
Progress of MRI-guided EP Interventions is Hampered by a Lack of
ECG-based Patient Monitoring – An Engineering Perspective
Johannes Krug Passand
1,2
and Georg Rose
1,2
1
Department of Medical Engineering, Otto-von-Guericke University Magdeburg, Germany
2
Forschungscampus Stimulate, Otto-von-Guericke University Magdeburg, Germany
Keywords:
Cardiology, CMR, ECG, EP, Minimally Invasive Intervention, MRI.
Abstract:
This position paper discusses the current developments and advances of electrophysiological (EP) interven-
tions guided by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and the associated technological challenges and difficul-
ties which need to be overcome in the future. MRI provides several advantages compared to other medical
imaging modalities. However, performing any kind of intervention or surgery in an MRI scanner is technical
challenging. EP procedures are a special case since they involve many sensitive electronic stimulation and
measurement devices and also require a high quality patient monitoring. Monitoring the patient’s electrocar-
diogram (ECG) inside an MRI is a challenging task due to the MRI’s hazardous environment. Hence, ECG
signals are highly distorted and are of limited diagnostic value. This limitation in ECG-based patient moni-
toring and the lack of a fully functional, MRI-conditional 12-lead ECG hampers or delays the progress of EP
procedures during MRI. We review and discuss the main reasons for this limitation and give an outlook and
recommendation for further research approaches.
1 INTRODUCTION
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical
imaging modality which is used for a wide range of
diagnostics purposes such as the identification of can-
cer tumors, for cardiovascular diseases or the function
of the brain. Cardiac MRI (CMR) is one very impor-
tant application of MRI used to study the anatomical
and functional properties of the heart muscle and the
related blood vessels. In addition to its diagnostic us-
age, MRI has a high potential for guiding minimally
interventions, where it is referred to as interventional
MRI (iMRI) (Barkhausen et al., 2017). One type of
these interventions are electrophysiological (EP) pro-
cedures which are used to diagnose and treat malfunc-
tions of the cardiac’s electrical generation and con-
duction system. EP procedures are minimally inva-
sive interventions, which are until now guided by X-
ray or flouroscopy. Specialized electrode catheters are
used to measure the electrical potentials at the inner
surface of the heart. Depending on the type of diagno-
sis, treatment can be performed subsequently, e. g. by
ablation catheters. EP procedures could benefit from
the advantages provided by MRI (Lederman, 2005).
For performing an EP procedure under MRI-
guidance, patient monitoring is a crucial aspect.
One of the most important physiological signals
in an EP procedure is the patient’s electrocardio-
gram (ECG) (Haines et al., 2014). However, acquir-
ing, processing and analysing an ECG during MRI is
a challenging task whereas the diagnostic value of the
processed ECG is nowadays very limited (Oster and
Clifford, 2017).
We represent the position that the lack of reliable,
ECG-based patient monitoring is one of the reasons
why the progress of MRI-guided EP interventions is
hampered and slowed down. In order to discuss our
position and perspective, this paper gives an overview
of trends in MRI-guided EP interventions, reviews the
currently existing challenges and gives a broad out-
look on future developments in terms of hardware and
software.
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Patient Monitoring in MRI
Patient monitoring during MRI exams or interven-
tions is a crucial task which is hampered by the
hazardous MRI environment. Several vital signs
Passand, J. and Rose, G.
Progress of MRI-guided EP Interventions is Hampered by a Lack of ECG-based Patient Monitoring – An Engineering Perspective.
DOI: 10.5220/0007485702010208
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2019), pages 201-208
ISBN: 978-989-758-353-7
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
201

of a patient can be monitored such as invasive and
non-invasive blood pressure, respiration, gas analysis,
oximetry, body temperature, or the ECG. There a sev-
eral conditions under which the vital signs of a pa-
tient should be monitored, among them: sedated pa-
tients, critical care patients, patients which are unable
to communicate, or patients undergoing an interven-
tional MRI.
During the last two decades, the demand for high-
quality patient monitoring systems raised due to the
potential and new applications of MRI and MRI-
guided interventions. This includes interventions
such as catherizations or biopsies (Razavi et al., 2003;
Ratnayaka and Lederman, 2010; Fischbach et al.,
2013) and MRI-guided EP interventions (Dukkipati
et al., 2008; Schmidt et al., 2009; Koopmann and
Marrouche, 2013; Piorkowski et al., 2013; Chubb
et al., 2017; Elbes et al., 2017; Mukherjee et al., 2018;
Sommer and Mont, 2018).
The following sections briefly review MRI-guided
EP procedures, give an overview of available or nec-
essary equipment to perform interventions in this en-
vironment and elucidate the need for a reliable, diag-
nostic ECG during MRI.
2.2 MRI-guided EP Procedures
Opposed to X-ray imaging or fluoroscopy, MRI pro-
vides a superior soft tissue contrast, allows a 2D,
3D or 4D visualisation of the heart and other organs
and is used as a standard diagnostic tool for a wide
range of medical applications. Considering interven-
tional EP procedures, MRI provides additional diag-
nostic information. It enables the detection of scar
tissue which can be found in patients with ventricular
tachycardia (Stevenson, 2009), or of febrosis seen in
patients with atrial fibrillation (Mewton et al., 2011;
Dzeshka et al., 2015). MRI also has the potential
to visualise lesions induced by radiofrequency abla-
tion (Vergara et al., 2011; Hunter et al., 2013).
