
Concept Design of a New Portable Medical Device for Lymphedema
Monitoring: A EIT Health ClinMed Summer School Project
Jordi Escuder Tisaire
1,
*
, Elena Martín Rodrigo
1,
*
, Sofia Ribeiro
2,3,
*
, Mariachiara Ricci
4,
*
,
Juan Sebastian Cuellar
5,
*
, Dimitrios Zeugolis
3,6
, Yves Bayon
2
and Isabel Rocha
7
1
Universitat de Barcelona (UB), Gran Via de les Corts Catalanes, 585, Barcelona, Spain
2
Medtronic, Sofradim Production, Avenue du Formans 116, Trevoux, France
3
Regenerative, Modular and Developmental Engineering Laboratory (REMODEL),
National University of Ireland Galway (NUI Galway), University Road, Galway, Ireland
4
Department of Electronic Engineering, University of Rome “Tor Vergata” (Rome), Via del Politecnico 1, Rome, Italy
5
Department of Biomechanical Engineering, Delft University of Technology, Mekelweg 2, Delft, The Netherlands
6
Science Foundation Ireland (SFI), Centre for Research in Medical Devices (CÚRAM),
National University of Ireland Galway (NUI Galway), University Road, Galway, Ireland
7
Faculty of Medicine and Cardiovascular Centre of University of Lisbon, Avenida Professor Egas Moniz MB,
Lisbon, Portugal
Keywords: Breast Cancer, Bioimpendance, Lymphedema, Screening, Self-Monitoring.
Abstract: Lymphedema is a chronic and progressive condition derived from impaired lymphatic system function.
Lymphedema is incurable, progressive, disfiguring, disabling and has adverse psychosocial effects. Upper
extremity lymphedema is mainly the consequence of breast cancer surgery. Several methods to diagnose
lymphedema exist; however, these diagnoses are performed once the disease is already close to an advanced,
irreversible stage. There is a need to monitor patients at risk with an efficient device. To solve this unmet
need, we propose a portable home-monitoring device for early diagnosis of lymphedema. This paper explores
all the aspects of the development of a new medical device, such as the assessment of the clinical need and
the state of the art, the specifications for the solution, the definition of the broad outlines of the development
plan and some considerations about the usability, the risk analysis, the market and the competitors.
1 CONTEXT
This work was born as a team project developed
during ClinMed 2018 summer school. ClinMed is a
summer school of EIT Health co-organized by
Inserm, Karolinska Institutet, University of
Grenoble-Alpes, University of Lisbon, Medtronics,
Becton Dickinson and Madopa. This summer school
aims to train participants on the technological
innovation in health by providing a global vision of
the maturation cycle of a medical device, i.e. from the
idea to the market, using the concept of experiential
learning. After an immersive stage at Rehabilitation
service at the Hospital Santa Maria (Lisbon, Portugal)
and the Pediatric Cardiology department at the
Hospital Santa Marta (Lisbon, Portugal), and in
collaboration with the clinicians, a real clinical need
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
was identified, and its solution explored during the
summer school.
2 INTRODUCTION
Lymphedema is a chronic and progressive disorder
which causes an accumulation of lymph fluid
(swelling) in parts of the body where lymph nodes or
lymphatic vessels are damaged or inadequate. It is
caused by an accumulation of fluid in the interstitial
tissues, due to the inability of the lymphatic system to
transport lymph fluid out of the affected area.
Lymphedema is classified as primary or secondary.
Primary lymphedema is rare, with an estimated
prevalence of 1 in 100,000 individuals and is caused
by lymphatic vascular anomalies (Grada and Phillips,
Tisaire, J., Rodrigo, E., Ribeiro, S., Ricci, M., Cuellar, J., Zeugolis, D., Bayon, Y. and Rocha, I.
Concept Design of a New Portable Medical Device for Lymphedema Monitoring: A EIT Health ClinMed Summer School Project.
DOI: 10.5220/0007696706110620
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2019), pages 611-620
ISBN: 978-989-758-353-7
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
611

2017). Secondary lymphedema is acquired and arises
because of an underlying systemic disease, trauma or
surgery (Kayiran et al., 2017).
Women who have undergone surgical or radiation
treatment for breast cancer, the most prevalent cancer
among women, are at a lifelong risk of developing
lymphedema. Some studies report an incidence of
lymphedema of 42% among the breast cancer
survivors (Norman et al., 2009). Lymphedema is a
significant problem in developing countries. It has
been reported that lymphedema affects as many as
200 million people worldwide and approximately 3
million people in the United States (Rockson and
Rivera, 2008).
The condition may result in physical and
psychological consequences, which can negatively
impact a woman's quality of life and compromise her
emotional well-being. It limits the range of motion, as
well as causing feelings of pain, heaviness, and
numbness. Psychologically, women may have
decreased self-confidence due to a disturbance in
body image, and experience negative emotions such
as anxiety, frustration, sadness, anger, and increased
self-consciousness (Taghian et al., 2014, Torres
Lacomba et al., 2010).
Lymphedema usually progresses through four
stages. At Stage 0, lymphatic flow is disturbed but
there is no apparent edema in the extremities; it is
possible to notice a difference in feeling, unusual
tiredness, or slight heaviness. At Stage 1, the
circumference of the extremities has increased but the
edema recedes with elevation because the skin and
tissues haven’t been permanently damaged. At Stage
2, the edema does not recede with elevation and may
present as pitting or nonpitting. Finally, at Stage 3 the
affected limb becomes very large and misshapen due
to the irreversible fluid collection(International
Society of Lymphology, 2003).
There is no cure for lymphedema. Treatments are
designed to reduce the swelling and the other
symptoms. The treatments include non-surgical
(complete decongestive therapy (CDT), compression
therapy, advanced pneumatic compression pumps
and exercise) and surgical options (physiological and
reductive methods), as shown in Table I.
These treatments, however, are only effective at
an early-stage of lymphedema (Kayiran et al., 2017,
Norman et al., 2009).
