
System Identification Algorithms Applied to Glottal Model Fitting
Piotr Barycki, Irene Murtagh and Barry Kirkpatrick
TU Dublin, Blanchardstown Campus, Dublin, Ireland
Keywords: Glottal Flow, Glottal Model, Pathological Speech, System Identification.
Abstract: This study proposes a new method of fitting a glottal model to the glottal flow estimate using system
identification (SI) algorithms. Each period of the glottal estimate is split into open and closed phases and each
phase is modelled as the output of a linear filter. This approach allows the parametric model fitting task to be
cast as a system identification problem and sidesteps issues encountered with standard glottal parametrisation
algorithms. The study compares the performance of two SI methods: Steiglitz-McBride and Prony. The tests
were performed on synthetic glottal signals (n=121) and real speech (n=50 healthy, n=23 pathological). The
effectiveness of the techniques is quantified by calculating the Normalised Root Mean Squared Error
(NRMSE) between the estimated glottal fit and the glottal estimate. Tests on synthetic glottal signals show
that the average performance of the Steiglitz-McBride method (97.25%) was better than the Prony method
(70.41%). Real speech tests produced results of 64.29% and 51.57% for healthy and pathological speech
respectively. The results show that system identification techniques can produce robust parametric model
estimates of the glottal waveform and that the Steiglitz-McBride method is superior to the Prony method for
this task.
1 INTRODUCTION
The glottal waveform represents the activity of the
vocal folds and can provide vital information about
the vocal folds and their behaviour. The glottal
waveform can be estimated from the speech signal
and is utilised in many speech processing
applications, including speech coding, synthesis and
speech disorder diagnosis (Klatt, 1990). Parametric
models of the glottal waveform are often employed
and despite the success of the glottal signal in
applications, challenges remain in accurately and
robustly estimating the parameters of these models.
This is the case for healthy speech but is particularly
notable for pathological speech. This study aims to
present a new model of the glottal waveform and test
methods to estimate the parameters of this model.
This is partly motivated by the need to develop a
method that can accurately and robustly estimate the
glottal parameters of pathological speech.
Parameterisation of the glottal signal consists of
two steps: (1) glottal waveform estimation and (2)
fitting a parametric model to the estimated glottal
waveform. Glottal waveform estimation is achieved
by removing the effect of the vocal tract from the
speech waveform, often by estimating a vocal tract
filter and inverse filtering the speech signal with this
filter to remove the vocal tract component. The
resulting glottal estimate will have the parametric
model fitted by applying an appropriate optimisation
procedure. This is typically a nonlinear optimisation
problem, depending on the particular glottal model
and how the problem is cast. This is the case for the
Liljencrants-Fant (LF) model, which is currently the
most widely adopted glottal waveform model. Both
of these steps have a number of known difficulties as
reported in (Li et al, 2011, 2012) (Fu, Murphy, 2006).
It is often impossible to fully remove the vocal
tract component from the speech waveform. This can
result in distortion of the glottal waveform often
presenting as ripples in the glottal waveform (Fant,
Lin 1987). This can also cause problems with correct
estimation of glottal opening and closing instants
(GOI and GCI respectively) and in turn, inaccurate
glottal parameter estimation. In fitting the parametric
model to the estimated glottal waveform, due to the
necessity to employ nonlinear optimisation methods,
the accuracy of the final glottal parameters depends
critically on the initial estimates used to initialise the
optimisation procedure (Strik, 1993). Bad initial
estimates will result in suboptimal estimation of the
parameters (Li et al, 2012). This problem becomes
124
Barycki, P., Murtagh, I. and Kirkpatrick, B.
System Identification Algorithms Applied to Glottal Model Fitting.
DOI: 10.5220/0007259801240131
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2019), pages 124-131
ISBN: 978-989-758-353-7
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
particularly challenging for pathological speech,
when the glottal parameters may be outside the
typical range expected for healthy speech.
This paper proposes a new way to model the
glottal waveform, which in turn allows the
application of new algorithms to estimate the glottal
parameters. The model being proposed considers the
open and closed phase of the glottal signal
individually and models the glottal signal within each
phase as the impulse response of a linear filter. This
allows fitting of the parametric model to the glottal
estimate to be cast as a system identification problem.
In this case the input is modelled as an impulse, the
output is either the open or closed phase of the glottal
estimate and the problem is to estimate the filter that
can best approximate the output for the given input
signal. Many system identification algorithms exist
that could be used for this task (Ljung, 1999),
including algorithms that have been developed to be
robust to noise in the output signal. This is
particularly beneficial for glottal signals with high
levels of aspiration noise, which is often the case for
pathological speech.
