
Path Predictions using Object Attributes and Semantic Environment
Hiroaki Minoura, Tsubasa Hirakawa, Takayoshi Yamashita and Hironobu Fujiyoshi
Chubu Univeysity, Kasugai, Aichi, Japan
Keywords:
Convolutional Neural Network, Long Short-Term Memory, Path Prediction.
Abstract:
Path prediction methods with deep learning architectures take into account the interaction of pedestrians and
the features of the physical environment in the surrounding area. These methods, however, process all pre-
diction targets as a unified category and it becomes difficult to predict a path suitable for each category. In
real scenes, it is necessary to consider not only pedestrians but also automobiles and bicycles. It is consi-
dered possible to predict the path corresponding to the type of target by considering the types of multiple
targets. Therefore, aiming to achieve path prediction in accordance with individual categories, we propose a
path prediction method that represents the target type as an attribute and simultaneously considers the physical
environment information. The proposed method inputs feature vectors in a long short-term memory that re-
presents i ) past object trajectory, ii) the attribute, and iii) the semantics of the surrounding area. This makes
it possible to predict a path that is proper for each target. Experimental results show that our approach can
predict a path with higher precision. Also, changes in accuracy were analyzed by introducing the attribute of
the prediction target and the physical environment information.
1 INTRODUCTION
Path prediction, one of the challenging tasks in the
field of computer vision, estimates how a target ob-
ject like a pedestrian or an automobile will move
and on what path. Path prediction is expected to
have a wide range of applications, such as preventing
car accidents (SchneiderNicolas and M., 2013)(Kel-
ler and Gavrila, 2014)(Kooij et al., 2014) or autono-
mously controlling robots (Ziebart et al., 2009)(Ka-
rasev et al., 2016)(Vemula et al., 2017)(A. Vemula
and OhSocial, 2017). Therefore, it has received much
attention and various prediction methods have alre-
ady been proposed (Rehder and Kloeden, 2015)(Hu-
ang et al., 2016)(Xie et al., 2013)(Walker et al.,
2014)(Park et al., 2016)(Su et al., 2017). In recent
years, because of advancements in deep leaning, pre-
diction methods utilizing a convolutional neural net-
work (CNN) (Lecun et al., 1989) or a long short-term
memory (LSTM) (S.Hochreiter, 1997) have also been
developed (A. Vemula and OhSocial, 2017)(Yi et al.,
2016)(Alahi et al., 2016)(Lee et al., 2017)(Fernando
et al., 2017b)(Fernando et al., 2017a)(Gupta et al.,
2018). To predict paths accurately, several factors are
introduced. For instance, the interactions between pe-
destrians (Alahi et al., 2016)(Lee et al., 2017)(Hel-
bing and Molnar, 1995)(Yamaguchi et al., 2011)(Ro-
bicquet et al., 2016)(Ma et al., 2017) are modeled
to predict and avoid collisions. Scene semantics are
also introduced for reliable prediction (Lee et al.,
2017)(Kitani et al., 2012)(Ballan et al., 2016). Ho-
wever, these approaches have a problem that all tar-
get objects are considered to be in the same class. In
practical scenes, it is necessary to predict the path of
a target object in an environment where there are a
variety of prediction targets, not only pedestrians but
also cars and bicycles. This means that the speed, tra-
veling distance, and area may differ depending on the
type of target object. If we simultaneously predict the
paths of multiple target objects, it would be difficult
to predict them in accordance with the type of target.
Although a naive solution for this problem is creating
models for each object type and making predictions
accordingly, it would be impractical.
In this paper, we propose a method to simultane-
ously predict paths of different types of target objects
such as pedestrians and bicycles (see Figure 1). Spe-
cifically, our method leverages three pieces of infor-
mation: the type of target object, the physical environ-
ment surrounding the target, and a past object trajec-
tory. We define the target object type (i.e., pedestrian,
bicycle) as an attribute and represent it as a one-hot
vector. For the physical environment, a feature vec-
tor is extracted from semantic scene labels (e.g., pa-
vement, grass, and building) via convolutional layers.
The past object trajectories correspond to coordinates
Minoura, H., Hirakawa, T., Yamashita, T. and Fujiyoshi, H.
Path Predictions using Object Attributes and Semantic Environment.
DOI: 10.5220/0007297500190026
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2019), pages 19-26
ISBN: 978-989-758-354-4
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
19

at each time step. We obtain a coordinate of the next
time step from the output of the network by input-
ting these vectors of current time step into an LSTM.