Therefore, it is essential to diagnose the condition
as soon as possible to prevent or minimize its
progression with the appropriate treatment (Network,
2011, Stout et al., 2012). Nowadays there are several
methods to diagnose lymphedema, however, most
cases arise after the symptoms are visible meaning the
disease is already at an advanced stage that could
become irreversible.
Recent research developments suggest that new
methods capable of detecting the underlying
deficiencies of the lymphatic transport system could
create a future where it is no longer necessary to wait
for the patient’s symptoms to become severe enough
to be detected. Although some of these methods are
already available in the market, they are far away to
become the new gold standard mainly due to its price.
Table 1: Lymphedema treatments.
Non-surgical treatments
Surgical treatments
Complete decongestive
therapy
Reductive techniques
Manual lymph drainage
Direct excision
Compression therapy
Liposuction
Exercise
Physiological techniques
Skin care
Lymphatic-lymphatic by-
pass
Compression garments
Lymphatic-venous by-pass
Advanced pneumatic
compression therapy
Lymph node transfer
Laser therapy
The quality of life of affected people would
increase considerably with an early diagnosis and
diligent care of the affected limb.
3 STATE OF THE ART
As mentioned previously, lymphedema should be
diagnosed as soon as possible. The goal of timely
intervention for breast cancer-related lymphedema is
decreased edema, smaller limbs, reduced joint aches,
muscle pain and tightness, decreased infection rates,
heightened patient desire to continue treatment,
decreased medical costs, and improved quality of life
(Soran et al., 2014). A delayed diagnosis or treatment
can result in rapid and unchecked progression of the
disease leading to complications, lack of mobility,
loss of function and disability, often leading to costly
emergency room visits and treatment (O'Toole et al.,
2013). It has been proved that progressive action can
diagnose lymphedema four times earlier compared to
the current diagnosis procedure (Soran et al., 2014,
Shih et al., 2009, Brunelle et al., 2015). To sum up,
the challenge facing clinicians is that there is no
reliable, affordable diagnostic capable of detecting
the disease before symptoms of lymphedema
develop.
Nowadays lymphedema diagnosis is made in a
clinical environment by thorough evaluation and
physical examination, by assessing volume and shape
ClinMed 2019 - Special Session on Designing Future Health Innovations as Needed
612

discrepancies and skin changes among the extremities
(Tahan et al., 2010, Kim et al., 2016). Volume
measurements can be done by including
circumferential measurement of the limbs with a non-
flexible tape, water displacement or perometry. The
perometry works similarly to computer-assisted
tomography, but uses infrared light instead X-rays
(O'Toole et al., 2013). Unfortunately, these methods
do not provide objective data about the localization of
the edema or the shape of the extremity, they are time-
consuming, difficult to perform and require
considerable experience from the clinician. They may
be difficult to use in individuals with large, loose skin
folds or in those with arthritis who cannot extend their
limbs.
New diagnostic approaches include non-invasive
measurements (tonometry, bioimpedance
spectroscopy) and imaging techniques
(lymphoscintigraphy, ultra-sonography, computed
tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging)
(Kayiran et al., 2017).
A tissue tonometer evaluates the tissue resistance
to compression. It can be used to assess the skin
pliability and fibrosis during lymphedema treatment.
While tissue dielectric constant can measure skin
texture and resistance, imaging techniques are able to
show the presence of extra fluid within the tissues
(Liu and Olszewski, 1992, Mayrovitz, 2009),
however they are expensive and inefficient. A
commercially available technology that use tissue
dielectric constant measurements is LymphScanner
by Delfin Technologies (Technologies).
Bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) is a non-
invasive technique that was first used by nutritionists
to assess body composition and has been used
recently as a reliable in early-stage diagnosis
technique of lymphedema since it assesses the
extracellular fluid compartment before visible
changes have settled (Cornish et al., 2001). BIS
involves applying a small electrical current at
frequencies ranging from 1-20 kHz to 1MHz through
the body and measures the opposition to the flow of
this current (defined as impedance). The electrical
current is primarily conducted by the water
containing fluids in the body; this water is contained
both within the cells, intracellular water, and external
to the cells, extracellular water. At low frequencies,
current passes through the extracellular fluid (ECF)
space and does not penetrate the cell membrane,
characterized by the theoretical resistance at zero
frequency (𝑅
0
). At high frequencies, however, the
current passes through both the intracellular fluid
(ICF) and ECF. Using this principle, a value of
impedance can be calculated. The measured
impedance is inversely proportional to the amount of
fluid (Erdogan Iyigun et al., 2015). An early report of
the use of this technique was published in 1996 where
it was shown that BIS technique is significantly more
sensitive than circumferential measurements and able
to detect small differences in the extracellular
volumes between the extremities of a patient (Cornish
et al., 2001). Recently, it has been shown that BIS
predicted the onset of lymphedema 10 months before
the condition could be clinically diagnosed, meaning
before there were visible symptoms (Erdogan Iyigun
et al., 2015).
Currently the existing commercially available
products using BIS as a diagnostic tool are
Lymphedema index (L-Dex) (Impedimed) and
SOZO® (SOZO) by Impedimed. A prospective
observational study demonstrated the impact of L-
Dex® measurements where it reduced the incidence
of clinical lymphedema from 36.4% to 4.4% in a
clinical practice (Soran et al., 2014). However, these
devices are costly and not portable. Only the most
specialized rehabilitation centres have access to
equipment that use BIS to obtain a more accurate
monitoring of the progression of lymphedema.
Performing the surveillance only at the hospital and
with big intervals between the check-ups leads to late
diagnosis and often lymphedema detection might be
done at an irreversible stage.
4 DESCRIPTION OF THE
DEVICE
Non-invasive regular patient monitoring in home
environment presents a high interest in healthcare
today. To follow regularly the patient’s health state, a
portable measurement device which is compact, low
cost, low power, and capable of performing
measurement with adequate accuracy is highly
desirable both for hospital and home use.
