
Classification of Cardiac Arrhythmias from Single Lead ECG
with a Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
J
´
er
ˆ
ome Van Zaen, Olivier Ch
´
etelat, Mathieu Lemay,
Enric M. Calvo and Ricard Delgado-Gonzalo
Swiss Center for Electronics and Microtechnology (CSEM), Rue Jaquet-Droz 1, Neuch
ˆ
atel, Switzerland
Keywords:
ECG, Cardiac Arrhythmias, Neural Networks, Deep Learning, Wearable Sensors.
Abstract:
While most heart arrhythmias are not immediately harmful, they can lead to severe complications. In par-
ticular, atrial fibrillation, the most common arrhythmia, is characterized by fast and irregular heart beats and
increases the risk of suffering a stroke. To detect such abnormal heart conditions, we propose a system com-
posed of two main parts: a smart vest with two cooperative sensors to collect ECG data and a neural network
architecture to classify heart rhythms. The smart vest uses two dry bi-electrodes to record a single lead ECG
signal. The biopotential signal is then streamed via a gateway to the cloud where a neural network detects and
classifies the heart arrhythmias. We selected an architecture that combines convolutional and recurrent layers.
The convolutional layers extract relevant features from sliding windows of ECG and the recurrent layer aggre-
gates them for a final softmax layer that performs the classification. Our neural network achieves an accuracy
of 87.50% on the dataset of the challenge of Computing in Cardiology 2017.
1 INTRODUCTION
Heart arrhythmias are caused by irregular electrical
conduction in cardiac tissue. Atrial fibrillation, which
affects 1–2% of the population (Camm et al., 2010),
is the most common one. Furthermore, its prevalence
increases with age, from <0.5% at 40–50 years to 5–
15% at 80 years. While not directly life-threatening,
it can lead to serious complications (January et al.,
2014). In particular, atrial fibrillation is associated
with a 3–5 fold increased risk of stroke and a 2-fold
increased risk of mortality (Kannel et al., 1998). It
is also associated with a 3-fold risk of heart failure
(Wang et al., 2003). Typical symptoms include heart
palpitations, shortness of breath, and fainting. How-
ever, about one third of the cases are asymptomatic
which prevents early diagnosis. This, in turn, pre-
cludes early therapies which might protect the patient
from the consequences of atrial fibrillation but also
from its progression. Indeed, atrial fibrillation causes
electrical and structural remodeling of the atria which
facilitates its further development (Frick et al., 2001;
Nattel et al., 2008).
The gold standard for diagnosing atrial fibrillation
and other heart arrhythmias is the 12-lead ECG. A
trained electrophysiologist can select the most appro-
priate treatment after reviewing ECG signals and the
patient history. This is, however, a time-consuming
task, especially for long recordings such as the ones
collected with Holter monitors. To alleviate this
task, several approaches have been proposed to de-
tect arrhythmias from ECG signals (Owis et al., 2002;
De Chazal et al., 2004). Even without perfect de-
tection accuracy, these approaches are useful as they
facilitate reviewing ECG by selecting relevant signal
excerpts.
Recently, neural networks have shown impressive
performance in various classification and regression
tasks. Image processing was the first field where
deep networks surpassed existing approaches by a
large margin (Krizhevsky et al., 2012). Since then,
they have been extensively applied to fields previ-
ously dominated by signal processing. In particular,
several architectures have been proposed to detect and
classify heart arrhythmias from ECG signals.
In the context of the challenge of Computing in
Cardiology 2017 (Clifford et al., 2017), a few neu-
ral network architectures were proposed to classify
single lead ECG signals into one of the following
classes: normal sinus rhythm, atrial fibrillation, other
rhythm, and noise. One of these architectures uses
logarithmic spectrograms computed over sliding win-
dows of ECG as input to two-dimensional convolu-
tional layers (Zihlmann et al., 2017). Aggregation
Van Zaen, J., Chételat, O., Lemay, M., Calvo, E. and Delgado-Gonzalo, R.
Classification of Cardiac Arrhythmias from Single Lead ECG with a Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network.
DOI: 10.5220/0007347900330041
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2019), pages 33-41
ISBN: 978-989-758-353-7
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
33

of successive windows is done with either temporal
averaging or a recurrent layer. However, the convo-
lutional and recurrent layers were trained separately
due to convergence issues. A similar approach used
a 16-layer convolutional neural network with skip
connections to classify arrhythmias from ECG sig-
nals (Xiong et al., 2017). Each layer is composed of
batch normalization, ReLU activation, dropout, one-
dimensional convolution, and averaging pooling.