At the time of prediction, we can make a prediction
that takes the past object trajectory into account by
sequentially inputting the network output to the input
of the next time step. Simultaneously introducing the
target attribute and semantic label enables us to pre-
dict a path considering the difference in the speed of
each target and the area where the target tends to move
preferably. Also, we use a relative coordinate, that is,
direction and magnitude obtained from the difference
between two successive coordinates. Introducing re-
lative coordinates prevents the prediction results from
depending on the trained scene and enables us to pre-
dict paths over multiple different scenes.
We have two contributions. i ) To the best of our
knowledge, this is the first attempt to predict paths of
different kinds of prediction targets with a unified fra-
mework. ii ) We contribute a scene label dataset that
is annotated for the path prediction dataset published
by Robicquet et al. (Robicquet et al., 2016).
2 RELATED WORK
Over the last decade, several approaches have been
proposed to solve the path prediction problem. One
classical approach is a method based on Bayesian mo-
dels (SchneiderNicolas and M., 2013)(Kooij et al.,
2014)(Ballan et al., 2016). Schneider et al. (Schnei-
derNicolas and M., 2013) proposed a path prediction
method based on an extended Kalman filter to predict
the walking path of a pedestrian captured by an onbo-
ard camera. Kooij et al. (Kooij et al., 2014) predicted
the movement of pedestrians crossing a pavement
using a Dynamic Bayesian Network (DBN)(Robinson
and Hartemink, 2009). They use the pedestrian’s head
direction, the distance between the pedestrian and a
car, and the distance the pedestrian to the curb as ob-
servations of the DBN and estimate a mode showing
whether the pedestrian stops or crosses the street.
These Bayesian prediction methods focus on pede-
strians while our approach handles multiple kinds of
target objects simultaneously.
In recent years, a path prediction method has
been proposed that uses deep learning architectu-
res, particularly LSTMs (Alahi et al., 2016)(Lee
et al., 2017)(Fernando et al., 2017b)(Fernando et al.,
2017a). Alahi et al. (Alahi et al., 2016) propo-
sed a method to predict paths of multiple pedestri-
ans in a scene. They aimed to predict collision avoi-
dance behaviors between pedestrians and proposed a
pooling layer called Social Pooling (S-Pooling). S-
Pooling encodes hidden states of other pedestrians al-
ong with the spatial relationships. Lee et al. (Lee
et al., 2017) proposed a path prediction method using
a RNN encoder-decoder (Cho et al., 2014) and a
conditional variational auto-encoder (Kingma et al.,
2014). This method achieved high prediction perfor-
mance by considering the semantic scene context of
the surrounding area in addition to the interaction bet-
ween the targets as with S-Pooling. However, they fo-
cused on predicting pedestrian targets or targets con-
sidered to be the same types of objects. In contrast,
our approach inputs the attribute of a prediction target
itself in addition to the surrounding physical environ-
ment.
Attempting to develop a method that takes into ac-
count the attribute of a target object, Ma et al. (Ma
et al., 2017) proposed a method to predict pedestrian
paths from a single image on the basis of an inverse
reinforcement learning framework. Assuming that the
walking speed of the pedestrian differs depending on
age and gender, they first estimate the pedestrian at-
tributes and then predict the paths of multiple pede-
strians. This method makes predictions for environ-
ments where there are only pedestrians and does not
use environmental data. Our method, however, pre-
dicts paths by simultaneously considering the attri-
bute of the target object and the environmental data
of the surrounding area.
3 PROPOSED METHOD
As mentioned in the previous sections, we focus on
predicting paths of multiple kinds of target objects.
We use the attribute of a target object and the sur-
rounding physical environment information as inputs
in addition to the past object trajectories.
Figure 1 illustrates the overview of our proposed
network. First, to represent the object type, the attri-
bute is embedded as a one-hot vector. Then, we ex-
tract a feature map via a convolutional neural network
(CNN) to describe the environment around the target.
A static scene label is used as an input for the CNN,
focusing on the target object in the scene. The one-
hot and feature vector are concatenated with the past
object trajectory and input in an LSTM. We obtain the
coordinates of the target object for the next time step
as an output of the LSTM.
Our prediction method is relatively simple com-
pared with other recent LSTM-based prediction
methods (A. Vemula and OhSocial, 2017)(Alahi
et al., 2016)(Lee et al., 2017)(Fernando et al.,
2017b)(Fernando et al., 2017a). Instead of modeling
complex architectures, we focused on reconsidering
VISAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
20

∆𝑦
#$%
∆𝑥
#$%
“Bicycle”
⋮
+
LSTM
Relative Coord.
