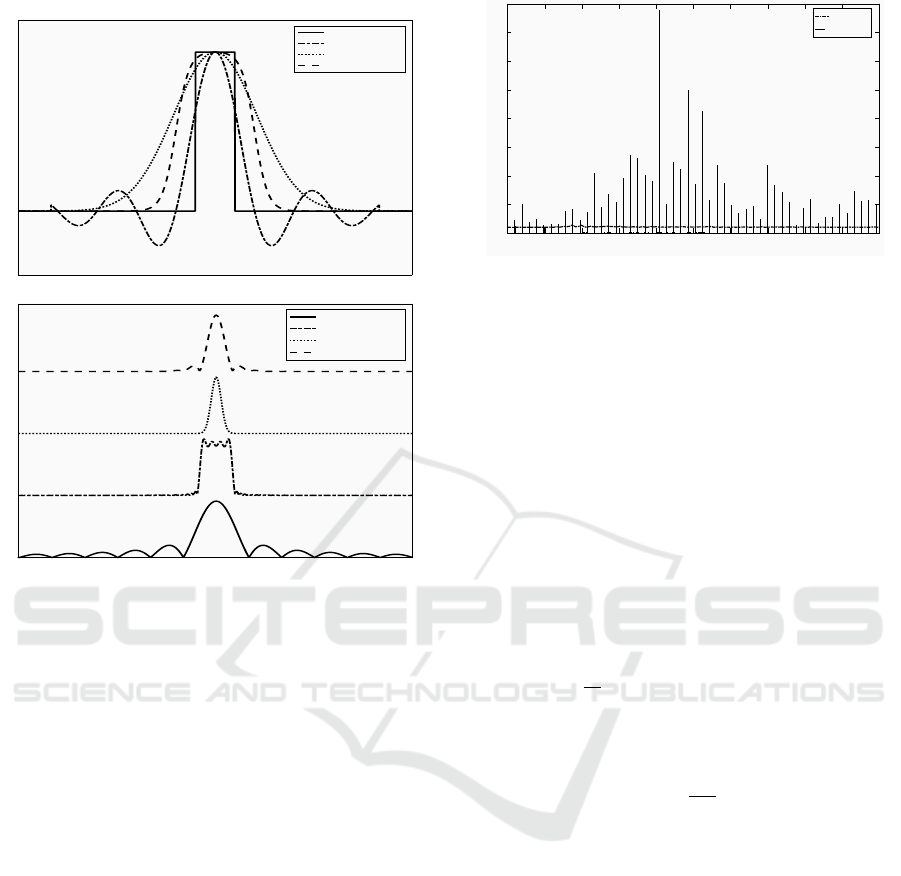
ples of RF pulses commonly used in practice. Fig. 2
gives time-continous temporal evolution (a) and spec-
trums (b) of some common RF pulses, namely rect-
angle, windowed sinus cardinal, Gaussian and Fermi
(Bernstein et al., 2004). Note that only the active part
(non null part) is drawn and figures axis are not given
in order to focus only on the shape. All the pulses are
time-limited. In the frequency domain, the Gaussian,
the windowed sinus cardinal and Fermi pulses are
characterized by band-limited spectrum while rectan-
gular pulse is characterized by an infinite frequency
support.
The RF pulses are repeated periodically in order
to acquire the whole image slices of the brain. Let’s
denote x(t) the RF pulse. According to its periodicity
property, its Fourier transform is a sum of dirac pulses
equally spaced in the frequency axis at frequencies
multiple of f
0
:
X( f ) =
∑
k∈Z
X
k
δ( f − k f
0
), (1)
where X
k
is the k
th
Fourier transform coefficient, cal-
culated during one period according to the following
formula:
X
k
=
1
T
0
Z
T
0
2
−T
0
2
x(t)e
− j2π
k
T
0
t
dt. (2)
The RF analog signal is converted to a digital one.
When sampled and according to Shannon theorem, a
spectral overlap can appears due to the duplication of
the spectrum around the multiples of the sample fre-
quency:
Xs( f )
4
= f
s
∑
l∈Z
X( f − l f
s
) = f
s
∑
k∈Z
∑
l∈Z
X
k
δ( f − l f
s
− k f
0
).
