
Character Motion in Function Space
Innfarn Yoo
1,2
, Marek Fi
ˇ
ser
2
, Kaimo Hu
2
and Bedrich Benes
2
1
Nvidia, Inc, U.S.A.
2
Purdue University, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Character Motion, Functional Principal Component Analysis, Orthonormal Basis Functions.
Abstract:
We address the problem of animated character motion representation and approximation by introducing a
novel form of motion expression in a function space. For a given set of motions, our method extracts a
set of orthonormal basis (ONB) functions. Each motion is then expressed as a vector in the ONB space or
approximated by a subset of the ONB functions. Inspired by the static PCA, our approach works with the
time-varying functions. The set of ONB functions is extracted from the input motions by using functional
principal component analysis (FPCA) and it has an optimal coverage of the input motions for the given input
set. We show the applications of the novel compact representation by providing a motion distance metric,
motion synthesis algorithm, and a motion level of detail. Not only we can represent a motion by using the
ONB; a new motion can be synthesized by optimizing connectivity of reconstructed motion functions, or by
interpolating motion vectors. The quality of the approximation of the reconstructed motion can be set by
defining a number of ONB functions, and this property is also used to level of detail. Our representation
provides compression of the motion. Although we need to store the generated ONB that are unique for each
set of input motions, we show that the compression factor of our representation is higher than for commonly
used analytic function methods. Moreover, our approach also provides lower distortion rate.
1 INTRODUCTION
Articulated character motion editing, capturing,
searching, and synthesizing present important chal-
lenges in computer animation. On one hand, the
amount of produced motion data grows rapidly which
further exacerbates these challenges. On the other
hand, despite the enormous progress in this field, the
existing methods still have limitations. Among them
the compact motion representation is one underlying
common problem. The motion data is usually stored
in its raw form as rotations and positions of the joints
(or velocities and accelerations) that is space consum-
ing and difficult to process. One of the promising ap-
proaches is encoding the motion data by using ana-
lytic basis functions (e.g., Fourier, Legendre polyno-
mials, or spherical harmonics). These representations
compress the input data, but they may introduce un-
wanted artifacts such as oscillations, and may require
high number of basis functions to capture all details.
Moreover, synthesizing new motions from those rep-
resentations is difficult.
A body of previous work addresses the problem of
motion synthesis. One class of methods uses motion
graphs for representing motion connectivity and syn-
thesizing new motions (Kovar et al., 2002a; Safonova
and Hodgins, 2007; Lee et al., 2010; Min and Chai,
2012). Functional analysis has been applied for en-
coding and searching motions (Unuma et al., 1995;
Ormoneit et al., 2005; Chao et al., 2012). Statisti-
cal approaches extract probabilities motion data with
the aim of low dimensional expression, predicting
smoothly connected motions (Ikemoto et al., 2009;
Lau et al., 2009; Wei et al., 2011; Levine et al., 2012),
and using physics-based representations to generate
new motions by simulation (Mordatch et al., 2010;
Wei et al., 2011). Although these methods are well-
suited for their particular area, they usually require
either a large amount of data to represent the motion,
or substantial effort for new motion synthesis.
Our work is motivated by advances in functional
data analysis and modeling in mathematics and statis-
tics (Ramsay and Silverman, 2006; Yao et al., 2005;
Coffey et al., 2011; Du et al., 2016). The key obser-
vation of our work is that for a given set of input mo-
tions, we can extract an optimal set of orthonormal
basis functions. While analytic basis functions have
been used for encoding motions, ours extracted ONB
functions are tailored for the given set of input mo-
tions and they are optimal in the sense that they pro-
110
Yoo, I., Fišer, M., Hu, K. and Benes, B.
Character Motion in Function Space.
DOI: 10.5220/0007456401100121
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2019), pages 110-121
ISBN: 978-989-758-354-4
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Multi‐dimensional
FunctionSpace
Optimal
Function
Space
Optimal
Function
Space
…
SynthesisSynthesis
Figure 1: A set of raw motion data (left) is used to find orthonormal basis functions by functional principal component analysis
(FPCA). Each input motion is encoded as a motion vector in the function space (center). While the novel representation
provides compression of the input data, the motion vectors synthesize new motions by interpolating their coordinates (right).
vide the best coverage for the range of the provided
input motions. Each input motion is then simply rep-
resented by its coordinates as a motion vector in the
ONB function inner-product space or approximated
by using a subset of ONB functions.
The input to our framework is a set of unlabeled
raw motion data of articulated characters, from mo-
tion capturing databases, hand-made animation, or re-
sults of physics-based simulation. In the first step we
extract the ONB functions for the input set by using
functional principal component analysis (FPCA) and
represent each input motion as a motion vector in the
ONB space just by its coordinates. This compresses
the input data and converts it into a compact repre-
sentation. The vector representation of motions al-
lows for continuous (linear, or higher order) interpo-
lation in the inner-product space formed by the ONB
functions. We can synthesize a new motion sim-
ply by selecting two points in the ONB space, and
by interpolating between a successions of the closest
points between the two motions. However, for some
motions a simple interpolation might not be suitable
because they are dissimilar or far from each other.
For this case, we have adopted the connectivity op-
timization from Kovar et al. (2002a) to work for mo-
tion vectors in the ONB. In addition, this representa-
tion allows for the measure of distance between mo-
tions and it provides a compression of motion data.
Although we need to store the generated ONB that
are unique for input motions, the compression fac-
tor is higher than the commonly used analytic func-
tion methods. We claim the following contributions:
1) a novel representation of motions by extracting op-
timal orthonormal basis functions, 2) compact repre-
sentation of motions by encoding motions as motion
vectors into function space, 2) scalable motion recon-
struction so that can be used for level-of-detail (LOD),
and 4) motion synthesis via interpolation and partial
connectivity optimization in function domain.
2 PREVIOUS WORK
Function Analysis of Motion. The idea of repre-
senting motion in some other domain is rather old.
For example, the Fourier transform has been used fre-
quently in signal processing. Unuma et al. (1995) ap-
ply the Fourier transform to analyze, extract, and syn-
thesize motions by comparing existing motion data.
Ormoneit et al. (2005) detect cyclic behavior of hu-
man motions using function analysis and extract func-
tional principal components in the Fourier domain to
remove high frequency components. Similarly, Chao
et al. (2012) use spherical harmonic (SH) basis for
compressing and encoding motion trajectories. They
also retrieved similar motions by encoding and com-
paring user’s trajectory sketches. Coffey et al. (2011)
used PCA to analyze human motion data, but they did
not provide a way of synthesizing new ones. Du et
al. (2016) used scaled FPCA to adapt different types
of motion for character animation in gaming.