Recently, a convolutional neural network was
shown to reach cardiologist-level arrhythmia detec-
tion (Rajpurkar et al., 2017). This 34-layer network
takes advantage of a very large dataset of 64,121
ECG signals, recorded from 29,163 patients, to rec-
ognize 12 different heart arrhythmias including atrial
fibrillation, atrial flutter, and ventricular tachycar-
dia. Another approach applied convolutional neural
networks for detecting atrial fibrillation from time-
frequency representations of ECG signals (Xia et al.,
2018). Two methods for computing these represen-
tations were compared: the short-time Fourier trans-
form or the stationary wavelet transform. In this case,
the neural network using coefficients from the second
transform yielded better classification accuracy.
Neural networks have thus shown promising re-
sults for the detection of abnormal cardiac rhythms.
Furthermore, as mentioned previously, it is of the ut-
most importance to detect arrhythmias as early as pos-
sible to improve treatment outcome. To tackle this is-
sue, we developed a system composed of two main el-
ements: a smart vest to record ECG signals and an al-
gorithm to detect and classify arrhythmias. The smart
vest includes two cooperative sensors to record a sin-
gle lead ECG signal and stream by Bluetooth the col-
lected data to a gateway. This gateway then forwards
the ECG signal to the cloud where it is processed by a
neural network in order to detect abnormal rhythms.
This article is structured as follows. First, the
dataset of ECG signals, our neural network architec-
ture, and the monitoring system are described in Sec-
tion 2. Then, the results are presented in Section 3
and discussed in Section 4. Finally, this article ends
with a short conclusion in Section 5.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Dataset
We used the dataset from the challenge of Computing
in Cardiology 2017 to train a neural network to clas-
sify cardiac arrhythmias. This dataset includes 8528
single lead ECG signals recorded with an AliveCor
device. The signals are sampled at 300 Hz and have
Table 1: Number of signals and mean duration for each
class.
Class Count Proportion Mean duration [s]
Normal rhythm 5076 59.52% 32.11
Atrial fibrillation 758 8.89% 32.34
Other rhythm 2415 28.32% 34.30
Noise 279 3.27% 24.38
Total 8528 100% 32.50
durations ranging from 9 to 60 seconds. Each signal
was acquired when the subject held each one of the
two electrodes in each hand resulting in a lead I (left
arm – right arm) ECG. As the device has no specific
orientation, many signals are inverted (right arm – left
arm).
All ECG signals are labeled with one of the fol-
lowing four classes: normal sinus rhythm, atrial fib-
rillation, other rhythm, and noise. The proportion of
each class in the dataset varies from 3.27% for noise
to 59.52% for normal rhythm. The full breakdown of
all classes is reported in Table 1.
The entries of the challenge of Computing in Car-
diology 2017 were ranked according to the following
score evaluated on a private test set:
S
CinC
=
F
1n
+ F
1a
+ F
1o
3
(1)
where F
1n
, F
1a
, and F
1o
denote the F
1
scores for nor-
mal rhythm, atrial fibrillation, and other rhythm. The
four winners (Teijeiro et al., 2017; Datta et al., 2017;
Zabihi et al., 2017; Hong et al., 2017) reached a score
of 0.83.
Several aspects of this dataset are challenging for
arrhythmia classification. First, many signals are in-
verted as mentioned previously. Second, the classes
are not balanced. There are very few signals labeled
atrial fibrillation or noise compared to the ones la-
beled normal rhythm. Furthermore, the durations of
the recordings are also different. They vary from 9
to 60 seconds. Figure 1 illustrates this issue. Most
ECG signals last 30 seconds but a significant portion
has shorter or longer durations. In addition, labeling
is relatively coarse as a single label is associated with
each ECG signal. In some cases, several labels could
be used for the same signal. Finally, the ECG quality
of a non-negligible part of the records is rather poor.
