
The Composition of Dense Neural Networks and Formal Grammars for
Secondary Structure Analysis
Semyon Grigorev
1,2
and Polina Lunina
1,2
1
St. Petersburg State University, 7/9 Universitetskaya nab., St.Petersburg, Russia
2
JetBrains Research, Universitetskaya emb., 7-9-11/5A, St.Petersburg, Russia
Keywords:
Dense Neural Network, DNN, Machine Learning, Secondary Structure, Genomic Sequences, Proteomic
Sequences, Formal Grammars, Parsing.
Abstract:
We propose a way to combine formal grammars and artificial neural networks for biological sequences pro-
cessing. Formal grammars encode the secondary structure of the sequence and neural networks deal with
mutations and noise. In contrast to the classical way, when probabilistic grammars are used for secondary
structure modeling, we propose to use arbitrary (not probabilistic) grammars which simplifies grammar
creation. Instead of modeling the structure of the whole sequence, we create a grammar which only describes
features of the secondary structure. Then we use undirected matrix-based parsing to extract features: the fact
that some substring can be derived from some nonterminal is a feature. After that, we use a dense neural net-
work to process features. In this paper, we describe in details all the parts of our receipt: a grammar, parsing
algorithm, and network architecture. We discuss possible improvements and future work. Finally, we provide
the results of tRNA and 16s rRNA processing which shows the applicability of our idea to real problems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Accurate, fast, and precise sequences classification
and subsequences detection are open problems in
such areas of bioinformatics as genomics and pro-
teomics. Challenge here is high variability of se-
quences belonging to the same class. Probabilistic
models, such as Hidden Markov’s Models (HMMs) or
probabilistic (stochastic) grammars (PCFGs, SCFGs),
help to deal with variability. Formal grammars are
more successful in handling long-distance connec-
tions. Moreover, grammars model the secondary
structure of sequences more explicitly.
For example, algorithms that can efficiently and
accurately identify and classify bacterial taxonomic
hierarchy became a focus in computational genomics.
The idea that the secondary structure of genomic se-
quences is sufficient for solving the detection and
classification problems lies at the heart of many
tools (Rivas and Eddy, 2000; Knudsen and Hein,
1999; Yuan et al., 2015; Dowell and Eddy, 2004).
The problem here is that the sequences obtained from
the real bacteria usually contain a huge number of
mutations and noise which renders precise methods
impractical. Probabilistic grammars and covariance
models (CMs) are a way to take the noise into ac-
count (Durbin et al., 1998), but it is difficult to create
(train or learn) high-quality grammar or model. How-
ever, CMs are successfully used in some tools, for ex-
ample, the Infernal tool (Nawrocki and Eddy, 2013).
Neural networks are another way to deal with
noisy data. The works (Sherman, 2017; Higashi et al.,
2009) utilize artificial neural networks for 16s rRNA
processing and demonstrate promising results.
In this work, we propose a way to combine for-
mal grammars and neural networks for sequences pro-
cessing. The key idea is not to try to model the full
(sub)sequence of interest by a grammar, but to cre-
ate a grammar which describes features of secondary
structure and to use a neural network for these fea-
tures processing. We show that it is possible to detect
features that are not expressible in the class of used
grammars using the proposed approach. For example,
the proposed combination of context-free grammar
and neural network can detect pseudoknots, although
they cannot be expressed by a context-free grammar.
We provide an evaluation of the proposed approach
for tRNA classification and 16s rRNA detection. Re-
sults show that the proposed approach is applicable to
real problems.
234
Grigorev, S. and Lunina, P.
The Composition of Dense Neural Networks and Formal Grammars for Secondary Structure Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0007472302340241
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2019), pages 234-241
ISBN: 978-989-758-353-7
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 PROPOSED SOLUTION
We combine neural networks and ordinary context-
free grammars (not probabilistic which are usually
used in this area) to handle information about the sec-
ondary structure of sequences. Namely, we propose
to extract secondary structure features by using an or-
dinary context-free grammar and use a dense neural
network for features processing. Our solution is not
dependent on the parsing algorithm: features can be
extracted by any parsing algorithm and then presented
as a boolean matrix. We choose the parsing algorithm
based on matrix multiplication.
In this section, we describe all the components of
our recipe and provide some examples end explana-
tions.
2.1 Context-free Grammars
The first component is a context-free grammar. It is
well known that the secondary structure of the se-
quence may be approximated by using formal gram-
mars. Several works utilize this fact (Rivas and Eddy,
2000; Dowell and Eddy, 2004; Zier-Vogel and Do-
maratzki, 2013; Knudsen and Hein, 2003).
Probabilistic context-free grammars are usually
used for secondary structure modeling because it
deals with variations (mutations or noise). As op-
posed to it, we use ordinary (not probabilistic) gram-
mars. Our goal is not to model the secondary structure
of the whole sequence (which requires probabilistic
grammars), but rather to describe features of the sec-
ondary structure, such as stems, loops, pseudoknots,
and their composition. Of course, the set of feature
types is limited by the class of grammar which we
use. For example, pseudoknots cannot be expressed
by context-free grammars but can be expressed by
conjunctive grammars (Devi and Arumugam, 2017;
Zier-Vogel and Domaratzki, 2013; Okhotin, 2001) or
multiple context-free ones (Seki et al., 1991; Riechert
et al., 2016).
The context-free grammar G
0
which we use in
our experiments is presented in figure 1. It is
a context-free grammar over the four-letters alpha-
bet Σ = {A, C, G, T } with the start nonterminal s1.
This grammar describes the composition of stems of
bounded minimal height.
First of all, we provide a brief description of gram-
mar specification language. The : sign separates the
left-hand side and the right-hand side of the rule.