The benefits of an MRI-guided EP can be summa-
rized as follows: 1) improved substrate identification
resulting in a more precise ablation targeting, 2) im-
proved guidance during the intervention and 3) an im-
proved assessment of the lesion formation after an ab-
lation (Chubb et al., 2017).
CMR enables the identification and differentia-
tion of atrial and ventricular arrhythmogenic sub-
strates (Ashikaga et al., 2007). This information is
increasingly used for guiding cardiac interventions. It
would be even more helpful and expedient when it is
directly available during the EP procedure.
Procedure guidance can be improved by CMR
compared to the conventional, established ap-
proaches. Currently, the more complex EP procedures
are performed by combining X-ray flouroscopy (for
anatomical guidance) and electroanatomic mapping
techniques. The structural information provided by
this approach is inferior to the anatomical and func-
tional information achievable by CMR. CMR pro-
vides more detailed information about the chamber of
interest but also about surrounding structures such as
coronary arteries.
Evaluation of ablation lesions is another potential
advantage of CMR over the other imaging modalities.
CMR could directly be used to assess acute ablation
lesions instead of a post-procedure analysis.
2.3 Selected iMRI Equipment
Performing an MRI-guided intervention in general
and a cardiac intervention in particular requires ded-
icated hard- and software. Starting with the basic re-
quirement, i. e. the MRI scanner, a wide-bore MRI
scanner with 1.5 T or 3 T is the most common choice
nowadays. Open bore MRI scanners systems would
be ideal for any kind of intervention but their produc-
tion was unfortunately discontinued (such as Philips’
Panorama HFO 1 T or GE’s SIGNA SP 0.5 T Open
Configuration). For displaying MR images inside the
scanner cabin, in-room displays are either provided
by the scanner manufacturers or by third party compa-
nies. The scanner vendors also provide software sup-
porting the interventions, such as the Interactive Front
End (Siemens, Germany) or the iSuite (Philips Re-
search Hamburg, Germany). Basic hardware for pa-
tient monitoring is often included in the MRI scanner
system, such as a simple ECG mainly used for trigger-
ing image sequences, a PPG or a respiratory belt sys-
tem. Third party patient monitors include further pa-
rameters such as noninvasive and invasive blood pres-
sure measurements, CO
2
, temperature and anaesthe-
sia gases. Exemplary MRI specific patient monitoring
devices are the Tesla M3 (MIPM GmbH, Germany),
the Maglife Serenity (Schiller AG, Switzerland) or the
Expression MR400 (Philips, The Netherlands). Be-
sides patient monitoring, MRI compatible anesthesia
carts are available, e. g. the Aestiva/5 MRI (Datex-
Ohmeda, GE Healtcare, USA). For performing MRI-
guided EP procedures, one MRI-specific ablation and
monitoring system is currently available including
an ablation catheter and a recording/stimulation sys-
tem (Imricor Medical Systems, USA). In general, the
wide range of tools available for X-ray guided in-
terventions such as different catheters, guidewires,
tracking systems, ablation generators and others are
not available for the MRI environment yet.
For enabling a complete cardiac monitoring, sev-
BIOSIGNALS 2019 - 12th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
202

eral companies and research institutions are working
on 12-lead ECG systems and hemodynamic monitor-
ing platforms since many years or even more than a
decade. But none of these systems is commercially
available or has an FDA clearance or approval. Ex-
amples are the PELEX-MAX (PinMed, USA), the
MiRTLE system (MiRTLE Medical, USA) or ACDx
system (All Clear Diagnostics, USA). There are also
open source research systems such as the Physiolog-
ical Recording in MRI Environment (PRiME) sys-
tem (Kakareka et al., 2018). None of these systems
can currently provide a diagnostic ECG. The reasons
for this circumstance will be explained in the follow-
ing sections.
3 ECG IN MRI - CHALLENGES
The different types of magnetic fields in an MRI
scanner severely distort the acquired ECG signals.
The signals picked up by the ECG electrodes in an
MRI can be summarized as follows (Felblinger et al.,
1999):
S(t) = S
ECG
+ S
MHD
+ S
G
+ S
IND
(1)
where S
ECG
is the ECG signal, S
MHD
is the signal
caused by the magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) effect,
S
G
are gradient distortions and S
IND
are other induced
distortions or noise. Inductions (S
IND
) can occur
when the ECG recorder or the cables are moved due
to respiratory motion. Other sources of induced dis-
tortions are the time-varying, switched gradient mag-
netic fields and the MRI scanner’s RF fields. The
RF fields of clinical scanners have a frequency of
f = 42.58MHz/T · B
0
where B
0
is the static mag-
netic field strength. This frequency is far beyond
the ECG’s frequency range (approximately 0.05 Hz-
150 Hz). Distortions due to the RF fields can be
caused by demixing effects in analogue electronic cir-
cuits. The influence of the RF fields can be reduced
by a proper shielding of the ECG hardware (Oster
et al., 2010b). This article only considers distortions
induced by the switched gradient magnetic fields and
the MHD effect.
3.1 Switched Gradient Magnetic Fields
The distortions induced by the switched gradient
magnetic fields are given as
S
IND
≈ S
G
∂G
x
(t)
∂t
,
∂G
y
(t)
∂t
,
∂G
z
(t)
∂t
(2)
where G
x
(t),G
y
(t),G
z
(t) are the gradients used for
image acquisition. The time-varying magnetic fields
0 2 4 6 8 10
−2
−1.5
−1
−0.5
0
Time in [s]
Voltage in [mV]
(a) ECG trace with gradient artefacts.
6.105 6.11 6.115 6.12 6.125
−1.5
−1
−0.5
Time in [s]
Voltage in [mV]
(b) Zoomed view of (a) showing a closer view of the artefact
properties.