The remainder of this paper is arranged as
follows. Section 2 presents some background on
existing glottal models before presenting the details
of the new approach being proposed in this paper.
Section 3 describes how the model and associated
algorithms are tested. Section 4 presents the results
with discussion and Section 5 presents the
conclusions.
2 MODELING THE GLOTTAL
WAVEF OR M
Many signal models of the glottal waveform have
been proposed in the literature. These include the
Rosenberg model (Rosenberg, 1971), the
KLGLOTT88 (Klatt, 1990), the R++ model
(Veldhuis,1998), the CALM model (Doval et al,
2003) and the LF model, among others. Signal
models of the glottal flow generally focus on the
differentiated glottal flow. Typically, a separate
mathematical function is used to model the open and
return phases of the differentiated glottal signal, such
that they join at the GCI and the glottal pulse is
differentiable at the GCI. An example model signal of
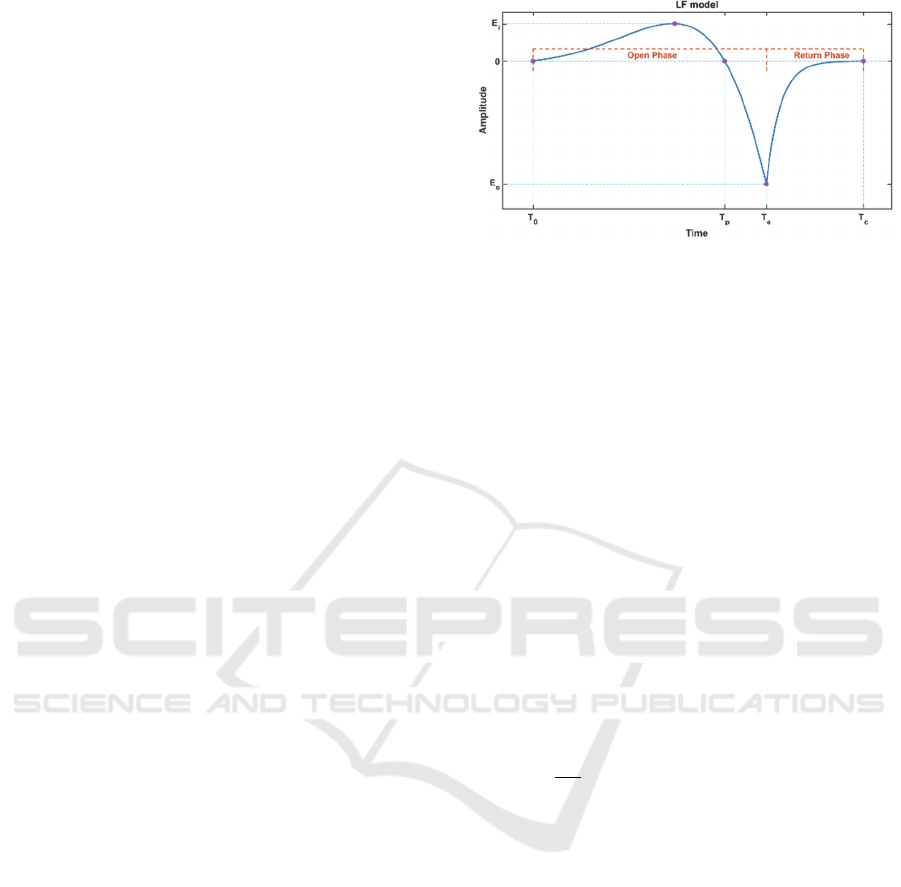
the differentiated glottal flow waveform generated
with the LF model is depicted in Figure 1.Most
models have a similar approach, in that they have a
separate
mathematical function for modelling the
Figure 1: LF model diagram of a differentiated glottal pulse.
open and return phases of the signal. The primary
difference between many of these models is the
functions employed to model each phase.
Currently the most widely adopted glottal model
is the LF model, equation 1. The model consists of
two parts, representing the open and return phases of
the glottal signal. The LF model is a five-parameter
model. The entire model can be defined using the
timing parameters T
a
, T
p
and T
e
, the pitch period T and
the amplitude of the glottal closure instant (GCI) E
e
.
