
Enhancing Spatial Keyframe Animations with Motion Capture
Bernardo F. Costa and Claudio Esperanc¸a
LCG/PESC, UFRJ, Av. Hor
´
acio Macedo 2030, CT, H-319 21941-590, Rio de Janeiro/RJ, Brazil
Keywords:
Motion Capture, Keyframing, Spatial Keyframe, Dimension Reduction, Multidimensional Projection.
Abstract:
While motion capture (mocap) achieves realistic character animation at great cost, keyframing is capable of
producing less realistic but more controllable animations. In this paper we show how to combine the Spatial
Keyframing Framework (SKF) of Igarashi et al.(Igarashi et al., 2005) and multidimensional projection tech-
niques to reuse mocap data in several ways. For instance, by extracting meaningful poses and projecting them
on a plane, it is possible to sketch new animations using the SKF. Additionally, we show that multidimen-
sional projection also can be used for visualization and motion analysis. We also propose a method for mocap
compaction with the help of SK’s pose reconstruction (backprojection) algorithm. This compaction scheme
was implemented for several known projection schemes and empirically tested alongside traditional temporal
decimation schemes. Finally, we present a novel multidimensional projection optimization technique that sig-
nificantly enhances SK-based compaction and can also be applied to other contexts where a back-projection
algorithm is available.
1 INTRODUCTION
Character animation focuses on bringing life to a par-
ticular character model. There are several ways of
animating a character in a scene. One popular way is
rigging a skeleton to a character model (a skin) such
that when the skeleton pose is changed, so does the
model. This binds the character movements to the de-
grees of freedom (DOF) of this skeleton.
In standard keyframe-based animation, some key
poses are created by artists and interpolated at each
frame, sometimes using manually adjusted B
´
ezier
curves. However, for complicated or extended anima-
tions, this process turns out to be difficult and time-
consuming. As an alternative, the approach known as
motion capture or mocap was developed. In it, a hu-
man actor wearing a special suit performs movements
which are recorded by a set of cameras and sensors.
After some processing, it is possible to build a com-
plete description of the actor’s movement in the form
of a set of skeleton poses and positions sampled with
high precision, both in time and space. A typical mo-
cap file has a description of the skeleton’s shape and
articulations, together with a set of poses, each con-
taining a timestamp, the rotation of each joint and a
translation vector of the root joint with respect to a
standard rest pose.
Another animation authoring framework called
spatial keyframing (SK) was proposed by Igarashi et
al. (Igarashi et al., 2005). The main idea is to asso-
ciate keyframes (poses) to carefully placed points on
a plane rather than to points in time. Although simple
in thesis, spatial keyframing still requires keyframe
poses to be authored manually, which is a time-
consuming task when many such poses are required
or when the skeleton contains many joints. One way
to help the process, therefore, is to harvest interest-
ing poses from raw mocap files. The present work
investigates algorithms and techniques to accomplish
just that. Moreover, we propose using multidimen-
sional projection techniques to automatically suggest
an optimal placement for the spatial keyframes on the
plane.
Another benefit of finding a good method to
project points in pose space to a plane is that it also
serves as a tool for the analysis of mocap files. The
idea is that the movement contained in a mocap can be
visualized as a trajectory in 2D space. Since a good
projection method ensures that similar poses are pro-
jected onto points close to each other, the plane itself
can be viewed as a pose similarity space. Thus, for
instance, a cyclic movement is commonly projected
onto a closed curve.
Finally, multidimensional projection of mocap
data can be used as a tool for motion compression.
Since mocap files ordinarily contain in excess of
Costa, B. and Esperança, C.
Enhancing Spatial Keyframe Animations with Motion Capture.
DOI: 10.5220/0007296800310040
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2019), pages 31-40
ISBN: 978-989-758-354-4
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
31

60 frames per second, a common lossy compres-
sion scheme consists of selecting important frames
and reconstructing the complete motion by interpo-
lation. Although this interpolation is frequently con-
ducted using time as parameter, we show how spatial
keyframing can be adapted for this purpose.
In a nutshell, this paper presents the following
contributions:
1. Repurposes multidimensional visualization tech-
niques to the problem of selecting key poses from
mocap data and project them on a plane so that
they can be used in the Spatial Keyframe anima-
tion Framework (SKF).
2. Shows how multidimensional projection can be
used as a visual aid in the analysis of mocap data.
3. Empirically evaluates several multidimensional
projection schemes in their application to mocap
data.
4. Describes the use of SKF in compressing mocap
data through decimation and reconstruction and,
in particular, introduces a non-linear projection
optimization algorithm that yields smaller recon-
struction errors. This algorithm is not specific to
mocap data, but can also be used with other data,
provided a backprojection algorithm and an error
metric are available.
2 RELATED WORK
In this section, we review the literature from areas re-
lated to the present work.
2.1 Pose Selection and Information
Extraction
Decimating irrelevant poses from mocap data is a
common way to produce a compact representation of
a movement. The reconstruction of the original data
is done by interpolating the small subset of poses that
survive this decimation process. Since these play the
same role of keyframes used in keyframe-based ani-
mation, the process is also called keyframe extraction.
A popular idea for extracting keyframes is curve
simplification. Lim and Thalmann (Lim and Thal-
mann, 2001) view mocap data as a curve parameter-
ized by time and propose using a technique (Lowe,
1987) for approximating such curves with a polygo-
nal line. Later, this algorithm became known as sim-
ple curve simplification (SCS). This idea was later en-
hanced by Xiao et al. (Xiao et al., 2006) by employ-
ing an optimized selection strategy, which they named
layered curve simplification (LCS). Both of these start
with a minimal subset of the original mocap data and
try to repeatedly select relevant keyframes by measur-
ing the similarity between a local interpolation and
the original frame. On the other hand, Togawa and
Okuda (Togawa and Okuda, 2005) start with the full
set and iteratively discard frames which least con-
tribute to the interpolation, naming their contribution
as position-based (PB) strategy.
Other possible approaches include clustering
methods and matrix factorization. Clustering meth-
ods divide frames into clusters and search for a rep-
resentative frame in each group. The works of Bu-
lut and Capin (Bulut and Capin, 2007) and Halit and
Capin (Halit and Capin, 2011) fall in this category.
Both also consider dynamic information in the clus-
tering metrics. Matrix factorization uses linear alge-
bra methods to reconstruct mocap data represented in
matrix format. Examples of such algorithms are the
work of Huang et al. (Huang et al., 2005), called key
probe, and that of Jin et al. (Jin et al., 2012).
2.2 Multidimensional Projection
The key motivation behind the use of dimensional-
ity reduction approaches in this paper is that much
of the redundancy found in mocap data can be at-
tributed to DOFs that are hierarchically or function-
ally related. Note that in the context of this work, the
terms “dimension reduction” and “multidimensional
projection” are used interchangeably. Arikan (Arikan,
2006) proposes to use principal component analysis
(PCA) on mocap data, together with clustering, to get
a good rate of compaction. Halit and Capin (Halit and
Capin, 2011), Safonova et al. (Safonova et al., 2004)
and Jin et al.(Jin et al., 2012) also use PCA as a way
to lower the data dimensionality and save computing
time.