In the right-hand side, one can use extended regu-
lar expressions over union alphabet of terminals and
nonterminals. Such constructions as bounded rep-
etition and alternative are available. For example,
s1: stem<s0>
any_str : any_smb*[2..10]
s0: any_str | any_str stem<s0> s0
any_smb: A | T | C | G
stem1<s>: A s T | G s C | T s A | C s G
stem2<s>: stem1< stem1<s> >
stem<s>:
A stem<s> T
| T stem<s> A
| C stem<s> G
| G stem<s> C
| stem1< stem2<s> >
Figure 1: Context-free grammar G
0
for RNA secondary
structure features extraction.
any_smb*[2..10] is a bounded repetition. It states
that the nonterminal any_smb may be repeated any
number of times from 2 up to 10. Example of the rule
which uses alternatives is any smb: A | T | C |
G which states that any_smb is one of the four termi-
nals.
The grammar specification language also has
parametric rules or meta-rules which are used to cre-
ate reusable grammar templates. One can find more
details on meta-rules in (Thiemann and Neubauer,
2008). The example of meta-rule in our gram-
mar is stem1<s>: A s T | G s C | T s A | C
s G. This rule is parametrized by s which stands for
something that should be embedded into a stem. Ap-
plication of this rule to any_str allows one to define
a stem with a loop of length from 2 up to 10. In our
grammar we use meta-rules in order to describe stems
with bounded minimal height: stem1<s> is a stem
with the height exactly 1, stem2<s> is a stem with
the height exactly 2, and stem<s> is a stem with the
height greater or equal 3.
Now we explain what this grammar means. This
grammar describes a recursive composition of stems.
To see it one can look at the rule for s0 which is re-
cursive and shows that composition of stems may be
embedded into the stem (stem<s0> in the right side
of this rule). Every stem should have the height not
lower than 3 and can be built only from classical base
pairs. Stems may be connected by an arbitrary se-
quence of length from 2 up to 10, and loops have the
same length. One can find the graphical explanation
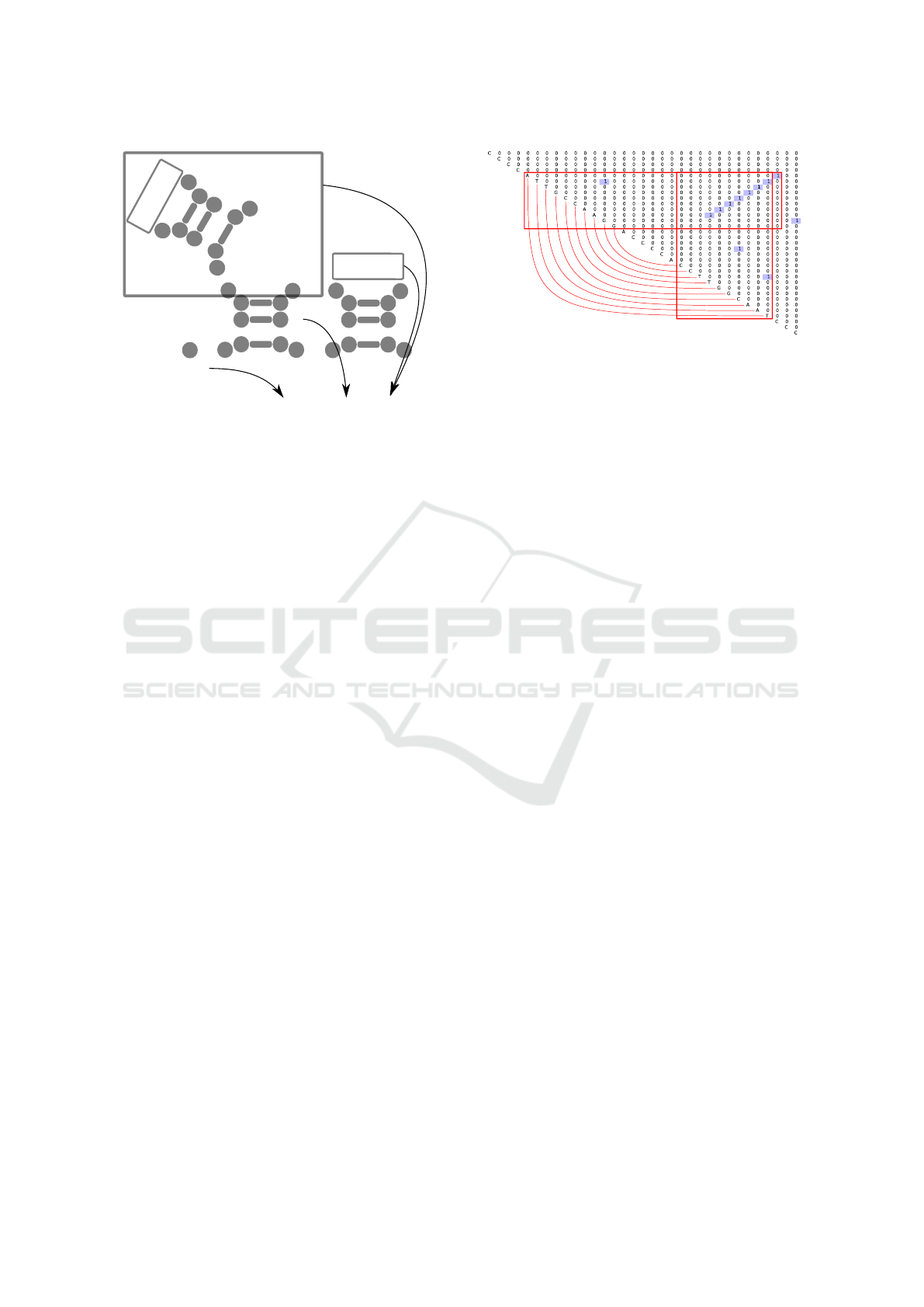
of this description in figure 2.
The Composition of Dense Neural Networks and Formal Grammars for Secondary Structure Analysis
235
s0: any_str | any_str stem<s0> s0
...
...
}
...
...
...
