
Effective 2D/3D Registration using Curvilinear Saliency Features and
Multi-Class SVM
Saddam Abdulwahab
1
, Hatem A. Rashwan
1
, Julian Cristiano
1
, Sylvie Chambon
2
and Domenec Puig
1
1
Department of Computer Engineering and Mathematics, Rovira i Virgili University, Tarragona, Spain
2
Department of Computing, IRIT, Universit
´
e de Toulouse, Toulouse, France
Keywords:
2D/3D Registration, Support Vector Machine, Cross Domain, Depth Images, Curvilinear Saliency.
Abstract:
Registering a single intensity image to a 3D geometric model represented by a set of depth images is still a
challenge. Since depth images represent only the shape of the objects, in turn, the intensity image is relative
to viewpoint, texture and lighting condition. Thus, it is essential to firstly bring 2D and 3D representations to
common features and then match them to find the correct view. In this paper, we used the concept of curvilinear
saliency, related to curvature estimation, for extracting the shape information of both modalities. However,
matching the features extracted from an intensity image to thousand(s) of depth images rendered from a 3D
model is an exhausting process. Consequently, we propose to cluster the depth images into groups based on
Clustering Rule-based Algorithm (CRA). In order to reduce the matching space between the intensity and
depth images, a 2D/3D registration framework based on multi-class Support Vector Machine (SVM) is then
used. SVM predicts the closest class (i.e., a set of depth images) to the input image. Finally, the closest view
is refined and verified by using RANSAC. The effectiveness of the proposed registration approach has been
evaluated by using the public PASCAL3D+ dataset. The obtaining results show that the proposed algorithm
provides a high precision with an average of 88%.
1 INTRODUCTION
Various object registration tasks and different compu-
ter vision applications such as human pose estimation,
face identification and robotics use 2D intensity ima-
ges as input. Recently, 3D geometries are also availa-
ble and popular. Accordingly, taking the benefit from
both modalities for 2D/3D matching has become ne-
cessary.
The 2D/3D registration is the problem of finding
the transformation and rotation of objects by mat-
ching their 3D models with 2D images. The matching
of a 2D image to a 3D model is considered a difficult
task since the appearance of an object dramatically
depends on its intrinsic characteristics (e.g., texture
and color/albedo), and extrinsic characteristics rela-
ted to the acquisition (e.g., the camera pose and the
lighting conditions). The 2D/3D matching problem is
mainly about answering two main questions. (1) What
is the appropriate representation method that can be
used for extracting features in both 2D and 3D data?
(2) how to match entities between the two modalities
in this common representation?
Many approaches have been proposed to extract
corresponding
depth image
SVM
Matching
(RANSAC)
3D model
Photograph
Cluster i
Prediction
Training
Test
Figure 1: General overview of the proposed 2D/3D regis-
tration algorithm.
features from 2D and 3D representation. For 3D mo-
dels, many possible ways are used to represent them.
To name few, synthetic images (Campbell and Flynn,
2001; Choy et al., 2015) of a 3D model were rende-
red. Silhouettes extracted from rendered images are
then matched to ones extracted from the intensity ima-
ges. However, these methods did not consider most
of the occluding contours that are useful for accurate
354
Abdulwahab, S., Rashwan, H., Cristiano, J., Chambon, S. and Puig, D.
Effective 2D/3D Registration using Curvilinear Saliency Features and Multi-Class SVM.
DOI: 10.5220/0007362603540361
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2019), pages 354-361
ISBN: 978-989-758-354-4
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

pose estimation. In addition, the silhouettes extrac-
ted from the image background can badly affect the
final matching. More recently, (Pl
¨
otz and Roth, 2017)
proposed average shading gradients (ASG), where the
gradient normals of all lighting directions were avera-
ged to cope with the unknown lighting of the query
image. The advantage of ASG is that it expresses the
3D model shape regardless of either colors or tex-
ture. Image gradients are then matched with ASG
images. However, image gradients are still affected
by image textures and background. Other works are
proposed in (Rashwan et al., 2016; Rashwan et al.,
2018). Where a collection of rendered images of the
3D models (i.e., depth images) from different view-
points were used to detect curvilinear features with
common basis definitions between depth and inten-
sity images. Furthermore, the authors in (Rashwan
et al., 2018) proposed three main steps. First, the rid-
ges and valleys of depth images rendered from the 3D
model were detected. In order to cope with the tex-
ture and background in 2D images, the features were
extracted by a multiscale scheme, and are then refi-
ned by only keeping infocus features. The final step
is to determine the correct 3D pose using a repeata-
ble K-NN registration algorithm (i.e., instance-based
learning) until finding the closest view. However, K-
NN algorithm is a simple machine learning algorithm
and a very exhausting process, as well as it is only
approximated locally.
