
A Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment Model for Dysphonia Therapy Games
Vanessa Lopes, Jo
˜
ao Magalh
˜
aes and Sofia Cavaco
NOVA LINCS, Departamento de Inform
´
atica, Faculdade de Ci
ˆ
encias e Tecnologia, Universidade Nova de Lisboa,
2829-516 Caparica, Portugal
Keywords:
Voice Disorders, Sustained Vowel Exercise, Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment Model, Maximum Phonation
Time.
Abstract:
Studies on childhood dysphonia have revealed considerable rates for voice disorders in 4 – 12 year-old chil-
dren. The sustained vowel exercise is widely used as a technique in the vocal (re)education process. However
this exercise can become tedious after a short practice. Here, we propose a novel dynamic difficulty adjust-
ment model to be used in a serious game with the sustained vowel exercise to motivate children on practicing
this exercise often. The model automatically adapts the difficulty of the challenges in response to the child’s
performance. The model is not exclusive to this game and can be used in other games for dysphonia treat-
ment. In order to measure the child’s performance, the model uses parameters that are relevant to the therapy
treatment. The proposed model is based on the flow model in order to balance the difficulty of the challenges
with the child’s skills.
1 INTRODUCTION
Many children have speech sound disorders (SSD)
that may affect not only their health, but also their
social interactions and development process (Furlong
et al., 2017b). Different types of SSD exist. Some
are related to language and speech disorders while
others are related to voice disturbances (Guimar
˜
aes,
2007). Deviations in the quality of an individual’s
voice are known as dysphonia, and can occur as a re-
sult of inappropriate vocal behavior or due to neuro-
logical, physiological or social factors, among others.
Studies on vocal analysis with children between the
ages of 2 to 12 years, report that voice disorders af-
fect from approximately 4 to 38% of children, with
hoarseness and breathy voice as the most frequent
problems (Duff et al., 2004; Oliveira et al., 2011;
Tavares et al., 2011). In some cases, voice patholo-
gies can be naturally corrected while children grow
up. In other cases the child may need to attend speech
therapy for recovery and vocal (re)education.
An important aspect of therapy is the repetition of
the exercises. Yet repeating the vocal exercises used
to correct voice problems may be monotonous and
tiring (Bowen, 2015; Eriksson et al., 2005). Thus,
speech and language pathologists (SLPs) usually try
to create more appealing sessions through the use of
several techniques, such as board games. Some SLPs
resort to PowerPoint animations or try to adapt com-
puter games that can be manually controlled: when
the child succeeds, the SLP uses the PowerPoint an-
imations or makes the game progress to motivate the
child on practicing the exercise.
In order to detect and treat dysphonia symp-
toms, SLPs commonly use the sustained vowel (SV)
exercise in therapy sessions with children (Ameri-
can Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA),
2018; El Sharkawi et al., 2002; Mota et al., 2012;
Swart et al., 2003). The goal of this exercise is to say
a vowel for as long as possible while maintaining the
voice intensity level stable. The SV exercise is widely
used in therapy sessions to evaluate the patient’s voice
quality, detect the existence of dysphonia, the sever-
ity of the pathology, as well as to complement the
treatment for dysphonia. Additionally, this exercise
is used with voice professionals like actors and jour-
nalists, who make a constant vocal effort and need to
learn how to correctly put the voice. This exercise
is also commonly used in therapy with patients with
Parkinson’s disease (El Sharkawi et al., 2002; Swart
et al., 2003).
As a contribution to improve the motivation of
children on doing the sustained vowel exercise, we
have developed the sustained vowel game, a serious
computer game for this exercise. A first simpler ver-
sion of this game was previously proposed (Lopes
et al., 2016). The new version includes several new
important characteristics that are proposed here. The
Lopes, V., Magalhães, J. and Cavaco, S.
A Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment Model for Dysphonia Therapy Games.
DOI: 10.5220/0007402901370144
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2019), pages 137-144
ISBN: 978-989-758-354-4
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
137

game’s current version includes (1) a set of different
scenarios and main characters that children can con-
trol with their voices. In this way, the game can be
interesting to children with different tastes and inter-
ests.
In order to keep the child motivated on playing
often, it is important that the difficulty of the game
adapts to the child’s performance. If the game is too
easy for the child it may become tedious, on the other
hand, if it is too difficult the child can get frustrated
for not reaching the end of the game. In other words,
if the challenge is too difficult it may cause a non-
desired effect: the child may be unmotivated to repeat
the exercise or can even reject doing it.
An important characteristic of the game, already
included in its previously proposed version, is that
it can be adjusted to each child’s needs through a
set of customizable parameters. In addition, we now
propose (2) a dynamic difficulty adjustment (DDA)
model that allows the game to meet the child’s chang-
ing needs and progress as well as capabilities so that
the child does not feel frustrated with the inability to
solve the tasks nor looses the motivation on doing the
exercise when the tasks are too easy for the child. For
that, the game automatically adapts the difficulty of
the challenge based on the child’s performance dur-
ing the previous trials. During each trial, the child’s
performance is measured based on a set of relevant
parameters in order to manage the automatic adapta-
tion of the difficulty.
