
The Impact of the Transversion/Transition Ratio on the Optimal Genetic
Code Graph Partition
Daniyah A. Aloqalaa
1
, Dariusz R. Kowalski
1,2
, Paweł Bła
˙
zej
3
, Małgorzata Wnetrzak
3
,
Dorota Mackiewicz
3
and Paweł Mackiewicz
3
1
Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool, U.K.
2
SWPS University of Social Sciences and Humanities, Warsaw, Poland
3
Faculty of Biotechnology, University of Wrocław, Poland
{dorota, pamac}@smorfland.uni.wroc.pl
Keywords:
Code Degeneracy, Graph Theory, Mutation, Set Conductance, Standard Genetic Code, Transition, Transver-
sion.
Abstract:
The standard genetic code (SGC) is a system of rules ascribing 20 amino acids and stop translation signal to 64
codons, i.e triplets of nucleotides. It was proposed that the structure of the SGC evolved to minimize harmful
consequences of mutations and translational errors. To study this problem, we described the SGC structure by
a graph, in which codons are vertices and edges correspond to single nucleotide mutations occurring between
the codons. We also introduced weights (W ) for mutation types to distinguish transversions from transitions.
Using this representation, the SGC is a partition of the set of vertices into 21 disjoint subsets. In this case,
the question about the potential robustness of the genetic code to the mutations can be reformulated into the
optimal graph clustering task. To investigate this problem, we applied an appropriate clustering algorithm,
which searched for the codes characterized by the minimum average calculated from the set W -conductance
of codon groups. Our algorithm found three best codes for various ranges of the applied weights. The average
W -conductance of the SGC was the most similar to that of the best codes in the range of weights corresponding
to the observed transversion/transition ratio in natural mutational pressures. However, it should be noted that
the optimization of the SGC was not as perfect as the best codes. It implies that the evolution of the SGC was
driven not only by the selection for the robustness against mutations or mistranslations but also other factors,
e.g. subsequent addition of amino acids to the code according to the expansion of amino acid metabolic
pathways.
1 INTRODUCTION
The questions about the origin and the structure of
the standard genetic code (SGC) have puzzled biolo-
gists since the first codons assignments were discov-
ered (Khorana et al., 1966; Nirenberg et al., 1966).
This nearly universal, with some rare exceptions, set
of coding rules is responsible for transmitting genetic
information stored in DNA molecules into the pro-
tein world. The code uses all possible 64 nucleotide
triplets, i.e. codons, to encode 20 canonical amino
acids and also the signal for stopping the protein syn-
thesis, i.e. the translation. Since the total number of
codons is greater then the number of encoded labels,
the SGC must be degenerate, i.e. there must exist an
amino acid that is encoded by more than one codon.
These redundant codons, called synonymous, are or-
ganized in specific groups. In most cases, the codons
in such groups differ at the third position, which can
be called a degenerate position. This fact suggested to
Francis Crick that only the first two codon positions
were important in a primordial code (Crick, 1968).
The redundancy of the SGC causes other interest-
ing consequences related to the process of single nu-
cleotide mutations. If these changes occur in the de-
generate codon position, then the originally encoded
amino acid will not be changed. These mutations
are called synonymous or silent, whereas those that
change the encoded amino acid or stop translation sig-
nal are named nonsynonymous. It should be noted
that there are two types of nucleotide changes, tran-
sitions and transversions. In the case of transition, a
purine nucleotide, i.e. adenine or guanine, mutates
to another purine (A↔G), or a pyrimidine nucleotide,
Aloqalaa, D., Kowalski, D., Bła
˙
zej, P., Wnetrzak, M., Mackiewicz, D. and Mackiewicz, P.
The Impact of the Transversion/Transition Ratio on the Optimal Genetic Code Graph Partition.
DOI: 10.5220/0007381000550065
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2019), pages 55-65
ISBN: 978-989-758-353-7
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
55

i.e. cytosine or thymine, changes into another pyrim-
idine (C↔T). Transversion are changes in which a
purine mutates to a pyrimidine or vice versa (A↔C,
A↔T, G↔C, G↔T). There are four possible transi-
tions and eight possible transversions. Transitions are
more often observed in sequences than transversions
(Duch
ˆ
ene et al., 2015; Gojobori et al., 1982; Kumar,
1996; Lynch, 2010; Lyons and Lauring, 2017; Petrov
and Hartl, 1999; Rosenberg et al., 2003; Wakeley,
1996). It may result from a higher mutation rate of
transitions than transversions in nucleic acids due to
physicochemical similarity of the nucleotides. More-
over, transitions are accepted with a greater probabil-
ity because they rarely lead to amino acid substitu-
tions in encoded proteins due to the specific codon
degeneracy. The transitions are also more frequent
during protein synthesis (Freeland and Hurst, 1998a).
It should be noted, that the synonymous substitu-
tions do not have to be completely neutral mutations,
even though they do not change a coded amino acid.
The specific codon usage can be associated with co-
translational modifications of amino acids, efficiency
and accuracy of translation as well as co-translational
folding of synthesized proteins (Bulmer, 1991; Her-
shberg and Petrov, 2008; Zhou et al., 2009). The syn-
onymous codon usage can be also modified as a con-
sequence of selection at the amino acid level (Morton,
2001; Bła
˙
zej et al., 2017b).
The tendency to minimize the number of non-
synonymous substitutions were noticed in the SGC
and this property suggested that the code could have
evolved to minimize harmful consequences of muta-
tions and translational errors (Ardell, 1998; Ardell
and Sella, 2001; Di Giulio, 1989; Di Giulio and
Medugno, 1999; Epstein, 1966; Freeland and Hurst,
1998a; Freeland and Hurst, 1998b; Freeland et al.,
2003; Freeland et al., 2000; Gilis et al., 2001; Gold-
berg and Wittes, 1966; Goodarzi et al., 2005; Haig
and Hurst, 1991; Woese, 1965). The robustness of the
code was usually measured as a difference between
the polarity values of amino acids encoded by codons
before and after a single-point mutation.