(3)
With an appropriate choice of the parameters of
the RF pulse, their bandwidth can be adjusted so
that the duplication of spectrum around sampling fre-
quency multiples allows to reduce/avoid overlapping.
While windowed sinus cardinal, Gaussian and Fermi
RF pulses can lead to non-overlapping (thanks to their
band-limited spectrum), the rectangle pulse generates
overlapping (because of its infinite frequency sup-
port). An alternative solution is to increase the sam-
pling frequency so that the overlap becomes less im-
portant (since the secondary lobes vanish when the
frequency increases). But increasing the sampling
frequency increases the number of samples acquired,
which is not necessarily interesting in term of data
amount.
BIOSIGNALS 2019 - 12th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
110
(a)
Rectangle
Windowed Sinc
Gaussian
Fermi
(b)
Rectangle
Windowed Sinc
Gaussian
Fermi
Figure 2: Some common RF pulses. Spectrums are shifted
for better legibility.
2.3 RF Pulses Properties as Noise in
EMG
To deal with a concrete example, we consider the case
where the repetition time is equal to T
R
= 2215ms and
N = 43 images are acquired. The frequency of repeti-
tion of RF pulses is f
0
= 1/T
0
= 9.706 Hz. The signal
of interest is the EMG signal of FDS muscle. Its max-
imum frequency is 500 Hz so that it should be ideally
sampled at 1 kHz. The RF interference acquired as
noise in EMG is sampled at the same frequency.
Fig. 3 shows the spectrum of noise generated
during real acquisition in the RMI tunnel (according
to the protocol described in subsection 2.1). Note
that frequency bins due to RF noise exist along the
whole frequency axis at frequencies multiple of f
0
=
9.706Hz. Their amplitudes differ from one frequency
to another. This noise spectrum is compared to the
one of an EMG signal which looks like a white noise
with relatively very low level compared to that of RF
pulses. Hence, the challenging task is to estimate this
noise and to reduce it.
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
Frequency (Hz)
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
Spectrum
RF pulses
EMG
Figure 3: Spectrum of EMG signal and noise generated dur-
ing a real acquisition in the RMI tunnel.
3 RF PULSES MODELISATION
Eq. 3 describes digital RF pulses as a weighted sum of
frequency bins. Hence, in time-domain, we propose
to model the periodic RF pulses as a weighted sum of
sine waves:
˜x(m) =
K−1
∑
k=0
a
k
(m)sin(2πkν
0
m + φ
k
(m)), (4)
where ˜x(m) is the modeled sample at time index
m, K is the number of harmonics. For each harmonic
k, a
k
(m) and φ
k
(m) represent the time-varying ampli-
tude and phase respectively. ν
0
is the normalized fre-
quency ν
0
=
f
0
f
s
. The number of harmonics is equal
to the nearest integer of the signal maximal frequency
( f s/2) over the fundamental frequency f
0
:
K = b
f s
2 f
0
c. (5)
For our practical case, the EMG signal is sampled
at f
s
= 1 kHz and RF fundamental frequency is f
0
=
9.706, so the number of harmonics is K = 51.
3.1 Model Parameters Calculs
To estimate the parameters of the model, the follow-
ing methodology is adopted. It is inspired from pre-
vious works developed on speech processing (see for
example (Pantazis, 2010)).
• In the RMI tunnel, the RF pulses generator is
turned on. EMG signals acquisition are placed on
the considered muscle and the subject is asked to
not do any muscular activity. The EMG acquisi-
tion system is turned on so that the acquired signal
is the environmental noise. It is composed of tech-
nical and physiological artefacts, static magnetic
field, RF pulses and gradient fields.
RF Pulses Modelization for EMG Signal Denoising in fRMI Environment
111
• Short-term analysis is done. The recorded signal
is decomposed into frames of length N and is win-
dowed using Hanning window for example. The
frame by frame analysis allows to assume that am-
plitudes and phases of the harmonics are constant
within a frame. The choice of the frame size will
be discussed later.
