
Motion Evaluation of Therapy Exercises by Means of
Skeleton Normalisation, Incremental Dynamic Time Warping and
Machine Learning: A Comparison of a Rule-Based and a
Machine-Learning-Based Approach
Julia Richter, Christian Wiede, Ulrich Heinkel and Gangolf Hirtz
Department of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology
Technische Universit
¨
at Chemnitz, Reichenhainer Str. 70, 09126 Chemnitz, Germany
Keywords:
Health Care, Medical Training Therapy, Motion Quality Assessment, Assistance Systems, Machine Learning,
Dynamic Time Warping, Skeleton Normalisation.
Abstract:
The assessment of motions by means of technical assistance systems is attracting widespread interest in fields
such as competitive sports, fitness and rehabilitation. Current research has achieved to generate feedback that
concerns quantity or the grade of similarity with regard to correct reference motions. In view of post-operative
rehabilitation exercises, such type of feedback is regarded as insufficient. That is why recent research aims
at providing a qualitative feedback by communicating motion errors. While existing systems investigated the
use of manually defined rules to detect motion errors, we suggest to employ machine learning techniques in
combination with dynamic time warping and to train classifiers with sample exercise executions represented by
3-D skeletons joint trajectories. This study describes both a rule-based and a machine-learning-based approach
and compares them with regard to their accuracy. In the second place, this study seeks to investigate the effect
of using normalised hierarchical coordinates on the classification accuracy if data of different persons is used
for the machine-learning-based approach. The results reveal that the performance of the machine-learning-
based method compares well with the rule-based concept. Another outcome to emerge from this study is that
normalised hierarchical coordinates allow to use data of different persons.
1 INTRODUCTION
Latest results from interviews with medical experts
from rehabilitation centres revealed that nowadays a
therapist has to supervise up to fifteen patients simul-
taneously (L
¨
osch et al., 2018). Consequently, patients
do not receive continuous feedback from a therapist
while they are performing therapy exercises, so that
incorrect motion executions are not detected and can-
not be instantly corrected.
A variety of studies have already demonstrated
that the manner of motion execution influences the
muscle activity during an exercise (Kang et al., 2016),
(Caterisano et al., 2002), (Gorsuch et al., 2013). For
this reason, it is of high importance to control the mo-
tion execution by means of feedback. In this way, mo-
tion errors can be avoided so that the intended muscles
are strained and the desired effects can be achieved.
A possible solution to provide feedback to a pa-
tient could be a technical assistance system that imita-
tes the therapist’s feedback. Such a system could not
only be beneficial in the post-operative rehabilitation
phase, but it could also be used by healthy persons at
home as a preventive measure for maintaining their
mobility.
Therefore, the overall objective that is pursued in
our work is to develop an assistance system to su-
pervise persons during their medical training therapy
when no therapist is present to supervise their perfor-
mance, either in rehabilitation centres or at home. For
this, the therapist’s knowledge and his or her visual
perception as well as the therapist’s real-time feed-
back shall be reproduced. This work includes the
recognition of exercise-specific motion errors during
the exercise execution to ensure the exercise quality.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 gives
an overview about extant systems and recent research
on motion analysis, whereupon the research issue is
described. Section 3 introduces the developed assis-
tance system. The system evaluation is presented in
Section 4. Finally, Section 5 summarises the paper
and draws conclusions about future work.
Richter, J., Wiede, C., Heinkel, U. and Hirtz, G.
Motion Evaluation of Therapy Exercises by Means of Skeleton Normalisation, Incremental Dynamic Time Warping and Machine Learning: A Comparison of a Rule-Based and a
Machine-Learning-Based Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0007260904970504
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2019), pages 497-504
ISBN: 978-989-758-354-4
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
497

2 RELATED WORK
The following sections introduce state-of-the-art
feedback systems and recent research that has been
carried out so far.
2.1 Extant Systems for Motion Analysis
A variety of systems that provide feedback to the user
can be found in the field of fitness training. Examples
of prominent providers are Technomex, Balori, Erg-
ofit, HUR and TecnoBody, which equip fitness cen-
tres with their devices. Table 1 provides an overview
about the above mentioned systems.
When taking a closer look at these existing solu-
tions, however, it becomes obvious that the focus lies
on monitoring exercise quantity rather than exercise
quality. Additionally, the feedback is mainly gene-
rated by means of sensors integrated in the devices,
such as force, acceleration and distance sensors. In
that way, motion amplitudes, velocities and the num-
ber of repetitions can be determined based on indi-
rectly measured parameters in the training machine,
e. g. the calculated torsional moment in the lever arm.
Another major drawback of these systems is that they
do not detect specific motion errors. Consequently,
information about the motion quality is not available.
A step further goes the system developed by Pix-
formance. Their system processes 3-D skeleton joints
in combination with manually defined rules in order
to detect motion errors. Similar to Pixformance, Zhao
et al. (Zhao et al., 2014) manually defined exercise-
specific rules in XML format in cooperation with cli-
nicians. Joint distances, joint angles, body segment
orientations and repetition velocities were evaluated
to assess motions.
2.2 Recent Research on Motion
Analysis
A possibility to identify incorrect motions and to sub-
sequently assess the person’s performance is to match
the executed motion against pre-defined references or
templates. Thereby, a variety of approaches employed
sensors that do not provide direct information about
joint positions. Yurtman et al. distributed wearable
motion sensors, i. e. accelerometers, gyroscopes and
magnetometers, over the human body in order to clas-
sify a therapy exercise as correct or incorrect (Yurt-
man and Barshan, 2013). They searched for occurren-
ces of defined template signals by using dynamic time
warping (DTW). For post-stroke rehabilitation, Tor-
mene et al. employed DTW on data provided by strain
sensors that were worn into a long-sleeve shirt (Tor-
mene et al., 2009). Tak et al. published a method for
human abnormality detection in video sequences, for
which they used DTW as well (Tak et al., 2011). Their
method compared distance curves calculated from the
detected foreground regions in each frame to find mo-
tion similarities.