Since the genetic code is a set of codons which
are related, e.g. by nucleotide mutations, the general
structure of this code can be well described by the
methodology taken from graph theory (Beineke and
Wilson, 2005; Lee et al., 2014). Similarly to (Tlusty,
2010; Bła
˙
zej et al., 2018a), we assume that the code
encodes 21 items, i.e. 20 amino acids and stop trans-
lation signal, and all 64 codons create the set of ver-
tices of the graph, in which the set of edges corre-
sponds to all possible single nucleotide mutations oc-
curring between the codons. This graph is undirected,
unweighted and regular. Moreover, according to this
representation, each genetic code is a partition of the
set of vertices into 21 disjoint subsets. Therefore, the
question about the potential genetic code optimality
in regard to the mutations can be reformulated into
the optimal graph clustering problem.
In the present study, we investigated the proper-
ties of the SGC using a more general model including
in the graph representation information about tran-
sition to transversion ratio, which was not consid-
ered by (Tlusty, 2010; Bła
˙
zej et al., 2018a). From a
mathematical point of view, we considered a weighted
graph, in which all weights are dependent on the type
of nucleotide substitutions. We also modified the set
conductance measure, which is widely used in the
graph theory (Lee et al., 2014) and has many prac-
tical interpretations, for example in the theory of ran-
dom walks (Levin et al., 2009) and social networks
(Bollob
´
as, 1998). In the problem considered here,
the conductance of a codon group is the ratio of the
weights of nonsynonymous mutations to the weights
of all possible single nucleotide mutations, in which
the codons in this group are involved. Therefore, this
parameter can be used as a measure of robustness
against the potential changes in protein-coding se-
quences generated by the single nucleotide mutations.
Basing on the methodology described in (Bła
˙
zej et al.,
2018a), we found some solutions, i.e. the genetic
code structures, of the optimal graph clustering prob-
lem.
2 PRELIMINARIES
2.1 Model Description
To study the general structure of the genetic code we
developed its graph representation. Let G(V, E) be
a graph in which V is the set of vertices represent-
ing all possible 64 codons, whereas E is the set of
edges connecting these vertices. All connections ful-
fil the property that the vertices, i.e. codons u, v ∈ V
are connected by the edge e(u, v) ∈ E (u ∼ v) if and
only if the codon u differs from the codon v in ex-
actly one position. Moreover, we claim that all tran-
sitions are given a weight which equals always to
one, while the transversions are given a weight W ,
where W ∈ [0, ∞). The larger weight indicates that the
transversions are more important than transitions, re-
spectively. The weight can be interpreted as transver-
sion to transition ratio. Hence, the graph G is undi-
rected, weighted and regular with the vertices degree
equal to 9. Moreover, from a biological perspec-
tive, the set of edges represents all possible single nu-
cleotide substitutions, which occur between codons in
BIOINFORMATICS 2019 - 10th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
56

a DNA sequence. What is more, this model includes
two important types of mutations.
Following the methodology presented in (Bła
˙
zej
et al., 2018a), each potential genetic code C, which
encodes 20 amino acids and stop translation signal is
a partition of the set V into 21 disjoint subsets, i.e.
groups of codons, S. Thus, we obtain the following
representation of the genetic code C:
C = {S
1
, S
2
, ··· , S
20
, S
21
: S
i
∩ S
j
= Ø,S
1
∪ S
2
∪ ·· · ∪ S
21
= V } .
In Figure 1 we showed an example of the parti-
tion of the graph G, which corresponds to the stan-
dard genetic code. From a biological point of view, it
is interesting to study the code structure according to
the types and also the number of connections between
and within the codon groups because these connec-
tions correspond to nonsynonymous and synonymous
substitutions, respectively. It should be noted that
each potential genetic code that minimizes the num-
ber of the nonsynonymous substitutions is regarded
the best in terms of decreasing the biological conse-
quences of mutations. Therefore, the conditions un-
der which the partitions of the graph vertices describe
the best genetic code, are worth finding.
There are many methods of the optimal graph par-
titioning, which are based on different approaches. In
this work, to investigate the theoretical features of ge-
netic codes in terms of the connections between the
codon groups, we decided to use the set conductance
measure, which plays a central role in the spectral
graph clustering method. The definition of the set W -
conductance measure including weights for edges is
as follows:
Definition 2.1. For a given weighted graph G let W
be a weight of transversion connections in G and S be
a subset of V . The W -conductance of S is defined as:
φ
S
(W ) =
E
tr
(S, S) + E
trv
(S, S) ·W
|S| · (3 + 6W )
,
where E
tr
(S, S) is the total number of transition edges
crossing from S to its complement S whereas E
trv
(S, S)
is the total number of transversion edges crossing
from S to its complement
S, and |S| is the number of
vertices belonging to S.
The definition of the set W -conductance is a good
staring point to describe a quality measure of a given
codon group. Large values of this measure mean that
a substantial fraction of substitutions in which these
codons are involved are nonsynonymous, i.e. they
change one amino acid to another. From the robust-
ness point of view, small values are desirable because
in this case many substitutions are neutral (synony-
mous) and do not change coded amino acids.
What is more, this approach allows us to char-
acterize the properties of the whole genetic code
because following the definition of the set W -
conductance we define the average W -conductance of
a genetic code:
Definition 2.2. The average W -conductance of a
given genetic code C and a given weight W is defined
as:
Φ
C
(W ) =
1
21
∑
S∈C
φ
S
(W ) .