Four examples of signals are shown in Figure 2. The
first two signals are labeled normal rhythm and atrial
fibrillation and have good overall quality. The third
example is a normal rhythm record with acceptable
quality except for a short segment of noise. The last
ECG signal is labeled as atrial fibrillation but has very
BIOSIGNALS 2019 - 12th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
34
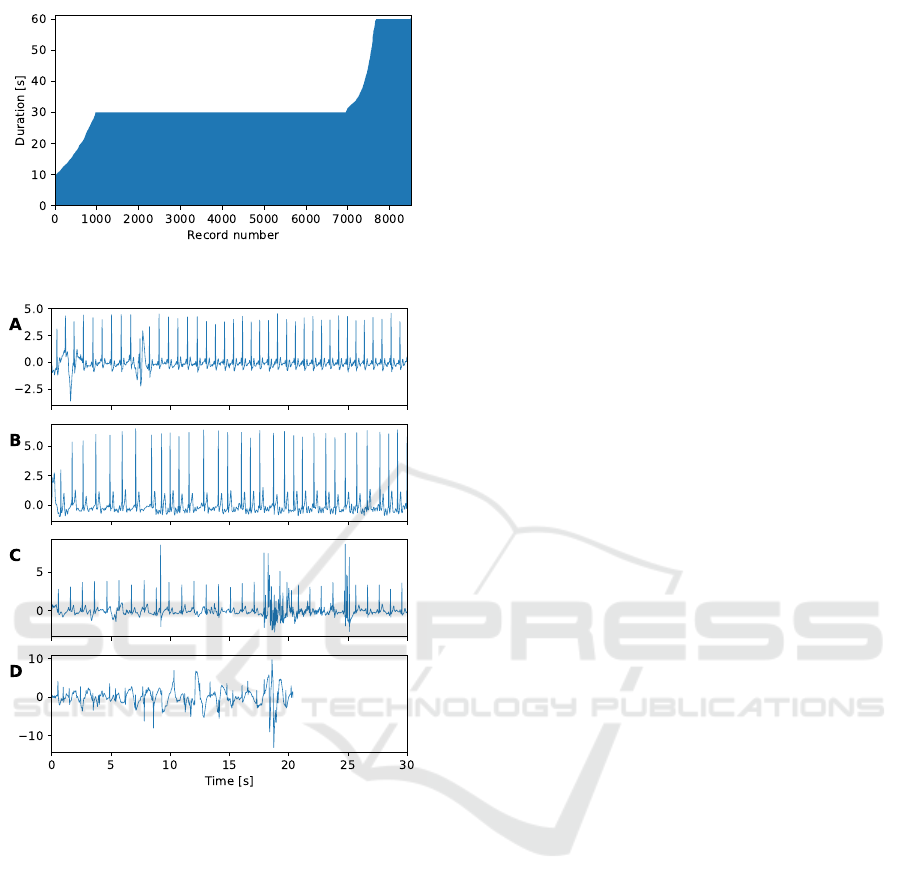
Figure 1: Record durations sorted in increasing order.
Figure 2: Examples of ECG records: (A) normal rhythm
from record A00001, (B) atrial fibrillation from record
A00004, (C) normal rhythm from record A00002, (D) atrial
fibrillation from record A00015.
poor quality due to large shifts of the baseline. It also
illustrates that all signals do not share the same dura-
tion.
The test set used during the challenge of Com-
puting in Cardiology was not yet publicly released.
Therefore, we split the dataset (which was originally
intended only for training) into a training set of 7000
records and a test set with the remaining 1528 records
while approximately preserving class repartition.
We applied the following pre-processing steps to
the dataset. First, we filtered the ECG signals with a
digital Butterworth band-pass filter between 0.5 and
40 Hz. The filter is applied in both forward and back-
ward directions to avoid distortions. The analog fil-
ter used by the recording device has similar cutoff
frequencies but still leaked some components outside
the pass-band. Then, we downsampled the signals to
200 Hz to reduce the number of samples. Finally, the
signals are scaled by the mean of the standard devi-
ations of all signals from the training set. Scaling is
helpful to accelerate training (LeCun et al., 2012).
2.2 Network Architecture
An approach to handle signals with different dura-
tions is to extract windows with the same length. The
label of a signal is then used for all included windows.
Fixed size inputs would make possible to apply a con-
volutional neural network to learn features useful to
classify arrhythmias. However, this approach is sub-
optimal as illustrated in Figure 2 where a signal la-
beled as normal rhythm includes a segment of noise.
Furthermore, all signals would need to be truncated to
the same length. This would lead to a large data loss
due to the considerable variations in signal durations.
A more appropriate approach is to use a recur-
rent neural network which is well-suited to process
sequences with varying lengths. While such a neural
network can, by design, remember past values over
long time intervals, they are not as efficient as con-
volutional neural networks for learning complex fea-
tures.
After reviewing the advantages and drawbacks of
these two approaches, we chose to combine them and
build a neural network that includes convolutional
and recurrent layers. Specifically, each ECG signal
was divided in sliding windows of 512 samples with
50% overlap. This corresponds to a window dura-
tion slightly above 2.5 seconds. The number of win-
dows extracted from each signal depends on its du-
ration. Seven convolutional layers were applied to
all windows of a signal. Each convolutional layer
is composed of a 1D convolution and a max pool-
ing operation. The convolution uses a kernel of size
5, zero padding, and a ReLU activation (Hahnloser
et al., 2000). The pool size for max pooling was set
to 2. The first convolutional layer has 8 output chan-
nels (from the single channel windows). Then, each
following layers double the number of channels while
max pooling halves the number of samples. After the
convolutional layers, a global averaging pooling layer
was applied. This results in 512 features for each in-
put window. The features were then processed with
a long short-term memory (LSTM) layer (Hochreiter
and Schmidhuber, 1997) with 128 units. Finally, a
softmax layer outputs the probability of each class for
the input ECG windows. This results in a neural net-
work with 1,203,364 trainable parameters including
874,656 for the convolutional part, 328,192 for the re-
Classification of Cardiac Arrhythmias from Single Lead ECG with a Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
35

Table 2: Neural network architecture. The output size is
given as N
w
× N
s
× N
c
where N
w
denotes the variable num-
ber of windows, N
s
the number of samples, and N
c
the num-
ber of channels.