In the remaining sections, we discuss related work
(section 2), a simple DDA model that depends only on
one of the parameters relevant to the SV exercise (sec-
tion 3.1) and we discuss the final DDA model used in
our game, which is a more complex model that uses
two parameters to measure the child’s performance
and decides how to increase the game’s difficulty
based on this performance measure (section 3.2).
2 RELATED WORK
Taking advantage of the current technological ad-
vances, several computer and mobile games have
been developed to complement traditional speech
therapy techniques (Eriksson et al., 2005; Furlong
et al., 2017a). Some of these games can assist SLPs
on keeping the children motivated on doing the ther-
apy exercises, such as the set of applications from
the LittleBeeSpeech (Hanks et al., 2018), Falar a
Brincar (Tavares et al., 2017) and sPeAK-MAN (Tan
et al., 2013), which focus on articulation problems, or
Flappy Voice (Lan et al., 2014) and Carvalho’s inter-
active game for training the Portuguese vowels (Car-
valho, 2008) which focus on problems like apraxia
and vowels recognition, respectively.
As different children have different needs, present
different kinds of sigmatism and with different levels
of severity, the parameterization of the games is an
important aspect of these systems. Another important
aspect to avoid that the children loose interest in play-
ing or even feel frustrated when the level of difficulty
is to high for them, is to adapt the level of difficulty
dynamically.
While a player-adaptable concept is used in some
of these systems, such as Flappy Voice, the concept
consists of a very simple approach (Hanks et al.,
2018; Lan et al., 2014; Tavares et al., 2017). Alterna-
tively, Yun et. al. proposed a methodology that auto-
matically adjusts the game difficulty using a profile-
based adaptive difficulty system (Yun et al., 2010).
They want to improve the gaming experience by using
player profiles to determine the best difficulty level to
each player. They use the players’ prior gaming ex-
perience and their preferences to create the players’
profiles. Afterwards, they use these parameters to set
the game difficulty adjustment thresholds, and they
use a performance-based algorithm to adjust the diffi-
culty settings. To do this, they transform the player’s
performance data into a point scale. If the output is
greater than the positive threshold they increase the
difficulty level. On the other hand, if the output is less
than the negative threshold they decrease the difficulty
level.
Demediuk and colleagues proposed another ap-
proach that changes the challenge level according to
the players’ performance (Demediuk et al., 2016).
They developed an adaptive training framework to
construct an opponent, whose strategies and behavior
adapt in response to the progress of the player. Their
goal is to alter the level of challenge of the opponent
according to the changes in the player’s proficiency.
There are several strategies that can be followed
in order to implement a serious game adaptability
model (Jonathan et al., 2012). These include the rub-
ber banding technique, which controls the state of the
game by varying global resources or specific exercise
variables. This technique is generally used in rac-
ing games, as the Mario Karts game (Jonathan et al.,
2012; Rietveld et al., 2015). The idea behind this
technique is based on the manipulation of the avail-
able resources in the game, so that the performance
of a player starts very limited, within a certain thresh-
old. This technique challenges the players to over-
come new tasks until they reach a maximum level,
where the resources are fully available.
In addition to this approach, the flow model tends
to be widely used (Schell, 2008). This model con-
HUCAPP 2019 - 3rd International Conference on Human Computer Interaction Theory and Applications
138

trols the resources and variables of the game accord-
ing to the player’s performance with the game plat-
form. More specifically, this control is achieved by
balancing the proposed challenge with the player’s
skills. The player is presented a repeating cycle of in-
creasing challenges, until a threshold is reached and
the player receives a reward or some new resources to
motivate him/her to keep on playing. The flow model
was defined as a generalized scheme and it is impor-
tant to understand the game variables that affect the
player’s experience in order to define how to make
the game progress.
Here we propose a dynamic difficulty adaptable
scheme that follows the principles of the flow model.
While some of the models described above may be
appropriate for the specific game to which they were
proposed, they may be inadequate for other applica-
tions. We use the proposed model in a serious game
for speech therapy, but the model is suitable for other
therapy games for voice pathologies. In this case, the
player’s experience should be maintained within the
flow channel, through the influence of the variables
relevant to therapy.
3 THE DYNAMIC DIFFICULTY
ADJUSTMENT MODEL
The SV exercise consists of producing a vowel for
as long as possible with a stable intensity level. The
phonation time achieved during the SV exercise is
an important measure of voice quality (Colton et al.,
2011). It helps evaluating the child’s ability to con-
trol the breathing while producing a sound at the re-
quested intensity level. The analysis of this variable
can be used both for assessing the individual’s aerobic
capacity and for vocal treatment, for example, for sta-
bilizing the intensity of the sound produced (Ameri-
can Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA),
2018). The repetition of the SV exercise helps chil-
dren improve their maximum phonation time (MPT)
and control their voice intensity and stability.
The proposed serious game implements the SV
exercise and is controlled by the child’s voice in real-
time (Lopes et al., 2016). The game’s goal is to make
the main character reach a target. In order to make
the main character move, the child has to produce a
sustained vowel while achieving the expected values
for the speech parameters of interest to the therapy
exercise: the phonation time and the intensity level.
