
Exploring Deep Spiking Neural Networks
for Automated Driving Applications
Sambit Mohapatra
1
, Heinrich Gotzig
1
, Senthil Yogamani
2
, Stefan Milz
3
and Raoul Z
¨
ollner
4
1
Valeo Bietigheim, Germany
2
Valeo Vision Systems, Ireland
3
Valeo Kronach, Germany
4
Heilbronn University, Germany
Keywords:
Visual Perception, Efficient Networks, Automated Driving.
Abstract:
Neural networks have become the standard model for various computer vision tasks in automated driving
including semantic segmentation, moving object detection, depth estimation, visual odometry, etc. The main
flavors of neural networks which are used commonly are convolutional (CNN) and recurrent (RNN). In spite
of rapid progress in embedded processors, power consumption and cost is still a bottleneck. Spiking Neural
Networks (SNNs) are gradually progressing to achieve low-power event-driven hardware architecture which
has a potential for high efficiency. In this paper, we explore the role of deep spiking neural networks (SNN)
for automated driving applications. We provide an overview of progress on SNN and argue how it can be a
good fit for automated driving applications.
1 INTRODUCTION
Autonomous driving is a rapidly progressing area
of automobile engineering that aims to gradually re-
duce human interaction in automobile driving. Divi-
ded into 5 levels of autonomy, level 4 and 5 target
the ultimate goal of automated driving, namely com-
plete removal of human interaction in vehicle driving.
The overall task of autonomous driving may be sub-
divided into 3 key groups of activities - (1) Environ-
mental sensing, (2) Environmental perception from
sensor data and (3) Actuation of drive action accor-
ding to perception. More often than not, it has been
seen that the type of sensor and its output, define the
approach most suitable for perception of the environ-
mental from the sensor data.
CNN (Convolutional Neural Networks) has made
huge leaps in accuracy for various computer vision
tasks like object recognition and semantic segmenta-
tion (Siam et al., 2017). They are also becoming do-
minant in geometric tasks like depth estimation, mo-
tion estimation, visual odometry, etc. It has played
a major role in achieving high accuracy for various
computer vision tasks which is critical for safe auto-
mated driving systems. However, they are computati-
onally expensive and power consumption is becoming
a bottleneck. For example, the recently announced
Nvidia platform Xavier provides 30 Tera-ops (TOPS)
of compute power but consumes 30 Watts. This ne-
cessitates an active cooling system which will con-
sume more power and add to operating costs.
SNN (Spiking Neural networks) have been pro-
gressing gradually as a power efficient neural net-
work. The functional capabilities of SNN neuron
model is discussed in detail in (Chou et al., 2018).
SNNs were proven to be effective in several problems
but it remained less competitive compared to CNNs.
Recently (Sengupta et al., 2018) demonstrated that
a deep SNN can achieve better accuracy than CNN
on a challenging dataset ImageNet. A detailed over-
view of deep learning in SNN is discussed in (Tava-
naei et al., 2018). (Wunderlich et al., 2018) discuss
the power consumption advantages of SNN when im-
plemented in neuromorphic hardware. In (Zhou and
Wang, 2018), SNN was shown to be effective for LI-
DAR object detection directly on analog signals. Mo-
tivated by the recent progress in SNN, we study the
potential of SNN for automated driving applications
in this paper.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows.
Section 2 provides an overview of Spiking neural net-
works (SNN) and compares it with popular version
548
Mohapatra, S., Gotzig, H., Yogamani, S., Milz, S. and Zöllner, R.
Exploring Deep Spiking Neural Networks for Automated Driving Applications.
DOI: 10.5220/0007469405480555
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2019), pages 548-555
ISBN: 978-989-758-354-4
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

of NNs namely CNNs and RNNs. Section 3 discus-
ses opportunities of SNNs for automated driving ap-
plications and provides motivating use cases. Finally,
section 4 summarizes the paper and provides potential
future directions.
