
Rehabvisual: Validation of an Application to Stimulate Visuomotor
Skills in Preterm Babies with Developmental Alterations
Catarina Santos
1
, Ana Ferreira
2,3
, Cláudia Quaresma
1,4
and Carla Quintão
1,4
1
Departamento de Física, Faculdade de Ciências e Tecnologia, Universidade Nova de Lisboa,
2829-516 Caparica, Portugal
2
Serviço Medicina Física e Reabilitação, Hospital de D. Estefânia, Centro Hospitalar de Lisboa Central,
1169-045 Lisboa, Portugal
3
Departamento de Saúde, Escola Superior de Saúde, Instituto Politécnico de Beja, 7800-111 Beja, Portugal
4
LIBPhys - UNL, Faculdade de Ciências e Tecnologia, Universidade Nova de Lisboa, 2829-516 Caparica, Portugal
Keywords: Rehabilitation, Visuomotor Skills, Pediatrics.
Abstract: The methods of evaluation and intervention related to the visuomotor skills, for children under the age of 18
months with neurological dysfunctions are not systematic and individualized. Hence, the RehabVisual
platform was developed. The aim of this article is to present the usability tests applied to the platform
validation, as well as describing the application of the platform in the therapy sessions of a baby with a clinical
diagnosis of prematurity. The study concludes that the application of the platform allows the treatment to be
more individualized and specific to the baby needs through a common method to all service. Through usability
tests, it was possible to ascertain that at the level of occupational therapy, this is a useful tool adapted to the
needs of its users.
1 INTRODUCTION
The RehabVisual platform was developed with the
objective of stimulating the visuomotor competences
in children up to 18 months with developmental
alterations resulting from preterm birth (Machado et
al., 2018). The platform allows to adapt the therapies
to the needs of infants and the assessment of their
performance over the course of the treatments.
Preterm babies have a higher probability of
developing complications related to organ system
immaturity and a higher risk of developing ocular
problems. So early stimulation is very important,
improving the capacity of fixation, follow-up, and
oculomotor coordination. This recovery can be
justified by the fact that during the first year of life
some processes of maturation in the brain still occur,
this period is called cerebral plasticity and allows an
adaptation and modification of the brain according to
the stimuli present (Alimovic, 2012).
The main objective of this article is to describe
and analyze the application of usability tests related
to the platform performed by occupational therapists.
As an example, a case of the application of the
intervention program to a child under the age of 18
months and with developmental alterations resulting
from preterm birth will be analyzed.
Usability tests are used in order to understand
whether the product developed takes into account the
needs of its users, not focusing only in the
functionalities of the same.
According to ISO 9241-11 (1998) the usability of
a product should ensure that a specific user can use it
in order to achieve its goals in a manner that is
efficient and with satisfaction in a given context of
use. These three concepts are defined as:
1. Effectiveness: is the precision capacity with
which the user completes his/her tasks
interaction with the application;
2. Efficiency: is the amount of resources
(cognitive, physical effort, and time) that the
user needs to carry out a task in order to obtain
a positive result;
3. Satisfaction: Evaluates the degree of
contentment that the user demonstrates during
the interaction with the application.
More recently, ISO 9126-1 (2003) defines
usability as the capacity of the product software to be
understood, learned, operated and attractive to the
user, when used under specific conditions. Thus,
applications are intended to be user-friendly and
attractive to their users, which influences their
adoption and their use in a common way.
248
Santos, C., Ferreira, A., Quaresma, C. and Quintão, C.
Rehabvisual: Validation of an Application to Stimulate Visuomotor Skills in Preterm Babies with Developmental Alterations.
DOI: 10.5220/0007567102480255
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2019), pages 248-255
ISBN: 978-989-758-353-7
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

To ensure that the technological solution
developed is useful and that captivate the end user to
include it in its daily tasks there are a set of steps that
are necessary to fulfill. These steps include conducting
surveys during the development phase, in order to
understand the needs and preferences of users and to
explore solutions that improve the quality of user
interaction and the application. After the development
phase, usability tests are applied with the purpose of
verifying whether the application is in accordance with
the requirements previously identified (Lyles et al.,
2014), (Kushniruk and Patel, 2004).