Driven by the launch of the Kinect version 1.0 in
2010, researchers have increasingly investigated as-
sessment methods that utilise the Kinect skeleton mo-
del (Shotton et al., 2013). Existing work examined
motions during sports, such as dancing, ballet training
and Tai Chi exercises, using the Kinect skeleton (Gal
et al., 2015), (Huang et al., 2013), (Muneesawang
et al., 2015), (Lin et al., 2013). These works introdu-
ced a variety of distance metrics in order to compare
a performed motion against a reference. Such me-
trics were, for example, angles between joints (Gal
et al., 2015), angles between body motion vectors
(Huang et al., 2013) or the mean Euclidean distance
between joint trajectories (Lin et al., 2013). Although
the presented algorithms originally were not designed
for therapy exercise assessment, their principle work-
flows were still inspiring for similarity assessment in
view of therapy.
Hence, in the field of physical rehabilitation, simi-
lar principles can be found. In order to assess moti-
ons, several of the presented works successfully de-
monstrated the use of DTW (Su et al., 2014), (Antu-
nes et al., 2016) or variants of DTW, such as Incre-
mental Dynamic Time Warping (IDTW) (Khan et al.,
2014) and Subsequence DTW (Baptista et al., 2017).
The principle of these approaches is to align the two
sequences and to calculate similarity measures or sco-
res. Antunes et al., for example, calculated and visu-
alised feedback vectors that show the difference bet-
ween the performed and the template motion of body
parts (Antunes et al., 2016). Baptista et al. exten-
ded this approach by investigating the alignment of
a template and the performed exercise by means of
Subsequence DTW and Temporal Commonality Dis-
covery, whereas one sequence is a subsequence of the
other (Baptista et al., 2017). Khan et al. introduced
a method for continuous real-time evaluation, which
is called IDTW, (Khan et al., 2014). The system they
developed provides a similarity score but does not de-
termine specific errors.
2.3 Research Issue
The purpose of this investigation is to explore approa-
ches that allow the recognition of errors that typically
occur during the performance of three selected exerci-
ses of therapeutic relevance: hip abduction, hip exten-
VISAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
498
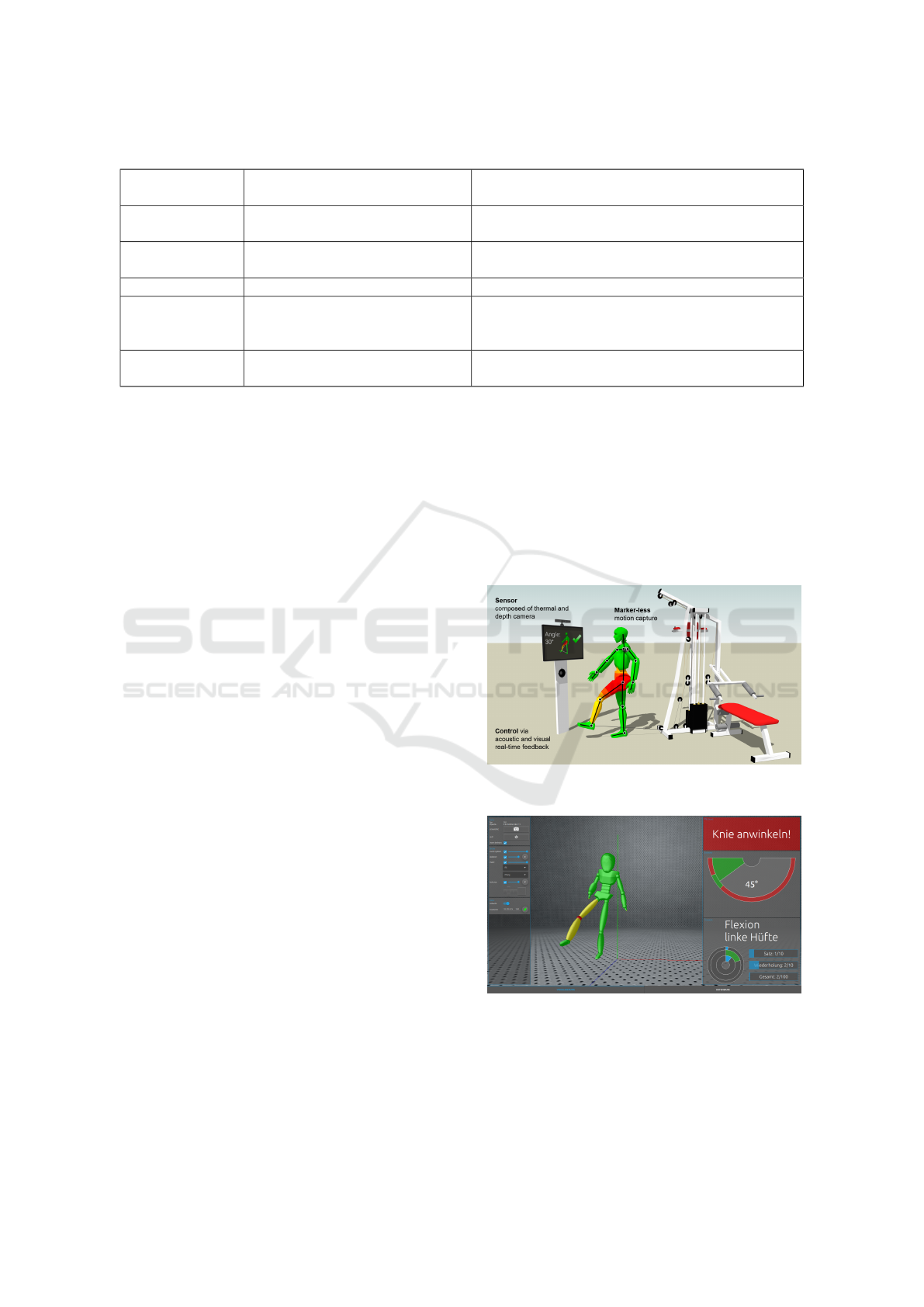
Table 1: Selection of feedback systems on the market.