Our method does not use analytic orthonormal ba-
sis (ONB) functions, but we extract ad hoc ONB func-
tions from existing motion data. Our extracted ONB
functions are guaranteed to be optimal in a sense that
we can determine the error threshold and minimize
the error based on the number of ONB functions.
Motion Graphs. Kovar et al. (2002a) provide a
new distance metric of keyframes and introduce a
graph structure, called motion graphs, for motion
keyframes’ connectivity. Synthesizing a new motion
can be done by following a path in the graphs. Their
work extends in many directions. Lai et al (2005) use
motion graphs for small crowds by simulation and
constraints. Heck and Gleicher (2007) find suitable
transitions of their parameterized motion space using
sampling methods. Reitsma and Pollard (2007) pro-
vide a task-based quality measure, such as different
types of motions, navigation ability, and embedding
additional data. Searching optimal interpolation path
Character Motion in Function Space
111

is researched in Safonova and Hodgins (2007). Beau-
doin et al. (2008) provide grouping of similar mo-
tions and construct a motif graph that allows search-
ing and constructing new motions. Zhao and Sa-
fonova (2009) improve the connectivity by construct-
ing well-connected motion graphs using interpolated
keyframes. Lee et al. (2010) show a novel method,
called motion fields, for interactively controlling lo-
comotion by introducing a new distance measure of
motions, which is combined with keyframe similarity
and velocity. Recently, Min and Chai (2012) com-
bined semantic information with motion graphs to
synthesize a new motion from simple sentences.
Our method represents motions as motion vectors
in an ONB function space and it allows for compact
motion representation and provides a distance met-
ric preservation. Also, an interpolation between any
two motions can be done by a simple vector interpola-
tion. We also generalize the optimization from motion
graphs for the ONB space.
Motion Clustering. Kovar et al. (2002a) generate
graph structures of motion data by calculating geo-
metric distances of motion keyframes. The motion
graphs were later extended in many ways, such as
by using different parametrization Kovar and Gle-
icher (2004); Heck and Gleicher (2007), they were
combined with clustering Beaudoin et al. (2008),
their connectivity was improved Zhao and Safonova
(2009), and optimal search was suggested Safonova
and Hodgins (2007), and their evaluations was in-
troduced in Reitsma and Pollard (2007). Barbi
ˇ
c et
al. (2004) show three different approaches based on
PCA and Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) for au-
tomatic segmentation of motion captured data. Our
method provides naturally defined distance metric in
function space that allows for an easy calculation of
similarity of motions and clustering.
Motion Dimensionality Reduction. Mordatch et
al. (2010) developed a method that can perform user-
specified tasks by using Gaussian processes (GP) and
learning motions in reduced low-dimensional space.
Zhou and De la Torre (2012) extend the DTW method
by introducing Generalized Time Warping (GTW)
that overcomes DTW drawbacks for human motion
data. Ikemoto et al. (2009) exploit generalizations
of GP for motion data so that it allows users to edit
motion easily. Arikan suggested a motion compres-
sion method that is based on clustered principal com-
ponent analysis (CPCA) in Arikan (2006). Liu and
McMillan (2006) applied segmentation and PCA for
motion, and compressed the motion data. In addi-
tion, Tournier et al. (2009) provided a novel princi-
pal geodesic analysis (PGA), and achieved high com-
pression ratio. Although those PCA-based method
or dimensionality reduction methods studied in many
directions, there are several differences between our
method and the previous approaches. Our method
provides several additional properties such as motion
distance metric, level-of-detail, and fast reconstruc-
tion. Moreover, we interpret motions as a set of con-
tinuous functions so that it provides mathematically
well-defined distance in function space. Also, our
method does not perform dimensionality reduction
and it allows for an easy motion synthesis by motion
vector interpolation or optimization.
3 OVERVIEW
Figure 2 shows an overview of our method that con-
sists of two parts: 1) function motion space construc-
tion and 1) motion synthesis. The input is a set of
input motions. During the first step, we extract or-
thonormal basis functions (ONB) and represent (ap-
proximate if we do not use all ONB) each input mo-
tion as a motion vector that form a function motion
space. In the second phase, the motion vectors are
used to synthesize new motions.
The input character motion data stores positions
and rotations of joints and the data can originate from
motion capturing, physics-based animation, manual
creation, or similar. In the first step we generate the
ONB by using functional principal component analy-
sis (FPCA) for all motions. Then, we obtain the co-
ordinates of each input motion in the ONB space. We
call the ONB encoded motions motion vectors, be-
cause they are represented only by their coordinates
in the corresponding ONB, and we call the set of en-
coded motions in the ONB the function motion space.
The resulting ONB and motion vectors are smaller
than the input data providing a compressed and com-
pact representation of the motions. Moreover, the
ONB representation allows for an easy motion syn-
thesis for each pair of vectors by simply interpolating
their coordinates. It is important to note that the ONB
form a space with a distance metric. We can therefore
measure the distance of two motions.
During the motion synthesis, the user defines the
start and the end of the motion by selecting two points
in the function motion space. The new motion can
be generated by interpolation, a process that is suit-
able for two closely positioned motions. If the points
are far from each other, we automatically traverse the
space and find the shortest path between the closest
motion vectors, effectively combining the animations
together from the closest possible candidates. Using
a subset of the OBN or points that are too far can re-
sult in the combination of two motions that is not vi-
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
112

FunctionMotionSpaceConstruction
Input
Motion
Database
FunctionalPrincipal
ComponentAnalysis
OrthonormalBasis
Functions
and
MotionVectors
Dynamic
TimeWarping
MotionSynthesis
Motion
Vectors
Selection
Motion
Interpolation
andOptimization
Synthesized
Motion
Time
Unwarping
Foot‐skating
Cleanup
Figure 2: An input set of motions is analyzed and an orthonormal basis is found by using functional principal component
analysis. The input motions are then encoded as a set of motion vectors in the ONB forming a function motion space. Novel
motion can be synthesized by interpolating through existing motion vectors or by optimization directly in the ONB.
sually plausible and introduce e.g., foot skating. In
this case we apply motion optimization from (Kovar
et al., 2002a) that has been modified and adapted to
work directly in the ONB.
4 ORTHONORMAL BASIS
FUNCTIONS AND MOTION
VECTORS EXTRACTION
The key idea of our approach is that an animated
character motion m(t) (see Section 5.3) can be rep-
resented as a vector with an optimal number of or-
thonormal basis function. Although, the idea of rep-
resenting motion data by using basis function has
been already used in computer graphics, previous ap-
proaches use given fixed (analytic) basis functions
such as Fourier (e.g., Unuma et al. (1995)) or Spheri-
cal Harmonics (e.g., Chao et al. (2012)). Those func-
tions attempt to cover all possible motions by a set
of a priori given analytic basis functions. Not only
this representation is not optimal for a given input set,
but also the analytic basis functions may need a large
number of coefficients to reduce oscillation of recon-
structed curves or to capture fine details.