Consequently, this work proposes an automatic
2D/3D registration approach reducing the matching
space and compensating the disadvantages of rende-
ring a large number of depth images. That is done
by clustering the features extracted from all rendered
images into N clusters using a Clustering Rule-based
Algorithm (CRA). The Histogram of Curviness Sa-
liency (HCS) is computed for each a depth image per
cluster. A multi-class SVM is then trained with the fe-
atures of each cluster for assigning a 2D real image to
the closest depth images. Finally, the closest view is
refined by RANdom SAmple Consensus (RANSAC)
algorithm (Fischler and Bolles, 1987) by matching the
input image to the depth images belonging to the pre-
dicted class. Figure 1 shows the overview of the pro-
posed 2D/3D registration method.
In summary, the contributions of this paper are the
followings:
• updating a robust feature extraction method ba-
sed on curvilinear saliency proposed in (Rashwan
et al., 2018) for both 2D and 3D representations.
• clustering the features of the rendered depth ima-
ges of a 3D model into K clusters using CRA.
• cross-domain classification based on a multi-class
SVM for assigning a query intensity image to a
class of the closest depth images.
• Determining the closest view using the RANSAC
algorithm.
The rest of the article is structured as follows:
Section 2 explains related works, and the proposed
methodology is detailed in Section 3. In addition, the
experiments and the results are shown in Section 4.
Finally, the conclusion and future work are discussed
in Section 5.
2 RELATED WORK
The problem of automatically aligning 2D intensity
images with a 3D model has been recently investi-
gated in depth. In the general case, the proposed
solution will be image-to-model registration to esti-
mate the 3D pose of the object. For various registra-
tion methods, the 3D models have been represented
in different ways (e.g., depth or synthetic images) and
then the features extracted from the query and rende-
red images are matched. In (Sattler et al., 2011; Lee
et al., 2013), correspondences were obtained by ma-
tching SIFT feature descriptors between SIFT points
extracted from the color images and from the 3D mo-
dels. However, establishing reliable correspondences
may be difficult due to the fact that the features in 2D
and 3D are not always similar, in particular, because
of the variability of the illumination conditions during
the 2D and 3D acquisitions. Other methods relying on
higher level features, such as lines (Xu et al., 2017),
planes (Tamaazousti et al., 2011), building bounding
boxes (Liu and Stamos, 2005) and Skyline-based met-
hods (Ramalingam et al., 2009) have been generally
suitable for Manhattan World scenes and hence appli-
cable only in such environments.
Recently, the histogram of gradients, HOG, de-
tector (Aubry et al., 2014; Lim et al., 2014) or its
fast version proposed (Choy et al., 2015) have been
also used to extract the features from rendering views
and real images. These approaches have not evalua-
ted the repeatability between the correspondences de-
tected in an intensity image and those detected in ren-
dered images. In turn, 3D corner points have been
detected in (Pl
¨
otz and Roth, 2017) using the 3D Har-
ris detector and the rendering ASG images have been
generated for each detected point. For a query image,
similarly, 2D corner pixels are detected in multiscale.
Then, the gradients computed for patches around each
pixel are matched with the database containing ASG
images using HOG descriptor. This method still re-
lies on extracting gradients of intensity images af-
fected by textures and background yielding erroneous
Effective 2D/3D Registration using Curvilinear Saliency Features and Multi-Class SVM
355

Rendering
Curviness Saliency Features
Detect Ridges using
Multi-scale
Curviness Saliency
Refine by
detecting
Focus Curves
Dataset Depth
Images Rendering
3D model
Photograph
MCS image MFC image
Testing
Training
CRA
Cluster 1
Cluster N
Clustering images
Feature
Extraction
using HCS
SVM
Register photograph to depth
images of Cluster i (RANSAC)
Cluster i
(N CS images)
Training
Prediction
viewpoint
(azimuth,elevation,distance)
Feature Extraction
using HCS
Vector
Cluster 1
Cluster N
Test
corresponding
depth image
Cluster 1
Cluster N
CS images
Figure 2: Registering a 2D image to a 3D model expressed by a collection of depth images rendered from different viewpoints,
and then extracting the curvilinear features of both depth and intensity images and after that, clustering the features of depth
images to k clusters using CRA. Training a multiclass SVM with the features of each cluster. Predicting the closest class to
the curvilinear features extracted with the query image. Finally, verifying the final viewpoint using RANSAC.
correspondences. Finally, in (Rashwan et al., 2018),
the authors proposed structural cues (e.g., curvilinear
shapes) based on curvilinear saliency that are more ro-
bust to intensity, color, and pose variations, and both
outer and inner (self-occluding) contours are repre-
sented in these features. In order to merge in the
same descriptor curvilinear saliency values and curva-
ture orientation, the histogram of curvilinear saliency
(HCS) descriptor is proposed to properly describe the
object shape.