System/ Provi-
der
Application Field Description
Technomex Fitness games with focus on mo-
tivation
Skeleton-based measurement, not meant for reha-
bilitation, no motion error detection
Pixformance Motion feedback in the field of fit-
ness training
Skeleton-based measurement, rule-based motion
error detection, manual rule specification
Balori Coordination and balance training Balance training based on pressure plate
HUR, Ergofit Motion feedback in the field of fit-
ness
Indirect measurement via sensors integrated in the
machine, feedback is visualised by means of inten-
sity bars and amplitude plots
TecnoBody Motion feedback in the field of fit-
ness
Skeleton-based measurement, no motion error de-
tection by means of joint trajectories
sion and hip flexion, which are performed on a pulley
machine and are error-prone due to the unrestricted
motion range the machine allows.
We firstly investigated a rule-based approach to
detect motion errors in real-time. Exercise-specific
rules had to be defined and suitable thresholds had
to be determined. The results of this approach serve
as a reference benchmark for the comparison against
the proposed machine-learning-based approach. Se-
condly, we designed, implemented and evaluated a
machine-learning base approach, which avoids the
manual specification of rules. The principle of the ap-
proach has already been presented in (Richter et al.,
2017b). In order to avoid taking pre-recordings and
examples of incorrect motions for new patients, we
investigated a normalisation method. Therefore, the
performance of two types of coordinate representati-
ons, i. e. local and normalised hierarchical coordina-
tes, was compared against each other by using three
different scenarios. Since we intend to give real-time
feedback, the approach adapted the IDTW algorithm
(Khan et al., 2014).
Two research questions arise at this point and shall
be answered in the course of this study:
a) Can we train a machine by means of example se-
quences, so that the classification performance is
similar to that of the rule-based approach?
b) Does the normalisation of skeleton data allow the
usage of training data that is different from the
person who finally uses the system?
3 DEVELOPED ASSISTANCE
SYSTEM
3.1 Concept Overview
The developed assistance system has already been
presented in (Richter et al., 2017a) and (Richter et al.,
2017b), whereas the focus lied on hip abduction.
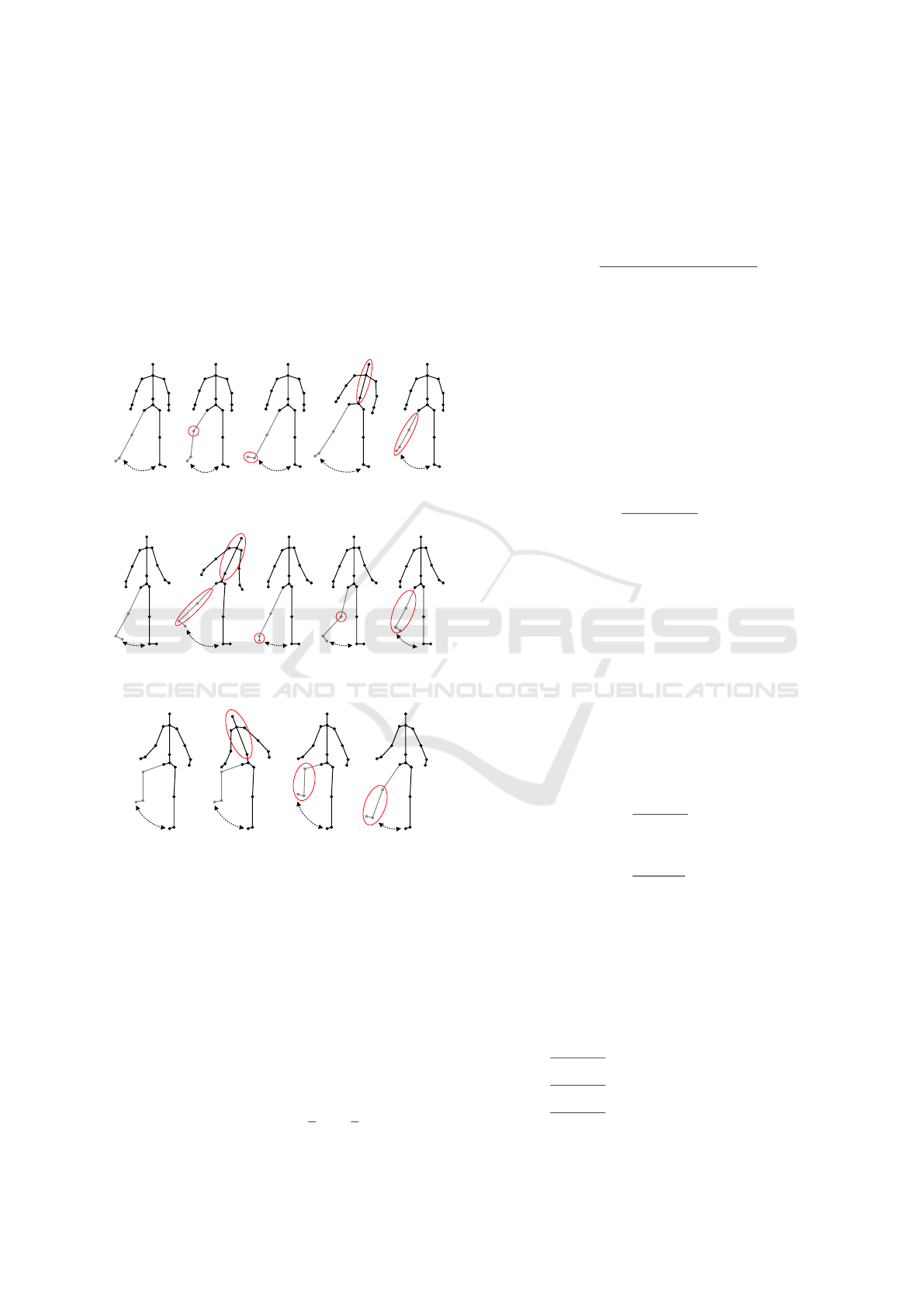
Figure 1 presents the concept of the assistance sy-
stem: It consist of a sensor, i. e. a Kinect version 1.0,
that measures the 3-D joint positions of a person’s
skeleton. Based on these positions, motion errors are
determined in real-time. This information is sent to
a feedback unit and visualised in form of feedback
messages and joints of an animated avatar that are co-
loured depending on their involvement in the detected
error. The feedback system is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 1: Concept of the assistance system (Richter et al.,
2017a).