In this paper it is proposed a portable home-
monitoring device for early diagnosis of lymphedema
following breast cancer surgery. The device is
intended to be used regularly to monitor the patient
and detect in time the lymphedema.
The system, shown in Figure 1, comprises a BIS
device and a mobile application. The device includes
two adjustable bracelets, a belt and a
recording/controller module. Each bracelet includes
an active electrode for delivering AC current and a
passive electrode for performing impedance
measurement and an inertial measurement unit (IMU)
to measure the accelerations. The belt includes an
active electrode and a passive electrode.
Concept Design of a New Portable Medical Device for Lymphedema Monitoring: A EIT Health ClinMed Summer School Project
613
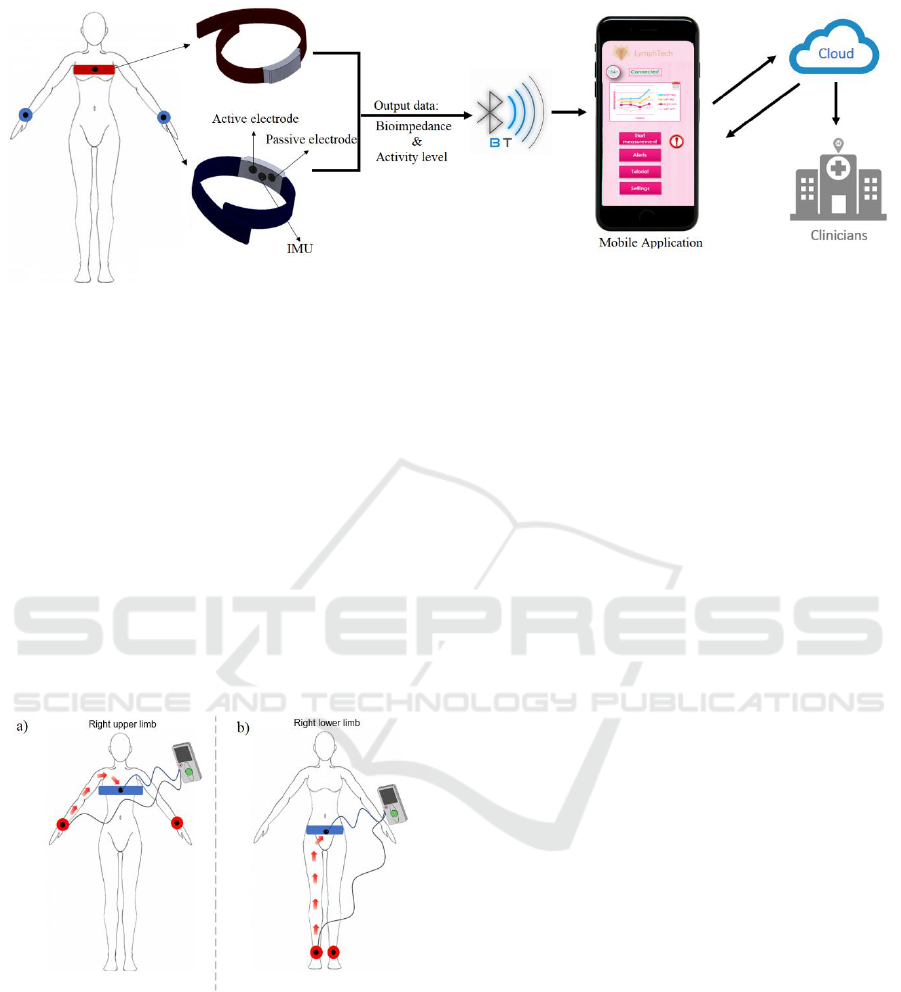
Figure 1: Detailed scheme of the operation: bioimpedance data, acquired by the wearable device, are transferred by Bluetooth
to a mobile phone application. After data analysis, biofeedback is sent to the patient and the clinicians. The device includes
two bracelets, a belt and a recording/controller module. Each bracelet includes an active electrode, a passive electrode and an
IMU. The belt includes an active electrode and a passive electrode.
The recording/controller module is designed to
send multi-frequency signals through the limbs, to
record the output and to process the signal to calculate
the lymphedema risk. The whole device is meant to
be portable using an internal rechargeable battery
encased into the recording/controller module.
To perform the upper limbs impedance
measurements, the user must wear the bracelets over
the wrists and the belt over the chest as shown in
Figure 2a. To perform the lower limbs impedance
measurements, the user must wear the bracelets over
the ankles and the belt over the hips as shown in
Figure 2b.
Figure 2: Electrodes’ positions to perform a measurement
with the device. For upper limb measurement (a), the
current passes from the wrist to the chest. For lower limb
measurement (b), the current passes from the ankle to the
hips.
Each limb is assessed separately by sending the
AC current from the belt to the bracelet by means of
active electrodes.
To avoid wrong measurements affected by
motion artefact the bioimpedance measurements are
only taken place once the level of activity measured
by the IMU is low. The bioimpedance measurements
are then stored to the memory card and sent via
Bluetooth module to the mobile phone.
The mobile application will provide the access to the
measured data, stored via Cloud, to the user. The app
will send notifications to remind the user to take the
measurement and alert the patient for increased risk
of developing the lymphedema.
4.1 Technical Requirements
The solution must: (1) provide multi-frequency
currents between two points located at the extremes
of the body parts of interest; (2) measure the related
bioimpedance and (3) store the measurements in a
flash memory and send them via Bluetooth module to
the mobile phone.
In addition, to avoid high signal noise by motion
or physical activity the bioimpedance measurements
can only take place once the activity level measured
is low. Therefore, an accelerometer sensor is included
as a technical aspect to control the measurement
process.
The schematic of our bioimpedance measurement
device is shown in Figure 3.