Usability questionnaires are a source of collection
of opinions and suggestions that allow the researchers
to assess certain aspects of application interaction and
usability. There are a set of questionnaires already
applied in the field of health applications, the most
used being the Post-Study System Usability
Questionnaire (PSSUQ) and the System Usability
Scale (SUS).
Regarding the health area, the developed
applications have specific characteristics that limit
their usability. Among which, the use of small
screens, with reduced font sizes, which can limit the
interaction between the user and the application and
there are applications that need to be permanently
available so as not to compromise the health of
patients (Zhou et al., 2017).
The integration of usability assessments also
allows the reduction of costs and time associated with
product changes after its development, since the
entire production process is carried out based on the
preferences of the end user (Johnson et al., 2005).
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Platform
The RehabVisual platform intends to accompany the
entire rehabilitation process of the baby, by
integrating the evaluation components and including
an intervention program to be used as a complement
to the therapy sessions. RehabVisual is adaptable to
the needs of each baby, or customized. It was built
taking into account five different types of users:
administrator; doctor; technician; occupational
therapist and care provider, corresponding to the
person accompanying the baby in the consultations
and sessions (Machado et al., 2018).
Regarding the functioning of the platform, a
record of the clinical information of the patient is
performed, which can subsequently be associated
with ophthalmologic assessments, behavioral,
functional assessments and response to the sessions
of Intervention Program.
The evaluation is performed as follows: in the
ophthalmologic evaluation the functioning of both
eyes and the visual system is described and in the
behavioral assessment it is intended to perceive the
way the baby uses the vision in performing tasks, the
level of focus of objects, visual attention and
visuomotor coordination (Alimovic, 2012). The
functional assessments and the intervention program
are based on the baby's response to a set of stimuli
available on the platform.
The stimuli developed allows the user to have a
wide range of options with different levels of
complexity in order to stimulate the child. This
stimulus is adaptable according to its evolution and in
order to decrease the probability of habituation and
consequent disinterest (Corn and Erin, 2010).
The evaluation of both the intervention program
and the functional evaluation is based on indicators
such as looking, smiling or balancing. The intention
was to perceive the fixation and persecution capacity
in relation to the stimuli to which the baby was
exposed.
In these assessments, it was adopted an evaluation
scale used in visual assessments (Machado et al.,
2018). The scale consists of the following parameters:
1. Never - (0%)
2. Rarely - (25%)
3. Occasionally - (50%)
4. Often - (75%)
5. Always - (100%)
In all assessments there is also the possibility of
inserting comments that allow the user to add relevant
information to the baby's condition.
2.2 Usability Questionnaire
The SUS questionnaire was used as part of this study.
This questionnaire consists of a set of 10 items in
which the participant should score them in a one to
five scale according to the level of agreement. The
fact that it is based on positive and negative
assertions, in which the participant has to classify
them with their level of agreement, makes the
participant more alert leading to more consistent
results in small population samples (Albert and Tullis,
2010). The choice of this protocol was made because it
is reliable, versatile, simple and with a reduced number
of parameters questionnaire. The latter being
extremely important as users testing the platform could
not be available to respond to longer questionnaires. In
addition, the final score obtained through this
questionnaire is easy to interpret (Klug, 2017).
Rehabvisual: Validation of an Application to Stimulate Visuomotor Skills in Preterm Babies with Developmental Alterations
249

Regarding the number of participants required to
ensure the validation of the usability tests, according
to the bibliography, there are at least five people,
allowing with this number of people to identify about
85% of possible problems, not at risk of appearing the
same type of error several times (Nielsen Norman
Group, 2012).
2.3 Platform Validation
The usability tests were performed at the Physical
Medicine and Rehabilitation (MFR) Service of
Hospital D. Estefânia (HDE). Additionally, they were
performed on occupational therapists from the
Rehabilitation Medicine Center of Alcoitão.
The script used during the tests describes a
scenario to simulate the use of the platform in the
context of therapies and consists of several tasks that
will be implemented by users in the context of the
therapies. The study was approved by the Central
Hospital of Lisbon (CHLC) Ethics Committee.