Figure 2: Feedback display: In this example, the person per-
forms the exercise hip flexion and does not bend the knee in
the correct way. A message with a suggestion how to cor-
rect the motion appears in real time (see top right, transla-
ted: Bend your knee!).
Motion Evaluation of Therapy Exercises by Means of Skeleton Normalisation, Incremental Dynamic Time Warping and Machine Learning:
A Comparison of a Rule-Based and a Machine-Learning-Based Approach
499
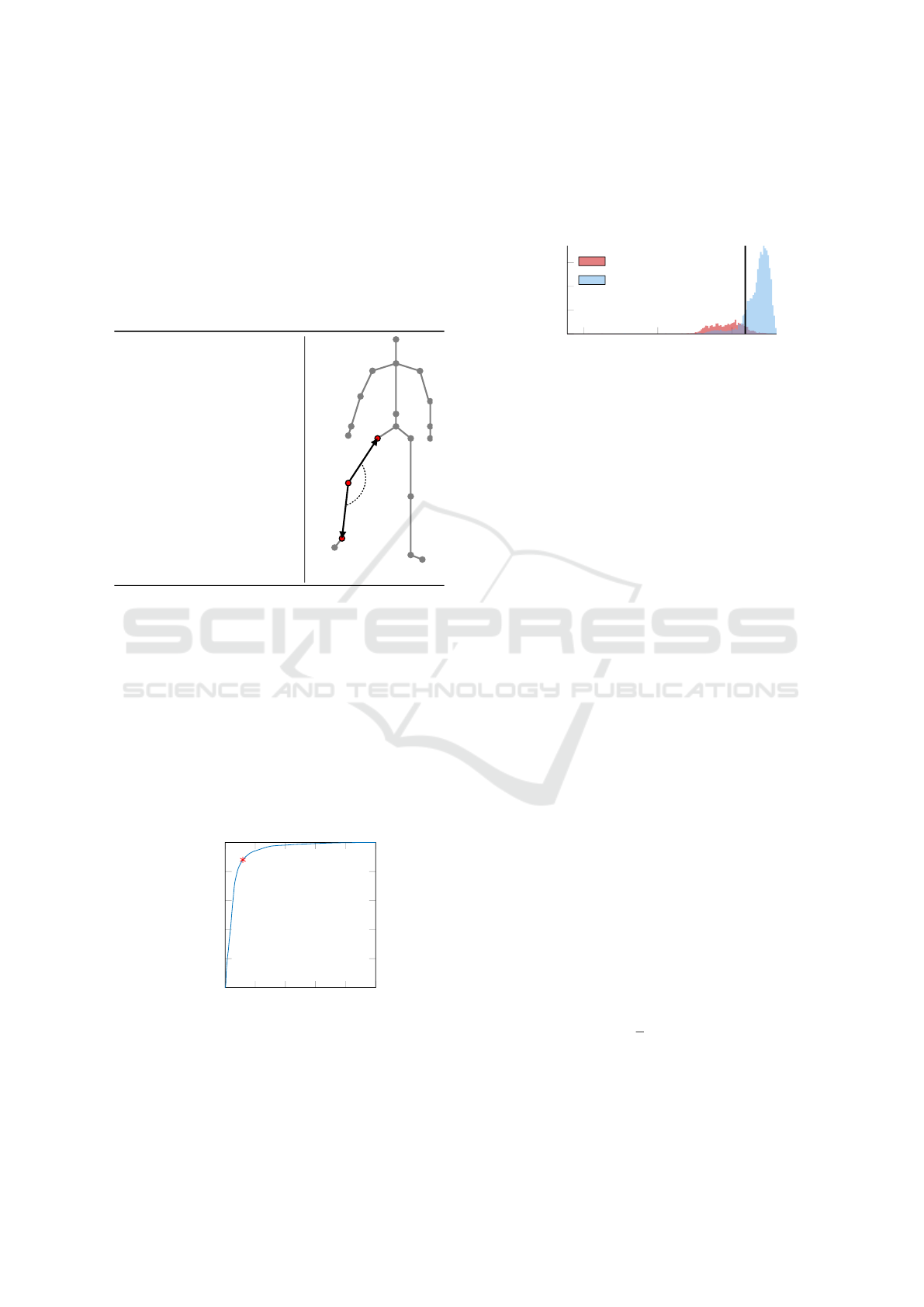
3.2 Motion Errors
This section presents the three exercises the study fo-
cusses on with their specific motion errors that have
to be detected.
In the Figures 3, 4 and 5, the gray part of the ske-
leton indicates the moving body parts. The regions in
red mark the error occurrences. The left skeletons re-
present the correct exercise executions with the class
label C. The remaining class labels UB, FO, BK, WP
and NBK correspond to the motion errors.
C
UBFO WP
BK
Figure 3: Motion errors for the exercise hip abduction.
C
BKFO WP
UB
Figure 4: Motion errors for the exercise hip extension.
C
NBKFO
UB
Figure 5: Motion errors for the exercise hip flexion.
3.3 Rule-Based Approach
3.3.1 Rule Modules
The rules are based on three function that are descri-
bed in the following sections. These rules were app-
lied on the 3-D joint positions represented in the 3-D
Kinect camera coordinate system.
M1 – Angle between 3-D Articulated Joints. The
angle between two articulated joints is calculated by
this module. The input parameters of the module are
two arbitrary articulated joints a
t
and b
t
in a frame t,
which are defined by their corresponding start posi-
tion a
1,t
and b
1,t
as well as their end position a
2,t
and
b
2,t
respectively. These positions are given by 1×3
vectors. The output angle ρ
t
is calculated according
to Equation 1.