2 RELATED WORK ON SNN
Sensors such as camera, lidar and radar generate enor-
mous amounts of data. Machine learning has proven
to be highly successful in tasks involving such high
dimensional data. Since most objects in the environ-
ment can be grouped into certain classes such as pe-
destrian, cars etc, the data presents a pattern, which
can be used to train classifiers that can then classify
objects with great accuracy. Historically, Convolutio-
nal Neural Networks (CNNs) have been the mainstay
of all major machine learning approaches to object
detection. Some prominent models that make use of
CNNs for object detection are Fast R-CNN (Girshick,
2015) which uses the fine-tuned CNN to extract fea-
tures from object proposals and Support Vector Ma-
chines (SVM) to classify them.
R-CNN based algorithms use a two-step process
for object detection namely - region proposal and re-
gion classification. Recently one-shot methods have
also been proposed such as YOLO (Redmon et al.,
2016) and SSD. All these methods generate feature
maps which make up the bulk of the computation and
then classification of the feature maps.
Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) are the most re-
cent addition to the family of neural networks and
machine learning. Considering the fact that they are
still in a preliminary stage of research, large scale
practical applications and implementations on har-
dware are rather few. Some of the most notable ap-
plications include (Diehl et al., 2015) that use con-
version techniques for converting a CNN into SNN to
achieve impressive error rate of 0.9% in MNIST digit
recognition application. Another notable application
is (Hunsberger and Eliasmith, 2015) where Leaky In-
tegrate and Fire (LIF) neuron model with smoothened
response is used to convert a CNN to SNN for object
recognition application on CIFAR-10 dataset.
2.1 Overview of SNN
Widely considered as the third generation of neural
models, Spiking Neural models differ from conventi-
onal neural models in the very way that information is
represented and processed by them. This is inspired
by information representation and processing in bio-
logical neurons where information is converted into a
Figure 1: Spiking neuron model.
voltage spike train generally of equal amplitude. The
duration and timing of the spikes encodes the actual
information. In its very basic form, information arri-
ves at a neuron from preceding neurons in the form
of spikes, which are integrated over time. Once accu-
mulated voltage reaches a certain threshold, a voltage
spike is sent out as the output from the neuron. Figure
1 illustrates a basic representation of a spiking neuron
model.
Spiking networks are capable of processing a large
pool of data using a small number of spikes (Thorpe
et al., 2001). Previous work has demonstrated that
SNNs can be applied to all common tasks to which
CNNs are applied and can do so in an effective way
(Maass, 1997). Spiking neuron models are highly
motivated by biological neurons and the way they
function (Bois-Reymond et al., 1848). There are 3
main characteristics: (1) It accept inputs from many
incoming synapses and produce single output spike.
(2) Inputs can be excitatory - if they increase the fi-
ring rate of a neuron or inhibitory - if they reduce fi-
ring rate of a neuron. (3) The neuron model is gover-
ned by at least one state variable. In spiking models,
the spike timings carry the information rather than the
amplitude or shape (Gerstner and Kistler, 2002).
A spike train can be described as
S(t) =
∑
f
δ(t −t
f
) (1)
where f = 1, 2, ... is the label of the spike δ(.) is a
Dirac function as defined below whose area is 1.
δ(t) =
(
1, if t = 0,
0, if t 6= 0.
(2)
Neuron models are used to represent the dynamics of
signal processing in a neuron mathematically. In case
of Spiking neurons, three commonly used models are
- Hodgkin-Huxley model, Izhikevich model and In-
tegrate and Fire model. While the Hodgkin-Huxley
model provides the closest modelling of actual biolo-
gical neurons, it’s mathematical complexity makes it
Exploring Deep Spiking Neural Networks for Automated Driving Applications
549

unsuitable for use in applications. A version of the In-
tegrate and Fire model known as the Leaky Integrate
and Fire (LIF) model is the most widely used neuro-
nal model for spiking neurons as it provides a balance
between mathematically complexity of implementa-
tion and closeness to biological process (Gerstner and
Kistler, 2002). LIFs are mathematically represented
as:
C
du
dt
(t) = −
u(t)
R
+ (i
o
(t) +
∑
w
j
i
j
(t)) (3)
where u(t): state variable (membrane potential),
C: membrane capacitance, R: input resistance, i
o
(t):
is the external current, i
j
(t): is the input current from
the j-th synaptic input w
j
: strength of the j-th syn-
apse. A neuron fires a spike at time t , if membrane
potential u reaches threshold(v). Immediately after a
spike the membrane potential is reset to a value less
than the threshold and held for the time known as
the refractory period. SNN can be represented as a
directed graph (V, S), with V being a set of neurons
and S representing a set of synapses (Maass, 1997).