...
s0
s0
h >2
}
s0
...
...
...
...
Figure 2: The graphical explanation of the pattern specified
by the grammar G
0
in figure 1.
Note, that grammar is a variable parameter of
our solution and may be tuned for specific cases.
The grammar presented above is a result of a set
of experiments, so there is no reason to state that
it is the best grammar for secondary structure fea-
tures extraction. For example, one can vary the
length of the unfoldable sequence by changing the
rule for any_str: any_str : any_smb*[0..10],
any_str : any_smb*[1..8], or something else.
Also, one can increase (or decrease) the minimal
height of stem or add some new features, such as
pseudoknots, to the grammar (in case one uses con-
junctive grammars instead of the context-free).
2.2 Parsing Algorithm
Parsing is used to determine if the given sequence can
be derived in the given grammar. Additionally, when
the sequence is derivable, a derivation tree may be
provided as a result of parsing. It is a classical way:
there is a huge number of works on modeling the sec-
ondary structure of the full sequence of interest by
using probabilistic grammars and respective parsing
techniques (Knudsen and Hein, 2003; Browny et al.,
1993; Knudsen, 2005). We propose to use parsing to
extract features: rather than checking the derivability
of the given string or find the most probable deriva-
tion we search for all the derivable substrings of the
given string for all nonterminals.
CYK (Younger, 1967) is a well-known classi-
cal algorithm for undirected parsing. This algo-
rithm and its modifications are traditionally used for
PCFG/SCFG processing and, as a result, are used in
a number of tools, but they demonstrate poor perfor-
mance on long sequences and big grammars (Liu and
Schmidt, 2005).
Figure 3: Parsing result for sequence which should folds to
stem.
An alternative approach is to use the algorithms
based on matrix multiplication, such as Valiant’s al-
gorithm (Valiant, 1975). From the practical stand-
point, matrix-based algorithms allow to easily utilize
advanced techniques, such as algorithms for sparse
and boolean matrices, GPGPU-based libraries, etc.
Moreover, the matrix-based approach can be
generalized to conjunctive and even boolean gram-
mars (Okhotin, 2014), as far as to multiple context-
free grammars (Cohen and Gildea, 2016), which can
provide a base for more expressive features descrip-
tions handling without significant changes in other
parts of our solution.
In our work, we use a version of the matrix-based
algorithm (Azimov and Grigorev, 2018). The the-
oretical time complexity of this algorithm is worse
than the complexity of the Valiant’s algorithm, but
it demonstrates better performance in practice along
with a simpler implementation since this algorithm
avoids machinery on submatrices manipulation.
2.3 Matrices
The result of parsing is a set of square boolean ma-
trices. Each matrix M
N
contains information of all
substrings which can be derived from the nonterminal
N. In other words, M
N
[i, j] = 1 iff N ⇒
∗
G
w[i, j − 1]
where w is the input sequence and G is a context-free
grammar, and N is a nonterminal. Thus, the result of
parsing is a set of matrices: one matrix for each non-
terminal from the grammar. For further processing,
we can select nonterminals of interest. In our case,
for grammar G
0
, we select the matrix for the nonter-
minal s1.
The example of such matrix is provided in fig-
ure 3. This matrix is a result of parsing of the se-
quence
w
1
=CCCCATTGCCAAGGACCCCACCTTGGCAATCCC
w.r.t the grammar G
0
. One can see an upper right
triangle of the parsing matrix (bottom left is always
BIOINFORMATICS 2019 - 10th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
236

empty, so omitted) with input string on the diago-
nal. Note that the string is added only for example
readability and a real matrix does not contain the in-
put string, only results of its parsing. Each filled cell
[i, j] which contains 1 denotes that the subsequence
w
1
[i, j − 1] is derivable from s1 in G
0
(so, this sub-
sequence folds to a stem of height 3 or more). In or-
der to find stems with the height of more than 3, one
should detect diagonal chains of 1-s: in our example
the stem is of height 10, and one can find chain of 1-s
of the length 8 = 10 − 2 (first 1 is a root of the stem
of height 3, and each next 1 is a new base pair upon
this stem — root of the stem with height increased by
one). Red boxes and contact map are added for navi-
gation simplification.
Our goal is to extract all the features of the sec-
ondary structure, so, our parser finds all the substrings
which can be derived from s1. As a result, there are
some 1-s out of the chain. These are correct results:
corresponded subsequences can be derived from s1.
In the current example, these 1-s may be treated as
noise in some sense, but such behavior may be useful
in some cases, as we show later. Moreover, for long
sequences with the complex structure, it may be not
evident, which features of the secondary structure are
most important.
We use these matrices as an input for the artificial
neural network which should detect sufficient features
(long chain in our example) and utilize them for ap-
plied problem solution (sequence detection or classi-
fication, for example). We drop out the bottom left tri-
angle and vectorize matrices row-by-row to get a bit
vector, then convert it to a byte vector and use it as an
input. The transition from bit vector to byte vector is
done in order to decrease the input size which is criti-
cal for long sequences. On the other hand, such oper-
ation may significantly complicate network architec-
ture and training, and it is a reason to try to use bitwise
networks (Kim and Smaragdis, 2016) in the future.
2.4 Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial neural networks are one possible choice
for different classification problems when data has a
hard-to-formalize principal for problem features and
contains noise. Different types of networks suit for
images, speech, and natural languages processing.
Classical scenario for classification problems is to
provide features vectors and to classify them, mean-
ing that the network can select important features for
each required class. In our case, the fact that w[i, j −1]
is derivable from nonterminal N is a feature. These
facts are encoded in the parsing matrix. So, the vec-
torized matrix is a vector of features which is a typical
input for a neural network.
We use dense neural network because data local-
ity is broken during vectorization and any convolu-
tions are inapplicable. Moreover, convolutions are
used mostly for features extraction, but in our case
features are already extracted by parsing. Thus we
need only to detect principal features and relations be-
tween them. It is best done with dense networks.
