
Proposing a Co-simulation Model for Coupling Heterogeneous Character
Animation Systems
Felix Gaisbauer
1,2
, Jannes Lehwald
1
, Philipp Agethen
1,2
, Julia Sues
2
and Enrico Rukzio
2
1
Daimler AG, Wilhelm-Runge-Str. 11, 89081 Ulm, Germany
2
Ulm University, James-Franck Ring, 89081 Ulm, Germany
Keywords:
Character Animation, Motion Synthesis Framework, Motion Model Unit, Co-simulation.
Abstract:
Nowadays, character animation systems are used in different domains ranging from gaming to production
industries. The utilized technologies range from physics based simulation, inverse kinematics and motion
blending to machine learning methods. Most of the available approaches are however tightly coupled with the
development environment, thus inducing high porting efforts if being incorporated into different platforms.
Currently, no standard exists which allows to exchange complex character animation approaches. A com-
prehensive simulation using these heterogeneous technologies is therefore not possible, yet. In a different
domain than character animation, the Functional Mock-up Interface (FMI) has already solved this problem.
Initially being tailored to industrial needs, the standards allows to exchange dynamic simulation approaches
like solvers for mechatronic components. Recently, based on this standard, a novel concept has been pro-
posed which allows to embed various character animation approaches within a common framework using so
called Motion Model Units. In this paper, we extend the proposed Motion Model Unit architecture and present
a novel co-simulation approach which orchestrates several sub-simulations in a common environment. The
proposed co-simulation can handle concurrent motions, generated by heterogeneous character animation tech-
nologies, while creating feasible results. The applicability of the novel co-simulation approach is underlined
by a user study.
1 INTRODUCTION
Motion synthesis is an important aspect of many sec-
tors in nowadays life, ranging from gaming to auto-
motive industry. In recent years, there has been a vast
progress in terms of character animation techniques,
ultimately increasing naturalness and realism. The
predominant proportion of the utilized approaches
rely on motion capture data and use motion blend-
ing techniques. Apart from this, there are approaches
which are based on artificial intelligence (Li et al.,
2017; Holden et al., 2017), physics based simulation
(Tsai et al., 2010) or statistical concepts (Min and
Chai, 2012). While motion blending techniques are
widely spread and provided by most target environ-
ments, the latter approaches are commonly tailored to
specific platforms and use-cases. To incorporate these
systems into novel platforms, high porting efforts are
usually the consequence. Standardized components,
embedding heterogeneous approaches would signif-
icantly reduce these porting efforts, while providing
additional benefits. For instance, complex scenarios
such as occurring in automotive production could be
simulated whereas specialized technologies for simu-
lations in collision-afflicted scenarios and data-driven
walk animations could be combined.
However, for exchanging context dependent char-
acter animation algorithms, there is no standardized
solution available, yet. In a different domain than
character animation, the Functional Mock-up Inter-
face (FMI) (Blochwitz et al., 2011) has already solved
this problem by encapsulating various simulation ap-
proaches using a common interface. Recently, based
on this FMI standard a novel concept has been pro-
posed which allows to embed various character an-
imation approaches within a common framework us-
ing so called Motion Model Units (MMU) (Gaisbauer
et al., 2018b). In this paper, we extend the proposed
Motion Model Interface architecture and present a
novel co-simulation approach which is able to or-
chestrates several sub-simulations embedded within
MMUs. The proposed co-simulation can handle con-
current motions, generated by heterogeneous charac-
ter animation technologies, while creating feasible re-
Gaisbauer, F., Lehwald, J., Agethen, P., Sues, J. and Rukzio, E.
Proposing a Co-simulation Model for Coupling Heterogeneous Character Animation Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0007356400650076
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2019), pages 65-76
ISBN: 978-989-758-354-4
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
65

sults. The applicability of the novel co-simulation ap-
proach is underlined by a user study.
The remainder of the paper is structured as fol-
lows: First the state of the art with regard to digital hu-
man simulation, co-simulation and the FMI standard
is revisited. Second, the concept of the Motion Model
Unit architecture, which forms the basis of the pro-
posed approach, is explained. Afterwards, the novel
co-simulation concept is presented in detail. Based on
a user study and exemplary task scenarios, the appli-
cability of the novel approach is evaluated. Finally, a
further conclusion and an outlook are given.
2 STATE OF THE ART
The concept of the novel co-simulation approach
builds upon a large body of related work. In the fol-
lowing, an overview of the state of the art in the con-
text of digital human simulation as well as regarding
co-simulation and the FMI standard is provided.
2.1 Character Animation Technologies
Character animation technologies are used through-
out heterogeneous domains. In general, the utilized
technologies can be subdivided into data-driven and
model-driven approaches (M
¨
uller et al., 2018).
The predominant proportion of the data-driven ap-
proaches are based on motion blending techniques
and utilize blending trees contained in state machines.
These methods provide natural motions while being
computationally efficient. The existent approaches
can be subdivided into Barycentric-, K-Nearest-
Neighbor-, Radial Basis Function-interpolation and
Inverse blending (Feng et al., 2012a). Based on the
automatic composition of segmented motion capture
clips, motion graphs allow to generate a sequence of
natural motions (Kovar et al., 2008). Min and Chai
(Min and Chai, 2012) presented a statistical approach
of the motion graphs to include the uncertainty of hu-
man motion. Due to the growing computational ca-
pabilities, recently, deep learning based approaches
received significant attention. Recent works present
deep learning based animation systems (Holden et al.,
2017; Li et al., 2017; Gaisbauer et al., 2018c) which
offer great potential for modeling natural motions.
Besides the data-driven approaches, model-driven
systems are also intense subject of research. In this
category physics based character animations are fre-
quently used. The approaches can be subdivided
into trajectory optimization and reinforcement learn-
ing (M
¨
uller et al., 2018). Approaches like (Tsai
et al., 2010) model the locomotion behaviour based
on an inverted pendulum. Others, such as (Falout-
sos et al., 2001) present composable controller for
physics based simulation. Moreover, inverse kinemat-
ics (IK) approaches such as (Aristidou and Lasenby,
2011; Buss, 2004) are also frequently used to com-
pute postures of digital avatars. In practice, IK is of-
tentimes utilized in combination with data-driven ap-
proaches or path planning algorithms.
Whereas data-driven approaches rely on recorded
motion capture data, model-driven approaches gener-
ate natural motions based on mathematical and phys-
ical models. Consequently, data-driven approaches
only cover the range which is given by the underly-
ing data, whereas model driven approaches are more
generic. The applicability of the different technolo-
gies therefore strongly depends on the use-case do-
main. For instance, in heavily collision-afflicted sce-
narios data-driven approaches are less suited since a
large amount of data sets is required.
2.2 Character Animation Systems
An exhaustive number of tools for simulating human
motion has been developed for various scopes of ap-
plications.
Tools like IPS IMMA (Hanson et al., 2014), San-
tos and Siemens Jack focus on the analysis and design
of workplaces and products. Since the addressed use-
cases often contain collision-afflicted environments,
the systems mainly utilize model-driven simulation
technologies. Musculoskeletal and bio-mechanical
modeling tools like AnyBody and OpenSim (Delp
et al., 2007) use highly-detailed DHMs including
a fine-grained representation of musculoskeletal- or
organ-system. These tools precisely model motions
of the human body, however, at the expense of the
real-time capability.