Figure 1: Gradient artefacts during an MRI sequence (gra-
dient echo).
induce voltages directly within the human torso
but also in the surface spanned by the ECG ca-
bles (Laudon et al., 1998; Felblinger et al., 1999).
Figure 1 shows an exemplary ECG with a gradient
induced distortion during an MRI sequence.
Applying an QRS detection algorithm to such
an ECG signal without further preprocessing would
result in a high number of false positive and false neg-
ative detections due to the high amount of distortions
and the QRS complexes hidden within them. Hence,
suppressing or removing the signal distortions origi-
nating from the time varying switched gradient mag-
netic fields is usually the first signal processing step.
3.2 The Magnetohydrodynamic Effect
The MHD effect results from the interaction between
the pulsatile blood flow, which is caused by the rhyth-
mic action of the heart and the static magnetic field
of the MRI scanner, B
0
. Blood plasma, which makes
up about 60 % of the total blood volume, contains ap-
proximately 10 % solutes including electrolytes such
as Na
+
, Cl
−
or HCO
−
3
ions and non-electrolytes (glu-
cose, urea). The ions (electrolytes) are moving inside
the vessels where they experience a force due to the
presence of the MRI scanner’s static magnetic field.
This force is known as Lorentz force,
~
F, where the
force per charge is given as
~
F
q
= (~v ×
~
B). (3)
Progress of MRI-guided EP Interventions is Hampered by a Lack of ECG-based Patient Monitoring – An Engineering Perspective
203
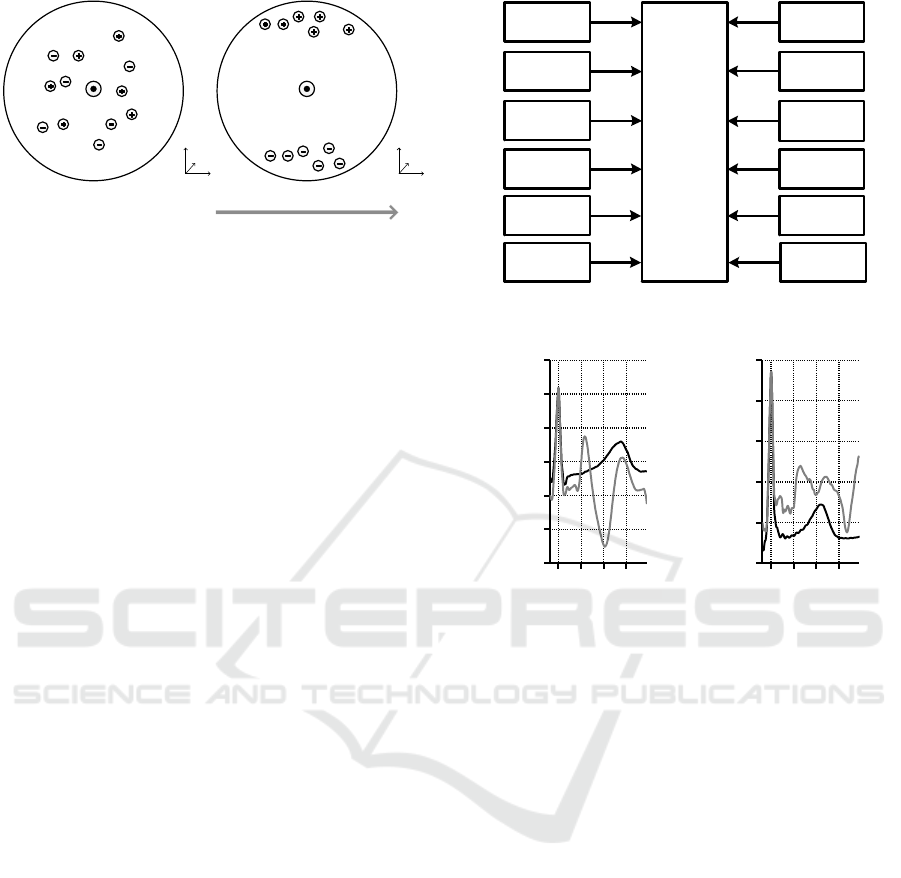
v(r)
Blood vessel
x
y
z
B
0
(a) Outside the MRI
v(r)
Blood vessel
B
0
x
y
z
(b) Inside the MRI
Figure 2: A simplified schematic of the MHD effect inside
a blood vessel. Positive and negative ions are moving with
the velocity v(r) along the blood vessel where r is the ves-
sel’s radius. Outside the MRI scanner, ions are randomly
distributed inside the vessel (a). Inside the MRI scanner
(under the influence of the static magnetic field), the ions
experience the Lorentz force (b).
It depends on the magnitude and orientation of the
blood flow velocity ~v of the charged particles q with
respect to the
~
B
0
field. This force causes the ions
to move perpendicularly to the direction of the blood
flow and perpendicularly to the MRI scanner’s static
magnetic field. The ions accumulate near the vessel’s
wall leading to a potential difference across the vessel
that can be expressed as
V ∝
Z
l
0
~v ×
~
B
0
d
~
l (4)
where l is the diameter of the vessel. The voltage es-
timated using Eq. 4 is called Hall voltage. Figure 2
schematically shows how the static magnetic field B
0
affects the moving ions inside the cross section of
a blood vessel. The resulting body surface potentials
of the MHD effect superimpose the ECG signal. Fig-
ure 3 summarizes several physiological and technical
parameters which influence the MHD effect.