The set V contains a subset of input and output
neurons.
Spiking Network Topologies:
1. Feedforward networks - The data flows from
input to output in a unidirectional manner across se-
veral layers. Applications include sensory systems,
e.g. in vision (Escobar et al., 2009), olfaction (Fu
et al., 2007) or tactile sensing (Cassidy and Ekana-
yake, 2006).
2. Recurrent networks - In this case, neuron
groups have feedback connections. This allows dyna-
mic temporal behavior of the network. However, this
feedback arrangement makes control more difficult in
such networks (Hertz et al., 1991).
3. Hybrid networks - Some of the neurons have
feedback connections while other are connected in a
feed-forward fashion.
Spike Coding Techniques:
Generally information available from sensors is not
in a form suitable for SNN processing. Hence, co-
ding such data into spike trains is a major factor in the
entire architecture. To address this problem several
neural coding strategies based on spike timing have
been proposed. Some of these strategies are listed be-
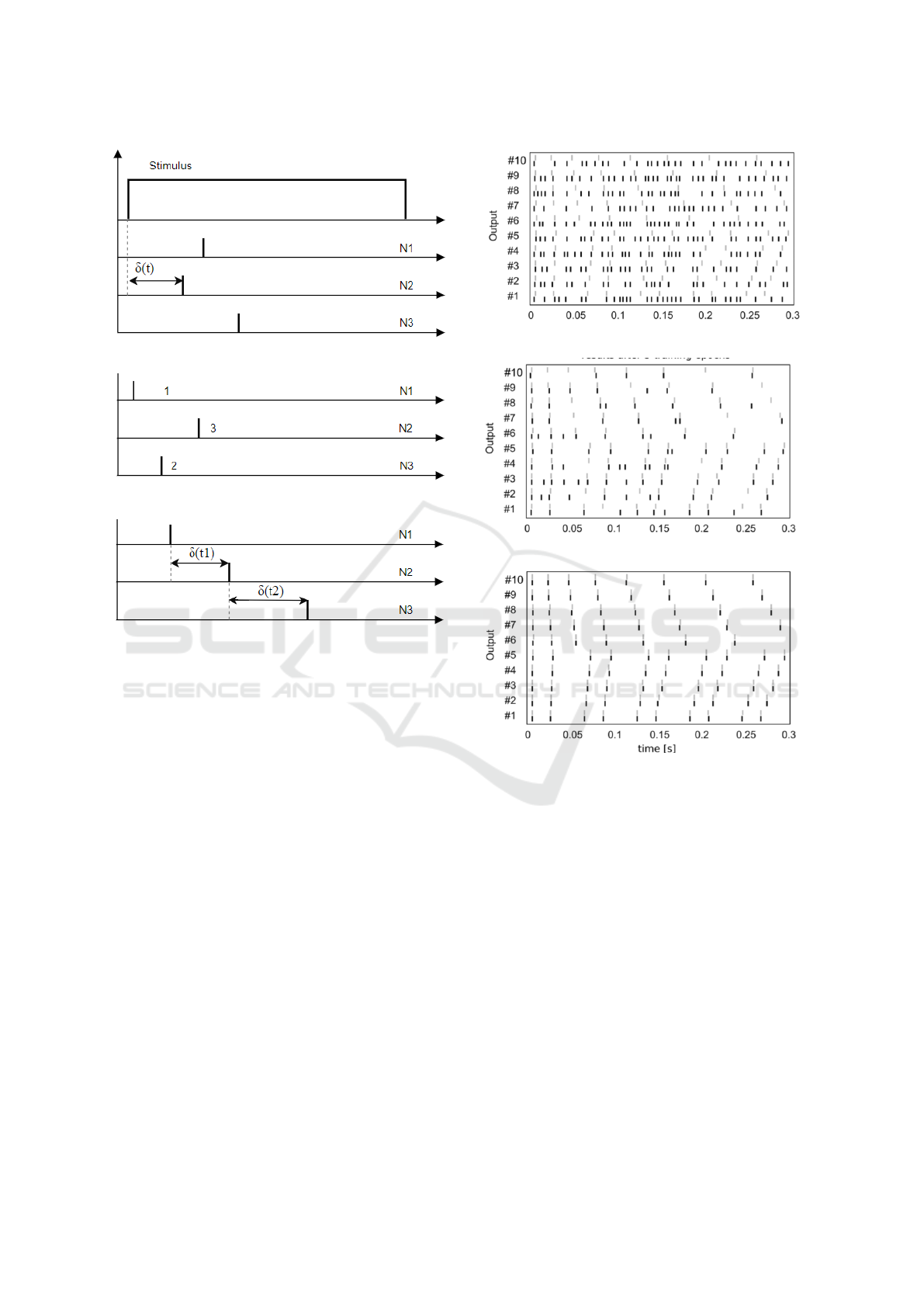
low and visualized in Figure 2. In some cases like
event based camera data, data arrives in a form more
suitable for SNNs.
