
Application of Artificial Intelligence in Microwave Radiometry
(MWR)
Christoforos Galazis
1
, Sergey Vesnin
3
and Igor Goryanin
1,2
1
University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, U.K.
2
Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology, Okinawa, Japan
3
Medical Microwave Radiometry Ltd., U.K.
Keywords: Microwave Radiometry, Breast Cancer, Diagnostic System, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning,
Neural Network, Cascade Correlation Neural Network, Convolutional Neural Network, Random Forest,
Support Vector Machine.
Abstract: Microwave radiometry is being developed more actively in recent years for medical applications. One such
application is for diagnosis or monitoring of cancer. Medical radiometry presents a strong alternative to
other methods of diagnosis, especially with recent gains in its accuracy. In addition, it is safe to use, non-
invasive and has a relative low cost of use. Temperature readings were taking from the mammary glands for
the purpose of detecting cancer and evaluating the effectiveness of radiometry. Building a diagnostic system
to automate classification of new samples requires an adequate machine learning model. Such models that
were explored were random forest, XGBoost, k-nearest neighbors, support vector machines, variants of
cascade correlation neural network, deep neural network and convolution neural network. From all these
models evaluated, the best performing on the test set was the deep neural network with a significant
difference from the rest.
1 INTRODUCTION
Microwave radiometry has seen in recent years in-
creased usage and interest for further development
and research within medical applications (Vesnin et
al., 2017). This has resulted in a significant
improvement of the system’s accuracy in taking
internal temperature measurements. One of its main
applications is for cancer detection and monitoring,
such as breast cancer which will be the focus of this
paper.
However, while gaining momentum in its
utilization it is still not widely adopted. Main reason
for this can be attributed to the fact that it has
recently being adopted for medical use and so
medical or clinical professionals have not yet
received adequate training to interpret the
information. However, this leads to the initial issue, if
the professionals are unable to use the system then
they will be more hesitant to acquire them.
The deadlock can be resolved with the
introduction of an automated diagnostic systems
which will extract useful information from the
readings and offer a diagnostic prediction. For this
paper, the focus will be in evaluating how effective
such data alone can be used for diagnosis of cancer,
using data collected from mammary glands.
Additionally, a furtherscope is to contribute into
determining an ideal machine learning algorithm for
such a task.
The paper will start off with a brief development
history of radiometry within the medical field, what
it captures and why it is an attractive system to be
used for cancer detection and monitoring. Following,
a description of the data set will be provided which
includes readings from radiometry of the mammary
glands for cancer detection. In addition, any pre-
processing that was conducted on the data will be
documented. After the setup information has been
provided, the description and results of various non-
neural network and neural network models will be
presented on classifying low or high risk of presence
of breast cancer. Finally, the paper will finish off with
the conclusions and some possible future work.
112
Galazis, C., Vesnin, S. and Goryanin, I.
Application of Artificial Intelligence in Microwave Radiometry (MWR).
DOI: 10.5220/0007567901120122
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2019), pages 112-122
ISBN: 978-989-758-353-7
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 MICROWAVE RADIOMETRY
Microwave radiometry’s started from the theoretical
research of James Clerk Maxwell and experimentally
verified by Heinrich Hertz, with development of the
first radars in the 1930s (Skolnik, 2018). Later, dur-
ing WWII Robert invented a kind of radio receiver,
was known as ”Dicke Radiometric Receiver” or just
”Dicke Radiometer”. His radiometer used a switch-
able resistor, the ”Dickle Resistor”, as a technique to
allow for noise temperature calibration (Dicke, 1982).
However, only later on, from 1970s, such
technology was first applied for medical and clinical
us- age (Myers et al., 1979; Bolomey et al., 1982;
Peronnet et al., 1983; Pichot et al., 1985). But there
was no significant investment until the late 1990s,
which gain a lot more interest from the medical sci-
entific community (Conceicao et al., 2016). Since
then it has found applications for detecting or mon-
itoring breast cancer (Vesnin et al., 2017), thermal
denaturation of albumin (Ivanov et al., 2018), carotid
artery diseases (Drakopoulou et al., 2018), brown adi-
pose tissue activity (Crandall et al., 2018), rheuma-
toid arthritis (Pentazos et al., 2018), inflammation lev-
els in joints (Laskari et al., 2018), brain temperature
(Rodrigues et al., 2018) and transcapillary water ex-
change in the lungs (Bondar et al., 2017).
It is able to capture the temperature at the skin or
at a depth from the surface, which is particular use-
ful for diagnosing and monitoring treatment progress
of cancerous tumors (Vesnin et al., 2017). It achieves
this by measuring the electromagnetic radiation omit-
ted by the tissues in the microwave range (Vesnin
et al., 2017). The measurement obtained depends on
the variation of the properties of the various biologi-
cal tissues (Semenov, 2009). In turn, these properties
are impacted by the level of water found in the tissue,
with a significant difference between muscle, which is
high in water levels, and fat and bone, which have low
levels (Gabriel et al., 1996a; Gabriel et al., 1996b). In
addition, both physiological and pathological condi-
tions can alter the levels of dielectric properties of the
tissues (Semenov, 2009).
Specifically for cancer, it has been found that
tumors emit heat which is connected to their growth
rate (Gautherie, 1980). As the tumorous cells grow,
they replicate themselves at a much higher rate
leading to the release of higher amounts of energy
compared to neighboring healthy cells. The tumors’
ability to cre- ate new vasculature will determine its
maximum vol- ume (Schneider and Miller, 2005). At
such a stage, cell growth and cell death rate reach an
equilibrium. However, when the growth slows down
this will result to near normal temperature readings
making cancer detection more difficult for such
cases (Vesnin et al., 2017).
It is an attractive complementary technique to
other methods of diagnosis of cancer, such as mam-
mography or biopsy (Vesnin et al., 2017). The main
reason stated by Vesnin et al. is that advances in the
system have allowed it to achieve high sensitiv- ity
and specificity in cancer detection. Also, it is a
non-iodizing safe method, noninvasive, results are
obtained quickly and has a low cost (Vesnin et al.,
2017; Semenov, 2009). Hence, this enables it to be
used at any frequency, for any age group and by
some- one during pregnancy or lactation. In addition,
it can also occupy a supportive role in decision
making for professionals as for it adds information
not obtainable from other methods. Such information
is the thermal activity of the tissue, the rate which
cancerous cells multiply and the level of risk for
mutagenesis (Vesnin et al., 2017).