ρ
t
= arccos
(a
2,t
− a
1,t
) · (b
2,t
− b
1,t
)
||a
2,t
− a
1,t
|| · ||b
2,t
− b
1,t
||
. (1)
M2 – Normalised Euclidean Distance between 3-D
Joints. The normalised Euclidean distance dj
t
bet-
ween two joints a and b, whose positions are given by
1×3 vectors, is calculated according to Equation 2. In
order to normalise this distance with regard to a per-
son’s height, the distance is divided by the sum of the
right lower and upper leg leg
l,t
and leg
u,t
. The right
leg was chosen here instead of the left supporting leg,
because in contrast to the left leg, the right leg is al-
ways visible during the exercise execution.
dj
t
=
||a
t
− b
t
||
leg
u,t
+ leg
l,t
. (2)
M3 – Normalised Signed Euclidean Distance of a
3-D Joint to a Defined Plane. This module allows
to calculate the distance dp
t
of a joint of interest p
oi,t
to the x-y, the x-z or the y-z plane of a Cartesian coor-
dinate system. This coordinate system is defined by
three joints a
t
, b
t
and c
t
as well as a joint p
0,t
that de-
fines the origin of the system. To obtain the distance,
the following steps have to be performed: Firstly, a
coordinate system with the rotation R and the origin
p
0,t
is calculated using a
t
, b
t
and c
t
. Secondly, p
oi,t
is
transformed into this coordinate system and results in
the transformed coordinates p
oi,trans,t
. These steps are
represented by the following Equations:
x
t
=
b
t
− a
t
k
b
t
− a
t
k
(3)
z
t
= (b
t
− a
t
) × (a
t
− c
t
) (4)
y
t
=
z
t
× x
t
k
z
t
× x
t
k
(5)
R
t
=
x
t
|
y
t
|
z
t
|
(6)
p
oi,trans,t
= R
t
·
p
|
oi,t
− p
|
0,t
. (7)
Finally, depending on the plane to which the norma-
lised signed distance shall be calculated, the x, y or z
coordinate of the transformed joint is returned accor-
ding to Equation 8.
dp
t
=
p
oi,trans,t
(z)
leg
u,t
+leg
l,t
, if distance to x-y plane,
p
oi,trans,t
(y)
leg
u,t
+leg
l,t
, if distance to x-z plane,
p
oi,trans,t
(x)
leg
u,t
+leg
l,t
, if distance to y-z plane.
(8)
VISAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
500
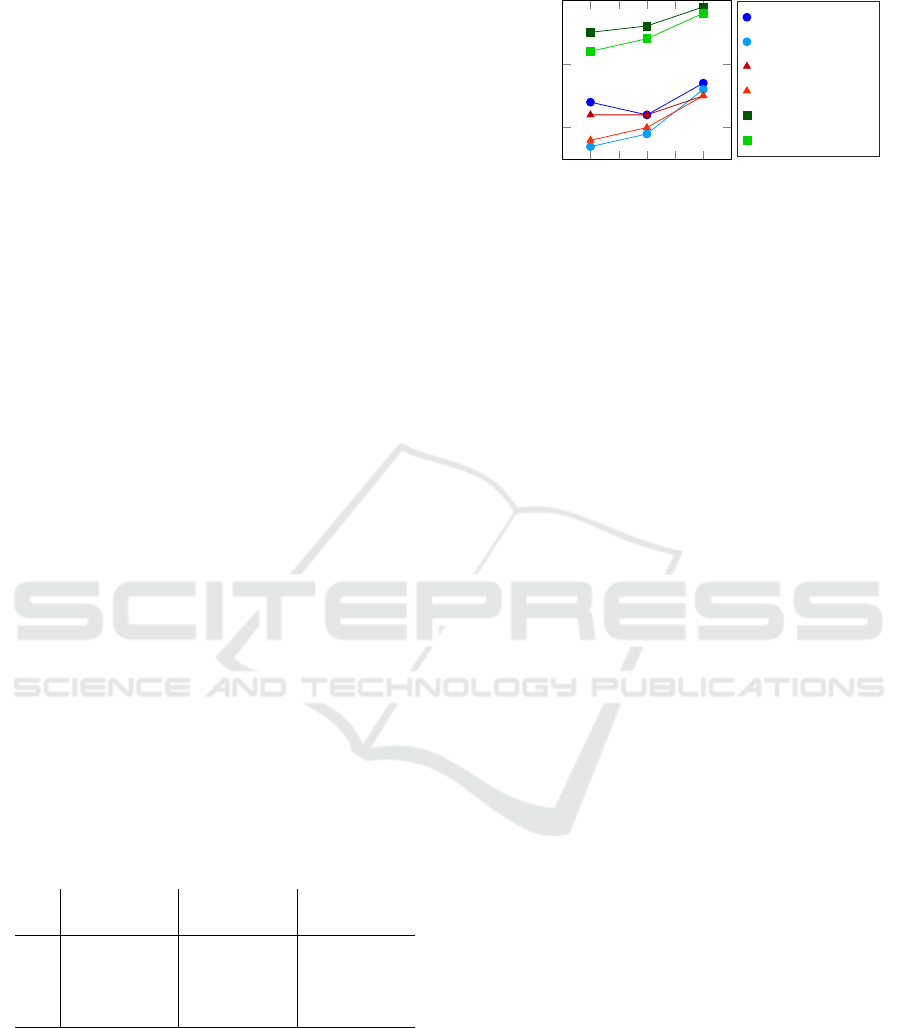
3.3.2 Rules
Due to limited space, this section presents only the
rule of BK for hip abduction in Table 2. If a rule is ful-
filled for a frame t, then the corresponding error was
detected in this frame. If none of the defined errors
were detected, the performed motion was considered
to be correct.
Table 2: Hip abduction: Bent Knee (BK).
Module: M1
ρ
t
: Angle between up-
per and lower right leg
Rule:
ρ
t
< thr
Abd,BK
ρ
t
a
1,t
b
1,t
b
2,t
a
2,t
3.3.3 Thresholds
The thresholds for every rule were determined by me-
ans of ROC (receiver operating characteristic) curves.