Conv. Layer
⋮
Attribute
“Pedestrian”
Scene Label
Pavement
Sidewalk
Tree
Grass
Building
t
t+1
𝑦
𝑥
Environment
∆𝑥
#
, ∆𝑦
#
+
⋮
Figure 1: The overview of the proposed method. Our method uses the attribute of a prediction target, a relative coordinate,
and the surrounding physical environment of the target as input for the network. The target attribute is embedded as a one-hot
vector and a feature vector is extracted from semantic scene labels via convolutional layers. These vectors and the relative
coordinate of the current time step are input to an LSTM and the relative coordinate of the next time step is output.
the information that can be useful for prediction. In
the following subsections we describe the method
used to represent the input data and how the data is
input in the network.
3.1 Attribute
To predict paths of multiple kinds of target objects,
we need to introduce some additional information re-
presenting object type as an input. We assume the
object type as an inherent attribute included in the
target and represent the attribute as a one-hot vector
(see Figure 2). Specifically, given target attributes
(e.g., pedestrian or car), these attributes are embed-
ded into N
attr
-dimensional vectors, where N
attr
is the
number of attributes being considered. The element
corresponding to the input attribute is set to 1 and the
others are set to 0. Inputting this vector enables us to
predict a unique path with respect to speed and turn.
Moreover, the area where the target tends to move is
also considered by combining the one-hot vector with
the feature vector representing physical environmen-
tal information.
3.2 Object Trajectory
We use relative coordinates as has been mentio-
ned. Specifically, we calculate the travel distance
(∆x
t
, ∆y
t
) from the past location data and the current
location data, that is, the difference in the absolute
coordinates. By using the relative coordinates as in-
put to the LSTM, we obtain the relative coordinates of
the next time step. Using relative coordinates enables
us to always set the current location of the target ob-
ject as the base point, i.e., (x
t
, y
t
) = (0, 0), and to make
a prediction without depending on implicit scene in-
formation derived from coordinates of training data.
Therefore, we can predict paths in multiple scenes.
3.3 Environment
The environmental information is also essential to im-
prove prediction performance. Accordingly, we ex-
tract a feature map that represents the surrounding en-
vironment by using semantic scene labels added to a
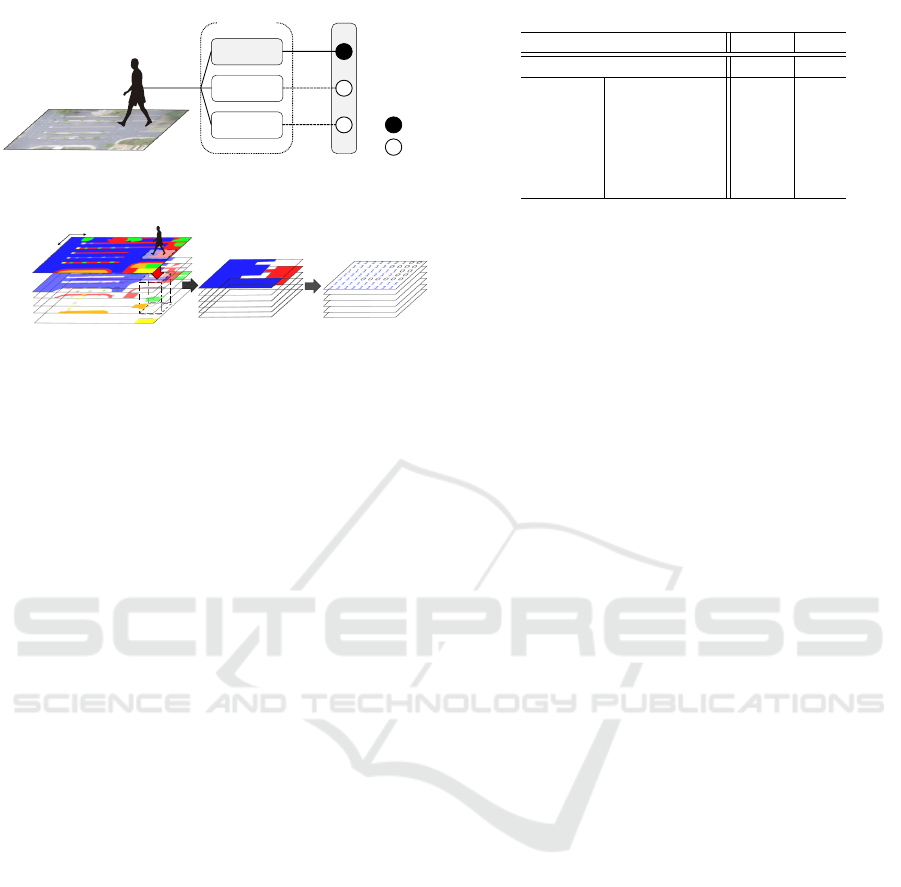
scene from a sidewalk, building, etc. Figure 3 shows
the procedure for extracting input data for the propo-
sed network from a whole semantic scene label. First,
we extract a label map by trimming the label of the
area (100×100 [pixels]) - focused on the target object
- from the scene label. Then, we convert the extracted
label map to a binary map whose channels correspond
to each semantic object (e.g., building and sidewalk).