2.3.1 Participants
The usability tests were performed by nine
occupational therapists, four from the MFR Service
of HDE and the remaining five from the
Rehabilitation Medicine Center of Alcoitão. Only two
of the HDE service participants had already been in
contact with the platform during therapy sessions
with the baby test group with development changes
and less than 18 months, having already made some
suggestions for changes during the development
phase of the platform.
2.3.2 Test Protocol
The test session is of an individual character and it is
initiated with a brief introduction to the platform, then
it is requested the user to perform the tasks indicated
in the protocol. Two protocols were elaborated with
tasks, one of larger extension for occupational
therapists of HDE and a shorter one for occupational
therapists of the Rehabilitation Medicine Center of
Alcoitão, due to the limited time they had to perform
usability testing.
In the larger protocol, there are various tasks
performed by occupational therapists since the
patient's registration, until the insertion of functional
assessments and intervention sessions, where it is also
requested to consult and edit previously submitted
assessments. In the shorter protocol, only the patient
form and the intervention program are approached,
which are the most used by occupational therapists.
2.3.3 Evaluation of the Test Protocol
The degree of user satisfaction is assessed throughout
the test session (at the end of specific tasks) and in a
more global way at the end of the protocol, through
the completion of the SUS questionnaire.
Additionally, participants can give their opinion and
suggestions for improvement.
Over the course of the session, the user is asked
about the ease of insertion, edition and research of data
regarding the patient's clinical record and assessments.
In the SUS questionnaire, the user's opinion is
requested on ten statements, each of which with five
hypotheses of response that go from "strongly
disagree" to "strongly agree". The assertions are:
1. I think I'd like to use this system often.
2. The system is unnecessarily complex.
3. I think the system is easy to use.
4. I think I need help from a technician to be able
to use the system.
5. I thought the various functions of this system
were well integrated.
6. I thought there were a lot of inconsistencies in
the system.
7. I imagine most people can learn to use the
system quickly.
8. I found the system very complicated to use.
9. I felt very confident using the system.
10. I need to learn many things before using the
system.
2.4 Use of the Platform in the Therapy
Sessions
The platform was also included in the occupational
therapy sessions of six babies up to 18 months of age
with developmental changes resulting from preterm
birth, performed by two occupational therapists
included in the validation of the platform.
Informed consent was requested to all parents, and
after their authorization, the use of the platform was
initiated in the occupational therapy sessions. The
choice of stimuli to be used in each session was
performed taking into account the analysis of the
occupational therapist of the baby's behavior in the
previous session and during the stimuli visualized
throughout the session, which allows to have a
personalized treatment for the needs of each baby. In
other words, the choice of stimuli is made taking into
account the evaluation of the acquisition of compe-
tencies by babies and not according to their diagnosis.
The platform was complemented by the therapy
sessions already attended at the HDE of MFR service,
and the number of sessions in which it was applied,
BIODEVICES 2019 - 12th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
250
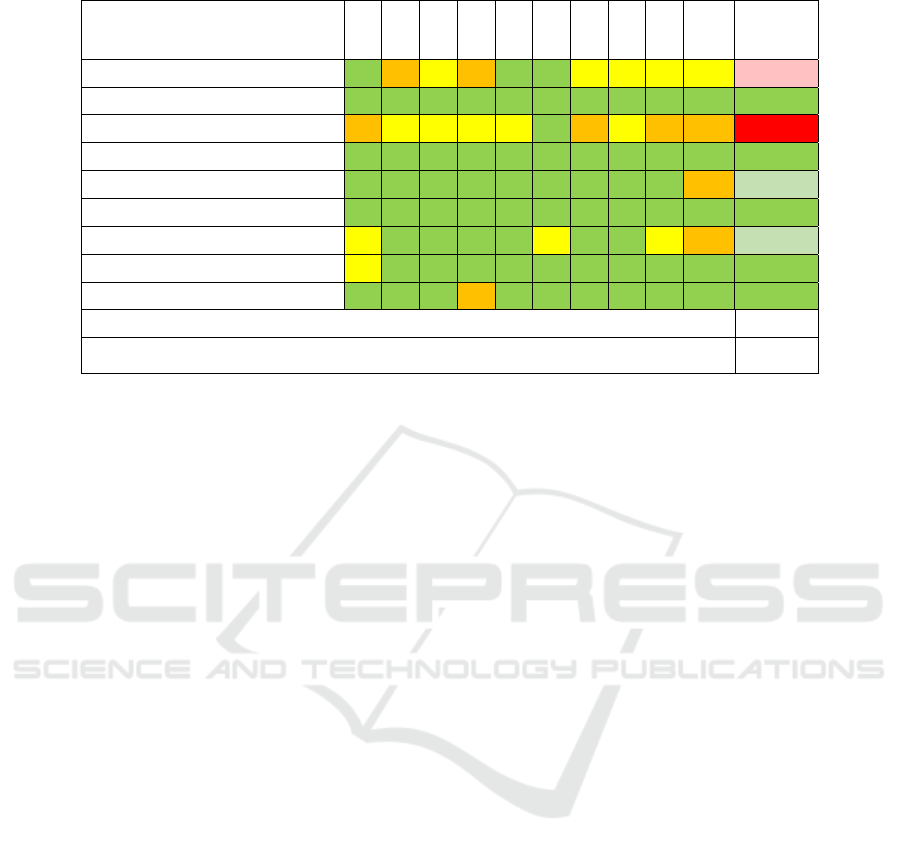
Table 1: SUS results.