Layer Output size
Input windows N
w
× 512 ×1
Convolutional layer 1 N
w
× 256 × 8
Convolutional layer 2 N
w
× 128 × 16
Convolutional layer 3 N
w
× 64 × 32
Convolutional layer 4 N
w
× 32 × 64
Convolutional layer 5 N
w
× 16 × 128
Convolutional layer 6 N
w
× 8 × 256
Convolutional layer 7 N
w
× 4 × 512
Global average pooling N
w
× 512
LSTM layer 128
Softmax layer 4
current part, and 516 for the final softmax layer. The
complete network architecture is summarized in Ta-
ble 2.
2.3 Data Augmentation
As the dataset is relatively small for fitting a neural
network, we applied different strategies to syntheti-
cally augment the number of ECG signals available
during training. The first strategy is to simply flip the
sign of each signal with probability 0.5. We found
it easier to let the neural network learn to take into
account inverted ECG signals instead of applying a
rectifying step during pre-processing.
Furthermore, when extracting sliding windows, it
is not possible to use all samples for the large ma-
jority of ECG signals. Indeed, the maximum number
of sliding windows N
w
in a signal with N samples is
given by
N
w
=
N − 512
256
+ 1
assuming N ≥ 512. In the previous expression, b·c
denotes the floor function. We took advantage of this
fact to place the first window at a random offset from
the start of the signal. This random offset is drawn
uniformly from
{0, 1, . . . ,N − (N
w
− 1) · 256 − 512}
for each signal at each epoch. The main idea behind
this strategy is to prevent the neural network from
learning the exact positions of the QRS complexes in
the training set. However, we always used the max-
imum number of sliding windows possible for each
signal to avoid wasting ECG samples.
The third strategy we applied is to resample each
signal at each epoch with probability 0.8 in order to
simulate slightly slower or faster heart rate and thus
help the neural network to reach better generaliza-
tion performance. Naturally, the resampling opera-
tion should not change the heart rate too much. Oth-
erwise, there is a risk to confuse a cardiac rhythm
for another one. Therefore, if a signal needs resam-
pling, its length is changed by a proportion sampled
uniformly between −5% and +5%.
2.4 Training
We implemented our neural network and strategies for
data augmentation in Python with the Keras library
(Chollet et al., 2015). We trained the neural network
for 200 epochs by minimizing the cross-entropy with
the Adam algorithm (Kingma and Ba, 2014). We set
the initial learning rate to 0.001. The learning rate
was divided by two if the cross-entropy evaluated on
the test set did not decrease for 5 consecutive epochs
with a lower limit at 10
−5
.
We used a batch size of 50 signals. As a batch
must include the same number of sliding windows for
each signal, we applied zero-padding. Specifically,
too short signals were prepended with all-zero win-
dows. To limit zero-padding as much as possible we
sorted the signals by duration and grouped them in
batches of similar lengths. This resulted in batches
with varying numbers of windows.
The LSTM layer was regularized by applying
dropout with a rate of 0.5 for both the input and re-
current parts (Srivastava et al., 2014; Gal and Ghahra-
mani, 2016). We monitored the accuracy on the test
set and selected the weights at the best epoch as the
final parameters of the neural network.
2.5 Monitoring System
The smart vest used to monitor ECG includes two
cooperative sensors illustrated in Figure 3. These
sensors use dry stainless steel bi-electrodes. This
technology, which was validated in a previous study,
yields high quality measurements of ECG and bio-
impedance signals, even in motion. No wetting of the
electrode is required. Moreover, the electrical connec-
tion linking both sensors does not have to be shielded,
nor insulated, which makes its integration in garment
easier and cheaper (a conductive fabric is sufficient).
The length of the connection is not limited to very
short distances and is therefore placed in the back so
BIOSIGNALS 2019 - 12th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
36

Figure 3: Cooperative sensors included in the smart vest for
monitoring ECG.
Figure 4: Smart vest during the validation protocol.
as to have space for a central zipper in the vest, which
makes donning and doffing easy, even for the elderly.
The two watertight sensors are clipped in the vest and
can be removed for washing and recharging. Opera-
tion is simplified to its maximum: the sensors auto-
matically switch to record mode as soon as they are
applied on the skin and return to standby mode when
removed.
This smart vest which was originally developed
for athletes also monitors the following biomedi-
cal signals: heart rate, transthoracic impedance, res-
piration rate, skin temperature, activity class (rest-
ing, walking, running), and posture (lying, stand-
ing/sitting). A quality index is associated with each
signal so that the reliability of the measurements can
be easily assessed. However, these additional signals
and the quality indices were not used in the present
study. Figure 4 shows the smart vest during the vali-
dation protocol.