When the ECG is measured inside an MRI scan-
ner, the MHD effect mainly affects the segment be-
tween two QRS complexes, i. e. the ST-segment, the
T-wave and the P-wave. Exemplary ECG signals
from two different subjects acquired outside and in-
side a 3 T MRI scanner are shown in Fig. 4. Since
the MHD effect is directly related to the blood flow,
it mostly affects the ECG during the ventricular sys-
tole where the blood is ejected from the ventricle into
the aorta and pulmonary artery. Hence, the diagnostic
information contained in the ECG’s ST-segment and
T-wave is hidden by the MHD effect which reduces
the diagnostic value of the ECG during an MRI exam
or intervention. For MRI scanners with magnetic field
strengths ≥ 7 T, QRS detection can be hampered due
to the large magnitude and slope of the MHD ef-
fect (Krug et al., 2013).
Blood pressure
Blood vessel
diameter
Blood flow
velocity
Stroke volume
Magnetic field
strength
Heart rate
Torso anatomy
MHD effect
Arrhythmia
Intraventricular
flow
Vessel anatomy
......
Figure 3: Selected physiological and technical parameters
affecting the MHD effect.
0 0.1 0.2 0.3
−1.5
−1
−0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
Time in [s]
Voltage in [mV]
(a) Subject A
0 0.1 0.2 0.3
−0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
Time in [s]
Voltage in [mV]
(b) Subject B
Figure 4: Comparison of the ECG signal waveform in
lead II in two different subjects acquired outside (black) and
inside (grey) a 3 T MRI scanner. The QRS complexes are
aligned at t = 0s. The MHD effect mainly affect the ECG’s
ST-segmentand T-wave.
4 CURRENT SITUATION
MRI specific ECG systems are available from differ-
ent MRI scanner manufactuers and third party ven-
dors. These systems enable the acquisition of ECG
signals under different conditions, i. e. under the pres-
ence of different magnetic field strengths and various
imaging sequences. It can be considered that safety
issues, especially due to RF-induced cable heating,
play a negligible role nowadays. The different ven-
dors optimized the ECG electrode positions (close
proximity to the heart), cable resistances (50kΩ to
100kΩ), shielding of the electronics and data trans-
mission in order to obtain a robust signal acquisition
system. A very extensive overview and summary of
these aspects is given in (Oster and Clifford, 2017).
The acquired ECG signals are contaminated by the
effect described in Section 3. Figure 5 briefly sum-
marizes different signal processing steps depending
on the usage of the ECG in MRI.
BIOSIGNALS 2019 - 12th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
204
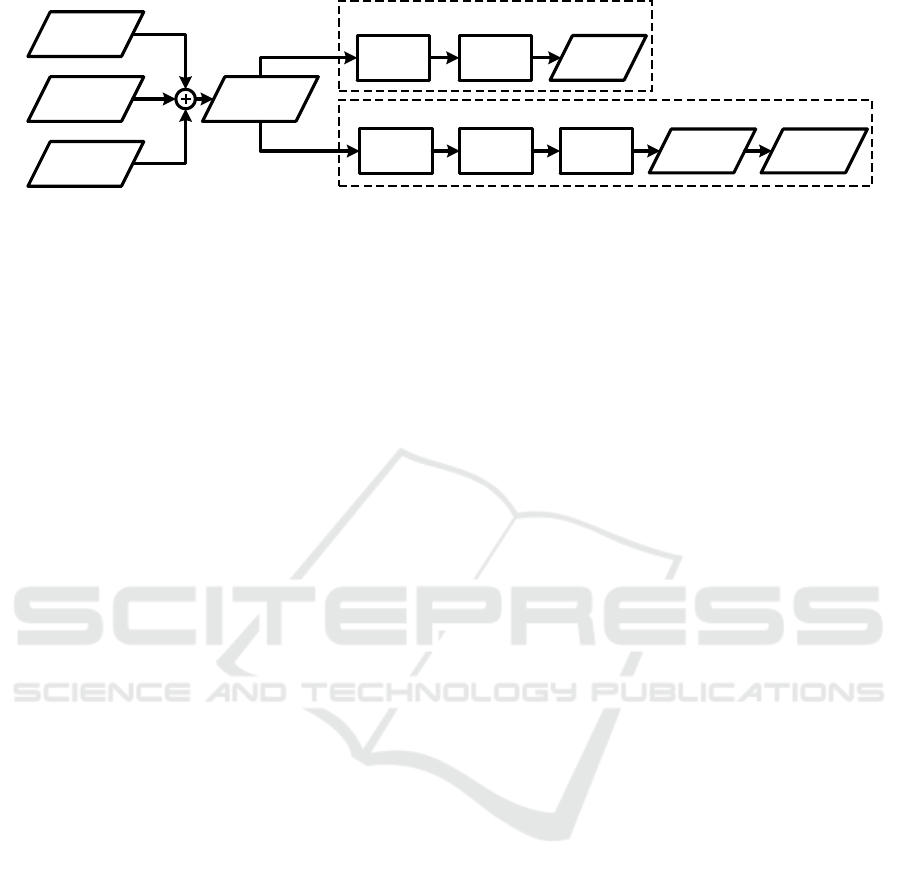
ECG
(Clean)
Gradients
MHD Effect
ECG
(Distorted)
Gradient Filter
Diagnostic ECG
QRS Detection
Gating/Triggering
Trigger
Signal
Gradient Filter QRS Detection
Morphological
Information
MHD Filter
Heart rate and
heart rhythm
Figure 5: Signal acquisition and processing chain. For diagnostic purposes, the MHD effect has to be filtered after gradient
filtering in order to enable a morphological analysis of the ECG.