1. Time to First Spike Information is encoded as
time between the beginning of stimulus and the time
of the first spike in response. As can be seen from
Figure 2-a, a group of three neurons N1, N2 and N3
spike in response to a stimulus. The time between the
start of the stimulus to the first spike by neuron N2 en-
codes the type of the stimulus. Such encoding scheme
is generally applied in applications such as artificial
tactile and olfactory sensors (Chen et al., 2011).
2. Rank-Order Coding (ROC) Here, informa-
tion is coded by the firing order of spikes from the
group of neurons that encode the information. As
seen in Figure 2-b, the neurons fire in the order N1
followed by N3 and N2 respectively. This sequence
of firing of the three neurons encodes the type of sti-
mulus.
3. Latency Code Information is coded by the
difference in time between firing of neurons. It is a
highly efficient method of encoding large amounts of
information using only a few spikes (Borst and Theu-
nissen, 1999). This is because, a slight change in the
timings can be used to encode a completely different
data sample. Figure 2-c shows the latency between
firing of neuron N1 and N2 as δ(t1). Similarly, the
latency in firing of N3 after N2 is depicted as δ(t2).
Training Spiking Neurons: The connections bet-
ween subsequent neurons are called synapses. In spi-
king neuron models, these connections or synapses
have certain weights or strength associated with them
that determine the the strength of the input that the
post-synaptic neuron receives from it’s pre-synaptic
neuron. These weights can be changed and this phe-
nomenon is called synaptic plasticity. Several strate-
gies for adjusting the plasticity have been suggested
such as depending upon the history of a neuron’s re-
sponse to certain inputs from a particular pre-synaptic
neuron. Other variants may use the simultaneous fi-
ring of a pre-synaptic and post-synaptic neuron as a
criteria for increasing the synaptic weight etc. Syn-
aptic plasticity is the key principle by which learning
is achieved in SNNs. Both supervised and unsupervi-
sed forms of learning can be modelled using synaptic
plasticity. Figure 3 shows a sample application of su-
pervised learning using the ReSuMe algorithm. Here
the objective was to learn the target firing times of a
group of 10 spiking neurons. As seen in the figure, af-
ter 15 epochs, most of the neurons have achieved the
desired firing times depicted as gray lines.
We briefly review the main unsupervised lear-
ning algorithm. Donald Hebb famously formulated
a rule for changing synaptic weights depending on
pre-synaptic and post-synaptic activity. According to
Hebb’s formula the synaptic weight between neurons
VISAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
550
(a) Time to first spike
(b) Rank-order coding
(c) Latency code
Figure 2: Different encoding schemes of information in spi-
kes - adapted from (Ponulak and Kasinski, 2011).
i and j, w
ji
, is increased if neurons i and j are simul-
taneously active. This method of changing synaptic
weights is purely dictated by the input spike train and
can lead to pattern recognition in an unsupervised way
and no correction based on error evaluation is needed
within the network (Hinton et al., 1999; Hertz et al.,
1991). The condition formulated by Hebb for in-
creasing or decreasing the synaptic weights between
neurons is called Spike-Timing-Dependent-Plasticity
(STDP).