Participant/affirmation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
SUS
results
Participant 1 4 4 3 4 5 1 3 3 3 3 57,5
Participant 2 4 1 5 1 5 2 5 1 4 1 92,5
Participant 3 2 3 3 3 3 2 2 3 2 4 42,5
Participant 4 5 1 5 2 5 2 4 1 4 2 87,5
Participant 5 4 2 4 2 4 2 5 1 4 4 75
Participant 6 4 2 4 2 5 1 4 1 4 1 85
Participant 7 3 1 5 2 4 3 4 1 3 4 70
Participant 8 3 2 5 2 4 1 5 1 4 2 82,5
Participant 9 5 1 5 4 5 1 4 1 4 1 87,5
SUS mean score 75,6
Confidence interval (95%) 12,63
which depended on the number of weekly therapy
sessions of each baby.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Usability Test
3.1.1 Results
Knowing that in the SUS questionnaire half of the
statements are of a positive nature and the remaining
negative ones, it is necessary to convert them into a
single result, as well: in the questions associated with
the odd number (positive questions) the answer is
subtracted by the value of 1 and in the questions
associated with the even number (negative questions)
the answer is subtracted by the value of 5. The values
are then summed, and this result is multiplied by the
value 2.5 in order to generate the SUS score, which is
between 0 and 100 (McLellan et al., 2012). The
average SUS score is 68, which corresponds to the
50
th
percentile. This score is affected by the
complexity of the system and the tasks that the user
has to perform (Klug, 2017).
A color map was used in table 1 in order to more
easily identify the positive responses so in the case of
the assertions of positive character the values 4 and 5
are marked green, the 3 is identified in yellow and 1
and 2 in orange. In the case of negative responses, the
representation is assigned inversely, as such the green
color is assigned to the scores of 1 and 2, the yellow
color is assigned to 3 and the orange color to scores
of 4 and 5 (McLellan et al., 2012).
With regard to participants, participants 1, 2, 3
and 4 correspond to the therapists of the HDE´s MFR
service who were already aware of the platform
before the day they performed the usability test,
although only two had used the platform in
occupational therapy environment. The remainder
correspond to the occupational therapists of the
Rehabilitation Medicine Center of Alcoitão, who
were only aware of the platform on the day they
performed the usability test.
Participants 1 and 4 followed the use of the
platform throughout the occupational therapies of the
test group.
From the analysis of the table 1 it is concluded
that the assessment made by users is generally
positive, and only two users (participant 1 and 3)
rated the platform negatively (SUS value less than
68). It should be noted that only participant 3 shows
a very negative result (SUS value less than 51). Of all
the participants with positive results, two classify the
platform as good (SUS value higher than 68 and less
than 80.3) and the remainder as excellent (SUS value
exceeding 80.3) (UX research, 2017).
The two participants with a SUS rating of less
than 68, during the test both stated that they do not
often use the computer which may have compromised
the answers given in the questionnaire.