Zhang and Cao (Zhang and Cao, 2015) and Jin
et al. (Jin et al., 2012) use locally linear embedding
(LLE) (Roweis and Saul, 2000), a dimension reduc-
tion tool, to ease their search for keyframes in the
frame set. LLE tries to find a projection where rel-
ative distances between each point and their nearest
neighbors in lower dimension space is preserved in
the least squares sense. The number of nearest neigh-
bors is a parameter of the algorithm.
Assa et al.(Assa et al., 2005) also project the mo-
tion curve onto a 2D space to find keyframe candi-
dates. They use a variant of multidimensional scaling
(MDS) (Cox and Cox, 2008) to project the motion
curve. MDS tries to find a projection such that rela-
tive distances in lower dimension space are as close as
possible to the corresponding distances in the original
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
32

space in the least squares sense. The distance defini-
tion is a parameter to be chosen. If the euclidean dis-
tance is chosen, MDS turns to produce the same result
as PCA. Jenkins and Matari
´
c (Jenkins and Matari
´
c,
2004) use another MDS sibling method called Isomap
(Tenenbaum et al., 2000) to reduce human motion to
a smaller dimension for clustering purposes. Isomap
turns to be MDS with geodesic distance as its distance
definition.
It is worth noting that dimension reduction tech-
niques such as PCA, MDS and LLE, besides be-
ing used for compaction, can also be employed for
other purposes, most notably for visualization of
multidimensional data. For instance, Tejada el al.
(Tejada et al., 2003) developed a fast iterative ap-
proach to project multidimensional data onto a 2D
space, based on neighborhood relationships. This ap-
proach is not guaranteed to be optimal but has been
shown to produce interesting results for data visu-
alization. Another dimension reduction technique
aimed at visualization of multidimensional data is the
t-Distributed Stochastic Neighborhood Embedding (t-
SNE) (van der Maaten and Hinton, 2008).
Joia et al. (Joia et al., 2011) created the so-called
local affine multidimensional projection (LAMP),
where a small subset of points – called control points
– are randomly picked from the original set and pro-
jected using some projection algorithm, whereas the
remaining points are projected by means of an affine
map expressed in terms of their distance to the con-
trol points in the original space. The control points
can be moved on the projection plane and thus affect
the projection of the whole set.
Amorim et al. (Amorim et al., 2014) propose an-
other two-step projection approach which is similar to
LAMP, but the affine map is replaced by radial basis
functions (RBFs) (Dinh et al., 2002). In this projec-
tion scheme – RBFP for short – control point selec-
tion is aided by a technique called regularized orthog-
onal least squares (ROLS), a more elaborate approach
compared to the random selection of LAMP. Notice
that RBFs have an advantage over affine maps in the
sense that they provide a smoother interpolation.
2.3 Backward Projection
“Unprojection” or backward projection is a less de-
veloped field compared to dimension reduction. It
aims at producing points in the original multidimen-
sional space which do not belong to the input data
set. For instance, the iLAMP (dos Santos Amorim
et al., 2012) approach uses the same LAMP(Joia et al.,
2011) heuristic to get a backward projection, swap-
ping high dimension with lower dimension. Amorim
et al. (Amorim et al., 2015) use RBF interpolation to
transport information from the reduced dimension to
the original space. Their work aims at exploring fa-
cial expression generation interpolated from a set of
control points selected with specialized heuristics.
Igarashi et al. (Igarashi et al., 2005) also use RBF
interpolation to back-project a 2D point onto a mul-
tidimensional skeleton pose, as a way to provide a
rapid prototyping environment for animators. In this
scheme, each input skeleton pose is modeled and as-
sociated with a marker point manually placed on a
plane. The idea is to build an RBF which maps any
point on the plane to a pose smoothly interpolated
from the marker point poses.
3 MOCAP COMPACTION
In this section we discuss the problem of mocap com-
paction (or compression), i.e., the problem of repre-
senting the data for a mocap session with only a few
of the original poses. A compression scheme is a cou-
pling between a pose selection strategy and a pose
interpolation (or reconstruction) algorithm. We dis-
tinguish two broad classes of mocap compression ap-
proaches. The first, what we may call the “traditional”
approach, consists of selecting a few representative
poses from the original set – the keyframes – while
the reconstruction uses time as the interpolating pa-
rameter. The second approach also selects represen-
tative poses, but uses multidimensional projection, so
that all poses are mapped to points in 2D, while the
reconstruction uses the 2 coordinates of this space as
interpolating parameters. This way, we could con-
sider the selected poses for schemes in the first ap-
proach as temporal keyframes while those for the sec-
ond approach could be more properly called spatial
keyframes.
3.1 Temporal Keyframe Schemes
The idea for these schemes is to obtain a compressed
representation of the original mocap data by care-
fully selecting a subset of poses, with their attached
timestamps, as shown in Fig. 2. Let the original mo-
cap contain n poses F = {p
1
, p
2
,..., p
n
} uniformly
spaced in time, and let the compressed representa-
tion consisting of a list with m < n keyframe poses
G = hp
i
1
, p
i
2
,..., p
i
m
i and a list of the corresponding
timestamp indices T = hi
1
,i
2
,...,i
m
i. Then, in order
to reconstruct a pose p
j
not in G we first find the two
closest poses p
i
k
and p
i
k+1
in G so that i
k
< j < i
k+1
.