One of the problems with arbitrary data process-
ing by using neural networks is the input size normal-
ization. The input layer of the network has fixed size,
but input sequence length and hence the length of vec-
torized parsing result may vary even for the fixed task.
For example, if we want to create a solution for tRNA
processing, we should handle sequences of the length
approximately from 59 up to 250. We propose two
possible ways to solve this problem. The first way
is subsequences processing: for some tasks, it may
be enough to process not a full sequence, but only its
subsequence. In this case, we can set the length of
subsequence lower than the shortest sequence which
we want to handle. This way is useful for long se-
quences processing (16s rRNA, for example) but can-
not be applied for short sequences processing because
of the information loss. The second way is to set an
upper bound and fill the gap with special symbols. For
example, while handling tRNAs we can set the input
length to 250, and when we want to process sequence
of length 60, then we should fill the rest 190 places by
selected special symbol.
The example of the neural network which we use
is presented in figure 8. We actively use dropout and
batch normalization because network should perform
a number of nontrivial transformations: decompress
data from bytes and prepare normalized input which
requires additional power. Although initially, batch
normalization is an alternative for dropout (Ioffe and
Szegedy, 2015), we use both of them together because
separate use has no effects.
3 EXAMPLES
Here we provide more examples of matrices and point
out some observations about it in order to provide bet-
ter intuition of our idea.
The first part is the observation about pseudo-
knots. Let consider the following sequence which can
fold to pseudoknot as an example:
w
2
=CCACTTACCTATGACCTAAGTCCTCATACC.
Note, that this sequence is synthetic. As men-
tioned above, pseudoknots cannot be expressed in
terms of context-free grammars. But one can think
The Composition of Dense Neural Networks and Formal Grammars for Secondary Structure Analysis
237
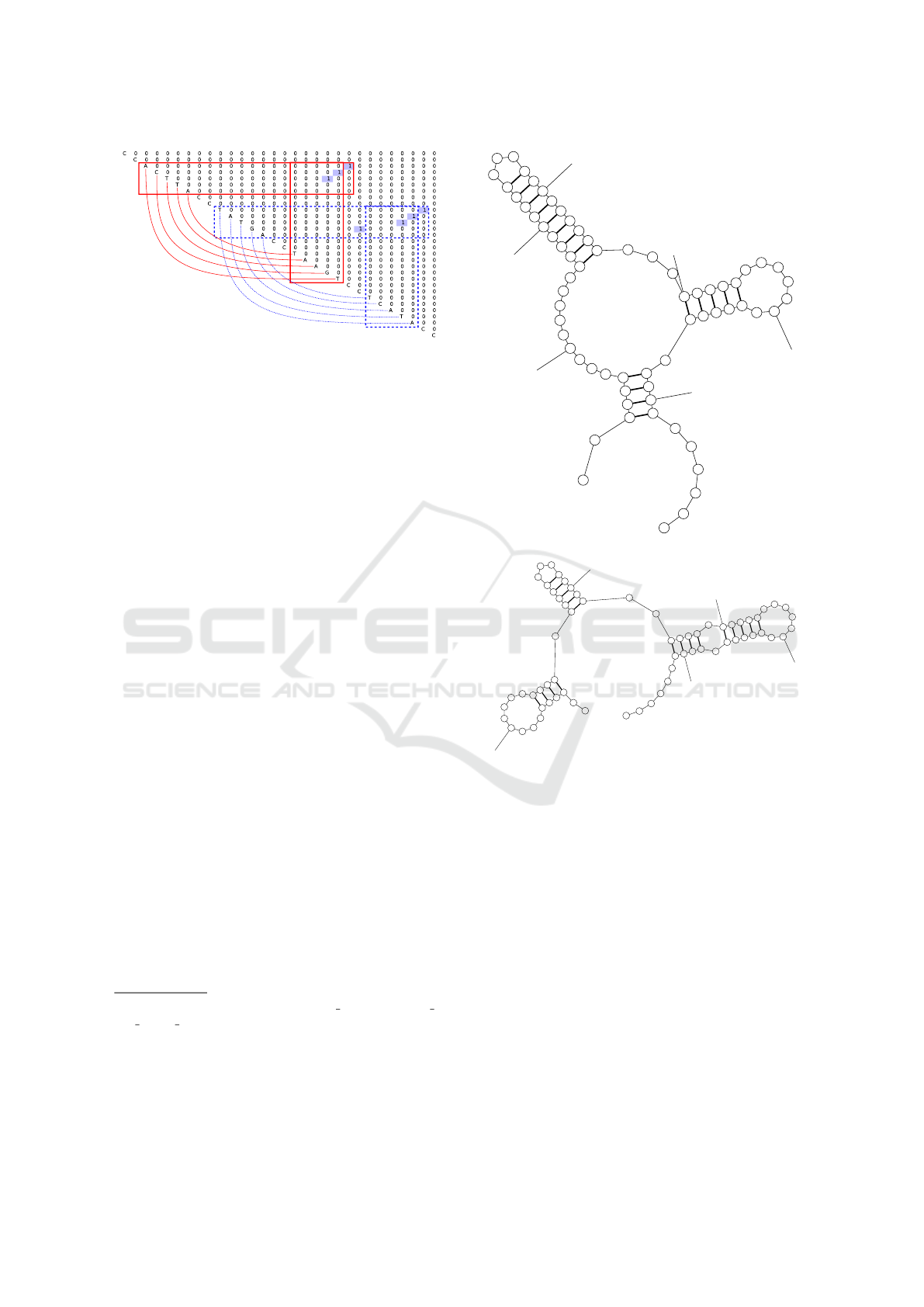
Figure 4: Parsing result for sequence which should folds to
pseudoknot.
of a pseudoknot as two crossing stems, and the parser
can extract both of them, as presented in figure 4.