2.2 CNN vs SNN
CNNs have shown tremendous progress in their suit-
ability to vision and image based tasks such as
image recognition, object detection, pattern recogni-
tion. However, the key elements of the networks, con-
volution, feature map generation, max pooling etc, in-
volve a lot of matrix multiplication and addition and
are compute intensive. Also, the frame based opera-
tion of CNNs involves processing the entire input in a
batch, hence individual input channels have to wait till
the entire frame of inputs is available. This introduces
(a) Spike timings before training
(b) Spike firing rates after 5 epochs training
(c) Spike timings after 15 epochs
Figure 3: Supervised learning with ReSuMe algorithm. A
single-layer feedforward network with 10 spiking neurons.
The task is to learn a sample target sequence of spikes assig-
ned individually to each LIF neuron. The gray vertical bars
are the target firing times and black bars are the actual time
of firing. It can be seen after 15 epochs, the target and actual
times are almost identical, describing learning (Ponulak and
Kasinski, 2011).
latency. Further, the inputs are processed in a layered
fashion and an output can only be produced when all
layers have finished processing a batch of inputs. This
causes latency in the output side. Due to these laten-
cies and compute intensive operations, inference in
data sets such as ImageNet (Russakovsky et al., 2015)
are not real-time and computationally un-economic.
However, meeting real-time on such targets is manda-
tory for autonomous driving applications.
Unlike CNNs, SNNs are event based, i.e, events
are processed as they are generated. This reduces
Exploring Deep Spiking Neural Networks for Automated Driving Applications
551

Figure 4: Spiking CNN architecture (Cao et al., 2015).
latency in input processing. Also, only those input
channels are evaluated and processed that have had a
change or an event. This reduces the number of inputs
that have to be processed in each cycle, as sensors do
not typically produce new data on every channel. This
reduces computational load and power consumption
greatly (Farabet et al., 2012).
CNNs can be implemented both in software and
in hardware and due to their frame based informa-
tion processing, the hardware resources can be mul-
tiplexed. Thus, higher memory bandwidth and faster
data transfer are key for real-time performance. Un-
like CNNs, SNNs process events instead of frames,
hence hardware needs to be always available as event
generation is not predictive. Though it may seem to
be a limitation, this means, the network is tightly cou-
pled to the hardware and can produce faster response
than an equivalent CNN. To improve the efficiency
of a SNN architecture, a modular and re-configurable
hardware is more suitable. (Farabet et al., 2012).
Given the potential benefits of SNNs, a general
question arises on whether CNNs can be adapted to
SNNs? Infact, adapting pre-trained CNNs to equiva-
lent SNNs is easier and produces better results that
building a SNN with STDP and unsupervised or su-
pervised learning. Such adaptations have some key
benefits:
1) A spiking convolution operator, analogous to
the convolution operator in CNNs would operate
much faster due to event based processing, while pro-
ducing similar results as traditional CNN.
2) Since events are asynchronous, each convolu-
tion operator, supported by its linked modules can
operate independent of others, if it has an event for
processing. This eliminates the need for a global syn-
chronization among the operators. Such an asynchro-
nous convolution operator may be then implemented
as a standard block in hardware for re-usability.
3) Since information is processed on a per-event
basis, power is also consumed on a per-event basis.
Since sensors typically produce a lot of redundant and
sparse data, this could bring a significant reduction in
power consumption and computational load.
Finally SNNs can be queried for results anytime
after the first spikes are produced at the output since
information processing is not frame based (Rueckauer
et al., 2017). Several implementations of deep SNNs
on neuromorphic hardware such as SpiNNaker and
Table 1: Comparison of ANN and SNN in various computer
vision datasets (Rueckauer et al., 2017).
Data set
ANN
error rate (%)
SNN
error rate (%)
MNIST [12] 0.86 0.86
CIFAR-10 11.13 11.18
ImageNet 23.88 25.4
BrainChip have demonstrated sensor applications that
support this potential of SNNs.
Some evidence to support the strong possibilities
in research of SNN based networks for object de-
tection is presented in Table 1. It is based on an im-
plementation by (Rueckauer et al., 2017). It presents
a comparison of classification error rates for CNNs
and SNN implementation on state of the art data sets
(Cao et al., 2015).