Thus, the reconstructed pose p
0
j
can be obtained by
linear interpolation of p
i
k
and p
i
k+1
. It is also possible
Enhancing Spatial Keyframe Animations with Motion Capture
33
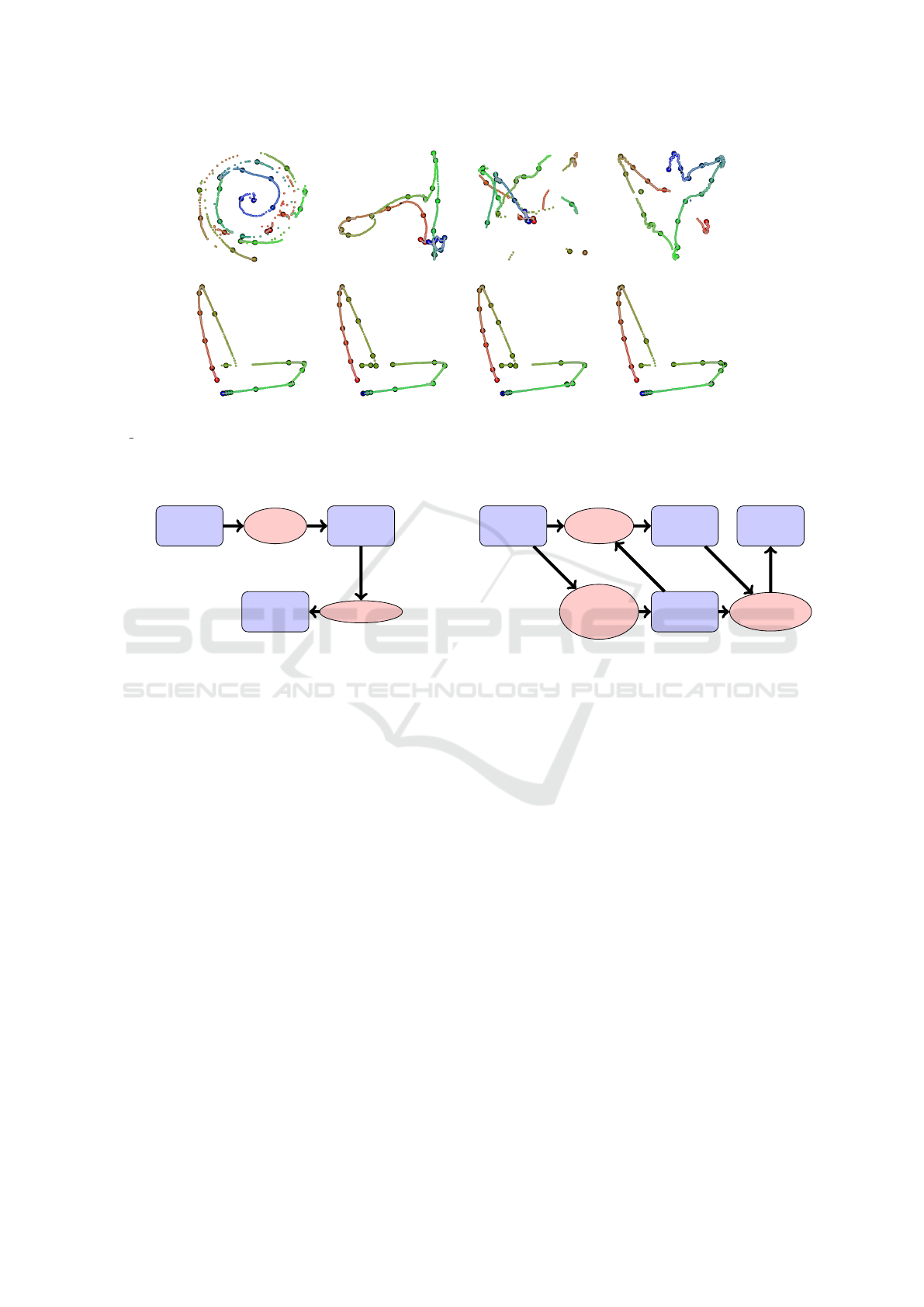
Figure 1: Implemented projection and keyframe extraction algorithms. Results obtained by projecting the poses in file
05 10.bvh from the CMU Motion Capture database. The color gradient from red to green to blue is used to indicate time.
Bigger dots with black border are keyframe poses (markers). First row from left to right: Force, MDS, PCA and t-SNE, where
3% of the poses are selected as keyframes by uniform sampling (US). Second row shows the results for LLE with keyframes
selected with US, SCS, PB and ROLS.
Mocap
data (F)
keyframe
selection
keyframes (G)
Interpolation
Rebuilt
mocap (F
0
)
Figure 2: Workflow for a temporal mocap compression and
reconstruction scheme.
to use a higher order function for interpolation, like a
cubic hermite curve, if we add the tangent at p
i
k
and
p
i
k+1
. In fact, in addition to these two, it is also pos-
sible to use infinite support reconstruction functions
(RBFs, say), which use all of G.
3.2 Spatial Keyframe Schemes
Time is a natural interpolating domain for mocap
data, since successive poses are necessarily similar
due to physics constrains. We may, however, imagine
an artificial “similarity” domain where two closely re-
lated poses are mapped to a pair of close points. We
propose constructing such a domain by using multi-
dimensional projection techniques. Thus, we propose
adding to the keyframing pipeline a step where poses
are first projected onto a plane. A skeleton pose is un-
derstood as a vector in high dimensional space, so that
a sequence of projected poses with their correspond-
ing timestamps can be regarded as a 2-dimensional
trajectory representing the motion. This trajectory can
be used to recover the original data with the help of a
back-projection algorithm. We adopt the algorithm
from Igarashi et al.(Igarashi et al., 2005) to recover
Mocap
data (F)
Key frame
selection
Multi-
dimensional
projection
2D projec-
tion (Q)
keyframes (G)
SK
interpolation
Rebuilt
mocap (F
0
)
Figure 3: Workflow for mocap compression and reconstruc-
tion with spatial keyframes.
the multidimensional pose from the projected pose,
since this algorithm was specifically devised for this
kind of data.
Fig. 3 illustrates the workflow for such schemes.
Mocap data will feed a keyframe selection algorithm,
just as in a temporal scheme, but an additional step is
required, where a multidimensional projection algo-
rithm is used to project all poses onto a plane. Thus,
in addition to a set G of keyframes, the compressed
representation also includes set Q = {q
1
,q
2
,...,q
n
},
where q
i
represents a projection of p
i
.
We should also distinguish common projection
approaches from those employing control points, such
as LAMP and RBFP. In the latter schemes, the set of
control points could conceivably be conflated with the
set of keyframes, in the sense that both consist of rep-
resentative subsets of the original data. Thus, RBFP-
based mocap compression and reconstruction follows
the slightly different workflow depicted in Figure 4.
For implementing any keyframe selection algo-
rithm in the context of motion capture, we need to
define a function for pose distance, i.e., a measure of
dissimilarity.
Equation (1) defines our distance metric in terms
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
34
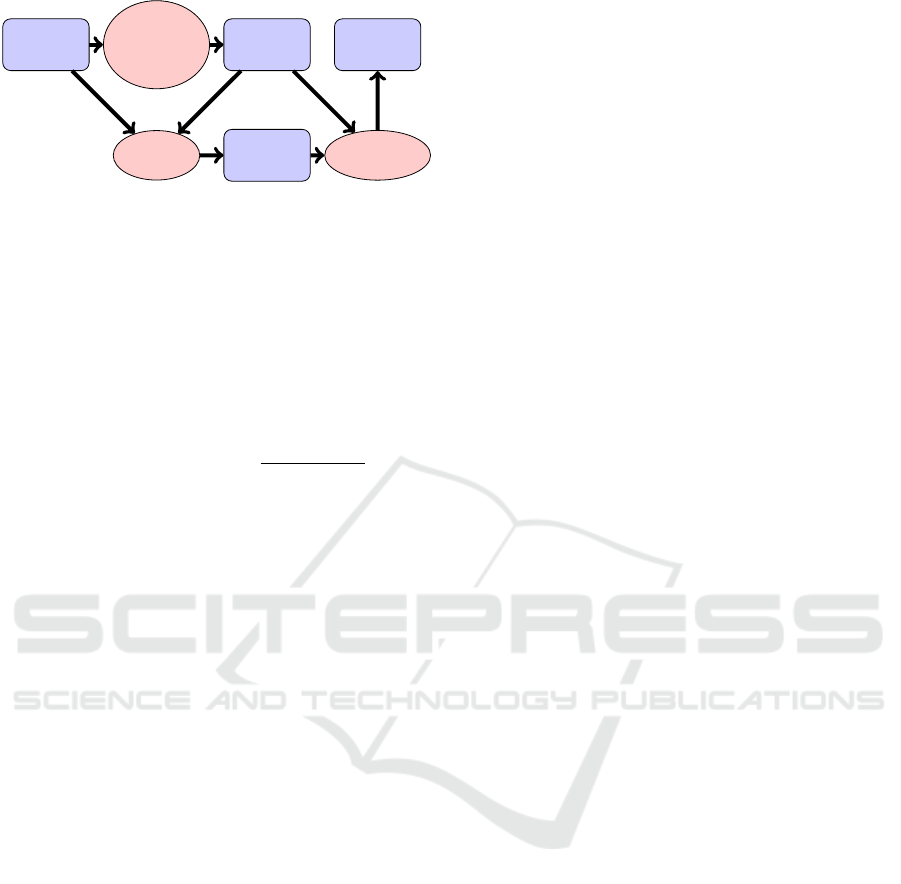
Mocap
data (F)
Subset
projection +
ROLS-based
selection
RBF
projection
Control
points /
keyframes (G)
2D projec-
tion (Q)
SK
interpolation
Rebuilt
mocap (F
0
)
Figure 4: Workflow for mocap compression and reconstruc-
tion with spatial keyframes and RBF projection.