The participants who have a positive SUS value,
participants 5, 7 and 9 present the following
justifications for the statements of the questionnaire
on which they disagree (presented in the table with
the orange color):
1. Participant 5, in statement 10 agrees that he
needs to learn many things before using the
system, justifying that the answer was given
Rehabvisual: Validation of an Application to Stimulate Visuomotor Skills in Preterm Babies with Developmental Alterations
251

not because he needs to learn many things in
the perspective of using the system, but in the
area of ophthalmology and problems
including assessments, intervention and
problems. The reason that leads to this
response may be related to the fact that this
participant did not have knowledge of the
project before the day of the usability test,
another possible reason was the fact that the
Participant belonged to the group that held a
more summarizing task protocol not
addressing all available menus on the
platform.
2. Participant 7 presents the same opinion as
participant 5 in the statement 10, having
justified the answer given in the same way.
Additionally, he also justifies the answer
given in statement 6 where he does not agree
or disagree with the assertion: "I found that
there are many inconsistencies in the system"
clarifying that although he does not detect
inconsistencies in the system itself, he
considers very important that the
criteria/conditions under which the
stimulation program should be applied is
defined, so that the results of system
assessments are
3. reliable.
4. Participant 9 only negatively classifies claim
4: "I think I need help from a technician to be
able to use the system ", justifying that this
help would be for an initial phase of use.
In general, it appears that the statements that have
caused more negative results were the statements 4
and 10, which can be explained by being people who
did not feel comfortable using technological
applications or to being part of the participants who
had no prior knowledge of the project.
3.1.2 Suggested Alterations
The changes suggested by the participants are mainly
centered on the aesthetics of the platform, especially
in the increase of the size of the letters and the colors
used in order to contrast more with the background.
Additionally, it was suggested to change the name of
some buttons in order to be more intuitive.
3.2 Example of a Participant in
Therapy Sessions
This article describes the application of the
intervention program in one of the participants in a
detailed manner.
The participant is male, aged 8 months at the
beginning of the study. It presents a clinical diagnosis
prematurity of 31 weeks and very low birth weight
(1020g). In the application of stimuli throughout all
sessions, the baby was in a room where there were no
other therapies taking place (which caused no noise)
and no adjustments were made to the luminosity of
the room.
In the first session, the black and white
stimulation program was applied, with the highest
contrast. In this session, it was analyzed the number
of videos that could be visualized without showing
signs of fatigue. In the protocol used a gradual
increase of the complexity of the videos was made,
they were visualized simple videos (with a single
figure) of the 4 figures established (circle, square,
triangle and mixed pattern) and one of the patterns of
minor complexity of the circular form (figure 1). The
baby showed signs of fatigue in the video with the
pattern, which is why the intervention program was
interrupted.
Figure 1: Examples of the videos used on the first session
(triangle simple video and pattern with minor complexity).
In the second session, four days later, the program
is adapted to the baby's response, a simple figure
video and a smaller complexity pattern in black-and-
white protocol was repeated. The choice of the videos
was made to confirm the consistency with the
previous session. The baby's answer in the simple
figure videos continued to be the maximum of the
scale, the response to the video with a smaller pattern
of complexity was slightly inferior.
In the third session, one week later, as the baby
had greater basic motor agitation, it was decided by
the therapist that it would not increase the level of
difficulty of the videos in relation to the previous
sessions.
In the fourth session, three days later, the behavior
of the baby remained agitated, the lower complexity
pattern stimuli were again introduced, in the black
and white protocol. However, the answer in this
category was better than in the previous session.