Using the definition presented above, we are able
to describe the best code in terms of the average W -
conductance, which is defined as follows:
Φ
min
(W ) = min
C
Φ
C
(W ) .
Φ
min
(W ) gives us the lower bound of the genetic
code robustness measured in terms of the average
code W -conductance.
2.2 The Clustering Algorithm
In this work we propose a new randomized clustering
algorithm to find the optimal genetic code with re-
spect to the minimum average W -conductance. More
formal description of Algorithm 1 provides the struc-
ture of the clustering algorithm. The generic struc-
ture of the clustering algorithm contains inputs, out-
puts (cf. input parameters and output variables in
Table 1), and three functions, namely: AVERAGE-
CONDUCTANCE, PICKFIRSTNODE, and PICKSEC-
ONDNODE. The main function is the AVERAGE-
CONDUCTANCE function, which aims to find the op-
timal genetic code with the minimum average W -
conductance. The function includes nested loops of
two levels. The main loop (lines 5-14) counts the
average conductance for each iteration. The second
level loop (lines 7-14) is for picking and merging
nodes from the graph until we have 21 clusters (su-
per nodes). The AVERAGECONDUCTANCE termi-
nates when the graph is clustered to 21 clusters for
each iteration and returns the best genetic code with
the minimum average conductance over all indepen-
dent iterations. The PICKFIRSTNODE (lines 16-30)
and the PICKSECONDNODE (lines 31-47) associate a
probability for each node in the graph and each func-
tion pick a node randomly.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The main goal of our work is to find the optimal ge-
netic codes in terms of the average W-conductance
Φ
min
(W ). Furthermore, we compare the properties of
The Impact of the Transversion/Transition Ratio on the Optimal Genetic Code Graph Partition
57

AAA
AAT
AAG
AAC
ATA
ATT
ATG
ATC
AGA
AGT
AGG
AGC
ACA
ACT
ACG
ACC
TAA
TAT
TAG
TAC
TTA
TTT
TTG
TTC
TGA
TGT
TGG
TGC
TCA
TCT
TCG
TCC
GAA
GAT
GAG
GTA
GTT
GTG
GTC
GGA
GGT
GGG
GGC
GCA
GCT
GCG
GCC
CAA
CAT
CAG
CAC
CTA
CTT
CTG
CTC
CGA
CGT
CGG
CGC
CCA
CCT
CCG
CCC
GAC
Figure 1: The standard genetic code as an example of the partition of the graph G(V, E). Every group of vertices with the
same colour corresponds to the respective set of codons, which code for the same amino acid or stop translation signal. The
edges represent all possible single nucleotide substitutions. According to (Bła
˙
zej et al., 2018a), modified.
Table 1: Input parameters and output variables for Algo-
rithm 1.
Input parameters:
1 Adjacent matrix of 64 codons, called A,
where A[i, j] can take:
A[i, j] =
1 if i 6= j and if and only if i differs
from j in exactly one position
0 otherwise
2 Adjacent transition matrix of codons, called B,
where B[i, j] can take 1 only with transition
connections i.e. A↔G, C↔T, otherwise 0
3 W ∈ [0,∞)
4 #iterations ← 20, 000
Output variables:
1 The minimum average conductance
2 The structure of the best genetic code that
gives the minimum average conductance
these codes with the standard genetic code, which is
interesting from the biological point of view.
We run the clustering algorithm (Algorithm 1)
20,000 times independently to find the minimum of
the W -average conductance and the structure of the
genetic code that gives the minimum average W -
conductance. We carried out the calculations for the
transversion weight W ∈ [0, 10]. The weights can
be interpreted as a relative ratio between transver-
sions and transitions. Smaller weights mean that tran-
sitions are more frequent than transversions, while
larger weights indicate that the transversions domi-
nate among point mutations.
We found three genetic codes that are best for dif-
ferent ranges of W ∈ [0, ∞]. The genetic code C1 was
best for every W ∈ [0,
37
70
], the code C2 for every W ∈
[
37
70
, 1] and the code C3 for every W ∈ [1, ∞]. The aver-
age W -conductance for these codes in the function of
weight W is Φ
C1
(W ) =
1
21
·
126W +31
6W +3
, Φ
C2
(W ) =
1
21
·
308W +130
9(2W +1)
, and Φ
C3
(W ) =
1
21
·
94W +52
6W +3
for every W ∈
[0,
37
70
], [
37
70
, 1], and [1, ∞], respectively. We conjecture
that these codes are optimal in the range of weights
corresponding to the observed transversion/transition
ratio in natural mutational pressures; though, as the
algorithm is randomized (but repeated a large num-
ber of times to reduce the probability of finding sub-
optimal solutions), the formal proof of their optimal-
ity is still an open question. Figure 2 shows the av-
BIOINFORMATICS 2019 - 10th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
58

Algorithm 1: The clustering algorithm.