We use basis functions that are extracted from (a
group of) input motions. We use functional principal
component analysis (FPCA) to extract our basis that
covers the important motions in decreasing order. It
also provides the best coverage of the space by the
set of functions (see (Ramsay and Silverman, 2006;
Yao et al., 2005) for details of FPCA). In this section
we introduce the orthonormal function basis extrac-
tion and show how it is applied to motion encoding.
The function representation
e
f (t) is an approxima-
tion of a function f (t) and is expressed as
e
f (t) = µ(t) +
n
∑
i=0
c
i
b
i
(t), (1)
where µ(t) is the mean function represent-
ing the average of the analyzed functions,
B = {b
0
(t), b
1
(t), ...,b
n
(t)} is the ONB, and
(c
0
,c
1
,...,c
n
) are the coordinates of
e
f (t) in the
inner-product function space.
The error E(t) of the approximation is
E(t) = k f −
e
f k =
Z
t
b
t
a
| f (s) −
e
f (s)|
2
ds
1/2
. (2)
Having two ONB functions (motion vectors)
e
f
1
(t) = µ(t) +
n
∑
i=1
c
1i
b
i
(t)
e
f
2
(t) = µ(t) +
n
∑
i=1
c
2i
b
i
(t),
the distance D(
e
f
1
(t),
e
f
2
(t)) between them in the ONB
is calculated as the distance between two functions in
the given inner-product space (see 8):
D(
e
f
1
(t),
e
f
2
(t)) =
Z
t
b
t
a
e
f
1
(s) −
e
f
2
(s)
2
ds
1/2
=
=
n
∑
i=1
(c
1i
−c
2i
)
2
hb
i
,b
i
i
1/2
=
n
∑
i=1
(c
1i
−c
2i
)
2
1/2
.
(3)
4.1 ONB Extraction using FPCA
The input to the ONB extraction is a set of K input
functions f
k
(t), k = 1,2,. ..,K. The f
k
(t) are time-
aligned components of the motion.We discretize func-
tions, f
i
(t
j
) to Y
i j
with equally spaced time steps
Y
i j
= f
i
(t
j
) + ε
i j
, (4)
where ε
i j
is the measurement error per data point
(e.g., the error caused by motion capture).
The output of the ONB extraction is the set of
ONB functions b
i
(t) and the mean component
µ(t) =
1
K
K
∑
k=1
f
k
(t), ˆµ(t
i j
) =
1
K
K
∑
i=1
Y
i j
. (5)
One of the important methods to extract orthonor-
mal basis in spatial domain is principal component
analysis (PCA) which maximizes space coverage for
a given number of basis function. Similarly, func-
tional principal component analysis (FPCA) (Ram-
say and Silverman, 2006) extracts ONB functions that
approximate the given set of functions. The FPCA
extract eigenfunctions that have maximal coverage
Character Motion in Function Space
113

of f
k
(t) and they are orthonormal to other eigenfunc-
tions in decreasing order of importance.
The FPCA uses the covariance function v(s,t)
v(s,t) =
1
n
n
∑
k=1
f
k
(s) f
k
(t).
To find the basis b
i
(t), we find Fredholm function
eigenequation that satisfies
Z
v(s,t)b
i
(t)dt = ρb
i
(s) (6)
subject to hb
i
,b
j
i = δ
i j
,
where δ
i j
is the Kronecker delta, ρ is an eigenvalue of
the principal component, the orthonormal basis b
i
(t)
is an eigenfunction, and the function inner-product
h f ,gi of two functions f (t) and g(t) is
h f
i
, f
j
i =
Z
t
b
t
a
f
i
(s) f
j
(s)ds, (7)
where t
0
≤ t
a
< t
b
≤ t
m
. The raw covariances are cal-
culated as
v
i
(t
i j
,t
il
) = (Y
i j
− ˆµ(t
i j
))(Y
i j
− ˆµ(t
il
)),i 6= j
and the estimation v(s,t) is
˜v(s,t) =
1
n
n
∑
i=1
v
i
(s,t) =
∑
λ
k
>0
ˆ
λ
k
ˆ
b
k
(s)
ˆ
b
k
(t) (8)
where
ˆ
λ is the estimated eigenvector, and
ˆ
b
k
is the es-
timated eigenfunction. Since E(e
i j
) = 0 and the vari-
ance of error is
Var(e) = σ
2
I,
the approximation of σ
2
can be estimated by
ˆ
σ
2
=
2
τ
Z
τ
(
ˆ
V (t) − ˜v(t,t))dt, (9)
where
ˆ
V (t) is smoothed diagonal elements of ˜v
i
. The
eigenfunctions b
k
can be obtained by
b
k
=
ˆ
λ
k
ˆ
b
k
ˆ
Σ
−1
Y
i
(Y
i
− ˆµ),
where
ˆ
Σ
Y
i
= ˜v +
ˆ
σ
2
I.
Each eigenfunction b
i
(t) provides some coverage
of the input and the algorithm is executed until the the
average length of the residuals of the input is under
user-defined percentage. This indirectly controls the
actual number of the ONB functions.
4.2 Coordinates in the ONB Function
Space
Having extracted the ONB b
i
(t) from f
k
(t), we can
represent each input function f
k
(t) in this space as
˜
f
k
(t) with its coordinates (c
0
,c
1
,...,c
n
) (see Eqn (1)).
The coordinates (c
0
,c
1
,...,c
n
) are found by
c
j
= h f
i
,b
j
i =
Z
t
b
t
a
f
i
(s)b
j
(s)ds, (10)
where b
1
(t), b
2
(t), ...,b
n
(t) are the ONB functions.
The coordinates (c
0
,c
1
,...,c
n
) are the coefficients
that are the best approximation in the space formed
by the given ONB functions.
The ONB functions form a Hilbert space that has
vector space characteristics such as distance measure
and triangle inequality. A motion can be represented
as a linear combination of coefficients (coordinates)
with ONB functions. Transition between two motions
is achieved by interpolating two motion vectors and
reconstructing the result back to the original motion
space. In addition, because of the nature of principal
component analysis, the order of orthonormal basis is
also the order of importance of the orthonormal axis.
5 CHARACTER MOTION
REPRESENTED AS
ORTHONORMAL BASIS
FUNCTIONS
We have shown how a function can be represented
by its coordinates in a function ONB space Eqn (1).
Moreover, we assumed there is a set of input func-
tions f
k
(t). From this input we extracted the ONB
b
i
(t) and each motion f
k
(t) is then represented (ap-
proximated) as
˜
f
k
(t) by its coordinates c
i
. In this sec-
tion we show how a character motion can be repre-
sented by using ONB function representation.