The feature map for the surrounding environment is
extracted from this binary map via a CNN. Inputting
the environmental data enables us to make path pre-
dictions in which any existing obstacles or areas are
taken into account in accordance with the attributes of
the target objects.
3.4 Method to Input Data in the
Network
By inputting the attributes, environmental feature
map, and relative coordinate in the LSTM, we obtain
Path Predictions using Object Attributes and Semantic Environment
21
“Bicycle”
“Pedestrian”
⋮
Attribute
⋮
:1
:0
“Car”
Pedestrian
Bicycle
Car
one-hot
vector
Figure 2: The representation of the attribute of a target ob-
ject. This shows that the attribute is a pedestrian.
100
Scene Label
Label Map
Pavement
Sidewalk
Tree
Grass
Building
𝑦
𝑥
Binary Map
100
Figure 3: The representation of the physical environment
surrounding a prediction target. We first extract a label map
by trimming the area centering around the target object from
the scene label. The trimmed label map is converted into a
binary map. A feature map is extracted from this binary
map via convolutional layers.
the location of the target object in the next time se-
quence. Specifically, we use the data of the target ob-
ject as the observation data and make a prediction.
We use the true value that the target object actually
moves as the observation data. We input the obser-
vation data sequentially in the frames until we start
predicting. When we make a prediction, we sequen-
tially input the prediction value (i.e., an output of the
LSTM) to the next time sequence. We carry out the
process until the prediction ends so we can make a
prediction.
4 EXPERIMENT
This section demonstrates the effectiveness of the pro-
posed path prediction method.
4.1 Dataset
For the evaluation, we used the Stanford Drone Data-
set (SDD) (Robicquet et al., 2016). The SDD consists
of eight different prediction scenes and each scene
contains several video clips filmed on different days
and/or times, consisting of a total of 60 video clips.
In the SDD, six classes of target objects (i.e., bicycle,
pedestrian, cart, car, bus, and skateboarder) are given
and these are added to annotated paths. In our experi-
ments, we used the six object classes as attributes. We
observed the coordinates of the path used in our expe-
riments every 20 frames. Because the SDD clips are
filmed at 30 fps, each time step corresponds to about
0.66 [s]. During the test time, we observed a path for
Table 1: Training and test data details.
train test
No. of scenes 52 8
bicycle 2,369 545
pedestrian 2,696 500
cart 71 15
attribute car 75 5
bus 17 2
skateboarder 137 15
the first five frames (i.e., 3.3 [s]) and then predicted
the following eight frames (i.e., about 5.3 [s]).
The proposed method leverages semantic scene
labels to extract the feature map of the physical en-
vironment. However, the SDD does not include such
scene semantics. We therefore annotated semantic
scene labels for every 60 prediction scenes with re-
spect to the following three movable region classes
and four obstacle classes: sidewalk, pavement, grass,
bicycle storage, tree, building, and roundabout. Fi-
gure 4 shows examples of annotated scene labels.
These scene labels do not reflect only the visual ap-
pearance from bird’s eye view images but also the
ground where prediction targets move. It should be
noted that the SDD contains a lot of incorrect and/or
inaccurate annotated paths; examples are shown in Fi-
gure 5. In these examples, lost, occlusion, and inter-
polation flags are annotated in addition to the coordi-
nates. However, as far as we were able to confirm, tar-
get objects corresponding to incorrect paths do not ex-
ist in the original video clips even if we take the flags
into account (see Figure 5 (a, b, c). Figure 5(d) pro-
vides an example of an inaccurately annotated path.