So, if a neural network is powerful enough, it can de-
tect that if these two features appear simultaneously,
then the sequence contains pseudoknot. As a result,
we can detect features which are not expressible in
context-free grammars.
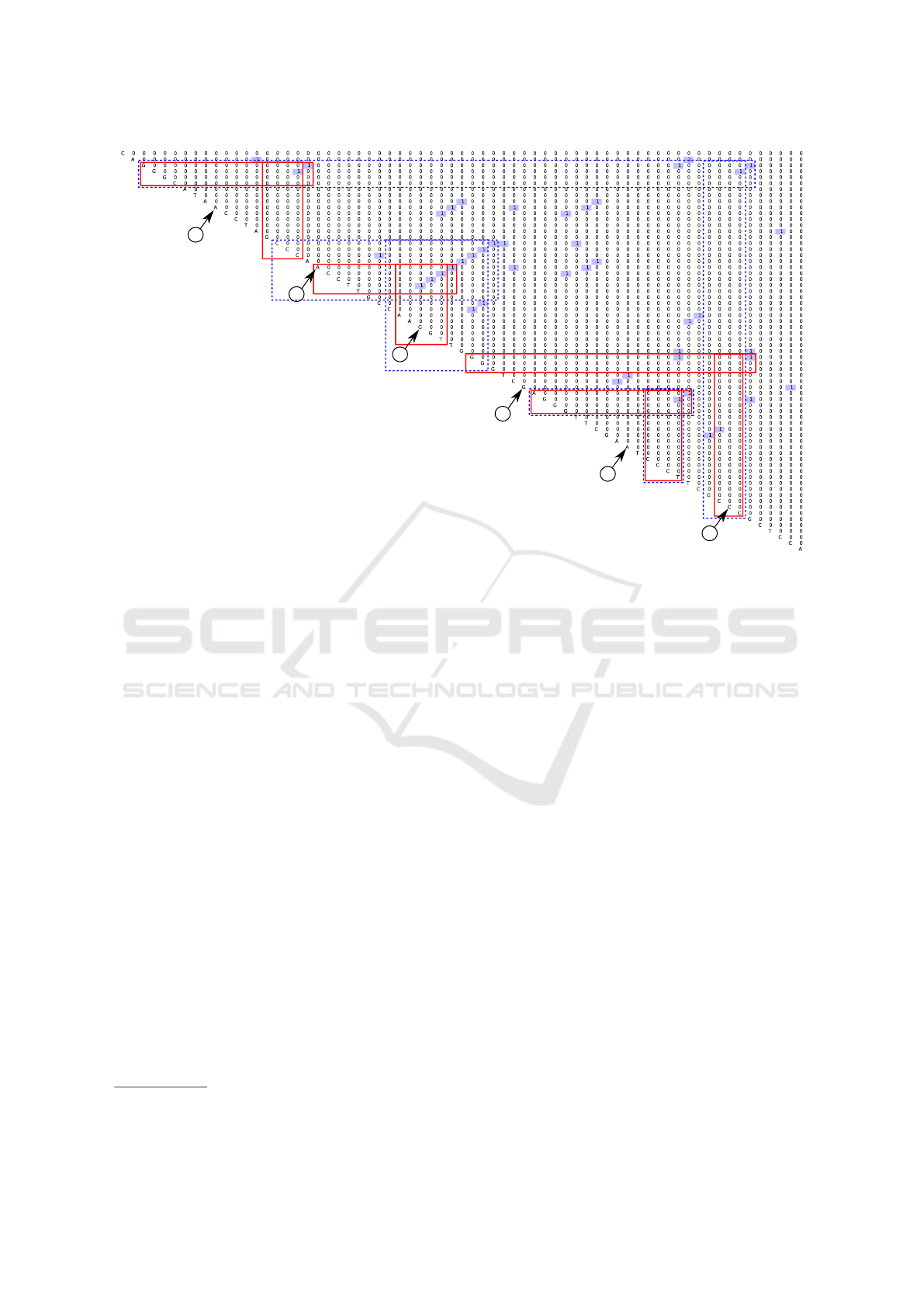
The second is an example of a matrix for the real
tRNA. Parsing result of the tRNA
1
sequence
w
3
=CAGGGCATAACCTAGCCCAACCTTGCCAAGG
TTGGGGTCGAGGGTTCGAATCCCTTCGCCCGCTCCA
is presented in figure 7. Also, one can see pre-
dicted secondary structures
2
(top two) in figures 5
and 6.
Colored boxes in figure 7 marks features which
correspond to these two predicted foldings: blue
dashed marks for 5 and red for 6. Note, that our
grammar G
0
handles only classical base pairs, so the
pair G - T which exists in predicted foldings, is not
presented in parsing result. Anyway, we can see that
all expected information on the secondary structure is
presented in the matrix with some additional features,
of course. And it is a field for neural networks — to
select appropriate features.
We conclude that powerful enough neural net-
works may detect very nontrivial compositions of sec-
ondary structure features. What kinds of applications
may be built by using such results is an interesting
question for future research.
1
The sequence Novosphingobium aromaticivorans D
SM 12444 chr.trna57-GlyGCC (268150-268084) Gly
(GCC) 67 bp Sc: 22.97. From GtRNAdb: http://gtrnadb
2009.ucsc.edu/download.html. Access date: 02.11.2018.
2
Predicted secondary structures are given by using the
Fold Web Server with default settings: http://rna.urmc.
rochester.edu/RNAstructureWeb/Servers/Fold/Fold.html
Access date: 02.11.2018.
C
A
G
G
G
C
A
T
A
10
A
C
C
T
A
G
C
C
C
A
20
A
C
C
T
T
G
C
C
A
A
30
G
G
T
T
G
G
G
G
T
C
40
G
A
G
G
G
T
T
C
G
A
50
A
T
C
C
C
T
T
C
G
C
60
C
C
G
C
T
C
C
A
Figure 5: Predicted secondary structure for w
3
.