T
a
and T
p
are times relative to the start of the pitch
period as depicted in Figure 1. T
a
is the time constant
of the exponential in the return phase. The time
parameter T
e
marks the instant of the glottal closure
and E
e
is the corresponding amplitude. Despite
having several more parameters, the LF model is
constrained by the five primary parameters and the
remaining parameters can be estimated from the
primary parameters.
sin
, 0
,
0,
(1)
Fu and Murphy (2006) proposed a new glottal
source estimation method based on a joint source-
filter separation technique using the LF model. Their
proposed technique estimates the parameters based
on the Rosenberg model and then converts them to
the LF parameters. They perform tests on synthetic
speech covering six phonation types and real healthy
speech files to verify the performance of their method
on ‘real-world’ data. They report a high accuracy of
the synthetic speech results and robustness against
additive glottal noise, stating that this allows their
new method to be applied to a wide range of voice
types. Tests on real speech report performance
comparable with that of the synthetic speech and state
that their model provides rather reliable estimation in
the case of natural utterances.
Li et al. (2011) proposed a new approach for LF
model based glottal source parameter estimation by
System Identification Algorithms Applied to Glottal Model Fitting
125

extended Kalman filtering and use synthetic speech to
conduct tests. They quantify the results by calculating
the error rates of the estimated shape controlling
parameters and report the method to be effective for
a wide range of LF parameters and overall, perform
better than the standard time-domain LF-model
fitting algorithm when tested on synthetic speech.
Work of Muthukumar et al. (2013) proposes
estimating the LF model parameters using a gradient
descent optimization algorithm. The accuracy of their
approach inherently depends on the accuracy of the
initial parameters. They iteratively fit a LF model to
the inverse filtered glottal signal and then optimise it
to minimize the RMS error. As a way of quantifying
the performance of their approach, they conducted a
listening test, comparing their model with a baseline
system described in (Yoshimura et al, 2001). The
majority of the listeners chose the proposed system as
more natural sounding and the results were deemed
statistically significant.
Previous studies on glottal fitting report
difficulties with the standard model fitting approach
and aim to overcome them in different ways. A major
problem is with estimating the vocal tract filter
without the glottal flow having an effect on the output
speech. This issue was already reported by Fant and
Lin back in (1987).
The glottal waveform estimation step can be
impacted by source-tract interaction and the
performance limitations inherent in some inverse
filtering algorithms (Quatieri, 2006). In the IAIF
method (Alku, 1991), the vocal tract filter is
estimated using an adaptive filter algorithm and
subsequently applied to estimate the glottal signal. A
more recent Quasi Closed Phase (QCP) method
described in (Airaksinen et al, 2014) eliminates the
source effect using weighted linear prediction (WLP)
and focuses on the samples located in the closed
phase. Recent work of Sahoo and Routray (2016)
implements system identification methods in a novel
glottal inverse filtering method. They report that
when compared to the most widely used IAIF and the
more recent QCP methods, their model using system
identification techniques produced results indicating
their model outperforms IAIF and QCP, however, at
the cost of computational speed.
2.1 Proposed Glottal Model
This study proposes modelling the open and return
phases of the glottal signal as the impulse response of
two linear filters. The input impulse occurs at the GCI
and the resulting filter outputs produce the open and
return phases of the glottal signal. For practical
purposes in processing the glottal signal the open
phase will be reversed in time and treated as a causal,
stable impulse response.
In the method proposed by Doval et al (2003), the
differentiated glottal flow signal is modelled as the
response of a linear filter. The model is referred to as
the causal-anticausal linear model (CALM), as the
glottal signal is modelled as having both causal and
anticausal components. The return phase corresponds
with the causal component and the open phase
corresponds with the anticausal component. The
method proposed in this study adopts a similar
approach, by modelling the glottal signal as the output
of linear filters. However, our approach treats the two
phases as outputs of two independent linear filters as
opposed to one a causal-anticausal linear filter model
considered by CALM, and models those filters using
SI methods.
The transfer functions requirements for the glottal
modelling filters are determined by matching them to
the LF model. The LF equation for the return phase is
a decaying exponential which corresponds with the
impulse response of a continuous time first order
filter. The open phase, when time reversed,
corresponds with a damped sinusoid or equivalently
the impulse response of a continuous time stable
second order filter. The corresponding transfer
functions in the Z transform domain are given in
equation 2 for the open phase transfer function,
(), and equation 3 for the return phase transfer
function,
(). The meeting point of the open and
return phases represents the GCI, T
e
, with amplitude
value of E
e
. The input impulse for each filter is set to
an amplitude of 1. For the open phase the input
impulse is applied at the sample corresponding with
the GCI. For the closed phased the impulse is applied
at the sample adjacent to the GCI within the closed
phase.