Gradient filtering is usually the first processing
step. Several dedicated filtering methods exist to
achieve this goal, e. g. based on independent compo-
nent analysis (Oster, 2009; Oster et al., 2009b), adap-
tive filtering (Kreger and Giordano, 1992; Laudon
et al., 1998; Felblinger et al., 1999; Ab
¨
acherli et al.,
2005; Odille et al., 2007; Wu et al., 2011), Bayesian
filters (Oster et al., 2010a; Oster et al., 2010b) or me-
dian filtering (Schmidt et al., 2018). The quality of
the different filtering approaches is difficult to com-
pare since it depends on the signal acquisition hard-
ware, the electrode placement and the wire configura-
tion, sampling rate, analogue filtering stages and oth-
ers. Hence, patient monitoring device manufacturers
employ different methods optimized for their specific
systems and hardware.
QRS detection: Once the gradients are filtered
from the ECG, the ECG is still superimposed by the
MHD effect. Without further filtering of the MHD
effect, QRS detection is possible in most cases. Ded-
icated QRS-detection algorithms were developed in
the past to cope with the MHD effect enabling a reli-
able QRS detection with a minimized number of false
positives. An early method was based on the vec-
torcardiogram (VCG) (Fischer et al., 1999), which
allowed a spatial separation of the ECG and MHD
signal components. Because of certain limitiations
of the VCG based method at higher magnetic fields
strengths (≥7 T), a modfified VCG based approach
was proposed (Krug, 2015). Wavelets were employed
for QRS detection by means of frequency decompo-
sition (Abi-Abdallah et al., 2006; Sabbah et al., 2007)
or singularity detection (Oster, 2009; Oster et al.,
2009a). Higher order statistics were used to detect
the high slopes of the QRS complex and suppress the
MHD effect (Schmidt et al., 2014).
MHD filtering: To reach the ultimate goal of hav-
ing a fully diagnostic ECG during MRI, MHD filter-
ing is the most crucial and most challenging aspect in
the whole signal acquisition and processing chain. As
described in Section 3.2, the MHD effect is mainly
caused by the blood flow in the aorta and is highly
correlated with the ECG signal and the cardiac cycle.
The ECG signal – which has its origin in the depo-
larization and repolarization of the cardiac cells – and
the MHD effect can be considered as spatially sepa-
rated sources. The spatial segregation of both sources
makes the problem ideal for source separations tech-
niques such as independent component analysis. Al-
though this method was successfully applied to simu-
lated data (Bhatt and Reddy, 2009), it failed with real
12-lead ECG signals (Krug et al., 2012). The reason
for that is that the different sources highly depend on
each other. The problem of MHD filtering was also
tackled by adaptive filters (Tse et al., 2014). How-
ever, this method requires a-priori knowledge about
different patient specific heart beat morphologies used
to train the adaptive filter. Such data is usually not
available during a real measurement. The most re-
cent research on MHD filtering employs a Baysian
filtering approach in which the ECG and MHD sig-
nal contributions and their (pseudo)-periodic nature
are modelled (Oster et al., 2013; Oster et al., 2015).
The method was applied to simulated and real ECG
datasets contaminated by the MHD effect where it
was shown that it is able to detect simulated patho-
logical alterations of the ECG such as the elongation
of the QT-interval.
5 DISCUSSION AND OUTLOOK
Considering all the potential advantages and bene-
fits of an MRI-guided EP procedure compared to a
fluoroscopy-driven intervention, one may ask why
MRI nowadays is rarely used for these interventions.
Several reasons can be given for the comparatively
slow progress in this field: 1) lack of MRI compat-
ible EP hardware, e. g. electrode catheters, ablation
catheters, ablation generators, external defibrillators,
2) patient monitoring hardware and signal processing
algorithms and 3) trained staff to perform interven-
tions in the MRI environment.
The aim of this paper was to emphasize that a di-
agnostic ECG is indispensable for the serious estab-
Progress of MRI-guided EP Interventions is Hampered by a Lack of ECG-based Patient Monitoring – An Engineering Perspective
205

lishment of MRI-guided EP procedures. Tremendous
advances were made in the last two decades includ-
ing the development of acquisition hardware as well
as the software for gradient artefact removal and QRS
detection. Triggering image sequences and monitor-
ing the patient’s heart rate are still the most common
applications of an ECG during MRI. Hence, only few
research was invested in providing a comprehensive
diagnostic (12-lead) ECG within the MRI scanner.
Currently, several prestigious heart centres around
the globe have the ambition to establish or trans-
fer certain EP procedures from X-ray fluoroscopy to
MRI. For this transition, a diagnostic ECG is one of
the key elements. To achieve this goal, the authors
identified two important issues or aspects which need
to be pursued or addressed by the international re-
search community as well as by the monitoring ven-
dors: 1) the development of an MRI-compatible stan-
dardized 12-lead ECG and 2) the suppression of the
MHD effect.
Several cardiac interventions require a 12-lead
ECG for an optimal disease diagnose or treatment.
Providing a 12-lead ECG in the MRI bore will be
challenging from the hardware development and sig-
nal processing point-of-view due to additional ECG
leads, cables and electrodes, larger electrode dis-
tances (Einthoven triangle) and additional electron-
ics. Current ECG systems used in the MRI scanner
are designed to reduce the influence of the switched
gradient magnetic fields and the MHD effect, basi-
cally by a minimization of the electrode distances.