The principle is described for the error BK (hip ab-
duction). In this study, the data of all recorded persons
was intentionally used, which results in the optimal
thresholds for this very test group. This means that, in
case of manual threshold selection, the results cannot
exceed the accuracy that is determined in this experi-
ment. The determined optimal threshold thr
Abd,BK
of
the error BK for hip abduction was 159
◦
.
0 0.2 0.4
0.6
0.8 1
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
FPR
TPR
Figure 6: ROC curve for hip abduction, Bent Knee (BK).
Figure 6 presents the according ROC curve with
the optimal operating point, i. e. the threshold that
separates the samples representing the error classes
from the rest of the samples. The red dot on the curve
indicates the optimal operating point. Figure 7 shows
the separation of the data by means of this determined
threshold.
50
100
150
0
200
400
600
Angle in degree
Absolute occurence
BK
˜BK
Figure 7: Samples separated by the determined threshold
for hip abduction, Bent Knee (BK).
3.4 Machine Learning-Based Approach
The machine learning-based approach has already
been published for hip abduction by Richter et al.
(Richter et al., 2017b). Their algorithm transforms
the obtained 3-D skeleton to normalised hierarchical
coordinates. The aim of this transformation is to nor-
malise skeletons of different persons and to make the
joint data rotation- and translation-invariant. In the
next step, the current motion of a person performing
an exercise was aligned with a correctly performed re-
ference by means of IDTW. The new idea in the work
of Richter et al. was to calculate a difference vector
between the reference and the current joint positions,
which was then fed to a set of support vector machi-
nes. Thereby, every machine voted for one single er-
ror. As a result, the machine could classify whether a
current exercise motion is correct or whether a speci-
fic motion error occurred.
4 EVALUATION
4.1 Evaluation Measures
To compare the performance of the different approa-
ches presented in this work, the accuracy of the single
classifiers η
s
and the overall accuracy η
all
, which is
the mean accuracy of all classifiers S for an exercise,
are used. Thereby, the overall accuracy is defined by
η
all
=
1
S
·
S
∑
s=1
η
s
, (9)
whereas S is the number of classifiers or error classes
used for one exercise.
Motion Evaluation of Therapy Exercises by Means of Skeleton Normalisation, Incremental Dynamic Time Warping and Machine Learning:
A Comparison of a Rule-Based and a Machine-Learning-Based Approach
501
4.2 Dataset Configurations
To investigate the effect of local and normalised hier-
archical coordinates on the classification accuracy,
three different scenarios were defined by Richter et
al. (Richter et al., 2017b):
Scenario 1. For every patient, an individual machine
was trained and tested with the individual patient’s
data and his or her own reference. In practice, trai-
ning data as well as the patient’s reference have to be
recorded for every new patient, which is rather im-
practical.
Scenario 2. In contrast to scenario 1, one single ma-
chine was trained with the motion data of three per-
sons and their individual reference data. Just as in
scenario 1, the test was performed with each test per-
son’s individual reference. In practice, only the new
patient’s reference, but not his or her training data, has
to be recorded.
Scenario 3. The machine was trained with the motion
data of the three persons mentioned in scenario 2. In
contrast to scenario 1 and scenario 2, the reference
has not been changed according to the person. For
testing, the very same reference was used for all test
samples of the ten test persons. This means that, in
practice, neither training data nor a reference has to
be recorded for a new patient.
4.3 Results and Discussion
4.3.1 Usage of Normalised Skeleton Data
Table 3 and Figure 8 present the results to answer the
research question b) raised in Section 2.3.
Table 3: Overall accuracies η
all
for the three scenarios S1,
S2 and S3 with local (L) and normalised hierarchical (H)
coordinates and accuracy differences D = S1 - S3 between
S1 and S3.
Abduction Extension Flexion
L H L H L H
S1 0.86 0.87 0.85 0.85 0.98 0.99
S2 0.79 0.82 0.80 0.82 0.94 0.96
S3 0.77 0.84 0.78 0.82 0.92 0.95
D 0.09 0.03 0.07 0.03 0.06 0.04
Table 3 compares the results of local and norma-
lised hierarchical coordinates for the three different
scenarios and Figure 8 visualised these numbers in a
graph.
When taking a closer look at the influence of hier-
archical and local coordinates, we notice the follo-
wing: In general, the accuracies for hierarchical coor-
dinates are higher than for local coordinates. Moreo-
ver, and what is the most important, is that hierarchi-
S3 S2 S1
0.8
0.9
1
Scenario
Accuracy η
all
Abduction H
Abduction L
Extension H
Extension L
Flexion H
Flexion L
Figure 8: Overall accuracies η
all
for the three scenarios S1,
S2 and S3 with local (L) and normalised hierarchical (H)
coordinates.
cal coordinates outperform local coordinates especi-
ally for S3, which is the scenario of highest practical
relevance. From the graph and the table above we
can see that the usage of local, i. e. non-normalised
coordinates results in a considerable deterioration of
the overall accuracy from scenario 1 to scenario 3.
This implies that, for non-normalised local coordina-
tes, the less personalised data is used, the higher is
the negative influence of factors, such as body size
and proportions, on the accuracy. The difference to
local coordinates becomes obvious when we have a
look at the overall accuracies when using normalised
hierarchical coordinates. It is apparent that, in con-
trast to local coordinates, the accuracy only slightly
decreases when using normalised hierarchical coordi-
nates. These results suggest to use normalised hierar-
chical coordinates instead of local coordinates should
the recording of personalised data for each new pa-
tient be avoided without loosing classification perfor-
mance, which correspond to scenario 3. Still, for sce-
nario 2 and even for hip flexion and abduction in sce-
nario 1, normalised hierarchical coordinates outper-
form the local ones. These results indicate that, in ge-
neral, normalised hierarchical coordinates are a suita-
ble representation of therapy exercise trajectories.
4.3.2 Rule-Based Versus
Machine-Learning-Based
Table 4 and Table 5 present the results to answer
the research question a), whereas Table 4 shows
the achieved performance of the rule-based approach
and Table 5 reveals the performance of the machine-
learning-based approach for the scenario 3.