Another important feature of the smart vest con-
sists in its capability to store all the recorded signals
locally as well as synchronize them in the cloud. This
is achieved by means of an accompanying gateway
that acts as a relay for the streamed data. The gate-
way is robust to poor network connectivity and up-
loads the newly available data to the cloud as it is
being streamed while an active connection is avail-
able. In our case, the gateway is composed of a simple
Raspberry Pi that connects to the smart vest via Blue-
tooth. The biomedical data is then collected, stored
locally in a compact format and relayed via telemetry
messages simultaneously to all the clients connected
to this gateway as well as a private cloud. The mes-
saging protocol chosen for this application is MQTT
1
(Message Queuing Telemetry Transport). This pro-
tocol, which uses the publish/subscribe paradigm, is
one of the most widely employed telemetry protocols
in IoT and real-time streaming. Once the ECG signal
is in the cloud, we can leverage the powerful comput-
ing capabilities and detect heart arrhythmias with our
neural network.
The ECG signals recorded with the smart vest de-
vice were pre-processed similarly to the data from the
challenge of Computing in Cardiology 2017. First,
the same band-pass filter between 0.5 and 40 Hz was
used to remove the baseline and high-frequency noise.
Then, the signals were resampled at 200 Hz. Finally,
we scaled each signal with its standard deviation. In-
deed, we could not use the scaling factor computed
on the training set as the two types of ECG signals
did not have the same range of values.
After pre-processing the ECG signals, we ex-
tracted sliding windows of 512 samples with 50%
overlap. We used groups of 25 such windows as in-
put to the neural network. We selected this specific
number of windows as it corresponds to segments of
approximately 33 seconds which is close to the me-
dian length of the signals used for training and testing
the model. Applying the neural network resulted in a
rhythm prediction for each group of 25 windows.
3 RESULTS
We evaluated three configurations. The first one used
the architecture described in Table 2 except that it
included only 6 convolutional layers. In addition,
all data augmentation strategies were applied during
training except resampling. The second configuration
used the full architecture with 7 convolutional layers
but again without resampling. Finally, the last con-
figuration was identical to the second one but with
resampling for further data augmentation. Figure 5
shows the evolution of the cross-entropy loss and the
accuracy during training for these three network con-
figurations. An additional convolutional layer helped
to increase the accuracy and reduce the loss. Resam-
pling the signals also slightly improved performance.
Despite our efforts, we could not completely elimi-
nate over-fitting as shown by the performance gap be-
tween training and test sets. Indeed, additional regu-
larization only decreased the performance of the net-
work. However, it is worth mentioning that resam-
1
https://mqtt.org
Classification of Cardiac Arrhythmias from Single Lead ECG with a Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
37

Figure 5: Cross-entropy loss (top) and accuracy (bottom)
evaluated during training for a network with 6 convolutional
layers without resampling (blue), a network with 7 con-
volutional layers without resampling (orange), and a net-
work with 7 convolutional layers with resampling (green).
Dashed lines denote results obtained on the training set and
solid lines results obtained on the test set.
pling helped to reduce over-fitting. The neural net-
work with the third configuration reached an accuracy
of 87.37% on the test set after 47 epochs. At the same
epoch, the accuracy on the training set was 90.90%.
After selecting the best neural network, we evalu-
ated it without zero-padding by selecting a batch size
of 1. In this case, the accuracy was 92.64% on the
training set and 87.50% on the test set. Sensitivity,
specificity, and F
1
score values are reported in Ta-
ble 3 for all classes. Unsurprisingly, the best F
1
score
was obtained for the class with the most samples (nor-
mal rhythm) and the worst one for the class with the
least samples (noise). Interestingly, the specificity for
atrial fibrillation was relatively high at 0.9784 while
the sensitivity was lower at 0.8382. Thus, the num-
ber of false positive is more larger than the number of
false negative which is an important property of the
model. Indeed, it missed only a few atrial fibrillation
cases while false detections can always be disproved
with additional analyses such as a full 12-lead ECG.
Furthermore, when evaluated in terms of the score
used during the challenge of Computing in Cardiol-
ogy 2017 (1), the neural network yielded 0.9156 and
0.8495 on the training and test sets. This is similar
to the best score obtained by the winners of the chal-
lenge. However, we could only evaluate our neural
network on 1528 ECG signals from the original train-
ing set since the official test set was not made public
yet. Therefore, it is difficult to compare the perfor-
Table 3: Performance metrics for the best neural network.
Class Metric Training set Test set
Normal rhythm
Sensitivity 0.9707 0.9263
Specificity 0.8955 0.8853
F
1
score 0.9509 0.9243
Atrial fibrillation
Sensitivity 0.9084 0.8382
Specificity 0.9942 0.9784
F
1
score 0.9232 0.8143
Other rhythm
Sensitivity 0.8380 0.7921
Specificity 0.9675 0.9352
F
1
score 0.8728 0.8099
Noise
Sensitivity 0.9345 0.7600
Specificity 0.9972 0.9871
F
1
score 0.9264 0.7103
mance of our approach with the winning entries.