Let’s denote x
l
(u) the u
th
sample (u = 0,..N − 1)
belonging to the frame number l of the signal.
• The frequency f
0
of RF pulses could be known
from the RMI scanner datasheet. Otherwise, it can
be estimated using any precise method of period-
icity measure or by spectrum peak picking. The
estimated normalized frequency is denoted
b
ν
0
.
• Each frame is converted to the analytic complex
signal using the Hilbert transform. It is denoted
x
H
l
(u).
• The estimation of the amplitudes a
k,l
and the
phases φ
k,l
of each harmonic k, for each frame
l is performed by minimizing the Least Squared
(LS) error between the Hilbert transformed signal
x
H
l
(u) and the Hilbert transformed modeled RF
noise
b
x
H
l
(u):
e
l
(u) = x
H
l
(u) −
b
x
H
l
(u)
= x
H
l
(u) −
K−1
∑
k=0
b
a
k,l
e
j
(
2πk
b
ν
0
u+
b
φ
k,l
)
. (6)
where
b
a
k,l
and
b
φ
k,l
are the parameters to be deter-
mined.
• Minimizing the Least Square error leads to the
following solution:
b
V
l
= (M
T
W
T
W M)
−1
M
T
W
T
W X
H
l
, (7)
where T is the transpose operator, X
H
l
=
[x
H
l
(0),x
H
l
(1),...,x
H
l
(N − 1)]
T
is the vector of
Hilbert transformed samples, W is the analyzing
window vector of length N, M is a matrix of di-
mension N × K containing the exponential terms
M(l,k) = e
j2π
b
ν
0
kl
.
b
V
l
= [
b
v
0,l
,
b
v
1,l
,...,
b
v
K−1,l
]
T
is the
unknown vector of parameters.
One term
b
v
k,l
is written:
b
v
k,l
=
b
a
k,l
cos
b
φ
k,l
− j
b
a
k,l
sin
b
φ
k,l
. (8)
The final solution is
b
a
k,l
extracted as the modulus
of
b
v
k,l
and
b
φ
k,l
which is its phase.
• Once the parameters estimated, the RF pulse
frame is written:
b
x
l
(u) =
K−1
∑
k=0
b
a
k,l
cos
2πk
b
ν
0
l +
b
φ
k,l
. (9)
• The whole estimated signal
b
x(m) is estimated by
concatenating estimated frames.
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000
Frame duration (ms)
18
18.5
19
19.5
20
20.5
Normalized Standard Deviation
Segmental Signal to Noise Ratio (dB)
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
Segmental Signal to Noise Ratio
Normalized Standard Deviation
Figure 4: Segmental Signal to Noise Ratio and Normalized
Standard Deviation versus frame length.
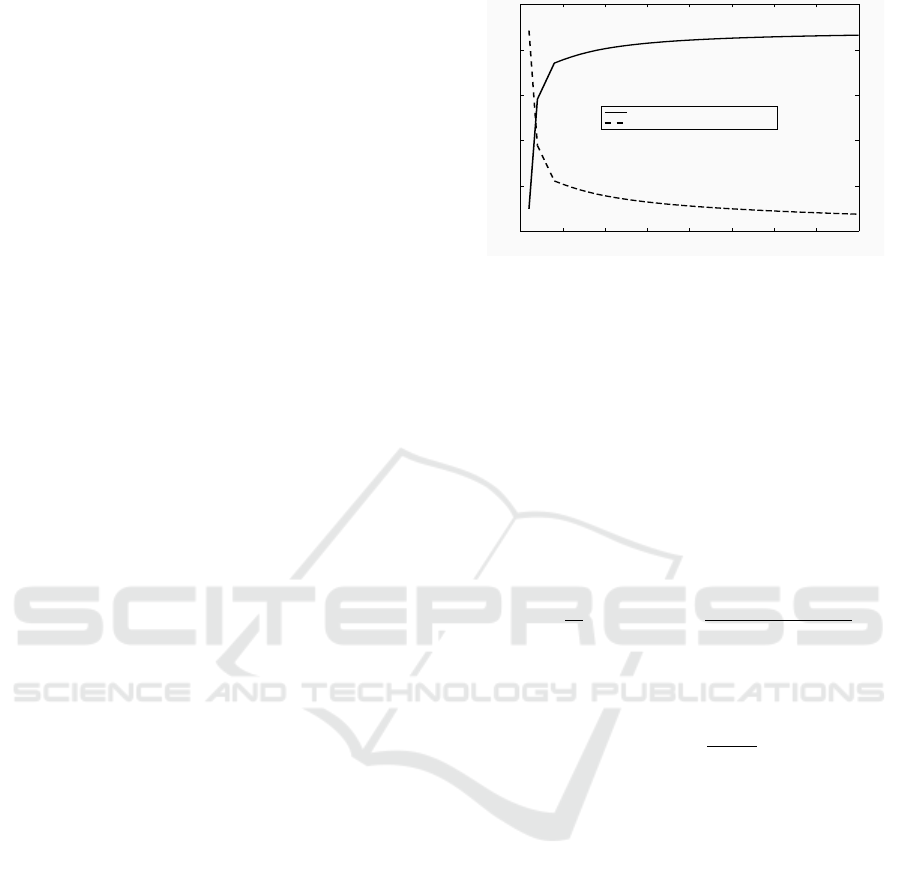
3.2 Frame Size Choice
The choice of frame size is crucial to obtain good RF
pulse modelization. Two criteria are used to quantify
the performances: the Segmental Signal to Noise Ra-
tio (SSNR) which is the mean value of the SNR (in dB)