Figure 6 compares the electrode placements of differ-
ent lead systems. Changing from an MRI-optimized
lead system to a conventional 12-lead ECG system
will imply several new problems due to increasing
signal distortions. Hence, new signal processing al-
gorithms or techniques will be required to cope with
these new problems. Having a 12-lead ECG would
facilitate the establishment of MRI-guided EP inter-
ventions. In a first step, when the MHD effect is still
present, a 12-lead ECG would enable to perform EP-
procedures mainly requiring information about the
QRS-complex, e. g. the diagnosis and treatment of
ventricular tachycardia. Other interventions requiring
a more detailed morphological analysis of the ECG
such as the P-wave or T-wave could not be performed
at this stage.
The major challenge for the research works within
the next years will be a reliable suppression of the
MHD effect. Much research is necessary for inves-
tigating and developing new signal processing tech-
niques to tackle this problem. Proper experiments and
studies have to be designed in order to collect appro-
priate ECG data from various subjects under different
A
C
N
Lead 2
Lead 1
B
(a) Reduced lead set
RA LA
LLN
V1
V2
V3
V4
V5
V6
Lead I
Lead III
(b) 12-lead ECG
Figure 6: (a) Typical ECG lead system used during MRI
exams and (b) the conventional 12-lead ECG system com-
prised of the Einthoven triangle and the precordial leads.
conditions. Most experiments conducted in the past
are based on data from healthy subjects, i. e. in the
absence of cardiac arrhythmias or pathologies. This is
the most important limitation of the works performed
in the recent years. One of the most crucial aspects
with the design of the experiments is the fact that the
measurement of an ECG with or without the MHD ef-
fect is not possible under the same condition, i. e. the
ECG during a sudden, unexpected arrhythmic event
will be either measured inside or outside the scan-
ner. However, especially the unforeseen, unknown
arrhythmic episodes where the ECG and MHD sig-
nal components change at the same time are the most
interesting aspect to be studied in the future.
From the authors point of view, the ECG is one
of many elements which play a key-role for the es-
tablishment of MRI-guided EP procedures. It is es-
sential for successful accomplishment of these pro-
cedures and for a positive patient outcome. The de-
velopment and establishment of an MRI-compatible
12-lead ECG will come along with several technolog-
ical challenges but it will enable the establishment of
certain EP procedures using MRI. Once certain pro-
cedures are established and their potential is more
visible to scanner manufacturers and medical device
providers, it can be assumed that this will lead to in-
creasing development efforts in this field.
In addition to a reliable diagnostic ECG, other
components such as catheter tracking, ablation and
electrode catheters, ablation generators or external de-
fibrillators need to be developed or adapted in order to
be operated under the very special conditions of the
MRI environment. MRI scanner manufacturers need
to provide appropriate real-time sequences, the inte-
gration of tracking solutions and an adapted workflow
to enable a smooth and efficient conduction of the
EP procedures. Only with a combination of different
hardware and software developments and close col-
laboration between scanner manufacturers and third-
party companies, the amazing and promising field of
MRI-guided EP procedures can be made accessible.
BIOSIGNALS 2019 - 12th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
206

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work of this paper was funded by the Euro-
pean Regional Development Fund under the operation
number ‘ZS /2016/04/78123’ as part of the initiative
“Sachsen-Anhalt WISSENSCHAFT Schwerpunkte”.
The authors have no conflict of interest.
REFERENCES
Ab
¨
acherli, R., Pasquier, C., Odille, F., Kraemer, M.,
Schmid, J., and Felblinger, J. (2005). Suppression of
MR gradient artefacts on electrophysiological signals
based on an adaptive real-time filter with LMS coeffi-
cient updates. MAGMA, 18(1):41–50.
Abi-Abdallah, D., Chauvet, E., Bouchet-Fakri, L., Batail-
lard, A., Briguet, A., Fokapu, O., et al. (2006). Ref-
erence signal extraction from corrupted ECG using
wavelet decomposition for MRI sequence triggering:
application to small animals. Biomed Eng Online,
5(1):1–12.
Ashikaga, H., Sasano, T., Dong, J., Zviman, M. M., Evers,
R., Hopenfeld, B., Castro, V., Helm, R. H., Dickfeld,
T., Nazarian, S., et al. (2007). Magnetic resonance–
based anatomical analysis of scar-related ventricular
tachycardia: implications for catheter ablation. Circu-
lation research, 101(9):939–947.
Barkhausen, J., Kahn, T., Krombach, G. A., Kuhl, C. K.,
Lotz, J., Maintz, D., Ricke, J., Schoenberg, S. O.,
Vogl, T. J., Wacker, F. K., et al. (2017). White Pa-
per: Interventional MRI: Current Status and Potential
for Development Considering Economic Perspectives,
Part 1: General Application. In R
¨
oFo-Fortschritte auf
dem Gebiet der R
¨
ontgenstrahlen und der bildgeben-
den Verfahren, volume 189, pages 611–623.
Bhatt, B. and Reddy, M. (2009). ICA Based Flow Artifact
Removal from ECG during MRI. In Proc Int Conf
ACT 09, pages 241–243.
Chubb, H., Williams, S. E., Whitaker, J., Harrison, J. L.,
Razavi, R., and O’Neill, M. (2017). Cardiac electro-
physiology under mri guidance: an emerging technol-
ogy. Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev, 6(2):85–93.
Dukkipati, S., Mallozzi, R., Schmidt, E., Holmvang, G.,
Avila, A., Guhde, R., Darrow, R., Slavin, G., Fung,
M., Malchano, Z., et al. (2008). Electroanatomic
Mapping of the Left Ventricle in a Porcine Model
of Chronic Myocardial Infarction With Magnetic
Resonance-Based Catheter Tracking. Circulation,
118(8):853–862.