After training and evaluation on the dataset of
the challenge of Computing in Cardiology 2017, we
applied the neural network to a few ECG signals
recorded with the smart vest. We also extracted the
times between consecutive R-waves from the ECG
signals (a.k.a. RR intervals) to facilitate visualization
of the heart rate. An example is shown in Figure 6.
In this case, the subject had a normal sinus rhythm
with two successive premature ventricular contrac-
tions characterized a very short RR interval followed
by a long recovery RR interval. These premature con-
tractions are clearly identifiable especially compared
to the stable RR intervals of a normal rhythm. The
neural network classified the this ECG segment as
normal rhythm except for the groups of windows in-
cluding the premature contractions which are classi-
fied as other rhythm.
Another example of classification is shown in Fig-
ure 7. In this case, no ECG signal was collected dur-
ing a few minutes due to poor skin-electrode contact
caused by motion. The neural network identified this
segment without signal as noise. Furthermore, two
segments preceding signal loss were classified as nor-
mal rhythm and other rhythm. The RR intervals were
stable in the first segment and there were a few prema-
ture ventricular contractions in the second one. After
the ECG signal was recovered, the RR intervals var-
ied widely and the neural network classified the data
as other rhythm.
BIOSIGNALS 2019 - 12th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
38
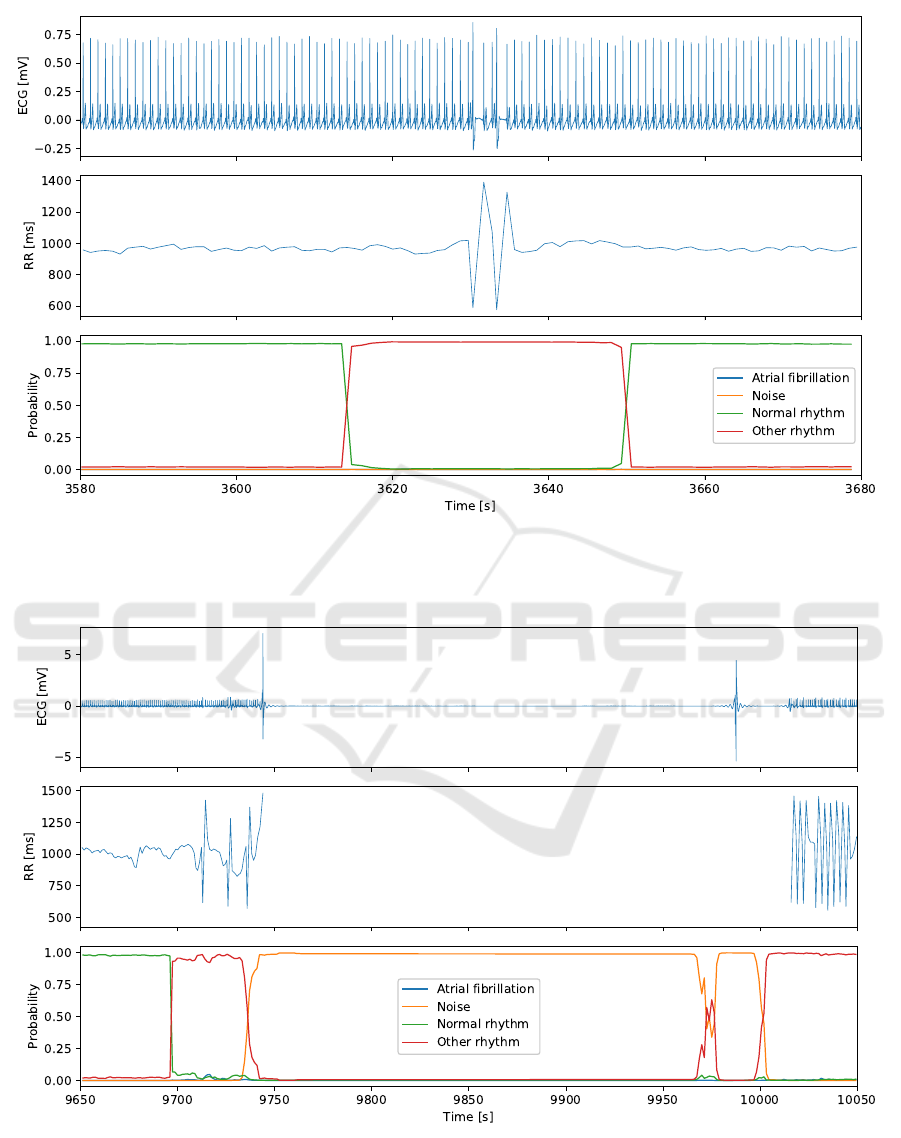
Figure 6: Cardiac rhythm classification from an ECG signal recorded with the smart vest. The ECG signal (top) includes two
premature ventricular contractions which are visible in the RR intervals (middle). The neural network correctly identifies this
segment of the signal as reflected by the class probabilities (bottom).