Another cluster which received significant atten-
tion during the last years, is the group of character an-
imation systems and game engines like Unity , Unreal
Engine and CryEngine. These tools provide gaming-
related platforms including various tools (e.g. retar-
geting of DHMs) to easily animate human motion.
Even though achieving outstanding results in terms of
naturalness, difficult movements in collision-afflicted
setting can only be scarcely simulated.
Smartbody (Thiebaux et al., 2008) provides an
animation system which is focused on the genera-
tion of human motion utilizing hierarchical motion
controllers. These controllers are embedded in the
Smartbody platform, thus being limited in their in-
teroperability. Moreover, the authors explicitly state
that they do not intent to create a platform indepen-
dent and modular architecture for exchanging char-
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
66

acter animations systems, since in their opinion those
architectures either under specify the interface and re-
strict the capabilities (Shapiro, 2011). Other frame-
works which provide a modular and exchangeable ar-
chitecture are Adapt (Shoulson et al., 2014) and Real
actor (Cerekovic et al., 2009). Whereas the first is
used for agent prototyping, Real actor represents a
behavior realization system for embodied conversa-
tional agents.
Recently, a novel framework which combines het-
erogeneous character animation approaches in a com-
mon system was presented (Gaisbauer et al., 2018b).
The framework is based on modular blocks called
Motion Model Units which encapsulate the specific
technologies and algorithms (Gaisbauer et al., 2018a).
The proposed concept within this work strongly
builds upon the presented Motion Model Unit archi-
tecture.
2.3 Co-simulation and FMI Standard
For exchanging motions between different simula-
tion tools, there are various formats such as Biovi-
sion Hierarchy (bvh) and Filmbox (fbx) available.
Even though these formats are widely used, they are
only capable of storing pre-generated motions (e.g.
recorded by a motion capture system). Hence, it is not
possible to integrate motion generations algorithms
within the files itself.
For exchanging simulation functionality in a dif-
ferent domain than motions, a widely used solution
is available. Functional Mock-up Interface (FMI) is a
standard that supports the exchange of dynamic simu-
lation models as well as its co-simulation while being
tool independent. This standard is based on a com-
bination of xml-files and compiled C-code (ITEA,
2011). An instance of a FMI component is called
a Functional Mock-up Unit (FMU). Using the FMI
standard, it is possible to perform a simulation of dif-
ferent FMUs, containing appropriate solvers, whereas
only the simulation results of the FMUs are ex-
changed after defined time steps. This approach is
called FMI for co-simulation (Blochwitz et al., 2011).
The concept of modular motion units, which is also
referred as Motion Model Interface (MMI) approach,
builds upon the idea of the FMI concept to further ex-
tend the standard to simulate human motion
Orchestrating various sub-simulations as intended
by the FMI or MMI approach, requires a supe-
rior instance managing the distributed sub-systems.
In general, this orchestration process is named co-
simulation, whereas the co-simulator updates the
components and incorporates the results. Recently,
in literature various co-simulation approaches for the
FMI standard have been proposed (Bastian et al.,
2011; Van Acker et al., 2015; Wang and Baras, 2013),
however, these systems predominantly focus on sig-
nal flow modeling mainly in the mechatronical do-
main. Since the co-simulation of character animation
systems has entirely different requirements, these so-
lutions can not be directly used.
Summarizing the state of the art with regard to
co-simulation approaches, it can be stated that no
approach is currently available for the orchestration
of heterogeneous character animation systems. To
bridge this gap, in this paper, a novel co-simulation
concept is proposed which can be applied to the MMI
approach. The concept allows to orchestrate and in-
corporate various character animation techniques in a
common system.
3 A MODULAR FRAMEWORK
FOR CHARACTER
ANIMATION SYSTEMS
Based on the FMI approach, a concept for exchanging
character animation systems is introduced in (Gais-
bauer et al., 2018b). With the FMI standard, com-
plex systems like industrial machines can be simu-
lated using specialized approaches such as solvers of
pneumatic cylinders or kinematic models. The re-
spective sub-simulations are embedded within stan-
dardized modules (FMUs) (Blochwitz et al., 2011).
Several of these co-simulations are sequenced by a
co-simulator. This component communicates with the
FMUs at discrete points in time and incorporates the
computed results of all heterogeneous approaches in
a common simulation. Transferring this concept to
the domain of character animation, so called Motion
Model Interfaces (MMIs) and their implementations
called Motion Model Units (MMUs) are presented
which allow to incorporate diverse character anima-
tion approaches into a common framework. Figure 1
shows the main idea of the approach.
3.1 Motion Model Units
The proposed MMUs are an essential part of this
modular concept and provide the basic interface for
encapsulating different character animation systems
and technologies (see Figure 1 top). These units
contain the actual animation approach, being imple-
mented in the required platform and programming
language. For instance, an actual MMU can com-
prise a data-driven algorithm implemented in Python,
as well as model-based approaches realized in C++.
Proposing a Co-simulation Model for Coupling Heterogeneous Character Animation Systems
67

Figure 1: Principle of the Motion Model Unit approach.
Using standardized units for encapsulating heterogeneous
character animation approaches and a co-simulation, multi-
ple systems can be incorporated into a common platform.
By utilizing a common interface, and inter-process
communication, the MMUs can be accessed indepen-
dent of the platform. Thus, the communication and
workflow is only driven by the functionality provided
by the interface and not by the specific environments.
Figure 2 gives an overview of the provided key func-
tionality of the interface.
The individual MMUs are responsible for gener-
ating specific kinds of motion (e.g. locomotion be-
haviour or grasp modeling). Each MMU provides the
functionality to set the intended motion instruction,
as well as getting prerequisites for executing the mo-
tion. Moreover, the MMUs comprise a do step rou-
tine which is executed for each frame to be simulated.
In this context, the actual posture at the given frame
is computed by the specific technology. For each
frame, the MMU provides output parameters describ-
ing the generated posture, it’s constraints, as well as
intended scene manipulations and events. Since most
motion generation approaches strongly rely on spatial
information of the environment and the digital human
representation, the communication with the scene is
an important aspect for realizing such an encapsula-
tion. Thus, each MMU can access the information
provided by the scene through a defined interface (see
Figure 2 scene access). In this way, the actual scene
representation can be embedded in diverse target envi-
ronments. Considering the concurrency between dif-
ferent MMUs, manipulations of the scene which are
Figure 2: Illustration of the key functionality of the pro-
posed Motion Model Unit interface.
intended by the MMUs are not directly written back
to the scene, instead these are provided as an output
of the simulation step and are furthermore processed
by a superior instance.
3.2 Concept of Co-simulation
Having distinct MMUs comprising specific simula-
tion approaches, the separately generated postures
must be merged and further processed to obtain nat-
ural motions. Therefore a co-simulator is required,
which orchestrates the actual execution of the MMUs.
In this context, the component merges and overlaps
the motions, while considering the constraints of the
postures. Since the scope of the framework is to in-
corporate strongly heterogeneous character animation
systems, the individual MMUs might comprise en-
tirely different skeleton structures and anthropome-
tries. To utilize these heterogeneous results in a
common platform, a retargeting to a global reference
skeleton is required for each MMU.
Moreover, since two consecutive MMUs might
start/end with a different posture (e.g. MMU1 ends
with t-Pose, MMU2 starts with idle pose), the tran-
sition between the respective units must be explic-
itly modeled. Even though the authors of (Gaisbauer
et al., 2018b) proposed the basic concept of the mod-
ular MMI architecture and a basic workflow for the
co-simulation, no detailed conception and implemen-
tation of such a co-simulation is available, yet.