3 DATA SET
3.1 Description
To conduct the evaluation of microwave radiometry
for its effectiveness in detecting cancer a data set
compromising temperature values from mammary
glands was used. The values were recorded using the
RTM-01-RES (www.mmwr.co.uk) device from vari-
ous medical centers (Zenovich et al., 2016). The de-
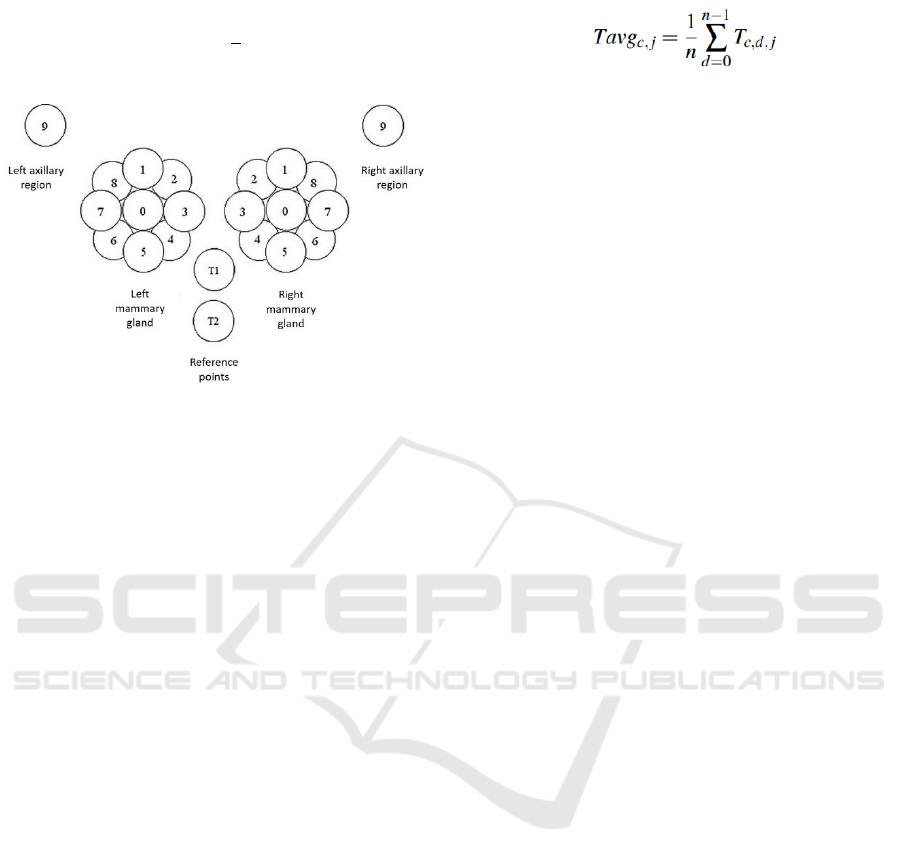
vice captures temperature readings at nine different
locations on each gland, one at the nipple (defined
as point 0) and the rest equidistant around the nip-
ple (points 1 to 8), plus at the axillary region (point
9). In addition, two more locations where captured at
the lower chest (defined as points T1 and T2), as ref-
erences to normalize ambient temperature variations.
For each of these points, the temperature was mea-
sured at the skin and at a depth from the skin of 5cm.
A graphical representation of the capture points can
be seen in Figure 1.
In total, there are 363 pairs of mammary glands of
which 77 are classified as healthy or low risk (labeled
as class 0) and 286 classified as potentially cancer-
ous or high risk (labeled as class 1). For each sam-
ple, to be classified as low risk both glands must be
considered as healthy and for it to be considered as
high risk then at least one must be of high risk. In-
dividual glands compromise of 319 low risk and 407
as high risk, which consist of 13 as diffused cancer,
185 as nodal cancer, 119 as diffuse changes with no
presence of cancer and 90 as nodal changes with no
presence of cancer. All the following experiments had
Application of Artificial Intelligence in Microwave Radiometry (MWR)
113
the data class balanced split into three sets, training,
validation and test set, with allocated percentage of
60% (low risk: 46 and high risk:171), 20% (low risk:
15 and high risk:57) and 20% (low risk: 16 and high
risk:58) respectively.
Figure 1: Sampling points on each mammary gland (0-8) in-
cluding the axillary point (9). Points T1 and T2 are used as
reference values when normalizing the values against ambi-
ent temperature (Zenovich et al., 2016).
3.2 Ambient Temperature
Normalization
Having collected the data at multiple locations and at
different times the ambient temperature varies for
each sample in which the values will not be directly
comparable. Typically, the measurements were taken
under temperatures ranging from 20 to 27 degrees
Celsius. When analyzing temperature values for
prediction systems breast size, age and external
conditions that can impact the results must be taken
into account (Anisimova, 2013; Kobrinskiy, 2008).
Hence, a previous research (Losev and Lvshinskiy,
2015) that used the same data set proposed and
evaluated a normalization algorithm to overcome this
issue. The algorithm was defined as such (Losev and
Lvshinskiy, 2015):
For every point t
d
,
i
,
j
captured, plot their values
against one of the control temperature points T
c
,
d
,
j
,
where i = 0...9, c ∈ {1, 2}, j ∈ {skin, depth} and
d = 0...n 1, with n the total number of samples:
1.
On the plotted graph between temperature
points and one of the reference values, we use linear
re- gression to find a and b such that the error is mini-
mized through least square fit method on the func-
tion:
t
d
,
i
,
j
=
a
∗
T
c
,
d
,
j
+
b
(1)
2.
Calculate the average value of the temperature
point such that:
(2)
3.
Update the temperature points:
t
d,i, j
= t
d,i, j
+ a∗ (Tavg
c, j
T
c,d, j
) (3)
4.
Replace the control points with the average
value found:
T
c
,
d
,
j
= Tavg
c
,
j
, (4)
for d = 0...n 1
Losev and Lvshinskiy showed that when apply-
ing their proposed algorithm, it improved the speci-
ficity and sensitivity of a regression prediction model.