Dzeshka, M. S., Lip, G. Y., Snezhitskiy, V., and Shantsila,
E. (2015). Cardiac fibrosis in patients with atrial fib-
rillation: mechanisms and clinical implications. J Am
Coll Cardiol, 66(8):943–959.
Elbes, D., Magat, J., Govari, A., Ephrath, Y., Vieillot, D.,
Beeckler, C., Weerasooriya, R., Jais, P., and Quesson,
B. (2017). Magnetic resonance imaging-compatible
circular mapping catheter: an in vivo feasibility and
safety study. EP Europace, 19(3):458–464.
Felblinger, J., Slotboom, J., Kreis, R., Jung, B., Boesch, C.,
et al. (1999). Restoration of Electrophysiological Sig-
nals Distorted by Inductive Effects of Magnetic Field
Gradients During MR Sequences. Magnet Reson Med,
41(4):715–721.
Fischbach, F., Lohfink, K., Gaffke, G., Wybranski, C.,
Mohnike, K., Wonneberger, U., Pech, M., Jung-
nickel, K., Ricke, J., and Strach, K. (2013). Mag-
netic resonance–guided freehand radiofrequency ab-
lation of malignant liver lesions: a new simplified and
time-efficient approach using an interactive open mag-
netic resonance scan platform and hepatocyte-specific
contrast agent. Invest Radiol, 48(6):422–428.
Fischer, S., Wickline, S., and Lorenz, C. (1999). Novel real-
time R-wave detection algorithm based on the vector-
cardiogram for accurate gated magnetic resonance ac-
quisitions. Magnet Reson Med, 42(2):361–370.
Haines, D. E., Beheiry, S., Akar, J. G., Baker, J. L., Bein-
born, D., Beshai, J. F., Brysiewicz, N., Chiu-Man, C.,
Collins, K. K., Dare, M., et al. (2014). Heart Rhythm
Society expert consensus statement on electrophysiol-
ogy laboratory standards: process, protocols, equip-
ment, personnel, and safety. Heart Rhythm, 11(8):e9–
e51.
Hunter, R. J., Jones, D. A., Boubertakh, R., Malcolme-
Lawes, L. C., Kanagaratnam, P., Juli, C. F., Davies,
D. W., Peters, N. S., Baker, V., Earley, M. J., et al.
(2013). Diagnostic accuracy of cardiac magnetic res-
onance imaging in the detection and characterization
of left atrial catheter ablation lesions: a multicenter
experience. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 24(4):396–
403.
Kakareka, J. W., Faranesh, A. Z., Pursley, R. H., Campbell-
Washburn, A., Herzka, D. A., Rogers, T., Kanter, J.,
Ratnayaka, K., Lederman, R. J., and Pohida, T. J.
(2018). Physiological Recording in the MRI En-
vironment (PRiME): MRI-compatible hemodynamic
recording system. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med.
Koopmann, M. and Marrouche, N. (2013). Why hesitate in-
troducing real-time magnetic resonance imaging into
the electrophysiological labs? Europace, 15(1):7–8.
Kreger, K. and Giordano, C. (1992). Biopotential adaptive
filtering in an MR environment. In Proceedings of the
SMRM 12th Annual Meeting, Berlin, volume 661.
Krug, J. (2015). Improved cardiac gating and patient mon-
itoring in high field magnetic resonance imaging by
means of electrocardiogram signal processing. Dis-
sertation, Otto-von-Guericke Universit
¨
at Magdeburg.
Krug, J., Rose, G., Clifford, G., and Oster, J. (2013). ECG-
Based Gating in Ultra High Field Cardiac MRI us-
ing an Independent Component Analysis Approach.
J Cardiovasc Magn Reson, 15(104):1–13.
Krug, J., Rose, G., Stucht, D., Clifford, G., and Oster, J.
(2012). Filtering the Magnetohydrodynamic Effect
from 12-lead ECG Signals using Independent Com-
ponent Analysis. In Proc IEEE Comput Cardiol,
Krakow, Poland.
Laudon, M. K., Webster, J. G., Frayne, R., and Grist, T. M.
(1998). Minimizing Interference from Magnetic Res-
onance Imagers During Electrocardiography. IEEE
Trans Biomed Eng, 45(2):160–164.
Progress of MRI-guided EP Interventions is Hampered by a Lack of ECG-based Patient Monitoring – An Engineering Perspective
207

Lederman, R. (2005). Cardiovascular Interventional Mag-
netic Resonance Imaging. Circulation, 112(19):3009–
3017.
Mewton, N., Liu, C. Y., Croisille, P., Bluemke, D., and
Lima, J. A. (2011). Assessment of myocardial fibro-
sis with cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Am Coll
Cardiol, 57(8):891–903.
Mukherjee, R. K., Whitaker, J., Williams, S. E., Razavi, R.,
and O’Neill, M. D. (2018). Magnetic resonance imag-
ing guidance for the optimization of ventricular tachy-
cardia ablation. EP Europace, 20(11):1721–1732.
Odille, F., Pasquier, C., Abacherli, R., Vuissoz, P., Zien-
tara, G., and Felblinger, J. (2007). Noise cancellation
signal processing method and computer system for
improved real-time electrocardiogram artifact correc-
tion during MRI data acquisition. IEEE Trans Biomed
Eng, 54(4):630–640.