of local rotation matrices, where A and B are skeleton
poses, R is the rotation joint set composed of matrices,
Tr[·] is the trace operator and w
r
is a weight assigned
to the r’th joint. In our experiments, we use this ro-
tational pose distance definition for pose projection.
The joint weight is the longest path between the joint
and the furthest end effector.
D
q
(A,B) =
∑
r∈R
w
r
arccos(
Tr[A
r
B
>
r
] − 1
2
) (1)
The following multidimensional projection meth-
ods were used in our experiments. Among the linear
methods, we have considered PCA (Smith, 2002), the
Force approach (Tejada et al., 2003) and MDS (Cox
and Cox, 2008). Among the non-linear methods, we
have considered LLE (Roweis and Saul, 2000), RBFP
(Amorim et al., 2014) and t-SNE (van der Maaten and
Hinton, 2008). Figure 1 contains sample results ob-
tained with all of these except RBFP. RBFP adopts
a two-step projection approach using control points.
In our experiments, the first step of RBFP was eval-
uated with the use of Force, MDS, LLE, PCA and t-
SNE. Recall that RBFP prescribes the use of ROLS
for keyframe selection. Figure 5 illustrates projec-
tions for the same dataset using these five RBFP vari-
ations.
4 PROJECTION OPTIMIZATION
In spatial keyframe schemes, the 2D projection of
a key pose is reconstructed exactly by the back-
projection algorithm, but we expect non-key poses to
be reconstructed only approximately. Therefore, an
important question is whether the projection of a non-
key pose, as prescribed by the projection algorithm, is
optimal, i.e., whether the back-projection of this point
yields the pose with minimum error with respect to
the original pose.
Having this in mind, we propose an optimization
algorithm that will help us to find a better projec-
tion of non-key poses. This is shown in Algorithm 1,
which takes as input the set of frames from the mocap
(F in Figures 3 and 4), the subset of keyframes (G), as
well as the projection and back-projection algorithms
and produces an optimized set of projected non-key
poses (Q). This algorithm implements gradient de-
scent(Burges et al., 2005) optimization where, at each
iteration, the gradient of a given function is estimated
and steps in the gradient direction are taken to reach
a local minimum. The original point computed by the
non-optimized projection algorithm is used as a seed
for the search.
An important component of the process is the esti-
mation of the gradient at a given point. The numerical
process used in our algorithm estimates the gradient
around a particular 2D point by back-projecting four
neighbor points within a disk of small radius and com-
puting the error with respect to the original pose. If all
points yield a bigger error than the original point, then
that point is a local minimum. Otherwise, a gradient
direction is computed based on the error variation. Pa-
rameters α and δ in the algorithm are typically chosen
in the interval [0,1] and were set to 0.5 in our experi-
ments.
Figure 6 shows the sample projections of Fig-
ure 1 optimized with Algorithm 1. We note that the
optimization tends to scatter non-key frames with re-
spect to the non-optimized projections. Clearly, cases
where greater differences exist between the optimized
and original projections can be attributed to the orig-
inal algorithm choosing poorer positions in the first
place. We also note that the optimization algorithm