Using such paths for training and evaluation decrea-
ses the prediction performance and makes fair com-
parisons difficult. Hence, we carefully selected only
the accurate and correct annotations. As a result, the
number of target objects selected was 5,365 for le-
arning and 1,082 for evaluation. Table 1 shows the
details of the data being used. This our annotated da-
taset will be publicly available after acceptance.
4.2 Evaluation Metrics and Baselines
In these experiments we used two metrics for quan-
titative evaluation. The first is final displacement er-
ror, which is a Euclidean distance for the ground truth
trajectory and the predicted trajectory in the last pre-
diction time steps. The second is average displace-
ment error, which is the average of Euclidean distan-
ces between the ground truth trajectory and the pre-
dicted trajectory in every prediction time step.
We compare our method with Kalman filter
(KF)(Kalman, 1960) and Social LSTM(S-LSTM) as
a baseline prediction approach.
VISAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
22

(c) bookstore
(a) coupa
(d) deathCircle (e) gates
(f) hyang (g) little (h) nexus
(b) quad
pavement
bicycle storage tree building
sidewalk
roundabout
grass
Figure 4: Examples of annotated scene labels in the SDD. For each sub-figure, the left shows an original scene image from
a bird’s eye view and the right shows the corresponding semantic scene labels. We annotated scenes into seven classes in
accordance with the ground rather than with the visual appearance of the scene images. These labels will be made publicly
available after acceptance.
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Figure 5: Examples of incorrect annotations in the SDD.
The green lines show the annotated paths.
4.3 Learning Details
Table 2 shows the details of the network architecture.
We trained our model with RMSprop optimizer (Tie-
leman and Hinton, 2012) with the initial learning rate
of 0.01, α = 0.99, and ε = 10
−8
. All prediction mo-
dels were trained for 100 epochs with a batch size of
10. During the training, we input ground truth coor-
dinates as past object trajectories through every time
step, i.e., from the beginning of observation to the end
of prediction. All the LSTM-based prediction models
were implemented using the Chainer framework and
trained with the Nvidia Titan Xp graphics card in an
end-to-end manner.
4.4 Results
Table 3 shows the quantitative results of prediction
methods and Figure 6 shows examples of prediction
results. Because past trajectories are only considered
as observations with KF, with this method the pre-
diction results follow the same direction as the obser-
vations and thus linear predictions without obstacle
regions are provided. The LSTM-based method pro-
vided similar prediction results when a trajectory is
used (Figure 6 (d)). However, in other cases its pre-
diction results were poorer than those of KF (Figure 6
Path Predictions using Object Attributes and Semantic Environment
23

Table 2: The detailed network architecture of the proposed
method. Convolutional layers are applied for the input with
respect to the environment. The feature map via the convo-
lutional layers and other inputs (i.e., attributes and coordi-
nates) are input to an LSTM.
layer kernel size output size remarks
input (attribute) 6
input (coordinate) 2
input (environment) (100, 100, 7)
conv1 (5, 5) (48, 48, 16) ReLU, stride=2
norm1 (48, 48, 16) batch norm.
pool1 (2, 2) (24, 24, 16) max pool.
conv2 (5, 5) (20, 20, 32) ReLU, stride=1
norm2 (20, 20, 32) batch norm.
pool2 (2, 2) (10, 10, 32) max pool.
conv3 (5, 5) (6, 6, 32) ReLU, stride=1
pool3 (2, 2) (3, 3, 32) max pool.
concat 296
LSTM 128
output 2
(a, c, g)). S-LSTM does not outperform our method
and even KF. Although we have carefully selected pa-
rameters to reproduce the result, we could not obtain
reasonable results. The obtained prediction results of
S-LSTM were catastrophic. Therefore, for the sake
of visibility, we do not show prediction results for S-
LSTM in Figure 6. The same problem is reported in
(Gupta et al., 2018).
As can be seen in Table 3, introducing other infor-
mation into the LSTM improves the prediction accu-
racy. In particular, introducing physical environment
information makes it possible to predict paths accura-
tely while avoiding obstacles (Figure 6 (h)). Howe-
ver, the improvement is relatively small from the vie-
wpoint of quantitative evaluation and the errors dif-
fer from the KF errors. Meanwhile, our proposed
method, trajectory + attribute + environment, outper-
forms the other methods. The proposed method was
able to predict paths close to the ground truth in Fi-
gure 6 (a, b, c, g).
Figure 6 (b, c) shows the trajectory of the bicycle;
the ground truth is moving while avoiding obstacles.