There was a strong linear correlation coefficient be-
tween all points 0-9 against either of the two refer-
ence points as the temperature increased. While they
showed comparing against both reference points re-
sulted in improvement in predictions, using reference
T2 obtained slightly better performance of overall
4%. Therefore, for the following experiments evaluat-
ing various prediction models this normalization algo-
rithm was applied against reference point T2. In turn,
this allowed the removal of the two control points as
for all samples would have the same value.
3.3 Oversampling
As described in section 3.1, the data set is heavily im-
balanced towards the high risk class with a total of 77
against 286 samples. Consequently, this introduces a
bias towards the higher proportion samples in which
most machine learning algorithms will favor when
classifying (Krawczyk, 2016). Some algorithms can
handle this imbalance by introducing sample weights
giving more importance to the least represented class
or by introducing an appropriate metric (He and Ma,
2013). While both of these techniques were used in
the experiments where applicable, applying oversam-
pling (He and Ma, 2013) guarantees consistency be-
tween the various algorithms.
The techniques explored were random re-
sampling, Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Tech-
nique (SMOTE) with regular, borderline 1, border-
line 2 and Support vector Machine (SVM) variations
(Chawla et al., 2002; Han et al., 2005) and Adaptive
Synthetic (ADASYN) (He et al., 2008). The over-
sampling techniques were compared using a random
forest (Breiman, 2001) from the scikit-learn library
(Pedregosa et al., 2011) having set a sample weight
BIOINFORMATICS 2019 - 10th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
114

importance to handle imbalance. Additionally, for
each case the tree was optimized using the hyperopt
(Bergstra et al., 2015) library with the tree of Parzen
(TPE) (Bergstra et al., 2011) optimizer and weighted
Geometric Mean (G-mean) loss (Kubat and Matwin,
1997; Barandela et al., 2003) as the loss function to
minimize on. Using both weight balance and G-Mean
loss means that it eliminates the need for oversam-
pling. However, we want to evaluate whether over-
sampling is equivalent and interchangeable with these
techniques and does not negatively impact the results.
The results of the various oversampling techniques
are summarized in Table 1. The main metric used for
comparison is G-mean loss then sensitivity and
specificity and lastly accuracy. Improvements against
no oversampling based on the loss function is
observed for SMOTE with all variations but SVM.
However, with borderline 1 variation one can observe
a significant improvement especially with specificity
without sacrificing significantly the model’s sensitiv-
ity. It obtained a G-mean loss value of 0.3268, sen-
sitivity of 0.8621, specificity of 0.5 and accuracy of
0.7838. Hence, for the model evaluations the low risk
class of the training set was oversampled using
SMOTE borderline 1. Oversampling was used until
the low risk class had the same number of samples
of that of the high risk, that is 286.
4 MODEL EVALUATIONS
4.1 Non-neural Network Models
Non-neural network models are still a vital alternative
to neural network ones and can set a good baseline for
future models (Wilkins et al., 1996; Lim et al., 2000).
Non-neural networks models usually can train their
weights with much less time than compared to their
counterparts. Also, this leads to requiring fewer com-
putational resources, allowing them to be trained on
personal machines. Lastly, they require less hyperpa-
rameter tuning and setup time and do not require an
architecture to be designed specifically for the prob-
lem, making them production-ready sooner. While
having all these benefits, the results can also be in
par with what is obtained from neural networks but
depends on the complexity of the problem at hand.
Additionally, the best non-neural network model can
act as a base line for comparison of various network
architectures.
The models evaluated were Random Forest (RF),
XGBoost (Chen and Guestrin, 2016), K-Nearest
Neighbors (K-NN) (Cover and Hart, 2006), Support
Vector Machine (SVM) with linear kernel and radial
basis function (RBF) (Burges, 1998; Cortes and Vap-
nik, 1995). The algorithms were obtained from the
scikit-learn library, apart from XGBoost which was
obtained from its own library (Chen and Guestrin,
2016). Each of these models, their optimal hapyer-
parameters were determined through the usage of the
hyperopt library with the TPE optimizer. Addition-
ally, the loss function used to minimize the error on
was the weighted G-mean loss.
From the models evaluated, the top performer
based on the lowest achieved weighted G-mean loss
value is XGBoost with a value of 0.3994. It also
obtained a decent sensitivity of 0.7069 but just 0.5 on
specificity and a biased accuracy of 0.6622.
Following came SVM with linear kernel obtaining a
weighted G-mean loss of 0.4241 and closely in third
RF with 0.4281. K-NN and SVM with RBF obtained
significantly worse results with a weighted G-mean
loss of 0.4829 and 0.5687 respectfully. The full
summary of the results on the test set are shown in
Table 2.
4.2 Neural Network Models
Here the neural networks will no longer directly use
the weighted G-mean loss function to optimize the
parameters on but instead use a categorical cross en-
tropy function (de Boer et al., 2005) to measure the
error of the network. The weighted G-mean loss was
not used because it is not possible to obtain a dif-
ferentiable global G-mean loss on batch operations.
However, to be able to compare the results to that
obtained in the non-neural networks a non-weighted
G-mean batch-wise loss function was applied. Also,
to be able to obtain a respective weighted loss value
from the batch-wise loss function class weight balanc-
ing was preferred over oversampling. Additionally, it
was used as an early stopping criteria on the valida-
tion set. Its implementation is the same as that of a
normal G-mean loss function and was executed at the
end of each batch, which was set to a size of 50 sam-
ples, during training and obtained the average at the
end of each epoch.
By using categorical cross entropy, the class labels
were transformed to binary values by applying one-
hot encoding. Hence, the classes were represented as
vectors with the low risk class (0) as (1, 0) and the
high risk (1) as (0, 1). Additionally, the loss function
assumes that the passed input represents the probabil-
ity for each encoding to be true. That is, it expects a
vector which sums to 1 and each individual value is
within [0, 1]. For the network to oblige by this con-
straint, the output layer’s activation function used was
a softmax function (Bishop, 2006) which from a vec-
Application of Artificial Intelligence in Microwave Radiometry (MWR)
115

Table 1: Summary of the results on the test set of a random forest classifier when using oversampling on the least
represented class (low risk) in the data set so it becomes balanced.
Oversampling G-Mean Loss Accuracy Sensitivity Specificity
No oversampling 0.3894 0.7702 0.8793 0.375
Random 0.3994 0.6622 0.7069 0.5
SMOTE regular 0.3749 0.6622 0.6897 0.5625
SMOTE borderline1 0.3268 0.7838 0.8621 0.5
SMOTE borderline2 0.3693 0.7568 0.8448 0.4375
SMOTE SVM 0.4126 0.7297 0.8276 0.375
ADASYN 0.401 0.7027 0.7759 0.4375
Table 2: Summary of the results on the test set for the non-neural network models.