1: function AVERAGECONDUCTANCE(A, B,W, iterations)
2: D = A − B Create transversion matrix
3: M = B + (W · D) Create matrix M
4: min-ave-cond ← 2
5: for each iteration do
6: g = [(node, edges) for each node in M] List g stores each node i in M and its edges
7: while (len(g) > 21 nodes) do Keep picking and merging nodes until we have 21 clusters
8: u ← PICKFIRSTNODE(g)
9: v ← PICKSECONDNODE(g)
10: Merge nodes u and v
11: conductance = compute conductance for each cluster in g List conductance stores conductance of 21
clusters using φ
S
(W ) formula in Definition 2.1
12: if min-ave-cond>sum(conductance)/len(conductance) then
13: min-ave-cond = sum(conductance)/len(conductance)
14: clusterings-min-ave-cond = g Stores the structure of the genetic code
15: return min-ave-cond, clusterings-min-ave-cond
16: function PICKFIRSTNODE(g)
17: cond ← [(i,φ
i
(W )) for each node i in g] List to store conductance for each node i in g
18: for for each node i in cond do
19: weight[i] ← (i, cond[i]
20
) List to store weight for each node i in cond list
20: for for each node i in weight do
21: prob[i] ← (i,
weight[i]
sum(weight)
) List to store probability of selecting each node i in weight list
22: R ← Generate a random number between 0 and 1
23: j ← 0
24: a ← prob[0]
25: while (R > a) do
26: j ← j + 1
27: a ← a + prob[ j]
28: return j
29: u ← cond[ j] Select the j
th
node in the cond list
30: return u
31: function PICKSECONDNODE(g)
32: cond1 ← cond − u Copy cond list without the selected node u
33: for for each node i in cond1 do
34: edges[i] ← (i, #edges between i and u)
35: for for each node i in cond1 do
36: weight[i] ← (i, (edges[i] + 1)
10
· cond1[i]
20
) List to store weight for each node i in cond1 list
37: for for each node i in weight do
38: prob[i] ← (i,
weight[i]
sum(weight)
) List to store probability of selecting each node i in weight list
39: R ← Generate a random number between 0 and 1
40: j ← 0
41: a ← prob[0]
42: while (R > a) do
43: j ← j + 1
44: a ← a + prob[ j]
45: return j
46: v ← cond1[ j] Select the j
th
node in the cond1 list
47: return v
The Impact of the Transversion/Transition Ratio on the Optimal Genetic Code Graph Partition
59

erage W -conductance for the best codes and the SGC
depending on the transversion weight.
The average conductance for the codes that are
best for W < 1 increases rapidly with W and then sta-
bilizes for large values. In the case of the code C3,
its conductance decreases at first and then also ap-
proaches a certain value. For small W values, the
average conductance is the smallest for the code C1
and the largest for codes C3. In turn, the opposite is
true for large W values. The code C1 is characterized
by the biggest difference between its average conduc-
tance values. The code is very well optimized for the
excess of transitions over transversions but it is very
bad in the opposite case. The average W -conductance
of the SGC shows the general course similar to that of
the C1 and C2 codes.
To compare the properties of the best codes with
the standard genetic code, we computed the func-
tion of the average W -conductance for the SGC,
Φ
SGC
(W ) =
1
21
·
10(33W +13)
9(2W +1)
. Then, we subtracted
Φ
SGC
(W ) from each of the average W-conductance
function of each best codes (C1,C2,C3) and calcu-
lated the derivative for each produced function as fol-
lows:
1. Define f 1(W ) = Φ
SGC
− Φ
C1
, then
f 1(W ) =
1
21
·
10(33W + 13)
9(2W + 1)
−
1
21
·
126W + 31
6W + 3
.
The derivative of f 1(W ) is
f 1
0
(W ) = −
122
189(2W + 1)
2
.
At W = 0, the value of f 1 is equal to 0.2 and
at W =
37
70
f 1 is is equal to 0.03. The values of
the conductance function for both codes are the
same at W =
37
48
. Below this weight the C1 code
shows a smaller Φ than the SGC and above this
weight, the opposite is true.
2. Define f 2(W ) = Φ
SGC
− Φ
C2
, then
f 2(W ) =
1
21
·
10(33W + 13)
9(2W + 1)
−
1
21
·
308W + 130
9(2W + 1)
.
The derivative of f 2(W ) is
f 2
0
(W ) =
22
189(2W + 1)
2
.
At W = 0, the C2 and the SGC codes have the
same values of Φ, i.e. f 2 = 0. Next, with the
growth of W , f 2 increases, which means that
the average W -conductance of the SGC becomes
larger than that of the C2 code. At W =
37
70
, the
value of f 2 is equal to 0.03 and at W = 1 f 2 is
equal to 0.04.
3. Define f 3(W ) = Φ
SGC
− Φ
C3
, then
f 3(W ) =
1
21
·
10(33W + 13)
9(2W + 1)
−
1
21
·
94W + 52
6W + 3
.
The derivative of f 3(W ) is
f 3
0
(W ) =
100
189(2W + 1)
2
.
For W <
13
24
, Φ
SGC
is smaller than Φ
C3
. Above this
weight, the opposite is true. At W = 1, the value
of f 4 is equal to 0.04 and at W = 3 f 3 is equal to
0.11.
The functions f 1(W ), f 2(W ) and f 3(W ) are dif-
ferences in the average W -conductance between the
SGC and three best codes depending on the transi-
tion weight W . It is evident that the standard genetic
code is optimized for more frequent transitions than
transversions. The SGC can obtain the same average
W -conductance as each of the optimized codes but for
different transversion weights. Nevertheless, the W
is always smaller than 1 in these cases. The mini-
mum distance between the SGC and the best genetic
codes in terms of the average conductance is 0.03
for W =
37
70
= 0.53 (Figure 3). Since there are twice
as many possible transversions as transitions, the ex-
pected ratio should be 2, if all nucleotide substitutions
happen with the same probability. Interestingly, the
weights for which Φ
SGC
is close to Φ of the best codes
is in the range of the transversion/transition ratio ob-
served in genomic mutational pressures, i.e. from
1.44 to 0.10 (Kowalczuk et al., 2001; Bła
˙
zej et al.,
2015). However, for each transversion weight, it is
possible to find a code better optimized than the SGC
in terms of the average W -conductance, so this code is
not perfectly optimized. Our preliminary analyses of
the alternative genetic codes in this respect showed
that the relationship between their average conduc-
tance depending on the transversion weight has the
course very similar to that of the SGC.