However, it has been confirmed that when only KF,
object trajectory, and attribute information are intro-
duced as input, a target will go straight ahead without
avoiding obstacles. In addition, when introducing en-
vironmental information, it predicts the trajectory to
take to avoid obstacles, but this confirms that pre-
dictions different from the ground truth can be made.
However, when both attribute and environmental in-
formation are introduced, a trajectory similar to the
ground truth is predicted. Figure 6(d, e, f) shows the
trajectory of the pedestrian. The results obtained in
this case showed that all the path prediction methods
traced a path close to the ground truth. This is proba-
bly because the path of the pedestrian can be predicted
easily because the movement intervals are narrower
than those for the bicycle. Figure 6(g) shows the tra-
jectory of the car, where the object to be predicted
along the roadway. However, when only KF, object
trajectory, and environmental information are intro-
duced as input, the prediction result is that it will go
straight ahead. When attributes are introduced in the
environment, it can be seen that a trajectory similar
to the ground truth is predicted. However, as shown
in Figure 6(h, i), when environmental information is
introduced the prediction results show a trajectory dif-
ferent from the ground truth.
The above results confirmed the proposed method
has the highest accuracy among the path prediction
methods compared. Although the conventional met-
hod KF predicts linear trajectories well, it is difficult
for it to predict nonlinear trajectories such as those
made in obstacle avoidance cases. To predict paths
more accurately, it is necessary to introduce attribu-
tes and environmental information into object trajec-
tories.
4.5 Failure Cases
Figure 7 shows examples of failed prediction results
with relative coordinates. Figure 7(a) shows a case
in which the speed of the bicycle suddenly changes
from slow to fast. In such cases, prediction methods
provide a slowly moving path by following the obser-
vations although the ground truth moves faster. In Fi-
gure 7(b), although the ground truth path turned left,
the prediction results are almost straight lines. In ca-
ses where there may be several prediction candida-
tes, our method follows the direction of the past mo-
vement. In Figure 7(c), the proposed method provides
paths that move towards the pavement so as to avoid
collisions with obstacles, while the ground truth takes
a different path. The reason is that a car moves in ac-
cordance with specific traffic rules, making it neces-
sary to consider common social practice. Figure 7(d,
e, f) are prediction results for a cart and skateboar-
ders. As shown in Table 1, there was insufficient trai-
ning data (and also test data) for these attributes. As
a result, the training was insufficient. Consequently,
all the prediction methods predicted incorrect paths
and could not even avoid obstacles (i.e., building and
roundabout). Hence, achieving efficient training for
cases involving rare attribute targets is a subject for
our future work.
VISAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
24
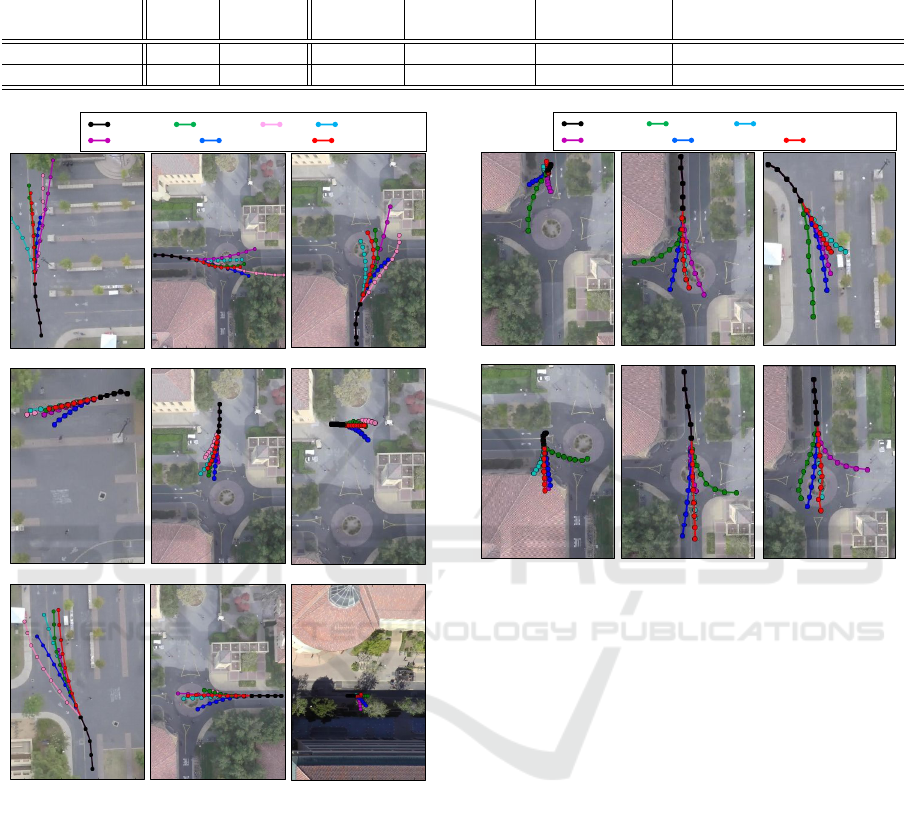
Table 3: Quantitative results for prediction methods (unit: pixels). Introducing attribute and environment information im-
proves the prediction performance. Our method, trajectory + attribute + environment, achieves the best performance with
respect to both final displacement error and average displacement error.