can be adapted to other uses of multidimensional pro-
jection for which a back-projection is available and an
error metric is defined.
5 EXPERIMENTS
The main question we face is if there is any gain in
terms of quality when using spatial keyframes over
traditional temporal schemes. To answer it, each com-
pression scheme is evaluated by measuring the error
between the reconstructed and the original animation,
for a set of mocap files. The reconstruction quality
is estimated using the error measured by Equation (1)
divided by the number of frames in the mocap file and
by the number of joints of the skeleton, to make this
measure independent of file size or skeleton topology.
We used as input data a subset of the CMU Mocap
database(CMU, ) with 70 files ranging in size from
129 to 1146 frames. In particular, we used files in
BVH format converted for the 3DMax animation soft-
ware.
Enhancing Spatial Keyframe Animations with Motion Capture
35
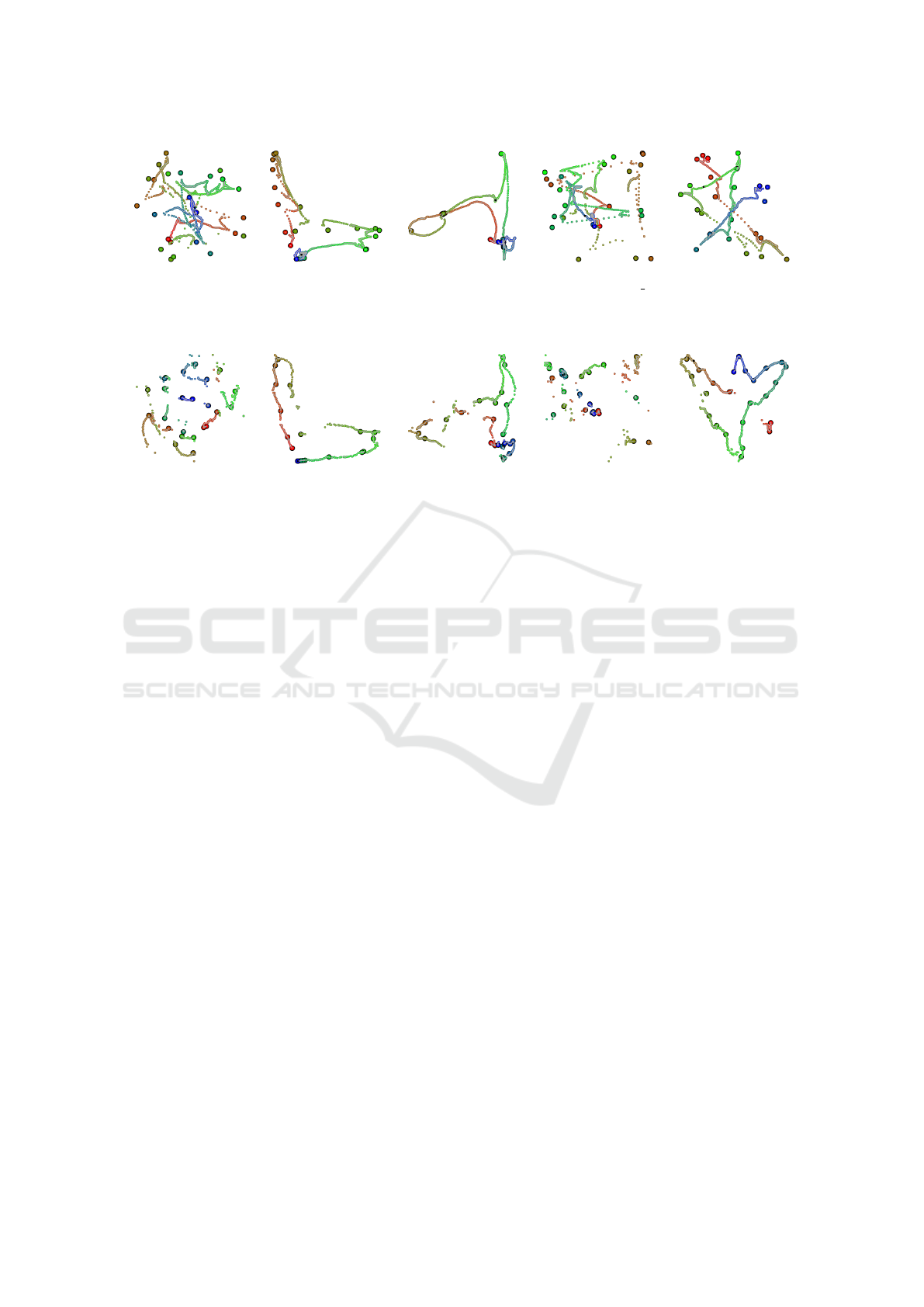
Figure 5: Results obtained by using two-step RBFP projection variants on poses of file 05 10.bvh of the CMU Motion
Capture database. The color gradient from red to green to blue is used to indicate time. Bigger dots with black border are
keyframe poses (markers). The projection for the first step was obtained using the following algorithms (from left to right):
Force, LLS, MDS, PCA and t-SNE.
Figure 6: Optimized versions of the projections using Uniform Sampling shown in Figure 1. The color gradient from red to
green to blue is used to indicate time. Bigger dots with black border are keyframe poses (markers). From left to right: Force,
LLS, MDS, PCA and t-SNE.
5.1 Reconstruction Evaluation
All experiments consist of compressing mocap data
and measuring the error of the reconstructed mocap
with respect to the original. The compaction schemes
vary according to three main aspects:
(a) The keyframe selection strategy, chosen from:
PB, SCS, ROLS, and Uniform Sampling (US),
which selects keyframes at regular time intervals.
(b) The interpolation algorithm. For temporal
schemes, these can be Linear or Hermitian in-
terpolation of rotations expressed with Euler an-
gles, or Spherical linear (Slerp) interpolation of
rotations expressed as quaternions. All spatial
schemes use the back-projection algorithm pro-
posed by Igarashi et al. (see Section 3.2).
(c) For experiments using spatial keyframes we
tested 5 main projection algorithms for the mark-
ers, namely: Force, MDS, LLE, PCA and t-
SNE. Our LLE implementation uses the 15 near-
est neighbors to reconstruct its surrounding areas.
Force uses 50 iterations to reach its final projec-
tion. Experiments with t-SNE use a perplexity
value of 50. The projection algorithms corre-
spond to multidimensional projection of frames
using the strategies discussed earlier. In addi-
tion to these single-step schemes, we also tested
5 RBFP-based projection schemes (see Figure 4)
where the first step (keyframe projection) is per-
formed with one of the former projection algo-
rithms and the remaining frames are projected
with RBFs.
A preliminary batch of tests was conducted in
order to investigate how the compaction schemes
fare with respect to the desired compaction ratio.
Since this ultimately depends on the ratio between
keyframes and total frames (KF ratio), we selected
9 representative animations and four compaction