Model G-Mean Loss Accuracy Sensitivity Specificity
RF 0.4281 0.7027 0.7931 0.375
XGBoost 0.3994 0.6622 0.7069 0.5
K-NN 0.4829 0.527 0.5345 0.5
SVM Linear Kernel 0.4241 0.6216 0.6551 0.5
SVM RBF Kernel 0.5687 0.7432 0.7826 0.0625
tor of real number outputs a probability distribution.
The optimal hyperparameters were found through the
usage of grid search based on the validation results
of the G-mean loss. Additionally, the architecture
which includes the number of layers and neurons,
activation functions, optimizers and regularization
methods were determined through experimentation
with a variety of combinations. All the networks
were implemented using Keras (Chollet et al., 2015)
with Tensorflow (Abadi et al., 2016) backend.
4.2.1 Cascade Correlation Neural Network
On this specific data set, the best performing diagnos-
tic model concluded from a variety of models from a
previous research (Zenovich et al., 2016) was a Cas-
cade Correlation Neural Network (CCNN) (Fahlman
and Lebiere, 1990). Subsequent goal of this paper is
to further explore and improve the CCNN. For the
evaluation, the previous network will be re-
implemented so results are comparable. This model
will be distinguished as the base CCNN model. Fur-
ther, taking advantage of the previously positive re-
sults, another two variations are being proposed in
this paper and are defined as improved and extended
CCNN models, in an attempt to further refine the re-
sults.
The CCNN was proposed by Fahlman and Lebiere
(1990) as an approach that is not only limited to tun-
ing the parameters of the network but also dynami-
cally determining the optimal architecture, constraint
to the number of hidden layers. The network initial
consists of a fully connected input and output layers,
which their size is defined by the problem. Then the
algorithm executes these following steps until conver-
gence:
• All weights of units connected to the output
layer are trained until the minimum error is
reached
• A pool of candidate units are generated which
• have as input the output of all previously
added layers excluding the output layer’s
• These candidate units are trained such that
their
• output maximizes the correlation coefficient
be- tween the residual error of the network
• The candidate that has the maximum
correlation
• is selected to be added to the network. Its
input weights are frozen and its output is
connected with the output layer
The network continues this iterative process until the
addition of a unit does not lead to a smaller error than
the previous execution.
The base CCNN model reflects closely the ini-
tially proposed algorithm (Fahlman and Lebiere,
1990) with some minor changes over and above those
mentioned in section 4.2. The hidden and candi-
date units used the sigmoid function as their activa-
tion function. Additionally, the weights were initial-
ized randomly from a normal distribution which had
a mean of 0 and standard deviation of 0.5 and the
bias was set to 0. After every loop the weights of the
BIOINFORMATICS 2019 - 10th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
116

output layer were reinitialized to avoid being stuck at
bad local minimums. Furthermore, the optimiza-
tion function used was Stochastic Gradient Descent
(SGD) (Bottou, 2010). Its learning rate was set to
0.00001 and 0.000005 for the output and hidden can-
didate layers respectively. Noting that in the previous
research (Zenovich et al., 2016) the authors used Sim-
ulated Annealing, but SGD was preferred hoping for
better generalization. Finally, the candidate pool size
was set to 16 and each candidate layer had two units,
the same as the output layer.
For the proposed improved model, only the
differences from the base one will be noted. The
focus of this CCNN model is to utilize more recent
techniques to improve performance. Firstly, the
weight initialization scheme was changed from
random distribution to Xavier (Glorot and Bengio,
2010) sampling from a normal distribution. Also, the
optimizer was changed to Adam (Kingma and Ba,
2014) as a further improvement to SGD. Its learning
rate was set to 0.00001 and 0.000005 for the output
and candidate layers respectively. For both cases,
the decay of first-order gradient to 0.9, decay of
second-order gradient to 0.99 and a small epsilon of
1e-08. Addition- ally, the activation functions of the
hidden layers were changed to Rectified Linear Units
(ReLUs) (Nair and Hinton, 2010). Lastly, for the
output layer warm-start weight initialization was
added to carry over weights that contributed the most
to lowering the loss value.
The extended model, building from the improved
model, focused on further expanding the capabilities
of dynamically constructing the architecture by also
introducing regularization layers to the pool in an at-
tempt to improve generalization. The hidden candi-
date layer was changed to have the following format
and strict order:
• Gaussian noise layer with a mean of 0 and a
standard deviation of 0.5
• Dense layer (original unit)
• Batch normalization layer (Ioffe and Szegedy,
2015) with momentum at 0.99, epsilon at
0.00001 and a trainable beta value
• Dropout layer (Srivastava et al., 2014), which
randomly drops one of the two units
The candidate pool consisted twice of all possible
combinations of the regularization layers, while
strictly maintaining the order presented. Thus, the
total pool size was maintained to 16 with only two
candidate layers being the same in comparison to all
16 in the two previous models.
Based on the G-mean loss value on the test set
the best performer from the CCNNs was the im-
proved variation with a value of 0.5417, accuracy of
0.5541, sensitivity of 0.6207 and specificity of 0.375.
A marginal difference followed the extended model
with G-mean loss of 0.5495 and lastly, with signifi-
cantly worse results, the base model with a value of
0.5889. The full summary of the results on the test set
can be found in Table 3.
On the validation results there is a significant point
to note out. The G-mean loss value obtained by the
models on the validation set were 0.3512, 0.2677,
0.1578 for the base, improved and extended models
respectively. The extended model was able to extract
more information from the training set to improve its
score on that of the validation. However, having
nearly the same score as the top performer, there was
at least no loss of information compared to the
improved model, but the recognition of patterns that
were useful on the validation set were not so for the
test set. This is possibly due to the fact that the data
set contains considerable number of outliers, as far as
the network is concerned. This in turn prevents sepa-
ration of the data in such a way that each set samples
from the possible distribution of the problem,
hindering generalization capabilities.
4.3 Deep Neural Network
A Deep Neural Network (DNN) was also constructed
to compare the performance of the cascade networks.