Therefore, a video of greater complexity with
movement was introduced with the aim of stimulating
BIODEVICES 2019 - 12th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
252
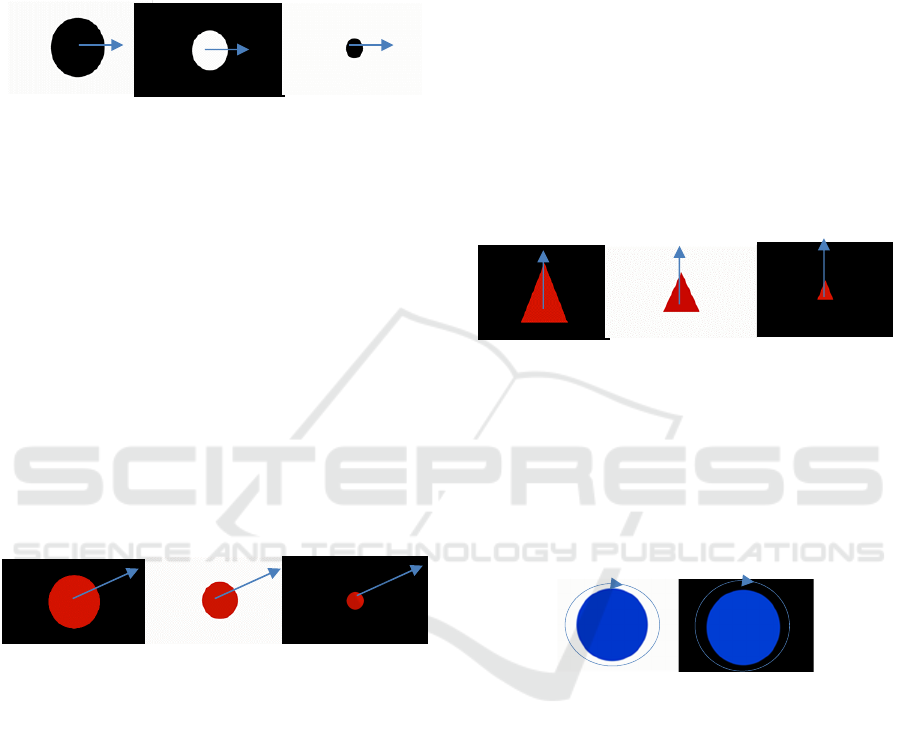
the baby (figure 2). In this video the baby only kept
the attentional focus in the larger figure.
In the fifth session, four days later, in addition to
the colors black and white the red color was
introduced. The simple stimulus was resumed, since
when introducing, in the previous session,
Figure 2: Fourth session, introduction of horizontal
movement with circular form.
the videos with movement (which correspond to the
videos of greatest demand) there was a decline in the
provision of the baby. So, it was attempted to realize
if starting with a video of inferior requirement to the
first visualized in the previous session, the installment
in the videos with motion would be better. There was
a slight improvement in the video with horizontal
motion although he had not kept the focus all the time.
The introduction of the red color was made in the last
video (diagonal movement with slow speed), in order
to stimulate the baby who begins to recognize this
color around 2/3 months of age, although the baby
never pursued or fixed the stimulus, which can be
justified by being a too demanding video for the baby
or for the stipulated time, not to be adjusted to the
attentional capacity of the baby (figure 3).
Figure 3: Fifth session, diagonal movement.
In the sixth session, two weeks and three days
later, stimuli of the black-and-white and color-
colored protocol were performed. Only medium
speed videos for horizontal movement (circular
figure) and fast speed (diagonal movement of mixed
pattern with fast speed) were used in order to verify
that the loss of attentional focus in previous sessions
was due to the speed of movement. The introduction
of the mixed pattern had the objective to perceive
whether with the change of figures during the video,
the baby was able to regain attentional focus. The
baby's visual response to the horizontal motion video
was better than in the diagonal motion video,
although in both, an improvement was registered in
relation to previous sessions.
In the seventh session, a week and four days later,
videos of the program of red color and blue color were
visualized. In this session we only opted for motion
videos with fast speed (vertical movement of fast
speed, fast diagonal movement with mixed pattern
and circular movement with fast speed). The choice
of the vertical motion video was made for being a
movement with a degree of complexity similar to that
of the horizontal movement and thus be able to
change the simplest stimulus introduced in this
session, since the horizontal motion video was
presented during three consecutive sessions. The red
color in this video was used instead of the blue color
subsequently were introduced two more complex
videos and so the red color allows to make the initial
stimulus easier because it is the first color recognized
by the baby. In vertical motion the baby pursued and
always fixed the stimulus (figure 4). In the diagonal
Figure 4: Seventh session, vertical movement.
movement, even though the fast speed video was
introduced. It is concluded that it is too long for the
baby to be able to visualize without losing its
attentional focus. For the circular motion the baby
pursued all the figures presented occasionally, but
lost the attentional focus along the movement of the
same figure (figure 5).
Figure 5: Seventh session, circular movement.
In the eighth session, a week and three days after
the previous, were only chosen videos of the blue
color program. The standard videos with medium
complexity of mixed pattern (video of less
complexity for this session) and the diagonal motion
with fast speed of mixed pattern were selected.