calculated for each frame and its Normalized Stan-
dard Deviation (NSD
SSNR
), useful to put into propor-
tion the SSNR deviation along frames compared to its
mean. The two criteria are defined as follows:
SSNR =
1
M
M
∑
l=1
10log10
N
∑
u=1
x
l
(u)
2
N
∑
u=1
[x
l
(u) −
b
x
l
(u)]
2
,
(10)
and
NSD
SSNR
=
σ
SSNR
m
SSNR
, (11)
where σ
SSNR
(resp. m
SSNR
) is the SSNR standard
deviation (resp. mean) and M is the total number of
frames. Fig. 4 plots the evolution of both criteria for
different frame lengths. One can see that SSNR in-
creases and NSD
SSNR
decreases when frame length
increases. It means that better modelisation is ob-
tained for longer frames. However, the rate of im-
provement begins to stabilize around a frame size of
one second. This duration is considered adequate for
this study.
4 INTEREST IN EMG SIGNAL
DENOISING
4.1 The Idea
One RF pulse modelled, it is possible to reduce its ef-
fect on acquired EMG signal when RMI scanning is
BIOSIGNALS 2019 - 12th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
112

turned on and when the subject is activating its mus-
cle and doing the requested muscular exercice. The
corrupted EMG signal y(m) can be presented as the
sum of the muscle signal emg(m), the RF signal x(m)
and any other additive noises n(m):
y(m) = emg(m) + x(m) + n(m). (12)
The enhanced emg signal should be simply obtained
by subtracting the modeled RF signal
b
s(m) from the
observation y(m):
d
emg(m) = y(m) −
b
x(m). (13)
Note that other additive noises are not yet consid-
ered during this step, because of their low level com-
pared to that of RF noise. Common technical artifacts
can be reduced, in a post processing stage, using other
approaches (see for example (Thakor and Zhu, 1991)
for reducing power line electrical noise, (Lu et al.,
2009) to suppress electrocardiogram (ECG) interfer-
ence, (De Luca et al., 2010) to remove noise associ-
ated to mechanical perturbations...).
4.2 Illustration
When acquired, the EMG signal is buried in noise and
there is no ground truth to quantitatively measure the
performance. The idea developed here is to compare
the signal with a reference which could be the sig-
nal acquired out of scanner. Hence, the same partici-
pant is asked to do the same handgrip exercice inside
and outside scanner according to the same experimen-
tal paradigm. In each case, he did 15 contractions of
duration 4.4 seconds approximatively, separated by a
rest time of 44 seconds.