C
A
G
G
G
C
A
T
A
10
A
C
C
T
A
G
C
C
C
A
A
C
C
T
T
G
C
C
A
A
30
G
G
T
T
G
G
G
G
T
C
40
G
A
G
G
G
T
T
C
G
A
50
A
T
C
C
C
T
T
C
G
C
60
C
C
G
C
T
C
C
A
Figure 6: Predicted secondary structure for w
3
.
4 EVALUATION
We evaluate the proposed approach on two cases: 16s
rRNA detection and tRNA classification. Note that
the goal of the evaluation is to demonstrate the appli-
cability of the approach described above. We do not
provide a comparison with existing tools because our
solution is a prototype. All of these are future work.
4.1 16s rRNA Sequences
The first problem is 16s rRNA detection. We spec-
ify context-free grammars which detect stems with
the height of more than two pairs and their arbi-
trary compositions (namely, G
0
). For network train-
ing, we use a dataset consisting of two parts: ran-
dom subsequences of 16s rRNA sequences from the
BIOINFORMATICS 2019 - 10th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
238
10
20
50
30
60
40
Figure 7: Parsing result for the real tRNA (w
3
).
Green Genes database (DeSantis et al., 2006) form
positive examples, while the negative examples are
random subsequences of full genes from the NCBI
database (Geer et al., 2010). All sequences have
the length of 512 symbols, totally up to 310000 se-
quences. After training, current accuracy is 90% for
validation set (up to 81000 sequences); thus we con-
clude that our approach is applicable.
4.2 tRNA Sequences
The second problem is tRNA classification: we train
a neural network to separate tRNAs into two classes:
prokaryotes and eukaryotes. We prepare 50000 se-
quences from GtRNADB (Chan and Lowe, 2009) for
training: 35000 for training and 15000 for testing. In
this case, we use the next trick for data size normal-
ization. We set the upper bound of sequence length to
220 and after that, we align the real tRNA sequence
w in the following way: the first k symbols of the in-
put are w (|w| = k) and the rest 220 − k symbols are
filled by $ — a special symbol which is not in input
alphabet.
Also, we prepare the validation set which con-
tains 217984 sequences for prokaryotes and 62656 se-
quences for eukaryotes. All data for validation was
taken from tRNADB-CE
3
(Abe et al., 2010).
3
tRNADB-CE: http://trna.ie.niigata-u.ac.jp/cgi-bin/ tr-
nadb/index.cgi. Access date: 31.10.2018
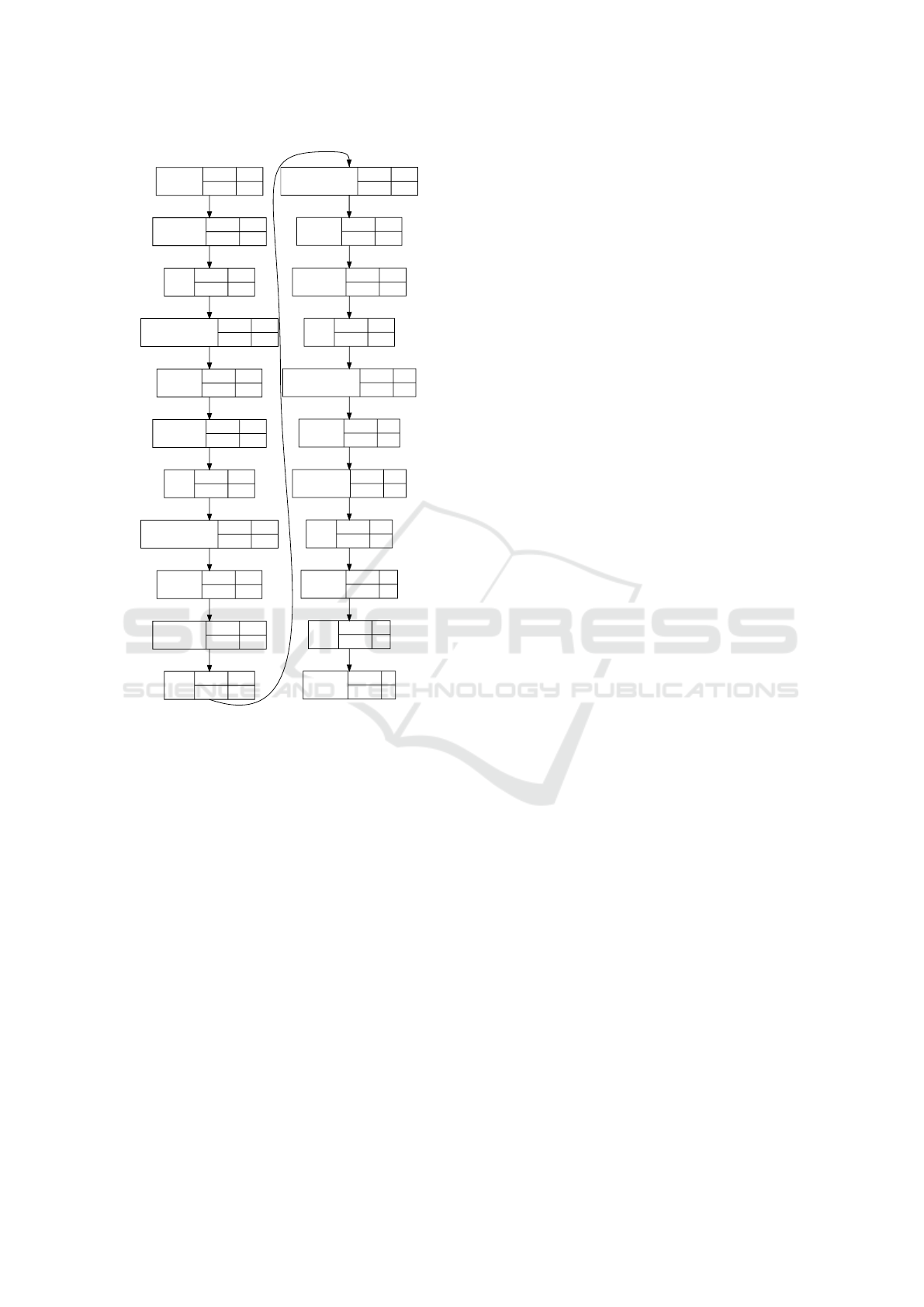
The architecture of the network which we use in
this experiment is presented in figure 8. Note that
it is a training configuration: it contains dropout and
batch normalization layers which will be removed af-
ter training. This network contains six dense layers
and uses relu and sigmoid activation functions.