3 METHODOLOGY
This section explains the main steps of the proposed
scheme, the tools and the resources that have been
used in this work, in addition to the features used to
represent the 3D models and 2D images, and the ma-
chine learning method proposed. Figure 2 shows the
graphical description of the system. It contains two
main modules. The first one is the SVM as a classi-
fier, which is trained on a large set of features extrac-
ted from rendered depth images to assign a query 2D
image to a group of depth images. In subsection 3.3,
we explain in detail how we trained the SVM. The se-
cond module finds the closest rendered depth image
that matches a query 2D image to the predicted depth
images by using RANSAC in order to find the final
viewpoint. This module is described in subsection
3.4.
3.1 Labeling Depth Images based on
CRA
Unlike, the work proposed in (Su et al., 2015) by
rendering images of the 3D models based on varying
only the Azimuth angle, we represent every a 3D mo-
del by a set of depth images generated from various
camera locations distributed on concentric spheres en-
capsulating, by sampling elevation and azimuth an-
gles, as well as the distance from the camera to the
object. We rendered these depth images of 3D mo-
dels available in the online 3D model repository, PAS-
CAL3D+ (Xiang et al., 2014).
To reduce the space of matching between a single
intensity image and thousand(s) of depth images, the
rendered depth images are clustered to a set of groups.
Each cluster contains a group of depth images belon-
ging to a range of viewpoints. To assign each depth
image into a certain cluster, we defined a set of rules
based on the azimuth and elevation angles, in addition
to the distance.
These rules are designed carefully to ensure that
all the samples in one category are inside a specific
range of viewpoints. Algorithm ?? shows the pro-
posed rules based on the maximum and minimum va-
lues of azimuth and elevation angles of rendering (i.e.,
A
max
, A
min
, E
max
and E
min
, respectively), in addition to
the the maximum and minimum values of the distance
of the camera to the 3D object (i.e., D
min
and D
max
).
In addition, Table 1 shows the clustering rules with
C = 9 used in this work.
VISAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
356

Data: dataset
Result: K of clusters
Input: A
max
,A
min
,E
max
,E
min
, D
max
,D
min
,K
Initialization:
a=(A
max
- A
min
) / C
e=(E
max
- E
min
) / C
while (i=1) <= C do
(A
S
∈ [A
min
+ (i −1) ×a + 1, A
min
+ i ×a])
(E
S
∈ [E
min
+ (i −1) ×e + 1, E
min
+ i ×e])
(D
S
∈ [D
min
,D
max
])
category=i
end
Algorithm 1: CRA used for clustering the depth images ba-
sed on (azimuth, elevation and distance) to G groups.
Table 1: CRA with C = 9 clusters of depth images consi-
dering A
max
= 180
o
and A
min
= 0
o
, E
max
= 90
o
and E
min
=
−90
o
, D
max
= 15 m and D
min
= 0.0 m.
Rule Category
(A
S
∈ [0,20] ∧E
S
∈ [−90,−70]∧D
S
∈ [0,15]) 1
(A
S
∈ [21,40] ∧E
S
∈ [−69,−50]∧D
S
∈ [0,15]) 2
(A
S
∈ [41,60] ∧E
S
∈ [−49,−30]∧D
S
∈ [0,15]) 3
(A
S
∈ [61,80] ∧E
S
∈ [−29,−10]∧D
S
∈ [0,15]) 4
(A
S
∈ [81,100] ∧E
S
∈ [−9,10] ∧D
S
∈ [0,15]) 5
(A
S
∈ [101,120] ∧E
S
∈ [11,30] ∧D
S
∈ [0,15]) 6
(A
S
∈ [121,140] ∧E
S
∈ [31,50] ∧D
S
∈ [0,15]) 7
(A
S
∈ [141,160] ∧E
S
∈ [51,70] ∧D
S
∈ [0,15]) 8
(A
S
∈ [161,180] ∧E
S
∈ [71,90] ∧D
S
∈ [0,15]) 9
4 FEATURE EXTRACTION AND
DESCRIPTION
In order to obtain a common representation related to
the curvature estimation between the 3D model and
the 2D image to properly match them, this work uses
Curvilinear Saliency (CS) proposed (Rashwan et al.,
2018) to extract features of rendered depth images.