schemes, two temporal (Linear and Slerp) and two
spatial (MDS and t-SNE), all run with SCS keyframe
selection strategy, and measured the obtained error for
ratios between 1 and 10%. This experiment reveals
that error decreases sharply until reaching a KF ra-
tio of about 4%, after which the error decreases at
a slower rate. We used this observation to restrict
further comparison tests to a KF ratio of 3%, since
a smaller ratio would probably lead to bad recon-
structions and a larger ratio would probably not reveal
much about advantages of one scheme over another.
It could be argued that rather than using a fixed KF
ratio, a better comparison would maintain a desired
minimum error and gauge what KF ratio would be re-
quired to attain it. Such an experimental setup, how-
ever, would be considerably more strenuous, since
each scheme would have to be run several times, ad-
justing the KF ratio until reaching the desired error.
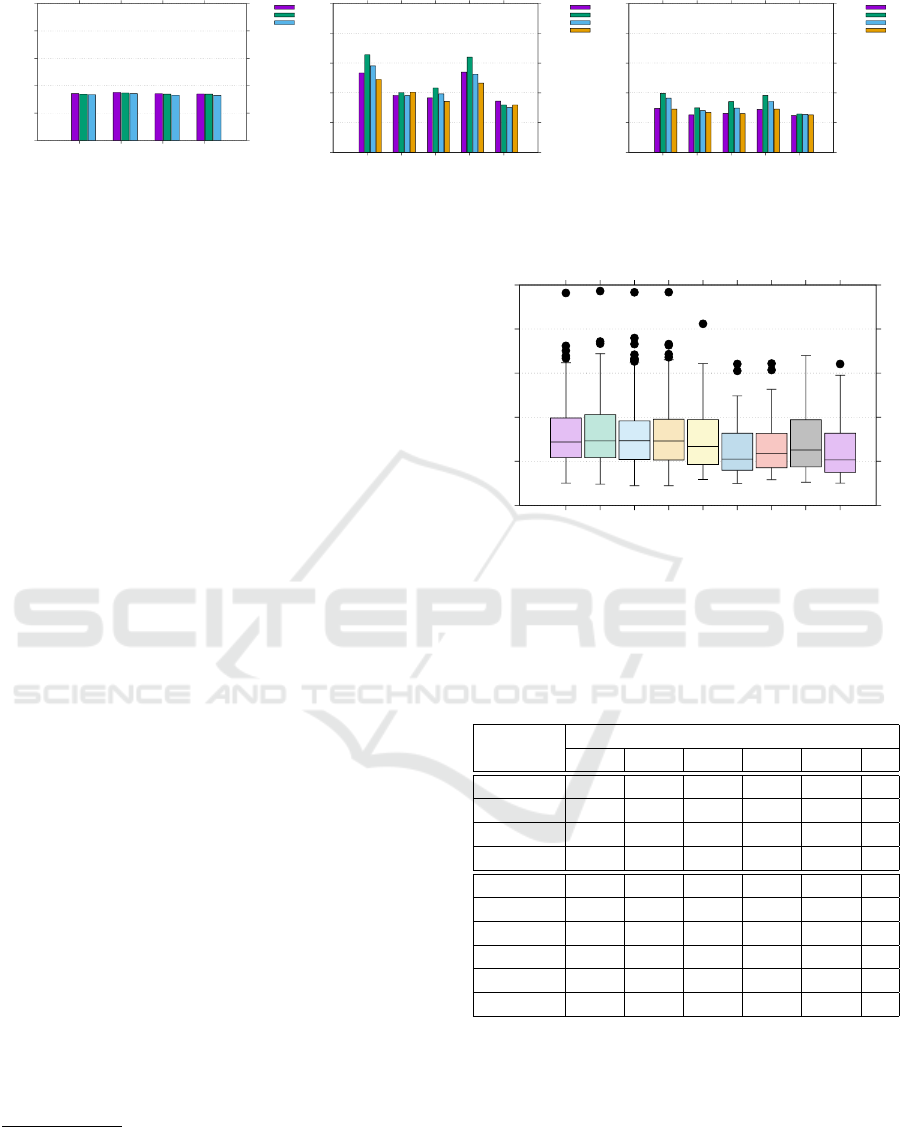
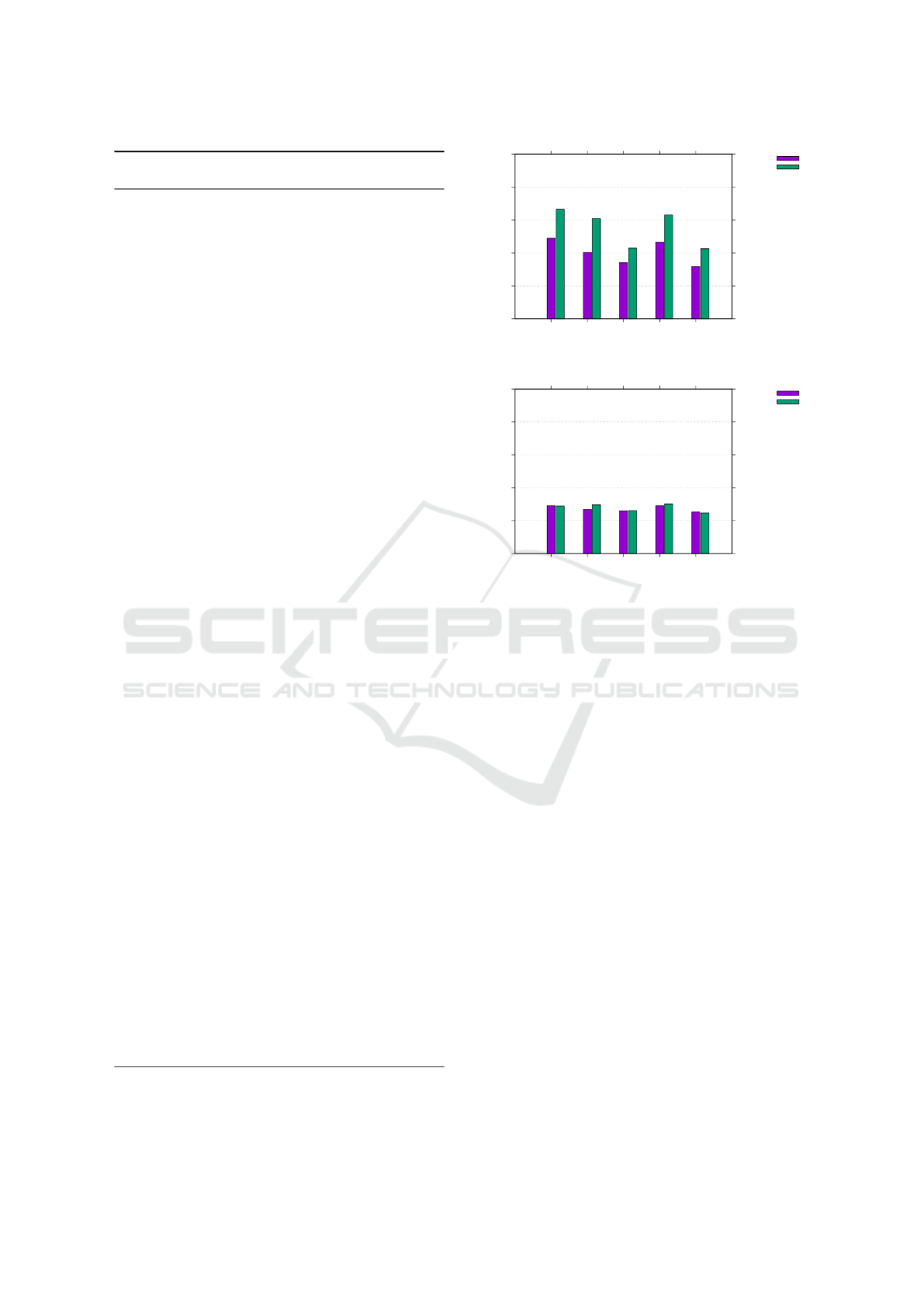
Figure 7 shows the average error per frame per
joint for various combinations of selection and inter-
polation strategies at 3% KF ratio. The examination
of these charts leads us to a few observations:
1. Temporal schemes as Slerp, Linear and Hermitian
interpolation work well and are quite similar in
terms of average error measure.
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
36
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
Hermitian
Linear
Slerp
1D-RBF
US
PB
SCS
(a) Temporal schemes
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
Force
LLE
MDS
PCA
t-SNE
US
PB
SCS
ROLS
(b) SK schemes
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
Force
LLE
MDS
PCA
t-SNE
US
PB
SCS
ROLS
(c) SK schemes (2D optimized)
Figure 7: Error per frame per joint for temporal and spatial keyframe (single-step) schemes with KF ratio of 3%. Average of
70 files.
2. More sophisticate keyframe selection algorithms
do not, in general, produce better results than the
naive uniform sampling.
3. Spatial keyframe schemes produce good results
but only if the optimized projection of (non-key)
frames is used.
In particular, the overall best result was obtained with
optimized t-SNE projection and uniform sampling,
with an average error of 0.618 per frame per joint.
On the other hand, the temporal scheme that yielded
the smallest average error – 0.826 per frame per joint
– was the Slerp interpolation combined with SCS
keyframe selection.
The results shown in Figure 7 were produced by
averaging the error over all 70 mocap files, which
might hide important outliers. For a more detailed
comparison, one may examine the box-plot shown in
Figure 8 (see also the numeric values in Table 1)
1
.
This chart omits the non-optimized spatial keyframe
schemes and the Slerp-based temporal scheme. All
experiments were run with keyframes selected by uni-
form sampling. The figure reveals that all tempo-
ral schemes exhibit a larger median than all spatial
keyframe schemes. In particular, t-SNE has the small-
est median and also the smallest first quartile. Isomap
has the lowest minimum and LLE has the lowest third
quartile. However, all except PCA show a few out-
liers. All spatial keyframe schemes with optimized
projection show improvements with respect to tem-
poral schemes.
Next, two-step projection schemes were evalu-
ated with respect to their analogous one-step versions.