4 NOVEL CO-SIMULATION
APPROACH
In principle, the above described framework allows to
technically incorporate heterogeneous character ani-
mation systems in a common framework. However,
several questions are left open. In particular it is un-
clear how the gathered results of different MMUs can
be combined to generate feasible postures. Moreover,
the handling of concurrent motions using distinct
MMUs has not been addressed yet. In the follow-
ing, we present a novel co-simulation concept which
is able to orchestrate various MMUs while produc-
ing feasible results. The co-simulation works inde-
pendently of the utilized animation technology within
the respective MMUs. Furthermore, the concurrent
behaviour of motions is considered and modeled.
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
68
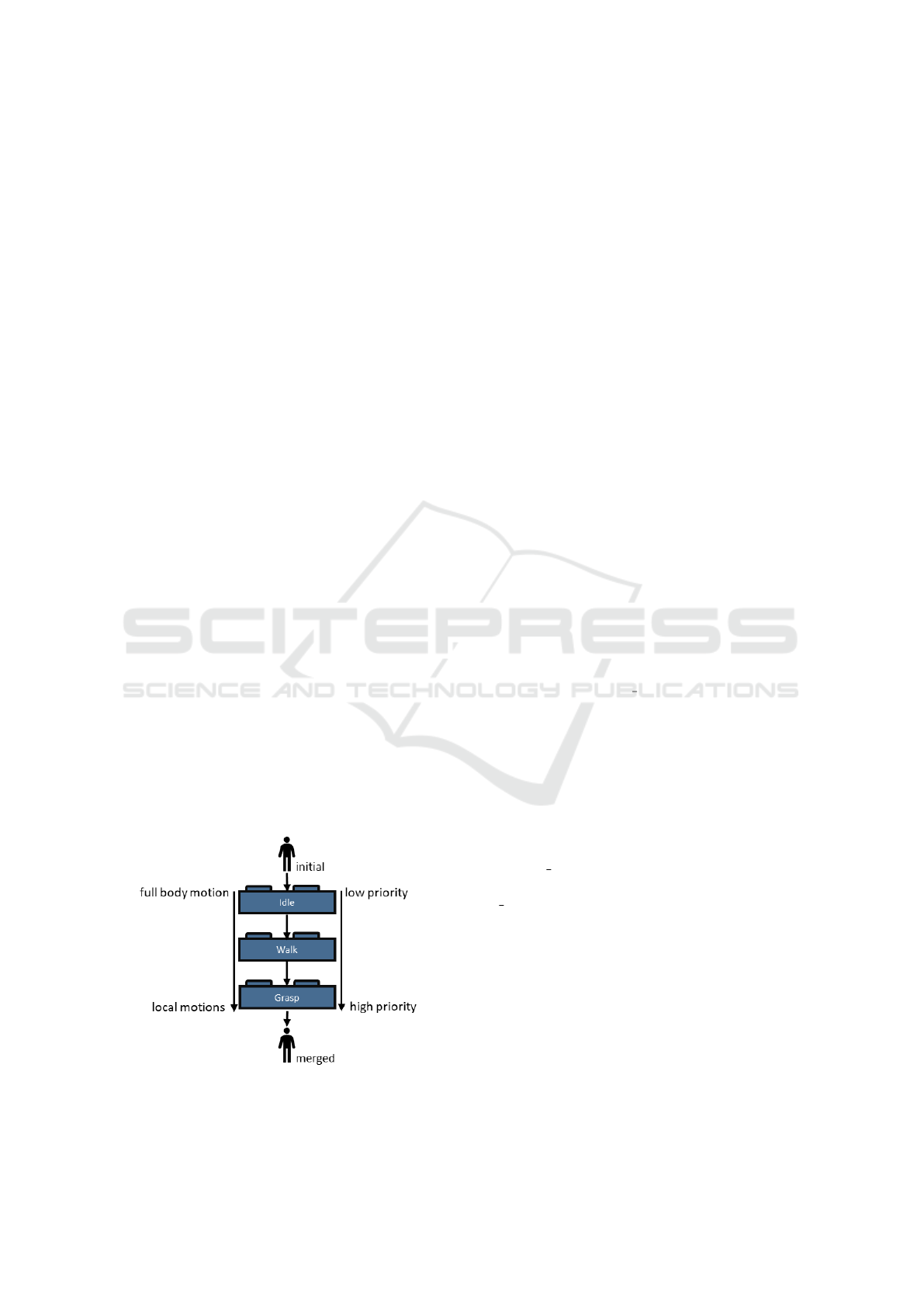
4.1 Co-simulation Process &
Hierarchical MMU Modeling
Based on specified motion instructions such as ”walk
to table” and ”pick up object from table”, the co simu-
lation needs to incorporate and overlap several differ-
ent postures generated by the MMUs. To realize the
desired behaviour, several concepts ranging from the
hierarchical modeling to constraint handling and the
actual workflow need to be defined.
Hierarchical MMU Modeling. The proposed co-
simulation model builds upon the concept of hier-
archical motion controllers first introduced by Kall-
mann et al. (Kallmann and Marsella, 2005). As de-
scribed in (Feng et al., 2012b), the state of the charac-
ter is manipulated by a series of stacked controllers.
The output of the previous controller is set as input of
the subsequent one. Figure 3 visualizes the concept
transferred to the MMUs.
Each controller knows the character state of the
previous step, as well as the state during the cur-
rent phase. The controller can either override, mod-
ify or ignore the state of the virtual character. In
(Feng et al., 2012b), the authors propose to uti-
lize a generalization-specialization hierarchy, which
means that lower priority controllers typically control
a greater number of body parts, while higher-priority
controllers control fewer. In this context a full body
motion (e.g. idle) is executed first, while more spe-
cific motions such as grasping are executed later/ with
a higher priority.
In the newly proposed co-simulation model, each
MMU has a specific priority in analogy to the afore-
mentioned concept. The priorities of the respective
MMUs are assigned by the co-simulator based on the
priority, characteristics and the involved body regions
Figure 3: Concept of hierarchical motion-controllers as
proposed by (Feng et al., 2012b) applied to the Motion
Model Units.
of the given motion instruction (e.g. walking = low
priority, grasping = high priority). Figure 4 gives an
overview of the newly proposed co-simulation model
and its workflow.
Constraint Definition. If the above illustrated con-
cept of hierarchical MMUs is strictly applied, the
MMUs with higher priorities might completely over-
write the results of the previous ones, thus neglecting
relevant criteria of the preceding posture. To prevent
this, each MMU can define specific body constraints
preserving the main features of the posture. For in-
stance, a MMU which focuses on locomotion can set
the foot and hip position as essential constraints of
the posture. On the other hand, a grasp motion marks
the hand position and finger transformations as crucial
constraint. The set of available constraint types in the
proposed framework is limited to a finite amount. The
co-simulator stores the constraints of the respective
MMUs (see Figure 4 Body Constraints) for further
considerations and processing. Analogously scene-
manipulations intended by the MMU are also stored
and further processed.
Co-simulation Workflow. In general, the input of
the co-simulation is a set of given motion instruc-
tions with logical dependencies between each other
(e.g. put-down starts after walk is finished). The co-
simulation evaluates these conditions and starts the
respective MMU via set command, if the conditions
are fulfilled. Afterwards, the started MMU is marked
as active. Analogously, termination criteria are also
handled by the co-simulation.