3 SNNs IN AUTOMATED
DRIVING
3.1 Use Cases in Automated Driving
Event Driven Computing: Automated driving
has a wide variety of scenarios. At high level, the
main scenarios are parking, highway driving and
urban driving (Heimberger et al., 2017). The scene
dynamics and understanding is typically different for
these scenarios and a customized model is generally
used for these scenarios. There are also various
scenarios based on weather condition like rainy, day
or night, foggy, etc. The combination of various
environmental condition is exponential and difficult
to have a customized model for each scenario. At
the same time, transfer function can be shared across
these different scenarios and event triggered mecha-
nism can be used to adapt the regions used. This
can be accomplished loosely using shared encoder
and gating mechanisms within CNN. However, SNN
naturally captures event triggered model. There is a
class of cameras called event based cameras which
encode information at the sensor level. Recently,
deep learning algorithms were demonstrated on event
based camera data (Maqueda et al., 2018).
Point Cloud: Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR)
sensors have recently gained prominence as state of
the art sensors in sensing the environment. They pro-
duce a 3D representation of the objects in the field of
view as distances of points from the source. This col-
lection of points over a 3D space is called a 3D Point
Cloud. Though cameras have been used for a long
time and they provide a more direct representation of
VISAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
552

the surrounding, LiDARs have gained ground because
of some critical advantages such as long range, robus-
tness to ambient light conditions and accurate locali-
zation of objects in 3D space. They produce sparse
data and hence suitable for SNNs.
3.2 Opportunities
SNNs have shown great potential to either aid or
replace CNNs in real-time tasks such as object de-
tection, posture recognition etc. (Hu et al., 2016).
Large SNN architectures can be implemented on neu-
romorphic spiking platforms such as TrueNorth (Ben-
jamin et al., 2014). and SpiNNaker (Furber et al.,
2014). The TrueNorth has demonstrated to consume
as low as couple hundred mW power while packing
a million neurons in it (Sawada et al., 2016). Driven
by the strong motivation to reduce power consump-
tion of integrated circuits, implementations of spiking
models have shown to consume in the order of nJ or
even pJ (Azghadi et al., 2014) for signal transmission
and processing (Indiveri et al., 2006). Some neuro-
morphic designs also feature on-chip learning (Indi-
veri and Fusi, 2007).
Spiking applications and spike based learning is
also suited to dynamic applications like speech re-
cognition systems. In such systems, training is not
sufficient at manufacture as it has to adapt to dynamic
conditions such as accents. Other similar sensors are
event based Dynamic Vision Sensor (DVS) (Lichtstei-
ner et al., 2008) (Lenero-Bardallo et al., 2010). Some
of the applications especially in the object detection
and perception based tasks that are of direct relevance
to the automotive industry as mentioned briefly below.
1. Object classification on the CIFAR-10 data-
set: (Cao et al., 2015) designed a Spiking equivalent
model of a CNN for object detection on the CIFAR-
10 data set. The CNN was trained on the dataset
and the trained model was then converted into spi-
king with each individual block such as convolution,
max pooling, ReLU, being replaced by spiking equi-
valents. Their transformed model achieves an error
rate of 22.57%. CIFAR-10 is a collection of 60,000
labeled images of 10 classes of objects (Cao et al.,
2015) The network architecture is illustrated in Figure
4.
2. Human action recognition: (Zhao et al., 2015)
constructed a network to recognize human actions
and posture and successfully tested it. The network
was trained on an event-based dataset of small video
sequences with simple human actions like sitting,
walking or bending. They achieved a detection
accuracy of 99.48%. This work is an indication
of how SNNs may be applied to such event based
inference tasks.
We summarize the key benefits of SNN for automated
driving:
• Event driven mechanism which brings adaptation
for different scenarios.
• Low power consumption when realized as neuro-
morphic hardware.
• Simpler learning algorithm which leads to possi-
bility of on-chip learning for longer term adapta-
tion.
• Ability to integrate directly to analog signals lea-
ding to tightly integrated system.
• Lower latency in algorithm pipeline which is im-
portant for high speed braking and maneuvering.
4 CONCLUSION
Spiking Neural Networks (SNN) are biologically in-
spired where the neuronal activity is sparse and event
driven in order to optimize power consumption. In
this paper, we provide an overview of SNN and com-
pare it with CNN and argue how it can be useful in au-
tomated driving systems. Overall power consumption
over the driving cycle is a critical constraint which has
to be efficiently used especially for electric vehicles.
Event driven architectures for various scenarios in au-
tomated driving can also have accuracy advantages.