5.1 Skeleton and Motion
Representation
The input of our framework is an animated character
and we use notation from Lee and Shin (1999). The
articulated character is a skeleton hierarchy structure
(Figure 4) represented as a directed graph X = (J, E),
where J = { j
0
, j
1
,..., j
|J|
} are the joints (we use 31
joints in our experiments) and E = {e
0
,e
1
,...,e
|E|
} is
a set of joint-index pairs. The root node of the hierar-
chy is denoted by j
0
and corresponds to the pelvis of
the character.
The articulated character motion is represented as
a set of translations of the root j
0
and the rotations of
each joint over time span t
0
,t
1
,...,t
m
where m + 1 is
the number of the input motion poses. Although the
input is a set of discrete poses, we consider it a con-
tinuous function. The velocity of the root is denoted
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
114

,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,⋯,
,
,
,
Re‐ordering&FPCA
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,⋯,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,⋯,
,
,
,
⋮ ⋮⋮⋮⋮⋮⋮⋮ ⋮⋮⋮⋮ ⋮⋮⋮⋮
Eigenfunctions(ONBfunctions) MotionVectors
Figure 3: Per component ONB is extracted for different components of the input motion data.
𝑗
0
Root
𝑗
28
Right hand
𝑗
21
Left hand
𝑗
4
Left foot
𝑗
9
Right foot
𝑞
21
𝑡
Left hand joint rotation
𝑝 𝑡
root motion
Figure 4: Skeleton and joint curves labeling.
by ~v(t) and the rotation of each joint is q
j
(t). The
rotations of the joints are quaternions. The character
motion is a set
m(t) = {
~
v(t), q
1
(t), ...,q
n
(t)}, (11)
where ~v is the velocity vector of root position (with-
out initial yaw rotation) and q
j
(t) is the rotation of
joint j at the time t in the local coordinate system of
the skeleton. The world coordinates of the joint are
calculated by recursively traversing the skeleton from
the root j
0
and concatenating the corresponding rota-
tions and translations.
5.2 Dynamic Time Warping
Although two input motions are similar, they may
have different speed (time-scale). To solve the issue,
we first calculate dynamic time warping (DTW)
input motions before extracting motion vectors and
ONB functions. We adopt the distance function be-
tween two keyframes by following (Lee et al., 2010)
d(m, m
0
) =
v
u
u
u
u
u
u
u
t
β
root
kv
root
− v
0
root
k
2
+
β
0
kq
0
( ˆu) −q
0
0
( ˆu)k
2
+
Σ
n
i=1
β
i
kp
i
( ˆu) − p
0
i
( ˆu)k
2
+
Σ
n
i=1
β
i
k(q
i
p
i
)( ˆu)−(q
0
i
p
0
i
)( ˆu)k
2
,
(12)
where p is a positional unit quaternion, q is a unit
quaternion of a joint’s velocity, v is velocity vector
(see Eqn 13), β
i
is a weight of a joint, and p( ˆu) and
q( ˆu) mean rotation of arbitrary vector, ˆu. We use the
same weights for β
i
as in (Lee et al., 2010). In par-
ticular, we set the weight of the hip β
0
= 0.5 and
others β
i
,i = 1, ... ,k are set to the length of the cor-
responding bone lengths. The hip joint is the root
of skeleton hierarchy and it is important for overall
movement of the skeleton, so it has higher weight.
The velocity v of a pose can be calculated as
v = x
0
x = (v
root
,q
0
,q
1
,...,q
n
)
= (x
0
root
− x
root
, p
0
0
p
−1
0
, p
0
1
p
−1
1
,..., p
0
n
p
−1
n
).
(13)
Based on the above keyframe distance, a DTW texture
is calculated for each pair of motions by accumulating
minimum distance as shown in Figure 6. The time
warping (time pairs from one to another) follows the
minimum distances in the given DTW texture. The
DTW improve the quality of FPCA and reduce the
number of basis functions (see Table 1).
Table 1: Error and Variance of FPCA result before and after
DTW (with precision of 0.9999). The DTW reduces the
error and the number of basis functions.
Avg Error Var. # of Basis Func
Before
DTW 0.003176 0.000079 10
After
DTW 0.002338 0.000088 6
Character Motion in Function Space
115

5.3 Motion as ONB
Let’s recall that the motion Eqn (11) has velocity of
the root ~v(t) and motion of each joint q
j
(t). The
components of ~v(t) = (~x(t),~y(t),~z(t)) and q
j
(t) =
(w
j
(t), x
j
(t), y
j
(t), z
j
(t)) are used in the function anal-
ysis (Section 4) as 1D functions. Let’s denote f (t)
and g(t) as 1D functions corresponding to any pair
of the above-described components of motion. In the
following text we will not use the parameter t when-
ever it is clear from the context.
a)
b)
Figure 5: Closely matched motions that were calculated by
our approximated motion distance (Eqn 14): a) two soccer
kicking motions (0.022) and b) different walking motions
(0.007).
The ONB extraction needs a set of input functions.
We can construct the ONB for all motions by tak-
ing all components and running the algorithm from
Section 4. Let’s recall that the ONB generation is
executed until 0.999999 of variance is covered that
also defines the number of basis functions. Without
loss of generality we group motions as shown in Fig-
ure 3. For example, all components of root velocity~v,
and joints’ quaternions q
i
, are merged and then ONB
functions are extracted.
To calculate the distance between two motion
vectors, we account for the importance of joints in
motion distance calculation by associated weights
of each joint and we use the approach of Tang et
al. (2008) who defined the joint weights. Let’s have
two motion vectors v
1
= {c
11
,c
12
,...,c
1m
} and v
2
=
{c
21
,c
22
,...,c
2m
}. We use a modified distance equa-
tion that accounts for the above-mentioned weighting:
e
D(
e
f
1
(t),
e
f
2
(t)) ≈
n
∑
i=1
w
2
i
(c
1i
− c
2i
)
2
1/2
, (14)
where w
i
is the weights of joints. Fig 5 shows exam-
ples of closely matched two motion sequences.
We experimented with three different ways of
combining functions for processing FPCA: a) per
component, b) per joint and per component, and c) all
functions together. As intuitively expected, collecting
Table 2: Average error, variance, and the required number
of basis functions for different configuration. Comparison
of three different ways of FPCA processing: 1) per compo-
nent (velocities x, y, z and quaternion w, x, y, z), 2) per joint
and per component (velocity x, y, z, and per joint quaternion
w, x, y, z), and 3) all together.