The structure of these best genetic codes is pre-
sented in Table 2. Although the code C1 and C3 are
best for different and extreme W values, they have the
same number of two- and four-codon groups, 10 and
11, respectively. The code C2 has in addition 3 groups
consisting of three codons as well as 8 two-codon
groups and 9 four-codon groups. The SGC is more
diversified in this respect because it has 2 one-codon
groups, 9 two-codon groups, 2 three-codon groups, 5
four-codon groups and 3 six-codon groups. Thereby,
it is more similar to the code C2.
The code C1 is best for smaller weights of
transversions. Therefore, such mutations are prefer-
ably involved in changes between codon groups of
this code in order to minimize these changes. Con-
sequently, all synonymous substitutions in this code
BIOINFORMATICS 2019 - 10th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
60
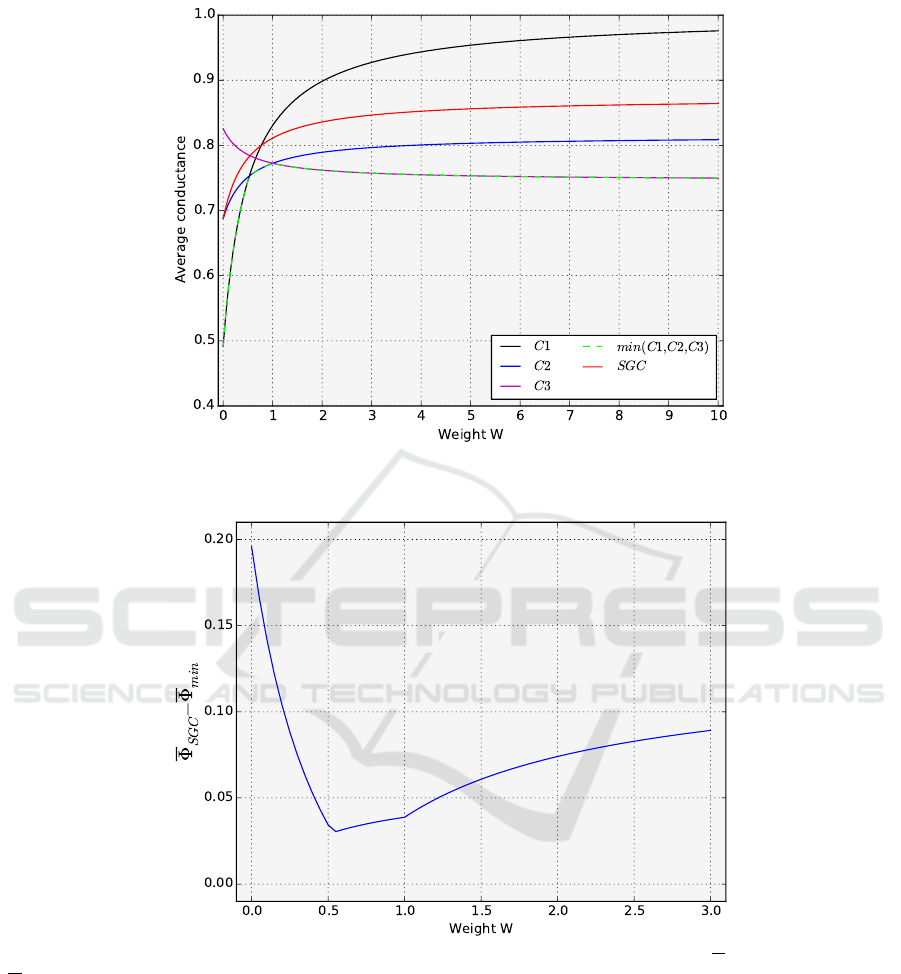
Figure 2: The average conductance for the best codes C1,C2,C3, and min(C1,C2,C3) as well as the standard genetic code
(SGC) for the weights of transversions W ∈ [0, 10].
Figure 3: The difference between the average conductance for the standard genetic code (SGC) (Φ
SGC
) and the best codes
(Φ
min
) for the weights of transversions W ∈ [0, 3].
are transitions. In the case of the code C3, which is
best for larger W , transversions were eliminated from
changes between codon groups as much as possible
to increase the number of transitions. In consequence,
all changes within two-codon groups of this code are
transversions. Since there are only two purines and
two pyrimidines, it is not possible to create four-
codon groups that can change to each other by only
transversions. Therefore, changes within such groups
are both transitions and transversions. The code C2
is a mixture in this respect because the codons in its
two-codon groups can change to each other only by
transitions, while in the other groups by the two types
of mutations. Considering only one point mutations
in the SGC, all changes within two-codon groups are
also transitions and within other groups both tran-
sitions and transversions with exception to the stop
codon group, which also involves only transitions.
Then the SGC is again more similar to the code C2
in this respect.
The Impact of the Transversion/Transition Ratio on the Optimal Genetic Code Graph Partition
61

Table 2: The structure of the best genetic codes C1,C2, and C3 for W ∈ [0,
37
70
], W ∈ [
37
70
, 1], and W ∈ [1, ∞], respectively. Each
row describes the codon group for a cluster.