(2)
(3)
This model establishes the framework for
estimating the parameters of the glottal waveform as
a system identification problem allowing us to bypass
the problems posed by the issues encountered with
standard glottal parametrisation algorithms. The input
and output signals for open and closed phases are
known and a method to estimate the system that can
produce the corresponding response is required to
estimate the glottal parameters.
BIOSIGNALS 2019 - 12th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
126

2.2 Parameter Estimation
Numerous algorithms exist that could be used to solve
the system identification problem to estimate the
glottal parameters for the proposed models (Ljung,
1999). For this study Prony’s method (Hayes, 2009)
and the Steiglitz McBride method (Steiglitz,
McBride, 1965) where selected to estimate the
parameters of the transfer function models of the open
and return phases of the glottal signal.
Prony’s method was selected as it has a relatively
low computational complexity only requiring the
solution of a set of linear equations, to provide the
parameters of a given model. A disadvantage of
Prony’s method is that it is known to have poor
performance when presented with a noisy output
signal (Kumaresan et al, 1984).
The Steiglitz-McBride algorithm is an iterative
technique of linear system identification. It works by
minimising the mean-square error between the output
of the system and the estimated model output and
improving the estimate at each iteration. The first
iteration of the Steiglitz-McBride algorithm requires
a means to make an initial estimate of the model
parameters to initialise the algorithm. This is often
achieved by applying Prony’s method. The Steiglitz-
McBride algorithm was selected for this study as it is
known to be robust to noise in the output signal and
can provide optimal estimates in the case of white
noise in the output signal (Steiglitz, McBride, 1965
and Stoica, Soderstrom, 1981). This study employs
Prony’s method to initialise the Steiglitz-McBride
algorithm.
3 THE EXPERIMENT
The aim of this study is to test a new model of the
glottal waveform that utilises SI algorithms to
parametrise the glottal signal. Two SI algorithms are
considered, the Prony method and the Steiglitz Mc
Bride algorithm, as described in section 2.2. The
experiment is designed to (1) quantify the
performance of the SI algorithm in terms of the
accuracy of the glottal fit, (2) to determine their
robustness to noise in the glottal estimate and (3) to
identify the performance of the algorithms in real
speech and identify differences in performance of
each algorithm between healthy and pathological
speech.
Tests are performed to fit the proposed glottal
model to glottal waveform estimates using each of the
two SI algorithms considered. These tests are
performed on both synthetic glottal pulses and on
glottal estimates from real speech, including
pathological speech. To quantify the quality of the
glottal fit to a glottal pulse the Normalised Root Mean
Square Error (NRMSE) is employed. The NRMSE
will be displayed in the form of a percentage in which
an NRMSE of 100% represents a perfect fit of the
model to the glottal estimate and 0% represents a
performance level corresponding with that of a best
line fit to the glottal waveform estimate. Testing is
performed on both synthetic glottal signals and glottal
estimates from real speech.
3.1 Synthetic Glottal Waveforms
The first part of this study tests the algorithms on
synthetic glottal signals. Synthetic glottal signals
allow the comparison between the glottal fit with the
true glottal signal, unlike for real speech in which the
true glottal signal is not known and only an estimate
is available. Glottal signal estimates from real speech
are likely to have unquantifiable sources of variation
introduced by errors in the inverse filtering algorithm
used to estimate the glottal signal. This typically
introduces features into the glottal signal that are not
accounted for by the glottal model and can impact the
results. Using synthetic glottal signals bypasses these
issues and allows the test set to cover a broad range
of glottal parameters and noise levels in a controlled
manner.
The tests with synthetic glottal signals consist of
3 parts:
Test 1 - The first part consists of testing 100
synthetic glottal pulses with no noise over a range of
voice types. This test determines the accuracy of the
proposed model and accompanying SI algorithms
across a range of voice types with no noise present.
Test 2 - The second part of the test is similar to
test 1, but with noise added. This test determines the
accuracy of the proposed model and accompanying
SI algorithms across a range of voice types when
noise is present in the glottal signal.
Test 3 - The third part of the test is to determine
the accuracy of the fit as the noise level is varied. The
parameters of the glottal pulse are held constant. This
test indicates the robustness of the methods to noise
in the glottal signal.