Specifically, it was used to evaluate the results,
training speed and memory usage between the
models. The design of the DNN was based on the
results obtained previously in section 4.2.1. Thus,
the network will also focus on using various
generalization methods.
The DNN’s hidden layers used ReLu for their
activation function and their weights were initialized
used Xavier’s method. Also, the optimizer used was
Adam with a learning rate of 0.00005, the decay of
first- order gradient at 0.9, decay of second-order
gradient at 0.999 and an epsilon value at 1e-8. For
regularization, Gaussian noise layers, with a standard
deviation of 0.2 and mean of 0, and dropout layers,
with 20% dropout rate, were included in the model.
Additionally, batch normalization layers were added
with momentum set to 0.99, epsilon to 0.00001 and a
trainable beta value. Lastly, details described in
section 4.2 still apply here. The final layout of the
network consists of five hidden layers, excluding the
input and output layers. The network’s architecture
was formed as following:
• Input layer with 40 units
• Batch normalization, Gaussian noise and
dense layer with 1000 units
Application of Artificial Intelligence in Microwave Radiometry (MWR)
117

Table 3: Summary of the results on the test set for the neural network models.
Model G-Mean Loss Accurac
y
Sensitivity Specificity
Base CCNN 0.5889 0.4324 0.4483 0.375
Improved CCNN 0.5417 0.5541 0.6207 0.3125
Extended CCNN 0.5495 0.5405 0.6034 0.3125
Deep Neural Networ
k
0.2843 0.7703 0.8103 0.625
Convolution Neural Networ
k
0.3637 0.6081 0.5862 0.6875
• Batch normalization, dropout, Gaussian noise
and dense layer with 200 units
• Batch normalization, dropout, Gaussian noise
and dense layer with 200 units
• Batch normalization, dropout, Gaussian noise
and dense layer with 200 units
• Batch normalization, dropout and dense layer
with 200 units
• Dense output layer with 2 units
The DNN was able to obtain a G-mean loss of
0.2843, accuracy of 0.7703, sensitivity of 0.8103
and specificity of 0.625 on the test set, as shown in
Table 3.The results obtained are significantly better
than that obtained from the improved CCNN, which
had a G-mean loss of 0.5417. It was also able to
achieve this with a noticeably faster training time.
However, the CCNN model was able to obtain its
results requir- ing less memory, as for it constructed
a network with a total of 47 hidden layers with 2
units each based on the improved variant. But with
today’s state of avail- able hardware the memory
usage from the DNN is not of a concern.
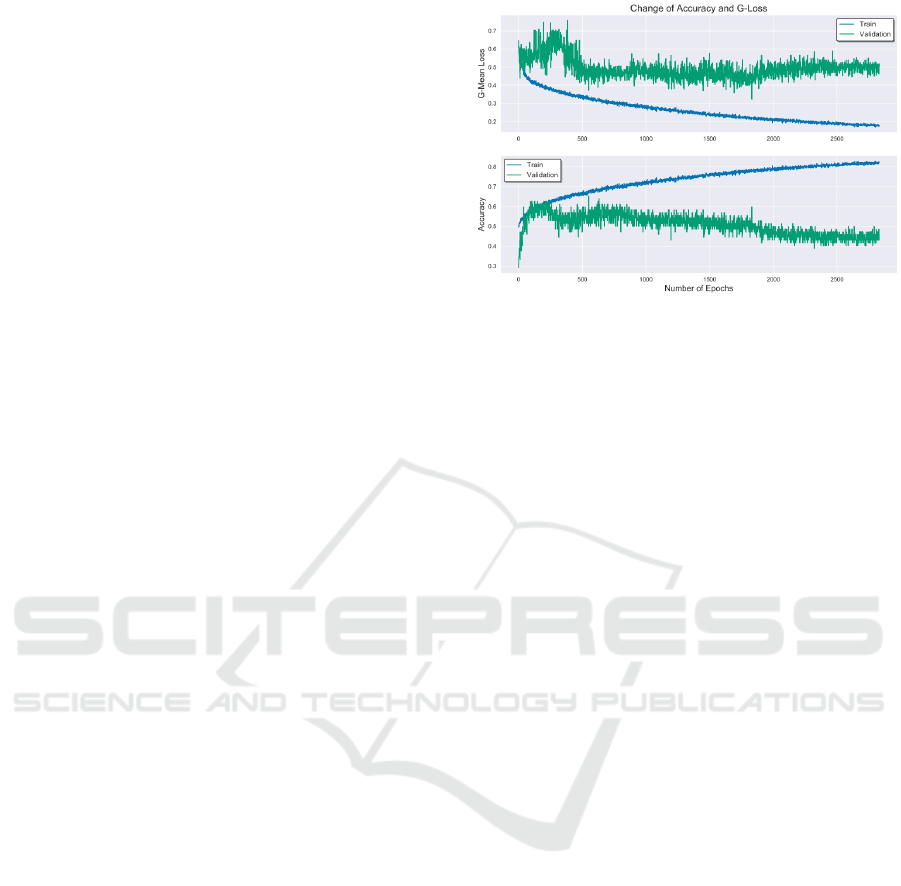
Figure 2: The average batch-wise G-mean loss and accu-
racy of the deep neural network as it is trained.
As seen in Figure 2, the regularization techniques
prevented overfitting the training data against the val-
idation. While the network has extracted all possi-
ble information from the training set need to classify
those samples, it does not cover all possible cases in
the validation set. The limitation of the model is de-
rived again from the limited available data in express-
ing an accurate distribution of the problem within the
three sets.
4.3.1 Convolutional Neural Network
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have shown
great results for detecting breast cancer using vari-
ous imaging data (Cires¸an et al., 2013; Spanhol et al.,
2016; Arajo et al., 2017). In an attempt to further im-
prove the results of the DNN, a CNN model was also
explored. Its design was based on the previously ob-
tained results with higher focus around its ability to
generalize.
Building a CNN implies that the input will be a
2D image with one or more channels (usually color).
Thus, the input vector was transformed to a 2D image
with two channels. The channels were used to rep-
resent the measured data at the skin and at a depth.
The image itself will be of size 13x6 containing the
normalized measurements from both glands and axil-
lary points. The positioning on the image resembles
closely to that of the Figure 1, while also obtaining
the average of neighboring positions to better
represent the overlap as depicted in Figure 3. The
values, before being formed to an image representa-
tion, they were centered using a robust scaler based
on the in- terquartile range to maintain outliers.