Avg Error Variance # of Basis
Per
Component 0.002525 0.000093 114
Per Joint
Component 0.002140 0.000051 2032
All Together 0.002255 0.000084 23
functions per joint and per component provides best
quality (i.e., lowest error and lowest variance). How-
ever, the overall number of basis functions was too
high and it will lower the compression ratio. As a re-
sult, we combine all functions together and run FPCA
to extract ONB functions. It provides comparable er-
ror, but much smaller number of basis functions as
can be seen in Table 2.
We measured different sizes of ONBs in various
configurations. Our experimentations show that there
is no significant difference if the motions are clustered
together in different ways, although a better insight
could be obtained by a careful evaluation.
6 MOTION SYNTHESIS USING
ONB
One advantage of the ONB representation is the in-
trinsic compression. Another advantage is the ease of
novel motion synthesis.
6.1 Motion Interpolation
Simple motion synthesis can be achieved by interpo-
lating two or more motion vectors, and then recon-
structing their spatial functions by using Eqn (1). This
corresponds exactly to a time step interpolation of the
original motions in the time domain, but it is achieved
in a very compact way simply as an interpolation of
the coordinates of motion vectors.
Let’s recall that the distance of motion vectors
is calculated by using Eqn (3). When n motions
are close enough, the interpolation and reconstruc-
tion create smooth motion transition between them.
In order to provide smooth interpolation of input mo-
tions, we calculate k nearest neighbors for each mo-
tion, and then provide the option to interpolate them.
If the points are close enough so that they belong to k
nearest neighbors, we apply B
´
ezier interpolation that
is suitable for short motion clip. In order to create
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
116

a) b)
Figure 6: A keyframe distance table is calculated by using Eqn 12. Then, minimum cost connectivity (time pairs) is calculated
by finding local minimum lines from the DTW texture.
longer sequences of motion, we need to connect the
motions by finding a partial connectivity of motion
clips.
6.2 Partial Similarity by Optimization
Some vectors can be too far to create a perceptually
good result. We compensate for this problem by op-
timization between the time sliding. We optimize
the objective function Eqn (15) that attempts to find
scaling and sliding of time u and v from given inter-
val [t
c
,t
d
] of two motions
argmin
u,v
N
∑
j=1
w
2
j
Z
t
d
t
c
e
f
1
(us + v) −
e
f
2
(s)
2
ds =
argmin
u,v
N
∑
j=1
w
2
j
Z
t
d
t
c
M(s) + A(s)
2
ds,
(15)
where N is the number of functions, M(s) = µ(us +
v) − µ(s), and A(s) =
∑
n
i=1
c
1i
b
i
(us + v) − c
2i
b
i
(s).
The resulting parameters u and v are the scaling and
sliding of time between two motions. This connectiv-
ity is similar to motion graphs (?). However, our ap-
proach is finding similar connectivity in inner-product
space, not keyframe distance in spatial domain.
6.3 Foot-skating Cleanup
The synthesized motions may contain foot-skating ar-
tifacts. We resolve this problem by detecting the foot-
plants and then smoothly adjusting the nearby root
and knee joint positions on their adjacent keyframes,
similar to (Ikemoto et al., 2006) and (Kovar et al.,
2002b).
The footplants are automatically detected from the
trained keyframes (Ikemoto et al., 2006). In the train-
ing process, the motion that contains the keyframe
with the farthest distance to the labeled keyframes
is selected for manual footplants marking. This it-
erative process terminates when the satisfied results
are achieved. In the detecting process, we calculate
the footplant values for each keyframe by averaging
the values of its k nearest neighbors in the trained
database.
Once the footplants are detected, we set the po-
sitions of the consecutive footplants as their average
values, and then smoothly relocate the root positions
of every keyframe in the sequence, such that their legs
are reachable to the positions. To avoid the pop-up
problems that may raise on the boundary of footplant
sequences, we linearly interpolate the root and foot
positions of the keyframes laying between the foot-
plants sequences. Additionally, the height of the root
for each keyframe is adjusted smoothly to make sure
its feet do not penetrate the ground. Finally, we ap-
ply the inverse kinematics on all the keyframes in the
synthesized motion.
a)
b)
Figure 7: The partial keyframe sequences before a) and after
foot-skating cleanup b). The adjacent keyframes containing
no footplants are also smoothly adjusted to avoid pop-up
problems.
7 IMPLEMENTATION AND
RESULTS
Our system is implemented in C++ and uses OpenGL
and GLSL to visualize results. All results were gen-
erated on an Intel
R
Xeon
R
E5-1650 CPU, running
at 3.20 GHz with 16 GB of memory, and rendered
Character Motion in Function Space
117

with an NVidia 970GTX GPU. All analysis and syn-
thesis computations were performed on a single CPU
thread. Initially, we used a FPCA library (PACE
package) that is implemented in Matlab. However,
it requires five hours to analyze 41 motions. To im-
prove the performance, we re-implement FPCA code
in C++ and by using CUDA. Our new implementation
provides significantly faster performance than Matlab
PACE package, the achieved speedup is 10x for 210
curves and 225x for 6, 510 curves. Once the ONB
has been generated, the motion synthesis and decod-
ing are interactive.
7.1 FPCA CUDA Implementation
We use Eigen math library to represent matrices and
vectors, ALGLIB for spline smoothing, Armadillo
for fast singular value decomposition (SVD), and fast
Moore-Penrose pseudoinverse is implemented by fol-
lowing Courrieu’s method (Courrieu, 2008).
While the Matlab implementation is general, we
did not require all the functionality in our code. We
only consider special case which sampling points are
regular. In addition, we speed up FPCA processing
by applying CUDA for large-scale vector dot product
in Local Weighted Least Square (LWLS) estimation,
and removing cross-validation of residuals. Table 5
shows the comparisons of Matlab PACE package and
our implementation. The CUDA implementation will
be available on our web site.
Table 3: Average Error.
a)
Test Case
Implementation 210 curves 6510 curves
PACE 0.00326511 0.00145804
Ours 0.00326484 0.00146001
Table 4: Max Error.
b)
Test Case
Implementation 210 curves 6510 curves
PACE 0.06804195 0.20938692
Ours 0.06802791 0.20937758
Table 5: Processing Time (sec).
c)
Test Case
Implementation 210 curves 6510 curves
PACE 24.2851400 784.976200
Ours 2.27931000 3.47349000
Comparison of FPCA implementations. Average error a),
maximum error b), and processing time c).
7.2 Evaluation
We compare our method against two other approaches
that use analytic basis functions: Fourier series and
Legendre polynomials. The advantage of the two ap-
proaches is that they do not need to store their an-
alytic basis functions because they are expressed as
equations. However, they generally need more coeffi-
cients to represent the function with the similar error
and the reconstruction artifacts are usually high fre-
quency oscillations that are unwanted in motion data.
Our method is less sensitive to these errors.