The current version offers several scenarios with
child appropriate themes that aim to keep the chil-
dren interested and comfortable, so that they see the
therapy not as a hassle but as a fun and challenging
experience. Some of the scenarios are illustrated in
figure 1. As an example, in the top left scenario, the
submarine should reach the crab with the gift, and in
the bottom left scenario, the boat should reach the gift
in the island.
The proposed game allows the SLP to parameter-
ize the expected MPT, that is, the MPT that the child
should reach, and which we call MPT
e
. During the
gameplay, MPT
e
is the time that the main character
needs to move (walk, fly, swim, etc.) to reach the
game target. The game offers five different possible
values for MPT
e
: 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 seconds as the
MPT estimated for children is 10 seconds (Prater and
Swift, 1995). We use the expression MPT
e
(r) to re-
fer to MPT
e
of trial run r. The MPT achieved by the
child at trial run r is called MPT
a
(r). For simplic-
ity, we sometimes refer to these functions simply as
MPT
a
and MPT
e
.
Depending on the pathology, the child may need
to train the SV exercise with a low, medium or high
intensity. Children who usually speak very low, must
train speaking at higher intensities, whereas children
who tend to increase the volume and, as a conse-
quence, strain their vocal cords, must practice speak-
ing at softer intensities. In order to correct these be-
haviors, children can practice the SV exercise with
a low, medium or high intensity, according to their
needs.
The game allows the SLP to choose the intensity
level to be practiced from three possible values (one
value for low intensity, one for medium and another
for high intensity) (Lopes et al., 2016). We call this
the expected intensity level (or expected loudness),
L
e
.
The child may have difficulties in stabilizing at the
requested intensity and obviously, it is not expected
that the child achieves a perfectly constant intensity
level. Thus small variations in intensity should be al-
lowed and it is essential to establish the allowed vari-
ation interval. Our model uses a minimum and max-
imum threshold, L
m
and L
M
, around L
e
to define this
interval:
∆L = [L
m
,L
M
], (1)
where L
e
∈ [L
m
,L
M
]. We use the expressions ∆L(r)
and L
e
(r) to refer to the intensity level interval and
expected intensity of trial run r, but we will often drop
the variable r for simplicity.
While the game’s first version used a fixed ∆L
size (Lopes et al., 2016), we now defined three inten-
sity level intervals for ∆L, such that different difficulty
levels use different intensity interval sizes (∆L
n
=
[L
n
m
,L
n
M
] with n ∈ {1,2,3}). The lowest difficulty
level allows the widest ∆L, while the highest difficulty
level allows the narrowest ∆L.
A Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment Model for Dysphonia Therapy Games
139

Figure 1: Some scenarios in the sustained vowel game.
Table 1: Allowed intensity levels and intensity interval sizes
in dB (SPL).
intensity
level
L
e
L
1
m
L
1
M
L
2
m
L
2
M
L
3
m
L
3
m
high 85 80 90 70 100 50 100
medium 60 50 70 47.5 75 45 80
low 40 35 45 30 50 30 55
The game’s difficulty depends on MPT
e
and ∆L.
Combining the different possibilities for the values of
MPT
e
and ∆L sizes, the game offers 15 different diffi-
culty levels (for each L
e
, that is, for the low, medium
and high intensity values). Table 1 shows the possi-
ble values for L
e
and the allowed intensity intervals,
which were chosen with the help of an SLP and re-
lated work (Fox and Boliek, 2012). Note that the ex-
pression ∆L(r) = ∆L
n
means that trial run r uses the
n-th intensity level interval size.
The game’s current version offers the option of
adapting the game’s difficulty manually or automat-
ically. In the latter case, the SLP chooses the ini-
tial difficulty level (defined through an initial value
for MPT
e
and an initial ∆L ), and afterwards the game
runs an algorithm for adapting the difficulty level be-
fore each new trial, that is, the game adapts the values
of MPT
e
and ∆L dynamically. For this algorithm we
propose a new dynamic difficulty adjustment model.
The main goal of the automatic adaptiation of the dif-
ficulty is to keep the child motivated on playing.
Difficulty adjustments should take into account
the player’s performance, and the player’s perfor-
mance should be a measure of the parameters to be
improved in therapy: the maximum phonation time
and the voice’s intensity and stability. If the child
achieves the expected values for these parameters,
the child is ready to access a more demanding level,
with more ambitious expected values. Otherwise, if
the values achieved are lower than what is expected,
it means that the child had a poor performance in
the game and the challenge difficulty should be de-
creased.
Below we first discuss a simple adaptation model
that measures the child’s performance only in terms
of the MPT achieved by the child (section 3.1), and
then we discuss the proposed DDA model, which is
a more complete model that measures performance
both in terms of the achieved MPT and speech pro-
duction intensity stability (section 3.2).
3.1 Maximum Phonation Time
It is intended that during the task the child obtains
MPT
a
(r) = MPT
e
(r). If the child is not be able to
reach the expected MPT (because MPT
a
< MPT
e
),
the main character will not reach the target. If this
happens for several trials, the child can feel frus-
trated with the game. In these situations, the child’s
achieved performance is below the expected perfor-
mance. Thus, it is important to define a lower value
for MPT
e
to avoid having a frustrated child.