As illustrated in Figure 4, in every simulation step,
the co-simulator executes each active MMU accord-
ing to its priority, starting with the lowest. At the be-
ginning of the frame, the initial state is provided as in-
put which corresponds to the merged result of the last
frame. Next, the respective MMU is executed by call-
ing the do step function, whereas the computed re-
sults of the current frame are obtained by utilizing the
get result method. The results comprise the generated
posture, body constraints, as well as intended scene
manipulations. The gathered results of the MMU are
stored by the co-simulator and are further integrated
into the current state of the character.
Furthermore, the constraint register is utilized to
generate a state which represents the constrained pos-
ture at the present evaluation stage. In total there are
three different states accessible from the MMU: ini-
tial, current state and current state constrained. In
particular, it is up to the specific MMU implementa-
tion of how to consider and incorporate these states
into the respective model. Note, that between each
Proposing a Co-simulation Model for Coupling Heterogeneous Character Animation Systems
69
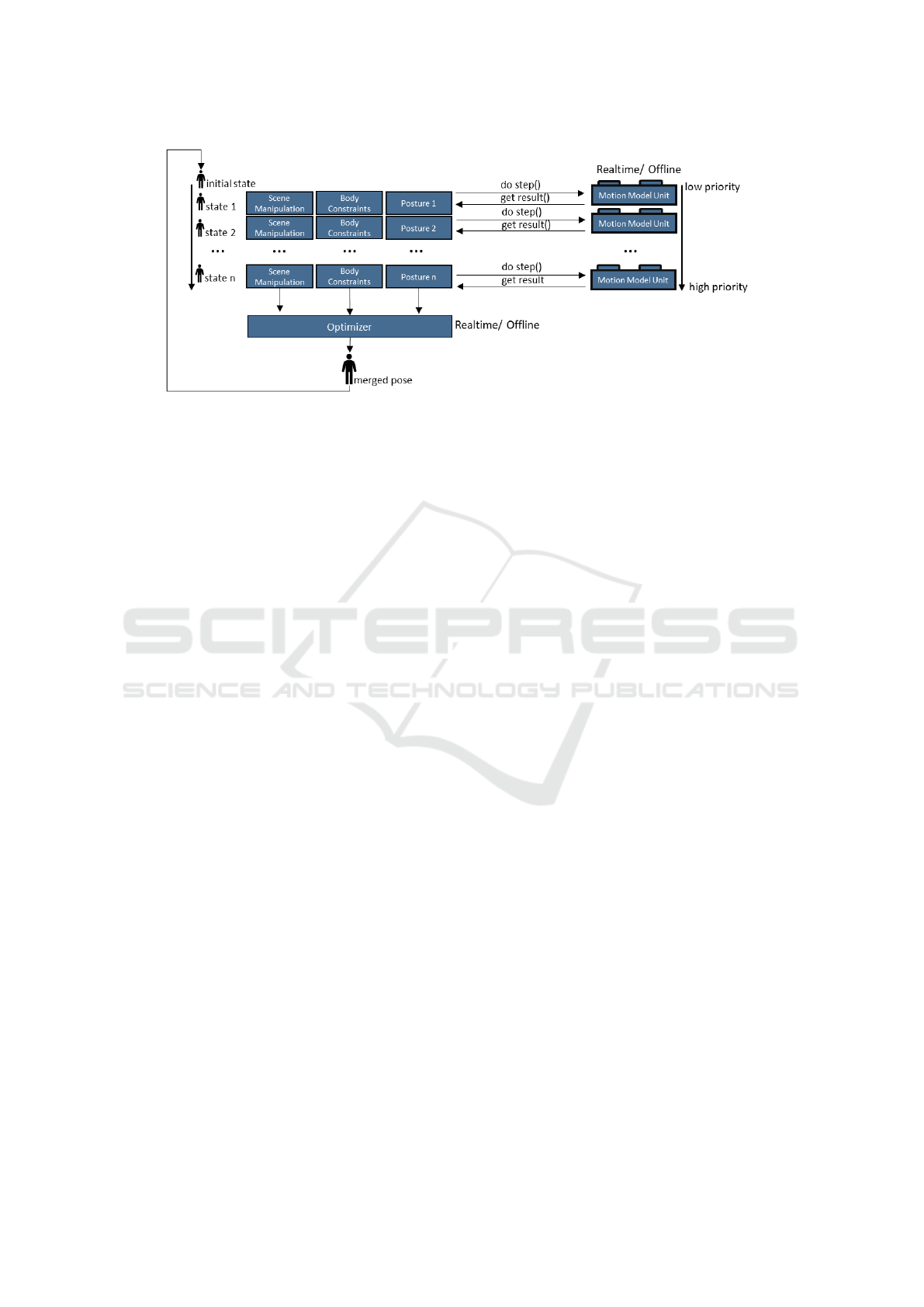
Figure 4: Illustration of the proposed co-simulation model. The MMUs are executed for each frame according to their priority.
The results which comprise the actual character posture, body constraints as well as scene manipulations are stored in a register
within the co-simulator. These results are later on merged to a single feasible posture by an optimization algorithm.
exchange of postures a retargeting between the differ-
ent skeletons is performed.
In general, depending on the available MMUs and
configurations, the merging and processing of the
postures might be already established by the hierar-
chical execution of the MMUs. However, to generate
optimized results fulfilling all constraints, a separate
optimization stage (see 4 Optimizer) is necessary.
Modeling the Transitions Between Postures. De-
spite the scheduling and posture merging process, the
modelling of the transition between postures of differ-
ent frames is an essential aspect to obtain feasible mo-
tions. In most animation systems, motion blending is
commonly used for this purpose. By applying cross-
fading between different motions, the transitions can
be smoothly interpolated. However, in contrast to an-
imation clips, the content of the specific MMU is not
known and dynamically generated. Moreover, each
MMU might have specific parameters for the tran-
sition between different postures. Therefore a sim-
ple, globally performed cross-fading is not possible,
without possibly violating constraints. To establish a
smooth transition between various postures generated
by different MMUs, the novel co-simulation approach
builds upon two concepts.
First, in the framework, the constraints defined
by the MMUs are not actively removed by the co-
simulator. Thus, if a MMU finishes the motion and
has end constraints such as ”keep hand position”
which preserve the posture, the constraints remain to
be considered by the posture optimization until be-
ing actively removed. Consequently, unnatural transi-
tions with gaps between the postures can be avoided
if end constraints are specified.
Second, if a MMU finishes its motion and has
no active constraints specified (e.g. grasp object), it
needs to ensure that the ending posture matches the
posture of the character. The transition modeling is
therefore internally performed by the MMU, whereas
the specific parameterization and knowledge of the
MMU can be used. The process can be principally
considered as a distributed modeling of the transitions
which is in contrast to commonly performed global
motion blending. In this way, it is ensured that smooth
transitions between the previous MMU in hierarchy
and the respective MMU are obtained, after the MMU
is finished.
Even though natural transitions can be obtained
by applying the above illustrated concept, in general,
the approach does not ensure a globally feasible solu-
tion. Therefore the posture transitions and constraints
are further considered within the posture optimization
stage.