Figure 7: Cardiac rhythm classification from an ECG signal recorded with the smart vest. The ECG signal (top) includes a
segment with no R waves due to poor skin-electrode contact. Consequently, the RR intervals (middle) could not be extracted.
The class probabilities (bottom) computed by the neural network are valid as the segment is labeled as noise.
Classification of Cardiac Arrhythmias from Single Lead ECG with a Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
39

4 DISCUSSION
The neural network architecture we developed
achieved a classification performance similar to the
winners of the challenge of Computing in Cardiology
2017. Although we could not evaluate our approach
on the same data since the true test set was not re-
leased yet, the results are promising. In particular,
the specificity for atrial fibrillation shows that only a
limited number cases are not detected. We could take
into account signals of different lengths by combin-
ing convolutional and recurrent layers. Indeed, the
convolutional layers extract features relevant for ar-
rhythmia classification from sliding windows of raw
ECG signal. With this approach, there is no need to
pre-process the data to extract spectrogram or wavelet
transform for instance. Furthermore, no feature engi-
neering is required as the neural network learns dur-
ing the training phase to extract high-level features
useful for classification. The only pre-processing we
used is band-pass filtering as well as scaling to accel-
erate training. We also used strategies for data aug-
mentation to reduce over-fitting and improve the gen-
eralization performance of the network. In particu-
lar, randomly flipping the sign of ECG signals forced
the neural network to learn to take into account both
regular and inverted waveforms. Without this simple
strategy, we would have needed to develop a robust
method to detect signals that had to be rectified.
In addition, we have shown that it is possible to
apply a neural network trained on a generic dataset
to ECG signals recorded by the smart vest with min-
imal changes. Indeed, there was no need to adapt
the network architecture. The method to standardize
the ECG signals was the only element that required a
modification. Of course, if the two measurement sys-
tems, the AliveCor device and the smart vest, did not
record the same ECG lead, additional changes would
be needed. However, it is difficult to determine the
extend of these changes without evaluating the neu-
ral network on a dataset of ECG signals from another
lead.
Taken together, these results demonstrate that our
system could be used to monitor the cardiac activity
of a subject for detecting abnormal rhythms over long
periods of time. Indeed, the smart vest is more com-
fortable to wear than a traditional Holter and it can
still collect high quality ECG signals since it was ini-
tially developed for athletes. After transmitting the
data to the cloud, our neural network can quickly
classify abnormal rhythms. While the accuracy of
our system is not perfect, it can still help to reduce
the time spent reviewing ECG by selecting segments
with potential abnormalities that require additional at-
tention. These segments can then be analyzed by a
trained specialist. If needed, a full 12-lead ECG can
be performed to refine or confirm the diagnosis.
5 CONCLUSION
We presented a system composed of a smart vest to
record a single lead ECG signal and a neural network
for detection and classification of heart arrhythmias.
We plan to aggregate several databases of ECG sig-
nals with rhythm annotations to extend the types of ar-
rhythmias that our algorithm can detect and improve
its accuracy. We will also investigate whether adding
skip connections in our network architecture further
improves classification performance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for
their valuable suggestions and comments.
REFERENCES
Camm, A. J. et al. (2010). Guidelines for the manage-
ment of atrial fibrillation. European Heart Journal,
31(19):2369–2429.
Chollet, F. et al. (2015). Keras. https://keras.io.
Clifford, G. D., Liu, C., Moody, B., Lehman, L.-w. H.,
Silva, I., Li, Q., Johnson, A., and Mark, R. G. (2017).
AF classification from a short single lead ECG record-
ing: The PhysioNet/Computing in Cardiology Chal-
lenge 2017. Proceedings of Computing in Cardiology,
44:1.
Datta, S., Puri, C., Mukherjee, A., Banerjee, R., Choudhury,
A. D., Singh, R., Ukil, A., Bandyopadhyay, S., Pal, A.,
and Khandelwal, S. (2017). Identifying normal, AF
and other abnormal ECG rhythms using a cascaded
binary classifier. In 2017 Computing in Cardiology
(CinC), pages 1–4.
De Chazal, P., O’Dwyer, M., and Reilly, R. B. (2004). Auto-
matic classification of heartbeats using ECG morphol-
ogy and heartbeat interval features. IEEE Transac-
tions on Biomedical Engineering, 51(7):1196–1206.
Frick, M., Frykman, V., Jensen-Urstad, M., and
¨
Ostergren,
J. (2001). Factors predicting success rate and re-
currence of atrial fibrillation after first electrical car-
dioversion in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation.