All synthetic glottal pulses were created using the
LF model equations as given in equation (1). The
parameters were varied to simulate the variations in
real human speech.
For test 1 the 100 pulses are split into 2 groups of
50 pulses, representative of male and female speech.
System Identification Algorithms Applied to Glottal Model Fitting
127

Table 1: Artificial speech timing parameters.
The 50 pulses representing male speech contain
100 samples per pitch period, this corresponds with a
pitch of 100 Hz and sampling frequency of 10000 Hz.
The 50 pulses representing female speech contain 41
samples per pitch period, this corresponds with a
pitch of 244 Hz and sampling frequency of 10000 Hz.
Within each set of 50 pulses the glottal parameters are
selected to have 10 pulses each of the voice types;
modal, fry, breathy, falsetto and harsh. The timing
parameters used to create these voice types are given
in Table 1 (Ghosh, Narayanan, 2011). To create 10
samples of each voice type, the timing parameters
were randomly varied in the range of 5% about the
values in Table 1.
For test 2, the signal to noise ratio (SNR) of the
glottal signals was set to 40 dB. This was achieved by
adding white noise to each of the glottal pulses in the
test set for test 1. The value of 40dB was chosen as it
is the typical SNR value reported for modal speech
(Ghosh, Narayanan, 2011). For test 3, 21 glottal
pulses were generated with SNR levels varying
between 0 and 100 dB, increasing in 5 dB increments.
The glottal pulses each contained 100 samples per
pitch period and had the timing parameters of modal
speech. Only the SNR value varied between the 21
glottal pulses.
3.2 Real Speech
Tests on synthetic glottal signals provide insight on
the effectiveness of the methods, but does not present
as challenging a task as real speech. The real speech
tests show how the method performs on samples with
levels of signal complexity not represented in the
synthetic glottal signals. It also indicates how the
performance is impacted when the methods being
tested are combined with non-ideal glottal estimation
algorithms. The real speech tests consist of two parts,
the first part investigates real healthy speech and the
second part investigates real pathological speech. The
real speech files have been accessed from the Speech
Synthesis book by D.G. Childers (Childers, 1999).
The study uses healthy and pathological speech
samples from patients 20 to 80 years old consisting of
/a/ and /i/ vowel utterances. The signals were sampled
at 10 kHz and recorded using a Bruel & Kjaer
microphone. The speech database assembled for this
study is as follows:
Healthy speech – 50 utterances of the vowel /a/,
25 male and 25 female.
Pathological speech - 23 utterances of the vowel
/i/, 8 male and 15 female.
The files were inverse filtered to extract the glottal
flow derivatives using the IAIF method described in
(Alku, 1991). The GCI locations were determined
using the SEDREAMS algorithm reported in
(Drugman, 2012). Using the GCI locations of the
inverse filtered signals, each glottal estimate signal
was divided into sections of individual pitch periods.
The glottal model fitting algorithms were then applied
to each pitch period. The NRMSE values were
calculated between each glottal signal and its glottal
model fit and the average NRMSE value for each
speech file was recorded.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The following section presents the test results in two
subsections, first section documents the synthetic
glottal signal results and the second presents the
results from real speech tests.
4.1 Tests Using Synthetic Glottal
Signals
The performance of the algorithms is compared by
investigating the NRMSE values between the
estimated fit and the original glottal signal. The
results for synthetic glottal signals are presented in
Table 2.
Test 1 – For the 50 pulses simulating a 100 Hz
male speech, the NRMSE values for Steiglitz-
McBride and Prony methods are 97.99% and 97.93%
respectively. Tests on the set of 50 pulses created to
simulate a 240 Hz speech signal sampled at 10000 Hz
produced the following results: The mean NRMSE
value for the Prony algorithm was 98.24% and
98.86% for the Steiglitz-McBride method. These
result shows that the performance of the two methods
was approximately equal for these tests.
Test 2 – The NRMSE values for the Prony and
Steiglitz-McBride algorithms tested on the 50 pulses
with added noise for male samples are 29.20% and
96.23% respectively. For female samples, the results
are 55.66 % and 96.55% for Prony and Steiglitz-
BIOSIGNALS 2019 - 12th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
128

McBride algorithms respectively. A notable drop in
performance occurs in the results for the Prony
method when noise is introduced, consistent with
reports that the Prony algorithm does not perform
well in noisy environments (Kumaresan et al, 1984).