4.2 Posture Optimization
After having obtained a set of different character pos-
tures, constraints and scene manipulations, all with
defined priorities, next these have to be merged in or-
der to generate a feasible posture and scene interac-
tions. In general, to obtain realistic motions two dif-
ferent kind of constraints must be considered. First
the posture constraints within the frame itself, second
the constraints between consecutive frames. The for-
mer are required to model an appropriate static pos-
ture considering the heterogeneous characteristics of
the different MMUs, while the latter are important to
model continuous and realistic motions.
Given the available input data and constraints, the
problem can be formulated as a constraint optimiza-
tion problem with specific constraints for the inter-
frame and posture suitability. In literature there are
various optimization algorithms for solving these kind
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
70

of problems available (Powell, 1978; Homaifar et al.,
1994). Depending on the desired quality and algo-
rithm, the optimization might take more time, than
available in a real-time simulation. For certain use-
cases like automotive production planning real-time
performance is not important. However, for gaming
related use-cases real-time performance is essential.
Therefore the optimization approach has to be care-
fully chosen regarding the desired performance. In
general two classes of optimization approaches are
suggested - namely real-time and offline.
Offline Optimization. An offline optimization can
consider all constraints and body postures obtained
from the MMUs to gather (near) optimal results. In
this context, ergonomic optimization/comfort func-
tions such as proposed by (Hanson et al., 2014) can
be integrated and combined with sophisticated IK ap-
proaches. Moreover, the postures between consecu-
tive frames can be optimized with regard to energy
consumption or smoothness. In general, these offline
optimization approaches are appropriate for use-cases
where highly accurate motions and transitions are re-
quired, whereas depending on the specific domain the
objective functions can be adjusted in a flexible man-
ner. Since the offline optimization has no real-time
requirements, the utilized MMUs do not necessarily
have to provide real-time performance. In this con-
text, MMUs for path planning, such as required for
modeling assembly paths in collision-afflicted envi-
ronments can be incorporated. In general, the MMUs
are also classified according to the real-time/ offline
scheme.
Real-time Optimization. For a real-time capable
optimization, it is not possible to use advanced op-
timization algorithms within each frame. Given the
hierarchical modeling of the MMUs, feasible postures
can be obtained for each frames, if the priorities are
specified in a correct way. Moreover, by applying the
transition modeling as proposed in 4.1, the MMUs in-
ternally handle the transition to the underlying char-
acter state or specify end constraints which preserve
the current posture. Utilizing an IK solver, the speci-
fied constraints can be applied with minimal compu-
tational overhead, whereas the transition modeling is
fully performed by the MMUs.
4.3 Modeling Concurrent Motions
Given the previously described architecture, it is pos-
sible to execute arbitrary MMUs based on their pri-
ority and generate a merged character posture for
each frame. In general, the sequence of motions to
be executed must be provided as an input to the co-
simulation. Using formats like the Behaviour Markup
Language (BML) (Feng et al., 2012b), a basic sce-
nario such as walk to, pick-up and put-down can be
formulated. In this case the pick-up motion starts after
the walk to motion has been finished. Analogously,
the put-down motion has the prerequisites, that walk
to and pick-up must be finished. With the BML lan-
guage these conditional constraints which depend on
other BML instructions can be formulated. It is also
possible to model timing constraints. However, given
the language it is difficult to formulate constraints
strongly related to the scene context, or which are
not known at the time the instructions are created.
Since the MMUs might comprise completely differ-
ent animation technologies, the prerequisites can only
be defined by the MMU algorithms itself. Therefore
each MMU provides the functionality to specify the
required prerequisites for executing a specific motion.
Examining humanoid motions, it can be encoun-
tered that most of the performed motions are com-
monly executed in parallel. For instance, a grasp mo-
tion might be performed during walking, the specific
time and location when the grasping starts, however,
strongly depends on spatial constraints and prereq-
uisites of the actual grasp motion. Thus, it is not a
straightforward task to define the exact timing and all
constraints in before. To nevertheless cover the con-
current modeling in a generic manner within the co-
simulation, the get prerequisites method of the MMU
interface can be utilized. This method returns all con-
straints which have to be fulfilled in order to start the
specific motion. Depending on the implementation
and motion to be modeled, the constraints can address
vastly heterogeneous aspects such as the distance to a
target object or the maximum velocity of the avatar.
For modeling concurrent behavior, first, the co-
simulation checks if all external conditions for start-
ing the MMU are fulfilled (e.g. time dependencies in
BML). If this is the case, next, the prerequisites of the
specific MMU instance are obtained and checked in
detail. If the prerequisites of the examined instruc-
tion are fulfilled, the respective motion can be started
using the motion instruction. Applied to the afore-
mentioned walking and grasping example, the grasp
motion can be automatically started during walking if
the required constraints such as distance to the target
object are fulfilled. By modeling the runtime specific
constraints in this way, the exact timing does not have
to be explicitly specified in before. Moreover, each
MMU implementation can adjust the constraints dy-
namically according to the used model.
Proposing a Co-simulation Model for Coupling Heterogeneous Character Animation Systems
71

5 EVALUATION
After having outlined the concept of the novel co-
simulation approach, in this section the applicability
for simulating specific human motion tasks is vali-
dated within a user study. Summarizing the role of
the co-simulation, the main task is to merge and in-
corporate different postures obtained from any het-
erogeneous MMUs, while generating feasible results.
Therefore the target of the evaluation is to verify
whether the co-simulation can generate results which
do not decrease the quality of the individual motions.
5.1 Experimental Design
The validity of the co-simulation approach is mea-
sured by a user-study in which the participants rate
the naturalness of the generated motions. The over-
all target is to validate whether the co-simulation
can incorporate heterogeneous animation technolo-
gies while preserving the naturalness of the original
motions contained in the MMUs. For evaluating the
naturalness, only a few quantitative metrics have been
proposed, either focusing on partial aspects such as
walking, or lacking in accuracy. In general, motions
that humans have seen repeatedly are judged natural,
whereas motions that happen very rarely are not (Ren
et al., 2005). Therefore a user study has been selected
as appropriate measure.
For the experiment, two sets of tasks to be per-
formed by the digital human are specified. Each
task-set comprises several sub-motions (e.g. walk,
pick-up, put-down) which are shown separately to
the participants. In addition to this, the sub-motions
generated by the novel co-simulation are shown as
well. Since the co-simulation overlaps various mo-
tions, the sub-motion walk can comprise additional
motions such as pick-up. To validate the overall nat-
uralness of the co-simulated result and its transitions,
a clip showing the overall task is also visualized. For
instance, this full clip can contain the motions walk,
pick-up and put-down, all temporally overlapped by
the co-simulator.
The participants have to rate the naturalness of the
motions, without knowing the different groups. Over-
all, the validity of the co-simulation can be proven if
the rating of the novel motions is not worse than the
individual sub-motions.
5.2 Apparatus
To measure the performance of the co-simulation, in
total two different task sets have been selected. Each
Figure 5: Experimental setup for task-set 1: The digital
character starts at (1), walks to the table and picks up the
red object (2). Finally the object is placed on the table (3).
task-set comprises three different sub-motions which
are realized by heterogeneous MMUs.
Task-set 1: Pick Up, Put Down One Handed. In
the first task-set, the digital avatar walks to a table
and picks up a cube. Afterwards, the avatar walks to
the front of a second table and places the cube on the
surface. Figure 5 illustrates the experimental setup.