Fig. 5 (resp. Fig. 6) shows the temporal evolu-
tion (resp. spectrogram) of an EMG signal acquired
in the fRMI environment described previously, the
denoised one using the proposed approach and the
acquired EMG outside the scanner (called the refer-
ence). One can notice that EMG signal emerges from
noise despite the presence of small residual noise, and
the contractions have the same aspect as the ones of
the reference.
5 PERFORMANCES AND
COMPARISON
5.1 Overview on Comb Filtering and
Spectral Subtraction Methods
According to the state of art, few methods are devel-
oped to extract RF pulses from physiological signals
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
10
5
-4
-2
0
2
Noisy
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
10
5
-2
-1
0
1
HNM
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Time (ms)
10
5
-1
0
1
Reference
Figure 5: Temporal evolution of noisy, denoised and refer-
ence EMG signals.
Figure 6: Spectrograms of noisy, denoised and reference
EMG signals.
acquired in RMI tunnel. The most common approach
is based on Comb filtering (see for example (Ganesh
et al., 2007)). It operates in the temporal domain and
makes use of a digital filter which cancels frequency
components situated at frequencies multiple of funda-
mental frequency of RF pulses while keeping intact
the other frequencies.
Another approach is based on spectral subtraction
(see for example (Ben Jebara, 2014)). It operates
in the frequency domain to estimate the noise spec-
trum and to subtract it from noisy observation spec-
trum. The noise estimation is based on spectral min-
RF Pulses Modelization for EMG Signal Denoising in fRMI Environment
113

ima tracking in each frequency bin without any dis-
tinction between muscle activity and muscle rest. But
it looks for connected time-frequency regions of mus-
cle activity presence to estimate a bias compensation
factor. The proposed approach denoted HNM (Har-
monic plus Noise Model) is compared to spectral sub-
traction and Comb filtering.
5.2 Comparison Criteria
To compare the methods, two criteria are used. The
first one is quantitative and has the form of Mean Sig-
nal To Noise Ratio (MSNR) while the second one is
qualitative and uses the contraction profile.
• The MSNR is calculated as a mean value of 285
SNR values obtained by studying FDS muscle
contractions made by 19 subjects, each repeating
the action 15 times. One SNR is calculated by tak-
ing data from a clean EMG signal acquired out-
side the tunnel. An additive real fRMI noise, ac-
quired in fRMI tunnel without exercing any con-
traction, was added by varying its level (artificial
attenuation and amplification). Thus, it is possible
to calculate noisy MSNR (denoted MSNR
Noisy
)
and one MSNR at the output of the denoiser (de-
noted MSNR
Denoised
).
• The contraction profile is a visual criteria used to
evaluate the quality of denoising. It is obtained
thanks to the Root Mean Square signal which is
a technique for rectifying the raw signal and con-
verting it to an amplitude envelope. It is defined
as follows:
RMS(m) =
v
u
u
t
1
N
N/2−1
∑
n=−N/2
x(m + n)
2
, (14)
where x(n) is the m
th
sample of the signal on in-
terest and L is the length of the rectifying window.
It is chosen equal to L = 512 for a sampling fre-
quency of f
s
= 1kHz.
5.3 Results
Fig. 7 shows the evolution MSNR
Denoised
for different
values of MSNR
Noisy
ranging from -16 dB to 10 dB
dB. One can notice that, unlike HNM whose perfor-
mances vary according to the level of noise, Comb fil-
tering and spectral subtraction lead to quasi-constant
values of MSNR
Denoised
, independently of the noise
level. Furthermore, Comb filtering and spectral sub-
traction give better MSNR
Denoised
for high level of
noise (MSNR
Noisy
< -7 dB) while HNM performs for
greater values of MSNR
Noisy
.
-20 -15 -10 -5 0 5 10
MSNR
Noisy
-2
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
MSNR
Denoised
COMB
SS
HNM
Figure 7: Evolution of MSNR
Denoised
versus MSNR
Noisy
.
Figure 8: Contractions profile.