After training, our network demonstrates the accu-
racy of 97%. For the validation set, we get the follow-
ing results: 3276 of eukaryotes (5.23% of all eukary-
otes in the validation set) are classified as prokaryotes
and 4373 of prokaryotes (2.01% of all prokaryotes in
the validation set) are classified as eukaryotes.
We conclude that input normalization by filling se-
quence to the upper bound of length with the special
symbol is working. Also, we can state that the sec-
ondary structure contains sufficient information for
classification.
5 DISCUSSION
The presented is a work in progress. The ongoing ex-
periment is finding all instances of 16s rRNA in full
genomes. Also, we plan to use the proposed approach
for the filtration of chimeric sequences and classifica-
tion. A composition of our approach with other meth-
ods and tools as well as grammar tuning and detailed
performance evaluation may improve the applicabil-
ity for the real data processing.
The Composition of Dense Neural Networks and Formal Grammars for Secondary Structure Analysis
239
Activation
relu
input:
output:
1024
1024
Dropout(0.9)
input:
output:
1024
1024
Dense
input:
output:
1024
512
BatchNormalization
input:
output:
512
512
Activation
relu
input:
output:
512
512
Dropout(0.75)
input:
output:
512
512
Dense
input:
output:
512
64
Activation
sigmoid
input:
output:
64
64
Dense
input:
output:
64
1
Activation
sigmoid
input:
output:
1
1
BatchNormalization
input:
output:
1024
1024
InputLayer
input:
output:
3028
3028
Dropout(0.3)
input:
output:
3028
3028
Dense
input:
output:
3028
8194
BatchNormalization
input:
output:
8194
8194
Activation
relu
input:
output:
8194
8194
Dropout(0.9)
input:
output:
8194
8194
Dense
input:
output:
8194
2048
BatchNormalization
input:
output:
2048
2048
Activation
relu
input:
output:
2048
2048
Dropout(0.9)
input:
output:
2048
2048
Dense
input:
output:
2048
1024
Figure 8: Architecture of the neural network for tRNA clas-
sification.
One problem of the proposed approach is that
parsing is a bottleneck. A possible solution is to con-
struct a network which can handle sequences instead
of parsing data. It may be done in the following way.
1. Create a training set of matrices using parsing.
2. Build and train the network NN
1
which can handle
vectorized matrices.
3. Create new network NN
2
by extending NN
1
with
a head (set of layers) which should convert the se-
quence to input for NN
1
4. Train NN
2
. Fix the weights of layers from NN
1
.
5. For the concrete problem, we can tune weights of
NN
2
to get an appropriate quality.
This way we can use parsing only for training which
is less performance critical step than usage in an ap-
plication.
Another task is to understand the features which
network extracts in order to get inspiration in, for ex-
ample, grammar tuning. It may be done by trained
network visualization. There is a set of tools for user-
friendly convolutional networks visualization, but not
for dense networks. It may be useful to create such a
tool and customize it for our domain.
We do some experiments in genomic sequence
analysis, but what about proteomics? Works on
grammar-based approaches to proteomics sequences
analysis have a long history (Jim
´
enez-Monta
˜
no, 1984;
Dyrka and Nebel, 2008; Sciacca et al., 2011). This
area provides new challenges, such as more complex
grammar, more symbols in the alphabet, more com-
plex rules of interactions, more complex features. As
a result, more powerful languages may be needed in
this area. So, we are curious to apply the proposed
approach to proteomics sequences analysis. One of
the possible crucial problems is to detect function-
ally equivalent sequences with sufficiently different
length.
Also, it may be reasonable to use other types
of neural networks. Bitwise networks (Kim and
Smaragdis, 2016) may be reasonable because the re-
sult of parsing is a bitwise matrix, so it looks natural
to use these networks to process such result. Another
direction is convolutional networks utilization. One
can treat parsing matrices as bitmaps: one can set a
specific color for each nonterminal and get a multi-
color picture as a sum of matrices. The problem here
is a picture size: typical matrix size is n × n where n
is a length of the input sequence.
An important part of work is training data prepa-
ration. One of the difficult problems is the creation of
a balanced dataset. Biological datasets (like Green-
Genes) contain a huge number of samples for some
well-studied organisms and a very small number of
samples for others. Moreover, datasets often contain
unclassified and unconfirmed sequences. It is not ev-
ident how to prepare datasets to get a high-quality
trained network.
To conclude, our work is at the beginning stage,
but current results are promising. There is a huge
number of experiments in different directions which
have potential. In order to choose the right direction,
we hope to discuss future work with the community.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research was supported by the Russian Science
Foundation grant 18-11-00100 and a grant from Jet-
Brains Research.
BIOINFORMATICS 2019 - 10th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
240

REFERENCES
Abe, T., Ikemura, T., Sugahara, J., Kanai, A., Ohara, Y.,
Uehara, H., Kinouchi, M., Kanaya, S., Yamada, Y.,
Muto, A., and Inokuchi, H. (2010). tRNADB-CE
2011: tRNA gene database curated manually by ex-
perts. Nucleic Acids Research, 39(Database):D210–
D213.