The different sub-motions are modeled using
varying technologies and platforms. The walk MMU
is based on the recent publication of (Holden et al.,
2017) which models the locomotion behaviour based
on deep neural networks (Unity, C#). The pick-
up implementation is based on a model-driven ap-
proach which uses path planning and inverse kinemat-
ics (C++). The put-down motion is realized using a
statistical motion synthesis approach in Python.
Task-set 2: Pick-up, Drill in Collision-afflicted
Area. The second task-set models a drill operation
in a collision-afflicted scenario (see Figure 6). First,
the avatar picks up an electric drill from a table. Next,
the avatar walks to the back of a vehicle and performs
a drill motion inside the trunk.
The walk MMU is based on the Unity Mecanim
animation system, whereas the pick-up motion is re-
alized by a physics based motion synthesis approach
build upon the avatar physics of deep motion (Unity,
C#). Moreover, for generating collision-free motions
within the car trunk, the drill motion is generated by
a model-driven approach using path planning and in-
verse kinematics (C++).
Figure 6: Experimental setup for task-set 2: The digital
character picks up an electric drill (1), walks to the car (2)
and performs a drill motion in the trunk (3).
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
72

Test System. The utilized co-simulation is imple-
mented in the Unity3D engine. All external MMUs
are accessed via TCP inter-process communication
using the defined MMU interface. The time accu-
racy of the simulation has been set to 15 ms. To
map the resulting postures of the MMUs to a com-
mon skeleton, the retargeting functionality provided
by the Unity3D engine has been used. The pri-
orities of the MMUs have been set according to
the generalization-specification approach proposed in
(Feng et al., 2012b).
5.3 Procedure
For validating the perceived realism of the simula-
tions, a questionnaire containing a five point Likert
scale has been used. Whereas 1 corresponds to a
strong disagreement, 5 corresponds to a very strong
agreement. The performed task sets are split into the
respective sub-tasks: walk, pick-up, put-down (task-
set 1) and pick-up, walk, drill (task-set 2). For each
sub-task the question targets the naturalness of the
motion. The recorded videos, which display the raw
motions, the co-simulated motions, as well as the
combined results are shown to each participant. To
control sequence effects, the order in which the clips
are shown is randomized for each participant. More-
over, all videos are presented in total twice.
5.4 Results
The results of the respective simulation approaches
are evaluated based on a survey conducted with 18
participants (5 females, 13 males, age: µ = 28.50,
σ = 8.15). Figure 7 illustrated the results of the per-
formed survey. For each task-set, three different plots
are shown. The first plot (Raw) visualizes the mean
measured naturalness scores for showing the individ-
ual motions of task 1 (e.g. walk, pick-up, put-down).
The second plot (Novel) shows the obtained scores
for the individual motions generated by the novel co-
simulator. Note that these sub-motions might com-
prise simultaneous motions (e.g. grasping during
walking). The third plot (Novel Complete) repre-
sents the score for the complete clip, as created by the
new co-simulation. This clip contains all sub-motions
within the task-set orchestrated by the co-simulation.
Analogously, the subsequent plots represent the natu-
ralness scores for the second task-set.
Task-set1. The original sub-motions of task-set 1
(walk, pick-up, put-down) are generally rated as par-
tially natural, as the median value (m) of 2.75 illus-
trates. Moreover, the mean value can be denoted with
2.88, whereas σ = .67. In contrast, the rating of the
individual motions generated by the co-simulator is
slightly increased with a median of 3.00, µ = 3.18
and σ = .66. Additionally, the overall clip which con-
tains the co-simulated sequence of all motions scores
higher with a median of 3.50, µ = 3.41 and σ = .90.
Figure 7 b) additionally shows the differences in
rating of the individual sub-motions, set relative to
the raw motions. A positive value means that the co-
simulated results achieved better ratings while a neg-
ative value corresponds to a worse rating of the co-
simulated results. The walk motion achieved a me-
dian value of .00, µ = −.02 and σ = .82. For the
pick-up motion a median difference of .75, µ = .67
and σ = .88 can be encountered. The put-down mo-
tion is rated with a median of .25, µ = .31 and σ = .71.
Task-set2. For task-set 2, it can be encountered that
the mean values have an overall higher naturalness
score (rather natural) than the first task-set. The raw
motions obtained from the MMUs are rated with a
median of 3.67, µ = 3.86 and σ = .46. The individual
motions generated by the novel co-simulator have a
median of 3.83, µ = 3.90 and σ = .39 Moreover, the
full clip comprising the sequence of all co-simulated
sub-motions scores a median value of 3.75, µ = 3.88
and σ = .49.
Evaluating the individual motions, it can be de-
noted, that the three sub-motions pick-up, walk and
drill achieved different naturalness scores. As illus-
trated by Figure 7 b), the pick-up motion of task-
set 2 achieved a median value of .00, µ = −.02 and
σ = .48. For the walk motion a median difference of
.00, µ = .02 and σ = .56 can be encountered. The
drill motion is rated with a median of .25, µ = .16 and
σ = .52.
5.5 Discussion
For evaluating the validity of the novel approach, no
significance tests were performed, since the hypothe-
sis does not raise the question whether the novel ap-
proach is better or worse. Instead, it should be exam-
ined whether the novel approach can generate results
which do not decrease the quality (are not worse). To
quantify this, an equivalence study as commonly per-
formed in medicine is required. Within these types of
studies the interval borders for equality have to be ex-
plicitly set. However, given the naturalness of human
motion and the underlying rating scale, no border for
equality is known, yet. Therefore the obtained results
are only discussed based on the representative sample
using descriptive statistics.
Proposing a Co-simulation Model for Coupling Heterogeneous Character Animation Systems
73
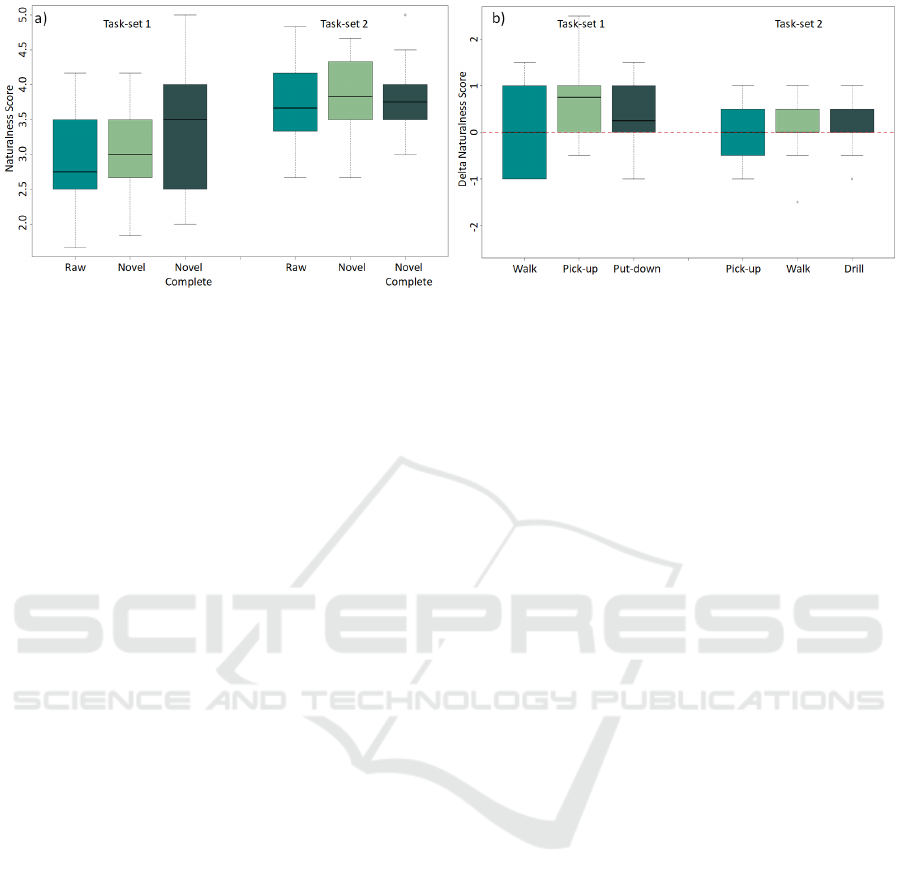
Figure 7: Boxplots displaying the results of the performed user study. Plot a) visualizes the absolute achieved naturalness
scores for both simulated task-sets. Each boxplot contains the combined mean naturalness values of the sub-motions (e.g.