HUCAPP 2019 - 3rd International Conference on Human Computer Interaction Theory and Applications
140
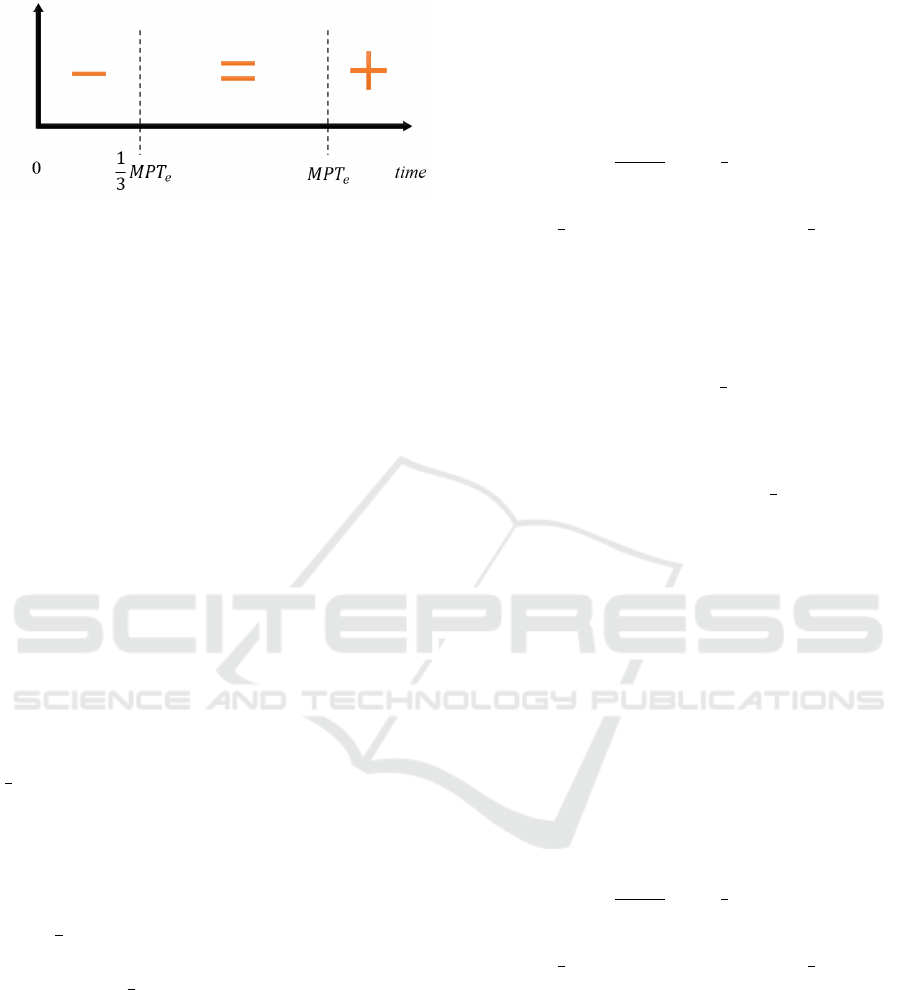
Figure 2: Scheme for updating MPT
e
. The difficulty level
should be decreased (− region), maintained (= region), or
increased (+ region).
On the other hand, if the child is achieving a positive
performance, that is, obtaining MPT
a
= MPT
e
in suc-
cessive trials, she may be ready for a higher difficulty
level, since she has already stabilized the aerobic ca-
pacity requested for the respective degree of difficulty.
It is important to define when to decrease or in-
crease MPT
e
. There are situations in which the child
achieves MPT
e
and we should not increase the ex-
pected MPT immediately. A difficulty level enhance-
ment should be difficult to achieve in order for the
child to stabilize his performance with the current de-
gree of difficulty. On the other hand, a lower level
should be easier to achieve to avoid frustration when
the level is not appropriate to the child’s ability. Also,
if the child fails once, it is not necessarily good to de-
crease MPT
e
immediately. In some cases, we should
give the child another chance and let him try again.
For instance, if the child does not reach MPT
e
but
MPT
e
− MPT
a
is small, we should let him try again.
However, if MPT
e
− MPT
a
is large, we should soon
decrease the value of MPT
e
. We use a threshold of
1
3
MPT
e
. This scheme is represented in figure 2 and
can be summarizes as follows:
1. If MPT
e
< MPT
a
we will shortly increase MPT
e
but first we let the child play a few more trials
with this M PT
e
so that the child stabilizes his per-
formance with the current MPT
e
.
2. If
1
3
MPT
e
< MPT
a
≤ MPT
e
we let the child try
again a few more trial runs before changing MPT
e
.
3. If MPT
a
≤
1
3
MPT
e
we will soon decrease MPT
e
.
The achieved MPT was much smaller than the ex-
petect MPT, which means that the exercise is too
difficult for the child with this MPT
e
value.