Reconstruction Comparison. We have used 41 mo-
tions and, in the first step, we have generated the
ONB representation covering 0.999 of the variance
and measured the error of the approximation. In the
next step we encoded the same motion set by using
Fourier series and Legendre polynomials while en-
forcing the same error as for the ONB. The results
are displayed in Figure 8 where the Fourier series is
in green, Legendre polynomials blue, original motion
curve black, and our method in red. The approxima-
tion by using analytic functions introduces unwanted
oscillations as can be seen in the inset showing a de-
tailed span of 30-120 frames in Figure 8 d) and in the
accompanying video. This is due to the fact that the
high order basis functions have high frequencies that
would require more coefficients to capture. In con-
trast, our basis functions adapt to the data and the re-
sulting reconstructed curve is smoother. At the same
time, while Fourier representation needed 476 basis
function and Legendre polynomials 293, our method
needed only 96 basis functions to approximate the
motion with the same error (see Table 6).
-0.2
-0.1
0
0.1
0.2
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350
Original FPCA
-0.2
-0.1
0
0.1
0.2
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350
Original Fourier (43)
-0.2
-0.1
0
0.1
0.2
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350
Original Legendre (61)
0.14
0.16
0.18
0.2
30 50 70 90 110
Original FPCA
Fourier (43) Legendre (61)
a)
b)
c)
d)
Figure 8: Comparison of the original motion to our method
a), Fourier b), and Legendre c). Detail of 30-110 sec-
onds shows the analytic basis functions have higher oscil-
lations b) when encoded with the same error as our method.
Another advantage of our method is the control
over the error of the approximation. In our approach
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
118
we do not need to specify the absolute error values.
We specify how much of the original information
should be preserved in the reconstructed curves and
run the corresponding ONB basis extraction. In all
experiments we set the error value to 0.1% (99.9%
quality).
Dimensions Comparison. We compared the space
needed for an accurate representation of all motion
curves per each component. We encoded all compo-
nent curves by using as few basis functions as possible
while making sure that 90th percentile error is below
a given error value. The comparison of the generated
number of basis vectors for our method, Fourier, and
Legendre is shown in Table 6. Overall our method
outperforms the other methods (96 : 476 with Fourier
and 96 : 293 to Legendre).
Table 6: Comparison of the required number of basis func-
tions.
90th percentile Number of basis functions
Comps. Our method Fourier Legendre
Total 96 476 293
Number of basis function for a given error.
Compression. Our ONB function space representa-
tion of the character motion provides compression of
the input data. Although the basis functions are gen-
erated for each set of motions and they need to be
stored in order to reconstruct the motion, they outper-
formed Fourier and Legendre approximation in our
experiments as shown in Table 6.
We have encoded 321 different motions (2,605
short sequences, each of 0.8-1.2 seconds length at
120 Hz) that represented a skeleton with 31 joints.
The size of the raw input data is 227 MB. The com-
pression ratios depends on the number of basis func-
tions. In motion vectors, we do not store the vector
elements with the absolute values less than 1e-7. For
the first 5 basis functions (mean function and the basis
functions), the compression ratios were 50× (see Fig-
ure 9), for Fourier 9×, and for Legendre polynomials
10×. The effect of the size of the ONB will further
diminish if more motions would be encoded and more
motion vectors would be present.
Our method cannot be directly compared to other
methods, such as (Arikan, 2006; Liu and McMillan,
2006; Tournier et al., 2009), since our method is not
used only for motion compressing, but it shares ONB
functions for further processing. In addition, the com-
pression ratio of our method can vary depending on
the number of used basis functions as shown in Fig 9.
Table 8 provides comparison of compression ra-
tio and distortion rate (%) based on the provided re-
sult from Liu and McMillan (2006) and Tournier et
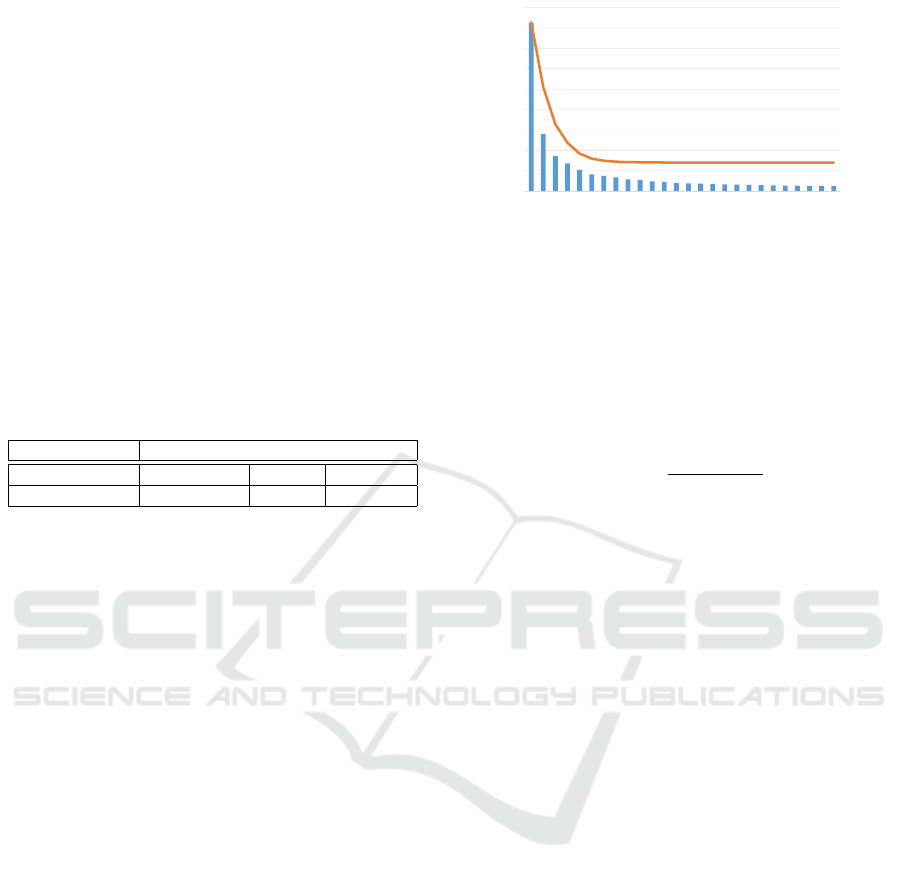
0
0.002
0.004
0.006
0.008
0.01
0.012
0.014
0.016
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25
AverageError
CompressionRatio
NumberofUsedONBFunctions
Error
CompressionRatio
Figure 9: The compression factor depends on the number
of basis functions. We removed motion vector elements
with the absolute values smaller than 1e-7 and calculated
the compression factors.
al. (2009). The same motion clips were used for
the comparison. The distortion rate is calculated by
Eqn (16) which was defined by Karni and Gotsman
in (Karni and Gotsman, 2004).
d = 100
kA −
˜
Ak
kA − E(A)k
, (16)
where A and
˜
A are the 3m × n matrices that consist of
absolute markers’ position of original motion and the
decompressed motion respectively, m is the number
of markers, n is the number of keyframes, and E(A)
is the mean of marker positions with respect to time.