REFERENCES
Azghadi, M. R., Iannella, N., Al-Sarawi, S. F., Indiveri, G.,
and Abbott, D. (2014). Spike-based synaptic plasti-
city in silicon: design, implementation, application,
and challenges. Proceedings of the IEEE, 102(5):717–
737.
Benjamin, B. V., Gao, P., McQuinn, E., Choudhary, S.,
Chandrasekaran, A. R., Bussat, J.-M., Alvarez-Icaza,
R., Arthur, J. V., Merolla, P. A., and Boahen, K.
(2014). Neurogrid: A mixed-analog-digital multichip
system for large-scale neural simulations. Procee-
dings of the IEEE, 102(5):699–716.
Bois-Reymond, Y. et al. (1848). Investigations on animal
electricity ”a t. Annalen der Physik, 151:463–464.
Borst, A. and Theunissen, F. E. (1999). Information theory
and neural coding. Nature neuroscience, 2(11):947.
Cao, Y., Chen, Y., and Khosla, D. (2015). Spiking deep
convolutional neural networks for energy-efficient ob-
ject recognition. International Journal of Computer
Vision, 113(1):54–66.
Exploring Deep Spiking Neural Networks for Automated Driving Applications
553

Cassidy, A. and Ekanayake, V. (2006). A biologically inspi-
red tactile sensor array utilizing phase-based computa-
tion. In Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference,
2006. BioCAS 2006. IEEE, pages 45–48. IEEE.
Chen, H. T., Ng, K. T., Bermak, A., Law, M. K., and Mar-
tinez, D. (2011). Spike latency coding in biologically
inspired microelectronic nose. IEEE transactions on
biomedical circuits and systems, 5(2):160–168.
Chou, C.-N., Chung, K.-M., and Lu, C.-J. (2018). On the
algorithmic power of spiking neural networks. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1803.10375.
Diehl, P. U., Neil, D., Binas, J., Cook, M., Liu, S.-C., and
Pfeiffer, M. (2015). Fast-classifying, high-accuracy
spiking deep networks through weight and threshold
balancing. In Neural Networks (IJCNN), 2015 Inter-
national Joint Conference on, pages 1–8. IEEE.
Escobar, M.-J., Masson, G. S., Vieville, T., and Kornprobst,
P. (2009). Action recognition using a bio-inspired
feedforward spiking network. International Journal
of Computer Vision, 82(3):284.
Farabet, C., Paz, R., P
´
erez-Carrasco, J., Zamarre
˜
no,
C., Linares-Barranco, A., LeCun, Y., Culurciello,
E., Serrano-Gotarredona, T., and Linares-Barranco,
B. (2012). Comparison between frame-constrained
fix-pixel-value and frame-free spiking-dynamic-pixel
convnets for visual processing. Frontiers in neuros-
cience, 6:32.
Fu, J., Li, G., Qin, Y., and Freeman, W. J. (2007). A pattern
recognition method for electronic noses based on an
olfactory neural network. Sensors and Actuators B:
Chemical, 125(2):489–497.
Furber, S. B., Galluppi, F., Temple, S., and Plana, L. A.
(2014). The spinnaker project. Proceedings of the
IEEE, 102(5):652–665.
Gerstner, W. and Kistler, W. M. (2002). Spiking neuron
models: Single neurons, populations, plasticity. Cam-
bridge university press.
Girshick, R. (2015). Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE
international conference on computer vision, pages
1440–1448.
Heimberger, M., Horgan, J., Hughes, C., McDonald, J., and
Yogamani, S. (2017). Computer vision in automated
parking systems: Design, implementation and chal-
lenges. Image and Vision Computing, 68:88–101.
Hertz, J., Krogh, A., and Palmer, R. G. (1991). Intro-
duction to the theory of neural computation. Addison-
Wesley/Addison Wesley Longman.
Hinton, G. E., Sejnowski, T. J., and Poggio, T. A. (1999).
Unsupervised learning: foundations of neural compu-
tation. MIT press.
Hu, Y., Liu, H., Pfeiffer, M., and Delbruck, T. (2016). Dvs
benchmark datasets for object tracking, action recog-
nition, and object recognition. Frontiers in neuros-
cience, 10:405.
Hunsberger, E. and Eliasmith, C. (2015). Spiking
deep networks with lif neurons. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1510.08829.