Metric KF S-LSTM trajectory
trajectory +
attribute
trajectory +
environment
trajectory +
attribute + environment
Final disp. error 174.42 206.22 196.13 173.04 172.12 109.44
Avg. disp. error 116.02 125.41 86.42 76.32 76.01 53.20
(a) bicycle
(d) pedestrian
(g) car
(b) bicycle (c) bicycle
(e) pedestrian (f) pedestrian
(h) car
(i) car
trajectory
trajectory + attr.
ground truthobservation
trajectory + env. trajectory + attr. + env.
KF
Figure 6: Examples of prediction results with relative coor-
dinates on SDD. From top to bottom row: prediction results
for a bicycle, pedestrian, and car.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we proposed a path prediction method
that takes target object attributes and physical envi-
ronment information into account. The method repre-
sents the attributes as one-hot vectors and encodes the
physical attributes via convolutional layers. Further-
more, we used relative coordinates as the past motion
history of prediction targets. Sequentially inputting
these data items in a long short-term memory enables
the method to make predictions. Experimental results
(e) skateboarder (f) skateboarder
(a) bicycle
(d) cart
(c) car(b) bicycle
trajectory
trajectory + attr.
ground truthobservation
trajectory + env. trajectory + attr. + env.
Figure 7: Selected failed prediction results. Our proposed
method cannot predict paths (a) that change their moving
speed suddenly, (b) that may have multiple candidates, and
(c) that follow common social practice. The bottom row
(d, e, f) shows the results obtained for rare attribute targets.
Trained models with fewer training samples predict incor-
rect paths.
obtained using the Stanford Drone Dataset show that
our approach to introducing those factors improves
the prediction performance. Our future work will in-
clude taking the interaction between the target objects
and dynamic environmental changes into considera-
tion.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported in part by JSPS KAKENHI
grant number JP16H06540. And, we gratefully
acknowledge the support of NVIDIA Corporation
with the donation of the Titan Xp GPU used for this
research.
Path Predictions using Object Attributes and Semantic Environment
25

REFERENCES
A. Vemula, K. M. and OhSocial, J. (2017). Attention: Mo-
deling attention in human crowds. International Con-
ference on Robotics and Automation.
Alahi, A., Goel, K., Ramanathan, V., Robicquet, A., Fei-
Fei, L., and Savarese, S. (2016). Social Lstm: Human
Trajectory Prediction in Crowded Spaces. In Compu-
ter Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 961–971.
Ballan, L., Castaldo, F., Alahi, A., Palmieri, F., and Sava-
rese, S. (2016). Knowledge transfer for scene-specific
motion prediction. In European Conference on Com-
puter Vision, pages 697–713.
Cho, K., van Merrienboer, B., G
¨
ulc¸ehre, C¸ ., Bougares,
F., Schwenk, H., and Bengio, Y. (2014). Learning
phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder
for statistical machine translation. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1406.1078.
Fernando, T., Denman, S., McFadyen, A., Sridharan, S.,
and Fookes, C. (2017a). Tree memory networks for
modelling long-term temporal dependencies. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1703.04706.
Fernando, T., Denman, S., Sridharan, S., and Fookes, C.
(2017b). Soft + hardwired attention: An lstm fra-
mework for human trajectory prediction and abnormal
event detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.05552.
Gupta, A., Johnson, J., Fei-Fei, L., Savarese, S., and Alahi,
A. (2018). Social gan: Socially acceptable trajectories
with generative adversarial networks. In The IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion, pages 2255–2264.
Helbing, D. and Molnar, P. (1995). Social force model for
pedestrian dynamics. Physical review E, 51(5):4282.
Huang, S., Li, X., Zhang, Z., He, Z., Wu, F., Liu, W., Tang,
J., and Zhuang, Y. (2016). Deep learning driven visual
path prediction from a single image. IEEE Transacti-
ons on Image Processing, 25(12):5892–5904.