mean of walk, pick-up, put-down). Novel complete represents the complete task-set generated by the co-simulation. Plot b)
shows the differences of the naturalness ratings between the co-simulated sub-motions and the raw motions within the MMUs.
The values are set relative to the raw motions (e.g. +1 means the co-simulated motions are rated better).
Task-set1. In the first task-set, the raw motions
of the MMUs achieved overall medium scores (µ =
2.88), whereas the sub-motions of the co-simulation
are judged as more natural (see Figure 7 a). Addition-
ally, the complete clip generated by the co-simulator
is rated more natural (µ = 3.41), which underlines
that the co-simulated motions do not decrease the per-
ceived naturalness of the motions.
Examining the underlaying data in a more fine-
grained manner, differences between the sub-motions
can be encountered. As illustrated in Figure 7 b) the
walk motion is rated similar to the raw motions of
the MMUs. Given the available results, no system-
atic difference can be derived, as the median value
of 0 and the mean −.02, are negligible compared to
the standard deviation of .82. In contrast, the pick-
up motion is rated higher if the co-simulation is ap-
plied (µ = +.67, m = +.75). The main difference be-
tween the two pick-up motions, is that the pick-up is
performed during walking if the co-simulation is ap-
plied, whereas Raw contains the pick-up in a static
posture. As underlined by the scores, the participants
perceived this as more natural compared to an isolated
pick-up motion. Moreover, the put-down motion of
the co-simulation shows a similar trend (µ = +.31,
m = +.25). Here again, the put-down was performed
during walking.
Analyzing the given sample, for task-set 1 it can
be concluded that the results generated by the co-
simulation can preserve the quality of the original
motions. Moreover, as the overall higher score for
the complete motion indicates, the co-simulator gen-
erates smooth-transitions between the individual mo-
tions which increase the overall perceived natural-
ness.
Task-set2. In the second task-set, all tested config-
urations are rated rather similar. However, the co-
simulated results (see Figure7 a) Novel) achieved a
higher median value of 3.83 compared to the raw mo-
tions (m = 3.67). Moreover, the complete clip com-
prising all motions, obtained a similar median score
of 3.75. This illustrates that the perceived naturalness
of the comprehensive motions does not decrease to a
large extent.
Analyzing the individual sub-motions additional
differences can be encountered. The median val-
ues of all three sub-motions is .00, the mean val-
ues, however, vary between −.02 for pick-up and .17
for drilling. These differences can be traced back
to the concurrent modeling of the motions. Analo-
gously to the pick-up motion of task-set 1, the drill
motion is already started during the walking if the co-
simulation is applied. In contrast, the pick-up mo-
tion within task-set 2 is sequentially simulated, which
means that no concurrent motions occur in both, the
raw MMU motion, as well as in the co-simulation.
The results underline that no systematic differences
in the ratings of the pick-up motion can be encoun-
tered, since µ = −.02 and m = .00 are negligible com-
pared to the standard deviation of .48. The walk mo-
tion achieved a slighty higher rating in mean value if
the co-simulation is applied (µ = +.02), compared to
the standard deviation of σ = .56, the effect can be
considered as negligible.
Overall, taking into account the minimal differ-
ences between the three configurations of task-set 2,
it can be concluded that the novel co-simulation can
produce results which do not evidently decrease the
quality of the original motions.
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
74

Findings. Both task-sets received vastly different
absolute ratings. As main possible reason for this
difference, the utilized MMUs can be denoted. The
MMUs comprise varying algorithms and technolo-
gies which generate different motions. Other reasons
which also might influence the ratings, are the dif-
ferent camera perspective, the utilized elements in the
virtual scene (e.g. electric drill, vehicle) or the content
of the tasks and its basic motions. However, the spe-
cific influence of these factors is currently not known
and could be investigated in future research.
Summarizing the findings, the performed user
study shows, that the novel co-simulation approach
can be applied to generate feasible human motion
based on distinct MMUs. In particular the co-
simulation is able to handle the execution of concur-
rent motions which especially leads to increased nat-
uralness scores in task-set 1. Even though these first
evaluations indicate the validity of the novel concept
and its implementation, the evaluations are just cover-
ing a small portions of the possible scenarios. More-
over, the findings are only valid for the given sample
since no statistical significance has been tested.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Within the paper, a novel co-simulation approach for
orchestrating different character animation systems is
presented. The validity of the novel concept has been
evaluated by a conducted user study investigating the
naturalness of the generated motions. Overall, the
novel co-simulation approach can preserve the quality
of the original motions contained within the MMUs,
while generating feasible results.
Limitations. Even though the generic problem of
orchestrating heterogeneous MMUs can be addressed
by the novel approach, there are still limitations.
Currently, the priorities of the respective MMUs
are statically assigned according the generalization-
specification scheme. If a system comprises multiple
MMUs which are active at the same time, the pri-
ority has to be carefully chosen. Recently, (Broman
et al., 2013) proposed an approach to dynamically de-
termine the priorities of modules within a FMI co-
simulation. To allow the automatic simulation of sev-
eral concurrent MMUs an automated priority assign-
ment could be utilized.
Given the proposed hierarchical co-simulation,
multiple MMUs can be principally combined in real-
time. However, since the input of each MMU con-
tains the result of the previous MMU, there is a strong
sequential dependency. Scaling up the amount of
MMUs therefore leads to a performance bottleneck,
since each MMU has to wait for the result of the pre-
vious MMU in hierarchy. The available frame time
for each MMU is therefore reduced with each addi-
tional MMU (e.g. 30Hz: 2 MMUs = 16.7ms, 3MMUs
= 8.3ms). To nevertheless allow systems which incor-
porate a large amount of MMUs in real-time, a paral-
lel co-simulation in which the input state is predicted
is a possible solution. In this context, the future state
of a MMU could be either predicted by the MMU it-
self or externally via approaches like Kalman filters.
Future Work. Despite the discussed limitations,
there are further consecutive topics which can be ad-
dressed in future work. In this context, aspects like the
modeling of the influence of previous and subsequent
actions on the current motions can be analyzed. For
instance, it is expected, that the specific parameteri-
zation of a put-down motion is strongly influenced by
the previous pick-up motion. Furthermore building
upon heterogeneous simulation approaches embed-
ded in MMUs, Monte-Carlo simulations which vary
the input parameters could be investigated. Moreover,
posture optimization approaches addressing specific
metrics such as ergonomics can be examined. Finally,
the MMU concept will be further developed and dis-
cussed in the international ITEA 3 research project
MOSIM (ITEA, 2018).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors acknowledge the financial support by the
Federal Ministry of Education and Research of Ger-
many within the MOSIM project (ITEA, 2018).