As said, in bioimpedance measurement system, a
small AC current passes through the body and the
opposition to the flow of this current (defined as
impedance) is measured. To achieve a suitable
accuracy is necessary that the output current is stable
and within safe magnitudes for a wide bandwidth.
For patient safety, a maximal AC-current of
0.5mA and frequency range between 1 kHz and
1MHz must be adopted.
Moreover, to keep the output current stable over
ClinMed 2019 - Special Session on Designing Future Health Innovations as Needed
614
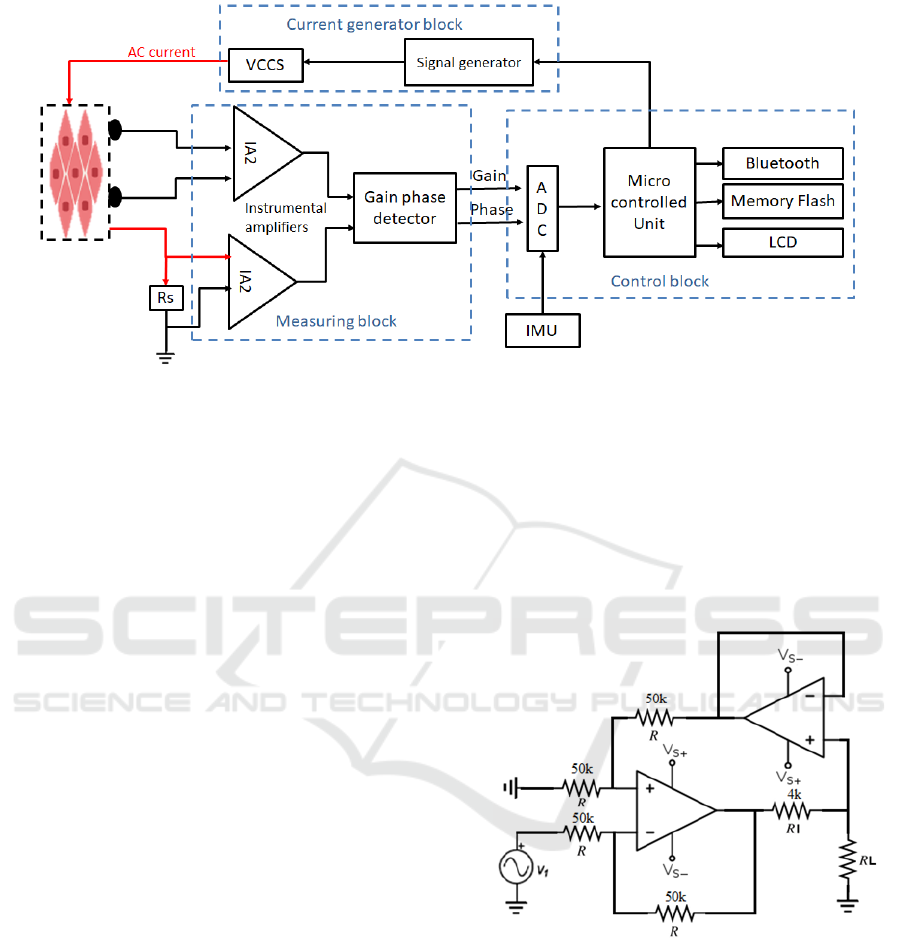
Figure 3: Schematics of the bioimpedance measurement device.
the frequency range independently of load changes,
the output impedance should be maintained higher
than the load impedance, so that the major part of the
current is given to the output and the inner losses of
the source are reduced.
4.2 Hardware
The recording/controller module includes a signal
(sine wave) generator, a voltage controlled current
source (VCCS), two identical instrumentation
amplifiers, a Gain Phase Detector (GPD), an
Analogue Digital Converter (ADC) and a
microcontroller unit (MCU). The battery needed for
the system, is a common rechargeable of 5V.
The signal generator and the VCCS generate a
sinusoidal current at pre-programmed frequencies in
the range of 1 kHz to 1 MHz. The amplified voltage
drops across the tissue and the reference resistor Rs,
are fed into the GPD which outputs two voltages
proportional to their magnitude’s ratio and phase
difference, respectively. The gain and the phase
extracted are used to compute the impedances at each
frequency and then the values are displayed on the
screen, sent to Bluetooth module and stored in on-
board memory by MCU.
As mentioned in the requirement section, the
accuracy and conformity of the excitation current can
affect the quality of the measurements and also the
safety of patients. Therefore, the VCCS block plays
an important role in the design.
A high-performance current source for portable
bioimpedance spectrometer should have high
bandwidth, high output impedance over the chosen
frequency range, and stable and safe injected current
lower than 0.5mA.
Different topologies of VCCS have been
proposed such as current conveyors, Howland current
source or Tietze current source (Bragos et al., 1994,
Tietze et al., 2014, Horowitz and Hill, 2015).
Among the available configuration, we opted for
the modified version of the Howland current source
proposed by P. Horwitz and W. Hill (Horowitz and
Hill, 2015) and showed in Figure 4.
Figure 4: Modified Howland current source.
In this version of the circuit all four resistors in
the positive and negative feedback lines have equal
values, so the circuit works without any
amplification. The load current depends only on input
voltage and value of current forcing resistor RI and is
independent of the load resistance. To ensure a stable
and accurate voltage controlled current source the
operational amplifier should be selected carefully. In
particular, amplifier with high common mode
rejection ratio (CMRR), low input voltage noise and
acceptable wide bandwidth are preferred.