C1 C2 C3
1 {AAA, AAG, AGG, AGA} {AAG, ACG, ATG} {ATA, AAA, AGA, ACA}
2 {AT T, ATC} {AGA, AGG} {AGC, ACC}
3 {TAG, TAA} {AGC, ATC, AAC, ACC} {ACT, TCT }
4 {TAC, TAT, T GT, T GC} {ACA, AAA, ATA} {ACG, AAG,AT G, AGG}
5 {T T T,CT T } {TAA, TAG} {T TA, TAA}
6 {T GA, T GG} {TAC,CAC} {T TC, TAC, TCC, T GC}
7 {TCT,CCT } {T TA,CTA, GTA} {T GG, TAG, TCG, T T G}
8 {TCG, T T G, T TA, TCA} {T T G,CT G} {TCA, T GA}
9 {TCC, T TC,CTC,CCC} {T GA, T GG, T GC, T GT } {GAT, AAT, TAT,CAT }
10 {GTA, ATA, GT G, AT G} {TCA, TCT, TCC, TCG} {GT T, ATT, T T T,CT T }
11 {GTC, GT T } {GAT, AAT, TAT,CAT } {GGA, GCA, GAA, GTA}
12 {GGA, GAA, GAG, GGG} {GAC, GGC, GCC, GTC} {GGT,CGT, AGT, T GT }
13 {GGT, GAT, AGT, AAT } {GT G, GAG, GGG, GCG} {GCG, GAG,GGG, GT G}
14 {GGC, AGC, AAC, GAC} {GGT, AGT} {GCC, GTC, GAC, GGC}
15 {GCG, GCA, ACA, ACG} {GCA, GGA, GAA} {CAA,CTA}
16 {GCC, ACC, GCT, ACT } {GCT, ACT } {CAC, AAC}
17 {CAT,CGT,CGC,CAC} {CAG,CAA} {CT G,CGG,CAG,CCG}
18 {CTA,CT G} {CT T, GT T, AT T, T T T } {CTC, ATC}
19 {CGA,CAA} {CTC, T TC} {CGC,CCC}
20 {CGG,CAG} {CGC,CGG,CGT,CGA} {CCA,CGA}
21 {CCG,CCA} {CCA,CCC,CCT,CCG} {CCT, GCT }
The changes between codons in one group of the
code C3 can occur only in one fixed codon position,
the first or the second one. The third codon position
can also be mutated in the code C2. However, the
code C1 contains also the groups in which any two
codon positions can be changed. The SGC contains
many codon groups with synonymous mutations in
the third codon position but there are also three codon
groups involving single changes in two codon posi-
tions.
The comparison of structures of the genetic codes
show that the assignments of amino acids to codons
is not ideally optimized in the SGC. Some similar-
ity of the SGC to the code C2 suggests that the stan-
dard genetic code could evolve under the transver-
sion/transition for which the code C2 is best.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Our results show that the general structure of the
genetic code and the problem of the genetic code
optimality can be successfully reformulated using a
methodology adapted from graph theory in the con-
text of optimal clustering of a specific graph. To eval-
uate the quality of the genetic code, we calculated
the average code W -conductance including weights
for mutation types. Thereby, we distinguished tran-
sitions and transversions. From the biological point
of view, this measure describes the code robustness
against amino acid and stop translation signal replace-
ments resulting from single nucleotide substitutions
between codons.
We found three best codes with respect to the av-
erage code conductance for various ranges of the ap-
plied weight. The structure of the codes was differ-
ent in comparison to the standard genetic code. The
W -conductance of the SGC was the most similar to
that of the best codes in the range of weights corre-
sponding to the observed small transversion/transition
ratio in the mutational pressure. Other researches
also showed that the SGC performs better for the ex-
cess of transitions over transversions (Freeland and
Hurst, 1998a; Freeland and Hurst, 1998b). It indi-
cates that the SGC is optimized to some extent in
terms of the minimization of amino acid and stop
translation replacements. However, the optimization
was not ideal and for each weight better theoreti-
BIOINFORMATICS 2019 - 10th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
62

cal codes could be found. In agreement with that,
other investigations also showed that the SGC is not
perfectly robust against point mutations or mistrans-
lations (Bła
˙
zej et al., 2018b; Bła
˙
zej et al., 2016;
Massey, 2008; Novozhilov et al., 2007; Santos and
Monteagudo, 2011; Santos and Monteagudo, 2017;
Wnetrzak et al., 2018).
Most likely, the robustness against mutations was
not the main force that drove the evolution of the ge-
netic code and amino acids were assigned to codons
according to expansion of biosynthetic pathways syn-
thesizing amino acids (Di Giulio, 1999; Di Giulio,
2008; Di Giulio, 2016; Di Giulio, 2017; Wong, 1975;
Wong et al., 2016; Wong, 2007; Di Giulio, 2018). In
this case, the potential minimization of mutation er-
rors could have occurred by the direct optimization of
the mutational pressure around the established genetic
code (Dudkiewicz et al., 2005; Mackiewicz et al.,
2008; Bła
˙
zej et al., 2013; Bła
˙
zej et al., 2017a; Bła
˙
zej
et al., 2015).
The results can have practical consequences in
the context of designing modified or extended genetic
codes (Xie and Schultz, 2006; Chin, 2014). The aim
of this engineering is to produce peptides or proteins
containing unnatural amino acids and showing an im-
proved activity or completely new functions.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Science
Centre, Poland (Narodowe Centrum Nauki, Polska)
under Grants number UMO-2017/27/N/NZ2/00403
and UMO-2017/25/B/ST6/02553.
REFERENCES
Ardell, D. H. (1998). On error minimization in a sequential
origin of the standard genetic code. Journal of Molec-
ular Evolution, 47(1):1–13.
Ardell, D. H. and Sella, G. (2001). On the evolution of
redundancy in genetic codes. Journal of Molecular
Evolution, 53(4-5):269–281.
Beineke, L. W. and Wilson, R. J. (2005). Topics in al-
gebraic graph theory. Cambridge University Press,
Cambridge, UK; New York.
Bła
˙
zej, P., Kowalski, D., Mackiewicz, D., Wnetrzak, M.,
Aloqalaa, D., and Mackiewicz, P. (2018a). The struc-
ture of the genetic code as an optimal graph clustering
problem. bioRxiv.