CS extracts saliency features in one scale and it can
be defined as:
CS = 4
k
∇
∇
∇
Z
k
2
(
¯
κ
2
−K) (1)
where ∇
∇
∇
Z
= [Z
x
,Z
y
]
>
is the first derivative of a depth
image,
¯
κ is the mean curvature and K its Gaussian
curvature.
In addition, to reduce the influence of the tex-
ture on the intensity images, we also use the curvili-
near saliency computation with a multi-scale scheme
(i.e., Multi-scale Curvilinear Saliency (MCS) pro-
posed in (Rashwan et al., 2018)) to extract scale-
invariant features of an intensity image. The curvi-
linear saliency of an intensity image at i scale can be
defined as:
CS
i
= α((I
2
i
x
+ I
2
i
y
)), (2)
where I
i
x
,I
i
y
is the first derivative of an intensity image
at scale i.
Furthermore, to reduce the effect of the back-
ground in color images, Multi-scale Focus Curves fe-
atures (MFC) proposed in (Rashwan et al., 2018) are
then used. MFC presents the focused features (i.e.,
curves) of a salient object in a scene and removes the
curves related to de-focused objects. The MFC featu-
res highlight salient features in intensity images that
are approximately similar to the detected features in
the depth images. This can be done by computing the
ratio between every two consecutive scales of the cur-
vilinear saliency scales R
i
as:
R
i
=
CS
i+1
CS
i
, (3)
given the maximum value R
i
in each scale level, the
blur amount s
i
at a scale can be calculated:
s
i
=
σ
i
√
R
i
−1
, (4)
where σ
i
is the standard deviation of the re-blur Gaus-
sian at a scale. When a pixel of s
i
has a high value at
all scales, the maximum value of the blur amount s
i
is
used to build the final MFC features:
MFC =
1
argmax
i
(s
i
)
. (5)
To represent the curvilinear features extracted, the
Histogram of curvilinear saliency (HCS) is compu-
ted. HCS is similar to Histogram of Gradients (HOG),
which is robust to lighting changes and small variati-
ons in the pose. In HCS, the orientation of the curvi-
linear features (i.e., CS, MCS or MFC) in local cells
are binned into histograms for representing an image
or a sub-image. HCS has then been proved one of
the most beneficial features in general object locali-
zation. In our experiments, we compute histograms
with 9 bins on cells of 5 ×5.
4.1 SVM Classifier
The 2D/3D matching in this work will be achieved
as a multi-class supervised classification problem ba-
sed on support vector machine (SVM). In particular,
a multi-class SVM is trained for features extracted of
depth images related to a cluster. A one-versus-all
training approach is applied. Thus, during the off-
line training stage, the SVM is trained with the fe-
ature vectors extracted from a set of depth images
that belong to a cluster. In turn, during the on-line
classification stage, an input feature vector extracted
from a query intensity image is used for finding the
Effective 2D/3D Registration using Curvilinear Saliency Features and Multi-Class SVM
357

corresponding class with the largest output probabi-
lity following a winner-takes-all strategy. The ex-
perimental results conducted in this work have yiel-
ded the best classification results by using non-linear
SVM with a kernel based on a Gaussian radial ba-
sis function (RBF) (γ = 0.2) and soft margin para-
meter (C = 1). In addition, the mapping kernel RBF
is defined as: K(x
i
,x
j
) = exp(−γkx
i
−x
j
k
2
), where
γ = 1/2σ
2
, kx
i
−x
j
k
2
is the squared Euclidean dis-
tance between the two feature vectors x
i
and x
j
, and σ
is a free parameter of the standard deviation.
Our classification problem can be considered as a
cross-domain classification. Since the training and the
validation, sets are related to a domain generated from
the features extracted from depth images, in turn, the
testing domain is the features extracted from 2D in-
tensity images.
The first step to train a multi-class classifier such
as SVM is to define a set of features from the in-
put images in dense real-valued vectors using the
HCS descriptor. As we explained in the afore-
mentioned subsection, we used the Curvilinear Sa-
liency Features (CS) (Rashwan et al., 2018) to ex-
tract the features of the training and the validation sets
(i.e., rendered depth images), in turn, the Multi-Scale
Curvilinear Saliency (MCS) or Multi-Focus Curves
(MFC) (Rashwan et al., 2018) are used to extract the
features of the testing set (intensity images). Once
we get all the samples for each cluster, the features of
each depth image are used for the SVM as a class to
train on. Then, the pre-trained model is used for the
on-line classification of an intensity image to assign it
to a group of depth images.
4.2 Matching
In order to estimate the final camera pose (i.e., azi-
muth, elevation and distance) of an input image rela-
tive to a 3D model, a 2D image will be matched to
depth images belonged to the predicted class provi-
ding from the SVM.