Concept Design of a New Portable Medical Device for Lymphedema Monitoring: A EIT Health ClinMed Summer School Project
615
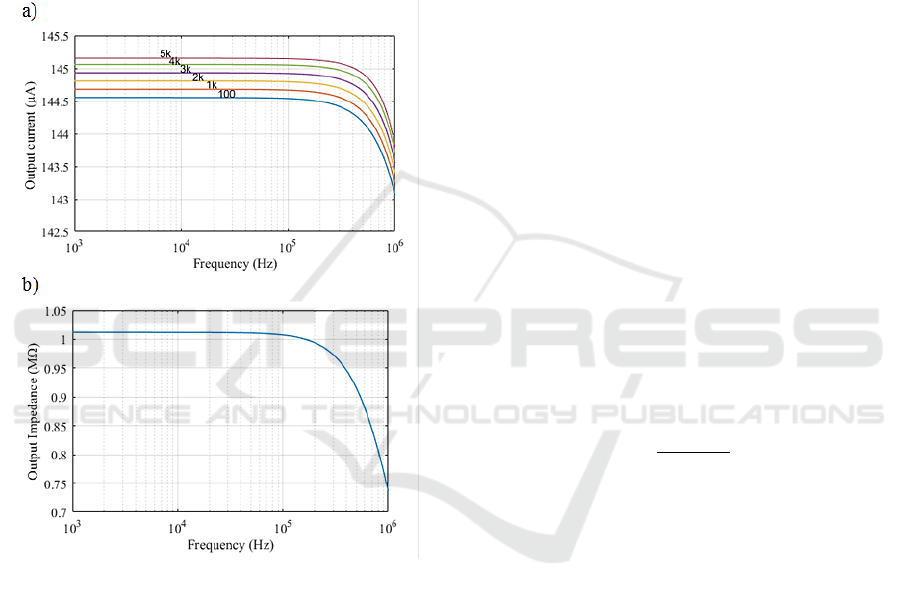
In order to verify the operation of the selected
circuit, computer simulation was per-formed with
Cadence
®
Pspice
®
Lite 16.6. The AD8021
operational amplifier was selected for its high low
input voltage noise (2.1 nV/√Hz) and wide bandwidth
(490 MHz). The current source was designed to
deliver sinusoidal current of maximum amplitude 150
µA for 0.6 V of input voltage, so the RI in this circuit
is 4 kΩ. Figure 5 shows the results of the output
current and output impedance of the circuits in
frequency domain varying the load impedance value
(R
L
) from 100 Ω to 5 kΩ.
Figure 5: (a) Output current of VCCS for RL=100 Ω, 1 kΩ,
2 kΩ, 3 kΩ, 4 kΩ, 5 kΩ. (b) Output impedance of VCCS.
The measuring block comprises two
instrumentation amplifiers with high bandwidth and
high CMRR and a gain phase detector.
The GDP was chosen because it is fast in
measurement and simple in design as compared to
bridge method (Steendijk et al., 1993) or the
quadrature demodulation method (Pallás-Areny and
Webster, 1993). It measures the gain and phase
difference of two signals as voltage outputs. AD8302
from Analog Devices is chosen as GDP. The outputs
of GDP are feed into ADCs of the microcontroller
system. Also, the accelerometer’s signal from IMU is
sent to MCU.
4.3 Software
The signal processing takes place in the MCU. The
microcontroller system performs different tasks with
the on-board components. It interfaces with the signal
generator sweeping the frequencies, calculates the
impedances from the signals of the GDP, displays the
results on LCD screen, stores them on a FLASH
memory and sends them through Bluetooth to the
smartphone, which stores the measurements in a
cloud server.
Every 5 sec the total energy, which correspond to
the activity level, is computed from the raw
accelerometer signal. If the energy is below the fixed
threshold, the MCU initiate the bioimpedance
measurements.
The gain and the phase extracted from GPD are
used to compute the impedance at each frequency.
The last part of analysis is done by the mobile
phone since requires a higher computational cost.
The impedance data are used to predict the
impedance at zero and infinite frequencies that cannot
be measured directly. As mentioned before, the
impedance at zero frequency (R
0
) represents the
extracellular water (ECW) compartment while the
impedance at infinite frequency (R
∞
) represents the
total tissue water. Thus, the impedance at zero
frequency is a measure of the water volume, including
lymph. To derive the intracellular fluid (ICF) instead
the following formula is used:
R
w
=
R
0
· R
∞
R
0
− R
∞
(1)
R
0
and R
∞
are computed using the Cole model
(Kyle et al., 2004).
Different methods have been used to assess
lymphedema with bioimpedance measures. However,
none of these provides an absolute measure of
lymphedema but rather a comparison of the affected
limb with that of the unaffected one (Cornish et al.,
2001, Erdogan Iyigun et al., 2015, Ward et al., 2011).
Clearly, there are some cases in which the
lymphedema presents in both limbs where this
approach cannot be used.
Therefore, the approach implemented in our
device is double. Instead of comparing the two limbs
at the same time, a measure of the patient at the time
of diagnosis, prior to surgical intervention can be
stored providing a baseline for computing the ratio.
This allows for the natural asymmetry that patient
may have between their arms to be accounted and
detect the bilateral lymphedema as well.
ClinMed 2019 - Special Session on Designing Future Health Innovations as Needed
616

Alternatively, if the measure at baseline is not
available, the ratio 𝑅
0
/𝑅
𝑤
can be computed. In fact,
the intracellular fluid volume is not affected by
lymphedema since it is an accumulation of an
extracellular fluid. A previous study has shown that
this ratio differs significantly (Ward et al., 2011).
Independently by the method used to calculate the
ratio, the incoming measure is compared to the stored
baseline to provide an alert to the user when it
exceeded the threshold. As reported in other studies,
the criterion indicative of lymphedema is set at the
mean +3 standard deviation of the control population
(Erdogan Iyigun et al., 2015, Cornish et al., 2001,
Ward et al., 2011).
The smartphone application will also show the
trends of the bioimpedance measurements.
4.4 Consideration about Usability, Risk
Analysis and Essential
Requirements
The intended use of our device is to monitor the
limb’s volume through bioimpedance. The target
users are the population that have undergone breast
cancer surgery, at risk of developing lymphedema.