Figure 3: Methodology in transforming a vector of temper-
ature measurements from the mammary glands, for both at
the skin and at a depth, to a 2D array. The L represents the
left gland and R the right gland. Any cells left blank have a
value of 0.
The training set used for the CNN was oversam-
pled, as described in section 3.3, and then applying
image augmentations. The intention of this was to
BIOINFORMATICS 2019 - 10th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
118
obtain a more rotation invariance network when de-
tecting features on the glands, which in turn should
further improve generalization. The type of augmen-
tations applied were image flipping on the vertical
axis and rotations of the outer pointer of the mam-
mary glands. The result was a total of 5472 samples
split equally between low and high risk for the train-
ing set.
The hidden layers of the network used ReLu acti-
vation functions and Adam optimizer with a learning
rate of 0.0000005, decay of first-order gradient at 0.9,
decay of second-order gradient at 0.999 and epsilon at
1e-8. Additionally, the weights of all the layers were
initialized using the Xavier method from a uniform
distribution. The type of layers used were dense, con-
volutional (Lecun et al., 2015), separable convolution
(Chollet, 2016), max pooling (Lecun et al., 2015),
global average pooling (Lin et al., 2013), dropout,
spatial dropout (Tompson et al., 2014), batch nor-
malization and Gaussian noise. The convolution and
pooling layers used a kernel of size 3x3, stride of 1
with the exception of spatial which used 2, padding
set to same and no bias value. Lastly, all dropout lay-
ers had a dropout percentage of 20%. The full net-
work architecture was defined as following:Input
layer of size 13x6x2 Convolutional with 64 units
Batch normalization, ReLu activation and convo-
lutional with 64 units
• Batch normalization, ReLu activation,
Gaussian noise with standard deviation of
0.01, max pool- ing and convolutional with
128 units
• Batch normalization, ReLu activation,
convolu-
• tional with 128 units
• Batch normalization, ReLu activation,
Gaussian noise with deviation of 0.001, max
pooling and convolutional with 256 units
• Batch normalization, ReLu activation and
convo-
• lutional with 256 units
• Batch normalization, ReLu activation,
Gaussian noise with deviation of 0.001, spatial
dropout, max pooling and separable
convolution with 512 units
• Gaussian noise with deviation of 0.0001, batch
• normalization, ReLu activation and separable
convolution with 512 units. Repeated four
times Gaussian noise with deviation of 0.0001,
batch normalization, ReLu activation, global
average pool, dense with 512 units
• Batch normalization, ReLu activation,
dropout, Gaussian noise with deviation of 0.1
and dense with 2 units
Figure 4: The average batch-wise G-mean loss and accu-
racy of the convolutional neural network as it is trained.
The CNN obtained a G-mean loss value of 0.3637,
accuracy of 0.681, sensitivity of 0.5862 and speci-
ficity of 0.6875, which are included in Table 3. The
network was not able to outperform that of the DNN
based on the G-mean loss but did obtain the highest
specificity rate from all other models. Additionally,
the Figure 4 shows the training and validation G-mean
loss and accuracy as the training of the network pro-
gresses. With the addition of augmentation it should
of helped with generalization, but there was still some
slight overfitting of the training set against the valida-
tion. Finally, there is a similar pattern as before where
limited information from the training set can be gen-
eralized to the validation.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The best performing model introduced in this paper is
the DNN, described in section 4.2.2, with a weighted
G-mean loss of 0.2843 on the test set. Followed was
the CNN with a loss value of 0.3637 and in third place
XGBoost with a value of 0.3994. The three variants
of CCNN were not able to outperform the non-
neural network models, with the exception of SVM
with RBF kernel.
The results of the DNN indicate the potential in
automating readings from radiometry for the purposes
of diagnosis or monitoring cancer patients, which is
not only limited to breast cancer. The models here
used only temperature readings so that the effective-
ness of microwave radiometry in medical applications
can be evaluated. Taking that into account, by
including additional information from other systems
and what is recorded from a clinical professional
about the physiological condition of each person
(Zenovich et al., 2016), it is expected to further
Application of Artificial Intelligence in Microwave Radiometry (MWR)
119

improve the capabilities of such a system. In
addition, a more exhaustive search on deep neural
networks should be conducted as they show
promising results and can potentially bring further
improvements.
As a potential diagnostic system to aid clinical
professionals in making decisions it currently re-
turns limited information, low or high risk of can-
cer with a prediction confidence. The problem is
oversimplified due to limited amount of data. As
more descriptive and broader data becomes available
it can be expanded from a binary to a multi-class
task. Some possible labels are benign and malignant
tumors, noncancerous tumors, inflammation,
infection and healthy patients. Additionally, as a
future scope, the networks can be reevaluated and
altered, as needed, when readings are obtained for
cancerous tumors at various body locations.
The proposed variants of the CCNNs can be even
further improved on the aspect of dynamic
construction of the architecture. Additional
suggestion is to allow the network to try against
various activation and optimization functions and
conduct hyperparameter optimization through an
online grid search. However, this drastically
increases the number of possible combinations for
the network to explore, hence in- creased training
time, for a possibly small improvement. Moreover,
there is a risk with the preferential selection of units
against the validation set. With such a fine level of
selection and with the added high amount of noise it
is possible to overfit the validation set. Hence,
shifting the problem from generalizing from the
training set to generalizing from the valida tion set.
REFERENCES
Abadi, M., Barham, P., Chen, J., Chen, Z., Davis, A.,
Dean,
J., Devin, M., Ghemawat, S., Irving, G., Isard, M., Kudlur,
M., Levenberg, J., Monga, R., Moore, S., Murray, D.
G., Steiner, B., Tucker, P., Vasudevan, V., Warden, P.,
Wicke, M., Yu, Y., and Zheng, X. (2016). Tensorflow:
A system for large-scale machine learning. In
Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Conference on
Operating Systems Design and Implementation,
OSDI’16, pages 265–283, Berkeley, CA, USA.
USENIX Association.
Anisimova, E. V. (2013). Intllktualnyy analiz dannykh i
algoritmy klassifikatsii v diagnostik vnoznykh
zabolvaniy po dannym kombinirovannoy trmomtrii:
avtorf. dis. kand. tkhn. nauk [data mining and
classification algorithms in the diagnosis of venous
diseases according to the combination of thermometry.
abstract of diss. and. of technical sciences]. Vol-
gograd, page 16.