If we compare the results of the rule-based ap-
proach in Table 4 with the results of the machine-
learning-based approach in Table 5, it can be seen
that the performance of the machine-learning-based
method is comparable to the rule-based method. As
a consequence, these results demonstrate that the de-
tection of motion errors by means of machine lear-
VISAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
502
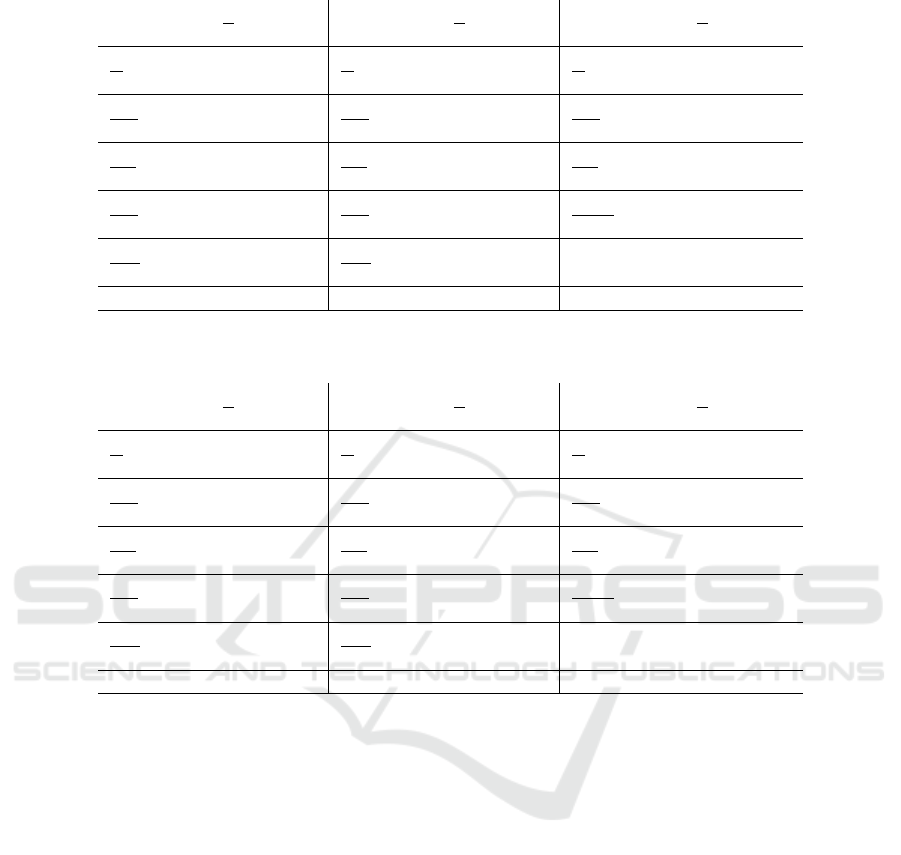
Table 4: Confusion matrices and corresponding accuracies η
s
and η
all
and overall accuracies η
all
for rule-based approach.
Abduction Extension Flexion
L L η
s
L L η
s
L L η
s
C 0.72 0.28
0.81
C 0.73 0.27
0.83
C 0.91 0.09
0.94
C 0.09 0.91 C 0.08 0.92 C 0.04 0.96
BK 0.88 0.12
0.91
UB 0.97 0.03
0.98
UB 1.00 0.00
1.00
BK 0.06 0.94 UB 0.02 0.98 UB 0.00 1.00
FO 0.78 0.22
0.73
FO 0.70 0.30
0.69
FO 0.89 0.11
0.90
FO 0.32 0.68 FO 0.31 0.69 FO 0.09 0.91
UB 0.91 0.09
0.93
BK 0.87 0.13
0.87
NBK 1.00 0.00
0.99
UB 0.05 0.95 BK 0.12 0.88 NBK 0.01 0.99
WP 0.84 0.16
0.83
WP 0.84 0.16
0.86
WP 0.18 0.82 WP 0.13 0.87
η
all
0.84 0.85 0.96
Table 5: Confusion matrices and corresponding accuracies η
s
and η
all
for scenario 3 for machine-learning-based approach.
Classifiers are regarded independently from each other.
Abduction Extension Flexion
L L η
s
L L η
s
L L η
s
C 0.84 0.16
0.80
C 0.92 0.08
0.84
C 0.84 0.16
0.91
C 0.24 0.76 C 0.24 0.76 C 0.01 0.99
BK 0.95 0.05
0.95
UB 0.90 0.10
0.90
UB 0.98 0.02
0.98
BK 0.05 0.95 UB 0.09 0.91 UB 0.02 0.98
FO 0.83 0.17
0.70
FO 0.54 0.46
0.67
FO 0.91 0.09
0.92
FO 0.44 0.56 FO 0.20 0.80 FO 0.08 0.92
UB 0.89 0.11
0.88
BK 0.87 0.13
0.86
NBK 1.00 0.00
0.99
UB 0.13 0.87 BK 0.16 0.84 NBK 0.02 0.98
WP 0.80 0.20
0.87
WP 0.73 0.27
0.84
WP 0.07 0.93 WP 0.04 0.96
η
all
0.84 0.82 0.95
ning techniques is equally reliable as the detection by
means of manually defined rules. In conclusion, we
provided evidence that a system can be trained with
a set of example sequences, so that motion errors can
be detected. This finally avoids the manual definition
of rules for every exercise, because the machine can
automatically derive the rules based on the provided
example sequences.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
To sum up, this study has found that the introdu-
ced machine-learning-based approach works equally
accurate as the rule-based version. As a consequence,
the manual definition of rules can be avoided because
the machine is able to learn motion errors by means of
annotated sample sequences. In addition, this study
has identified that normalised hierarchical coordina-
tes allow to employ training samples of persons that
are different from those who finally use the system.