The usage involves the examination of parts and
battery status of the device, the placement of the
sensors and the disposition into resting position. The
resting position requires the patient to sit
comfortably, stay awake but relaxed and to extend
his/her arms on a medium-height table. Prior to the
bioimpedance measurement, a 1-minute stabilization
period is held on. The measurements take 10 minutes
to be carried out during which the patient must stay
relaxed in the resting position. As well, consistency
among measurements is required.
The device we proposed is a result of a design
process, where consideration about the wearability,
electrodes position and easy-to-use were considered
in light of unsupervised environments use.
Figure 2 represents the intended position of the
electrodes since lymphedema commonly appears in
the limbs. The bracelets and the belt are adjustable
and made with Velcro in order to provide a general
solution for fitting people of different sizes, without
influencing the comfort by tightness.
To ease the system setup and improve usability,
before the start of the measurements, a tutorial is
shown to the user to inform about the correct use and
position of the device. The interface also provides the
automatically check of the correct skin contact.
The identification of hazards derives from the
known and foreseeable hazards associated with the
medical device in both normal and fault conditions.
The hazards have been categorized into the following
groups:
Energy hazards: electrostatic discharge and
external electromagnetic fields influence, metallic
implant in region of measurement, electric
implant/pacemaker, burn due to external tattoo in
the evaluation area.
Biological/chemical hazards: pregnancy,
irritation of skin due to previous lesion, usage
during coagulant/anticoagulant medication.
Operational hazards: lesion due to difficulty to
adapt sensors, irritation due to pressure, humidity
and/or temperature, contact with liquids during
normal use.
Information hazards: misuse due to incomplete
instruction, labelling or packaging.
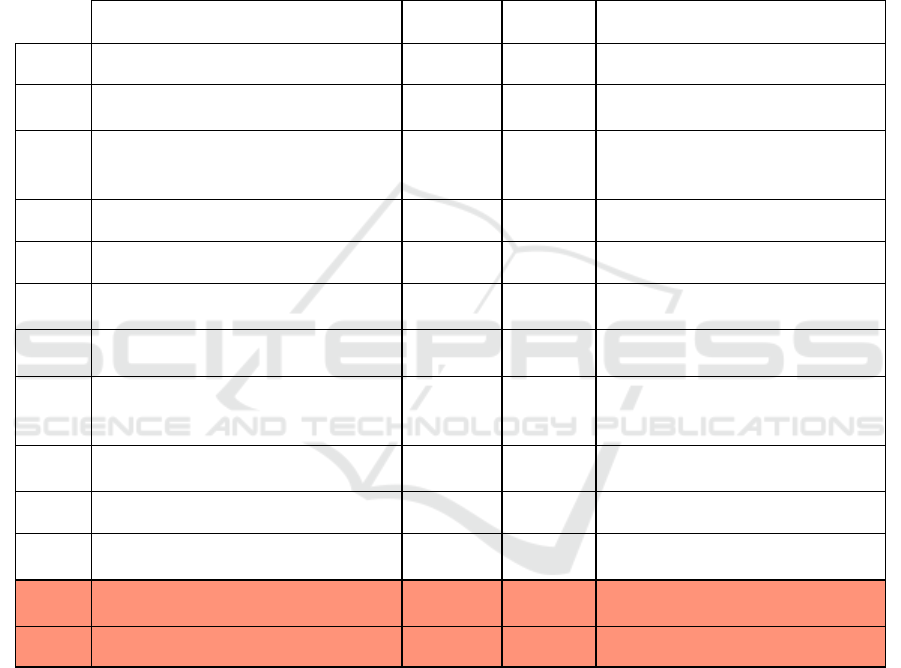
The assessment of acceptability is based upon the
criteria for the acceptance of the combinations of
harm probability and harm severity. A semi-
quantitative risk evaluation matrix is presented in
Annex Table 1 along with the definitions of
occurrence probability levels of hazards and harm
severity.
5 FROM CONCEPT TO
PRODUCT
As is well known, the translation of novel ideas into
a product faces many challenges. The idea must be
aligned both with the clinical and market needs. It is
therefore essential to establish if the product meets
the unmet needs and that there is a clear path to
penetrate the market.
Lymphedema is a significant problem, that affect
3-5 million of Americans and 4 million people in
Europe, where three-quarters of lymphedema cases
are at stage 0 and 1, that is more than ALS, Cystic
Fibrosis, Multiple Sclerosis, Muscular Dystrophy,
and Parkinson’s Disease combined. Moreover, only
in early-stage lymphedema, the conservative
treatment has been shown to be effective. Thus, there
is a clear clinical need.
From the economic prospective, the early
intervention reduces the need for intensive
rehabilitation and it costs five times less. According
to the International Lymphedema Framework, the
financial impact of lymphedema in Europe is about
€4 billion in loss of earnings, close to 1 billion € in
health and social welfare bill and about 2 billion to
treat cellulitis (International Lymphedema
Framework). Shih et al (Shih et al., 2009) found that
Concept Design of a New Portable Medical Device for Lymphedema Monitoring: A EIT Health ClinMed Summer School Project
617

the 2‐year mean costs for women with lymphedema
were a significant $23,167 higher than for patients
with breast cancer without lymphedema. Stout et al.
(Stout et al., 2012) reported that the cost to manage
early-stage lymphedema is $636.19 vs. $3,124.92 per
patient per year in the more advanced stages,
requiring intensive therapy.
This means that for the healthcare payers’ point
of view, less associate cost; for the patients, an
increased quality of life and for the clinicians’
perspective, a deeper understanding of the
phenomenon and reduced time for the visits.
Options regarding funding have being explored
and structured around a combination of grants, loans,
investors and equity shares. Given the social impact
of breast cancer and the prevention of an associated
chronic condition, a crowdfunding campaign could be
expected to obtain funding to a certain extent.
The development plan for the product presented
in this paper can be summarized in: data acquisition,
data extraction, software component. Data
acquisition mainly involves the design of the
hardware that will achieve a proper acquisition of the
measurements, good usability and testing. Data
extraction concerns the validation of optimized signal
processing. Software component involves the design
of easy-to-use mobile application.