Arajo, T., Aresta, G., Castro, E., Rouco, J., Aguiar, P., Eloy,
C., Polnia, A., and Campilho, A. (2017). Classifica-
tion of breast cancer histology images using convolu-
tional neural networks. PLOS ONE, 12(6):1–14.
Barandela, R., Sanchez, J., Garca, V., and Rangel, E.
(2003). Strategies for learning in class imbalance
problems. 36:849–851.
Bergstra, J., Bardenet, R., Bengio, Y., and Ke´gl, B.
(2011). Algorithms for hyper-parameter optimization.
In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on
Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS’11,
pages 2546–2554, USA. Curran Associates Inc.
Bergstra, J., Yamins, D., and Cox, D. D. (2015).
Hyperopt: A python library for optimizing the
hyperparameters of machine learning algorithms.
Bishop, C. M. (2006). Pattern Recognition and Machine
Learning (Information Science and Statistics).
Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Bolomey, J. C., Izadnegahdar, A., Jofre, L., Pichot, C.,
Peronnet, G., and Solaimani, M. (1982). Microwave
diffraction tomography for biomedical applications.
IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Tech-
niques, 30(11):1998–2000.
Bondar, S. S., Terekhov, I. V., Voevodin, A. A., Leonov,
B. I., and Khadartsev, A. A. (2017). Assessment of
transcapillary water exchange in the lungs by active
radiometry. Biomedical Engineering, 51(3):211–214.
Bottou, L. (2010). Large-scale machine learning with
stochastic gradient descent. In Lechevallier, Y. and
Saporta, G., editors, Proceedings of COMP-
STAT’2010, pages 177–186, Heidelberg. Physica-
Verlag HD.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine Learning,
45(1):5–32.
Burges, C. J. C. (1998). A tutorial on support vector
machines for pattern recognition. Data Mining and
Knowledge Discovery, 2:121–167.
Chawla, N. V., Bowyer, K. W., Hall, L. O., and Kegelmeyer,
W. P. (2002). Smote: Synthetic minority over- sampling
technique. J. Artif. Int. Res., 16(1):321–357.
Chen, T. and Guestrin, C. (2016). Xgboost: A scalable tree
boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22Nd ACM
SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge
Discovery and Data Mining, KDD ’16, pages 785–
794, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Chollet, F. (2016). Xception: Deep learning with depthwise
separable convolutions. CoRR, abs/1610.02357.
Chollet, F. et al. (2015). Keras. https://keras.io.
Cires¸an, D. C., Giusti, A., Gambardella, L. M., and
Schmidhuber, J. (2013). Mitosis detection in breast
cancer histology images with deep neural networks. In
Mori, K., Sakuma, I., Sato, Y., Barillot, C., and Navab,
N., editors, Medical Image Computing and Computer-
Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2013, pages 411– 418,
Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Conceicao, R., O’Halloran, M., and Mohr, J. (2016). An
Introduction to Microwave Imaging for Breast Cancer
Detection.
BIOINFORMATICS 2019 - 10th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
120

Cortes, C. and Vapnik, V. (1995). Support-vector
networks.
Mach. Learn., 20(3):273–297.
Cover, T. and Hart, P. (2006). Nearest neighbor pattern clas-
sification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theor., 13(1):21–27.
Crandall, J. P., O, J. H., Gajwani, P., Leal, J. P.,
Mawhinney, D. D., Sterzer, F., and Wahl, R. L. (2018).
Measurement of brown adipose tissue activity using
microwave radiometry and 18f-fdg pet/ct. Journal of
nuclear medicine: official publication, Society of Nu-
clear Medicine, 59(8):12431248.
de Boer, P.-T., Kroese, D. P., Mannor, S., and Rubinstein,
R. Y. (2005). A tutorial on the cross-entropy method.
Annals of Operations Research, 134(1):19–67.
Dicke, R. H. (1982). The Measurement of Thermal Ra-
diation at Microwave Frequencies, pages 106–113.
Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht.
Drakopoulou, M., Moldovan, C., Toutouzas, K., and Tou-
soulis, D. (2018). The role of microwave radiometry in
carotid artery disease diagnostic and clinical
prospective. Current Opinion in Pharmacology, 39:99 –
104. Cardiovascular and renal.
Fahlman, S. E. and Lebiere, C. (1990). Advances in neural
information processing systems 2. chapter The
Cascade-correlation Learning Architecture, pages 524–
532. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., San
Francisco, CA, USA.
Gabriel, S., Lau, R. W., and Gabriel, C. (1996a). The
dielectric properties of biological tissues: Ii.
measurements in the frequency range 10 hz to 20 ghz.
Physics in Medicine and Biology, 41(11):2251.
Gabriel, S., Lau, R. W., and Gabriel, C. (1996b). The di-
electric properties of biological tissues: III. parametric
models for the dielectric spectrum of tissues. Physics
in Medicine and Biology, 41(11):2271.
Gautherie, M. (1980). Thermopathology of breast cancer:
Measurement and analysis of in vivo temperature and
blood flow. Annals of the New York Academy of Sci-
ences, 335(1):383–415.
Glorot, X. and Bengio, Y. (2010). Understanding the
difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks.
In Teh, Y. W. and Titterington, M., editors, Proceedings
of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artifi-
cial Intelligence and Statistics, volume 9 of Proceed-
ings of Machine Learning Research, pages 249–256,
Chia Laguna Resort, Sardinia, Italy. PMLR.
Han, H., Wang, W.-Y., and Mao, B.-H. (2005). Borderline-
smote: A new over-sampling method in imbalanced
data sets learning. In Proceedings of the 2005 Interna-
tional Conference on Advances in Intelligent Comput-
ing - Volume Part I, ICIC’05, pages 878–887, Berlin,
Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
He, H., Bai, Y., Garcia, E. A., and Li, S. (2008). Adasyn:
Adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced
learning. In 2008 IEEE International Joint Confer-
ence on Neural Networks (IEEE World Congress on
Computational Intelligence), pages 1322–1328.
He, H. and Ma, Y. (2013). Imbalanced Learning: Foun-
dations, Algorithms, and Applications. Wiley-IEEE
Press, 1st edition.
Ioffe, S. and Szegedy, C. (2015). Batch normalization: Ac-
celerating deep network training by reducing internal
covariate shift. CoRR, abs/1502.03167.