Indiveri, G., Chicca, E., and Douglas, R. J. (2006). A vlsi
array of low-power spiking neurons and bistable syn-
apses with spike-timing dependent plasticity. IEEE
transactions on neural networks, 17(1).
Indiveri, G. and Fusi, S. (2007). Spike-based learning in
vlsi networks of integrate-and-fire neurons. In Circuits
and Systems, 2007. ISCAS 2007. IEEE International
Symposium on, pages 3371–3374. IEEE.
Lenero-Bardallo, J. A., Serrano-Gotarredona, T., and
Linares-Barranco, B. (2010). A signed spatial contrast
event spike retina chip. In Circuits and Systems (IS-
CAS), Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Sym-
posium on, pages 2438–2441. IEEE.
Lichtsteiner, P., Posch, C., and Delbruck, T. (2008). A
128x128 120 db 15 microsec latency asynchronous
temporal contrast vision sensor. IEEE journal of solid-
state circuits, 43(2):566–576.
Maass, W. (1997). Networks of spiking neurons: the third
generation of neural network models. Neural net-
works, 10(9):1659–1671.
Maqueda, A. I., Loquercio, A., Gallego, G., Garcıa, N.,
and Scaramuzza, D. (2018). Event-based vision meets
deep learning on steering prediction for self-driving
cars. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 5419–
5427.
Ponulak, F. and Kasinski, A. (2011). Introduction to spi-
king neural networks: Information processing, lear-
ning and applications. Acta neurobiologiae experi-
mentalis, 71(4):409–433.
Redmon, J., Divvala, S., Girshick, R., and Farhadi, A.
(2016). You only look once: Unified, real-time object
detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on
computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 779–
788.
Rueckauer, B., Lungu, I.-A., Hu, Y., Pfeiffer, M., and Liu,
S.-C. (2017). Conversion of continuous-valued deep
networks to efficient event-driven networks for image
classification. Frontiers in neuroscience, 11:682.
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S.,
Ma, S., Huang, Z., Karpathy, A., Khosla, A., Bern-
stein, M., et al. (2015). Imagenet large scale visual
recognition challenge. International Journal of Com-
puter Vision, 115(3):211–252.
Sawada, J., Akopyan, F., Cassidy, A. S., Taba, B., De-
bole, M. V., Datta, P., Alvarez-Icaza, R., Amir, A.,
Arthur, J. V., Andreopoulos, A., et al. (2016). Tru-
enorth ecosystem for brain-inspired computing: sca-
lable systems, software, and applications. In Procee-
dings of the International Conference for High Perfor-
mance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis,
page 12. IEEE Press.
Sengupta, A., Ye, Y., Wang, R., Liu, C., and Roy,
K. (2018). Going deeper in spiking neural net-
works: Vgg and residual architectures. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1802.02627.
Siam, M., Elkerdawy, S., Jagersand, M., and Yogamani, S.
(2017). Deep semantic segmentation for automated
driving: Taxonomy, roadmap and challenges. In In-
telligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), 2017 IEEE
20th International Conference on, pages 1–8. IEEE.
VISAPP 2019 - 14th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
554

Tavanaei, A., Ghodrati, M., Kheradpisheh, S. R., Masque-
lier, T., and Maida, A. S. (2018). Deep lear-
ning in spiking neural networks. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1804.08150.
Thorpe, S., Delorme, A., and Van Rullen, R. (2001). Spike-
based strategies for rapid processing. Neural net-
works, 14(6-7):715–725.
Wunderlich, T., Kungl, A. F., Hartel, A., Stradmann, Y.,
Aamir, S. A., Gr
¨
ubl, A., Heimbrecht, A., Schreiber,
K., St
¨
ockel, D., Pehle, C., et al. (2018). Demonstra-
ting advantages of neuromorphic computation: A pilot
study. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.03618.
Zhao, B., Ding, R., Chen, S., Linares-Barranco, B., and
Tang, H. (2015). Feedforward categorization on aer
motion events using cortex-like features in a spiking
neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learning
Syst., 26(9):1963–1978.
Zhou, S. and Wang, W. (2018). Object detection based on
lidar temporal pulses using spiking neural networks.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.12436.
Exploring Deep Spiking Neural Networks for Automated Driving Applications
555