We remind the reader that two-step methods such as
LAMP and RBFP differ from their one-step coun-
terparts in that only control points (keyframes in our
case) are projected in the first step, while the remain-
1
This boxplot chart variation draws the bottom
“whisker” at the value of the lowest data point greater than
Q
1
− 1.5IQR, where Q
1
is the first quartile and IQR is the
interquartile range. Similarly, the top “whisker” is the high-
est data point smaller than Q
3
+ 1.5IQR. Values lying out-
side the range between whiskers are considered outliers.
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
Hermitian
Linear
Slerp
1D-RBF
Force
LLE
MDS
PCA
t-SNE
Figure 8: Error per frame per joint boxplot for temporal and
spatial keyframe schemes with KF ratio of 3%. Values are
available at Table 1.
Table 1: Boxplot values. W
bot
and W
top
are the values for
bottom and top whiskers, Q
1
and Q
3
are first and third quar-
tiles, Q
2
is the median and O is the number of outliers.
Scheme Boxplot values
W
bot
Q
1
Q
2
Q
3
W
top
O
Hermite 0.25 0.54 0.72 1 1.62 5
Linear 0.24 0.55 0.73 1.03 1.72 3
Slerp 0.22 0.52 0.73 0.96 1.58 9
1D-RBF 0.22 0.52 0.73 0.96 1.61 8
Force 0.3 0.46 0.67 0.97 1.61 1
Isomap 0.25 0.43 0.54 0.86 1.29 4
LLE 0.25 0.4 0.53 0.81 1.24 2
MDS 0.29 0.43 0.59 0.82 1.32 2
PCA 0.26 0.44 0.63 0.97 1.7 0
t-SNE 0.25 0.39 0.52 0.81 1.48 1
der points use a different projector – affine maps in
the case of LAMP and RBFs in the case of RBFP.
Since early experiments using LAMP yielded consis-
tently bad reconstructions, we present here only ex-
periments with RBFP coupled with the ROLS selec-
tion strategy as suggested in (Amorim et al., 2014).
Figure 9 shows a comparison chart between 1- and 2-
step schemes, which indicates that RBFP yields poor
results unless followed by optimization.
Enhancing Spatial Keyframe Animations with Motion Capture
37
Algorithm 1: Gradient descent optimization for pose pro-
jection.
1: function GETOPTIMIZEDPROJECTION(F, Q, G)
Optimizes projection Q. Where F - frame array,
Q - projected pose array, G - keyframe array.
2: O ←
/
0
3: for i ← 1, maxtries do
4: done ← true
5: for all f
i
∈ F \ {G ∪ O} do
6: if gradientDescent( f
i
,F,Q,G) then
7: O ← O ∪ { f
i
}
8: done ← false
9: end if
10: end for
11: if done then
12: break
13: end if
14: end for
15: end function
16: function GRADIENTDESCENT( f
i
, F, Q, G)
Updates q
i
∈ Q and returns if q
i
has changed.
Where f
i
- frame, F - frame set, Q - projected
pose set, G - keyframe set.
17: h ← (0, 0)
18: v
x
← (1, 0)
19: v
y
← (0, 1)
20: q
i
← projection of f
i
stored in Q
21: q
i+1
← projection of f
i+1
stored in Q
22: q
i−1
← projection of f
i−1
stored in Q
23: r ← (kq
i
− q
i−1
k + kq
i
− q
i+1
k)/2
24: e
o
← Err( f
i
,BackPro j(q
i
,F,Q,G))
25: e
xp
← Err( f
i
,BackPro j(q
i
+ δrv
x
,F,Q,G))
26: e
xn
← Err( f
i
,BackPro j(q
i
− δrv
x
,F,Q,G))
27: e
yp
← Err( f
i
,BackPro j(q
i
+ δrv
y
,F,Q,G))
28: e
yn
← Err( f
i
,BackPro j(q
i
− δrv
y
,F,Q,G))
29: if (e
o
> e
xp
) ∨ (e
o
> e
xn
) then
30: h ← h + v
x
(e
xn
− e
xp
)
31: end if
32: if (e
o
> e
yp
) ∨ (e
o
> e
yn
) then
33: h ← h + v
y
(e
yn
− e
yp
)
34: end if
35: if khk > 0 then
36: h ← rh/khk
37: q
0
i
← q
i
+ αh
38: replace q
i
by q
0
i
in Q
39: return true
40: else
41: return false
42: end if
43: end function
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
Force
LLE
MDS
PCA
t-SNE
1 step
2 step
(a) SK schemes
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
Force
LLE
MDS
PCA
t-SNE
1 step
2 step
(b) SK schemes (2D optimized)
Figure 9: Error per frame per joint for ROLS keyframe se-
lection with 1 and 2 step projection approach. KF ratio is
3%. Average of 70 files.
5.2 Compression Evaluation
Our first tests with this framework showed a poor
reconstruction for in-betweens if we neglected the
2D projection for each frame and tried to reconstruct
mocap by tracing the 2D controller trajectory, us-
ing only a simple interpolation between the projected
keyframes. This comes from the fact that mocap data
is complex and 2D projections, in particular those ob-
tained with optimization, are not smooth but contain
cusps and gaps. Thus, the easiest way to encode such
trajectories is to store the coordinates of all frame
projections. This is not required for temporal com-
pression schemes which only record keyframe times-
tamps. Once we add more information to encode tra-
jectories, a trade-off arises between better reconstruc-
tion quality and a less compact format.
The uncompressed data size can be stated as a
function of the number of frames, as described in
Equation 2, where h is the header size needed for de-
scribing the skeleton hierarchy and other constant pa-
rameters, f is the number of frames and do f the num-
ber of joints. The compressed data size for temporal
schemes is described in Equation 3, where r
k f
is the
ratio between keyframes and the number of frames.
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
38

Remember that for each keyframe, we still need to
keep all rotations and a timestamp or frame id to lo-
cate it in time. Also, note that the root joint data is
not compressed and should be addressed by a sep-
arate scheme. Equation 4 describes the compressed
data size for spatial keyframe schemes, adding two
more coordinates to the format.
Considering that for our experiments we have
do f = 31 and r
k f
= 3%, we can state that the theo-
retical lower bound for temporal schemes is near 6%,
given that lim
f →∞
c
t
( f )
m( f )
≈ 6.06%. Spatial keyframe
schemes have a bigger lower bound at around 8%,
given that lim
f →∞
c
sk f
( f )
m( f )
≈ 8.15%. The price of using
the frame projection imposes at around 2% of lost in
compression size, but is probably less if we consider a
header size between 0.5% to 5% of the uncompressed
file size.
m( f ) = h + f (3do f + 3) (2)
c
t
( f ) = h + f (r
k f
(3do f + 1) + 3) (3)
c
sk f
( f ) = h + f (r
k f
(3do f + 1) + 5) (4)
6 LIMITATIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this work, we have evaluated the use of spatial
keyframing together with motion capture in two con-
texts: data visualization and compression. Our proto-
type handles SK-inspired animation authoring where
poses can be harvested directly from the mocap and
automatically associated with markers on a plane.