Clinical Cardiology, 24(3):238–244.
Gal, Y. and Ghahramani, Z. (2016). A theoretically
grounded application of dropout in recurrent neural
networks. In Advances in neural information process-
ing systems, pages 1019–1027.
BIOSIGNALS 2019 - 12th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
40

Hahnloser, R. H., Sarpeshkar, R., Mahowald, M. A., Dou-
glas, R. J., and Seung, H. S. (2000). Digital selec-
tion and analogue amplification coexist in a cortex-
inspired silicon circuit. Nature, 405(6789):947.
Hochreiter, S. and Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term
memory. Neural Computation, 9(8):1735–1780.
Hong, S., Wu, M., Zhou, Y., Wang, Q., Shang, J., Li, H., and
Xie, J. (2017). ENCASE: An ENsemble ClASsifiEr
for ECG classification using expert features and deep
neural networks. In 2017 Computing in Cardiology
(CinC), pages 1–4.
January, C. T., Wann, L. S., Alpert, J. S., Calkins, H., Cigar-
roa, J. E., Cleveland, J. C., Conti, J. B., Ellinor, P. T.,
Ezekowitz, M. D., Field, M. E., Murray, K. T., Sacco,
R. L., Stevenson, W. G., Tchou, P. J., Tracy, C. M., and
Yancy, C. W. (2014). 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guide-
line for the management of patients with atrial fibril-
lation: a report of the American College of Cardiol-
ogy/American Heart Association task force on prac-
tice guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Journal
of the American College of Cardiology, 64(21):e1–
e76.
Kannel, W. B., Wolf, P. A., Benjamin, E. J., and Levy, D.
(1998). Prevalence, incidence, prognosis, and predis-
posing conditions for atrial fibrillation: population-
based estimates. The American journal of cardiology,
82(7):2N–9N.
Kingma, D. P. and Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A
method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1412.6980.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E. (2012). Im-
ageNet classification with deep convolutional neural
networks. In Advances in Neural Information Pro-
cessing Systems 25, pages 1097–1105.
LeCun, Y. A., Bottou, L., Orr, G. B., and M
¨
uller, K.-
R. (2012). Efficient backprop. In Neural networks:
Tricks of the trade, pages 9–48. Springer.
Nattel, S., Burstein, B., and Dobrev, D. (2008). Atrial re-
modeling and atrial fibrillation: mechanisms and im-
plications. Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophys-
iology, 1(1):62–73.
Owis, M. I., Abou-Zied, A. H., Youssef, A.-B., and Kadah,
Y. M. (2002). Study of features based on nonlinear
dynamical modeling in ECG arrhythmia detection and
classification. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical En-
gineering, 49(7):733–736.
Rajpurkar, P., Hannun, A. Y., Haghpanahi, M., Bourn, C.,
and Ng, A. Y. (2017). Cardiologist-level arrhythmia
detection with convolutional neural networks. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1707.01836.
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I.,
and Salakhutdinov, R. (2014). Dropout: a simple way
to prevent neural networks from overfitting. The Jour-
nal of Machine Learning Research, 15(1):1929–1958.
Teijeiro, T., Garc
´
ıa, C. A., Castro, D., and F
´
elix, P. (2017).
Arrhythmia classification from the abductive interpre-
tation of short single-lead ECG records. In 2017 Com-
puting in Cardiology (CinC), pages 1–4.
Wang, T. J., Larson, M. G., Levy, D., Vasan, R. S., Leip,
E. P., Wolf, P. A., D’Agostino, R. B., Murabito, J. M.,
Kannel, W. B., and Benjamin, E. J. (2003). Temporal
relations of atrial fibrillation and congestive heart fail-
ure and their joint influence on mortality: the Fram-
ingham heart study. Circulation, 107(23):2920–2925.
Xia, Y., Wulan, N., Wang, K., and Zhang, H. (2018). De-
tecting atrial fibrillation by deep convolutional neu-
ral networks. Computers in Biology and Medicine,
93:84–92.
Xiong, Z., Stiles, M. K., and Zhao, J. (2017). Robust ECG
signal classification for detection of atrial fibrillation
using a novel neural network. In 2017 Computing in
Cardiology (CinC), pages 1–4.
Zabihi, M., Rad, A. B., Katsaggelos, A. K., Kiranyaz, S.,
Narkilahti, S., and Gabbouj, M. (2017). Detection
of atrial fibrillation in ECG hand-held devices using
a random forest classifier. In 2017 Computing in Car-
diology (CinC), pages 1–4.
Zihlmann, M., Perekrestenko, D., and Tschannen, M.
(2017). Convolutional recurrent neural networks for
electrocardiogram classification. In 2017 Computing
in Cardiology (CinC), pages 1–4.
Classification of Cardiac Arrhythmias from Single Lead ECG with a Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
41