Azimov, R. and Grigorev, S. (2018). Context-free path
querying by matrix multiplication. In Proceedings
of the 1st ACM SIGMOD Joint International Work-
shop on Graph Data Management Experiences & Sys-
tems (GRADES) and Network Data Analytics (NDA),
GRADES-NDA ’18, pages 5:1–5:10, New York, NY,
USA. ACM.
Browny, M., Underwoody, R. C., Mianx, I. S., and Haus-
sleryy, D. (1993). Stochastic context-free grammars
for modeling rna.
Chan, P. P. and Lowe, T. M. (2009). GtRNAdb: a database
of transfer RNA genes detected in genomic sequence.
Nucleic Acids Research, 37(Database):D93–D97.
Cohen, S. B. and Gildea, D. (2016). Parsing linear context-
free rewriting systems with fast matrix multiplication.
Computational Linguistics, 42(3):421–455.
DeSantis, T. Z., Hugenholtz, P., Larsen, N., Rojas, M.,
Brodie, E. L., Keller, K., Huber, T., Dalevi, D., Hu, P.,
and Andersen, G. L. (2006). Greengenes, a chimera-
checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench
compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.,
72(7):5069–5072.
Devi, K. K. and Arumugam, S. (2017). Probabilistic con-
junctive grammar. In Theoretical Computer Science
and Discrete Mathematics, pages 119–127. Springer
International Publishing.
Dowell, R. D. and Eddy, S. R. (2004). Evaluation of several
lightweight stochastic context-free grammars for rna
secondary structure prediction. BMC bioinformatics,
5(1):71.
Durbin, R., Eddy, S. R., Krogh, A., and Mitchison, G.
(1998). Biological sequence analysis: probabilistic
models of proteins and nucleic acids. Cambridge uni-
versity press.
Dyrka, W. and Nebel, J.-C. (2008). A stochastic context
free grammar based framework for analysis of protein
sequences. BMC Bioinformatics, 10:323 – 323.
Geer, L. Y., Marchler-Bauer, A., Geer, R. C., Han, L., He,
J., He, S., Liu, C., Shi, W., and Bryant, S. H. (2010).
The NCBI BioSystems database. Nucleic Acids Res.,
38(Database issue):D492–496.
Higashi, S., Hungria, M., and Brunetto, M. (2009). Bac-
teria classification based on 16s ribosomal gene using
artificial neural networks. In Proceedings of the 8th
WSEAS International Conference on Computational
intelligence, man-machine systems and cybernetics,
pages 86–91.
Ioffe, S. and Szegedy, C. (2015). Batch normalization: Ac-
celerating deep network training by reducing internal
covariate shift. CoRR, abs/1502.03167.
Jim
´
enez-Monta
˜
no, M. A. (1984). On the syntactic struc-
ture of protein sequences and the concept of gram-
mar complexity. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology,
46(4):641–659.
Kim, M. and Smaragdis, P. (2016). Bitwise neural net-
works. CoRR, abs/1601.06071.
Knudsen, B. and Hein, J. (1999). Rna secondary structure
prediction using stochastic context-free grammars and
evolutionary history. Bioinformatics (Oxford, Eng-
land), 15(6):446–454.
Knudsen, B. and Hein, J. (2003). Pfold: Rna sec-
ondary structure prediction using stochastic context-
free grammars. Nucleic acids research, 31(13):3423–
3428.
Knudsen, M. (2005). Stochastic context-free grammars and
rna secondary structure prediction.
Liu, T. and Schmidt, B. (2005). Parallel RNA sec-
ondary structure prediction using stochastic context-
free grammars. Concurrency and Computation: Prac-
tice and Experience, 17(14):1669–1685.
Nawrocki, E. P. and Eddy, S. R. (2013). Infernal 1.1: 100-
fold faster RNA homology searches. Bioinformatics,
29(22):2933–2935.
Okhotin, A. (2001). Conjunctive grammars. J. Autom.
Lang. Comb., 6(4):519–535.
Okhotin, A. (2014). Parsing by matrix multiplication gen-
eralized to boolean grammars. Theoretical Computer
Science, 516:101 – 120.
Riechert, M., H
¨
oner zu Siederdissen, C., and Stadler, P. F.
(2016). Algebraic dynamic programming for mul-
tiple context-free grammars. Theor. Comput. Sci.,
639(C):91–109.
Rivas, E. and Eddy, S. R. (2000). The language of rna: a
formal grammar that includes pseudoknots. Bioinfor-
matics, 16(4):334–340.
Sciacca, E., Spinella, S., Ienco, D., and Giannini, P. (2011).
Annotated stochastic context free grammars for anal-
ysis and synthesis of proteins. In EvoBio.
Seki, H., Matsumura, T., Fujii, M., and Kasami, T. (1991).
On multiple context-free grammars. Theoretical Com-
puter Science, 88(2):191 – 229.
Sherman, D. (2017). Humidor: Microbial community clas-
sification of the 16s gene by training cigar strings with
convolutional neural networks.
Thiemann, P. and Neubauer, M. (2008). Macros for context-
free grammars. In Proceedings of the 10th Inter-
national ACM SIGPLAN Conference on Principles
and Practice of Declarative Programming, PPDP ’08,
pages 120–130, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Valiant, L. G. (1975). General context-free recognition in
less than cubic time. J. Comput. Syst. Sci., 10(2):308–
315.
Younger, D. H. (1967). Recognition and parsing of context-
free languages in time n
3
. Information and Control,
10:189–208.
Yuan, C., Lei, J., Cole, J., and Sun, Y. (2015). Reconstruct-
ing 16s rrna genes in metagenomic data. Bioinformat-
ics, 31(12):i35–i43.
Zier-Vogel, R. and Domaratzki, M. (2013). Rna pseudoknot
prediction through stochastic conjunctive grammars.
Computability in Europe 2013. Informal Proceedings,
pages 80–89.
The Composition of Dense Neural Networks and Formal Grammars for Secondary Structure Analysis
241