These features, allied with a sketching interface and
the visualization capabilities provided by projection
certainly helps the task of creating new animations,
but while the system is capable of handling more
poses and longer animations than the original SK
framework proposed by Igarashi et al., certain lim-
itations of that work are still present, namely those
regarding the embedding of the animation in a real
scene, like the root joint translations for a skeleton
moving in the scene. We plan to lift some of these
restrictions with future versions of this prototype by
employing some alternative scheme based on physical
simulation such as (Wilke and Semwal, 2017). Also,
a formal evaluation of the tool by professional anima-
tors might help us address some of its limitations.
Our investigation of the use of multidimensional
projection and SK for mocap compression showed
that SK generally attains smaller errors for the same
amount of keyframes than temporal compression.
Unfortunately, SK compression has not been shown to
yield substantial gains with respect to standard tempo-
ral compression schemes in practice, mostly because
in our experiments trajectories in 2D space had to be
stored with no compression. Although our experi-
mentation has been extensive, we still plan on inves-
tigating other projection algorithms, as well as using
3D projections which might yield better compression
rates.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was financed in part by the Coordenac¸
˜
ao
de Aperfeic¸oamento de Pessoal de Ni
´
ıvel Superior -
Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001.
REFERENCES
The daz-friendly bvh release of cmu’s motion capture
database – cgspeed. https://sites.google.com/a/
cgspeed.com/cgspeed/motion-capture/daz-friendly-
release. Accessed: 2017-05-19. Also available at
http://mocap.cs.cmu.edu/.
Amorim, E., Brazil, E. V., Mena-Chalco, J., Velho, L.,
Nonato, L. G., Samavati, F., and Sousa, M. C. (2015).
Facing the high-dimensions: Inverse projection with
radial basis functions. Computers & Graphics, 48:35
– 47.
Amorim, E., Vital Brazil, E., Nonato, L. G., and Sama-
vati, Faramarz Costa Sousa, M. (2014). Multidimen-
sional projection with radial basis function and control
points selection. In Pacific Visualization Symposium
(PacificVis), 2014 IEEE, Pacific Vis’14, pages 209–
216.
Arikan, O. (2006). Compression of motion capture
databases. ACM Trans. Graph., 25(3):890–897.
Assa, J., Caspi, Y., and Cohen-Or, D. (2005). Action syn-
opsis: Pose selection and illustration. ACM Trans.
Graph., 24(3):667–676.
Bulut, E. and Capin, T. (2007). Key frame extraction from
motion capture data by curve saliency. Computer An-
imation and Social Agents, page 119.
Burges, C., Shaked, T., Renshaw, E., Lazier, A., Deeds, M.,
Hamilton, N., and Hullender, G. (2005). Learning to
rank using gradient descent. In Proceedings of the
22Nd International Conference on Machine Learning,
ICML ’05, pages 89–96, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Cox, M. A. A. and Cox, T. F. (2008). Multidimensional
Scaling, pages 315–347. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,
Berlin, Heidelberg.
Dinh, H. Q., Turk, G., and Slabaugh, G. (2002). Recon-
structing surfaces by volumetric regularization using
radial basis functions. IEEE Transactions on Pat-
tern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 24(10):1358–
1371.
Enhancing Spatial Keyframe Animations with Motion Capture
39

dos Santos Amorim, E. P., Brazil, E. V., II, J. D., Joia, P.,
Nonato, L. G., and Sousa, M. C. (2012). ilamp: Ex-
ploring high-dimensional spacing through backward
multidimensional projection. In IEEE VAST, pages
53–62. IEEE Computer Society.
Halit, C. and Capin, T. (2011). Multiscale motion saliency
for keyframe extraction from motion capture se-
quences. Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds,
22(1):3–14.
Huang, K.-S., Chang, C.-F., Hsu, Y.-Y., and Yang, S.-
N. (2005). Key probe: a technique for anima-
tion keyframe extraction. The Visual Computer,
21(8):532–541.
Igarashi, T., Moscovich, T., and Hughes, J. F. (2005).
Spatial keyframing for performance-driven anima-
tion. In Proceedings of the 2005 ACM SIG-
GRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer An-
imation, SCA ’05, pages 107–115, New York, NY,
USA. ACM.
Jenkins, O. C. and Matari
´
c, M. J. (2004). A spatio-temporal
extension to isomap nonlinear dimension reduction.
In Proceedings of the Twenty-first International Con-
ference on Machine Learning, ICML ’04, pages 56–,
New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Jin, C., Fevens, T., and Mudur, S. (2012). Optimized
keyframe extraction for 3d character animations.
Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds, 23(6):559–
568.
Joia, P., Paulovich, F., Coimbra, D., Cuminato, J., and
Nonato, L. (2011). Local affine multidimensional pro-
jection. Visualization and Computer Graphics, IEEE
Transactions on, 17(12):2563–2571.
Lim, I. S. and Thalmann, D. (2001). Key-posture extrac-
tion out of human motion data by curve simplification.
Annual Reports of the Research Reactor Institute, Ky-
oto University. Kyoto University. Swiss Federal Inst.
Technol. (EPFL), CH-1015 Laussane, Switzerland.
Lowe, D. G. (1987). Three-dimensional object recogni-
tion from single two-dimensional images. Artif. In-
tell., 31(3):355–395.
Roweis, S. T. and Saul, L. K. (2000). Nonlinear dimension-
ality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science,
290(5500):2323–2326.
Safonova, A., Hodgins, J. K., and Pollard, N. S. (2004).
Synthesizing physically realistic human motion in
low-dimensional, behavior-specific spaces. ACM
Trans. Graph., 23(3):514–521.
Smith, L. I. (2002). A tutorial on principal components
analysis. Technical report, Cornell University, USA.
Tejada, E., Minghim, R., and Nonato, L. G. (2003). On
improved projection techniques to support visual ex-
ploration of multidimensional data sets. Information
Visualization, 2(4):218–231.
Tenenbaum, J. B., Silva, V. d., and Langford, J. C. (2000).
A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimen-
sionality reduction. Science, 290(5500):2319–2323.
Togawa, H. and Okuda, M. (2005). Position-based
keyframe selection for human motion animation. In
Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2005. Proceedings.
11th International Conference on, volume 2, pages
182–185.
van der Maaten, L. and Hinton, G. (2008). Visualizing data
using t-SNE. Journal of Machine Learning Research,
9:2579–2605.
Wilke, B. and Semwal, S. K. (2017). Generative ani-
mation in a physics engine using motion captures.
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Con-
ference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Com-
puter Graphics Theory and Applications - Volume
1: GRAPP, (VISIGRAPP 2017), pages 250–257. IN-
STICC, SciTePress.
Xiao, J., Zhuang, Y., Yang, T., and Wu, F. (2006). An effi-
cient keyframe extraction from motion capture data.
In Nishita, T., Peng, Q., and Seidel, H.-P., editors,
Computer Graphics International, volume 4035 of
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 494–501.
Springer.
Zhang, Y. and Cao, J. (2015). A novel dimension reduc-
tion method for motion capture data and application
in motion segmentation. In Parallel and Distributed
Systems, 2005. Proceedings. 11th International Con-
ference on, volume 12, pages 6751–6760.
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
40