Bła
˙
zej, P., Mackiewicz, D., Grabinska, M., Wnetrzak, M.,
and Mackiewicz, P. (2017a). Optimization of amino
acid replacement costs by mutational pressure in bac-
terial genomes. Scientific Reports, 7:1061.
Bła
˙
zej, P., Mackiewicz, D., Wnetrzak, M., and Mackiewicz,
P. (2017b). The impact of selection at the amino acid
level on the usage of synonymous codons. G3-Genes
Genomes Genetics, 7(3):967–981.
Bła
˙
zej, P., Mackiewicz, P., Cebrat, S., and Wa
´
nczyk, M.
(2013). Using evolutionary algorithms in finding
of optimized nucleotide substitution matrices. In
Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference,
GECCO’13, pages 41–42. Companion ACM.
Bła
˙
zej, P., Miasojedow, B., Grabinska, M., and Mack-
iewicz, P. (2015). Optimization of mutation pressure
in relation to properties of protein-coding sequences
in bacterial genomes. PLoS One, 10:e0130411.
Bła
˙
zej, P., Wnetrzak, M., Mackiewicz, D., and Mackiewicz,
P. (2018b). Optimization of the standard genetic code
according to three codon positions using an evolution-
ary algorithm. PLoS One, 13(8):e0201715.
Bła
˙
zej, P., Wne¸trzak, M., and Mackiewicz, P. (2016). The
role of crossover operator in evolutionary-based ap-
proach to the problem of genetic code optimization.
Biosystems, 150:61–72.
Bollob
´
as, B. (1998). Modern graph theory, graduate texts
in mathematics vol. 184.
Bulmer, M. (1991). The selection-mutation-drift theory of
synonymous codon usage. Genetics, 129(3):897–907.
Chin, J. W. (2014). Expanding and reprogramming the ge-
netic code of cells and animals. Annual Review of Bio-
chemistry, 83:379–408.
Crick, F. H. (1968). The origin of the genetic code. Journal
of Molecular Biology, 38(3):367–379.
Di Giulio, M. (1989). The extension reached by the mini-
mization of the polarity distances during the evolution
of the genetic code. Journal of Molecular Evolution,
29(4):288–293.
Di Giulio, M. (1999). The coevolution theory of the origin
of the genetic code. Journal of Molecular Evolution,
48(3):253–5.
Di Giulio, M. (2008). An extension of the coevolution the-
ory of the origin of the genetic code. Biology Direct,
3.
Di Giulio, M. (2016). The lack of foundation in the mech-
anism on which are based the physico-chemical theo-
ries for the origin of the genetic code is counterposed
to the credible and natural mechanism suggested by
the coevolution theory. Journal of Theoretical Biol-
ogy, 399:134–40.
Di Giulio, M. (2017). Some pungent arguments against the
physico-chemical theories of the origin of the genetic
code and corroborating the coevolution theory. Jour-
nal of Theoretical Biology, 414:1–4.
Di Giulio, M. (2018). A discriminative test among the dif-
ferent theories proposed to explain the origin of the
genetic code: The coevolution theory finds additional
support. Biosystems, 169:1–4.
Di Giulio, M. and Medugno, M. (1999). Physicochemical
optimization in the genetic code origin as the number
of codified amino acids increases. Journal of Molecu-
lar Evolution, 49(1):1–10.
Duch
ˆ
ene, S., Ho, S. Y., and Holmes, E. C. (2015). Declin-
ing transition/transversion ratios through time reveal
The Impact of the Transversion/Transition Ratio on the Optimal Genetic Code Graph Partition
63

limitations to the accuracy of nucleotide substitution
models. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 15(1):36.
Dudkiewicz, A., Mackiewicz, P., Nowicka, A., Kowalezuk,
M., Mackiewicz, D., Polak, N., Smolarczyk, K., Ba-
naszak, J., Dudek, M. R., and Cebrat, S. (2005). Cor-
respondence between mutation and selection pressure
and the genetic code degeneracy in the gene evolution.
Future Generation Computer Systems, 21(7):1033–
1039.
Epstein, C. J. (1966). Role of the amino-acid “code” and of
selection for conformation in the evolution of proteins.
Nature, 210(5031):25–28.
Freeland, S. J. and Hurst, L. D. (1998a). The genetic code
is one in a million. Journal of Molecular Evolution,
47(3):238–248.
Freeland, S. J. and Hurst, L. D. (1998b). Load minimiza-
tion of the genetic code: history does not explain the
pattern. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London
B: Biological Sciences, 265(1410):2111–2119.
Freeland, S. J., Knight, R. D., Landweber, L. F., and Hurst,
L. D. (2000). Early fixation of an optimal genetic
code. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 17(4):511–
518.
Freeland, S. J., Wu, T., and Keulmann, N. (2003). The
case for an error minimizing standard genetic code.
Origins of Life and Evolution of the Biosphere, 33(4-
5):457–477.
Gilis, D., Massar, S., Cerf, N. J., and Rooman, M. (2001).
Optimality of the genetic code with respect to protein
stability and amino-acid frequencies. Genome Biol-
ogy, 2(11):research0049–1.
Gojobori, T., Li, W.-H., and Graur, D. (1982). Patterns of
nucleotide substitution in pseudogenes and functional
genes. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 18(5):360–
369.
Goldberg, A. L. and Wittes, R. E. (1966). Genetic code:
aspects of organization. Science, 153(3734):420–424.
Goodarzi, H., Najafabadi, H. S., and Torabi, N. (2005).
Designing a neural network for the constraint opti-
mization of the fitness functions devised based on the
load minimization of the genetic code. Biosystems,
81(2):91–100.