For reconstructing a frame, our method only requires
a few calculations by following Eqn (1) so that it can
reconstruct frames on the fly.
8 CONCLUSION
We have introduced a novel compact representation
of motion for character animation. Our method is
inspired by analytic basis methods, such as Fourier
and Legendre polynomials, but instead of using an-
alytic representation the orthonormal basis (ONB) is
extracted automatically by using functional principal
analysis (FPCA) for each input set of motions. The
ONB is unique for each input set and because of the
FPCA the basis are ordered by their importance it
provides optimal coverage of the input space. Our
method not only provides better compression of the
raw input data than the analytic basis approximations,
it also allows for an easy motion synthesis. Each mo-
tion from the input set is represented as a motion vec-
tor and motion is performed by simply interpolating
motion vector coordinates and connecting partially
similar motions. We also provide optimization in the
ONB for more complex motions.
There are several limitations and avenues for fu-
ture work. One limitation is that the FPCA processes
Character Motion in Function Space
119
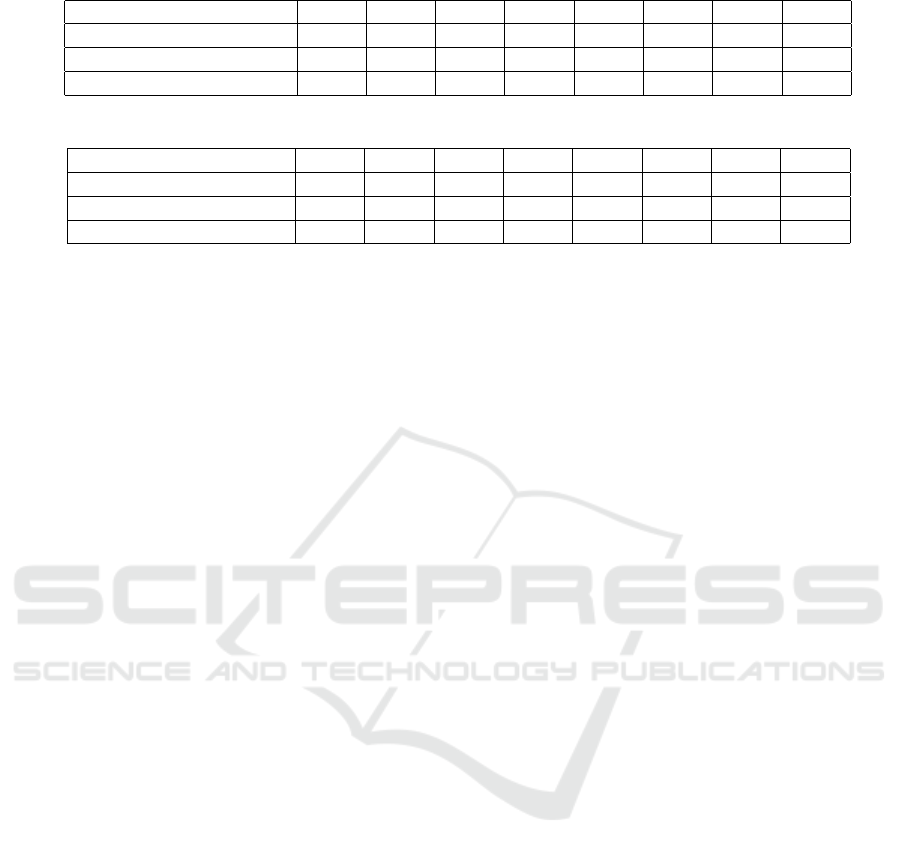
Table 7: Compression Ratio.
a)
Method\Motion 09/06 13/29 15/04 17/08 17/10 85/12 86/02 86/08
Liu and McMillan (2006) N/A 1:55 N/A N/A N/A 1:18 1:53 1:56
Tournier et al. (2009) 1:18 N/A 1:69 1:182 1:61 1:97 N/A N/A
Ours (motion vector only) 1:19 1:33 1:63 1:34 1:33 1:34 1:34 1:29
Table 8: Distortion Rate (%).
b)
Method\Motion 09/06 13/29 15/04 17/08 17/10 85/12 86/02 86/08
Liu and McMillan (2006) N/A 5.1 N/A N/A N/A 7.1 5.1 5.4
Tournier et al. (2009) 0.36 N/A 1.55 0.049 0.49 0.56 N/A N/A
Ours 1.11 0.30 0.21 0.39 0.23 0.34 0.38 0.40
The comparison between our method and other approaches. Note that we only used vector size for calculating compression
ratio, because our method the ONB functions are shared for all motions. In this table, lower than 1e-5 values are not saved,
and 6 basis functions were used.
only 1D functions. Theoretically, it would be possi-
ble to apply the FPCA directly to n-dimensional char-
acter animation and the per component optimizations
would not be necessary. Moreover, FPCA assumes
that the input functions are smooth, and also inter-
nally smooth the resulting ONB functions. As a side
effect, this could hide oscillations. Another limitation
is that the FPCA is always lossy due to numerical er-
rors in the computation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors acknowledge the support of the OP
VVV MEYS funded project CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16
019/0000765 Research Center for Informatics.
REFERENCES
Arikan, O. (2006). Compression of motion capture
databases. ACM Trans. Graph., 25(3):890–897.
Barbi
ˇ
c, J., Safonova, A., Pan, J.-Y., Faloutsos, C., Hodgins,
J. K., and Pollard, N. S. (2004). Segmenting motion
capture data into distinct behaviors. In Proceedings of
Graphics Interface 2004, pages 185–194.
Beaudoin, P., Coros, S., van de Panne, M., and Poulin, P.
(2008). Motion-motif graphs. In Proceedings SCA,
pages 117–126.
Chao, M.-W., Lin, C.-H., Assa, J., and Lee, T.-Y. (2012).
Human motion retrieval from hand-drawn sketch.
IEEE TVCG, 18(5):729–740.
Coffey, N., Harrison, A., Donoghue, O., and Hayes, K.
(2011). Common functional principal components
analysis: A new approach to analyzing human move-
ment data. Human Movement Science, 30(6):1144 –
1166.
Courrieu, P. (2008). Fast computation of moore-penrose
inverse matrices. CoRR, abs/0804.4809.