The Steiglitz McBride results are comparable with the
results recorded when no noise was present in the
glottal signal.
Test 3 – The results of this test are illustrated in
Figure 2. The NRMSE values are plotted against the
corresponding SNR values. This indicates the decline
in performance as noise levels increase for each
algorithm. It can be noted from Figure 2 that between
SNR of 100 and 70 dB, both algorithms perform
similarly. As the noise level increases, the
performance of the Prony method begins to
deteriorate noticeably more than the performance of
the Steiglitz-McBride algorithm. Taking the 90%
NRMSE value as a reference point, it can be seen that
the performance of the Prony method drops below
this level at SNR at approximately 60 dB while the
Steiglitz-McBride algorithm provides a 90%+ fit to
approximately 30 dB SNR level. This indicates that
the Steiglitz-McBride method performs more
robustly than the Prony method for noisy glottal
signals.
A statistical analysis test was carried out to verify
whether the results provide any statistical
significance. The results of Steiglitz-McBride and
Prony algorithms were compared using the student t-
test. The null hypothesis states that the samples from
the two datasets have the same mean at the 5%
significance level. In all cases, the null hypothesis is
rejected indicating the difference in the means is
statistically significant.
Figure 2: Graph comparing NRMSE values with their
respective SNR values for Prony and Steiglitz-McBride
methods.
4.2 Tests Using Real Speech
The second part of the study consisted of performing
tests on real speech, including both healthy and
pathological speech. The results are presented in
Table 3. For healthy speech the mean NRMSE value
for the Prony method was 29.23% and for the
Steiglitz-McBride method was 64.29%. For the
pathological speech results, the Prony methods mean
NRMSE value was 25.66% while the mean NRMSE
Table 2: Artificial speech test results.
Table 3: Real speech test results.
value of the Steiglitz-McBride method is 51.57%.
The Steiglitz-McBride method demonstrated better
accuracy at fitting the glottal model to the estimated
glottal waveform for both healthy and pathological
speech. The results for real speech are notably lower
than those reported for synthetic glottal signals.
To verify the statistical significance of the results
for real speech, we again used the student t-test, with
the same null hypothesis and levels of significance.
For both, healthy and pathological results, the test
rejected the null hypothesis indicating the difference
in the means is statistically significant, when
comparing Steiglitz-McBride and Prony algorithms.
4.3 Sample Fits
This section presents sample fits of the glottal model
to the inverse filtered estimate for both healthy and
pathological speech using the Steiglitz-McBride
algorithm. The example glottal fit in Figure 3 is for a
healthy glottal pulse and has a match of 75.57%. The
fit in Figure 4 illustrates the Steiglitz-McBride
method applied to the glottal waveform of a
pathological speech sample and has an NRMSE of
54.17%.
System Identification Algorithms Applied to Glottal Model Fitting
129
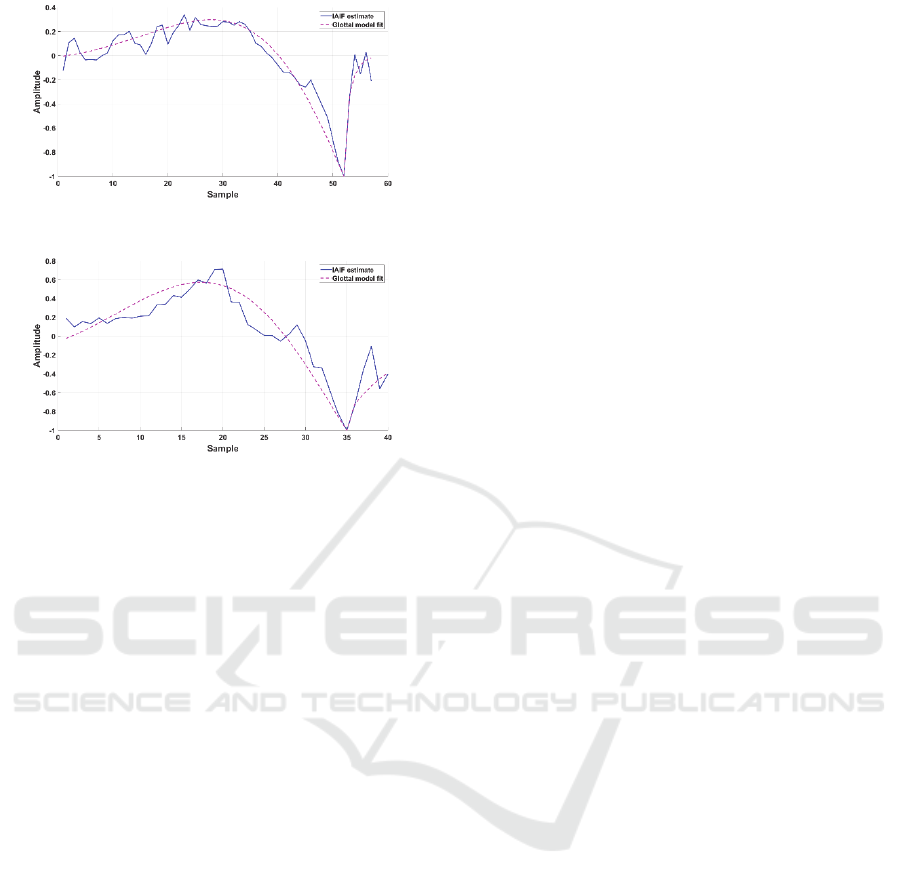
Figure 3: 75.57% NRMSE glottal fit.