We sampled the curvilinear features of the input
image and all depth images related to the predicted
class to a set of key points. Matching between the
features represented by HCS for both real image and
depth images is then performed. RANSAC is finally
used to refine the closest view and estimate the fi-
nal pose. As proposed in (Plotz and Roth, 2015), in
each iteration of the inner RANSAC loop, we sam-
ple 6 correspondences to estimate both the extrinsic
and intrinsic parameters of the camera using the di-
rect linear transformation algorithm (Hartley and Zis-
serman, 2003). Few iterations of RANSAC (i.e., 20
iterations in this work) are sufficient to find a good re-
finement. The refinement of coarse poses from a true
correspondence will usually converge to poses near
the ground truth.
5 EXPERIMENT AND RESULTS
This section describes the experiments performed to
evaluate the proposed model, in addition to the dataset
and the evaluation metrics used in the experiments.
Database
In this work, we used the PASCAL3D+ dataset (Xi-
ang et al., 2014), which contains 12 objects catego-
ries. Where every object contains around ten or more
3D models and more than 1000 real images related
to the category. All the real images are captured un-
der different conditions like lighting, complex back-
ground and low contrast. The depth images of the 3D
CAD models have been rendered using the viewpoint
information of the dataset. For all the tested 3D mo-
dels, we have rendered depth images using MATLAB
3D Model Renderer 7
1
from multi-viewpoint based
on changing azimuth and elevation angles, in addition
to the distance between the camera and the 3D model.
Results and Discussion
In all experiments, we tested the features extracted
from real images against the features extracted from
3D models. For each category of the PASCAL3D+
dataset, we computed the precision rate for detecting
the correct views after using the two aforementioned
methods for the 3D model representation, (i.e., CS,
and ASG), against the two techniques for the inten-
sity image representation (i.e., MCS and MFC). That
generates four variations of features used in the eva-
luation, such as MFC/CS, MCS/CS, MFC/ASG and
MCS/ASG. Some examples of the PASCAL3D+ da-
taset with CS, MCS and MFC features are shown in
figure 3.
Firstly, we tested the effect of dividing the image
(i.e., color or depth) into a number of cells with a spe-
cific size for describing an image on the accuracy of
the proposed 2D/3D registration. Thus, we computed
the precision rate of the registration process between
input intensity images and the rendered depth ima-
ges of each category of the PASCAL3D+ dataset with
different cell sizes, i.e., 3 ×3, 5 ×5 and 7 ×7 of the
HCS descriptor. Quantitative results with the average
precision rate over the 12 categories of PASCAL3D+
1
https://www.openu.ac.il/home/hassner/projects/poses/
VISAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
358

Table 2: Average Precision rates of the 5 categories of PASCAL3D+ with different cell sizes of the HCS descriptor.
Methods MFC/CS + SVM MCS/CS + SVM MFC/ASG + SVM MCS/ASG + SVM
HCS 3 × 3 0.65 0.53 0.56 0.53
HCS 5 × 5 0.88 0.84 0.84 0.79
HCS 7 × 7 0.77 0.73 0.72 0.66
Figure 3: intensity images (row 1), MCS resulting with 4
scales (row 2), MFC with 4 scales (row 3), CS (row 4)
and depth images (row 5). As it is shown, the curvilinear
saliency provided features closer to the features extracted
from depth images.
are shown in Table 2. As shown, the HCS with a cell
size 5 ×5 yielded the highest average precision with
the four variations of features. Therefore, we recom-
mended the HCS descriptor with a 5 ×5 cell size for
representing an image (depth or intensity).
Table 3 shows the effect of four different repre-
sentation of intensity images and 3D models (i.e.,
MFC/CS, MCS/CS, MFC/ASG and MCS/ASG) and
the classifiers (i.e., KNN and SVM), on the average
precision rate of the closest group. With all catego-
ries of PASCAL3D+, the performance of the propo-
sed model with SVM yielded better results than the
model with KNN. In addition For instance, with the
category of AEROPLANE and based on the represen-
tation of MFC/CS, the average precision rate with the
SVM was increased by 11% more than the KNN. In
turn, with TRAIN category, SVM yielded an impro-
vement of only 2%. The model with SVM as a classi-
fier yielded an improvement in the average precision
rate of 6% with all categories of the PASCAL3D+.