If we consider a real acquisition system: Biopac
MP150 system to digitize EMG data and General
Electric Medical System 3-Tesla whole-body MRI
system to generate RF pulses, a typical value of
MSNR
Noisy
is in the range [0 1] dB. In such case,
HNM should be used.
Fig. 8 draws the contraction profiles for the ref-
erence signal acquired outside the scanner and the
ones obtained after denoising. It is important to notice
that the contraction durations are not exactly the same
even though the volunteers were asked the follow the
same paradigm. The contraction durations are artifi-
cially contracted/expanded in time so that comparison
is confortable. Fig. 8 shows that contractions profiles
are well restored. Their level is attenuated with comb
filtering, their duration (at the beginning and at the
end) is extended with spectral subtraction. It seems
that HNM gives the best profile.
BIOSIGNALS 2019 - 12th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
114

6 CONCLUSION
In this paper, the problem of RF pulses noise contam-
inating the EMG signal acquired in fRMI scanner is
addressed. Thanks to its description in the frequency
domain and to its modelization using Harmonic plus
Noise model, it was possible to subtract it from EMG
signal, rmaking it exploitable for further analysis and
processing.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are thankful to the team ’Biomechan-
ics, Imagery and Physiology Movement Analysis’ of
Movement and Sport Research Centre (CeRSM) at
Paris 10 University, for asking the resolve the problem
of EMG enhancement and providing the experimental
data.
REFERENCES
Ben Jebara, S. (2014). Electromyogram signal enhance-
ment in frmi noise using spectral subtraction. In
Proceedings of the 22nd European Signal Processing
Conference, pages 1980–1984.
Bernstein, M. A., King, K. F., and Zhou, X. J. (2004).
Handbook of MRI pulse sequences. Elsevier.
De Luca, C. J., Gilmore, L. D., Kuznetsov, M., and Roy,
S. H. (2010). Filtering the surface emg signal: Move-
ment artifact and baseline noise contamination. Jour-
nal of biomechanics, 43(8):1573–1579.
Dougherty, J. B. (2010). A novel and comprehensive artifact
reduction strategy for EMG collected during fMRI at
3 Tesla. PhD thesis, Drexel University.
El Tatar, A. (2013). Caract
´
erisation et mod
´
elisation
des potentiels induits par les commutations des
gradients de champ magn
´
etique sur les signaux
´
electrophysiologiques en IRM. PhD thesis, Universit
´
e
de Technologie de Compi
`
egne.
Ganesh, G., Franklin, D. W., Gassert, R., Imamizu, H., and
Kawato, M. (2007). Accurate real-time feedback of
surface emg during fmri. Journal of neurophysiology,
97(1):912–920.
Garreffa, G., Carnı, M., Gualniera, G., Ricci, G., Bozzao,
L., De Carli, D., Morasso, P., Pantano, P., Colonnese,
C., Roma, V., et al. (2003). Real-time mr artifacts fil-
tering during continuous eeg/fmri acquisition. Mag-
netic resonance imaging, 21(10):1175–1189.
Hoffmann, A., J
¨
ager, L., Werhahn, K., Jaschke, M.,
Noachtar, S., and Reiser, M. (2000). Electroen-
cephalography during functional echo-planar imag-
ing: detection of epileptic spikes using post-
processing methods. Magnetic Resonance in
Medicine: An Official Journal of the Interna-
tional Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine,
44(5):791–798.
Hornak, J. P. (2006). The basics of mri. http://www. cis. rit.
edu/htbooks/mri.
Lu, G., Brittain, J. S., Holland, P., Yianni, J., Green, A. L.,
Stein, J. F., and Wang, S. (2009). Removing ecg noise
from surface emg signals using adaptative filtering.
Neuroscience letters, 462(1):14–19.
Pantazis, Y. (2010). Decomposition of AM-FM signals with
applications in speech processing. PhD thesis, Uni-
versity of Crete.
Thakor, N. V. and Zhu, Y.-S. (1991). Applications of adap-
tive filtering to ecg analysis: noise cancellation and
arrhythmia detection. IEEE Transactions on biomedi-
cal engineering, 38(8):785–794.
RF Pulses Modelization for EMG Signal Denoising in fRMI Environment
115