Ivanov, Y., Kozlov, A. F., Galiullin, R. A., Tatur, V. Y., Zi-
borov, V. S., Ivanova, N. D., Pleshakova, T. O., Ves-
nin, S. G., and Goryanin, I. (2018). Use of microwave
radiometry to monitor thermal denaturation of albu-
min. Frontiers in Physiology, 9:956.
Kingma, D. P. and Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A method for
stochastic optimization. CoRR, abs/1412.6980.
Kobrinskiy, B. A. (2008). Konsultativny intllktualny
mditsinski sistmy: klassifikatsiya, printsipy postron-
iya, effktivnost [consulting intelligent medical sys-
tems: Classification, principles of construction, effi-
ciency]. Volgograd, (2):38–47.
Krawczyk, B. (2016). Learning from imbalanced data: open
challenges and future directions. Progress in Artificial
Intelligence, 5(4):221–232.
Kubat, M. and Matwin, S. (1997). Addressing the curse of
imbalanced training sets: One-sided selection. In In
Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Confer-
ence on Machine Learning, pages 179–186. Morgan
Kaufmann.
Laskari, K., Pitsilka, D., Pentazos, G., Siores, E., Tek-
tonidou, M., and Sfikakis, P. (2018). Sat0657
microwave radiometry-derived thermal changes of
sacroiliac joints as a biomarker of sacroiliitis in
patients with spondyloarthropathy. Annals of the
Rheumatic Diseases, 77(Suppl 2):1178–1178.
Lecun, Y., Bengio, Y., and Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learn-
ing. Nature, 521(7553):436–444.
Lim, T.-S., Loh, W.-Y., and Shih, Y.-S. (2000). A
compar- ison of prediction accuracy, complexity, and
training time of thirty-three old and new classification
algo- rithms. Machine Learning, 40(3):203–228.
Lin, M., Chen, Q., and Yan, S. (2013). Network in
network. CoRR, abs/1312.4400.
Losev, A. G. and Lvshinskiy, V. V. (2015). Regressionnaya
model diagnostiki patologiy molochnykh zhelez po
dannym mikrovolnovoy radiotermometrii [regression
model for diagnosis of breast pathology according to
microwaves radiometry data]. Vestnik Volgogradskogo
gosudarstvennogo universiteta. Seriya 1. Mathemat-
ica. Physica [Science Journal of Volgograd State Uni-
versity. Mathematics. Physics], 6(31):72–82.
Myers, P. C., Sadowsky, N. L., and Barrett, A. H. (1979).
Microwave thermography: Principles, methods and
clinical applications. Journal of Microwave Power,
14(2):105–115.
Nair, V. and Hinton, G. E. (2010). Rectified linear units im-
prove restricted boltzmann machines. In Proceedings
of the 27th International Conference on International
Conference on Machine Learning, ICML’10, pages
807–814, USA. Omnipress.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V.,
Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer, P.,
Weiss, R., Dubourg, V., Vanderplas, J., Passos, A.,
Cournapeau, D., Brucher, M., Perrot, M., and Duch-
esnay, E. (2011). Scikit-learn: Machine learning in
python. J. Mach. Learn. Res., 12:2825–2830.
Application of Artificial Intelligence in Microwave Radiometry (MWR)
121

Pentazos, G., Laskari, K., Prekas, K., Raftakis, J., P.
Sfikakis, P., and Siores, E. (2018). Microwave
radiometry-derived thermal changes of small joints as
additional potential biomarker in rheumatoid arthritis:
A prospective pilot study. 24:1.
Peronnet, G., Pichot, C., Bolomey, J. C., Jofre, L., Izad-
negahdar, A., Szeles, C., Michel, Y., Guerquin-Kern,
J. L., and Gautherie, M. (1983). A microwave diffrac-
tion tomography system for biomedical applications.
In 1983 13th European Microwave Conference, pages
529–533.
Pichot, C., Jofre, L., Peronnet, G., and Bolomey, J. (1985).
Active microwave imaging of inhomogeneous bod-
ies. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,
33(4):416–425.
Rodrigues, D. B., Stauffer, P. R., Pereira, P. J. S., and Mac-
carini, P. F. (2018). Microwave Radiometry for Non-
invasive Monitoring of Brain Temperature, pages 87–
127. Springer International Publishing, Cham.
Schneider, B. P. and Miller, K. D. (2005).
Angiogenesis of breast cancer. Journal of Clinical
Oncology, 23(8):1782–1790. PMID: 15755986.
Semenov, S. (2009). Microwave tomography: Review of
the progress towards clinical applications. Philosoph-
ical Transactions: Mathematical, Physical and Engi-
neering Sciences, 367(1900):3021–3042.
Skolnik, M. I. (2018). Radar. Encyclopdia Britannica.
Available at https://www.britannica.com/technology/
radar/History- of-radar, Access date: 27/07/2018.
Spanhol, F. A., Oliveira, L. S., Petitjean, C., and Heutte, L.
(2016). Breast cancer histopathological image
classification using convolutional neural networks. In
2016 International Joint Conference on Neural
Networks (IJCNN), pages 2560–2567.
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I.,
and Salakhutdinov, R. (2014). Dropout: A simple way
to prevent neural networks from overfitting. Journal of
Machine Learning Research, 15:1929–1958.
Tompson, J., Goroshin, R., Jain, A., LeCun, Y., and
Bregler, C. (2014). Efficient object localization using
convolu- tional networks. CoRR, abs/1411.4280.
Vesnin, S., Turnbull, A., Michael Dixon, J., and Goryanin,
I. (2017). Modern microwave thermometry for breast
cancer. 7.
Wilkins, M. F., Boddy, L., Morris, C. W., and Jonker, R.
(1996). A comparison of some neural and non-neural
methods for identification of phytoplankton from flow
cytomery data. Bioinformatics, 12(1):9–18.
Zenovich, A. V., Glazunov, V. A., Oparin, A. S., and Pri-
machenko, F. G. (2016). Algoritmy prinyatiya resh-
eniy v konsultativnoy intellektualnoy sisteme diag-
nostiki molochnykh zhelez [algorithms of decision-
making in the advisory intellectual system of diagnos-
tics of mammary glands]. Mathematical physics and
computer modeling, 6:129–142.
BIOINFORMATICS 2019 - 10th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
122