Hence, we lay a foundation towards a more quali-
tative feedback during therapy exercises. This work
contributes to an automatic inclusion of new exercises
by simply recording sample sequences of an exercise
along with sequences containing specific errors. In
future work, we therefore aim at an automated anno-
tation process for the training data, which is labelled
manually at the moment. Finally, further exercises
shall be included, for example by a therapist who spe-
cifies both the correct execution and the errors that
shall be detected. In this way, it could be possible
in future to remotely create exercises for different pa-
tients or to simply pre-train systems with new exerci-
ses without taking pre-recordings of every person that
uses the system.
REFERENCES
Antunes, M., Baptista, R., Demisse, G., Aouada, D., and
Ottersten, B. (2016). Visual and human-interpretable
feedback for assisting physical activity. In Euro-
Motion Evaluation of Therapy Exercises by Means of Skeleton Normalisation, Incremental Dynamic Time Warping and Machine Learning:
A Comparison of a Rule-Based and a Machine-Learning-Based Approach
503

pean Conference on Computer Vision, pages 115–129.
Springer.
Baptista, R., Antunes, M., Aouada, D., and Ottersten, B.
(2017). Video-based feedback for assisting physical
activity. In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint
Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Com-
puter Graphics Theory and Applications - Volume 5:
VISAPP, (VISIGRAPP 2017), pages 274–280.
Caterisano, A., Moss, R., Pellinger, T., Woodruff, K., Le-
wis, V., Booth, W., and Khadra, T. (2002). The effect
of back squat depth on the EMG activity of 4 superfi-
cial hip and thigh muscles. The Journal of Strength &
Conditioning Research, 16(3):428–432.
Gal, N., Andrei, D., Neme, D. I., Ndan, E., and Stoicu-
Tivadar, V. (2015). A Kinect based intelligent e-
rehabilitation system in physical therapy. Digital He-
althcare Empowering Europeans, pages 489–493.
Gorsuch, J., Long, J., Miller, K., Primeau, K., Rutledge, S.,
Sossong, A., and Durocher, J. J. (2013). The effect of
squat depth on multiarticular muscle activation in col-
legiate cross-country runners. The Journal of Strength
& Conditioning Research, 27(9):2619–2625.
Huang, T.-C., Cheng, Y.-C., and Chiang, C.-C. (2013). Au-
tomatic Dancing Assessment Using Kinect. In Advan-
ces in Intelligent Systems and Applications-Volume 2,
pages 511–520. Springer.
Kang, S.-Y., Choung, S.-D., and Jeon, H.-S. (2016). Modi-
fying the hip abduction angle during bridging exercise
can facilitate gluteus maximus activity. Manual ther-
apy.
Khan, N. M., Lin, S., Guan, L., and Guo, B. (2014). A
visual evaluation framework for in-home physical re-
habilitation. In Multimedia (ISM), 2014 IEEE Inter-
national Symposium on Multimedia, pages 237–240.
IEEE.
Lin, T.-Y., Hsieh, C.-H., and Lee, J.-D. (2013). A kinect-
based system for physical rehabilitation: Utilizing tai
chi exercises to improve movement disorders in pa-
tients with balance ability. In 2013 7th Asia Modelling
Symposium, pages 149–153. IEEE.
L
¨
osch, C., Weigert, M., Nitzsche, N., Richter, J., Wiede,
C., and Schulz, H. (2018). Einsatz und Bedeutung
von Seilz
¨
ugen in der Medizinischen Trainingstherapie
am Beispiel H
¨
uft-Totalendoprothese Eine Experten-
perspektive. In Bewegungstherapie und Gesundheits-
sport.
Muneesawang, P., Khan, N. M., Kyan, M., Elder, R. B.,
Dong, N., Sun, G., Li, H., Zhong, L., and Guan, L.
(2015). A machine intelligence approach to virtual
ballet training. IEEE MultiMedia, 22(4):80–92.
Richter, J., Wiede, C., Apitzsch, A., Nitzsche, N., L
¨
osch, C.,
Weigert, M., Kronfeld, T., Weisleder, S., and Hirtz, G.
(2017a). Assisted Motion Control in Therapy Envi-
ronments Using Smart Sensor Technology: Challen-
ges and Opportunities. In Ambient Assisted Living, 9.
AAL-Kongress, Frankfurt/M, Germany, April 20 - 21,
2016, pages 119–132. Springer Verlag.
Richter, J., Wiede, C., Shinde, B., and Hirtz, G. (2017b).
Motion Error Classification for Assisted Physical
Therapy - A Novel Approach using Incremental Dyn-
amic Time Warping and Normalised Hierarchical Ske-
leton Joint Data. In Proceedings of the 6th Internati-
onal Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications
and Methods - Volume 1: ICPRAM, pages 281–288.
Shotton, J., Girshick, R., Fitzgibbon, A., Sharp, T., Cook,
M., Finocchio, M., Moore, R., Kohli, P., Criminisi,
A., Kipman, A., et al. (2013). Efficient human pose
estimation from single depth images. IEEE Transacti-
ons on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,
35(12):2821–2840.
Su, C.-J., Chiang, C.-Y., and Huang, J.-Y. (2014). Kinect-
enabled home-based rehabilitation system using Dy-
namic Time Warping and fuzzy logic. Applied Soft
Computing, 22:652–666.
Tak, Y.-S., Rho, S., and Hwang, E. (2011). Mo-
tion Sequence-Based Human Abnormality Detection
Scheme for Smart Spaces. Wireless Personal Commu-
nications, 60(3):507–519.
Tormene, P., Giorgino, T., Quaglini, S., and Stefanelli, M.
(2009). Matching incomplete time series with dyn-
amic time warping: an algorithm and an application
to post-stroke rehabilitation. Artificial intelligence in
medicine, 45(1):11–34.
Yurtman, A. and Barshan, B. (2013). Detection and evalu-
ation of physical therapy exercises by dynamic time
warping using wearable motion sensor units. In Infor-
mation Sciences and Systems 2013, pages 305–314.
Springer.
Zhao, W., Lun, R., Espy, D. D., and Reinthal, M. A. (2014).
Rule based realtime motion assessment for rehabilita-
tion exercises. In IEEE Symposium on Computational
Intelligence in Healthcare and e-health (CICARE),
2014, pages 133–140. IEEE.
VISAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
504