In the video with medium complexity pattern, the
baby occasionally pursued, altering the attentional
focus between the various figures presented in
although not during the entire time of the pattern
display. When the pattern altered, he regained
attentional focus. In the diagonal movement, he
pursued and focused only part of the movement of
each of the figures, not being able to follow any of the
movements to the end.
Rehabvisual: Validation of an Application to Stimulate Visuomotor Skills in Preterm Babies with Developmental Alterations
253
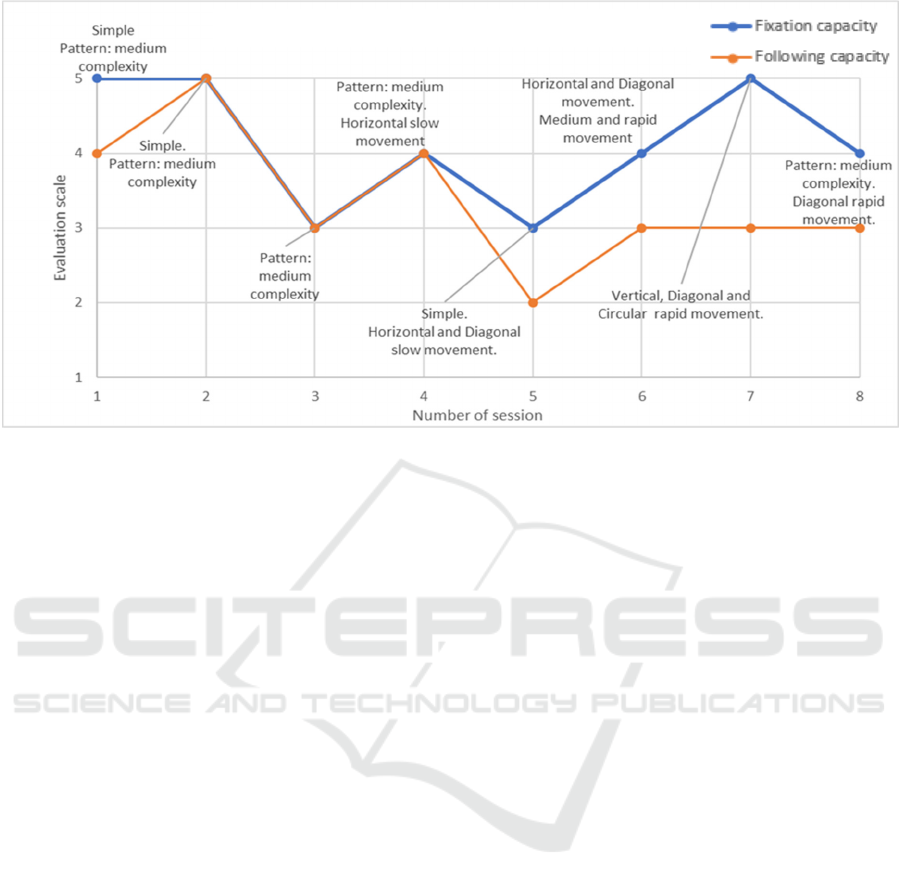
Figure 6: Results of the patient (fixation and following capacity) during therapy sessions.
Generally speaking, during the sessions, it is
concluded that the parameter of fixing the stimuli is
the one that presents the best results, which on one
hand can be explained by initially the baby acquire
the ability to fix and only after the ability to pursue an
object. It is also noted that in relation to simple
figures, the baby always has a very positive response
throughout the sessions. In the videos with medium
complexity, the response was also generally
improving as they were being inserted in the
therapies. In relation to stimuli with movement it is
concluded that the most adjusted to the baby are the
medium and fast speed, although in the case of videos
with diagonal motion these two speeds need to be
misadjusted to the baby's attention period (figure 6).
4 CONCLUSIONS
Through the usability tests it was possible to ascertain
that at the level of occupational therapy, this is a
useful tool and is adapted to the needs of its users
(since the average result of the SUS questionnaire and
the result of the questions made after the performing
the tasks were positive). However, it is necessary to
pay attention to the sample of the platform users, to
what people who are not familiar with computer tools
might sense in the introduction of the application on
their work.