The design reviews will take place throughout the
product development process to evaluate the design
against technical specifications, small- and large-
scale manufacturing, risk assessment and usability.
Throughout the development, interviews on the
design of the device with professionals and patient
associations will be performed from the early stages
to the market launch.
An important milestone is obtaining the proof of
concept that will demonstrate the effectiveness, safety
and usability of the device. This involves the in vitro
testing, side by side testing with other BIS devices,
pilot clinical trial, usability and acceptability studies
with both patient and healthcare providers.
Once a functional device has been developed the
next logical step would be to obtain clinical
validation, regulatory approval, IP protection and
finally scalability and launch.
6 DISCUSSION
The device presented in this paper is the first medical
device that permits accurate monitoring of
lymphedema progression by the user.
In addition to the time needed for medical
appointments, other solutions require the acquisition
of expensive equipment and/or certain level of
medical expertise and have to be used at the hospital.
Measurement of limb volume with water
displacement can be cumbersome and difficult to
perform in the physician’s office; circumferential
measurement of limb volume using a tape is
unreliable; the use of infrared perometry is limited by
the fact that the equipment is not portable and requires
individuals to come into a clinic. BIS, instead, is a
direct measurement of extracellular fluid volume.
This technique has been studied as a tool to detect
early signs of subclinical lymphedema. The existing
commercially products using BIS as a diagnostic tool
are costly, not portable so they are available only in
specialized rehabilitation centres. The capital cost of
the L‑Dex U400, SOZO® is £7,500 £8,000 per unit
respectively and can be used only by trained nurse or
physiotherapist, as a part of routine screening.
The solution presented is easy to implement and
affordable to patients
The method proposed for the measurements can
be applied to every part of the human body
independently of anatomical characteristics of
specific individuals (e.g. body weight, size, etc.).
The risk analysis shows that any potential damage
is very unlikely thus making the operation of the
device safe for individual use without any
surveillance or support.
Future usability and acceptability studies should
be performed involving patients in order to optimize
the interface between the device and the user.
All the added values of this new design make it a
highly competitive solution compared to all existing
alternatives.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank all the organizers of
the EIT Health ClinMed 2018 summer school.
Without them this project would have never born.
Special thanks for all the mentors who helped us
to improve and better define this work.
The authors would also like to thank the
Rehabilitation service at the Hospital Santa Maria
(Lisbon, Portugal) and the Pediatric Cardiology
department at the Hospital Santa Marta (Lisbon,
Portugal) for hosting and enables us to have a broader
view of the different healthcare providers which
allows us to implement all this knowledge to design a
better solution.
ClinMed 2019 - Special Session on Designing Future Health Innovations as Needed
618

REFERENCES
Bragos, R., Rosell, J. and Riu, P. 1994. A wide-band AC-
coupled current source for electrical impedance
tomography. Physiol. Meas., 15, A91-A99.
Brunelle, C., Skolny, M., Ferguson, C., Swaroop, M.,
O'toole, J. & Taghian, A. G. 2015. Establishing and
sustaining a prospective screening program for breast
cancer-related lymphedema at the massachusetts general
hospital: lessons learned. J Pers Med, 5, 153-64.
Cornish, B. H., Chapman, M., Hirst, C., Mirolo, B., Bunce,
L. H., Ward, L. C. & Thomas, B. J. 2001. Early
Diagnosis of Lymphedema using multiple frequency
bioimpedance. Lymphology, 34, 2.11.
Erdogan Iyigun, Z., Selamoglu, D., Alco, G., Pilanci, K. N.,
Ordu, C., Agacayak, F., Elbuken, F., Bozdogan, A.,
Ilgun, S., Guler Uysal, F. & Ozmen, V. 2015.
Bioelectrical impedance for detecting and monitoring
lymphedema in patients with breast cancer. Preliminary
results of the florence nightingale breast study group.
Lymphat Res Biol, 13, 40-5.
Grada, A. A. and Phillips, T. J. 2017. Lymphedema:
Pathophysiology and clinical manifestations. J Am
Acad Dermatol, 77, 1009-1020.
Horowitz, P. and Hill, W. 2015. The Art of Electronics,
New York, USA, Cambridge University Press New
York.
IMPEDIMED. A Non-Invasive, Fluid-Specific Break
Through: The Lymphedema Index (L-Dex) [Online].
https://www.impedimed.com/products/l-dex-u400/.
[Accessed 09-12-2018.
International Lymphedema Framework. [Online]
https://www.lympho.org/. [Accessed 18-12-2018]
International Society Of Lymphology. 1995. Executive
Committee. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral
Lymphedema. Lymphology 28, 113-117
Kayiran, O., De La Cruz, C., Tane, K. and Soran, A. 2017.
Lymphedema: From diagnosis to treatment. Turk J
Surg, 33, 51-57.
Kim, M., Shin, K. H., Jung, S. Y., Lee, S., Kang, H. S., Lee,
E. S., Chung, S. H., Kim, Y. J., Kim, T. H. and Cho, K.
H. 2016. Identification of Prognostic Risk Factors for
Transient and Persistent Lymphedema after
Multimodal Treatment for Breast Cancer. Cancer Res
Treat, 48, 1330-1337.
Kyle, U. G., Bosaeus, I., De Lorenzo, A. D., Deurenberg,
P., Elia, M., Gomez, J. M., Heitmann, B. L., Kent-
Smith, L., Melchior, J. C., Pirlich, M., Scharfetter, H.,
Schols, A. M., Pichard, C. & Composition of the
ESPEN Working Group. 2004. Bioelectrical impedance
analysis--part I: review of principles and methods. Clin
Nutr, 23, 1226-43.
Liu, N. F. and Olszewski, W. 1992. Use of tonometry to
assess lower extremity lymphedema. Lymphology, 25,
155-8.
Mayrovitz, H. N. 2009. Assessing lymphedema by tissue
indentation force and local tissue water. Lymphology,
42, 88-98.