Haig, D. and Hurst, L. D. (1991). A quantitative measure
of error minimization in the genetic code. Journal of
Molecular Evolution, 33(5):412–417.
Hershberg, R. and Petrov, D. A. (2008). Selection on codon
bias. Annual Review of Genetics, 42:287–299.
Khorana, H. G., B
¨
uuchi, H., Ghosh, H., Gupta, N., Jacob,
T., K
¨
ossel, H., Morgan, R., Narang, S., Ohtsuka, E.,
and Wells, R. (1966). Polynucleotide synthesis and
the genetic code. In Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on
Quantitative Biology, volume 31, pages 39–49. Cold
Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Kowalczuk, M., Mackiewicz, P., Mackiewicz, D., Nowicka,
A., Dudkiewicz, M., Dudek, M. R., and Cebrat, S.
(2001). High correlation between the turnover of nu-
cleotides under mutational pressure and the dna com-
position. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 1(1):13.
Kumar, S. (1996). Patterns of nucleotide substitution in mi-
tochondrial protein coding genes of vertebrates. Ge-
netics, 143(1):537–548.
Lee, J. R., Gharan, S. O., and Trevisan, L. (2014). Mul-
tiway spectral partitioning and higher-order cheeger
inequalities. Journal of the ACM (JACM), 61(6):37.
Levin, D. A., Peres, Y., and Wilmer, E. L. (2009). Markov
chains and mixing times. American Mathematical So-
ciety, Providence, Rhode Island.
Lynch, M. (2010). Rate, molecular spectrum, and conse-
quences of human mutation. Proceedings of the Na-
tional Academy of Sciences of the United States of
America, 107(3):961–968.
Lyons, D. M. and Lauring, A. S. (2017). Evidence for the
selective basis of transition-to-transversion substitu-
tion bias in two rna viruses. Molecular Biology and
Evolution, 34(12):3205–3215.
Mackiewicz, P., Biecek, P., Mackiewicz, D., Kiraga, J.,
Baczkowski, K., Sobczynski, M., and Cebrat, S.
(2008). Optimisation of asymmetric mutational pres-
sure and selection pressure around the universal ge-
netic code. Computational Science - ICCS 2008,
Proceedings, Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
5103:100–109.
Massey, S. E. (2008). A neutral origin for error minimiza-
tion in the genetic code. Journal of Molecular Evolu-
tion, 67(5):510–516.
Morton, B. R. (2001). Selection at the amino acid level can
influence synonymous codon usage: Implications for
the study of codon adaptation in plastid genes. Genet-
ics, 159(1):347–358.
Nirenberg, M., Caskey, T., Marshall, R., Brimacombe,
R., Kellogg, D., Doctor, B., Hatfield, D., Levin, J.,
Rottman, F., Pestka, S., et al. (1966). The rna code
and protein synthesis. In Cold Spring Harbor sym-
posia on quantitative biology, volume 31, pages 11–
24. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Novozhilov, A. S., Wolf, Y. I., and Koonin, E. V. (2007).
Evolution of the genetic code: partial optimization of
a random code for robustness to translation error in a
rugged fitness landscape. Biology Direct, 2.
Petrov, D. A. and Hartl, D. L. (1999). Patterns of nucleotide
substitution in drosophila and mammalian genomes.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of
the United States of America, 96(4):1475–1479.
Rosenberg, M. S., Subramanian, S., and Kumar, S. (2003).
Patterns of transitional mutation biases within and
among mammalian genomes. Molecular biology and
evolution, 20(6):988–993.
Santos, J. and Monteagudo,
´
A. (2011). Simulated evolution
applied to study the genetic code optimality using a
model of codon reassignments. BMC Bioinformatics,
12.
Santos, J. and Monteagudo,
´
A. (2017). Inclusion of the fit-
ness sharing technique in an evolutionary algorithm
to analyze the fitness landscape of the genetic code
adaptability. BMC Bioinformatics, 18(1):195.
Tlusty, T. (2010). A colorful origin for the genetic code: In-
formation theory, statistical mechanics and the emer-
gence of molecular codes. Physics of Life Reviews,
7(3):362–376.
BIOINFORMATICS 2019 - 10th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
64

Wakeley, J. (1996). The excess of transitions among nu-
cleotide substitutions: new methods of estimating
transition bias underscore its significance. Trends in
Ecology & Evolution, 11(4):158–162.
Wnetrzak, M., Bła
˙
zej, P., Mackiewicz, D., and Mackiewicz,
P. (2018). The optimality of the standard genetic
code assessed by an eight-objective evolutionary al-
gorithm. BMC Evolutionary Biology, in press, DOI:
10.1186/s12862-018-1304-0.
Woese, C. R. (1965). On the evolution of the genetic code.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of
the United States of America, 54(6):1546–1552.
Wong, J. T. (1975). A co-evolution theory of the genetic
code. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sci-
ences of the United States of America, 72(5):1909–12.
Wong, J. T., Ng, S. K., Mat, W. K., Hu, T., and Xue, H.
(2016). Coevolution theory of the genetic code at age
forty: Pathway to translation and synthetic life. Life
(Basel), 6(1):E12.
Wong, J. T. F. (2007). Coevolution theory of the genetic
code: A proven theory. Origins of Life and Evolution
of Biospheres, 37(4-5):403–408.
Xie, J. M. and Schultz, P. G. (2006). Innovation: A chemical
toolkit for proteins - an expanded genetic code. Nature
Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 7(10):775–782.
Zhou, T., Weems, M., and Wilke, C. O. (2009). Translation-
ally optimal codons associate with structurally sensi-
tive sites in proteins. Molecular Biology and Evolu-
tion, 26(7):1571–1580.
The Impact of the Transversion/Transition Ratio on the Optimal Genetic Code Graph Partition
65