Figure 4: 54.17% NRMSE glottal fit.
Many factors can influence the quality of the
glottal fit and the NRMSE value, including the
complexity of the signal, the presence of noise in the
glottal signal, the number of samples available for
parameter estimation in each pitch period and the
accuracy of the GCI locations. The presence of noise
in the glottal signal causes the NRMSE values to
decrease, even when a good fit is achieved. The fit in
Figure 3 is a representative example of this.
Pathological speech typically contains more
aspiration noise than healthy speech and may have
features not modelled by existing glottal models. The
accuracy of the glottal fitting depends on the accuracy
of the glottal estimation algorithms. If the inverse
filtering method is not accurate, it can lead to artefacts
in the glottal estimate. All these factors can affect the
performance of the model fitting algorithms and in
turn the accuracy of the fit. This is notably evident in
Figure 4, in which the glottal pulse contains features
that cannot be captured by the model, which is
reflected in the NRMSE value.
5 CONCLUSION
Accurate glottal model parametrisation for real
speech proves to be challenging problem, most
notably for pathological speech. The purpose of this
study was to investigate if this challenge can be
overcome by using a different approach.
The results of this study show that it is possible to
reliably fit and parametrise the glottal model of the
speech signal using system identification algorithms
applied through the newly proposed approach. The
method created accurate fits for artificial speech
samples and fit the glottal models with the average
accuracy of 64.29% for healthy and 51.57% for
pathological speech using the Steiglitz-McBride
method. The method demonstrates the effectiveness
of the proposed approach for a wide range of voice
qualities and different levels of noise in the glottal
signal.
The study also found that out of the two methods
used, the Steiglitz-McBride algorithm performs the
operation more robustly in both, synthetic and real
speech. The synthetic speech test results for samples
without additive noise show that both algorithms have
similar performance, however, results from samples
containing noise show superior performance of the
Steiglitz-McBride method. The Prony method was
found to perform poorly in noisy environments.
Results from real speech tests show that the Steiglitz-
McBride method outperforms the Prony method in all
cases.
This study shows promising results of the
proposed approach and indicate that it could be an
effective tool in estimating glottal models for healthy
speech and for the more challenging case of
pathological speech. Further research is required to
more comprehensively evaluate the method, on larger
real speech datasets and with a broader range of
performance metrics, to identify the strengths and
weaknesses of the method and compare it with
existing glottal model fitting methods.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors would like to acknowledge the
Technological University Dublin for funding this
research project.
REFERENCES
Airaksinen, M. et al. (2014) Quasi Closed Phase Glottal
Inverse Filtering Analysis with Weighted Linear
Prediction. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech
and Language Processing (TASLP). 22 (3), pp. 596-
607.
Airas, M. (2008) TKK Aparat: An Environment for Voice
Inverse Filtering and Parameterization. Logopedics
Phoniatrics Vocology. 33 (1), pp. 49-64.
Alku, P. (1992) Glottal Wave Analysis with Pitch
Synchronous Iterative Adaptive Inverse
Filtering. Speech Communication. 11 (2-3), pp. 109-
118.
BIOSIGNALS 2019 - 12th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
130

Boersma, P. (2006) Praat: Doing Phonetics by
Computer. Http://www.Praat.Org/.
Childers, D.G. (1999) Speech Processing. : John Wiley &
Sons, Inc.