In order to define when and how to change MPT
e
,
we use a cumulative value that measures the time-
evolving maximum phonation time performance,
P
MPT
(r), where r represents the trial run. The value
of P
MPT
increases (that is, P
MPT
(r) > P
MPT
(r − 1))
when the child has a good performance, and de-
creases otherwise. We increase or decrease the value
of MPT
e
by 2 seconds depending on the value of
P
MPT
. P
MPT
of the current trial r is updated as
follows:
P
MPT
(r) =
P
MPT
(r − 1) + MPT
a
(r) , i f MPT
e
(r) ≤ MPT
a
(r)
P
MPT
(r − 1) −
MPT
e
(r)
MPT
a
(r)
, i f
1
3
MPT
e
(r) < MPT
a
(r)
≤ MPT
e
(r)
−
1
3
MPT
e
(r) , i f MPT
a
(r) ≤
1
3
MPT
e
(r)
(2)
with P
MPT
(0) = 0 (the initial value of P
MPT
before the
start of the first trial).
In addition to defining the function’s behavior, it
is necessary to establish the limits between which the
P
MPT
may vary before there is an update of the value
of MPT
e
. The interval ] −
1
3
MPT
e
(r), 2 MPT
e
(r)[
determines the possible variation for P
MPT
(r). Thus,
MPT
e
(r + 1) =
MPT
e
(r) − 2 , i f P
MPT
(r) ≤ −
1
3
MPT
e
(r)
∧MPT
e
(r) ≥ 4
MPT
e
(r) + 2 , i f P
MPT
(r) ≥ 2 MPT
e
(r)
∧MPT
e
(r) ≤ 8
MPT
e
(r) , otherwise
(3)
Note that when the level change is reached, the
current performance is reset, that is, it is reduced to
0. Thus, we add the following first line to equation 2:
P
MPT
(r) =
0, MPT
e
(r − 1) 6= MPT
e
(r)
∨r = 0
P
MPT
(r − 1) + MPT
a
(r) , i f MPT
e
(r) ≤ MPT
a
(r)
P
MPT
(r − 1) −
MPT
e
(r)
MPT
a
(r)
, i f
1
3
MPT
e
(r) < MPT
a
(r)
≤ MPT
e
(r)
−
1
3
MPT
e
(r) , i f MPT
a
(r) ≤
1
3
MPT
e
(r)
(4)
3.2 Speech Intensity Level
While it is important to consider the MPT
a
by the
child at trial run r to decide the value of MPT
e
of
the next trial, it is also important to consider how
the speech production intensity varies during the trial.
When the game starts, the SLP chooses an appropri-
ate expected intensity level, L
e
. While performing the
SV exercise, one must keep the intensity level as sta-
ble as possible and as close to L
e
as possible. Thus,
A Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment Model for Dysphonia Therapy Games
141
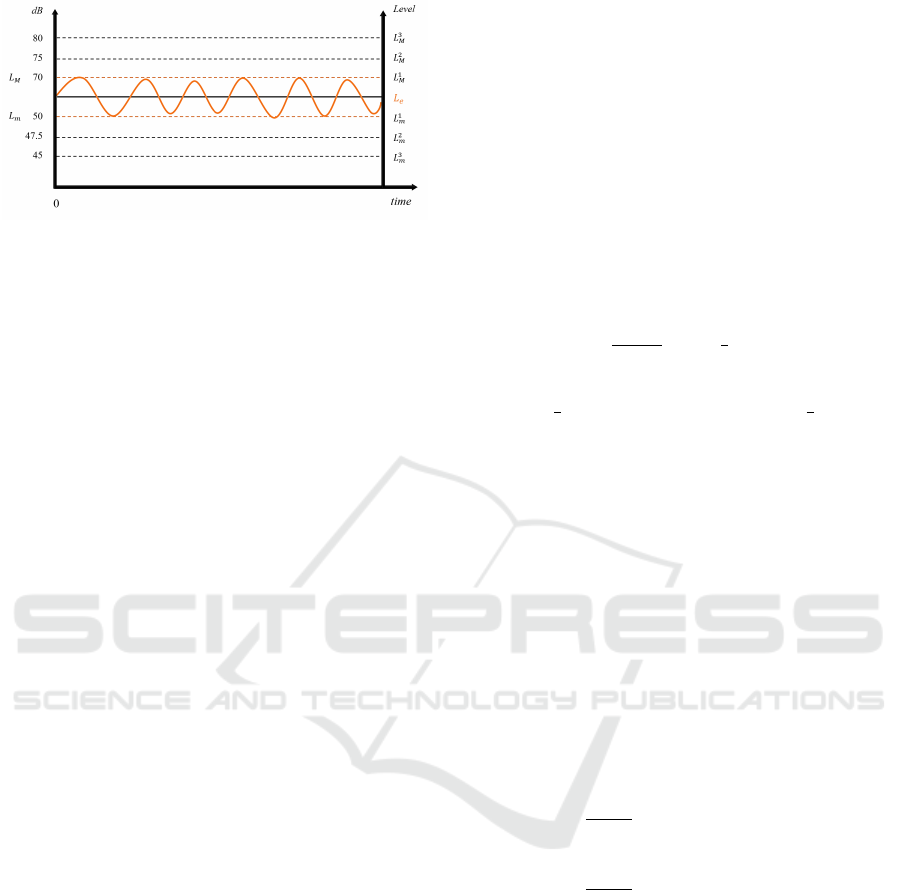
Figure 3: Allowed variation intensity level intervals, ∆L.