At the level of therapy sessions, the tool is quite
versatile since new stimuli can be easily introduced
more adapted to the needs of the infants and their
ages, making the treatment more individualized and
specific to the population in question.
Currently, the included stimuli already provides
a very wide choice that allows the therapist to adapt
the sessions according to the baby's response
throughout the treatment so that no signs of
habituation arise or that the level of difficulty is
misadjusted to the baby.
The platform also allows obtaining a
standardized evaluation that facilitates registration,
as well as the subsequent interpretation of the results
during the real-time monitoring of the baby along
the treatment so that it can always be adapted
whenever possible.
5 FUTURE WORK
As future work it would be interesting to add an eye
tracker to the platform in order to verify if the infant
is really fixating or pursuing the image, which would
make the assessment easier and more correct.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank all the healthcare
professionals of the Physical Medicine and
Rehabilitation Service at D. Estefânia Hospital.
Evaluation per Session: Abilit
y
to fix and follow
BIODEVICES 2019 - 12th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
254

REFERENCES
Albert W. and Tullis T. (2010) Measuring the User
Experience: Collecting, Analyzing, and Presenting
Usability Metrics. Massachusetts, EUA: Morgan
Kaufmann. Available at: https://books.google.pt/
books?id=KsjpuMJ6T-YC.
Alimovic, S. (2012). ‘The assessment and rehabilitation of
vision in infants’, Paediatria Croatica, 56(1), 56, pp.
218–226.
Corn, A. and Erin, J. (2010) Foundations of low vision,
New York, NY: AFB Press.
Johnson, C.M., Johnson, T.R. and Zhang, J. (2005). ‘A
user-centered framework for redesigning health care
interfaces’, Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 38(1),
pp.75-87. Available at: http://www.sciencedirect.com/
science/article/pii/S1532046404001534.
Klug, B. (2017). ‘An Overview of the System Usability
Scale in Library Website and System Usability
Testing’, Weave: Journal of Library User Experience,
1(6). Available at: https://quod.lib.umich.edu/w/weave/
12535642.0001.602?view=text;rgn=main.
Kushniruk, A.W. and Patel, V.L. (2004). ‘Cognitive and
usability engineering methods for the evaluation of
clinical information systems’, Journal of Biomedical
Informatics, 37(1), pp.56-76. Available at: http://www.
sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1532046404000
206.
Lyles, C.R., Sarkar, U. and Osborn, C.Y. (2014). ‘Getting a
Technology-Based Diabetes Intervention Ready for
Prime Time: a Review of Usability Testing Studies’,
Current Diabetes Reports, 14(10). Available at:
https://www.ncbi.nlm. nih.gov/pubmed/25173689.
Machado, R., Ferreira, A., Quintão C., and Quaresma C.
(2018) ‘Rehabvisual: Development of an application to
stimulate visuomotor skills’, Proceedings of the 11th
International Joint Conference on Biomedical
Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC
2018), BIODEVICES, Funchal, Madeira, Portugal,
pp.173-178. Available at: //doi.org/10.5220/000659700
1730178.
McLellan, S., Muddimer, A. and Peres S.C (2012). ‘The
eect of experience on system usability scale ratings’,
Journal of usability studies, 7(2). pp. 56–67. Available
at: http://uxpajournal.org/the-effect-of-experienceon-
system-usability-scale-ratings/.
Nielsen Norman Group (2012). How Many Test Users in a
Usability Study? Available at: https://www.nngroup.
com/articles/how-many-test-users/?lm=eyetrackingtas
k-scenarios&pt=youtubevideo (Accessed 28 Jul. 2018).
UX research. (2017). Measuring and interpreting system
usability scale (sus). Available at: https://uiuxtrend.
com/measuring-system-usabilityscale-sus/ (Accessed
23 Mar. 2018).
Zhou, L., Bao, J. and Parmanto, B. (2017). ‘Systematic
Review Protocol to Assess the Effectiveness of
Usability Questionnaires in mHealth App Studies’,
JMIR Research Protocols, 6(8), p.e151. Available at:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5558
042/.
Rehabvisual: Validation of an Application to Stimulate Visuomotor Skills in Preterm Babies with Developmental Alterations
255