National Lymphedema Network. 2011. Screening and early
detection of breast cancer-related lymphedema: The
imperative. [Online]. http://www.lymphnet.org/pdf
Docs/PP_Lymphedema_BC_Supplement.pdf. [Acce-
ssed 09-12-2018.
Norman, S. A., Localio, A. R., Potashnik, S. L., Simoes
Torpey, H. A., Kallan, M. J., Weber, A. L., Miller, L.
T., Demichele, A. & Solin, L. J. 2009. Lymphedema in
breast cancer survivors: incidence, degree, time course,
treatment, and symptoms. J Clin Oncol, 27, 390-7.
O'toole, J., Jammallo, L. S., Miller, C. L., Skolny, M. N.,
Specht, M. C. and Taghian, A. G. 2013. Screening for
breast cancer-related lymphedema: the need for
standardization. Oncologist, 18, 350-2.
Pallás-Areny, R. and Webster, J. G. 1993. Bioelectric
Impedance Measurements Using Synchronous
Sampling. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical
Engineering, 40, 824-829.
Rockson, S. G. and Rivera, K. K. 2008. Estimating the
population burden of lymphedema. Ann N Y Acad Sci,
1131, 147-54.
Shih, Y. C., Xu, Y., Cormier, J. N., Giordano, S., Ridner, S.
H., Buchholz, T. A., Perkins, G. H. and Elting, L. S.
2009. Incidence, treatment costs, and complications of
lymphedema after breast cancer among women of
working age: a 2-year follow-up study. J Clin Oncol,
27, 2007-14.
Soran, A., Ozmen, T., Mcguire, K. P., Diego, E. J.,
Mcauliffe, P. F., Bonaventura, M., Ahrendt, G. M.,
Degore, L. and Johnson, R. 2014. The importance of
detection of subclinical lymphedema for the prevention
of breast cancer-related clinical lymphedema after
axillary lymph node dissection; a prospective
observational study. Lymphat Res Biol, 12, 289-94.
SOZO. The Power of SOZO [Online].
https://www.hellosozo.com/. [Accessed 09-12-2018.
Steendijk, P., Mur, G., Van Der Velde, E. T. & Baan, J.
1993. The Four-Electrode Resistivity Technique In
Anisotropic Media: Theoretical Analysis and
Application on Myocardial Tissue In Vivo. IEEE
Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 40, 1138-1148.
Stout, N. L., Pfalzer, L. A., Springer, B., Levy, E.,
Mcgarvey, C. L., Danoff, J. V., Gerber, L. H. and
Soballe, P. W. 2012. Breast cancer-related
lymphedema: comparing direct costs of a prospective
surveillance model and a traditional model of care. Phys
Ther, 92, 152-63.
Taghian, N. R., Miller, C. L., Jammallo, L. S., O'toole, J.
and Skolny, M. N. 2014. Lymphedema following breast
cancer treatment and impact on quality of life: a review.
Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 92, 227-34.
Tahan, G., Johnson, R., Mager, L. and Soran, A. 2010. The
role of occupational upper extremity use in breast
cancer related upper extremity lymphedema. J Cancer
Surviv, 4, 15-9.
TECHNOLOGIES, D. LymphScanner - Regional
lymphedema [Online]. http://www.delfintech.com/ en/
product_information/lymphscanner/. [Accessed 09-12-
2018.
Tietze, U., Schenk, C. and Gamm, E. 2014. Electronic
Circuits - Handbook for Design and Application.
Concept Design of a New Portable Medical Device for Lymphedema Monitoring: A EIT Health ClinMed Summer School Project
619
Torres Lacomba, M., Yuste Sanchez, M. J., Zapico Goni,
A., Prieto Merino, D., Mayoral Del Moral, O., Cerezo
Tellez, E. and Minayo Mogollon, E. 2010.
Effectiveness of early physiotherapy to prevent
lymphoedema after surgery for breast cancer:
randomised, single blinded, clinical trial. BMJ, 340,
b5396.
Ward, L. C., Dylke, E., Czerniec, S., Isenring, E. and
Kilbreath, S. L. 2011. Confirmation of the reference
impedance ratios used for assessment of breast cancer-
related lymphedema by bioelectrical impedance
spectroscopy. Lymphat Res Biol, 9, 47-51.
ANNEX
Table 2: Semi-quantitative risk evaluation matrix. In red, the unacceptable residual risks and not allowed usage for those
risks’ conditions.
Risk Severity Frquency Control measures
R1
Irritation due to pressure, temperature
and/or humidity
Minor Occasional -
R2
External electromagnetic fields influence Negligible Remote -
R3
Electrostatic discharge Minor Remote
Make sure the patient is not touching
metal and that there is no skin-skin
contact
R4
Contact with liquids during normal use Serious Remote
Specify avoidance of liquids near the
sensors in the instructions of use
R5
Usage during coagulant/anticoagulant
medication
Catastrophic Improbable -
R6
Lesion due to difficulty to adapt sensors Minor Probable
Reevaluation of the instructions and
adjustable sensors
R7
Mismeasurement due to difficulty to adapt
sensors
Minor Probable
Reevaluation of the instructions and
adjustable sensors
R8
Incorrect skin contact Minor Probable
Alert message to rearrange the sensors
of the device
R9
Metalic implant in region of measurement Serious Probable
Useage not allowed in the region where
there is a metallic implant
R10
Misusage due to incomplete instructions Serious Occasional
Reevaluation of the instructions of use
with patient and doctors feedback
R11
Burn due to external tattoo in evalution area Serious Occasional
metallic tattoos, usually older, in the
region of evaluation are banned
R12 Usage during pregnancy Catastrophic Remote Usage not allowed during pregnancy
R13 Patient has an electric implant/pacemaker Catastrophic Occasional
Usage not allowed in the presence of
pacemakers
ClinMed 2019 - Special Session on Designing Future Health Innovations as Needed
620