For the features extracted from intensity images,
the image representation MFC with both representa-
tions of 3D models CS and ASG yielded a high pre-
cision rate comparing with the image representation
MCS. In addition, the 3D model representation CS
provided a higher precision rate than ASG. More pre-
cisely, MFC/CS with the SVM obtained an average
precision of around 88% with all categories of PAS-
CAL3D+. In addition, MFC/ASG with the SVM pro-
vided an average precision of about 83%. In turn,
MCS/CS with the SVM yielded an average precision
of around 83%, in turn, 80% with MCS/ASG. Accor-
ding to Table 3, the proposed model with MFC as an
intensity image representation, CS as a 3D model re-
presentation and SVM as a classifier, performed better
regarding the average precision rate comparing with
the other variations models. We consider the above
results to be promising, as they are quite close to the
labelling of PASCAL3D+. Three examples of the fi-
nal registration based on MFC/CS and with SVM are
shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: Three examples of the proposed 2D/3D regis-
tration model with the Pascal3D+ dataset, query intensity
images (row 1), the resulted final depth images (row 2) and
the composite image from the intensity and resulted depth
image (row 3). As shown even if the 3D model does not
have the same detailed shape, the registration can properly
be achieved.
For viewpoint evaluation, we compare with three
methods using the same dataset, PASCAL3D+. A re-
cent work has been proposed in (Tulsiani and Ma-
lik, 2015), which introduced to a CNN architecture
to predict viewpoint, and combines multiscale ap-
pearance with a viewpoint conditioned likelihood to
predict key-points to capture the finer details to cor-
rectly detect the bound-box of the objects. In addi-
tion, our model was compared with the work propo-
sed in (Szeto and Corso, 2017), which presented a
deep model based on CNN for monocular viewpoint
estimation by using key points information provided
Effective 2D/3D Registration using Curvilinear Saliency Features and Multi-Class SVM
359
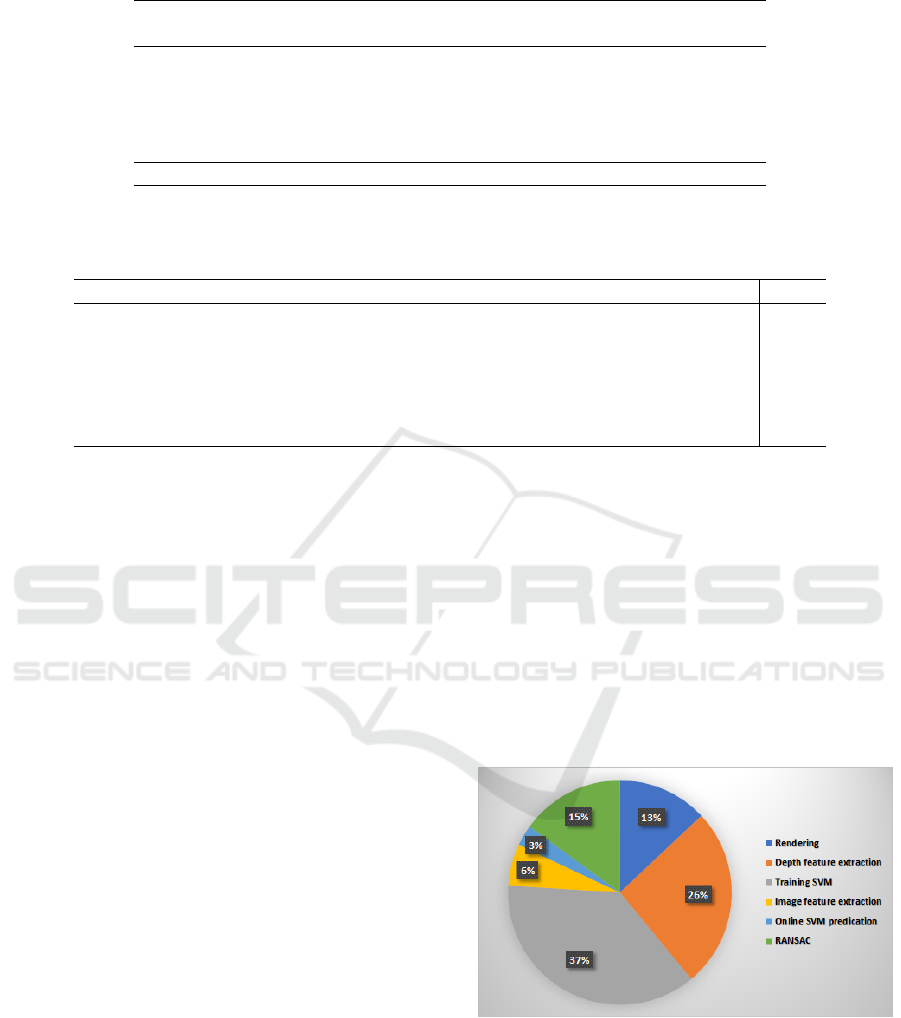
Table 3: Precision of pose estimation CS, ASG against MFC, MCS using SVM and KNN.