The figure illustrates a case with L
m
= 50 dB, L
M
= 70 dB,
and L
e
= 60 dB. The orange line illustrates the time-varying
speech intensity level achieved by the child, L
a
(t).
the sound intensity level achieved by the child, L
a
, is
one of the variables measured by our algorithm.
The intensity of the speech production, L
a
, is al-
lowed to fluctuate within the interval ∆L. The speech
intensity level achieved by the child is a time-varying
function, L
a
(t) (figure 3). During the game, the
main character moves towards the target, exclusively,
when the speech production intensities (L
a
(t
0
), L
a
(t
1
),
L
a
(t
2
), ...) are within the defined thresholds, that is,
within ∆L.
As explained above, different difficulty levels use
different intensity interval sizes ∆L. Figure 3 illus-
trates the three allowed interval sizes. The first trial
run always starts with the widest intensity interval
size, ∆L(1) = ∆L
3
.
Now let us analyze how the difficulty of the game
changes in reaction to L
a
, that is, how MPT
e
and ∆L
of the next trial are updated. Like in the previous sec-
tion, here we also measure the child’s performance
to determine when to change the game’s difficulty.
There are several situations that we must take into ac-
count. (1) If the child is able to keep L
a
within the
expected limits during the whole trial run r, that is,
if MPT
e
(r) ≤ MPT
a
(r) and L
a
(t) ∈ ∆L(r), for all t,
then the difficulty of the next trial run can increase
by reducing the size of ∆L or increasing MPT
e
. (1.1)
Let us suppose that ∆L(r) is too wide (for instance,
∆L(r) = ∆L
3
). In this case, before increasing MPT
e
for the next trial, we should reduce the size of the
intensity level interval, that is, if ∆L(r) = ∆L
n
then
∆L(r + 1) = ∆L
n−1
. (1.2) However, if ∆L(r) = ∆L
1
,
the narrowest interval size, then since the intensity in-
terval size cannot be reduced anymore, to increase the
difficulty of the next trial run, we can increase the size
of MPT
e
. (1.3) Another possibility is when we have a
wide ∆L(r) = ∆L
n
but the child achieves an intensity
variation within ∆L
n−i
, with i > 1. In this case, we
can make a bigger reduction on the size of ∆L.
On the other hand, (2) if the child registers a
variation that exceeds the limits (L
a
(t) /∈ ∆L, for a
few t), his intensity levels are not stable. Note that,
if the intensity variation is too discrepant, there is
no point in having the child trying to achieve a long
MPT and maintain or increase ∆L. It is preferable to
reduce the expected MPT and have the child learn
how to stabilize his voice for a shorter time.
P
MPT
(r) =
0, MPT
e
(r − 1) 6= MPT
e
(r)
∨r = 0
P
MPT
(r − 1) + MPT
a
(r) , i f MPT
e
(r) ≤ MPT
a
(r)
∧∀
t
L
a
(t) ∈ ∆L
1
P
MPT
(r − 1) −
MPT
e
(r)
MPT
a
(r)
, i f
1
3
MPT
e
(r) < MPT
a
(r)
≤ MPT
e
(r)
−
1
3
MPT
e
(r) , i f MPT
a
(r) ≤
1
3
MPT
e
(r)
∧ ∃
t
L
a
(t) /∈ ∆L
n+1
,n < 3
(5)
MPT
e
(r) is still defined by equation 3 but P
MPT
(r)
is now defined by equation 5. Note that there
are slight differences between the old definition of
P
MPT
(r) (equation 4) and its new definition (equa-
tion 5).
In order to decide when to update ∆L we use an-
other measure of performance that takes into account
both the achieved MPT and intensity variation. We
call this measure P
∆L
:
P
∆L
(r) =
0 i f ∆L(r − 1) 6= ∆L(r)
∨r = 0 ∨ MPT
e
(r − 1) 6= MPT
e
(r)
P
∆L
(r − 1) +
1
|∆L
a
(r)|
i f MPT
e
(r) ≤ MPT
a
(r)
∧∀
t
L
a
(t) ∈ ∆L(r)
P
∆L
(r − 1) −
|∆L
a
(r)|
|∆L(r)|
i f |∆L
a
(r)| > |∆L
n
|
where∆L(r) = ∆L
n
P
∆L
(r − 1) otherwise
(6)
where |∆L
a
| measures the achieved intensity varia-
tion. |∆L
a
| = L
amax
−L
amin
, where L
amax
≥ L
a
(t) and
L
amin
≤ L
a
(t) for every L
a
(t) in trial run r. Note that
if the difficulty level changes (because there is a re-
duction on the size of the allowed intensity interval
or in the value of MPT
e
) the performance P
∆L
is reset
to 0. The performance P
∆L
increases for situation (1)
above. On the other hand, it should decrease for sit-
uation (2) when ∆L
a
(r) exceeds ∆L
n
. Considering a
trial, where the MPT
e
increased, the ∆L(r) = ∆L
1
. If
the child experienced a bad performance during con-
secutive trials, the game should give the chance to try
HUCAPP 2019 - 3rd International Conference on Human Computer Interaction Theory and Applications
142

with the next larger ∆L. However, if the child’s per-
formance remains low, the P
MPT
decrements and the
MPT
e
will decrease.