Du, H., Hosseini, S., Manns, M., Herrmann, E., and Fis-
cher, K. (2016). Scaled functional principal compo-
nent analysis for human motion synthesis. In Pro-
ceedings of the Intl. Conf. on Motion in Games, pages
139–144.
Heck, R. and Gleicher, M. (2007). Parametric motion
graphs. In Proceedings of the I3D.
Ikemoto, L., Arikan, O., and Forsyth, D. (2006). Knowing
when to put your foot down. In Proceedings of the
I3D, pages 49–53.
Ikemoto, L., Arikan, O., and Forsyth, D. (2009). Generaliz-
ing motion edits with gaussian processes. ACM Trans.
Graph., 28(1):1:1–1:12.
Karni, Z. and Gotsman, C. (2004). Compression of soft-
body animation sequences. Computers & Graphics,
28(1):25 – 34.
Kovar, L. and Gleicher, M. (2004). Automated extraction
and parameterization of motions in large data sets.
ACM Trans. Graph., 23(3):559–568.
Kovar, L., Gleicher, M., and Pighin, F. (2002a). Motion
graphs. ACM Trans. Graph., 21(3):473–482.
Kovar, L., Schreiner, J., and Gleicher, M. (2002b). Foot-
skate cleanup for motion capture editing. In Proceed-
ings of the SCA, pages 97–104.
Lai, Y.-C., Chenney, S., and Fan, S. (2005). Group motion
graphs. In Proceedings of the SCA, pages 281–290.
Lau, M., Bar-Joseph, Z., and Kuffner, J. (2009). Modeling
spatial and temporal variation in motion data. ACM
Trans. Graph., 28(5):171:1–171:10.
Lee, J. and Shin, S. Y. (1999). A hierarchical approach to
interactive motion editing for human-like figures. In
Proc. of the Annual Conf. on Comp. Graph. and Inter-
active Techniques, pages 39–48.
Lee, Y., Wampler, K., Bernstein, G., Popovi
´
c, J., and
Popovi
´
c, Z. (2010). Motion fields for interactive char-
acter locomotion. ACM Trans. Graph., 29(6):138:1–
138:8.
Levine, S., Wang, J. M., Haraux, A., Popovi
´
c, Z., and
Koltun, V. (2012). Continuous character control with
low-dimensional embeddings. ACM Trans. Graph.,
31(4):28:1–28:10.
Liu, G. and McMillan, L. (2006). Segment-based human
GRAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
120

motion compression. In Proceedings of the SCA,
pages 127–135.
Min, J. and Chai, J. (2012). Motion graphs++: A compact
generative model for semantic motion analysis and
synthesis. ACM Trans. Graph., 31(6):153:1–153:12.
Mordatch, I., de Lasa, M., and Hertzmann, A. (2010). Ro-
bust physics-based locomotion using low-dimensional
planning. ACM Trans. Graph., 29(4):71:1–71:8.
Ormoneit, D., Black, M. J., Hastie, T., and Kjellstrom,
H. (2005). Representing cyclic human motion us-
ing functional analysis. Image and Vision Computing,
23(14):1264 – 1276.
Ramsay, J. and Silverman, B. W. (2006). Functional data
analysis. Wiley Online Library.
Reitsma, P. S. A. and Pollard, N. S. (2007). Evaluating
motion graphs for character animation. ACM Trans.
Graph., 26(4).
Safonova, A. and Hodgins, J. K. (2007). Construction and
optimal search of interpolated motion graphs. ACM
Trans. Graph., 26(3).
Tang, J. K. T., Leung, H., Komura, T., and Shum, H. P. H.
(2008). Emulating human perception of motion simi-
larity. Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds, 19(3-
4):211–221.
Tournier, M., Wu, X., Courty, N., Arnaud, E., and
Revret, L. (2009). Motion compression using prin-
cipal geodesics analysis. Computer Graphics Forum,
28(2):355–364.
Unuma, M., Anjyo, K., and Takeuchi, R. (1995). Fourier
principles for emotion-based human figure animation.
In Proc. of the Annual Conf. on Comp. Graph. and
Interactive Techniques, pages 91–96.
Wei, X., Min, J., and Chai, J. (2011). Physically valid sta-
tistical models for human motion generation. ACM
Trans. Graph., 30(3):19:1–19:10.
Yao, F., Mueller, H.-G., and Wang, J.-L. (2005). Functional
linear regression analysis for longitudinal data. Ann.
Statist., 33(6):2873–2903.
Zhao, L. and Safonova, A. (2009). Achieving good connec-
tivity in motion graphs. Graphical Models, 71(4):139
– 152.
Zhou, F. and De la Torre, F. (2012). Generalized time warp-
ing for multi-modal alignment of human motion. In
IEEE Conference on CVPR, pages 1282–1289.
APPENDIX
Distance of Two Vectors in ONB Space
Let’s assume that two functions, f
1
(t) and f
2
(t),
are approximated by orthonormal basis functions,
b
1
(t), b
2
(t), ...,b
n
(t), so that the coefficients are
c
11
,c
12
,...,c
1n
for
e
f
1
(t) and c
21
,c
22
,...,c
2n
for
e
f
2
(t).
The mean function of the two functions are µ(t),
so that the approximated functions,
e
f
1
(t) = µ(t) +
∑
n
i=1
c
1i
b
i
(t) and
e
f
2
(t) = µ(t) +
∑
n
i=1
c
2i
b
i
(t).
The squared distance between the two functions is
D(
e
f
1
(t),
e
f
2
(t))
2
=
Z
t
b
t
a
e
f
1
(s)−
e
f
2
(s)
2
ds =
Z
t
b
t
a
n
∑
i=1
(c
1i
−c
2i
)b
i
(s)
2
ds
Since b
1
(t), b
2
(t), ...,b
n
(t) are orthonor-
mal basis functions, any two basis func-
tions, b
i
(t) and b
j
(t) satisfies hb
i
,b
j
i = δ
i j
,
where δ
i j
is kronecker delta function. Thus,
Z
t
b
t
a
(c
11
− c
21
)b
1
(s) +··· + (c
1n
− c
2n
)b
n
(s)
2
ds =
Z
t
b
t
a
(c
11
− c
21
)
2
b
1
(s)
2
ds + ··· +
Z
t
b
t
a
(c
1n
− c
2n
)
2
b
n
(s)
2
ds =
n
∑
i=1
Z
t
b
t
a
(c
1i
− c
2i
)
2
b
i
(s)
2
ds =
n
∑
i=1
(c
1i
− c
2i
)
2
Z
t
b
t
a
b
i
(s)
2
ds =
n
∑
i=1
(c
1i
− c
2i
)
2
hb
i
,b
i
i =
n
∑
i=1
(c
1i
− c
2i
)
2
The distance between two approximated functions is
just distance of their coefficients.
Character Motion in Function Space
121