MFC/CS MCS/CS MFC/ASG MCS/ASG
Methods
SVM KNN SVM KNN SVM KNN SVM KNN
aere 0.93 0.85 0.85 0.83 0.91 0.84 0.81 0.80
bus 0.92 0.87 0.84 0.82 0.83 0.82 0.80 0.80
car 0.92 0.86 0.87 0.85 0.89 0.86 0.85 0.83
sofa 0.75 0.85 0.73 0.81 0.68 0.81 0.72 0.72
train 0.88 0.87 0.87 0.86 0.85 0.81 0.82 0.82
mean 0.88 0.86 0.83 0.83 0.83 0.83 0.80 0.79
Table 4: Viewpoint estimation with ground truth bounding box. Evaluation metrics are defined in (Tulsiani and Malik, 2015),
where Acc
π/6
measures accuracy (the higher the better). N/A means that the tested work did not show the results with these
categories.
aera bus car sofa train mean
Acc
π/6
(Su et al., 2015) 0.74 0.91 0.88 0.90 0.86 0.86
Acc
π/6
(Tulsiani and Malik, 2015) 0.81 0.98 0.89 0.82 0.80 0.86
Acc
π/6
( (Szeto and Corso, 2017) KPC Only) N/A 0.91 0.86 N/A N/A 0.89
Acc
π/6
( (Szeto and Corso, 2017) KPM Only) N/A 0.91 0.82 N/A N/A 0.87
Acc
π/6
( (Szeto and Corso, 2017) Full Model) N/A 0.97 0.90 N/A N/A 0.94
Acc
π/6
(Our Model) 0.93 0.92 0.92 0.75 0.88 0.88
by humans at inference time to more accurately es-
timate the viewpoint of an object. Furthermore, we
compared our model to the work introduced in (Su
et al., 2015) that rendered millions of synthetic ima-
ges from 3D models under varying illumination, lig-
hting and backgrounds and then used them to train a
CNN model for viewpoint estimation of real images.
We used the same metrics Acc
π/6
as in (Tulsiani and
Malik, 2015), for more details of the metric definition,
please refer to (Tulsiani and Malik, 2015). Quanti-
tative results are shown in Table 4. As shown, we
shows the final results of finer viewpoint estimation
that used the SVM classifier with HCS and RANSAC
to refine the final 3D pose. Our model yielded the
best average accuracy among all tested methods with
88%. The works proposed in (Su et al., 2015; Tulsiani
and Malik, 2015) yielded an acceptable accuracy of
86%. These methods have rendered millions of synt-
hetic images to train their deep models. Note that the
authors of (Szeto and Corso, 2017) have shown only
the results of two categories, thus the average accu-
racy was computed for just these two categories. The
proposed model achieved a high accuracy with the
AEROPLANE and CAR categories, since MFC can
provide adequate shape features for these types of ob-
jects. Moreover, real images used in testing always
contain simple backgrounds. However, the SOFA ca-
tegory did not provide a high accuray, since the most
of 3D model of SOFA have a similar shape. In ad-
dition, real images have more complex backgrounds
than other categories.
The proposed model was implemented using
MATLAB on a 64-bit CPU with 3.40 GHz, 16 GB
memory, and NVIDIA GTX 1070 GPU. In figure 5,
the complexity of the computational time of each task
of the proposed method, i.e., rendering, depth feature
extraction, training SVM, image feature extraction
(MFC, MCS, CS), on-line SVM prediction and RAN-
SAC, is shown as a Pie chart. As shown, the most exe-
cution time that is about 76% of the total time is rela-
ted to off-line tasks, such as rendering, depth features
extraction and training SVM. In turn, to predict the
final viewpoint that means the online prediction, the
other three tasks (i.e., feature extraction of an image,
on-line SVM prediction and RANSAC) take around
24% of the total computational time.
Figure 5: The percentage of the time consuming with each
subsystem of the proposed approach.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this work, we have proposed an automatic 2D/3D
registration approach compensating the disadvantages
of rendering a large number of images of 3D models
VISAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
360

(i.e., depth images) by reducing the matching space
between the 2D intensity and 3D depth images. The
depth images rendered of a 3D model were represen-
ted with the curvilinear saliency features. In addition,
an accurate representation based on multi-scale curvi-
linear saliency with focus features was used to reduce
the effect of texture and background on the extrac-
ted features of an intensity image. The depth ima-
ges were clustered with a rule-based clustering met-
hod. The features of each cluster of depth images
were used to train a multi-class SVM for estimating
a group of depth images that are close to the input in-
tensity image. The matching between the input image
and the predicted class was then performed to esti-
mate the correct 3D pose. The RANSAC algorithm
was used to refine and verify the final viewpoint. The
effectiveness of the proposed system has been evalu-
ated on the public PASCAL3D+ dataset. The propo-
sed 2D/3D registration algorithm yielded promising
results with a high precision rate and acceptable com-
putational timing. Future work aims to extend the pre-
sented 2D/3D registration algorithm using a deep le-
arning system.