As mentioned above, the game starts with the
widest interval size. Once the child starts to achieve
a good performance with this interval size, the in-
terval size decrements. As mentioned above, it is
possible to have big decrements on the size of ∆L
when the intensity variation achieved by the child is
much smaller than |∆L|. On the other hand, once the
child has reached the narrowest interval size (∆L
1
),
it is possible to increase the difficulty level by in-
creasing MPT
e
. If with this new value of MPT
e
the
child’s intensity variation is wider than |∆L
1
|, then
we increase the interval size a bit, to give the child
some more time to stabilize his voice for this longer
MPT. In this case, we increase the interval to ∆L
2
but
we will not increase it further than that, because the
child has already achieved a smaller interval size for
a shorter MPT. The following expression reflects how
and when to change ∆L:
∆L(r + 1) =
∆L
2
, i f ∆L(r) = ∆L
1
∧ P
∆L
(r) ≤ 0
∆L
n−i
, i f ∆L(r) = ∆L
n
∧ P
∆L
(r) >
2
|∆L(r)|
∧ n > 1
∆L(r) , otherwise
(7)
where i determines the size of the decrement on ∆L
and is defined as follows: 1 ≤ i ≤ n − 1 and i = n −n
0
where |∆L
a
| ≤ |∆L
n
0
| and (n
0
= 1 ∨|∆L
a
| > |∆L
n
0
−1
|),
with n
0
< n. For instance, if ∆L(r) = ∆L
3
and the
child is able to make a correct sound production with
|∆L
a
| ≤ |∆L
1
|, then ∆L(r + 1) can be updated to ∆L
1
.
The proposed model was developed taking into
consideration the variables in the therapy process rel-
evant for the SV exercise. In cases in which the child’s
performance is low for a specific variable, the cor-
respondent performance is decremented. Otherwise,
if the child performs the exercise correctly, the vari-
ables’ performances are positively updated.
Additionally, when the performance of a variable
reaches a lower or upper boundary, the game’s param-
eters related to that variable become easier or harder,
respectively. This was done to try avoiding that the
children’s experience moves them out of the flow
channel nor triggers a feeling of anxiety or boredom
with the gameplay experience.
4 CONCLUSION
Different children can have different levels of a spe-
cific pathology and children of different ages may
achieve different performances during their in-game
experience. Therefore, it is desirable that the therapy
games can be adjusted to each child situation. In re-
sponse to these needs, we have previously proposed
a serious game for voice pathologies that uses the
SV exercise. The previous version of this game pro-
vides the possibility of manually adapting the diffi-
culty, by allowing the SLP to choose the desired max-
imum phonation time and intensity level. Therefore,
the SLP can customize the variables thresholds, ac-
cording to the child needs.
Here we propose an automatic difficulty adjust-
ment model that evaluates the child’s performance
in real-time and adjusts the state of the game vari-
ables dynamically. This model is used in our SV
game and is suitable for games for voice pathologies.
The model relies on the basic principles of the flow
model. It measures performance based on specific
parameters of interest to speech therapy and allows
the fluctuation between tense and release moments,
keeping the child engaged to hold on playing, while
increasing her skills. This technique will allow differ-
ent children to practice therapy exercises, repetitive
and monotonous, in a motivating way that challenges
themselves. Thus, it has the potential to help the SLP
on creating a fun and relaxing environment that mo-
tivates children to practice therapy exercises repeat-
edly.
The proposed model uses the maximum phonation
time and vocal intensity to measure the player’s per-
formance. These are the most relevant variables to the
treatment of many dysphonia types. However, there
are other sound features that may be extracted, ana-
lyzed and carefully included in a future extension of
the model. The right correlation between all variables
must be ensured, as well as the evolution of an effi-
cient and enthusiastic child’s learning curve in all of
them, independently. Finally, in order to validate if
the proposed DDA model enhances the child gaming
experience and motivates the child to continue play-
ing, as future work, we will run a user test in which
children interact with the game using the proposed
model.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Portuguese Foun-
dation for Science and Technology under projects
BioVisualSpeech (CMUP-ERI/TIC/0033/2014) and
NOVA-LINCS (PEest/UID/CEC/04516/2013).
A Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment Model for Dysphonia Therapy Games
143

REFERENCES
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA)
(2018). Voice Disorders: Treatment. Retrieved from
https://www.asha.org/ in Jun/2018.
Bowen, C. (2015). Childhood apraxia of speech, page
343–350. John Wiley and Sons, L.td., 2 edition.
Carvalho, M. (2008). Interactive game for the training of
portuguese vowels. M.Sc. thesis.
Colton, R. H., Casper, J. K., and Leonard, R. (2011). Un-
derstanding voice problem: A physiological perspec-
tive for diagnosis and treatment: Fourth edition , pages
202–205.
Demediuk, S., Raffe, W. L., and Li, X. (2016). An adaptive
training framework for increasing player proficiency
in games and simulations. Proceedings of the 2016
Annual Symposium on Computer-Human Interaction
in Play Companion Extended Abstracts - CHI PLAY
Companion ’16.