Doval, B., d'Alessandro, C. & Henrich, N. (2003) The
Voice Source as a causal/anticausal Linear Filter. ISCA
Tutorial and Research Workshop on Voice Quality:
Functions, Analysis and Synthesis.
Drugman, T. (2012) Glottal Analysis Toolbox
(Gloat). Downloaded November.
Fant, G., Liljencrants, J. & Lin, Q. (1985) A Four-
Parameter Model of Glottal Flow. Stl-Qpsr. 4 (1985),
pp. 1-13.
Fu, Q. & Murphy, P. (2006) Robust Glottal Source
Estimation Based on Joint Source-Filter Model
Optimization. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech,
and Language Processing. 14 (2), pp. 492-501.
Ghosh, P.K. & Narayanan, S.S. (2011) Joint Source-Filter
Optimization for Robust Glottal Source Estimation in
the Presence of Shimmer and Jitter. Speech
Communication. 53 (1), pp. 98-109.
Hanratty, J., Deegan, C., Walsh, M. and Kirkpatrick, B.,
(2016) Analysis of Glottal Source Parameters in
Parkinsonian Speech. . 2016.
Hayes, M.H. (2009) Statistical Digital Signal Processing
and Modeling. : John Wiley & Sons.
Klatt, D.H. & Klatt, L.C. (1990) Analysis, Synthesis, and
Perception of Voice Quality Variations among Female
and Male Talkers. The Journal of the Acoustical Society
of America. 87 (2), pp. 820-857.
Kumaresan, R., Tufts, D. & Scharf, L.L. (1984) A Prony
Method for Noisy Data: Choosing the Signal
Components and Selecting the Order in Exponential
Signal Models. Proceedings of the IEEE. 72 (2), pp.
230-233.
Li, H., O'Brien, D. & Scaife, R. (2012) Comparison of
Time-and Frequency-Domain Based LF-Model Fitting
Methods for Voice Source Parametrisation.
Li, H., Scaife, R. & O’Brien, D. (2011) LF Model Based
Glottal Source Parameter Estimation by Extended
Kalman Filtering. Proceedings of the 22nd IET Irish
Signals and Systems Conference.
Li, H., Scaife, R. & O'Brien, D. (2012) Automatic LF-
Model Fitting to the Glottal Source Waveform by
Extended Kalman Filtering. Signal Processing
Conference (EUSIPCO), 2012 Proceedings of the 20th
European. : IEEE, pp. 2772.
Ljung, L. (1999) System Identification-Theory for the User
2nd Edition PTR Prentice-Hall. Upper Saddle River,
NJ.
Muthukumar, P.K., Black, A.W. & Bunnell, H.T. (2013)
Optimizations and Fitting Procedures for the
Liljencrants-Fant Model for Statistical Parametric
Speech Synthesis. Interspeech. pp. 397.
Quatieri, T.F. (2006) Discrete-Time Speech Signal
Processing: Principles and Practice. : Pearson
Education India.
Rosenberg, A.E. (1971) Effect of Glottal Pulse Shape on
the Quality of Natural Vowels. The Journal of the
Acoustical Society of America. 49 (2B), pp. 583-590.
Sahoo, S. & Routray, A. (2016) A Novel Method of Glottal
Inverse Filtering. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio,
Speech and Language Processing (TASLP). 24 (7), pp.
1230-1241.
Steiglitz, K. & McBride, L. (1965) A Technique for the
Identification of Linear Systems. IEEE Transactions on
Automatic Control. 10 (4), pp. 461-464.
Stoica, P. & Soderstrom, T. (1981) The Steiglitz-McBride
Identification Algorithm Revisited--Convergence
Analysis and Accuracy Aspects. IEEE Transactions on
Automatic Control. 26 (3), pp. 712-717.
Strik, H., Cranen, B. & Boves, L. (1993) Fitting a LF-
Model to Inverse Filter Signals. Third European
Conference on Speech Communication and
Technology.
Veldhuis, R. (1998) A Computationally Efficient
Alternative for the liljencrants–fant Model and its
Perceptual Evaluation. The Journal of the Acoustical
Society of America. 103 (1), pp. 566-571.
Yoshimura, T., Tokuda, K., Masuko, T., Kobayashi, T. &
Kitamura, T. (2001) Mixed Excitation for HMM-Based
Speech Synthesis. Seventh European Conference on
Speech Communication and Technology.
System Identification Algorithms Applied to Glottal Model Fitting
131