REFERENCES
Aubry, M., Maturana, D., Efros, A. A., Russell, B. C., and
Sivic, J. (2014). Seeing 3d chairs: exemplar part-
based 2d-3d alignment using a large dataset of cad
models. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on
computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 3762–
3769.
Campbell, R. J. and Flynn, P. J. (2001). A survey of free-
form object representation and recognition techni-
ques. Computer Vision and Image Understanding,
81(2):166–210.
Choy, C. B., Stark, M., Corbett-Davies, S., and Savarese, S.
(2015). Enriching object detection with 2d-3d regis-
tration and continuous viewpoint estimation. In Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2015
IEEE Conference on, pages 2512–2520. IEEE.
Fischler, M. A. and Bolles, R. C. (1987). Random sample
consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with appli-
cations to image analysis and automated cartography.
In Readings in computer vision, pages 726–740. Else-
vier.
Hartley, R. and Zisserman, A. (2003). Multiple view geome-
try in computer vision. Cambridge university press.
Lee, Y. Y., Park, M. K., Yoo, J. D., and Lee, K. H. (2013).
Multi-scale feature matching between 2d image and
3d model. In SIGGRAPH Asia 2013 Posters, page 14.
ACM.
Lim, J. J., Khosla, A., and Torralba, A. (2014). Fpm: Fine
pose parts-based model with 3d cad models. In Euro-
pean Conference on Computer Vision, pages 478–493.
Springer.
Liu, L. and Stamos, I. (2005). Automatic 3d to 2d registra-
tion for the photorealistic rendering of urban scenes.
In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2005.
CVPR 2005. IEEE Computer Society Conference on,
volume 2, pages 137–143. IEEE.
Plotz, T. and Roth, S. (2015). Registering images to untex-
tured geometry using average shading gradients. In
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on
Computer Vision, pages 2030–2038.
Pl
¨
otz, T. and Roth, S. (2017). Automatic registration of
images to untextured geometry using average shading
gradients. International Journal of Computer Vision,
125(1-3):65–81.
Ramalingam, S., Bouaziz, S., Sturm, P., and Brand, M.
(2009). Geolocalization using skylines from omni-
images. In Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Works-
hops), 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on,
pages 23–30. IEEE.
Rashwan, H. A., Chambon, S., Gurdjos, P., Morin, G., and
Charvillat, V. (2016). Towards multi-scale feature
detection repeatable over intensity and depth images.
In Image Processing (ICIP), 2016 IEEE International
Conference on, pages 36–40. IEEE.
Rashwan, H. A., Chambon, S., Gurdjos, P., Morin, G., and
Charvillat, V. (2018). Using curvilinear features in fo-
cus for registering a single image to a 3d object. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1802.09384.
Sattler, T., Leibe, B., and Kobbelt, L. (2011). Fast image-
based localization using direct 2d-to-3d matching. In
Computer Vision (ICCV), 2011 IEEE International
Conference on, pages 667–674. IEEE.
Su, H., Qi, C. R., Li, Y., and Guibas, L. J. (2015). Render for
cnn: Viewpoint estimation in images using cnns trai-
ned with rendered 3d model views. In Proceedings of
the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vi-
sion, pages 2686–2694.
Szeto, R. and Corso, J. J. (2017). Click here: Human-
localized keypoints as guidance for viewpoint estima-
tion. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.09859.
Tamaazousti, M., Gay-Bellile, V., Collette, S. N., Bour-
geois, S., and Dhome, M. (2011). Nonlinear refine-
ment of structure from motion reconstruction by ta-
king advantage of a partial knowledge of the envi-
ronment. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion (CVPR), 2011 IEEE Conference on, pages 3073–
3080. IEEE.
Tulsiani, S. and Malik, J. (2015). Viewpoints and keypoints.
In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1510–1519.
Xiang, Y., Mottaghi, R., and Savarese, S. (2014). Beyond
pascal: A benchmark for 3d object detection in the
wild. In Applications of Computer Vision (WACV),
2014 IEEE Winter Conference on, pages 75–82. IEEE.
Xu, C., Zhang, L., Cheng, L., and Koch, R. (2017). Pose
estimation from line correspondences: A complete
analysis and a series of solutions. IEEE transacti-
ons on pattern analysis and machine intelligence,
39(6):1209–1222.
Effective 2D/3D Registration using Curvilinear Saliency Features and Multi-Class SVM
361