Duff, M. C., Proctor, A., and Yairi, E. (2004). Prevalence
of voice disorders in African American and European
American preschoolers. Journal of Voice, 18(3):348–
353.
El Sharkawi, A., Ramig, L., Logemann, J. A., Pauloski,
B. R., Rademaker, A. W., Smith, C. H., Pawlas,
A., Baum, S., and Werner, C. (2002). Swallowing
and voice effects of Lee Silverman Voice Treatment
(LSVT
R
): A pilot study. Journal of Neurology Neu-
rosurgery and Psychiatry, 72(1):31–36.
Eriksson, E., Balter, O., Engwall, O., Oster, A.-M., and
Kjellstrom, H. (2005). Design recommendations for a
computer-based speech training system based on end-
user interviews. 2005 (SPECOM).
Fox, C. M. and Boliek, C. A. (2012). Intensive Voice Treat-
ment (LSVT LOUD) for Children With Spastic Cere-
bral Palsy and Dysarthria. Journal of Speech Lan-
guage and Hearing Research, 55(3):930.
Furlong, L., Erickson, S., and Morris, M. E. (2017a).
Computer-based speech therapy for childhood speech
sound disorders. Journal of Communication Disor-
ders, 68:50–69.
Furlong, L., Erickson, S., and Morris, M. E. (2017b). Re-
view: Computer-based speech therapy for childhood
speech sound disorders. Journal of Communication
Disorders, 68:50 – 69.
Guimar
˜
aes, I. (2007). A ci
ˆ
encia e a arte da voz humana.
ESSA, 1 edition.
Hanks, H., Hanks, C., and Suman, M. (2018). Little Bee
Speech. Retrieved from http://littlebeespeech.com/ in
Dec/2018.
Jonathan, T., Bruno, B., and Abdenour, B. (2012). Under-
standing and implementing adaptive difficulty adjust-
ment in video games. In Algorithmic and Architec-
tural Gaming Design: Implementation and Develop-
ment, chapter 5, pages 82–106.
Lan, T., Aryal, S., Ahmed, B., Ballard, K., Gutierrez-
Osuna, R., Gutierez-osuna, R., and Texas, A. (2014).
Flappy Voice: An Interactive Game for Childhood
Apraxia of Speech Therapy. Proceedings of the
First ACM SIGCHI Annual Symposium on Computer-
human Interaction in Play, 2(1):429–430.
Lopes, M., Magalh
˜
aes, J., and Cavaco, S. (2016). A voice-
controlled serious game for the sustained vowel exer-
cise. In Proceedings of the 13th International Confer-
ence on Advances in Computer Entertainment Tech-
nology, ACE ’16, pages 32:1–32:6, New York, NY,
USA. ACM.
Mota, L., Santos, C., Vasconcelos, J., Mota, B., and Mota,
H. (2012). Applying the technique of sustained maxi-
mum phonation time in a female patient with adductor
spasmodic dysphonia: a case report. Revista da So-
ciedade Brasileira de Fonoaudiologia, 17:351 – 356.
Oliveira, R., Teixeira, L., Gama, A. C., and de Medeiros,
A. (2011). An
´
alise perceptivo-auditiva, ac
´
ustica e
autopercepc¸
˜
ao vocal em crianc¸as. Jornal da So-
ciedade Brasileira de Fonoaudiologia, 23(2):158–
163.
Prater, R. J. and Swift, R. (1995). Manual de Terapeutica
de la voz. Masson-Litle, Brown.
Rietveld, A., Bakkes, S., and Roijers, D. (2015). Circuit-
adaptive challenge balancing in racing games. In Con-
ference Proceedings - 2014 IEEE Games, Media, En-
tertainment Conference, IEEE GEM 2014.
Schell, J. (2008). The Art of Game Design: A Book of
Lenses. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., San Fran-
cisco, CA, USA.
Swart, B. J. D., Willemse, S. C., Maassen, B., and Horstink,
M. W. (2003). Improvement of voicing in patients
with parkinsons disease by speech therapy. Neurol-
ogy, 60(3):498–500.
Tan, C. T., Johnston, A., Ballard, K., Ferguson, S., and
Perera-Schulz, D. (2013). {sPeAK-MAN:} towards
popular gameplay for speech therapy. In Proceedings
of The 9th Australasian Conference on Interactive En-
tertainment: Matters of Life and Death, page 28.
Tavares, E. L. M., Brasolotto, A., Santana, M. F., Padovan,
C. A., and Martins, R. H. G. (2011). Epidemiological
study of dysphonia in 4-12 year-old children. Brazil-
ian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, 77(6):736–746.
Tavares, J., Lopes, J., Cunha, M., and Saldanha,
R. (2017). Falar a Brincar. Retrieved from
https://falarabrincar.wordpress.com in Sep/2017.
Yun, C., Trevino, P., Holtkamp, W., and Deng, Z. (2010).
PADS: Enhancing Gaming Experience Using Profile-
Based Adaptive Difficulty System. In Proceedings of
the 5th ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Video Games
- Sandbox ’10, pages 31–36.
HUCAPP 2019 - 3rd International Conference on Human Computer Interaction Theory and Applications
144