REFERENCES
Aristidou, A. and Lasenby, J. (2011). Fabrik: A fast, itera-
tive solver for the inverse kinematics problem. Graph-
ical Models, 73(5):243–260.
Bastian, J., Clauß, C., Wolf, S., and Schneider, P. (2011).
Master for co-simulation using fmi. In Proceedings
of the 8th International Modelica Conference; March
20th-22nd; Technical Univeristy; Dresden; Germany,
number 63, pages 115–120. Link
¨
oping University
Electronic Press.
Blochwitz, T., Otter, M., Arnold, M., Bausch, C., Elmqvist,
H., Junghanns, A., Mau\s s, J., Monteiro, M., Neid-
hold, T., and Neumerkel, D. (2011). The functional
mockup interface for tool independent exchange of
simulation models. In Proceedings of the 8th In-
ternational Modelica Conference, pages 105–114.
Linkoeping University Electronic Press.
Proposing a Co-simulation Model for Coupling Heterogeneous Character Animation Systems
75

Broman, D., Brooks, C., Greenberg, L., Lee, E. A., Masin,
M., Tripakis, S., and Wetter, M. (2013). Determinate
composition of fmus for co-simulation. In Proceed-
ings of the Eleventh ACM International Conference on
Embedded Software, page 2. IEEE Press.
Buss, S. R. (2004). Introduction to inverse kinematics with
jacobian transpose, pseudoinverse and damped least
squares methods. IEEE Journal of Robotics and Au-
tomation, 17(1-19):16.
Cerekovic, A., Pejsa, T., and Pandzic, I. S. (2009). Re-
alactor: character animation and multimodal behavior
realization system. In International Workshop on In-
telligent Virtual Agents, pages 486–487. Springer.
Delp, S. L., Anderson, F. C., Arnold, A. S., Loan, P.,
Habib, A., John, C. T., Guendelman, E., and The-
len, D. G. (2007). Opensim: open-source software
to create and analyze dynamic simulations of move-
ment. IEEE transactions on biomedical engineering,
54(11):1940–1950.
Faloutsos, P., Van de Panne, M., and Terzopoulos, D.
(2001). Composable controllers for physics-based
character animation. In Proceedings of the 28th an-
nual conference on Computer graphics and interac-
tive techniques, pages 251–260. ACM.
Feng, A., Huang, Y., Kallmann, M., and Shapiro, A.
(2012a). An analysis of motion blending techniques.
In International Conference on Motion in Games,
pages 232–243. Springer.
Feng, A. W., Xu, Y., and Shapiro, A. (2012b). An example-
based motion synthesis technique for locomotion and
object manipulation. In Proceedings of the ACM SIG-
GRAPH Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and
Games, pages 95–102. ACM.
Gaisbauer, F., Agethen, P., B
¨
ar, T., and Rukzio, E. (2018a).
Introducing a Modular Concept for Exchanging Char-
acter Animation Approaches. In Jain, E. and Kosinka,
J., editors, EG 2018 - Posters. The Eurographics As-
sociation.
Gaisbauer, F., Agethen, P., Otto, M., B
¨
ar, T., Sues, J., and
Rukzio, E. (2018b). Presenting a modular framework
for a holistic simulation of manual assembly tasks.
Procedia CIRP, 72:768–773.
Gaisbauer, F., Froehlich, P., Lehwald, J., Agethen, P., and
Rukzio, E. (2018c). Presenting a Deep Motion Blend-
ing Approach for Simulating Natural Reach Motions.
In Jain, E. and Kosinka, J., editors, EG 2018 - Posters.
The Eurographics Association.
Hanson, L., H
¨
ogberg, D., Carlson, J. S., Bohlin, R., Brolin,
E., Delfs, N., M
˚
ardberg, P., Stefan, G., Keyvani, A.,
and Rhen, I.-M. (2014). Imma–intelligently moving
manikins in automotive applications. In Third Inter-
national Summit on Human Simulation (ISHS2014).
Holden, D., Komura, T., and Saito, J. (2017). Phase-
functioned neural networks for character control.
ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 36(4):42.
Homaifar, A., Qi, C. X., and Lai, S. H. (1994). Con-
strained optimization via genetic algorithms. Simu-
lation, 62(4):242–253.
ITEA (2011). ITEA Project 07006 MODELISAR - website
www.itea3.org/project/modelisar.html.
ITEA (2018). ITEA Project 17028 MOSIM - website
www.itea3.org/project/mosim.html.
Kallmann, M. and Marsella, S. (2005). Hierarchical mo-
tion controllers for real-time autonomous virtual hu-
mans. In International Workshop on Intelligent Vir-
tual Agents, pages 253–265. Springer.
Kovar, L., Gleicher, M., and Pighin, F. (2008). Motion
graphs. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2008 classes, page 51.
ACM.
Li, Z., Zhou, Y., Xiao, S., He, C., and Li, H. (2017). Auto-
Conditioned LSTM Network for Extended Com-
plex Human Motion Synthesis. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1707.05363.
Min, J. and Chai, J. (2012). Motion graphs++: a com-
pact generative model for semantic motion analysis
and synthesis. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG),
31(6):153.
Powell, M. J. (1978). A fast algorithm for nonlinearly con-
strained optimization calculations. In Numerical anal-
ysis, pages 144–157. Springer.
Ren, L., Patrick, A., Efros, A. A., Hodgins, J. K., and
Rehg, J. M. (2005). A data-driven approach to quanti-
fying natural human motion. In ACM Transactions
on Graphics (TOG), volume 24, pages 1090–1097.
ACM.
Shapiro, A. (2011). Building a character animation system.
In International Conference on Motion in Games,
pages 98–109. Springer.
Shoulson, A., Marshak, N., Kapadia, M., and Badler, N. I.
(2014). Adapt: the agent developmentand prototyp-
ing testbed. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and
Computer Graphics, 20(7):1035–1047.
Thiebaux, M., Marsella, S., Marshall, A. N., and Kall-
mann, M. (2008). Smartbody: Behavior realiza-
tion for embodied conversational agents. In Pro-
ceedings of the 7th international joint conference on
Autonomous agents and multiagent systems-Volume
1, pages 151–158. International Foundation for Au-
tonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems.
Tsai, Y.-Y., Lin, W.-C., Cheng, K. B., Lee, J., and Lee, T.-Y.
(2010). Real-time physics-based 3d biped character
animation using an inverted pendulum model. IEEE
transactions on visualization and computer graphics,
16(2):325–337.
Van Acker, B., Denil, J., Vangheluwe, H., and De Meule-
naere, P. (2015). Generation of an optimised master
algorithm for fmi co-simulation. In Proceedings of
the Symposium on Theory of Modeling & Simulation:
DEVS Integrative M&S Symposium, pages 205–212.
Society for Computer Simulation International.
Wang, B. and Baras, J. S. (2013). Hybridsim: A modeling
and co-simulation toolchain for cyber-physical sys-
tems. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/ACM 17th In-
ternational Symposium on Distributed Simulation and
Real Time Applications, pages 33–40. IEEE Computer
Society.
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
76