Kalman, R. E. (1960). A new approach to linear filtering
and prediction problems. Journal of basic Engineer-
ing, 82(1):35–45.
Karasev, V., Ayvaci, A., Heisele, B., and Soatto, S. (2016).
Intent-aware long-term prediction of pedestrian mo-
tion. In International Conference on Robotics and Au-
tomation, pages 2543–2549.
Keller, C. G. and Gavrila, D. M. (2014). Will the pede-
strian cross? a study on pedestrian path prediction.
IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Sys-
tems, 15(2):494–506.
Kingma, D. P., Mohamed, S., Jimenez Rezende, D., and
Welling, M. (2014). Semi-supervised learning with
deep generative models. In Advances in Neural Infor-
mation Processing Systems, pages 3581–3589.
Kitani, K. M., Ziebart, B. D., Bagnell, J. A., and Hebert, M.
(2012). Activity forecasting. In European Conference
on Computer Vision, pages 201–214.
Kooij, J. F. P., Schneider, N., Flohr, F., and Gavrila, D. M.
(2014). Context-based pedestrian path prediction.
In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages
618–633.
Lecun, Y., Boser, B., Denker, J., Henderson, D., Howard,
R., Hubbard, W., and Jackel, L. (1989). Backpropa-
gation Applied to handwritten Zip Code Recognition.
Neural Computation, 1(4):541–551.
Lee, N., Choi, W., Vernaza, P., Choy, C. B., Torr, P. H. S.,
and Chandraker, M. (2017). Desire: Distant future
prediction in dynamic scenes with interacting agents.
In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages
336–345.
Ma, W., Huang, D., Lee, N., and Kitani, K. M. (2017). Fore-
casting interactive dynamics of pedestrians with ficti-
tious play. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion, pages 774–782.
Park, H. S., Hwang, J. J., Niu, Y., and Shi, J. (2016). Ego-
centric future localization. In Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, pages 4697–4705.
Rehder, E. and Kloeden, H. (2015). Goal-directed pede-
strian prediction. In Workshop on International Con-
ference on Computer Vision, pages 139–147.
Robicquet, A., Sadeghian, A., Alahi, A., and Savarese, S.
(2016). Learning social etiquette: Human trajectory
understanding in crowded scenes. In European Con-
ference on Computer Vision, pages 549–565.
Robinson, J. W. and Hartemink, A. J. (2009). Non-
stationary dynamic bayesian networks. In Advances in
Neural Information Processing Systems, pages 1369–
1376.
SchneiderNicolas and M., G. (2013). Pedestrian path pre-
diction with recursive bayesian filters: A comparative
study. In German Conference on Pattern Recognition,
pages 174–183.
S.Hochreiter (1997). LONG SHORT-TERM MEMORY.
Neural Computation, 9(8):1735–1780.
Su, S., Hong, J. P., Shi, J., and Park, H. S. (2017). Predicting
behaviors of basketball players from first person vi-
deos. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognitionr,
pages 1502–1510.
Tieleman, T. and Hinton, G. (2012). Lecture 6.5-rmsprop:
Divide the gradient by a running average of its recent
magnitude. COURSERA: Neural networks for ma-
chine learning.
Vemula, A., Muelling, K., and Oh, J. (2017). Modeling
cooperative navigation in dense human crowds. In In-
ternational Conference on Robotics and Automation,
pages 1685–1692. IEEE.
Walker, J., Gupta, A., and Hebert, M. (2014). Patch to the
future: Unsupervised visual prediction. In Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 3302–3309.
Xie, D., Todorovic, S., and Zhu, S. C. (2013). Inferring
‘Dark Matter’ and ‘Dark Energy’ from videos. In
International Conference on Computer Vision, pages
2224–2231.
Yamaguchi, K., Berg, A. C., Ortiz, L. E., and Berg, T. L.
(2011). Who are you with and where are you going?
In CVPR 2011, pages 1345–1352.
Yi, S., Li, H., and Wang, X. (2016). Pedestrian behavior un-
derstanding and prediction with deep neural networks.
In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages
263–279.
Ziebart, B., Ratliff, N., Gallagher, G., Mertz, C., Peterson,
K., Bagnell, J., Hebert, M., Dey, A., and Srinivasa,
S. (2009). Planning-based prediction for pedestrians.
In International Conference on Intelligent Robots and
Systems, pages 3931–3936.
VISAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
26