Oster, J. (2009). Traitement en temps r
´
eel des signaux
´
electrophysiologiques acquis dans un environnement
d’Imagerie par R
´
esonance Magn
´
etique. Ph.D. Thesis,
Universite Henri Poincare Nancy (France).
Oster, J. and Clifford, G. (2017). Acquisition of electrocar-
diogram signals during magnetic resonance imaging.
Physiol Meas, 38(7):R119–R142.
Oster, J., Geist, M., Pietquin, O., and Clifford, G. (2013).
Filtering of pathological ventricular rhythms during
MRI scanning. Int J Bioelectromagn, 15(1):54–59.
Oster, J., Llinares, R., Payne, S., Tse, Z. T. H., Schmidt,
E. J., and Clifford, G. D. (2015). Comparison of three
artificial models of the magnetohydrodynamic effect
on the electrocardiogram. Comput Methods Biomech
Biomed Engin, 18(13):1400–1417.
Oster, J., Pietquin, O., Abacherli, R., Kraemer, M., and Fel-
blinger, J. (2009a). A specific QRS detector for elec-
trocardiography during MRI: Using wavelets and lo-
cal regularity characterization. In Proc IEEE ICASSP,
pages 341–344. IEEE.
Oster, J., Pietquin, O., Ab
¨
acherli, R., Kraemer, M., and Fel-
blinger, J. (2009b). Independent component analysis-
based artefact reduction: application to the electro-
cardiogram for improved magnetic resonance imaging
triggering. Physiol Meas, 30:1381–1397.
Oster, J., Pietquin, O., Kraemer, M., and Felblinger, J.
(2010a). Bayesian framework for artifact reduction on
ECG IN MRI. In Proc IEEE ICASSP, pages 489–492.
Oster, J., Pietquin, O., Kraemer, M., and Felblinger, J.
(2010b). Nonlinear Bayesian Filtering for Denois-
ing of Electrocardiograms Acquired in a Magnetic
Resonance Environment. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng,
57(7):1628–1638.
Piorkowski, C., Grothoff, M., Gaspar, T., Eitel, C., Sommer,
P., Huo, Y., John, S., Gutberlet, M., and Hindricks,
G. (2013). Cavotricuspid isthmus ablation guided by
real-time magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation:
Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology, 6(1):e7–e10.
Ratnayaka, K. and Lederman, R. (2010). Interventional car-
diovascular MR–The next stage in pediatric cardiol-
ogy. Prog Pediatr Cardiol, 28(1-2):59–67.
Razavi, R., Hill, D. L., Keevil, S. F., Miquel, M. E.,
Muthurangu, V., Hegde, S., Rhode, K., Barnett, M.,
Van Vaals, J., Hawkes, D. J., et al. (2003). Car-
diac catheterisation guided by MRI in children and
adults with congenital heart disease. The Lancet,
362(9399):1877–1882.
Sabbah, M., Alsaid, H., Fakri-Bouchet, L., Pasquier, C.,
Briguet, A., Canet-Soulas, E., and Fokapu, O. (2007).
Real-time gating system for mouse cardiovascular MR
imaging. Magn Reson Med, 57(1):29–39.
Schmidt, E., Mallozzi, R., Thiagalingam, A., Holmvang,
G., Avila, A., Guhde, R., Darrow, R., Slavin, G., Fung,
M., Dando, J., Foley, L., Dumoulin, L., and Reddy,
V. (2009). Electroanatomic Mapping and Radiofre-
quency Ablation of Porcine Left Atria and Atrioven-
tricular Nodes Using Magnetic Resonance Catheter
Tracking. Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophysi-
ology, 2(6):695–704.
Schmidt, M., Krug, J., Gierstorfer, A., and Rose, G. (2014).
A Real-time QRS Detector Based on Higher-order
Statistics for ECG Gated Cardiac MRI. In Proc IEEE
Comput Cardiol, Boston, USA.
Schmidt, M., Krug, J., Rosenheimer, M. N., and Rose, G.
(2018). Filtering of ECG signals distorted by mag-
netic field gradients during MRI using non-linear fil-
ters and higher-order statistics. Biomedical Engineer-
ing/Biomedizinische Technik, 63(4):395–406.
Sommer, P. and Mont, L. (2018). Cardiac magnetic reso-
nance based ablation procedures: ready for take-off?
EP Europace.
Stevenson, W. G. (2009). Ventricular scars and ventricular
tachycardia. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc, 120:403–
412.
Tse, Z., Dumoulin, C., Clifford, G., Schweitzer, J.,
Qin, L., Oster, J., Jerosch-Herold, M., Kwong, R.,
Michaud, G., Stevenson, W., and Schmidt, E. (2014).
A 1.5T MRI-Conditional 12-Lead Electrocardiogram
for MRI and Intra-MR Intervention. Magnet Reson
Med, 71(3):1336–1347.
Vergara, G., Vijayakumar, S., Kholmovski, E., Blauer, J.,
Guttman, M., Gloschat, C., Payne, G., Vij, K., Ak-
oum, N., Daccarett, M., et al. (2011). Real-time mag-
netic resonance imaging–guided radiofrequency atrial
ablation and visualization of lesion formation at 3
Tesla. Heart Rhythm, 8(2):295–303.
Wu, V., Barbash, I., Ratnayaka, K., Saikus, C., Sonmez, M.,
Kocaturk, O., Lederman, R., and Faranesh, A. (2011).
Adaptive Noise Cancellation to Suppress Electrocar-
diography Artifacts During Real-Time Interventional
MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging, 33:1184–93.
BIOSIGNALS 2019 - 12th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
208
